Синтопические взаимоотношения мышцы, поднимающей задний проход, с прямой кишкой и стенкой таза человека по данным классических и цифровых морфологических методов исследования
Автор: Чемидронов С.Н., Колсанов А.В., Суворова Г.Н.
Журнал: Вестник медицинского института "РЕАВИЗ": реабилитация, врач и здоровье @vestnik-reaviz
Рубрика: Морфология. Патология
Статья в выпуске: 4 т.13, 2023 года.
Бесплатный доступ
В последнее время одним из наиболее актуальных вопросов современной медицины является дисфункция тазового дна, которая включает в себя пролапс органов малого таза, недержание мочи, кишечных газов и кала [1-3]. Ведущая роль в поддержании органов малого таза отводится мышце, поднимающей задний проход. Исследование особенностей прикрепления мышцы к стенкам таза, прямой кишке позволит прояснить патогенез недостаточности тазового дна и развитие симптомов недержания и пролапса органов малого таза. Использование в работе классических морфологических и новейших технологий аппаратно-программного комплекса «Автоплан» (Государственный контракт Минпромторга РФ от 07.04.2014 г. № 14411.2049999.19.013 «4.3-Автоплан-2014»), на основании данных МРТ позволило выявить морфологически более плотные и разреженные зоны стенки дистальных отделов прямой кишки, непосредственно связанных с прикреплением к ней волокон мышцы, поднимающей задний проход.
Мышца, поднимающая задний проход, прямая кишка, продольный слой гладкомышечных клеток прямой кишки
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143180697
IDR: 143180697 | УДК: 611.736.911 | DOI: 10.20340/vmi-rvz.2023.4.MORPH.1
Текст научной статьи Синтопические взаимоотношения мышцы, поднимающей задний проход, с прямой кишкой и стенкой таза человека по данным классических и цифровых морфологических методов исследования
Вертикальное положение человека в процессе эволюции привело к существенной функциональной перестройке структур тазового дна для осуществления, с одной стороны, противодействия гравитации, а с другой -противодействия внутрибрюшному давлению.
Мышца, поднимающая задний проход, является ключевым компонентом тазового дна, который, помимо удержания органов малого таза, регулирует эвакуацию содержимого из дистальных отделов желудочно-кишечного тракта и мочеполового аппарата. Исследование особенностей прикрепления мышцы, поднимающей задний проход, позволит не только понимать морфофункциональные аспекты поведения мышц диафрагмы таза и промежности при физиологических процессах (мочеиспускание, дефекация, родовая деятельность и т.д.), но и сформировать картину о возможных причинах развития недостаточности тазового дна с точки зрения возникновения недержания мочи, кала, сексуальных дисфункциях и пролапса органов малого таза [2,3].
Мышца, поднимающая задний проход, была открыта Андреем Везалием ещё в 1555 году и названа им «т. seddem attolens» [4]. Однако детальное исследование анатомии данной мышцы, её морфофункциональные взаимоотношения с другими мышцами промежностной области и органами мочеполового аппарата были проведены лишь в течение последних 50 лет и представлены немногочисленными публикациями.
Исследования тазового дна
С точки зрения синтопических взаимоотношений мышцы, поднимающей задний проход, большой интерес представляют работы египетского анатома Ахмеда Шафика [1-3, 5-7]. Тщательное скрупулёзное препарирование промежностной области трупов взрослых мужчин и женщин позволило выявить некоторые детали прикрепления отделов мышцы, поднимающей задний проход.
А. Шафик описывал две основные порции мышцы, поднимающей задний проход: лобково-копчиковую и подвздошно-копчиковую, которая, по его мнению, у человека является рудиментарной [2, 7]. Подвздошно-копчиковая мышца обычно тонкая и может отсутствовать или в значительной степени замещаться фиброзной тканью. Лобково-копчиковая порция имеет воронкообразную форму и состоит из поперечной части, формирующей плоскость тазового дна, и вертикальной части, называемой поддерживающей петлёй. Мышца начинается от задней поверхности тела лобковой кости и запирательной фасции, направляясь кзади, образует диафрагму таза. На уровне шейки мочевого пузыря уплощенная порция лобково-копчиковой мышцы резко заворачивается, образуя подвешивающую петлеобразную структуру.
Результаты препарирования Шафика подтверждают данные доступной литературы. Мышца, поднимающая задний проход, образует урогенитальную расщелину, hiatus urogenitalis, овальной формы, открывающуюся косо кпереди и вниз; а сзади - ограниченной анально-копчиковой связкой. Урогенитальная расщелина имеет большие поперечные размеры у пожилых людей женского пола;
при этом с возрастом из овальной формы у молодых она имеет тенденцию становиться округлой у пожилых.
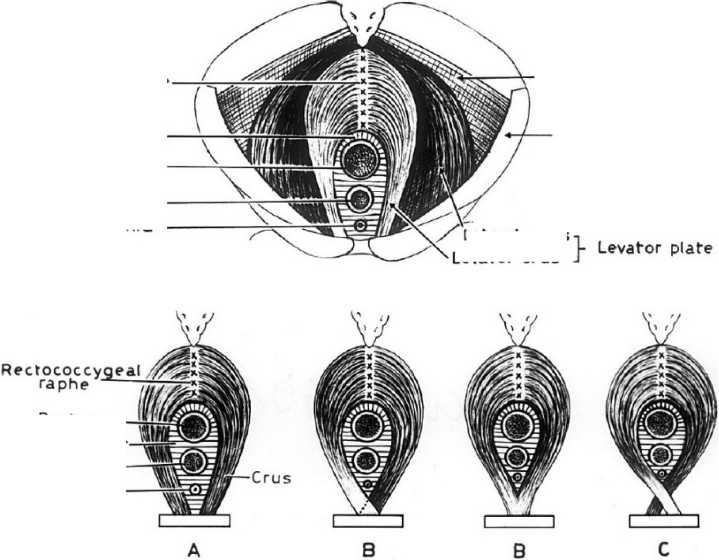
В мышце, поднимающей задний проход, Шафик выделяет две основные порции: латеральные порции треугольной формы, отходящие от фасции внутренней запирательной мышцы, он называет «латеральные массы»; медиальные пучки формируют «ножки» [2]. Мышечные пучки, конвергируясь, продолжаются кзади, и, перекрещиваясь своими сухожильными порциями, формируют анальнокопчиковую связку, и, далее, вплетаются в копчик. Каждая «ножка» мышцы, поднимающей задний проход, начинается от задненижних отделов лобковых костей. В ходе препарирования 23-х трупов возрастом от 18 до 50 лет Шафик описывает четыре основных варианта начала медиальных «ножек» (m. pubo-coccygeus): классический, наложение полное, наложение частичное, перекрест по типу ножниц (рис. 1).
Классический вариант представляет собой отдельное начало правой и левой лобково-копчиковых мышц от ипсилатеральных лобковых костей без перекрытия и наложения друг на друга -16 случаев. При варианте частичного или полного наложения волокон лобково-копчиковые мышцы начинаются от лобкового симфиза. Одна ножка прикрепляется выше другой в трёх случаях, у двух людей лобково-копчиковая мышца начинается одним общим сухожилием от лобкового симфиза и лобковых костей, после чего разделяется на правую и левую мышцы. В двух оставшихся случаях каждая «ножка» мышцы, поднимающей задний проход, начинается на нижней ветви противоположной лобковой кости. Ножки перекрещиваются, накладываясь друг на друга по типу ножниц, или вплетаются своими волокнами друг в друга в толщину брюшка противоположной мышцы.
Научное наследие Ахмеда Шафика сыграло большую роль в исследовании тазового дна и, в частности, мышцы, поднимающей задний проход.
Цель исследования: выявить особенности синтопи-ческих взаимоотношений мышцы, поднимающей задний проход, с прямой кишкой и стенкой таза на основании данных классических и инструментальных методов исследования.
Материалы и методы исследования
Материалом для томографического исследования послужили данные магнитно-резонансной томографии (МРТ) 63 женщин и 59 мужчин первого и второго периодов взрослого возраста, пожилого и старческого возраста без патологии со стороны органов малого таза и костного таза. Для проведения гистологического метода исследования использовался материал 10 плодов обоих полов среднего триместра беременности (22-26 недель). Этические принципы проведения медицинских исследований при работе с пациентами лечебных учреждений соблюдены согласно Хельсинской декларации Всемирной медицинской ассоциации в редакции 2000 г. (выписка из протокола заседания ЛЭК ФГБОУ ВО СамГМУ Минздрава России № 188 от 27.11.2017 г.).
Iliococcygeus
Anococcygeal raphe
VaginaUrethra
Hiatal ligament Rectum-
Obturator internus fascia
Рисунок 1. Схема прикрепления лобково-копчиковой порции мышцы, поднимающей задний проход, по A. Shafik (оригинальный рисунок): А - классический вариант, В - вариант с полным и частичным перекрытием; С - вариант «ножницы» с началом мышцы от лобковой кости противоположной стороны. Anococcygeal raphe - анально-копчиковая связка (шов); Hiatal ligament - хиатальная связка; Rectum -прямая кишка; vagina - влагалище; urethra - мочеиспускательный канал; crus (levator crus) - ножка (лобково-копчиковая мышца по Шафику); Iliococcygeus - подвздошно-копчиковая мышца; Levator plate - плоскость m. levator ani; Lateral mass - латеральная порция лобково-копчиковой мышцы по Шафику; obturator internus fascia - фасция внутренней запирательной мышцы
Figure 1. Scheme of attachment of the pubococcygeal portion of the muscle elevating the anus according to A. Shafik (original figure): A - classic variant, В - variant with full and partial overlap; C - "scissors" variant with the beginning of the muscle from the pubic bone of the opposite side. Anococcygeal raphe - anal-copal ligament (suture); Hiatal ligament - chiatai ligament; Rectum - rectum; vagina - vagina; urethra - urethra; crus (levator crus) - pedicle (pubococcygeal muscle according to Shafik); Iliococcygeus - iliococcygeus muscle; Levator plate - plane of m. levator ani; Lateral plate - plane of m. levator ani. levator ani; Lateral mass - lateral portion of the pubococcygeus muscle according to Shafik; obturator internus fascia - fascia of the internal constrictor muscle
Rec turn — Hiatal ligament
Vagina----
Urethra—
Lateral mass
Levator crus
Результаты и обсуждение
Исследуя структуры тазового дна, по данным МРТ мы обнаружили у всех объектов только классический вариант начала лобково-копчиковой мышцы от лобковых костей -каждая мышца начиналась от нижней ветви ипсилатеральной лобковой кости (рис. 2).
МРТ позволяет детально визуализировать не только отделы мышцы, поднимающей задний проход, но и урогенитальную расщелину и проходящие через неё дистальные отделы мочеполового аппарата и прямой кишки. К сожалению, в работах А. Шафика не были представлены нативные данные его исследований в отношении вариантов начала лобково-копчиковой мышцы (полное и частичное наложение, перекрест по типу ножниц). Возможно, представленные схемы начала m. pubo-coccygeus основаны на артефактах, полученных в результате препарирования; за лобково-копчиковую мышцу была принята лобковопузырная порция m. levator ani, которая при выделении, вследствие изменения топографии, была принята за мышцу противоположной стороны.
Взаимоотношение сухожильной дуги мышцы, поднимающей задний проход со внутренней запирательной мышцей
Относительно недавно в литературе появилась интересная статья Muro о взаимоотношении мышцы, поднимающей задний проход, со внутренней запирательной мышцей [8].
Некоторые японские исследователи (Baba и соавт., Okumura и соавт., Tamaki и соавт.) описывали недержание мочи и кала у пациентов с нарушением функции тазобедренного сустава и внутренней запирательной мышцы [11-13]. Было выдвинуто предположение, что m. levator ani как-то связана с пл. obturator internus. В доступной литературе описано, что подвздошно-копчиковая порция мышцы, поднимающей задний проход, берет начало от утолщения запирательной фасции, получившей название сухожильной дуги мышцы, поднимающей задний проход, arcus tendineus m. levatoris ani [13-15].
Нами была проведена виртуальная диссекция области латерального миофасциального взаимодействия пл. ilio-coccygeus с f. obturatoria (включая сухожильную дугу мышцы, поднимающей задний проход) в аппаратно-программном комплексе «Автоплан» [15-18]. В корональной проекции волокна сухожилия подвздошно-копчиковой мышцы «прободают» внутреннюю запирательную мышцу, доходя до уровня запирательной мембраны, создавая оптически неоднородную структуру в толще пл. obturator internus. (рис. 3).
Такие пучки фиброзных волокон хорошо визуализируются и у людей эктоморфного типа телосложения (рис. 4).
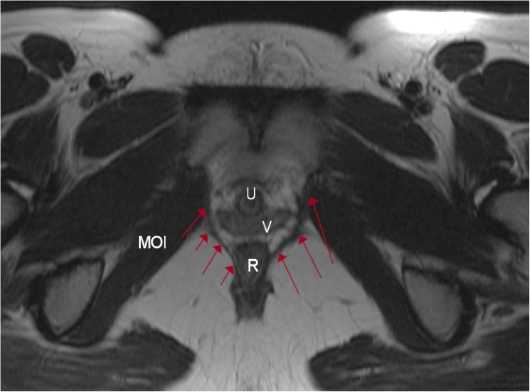
Рисунок 2. Аксиальная (поперечная) проекция области таза женщины 60 лет (MPT): R - прямая кишка; U - мочеиспускательный канал; V - влагалище; MOI - внутренняя запирательная мышца; стрелками показана лобково-копчиковая мышца, ограничивающая со внутренней стороны урогенитальную расщелину
Figure 2. Axial (transverse) projection of the pelvic region of a 60-year-old woman (MRI): R - rectum; U - urethra; V - vagina; MOI - internal hock muscle; arrows show the pubocococcygeal muscle, which limits the urogenital cleft on the inner side
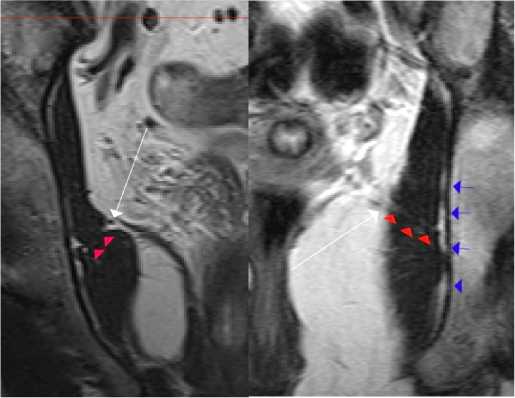
Рисунок 3. Корональная проекция таза на уровне анального канала: слева - мужчина эндоморфного типа телосложения второго возрастного периода; справа - женщина мезоморфного типа телосложения первого возрастного периода. Белая стрелка - сухожильная дуга мышцы, поднимающей задний проход; красные стрелки - продолжение фиброзных волокон от сухожильной дуги в толщу внутренней запирательной мышцы до уровня запирательной мембраны (синие стрелки)
Figure 3. Coronal projection of the pelvis at the level of the anal canal: left - male endomorphic body type of the second age period; right -female mesomorphic body type of the first age period. White arrow -tendon arch of the muscle that lifts the anus; red arrows - continuation of fibrous fibers from the tendon arch into the thickness of the internal constrictor muscle to the level of the constrictor membrane (blue arrows)
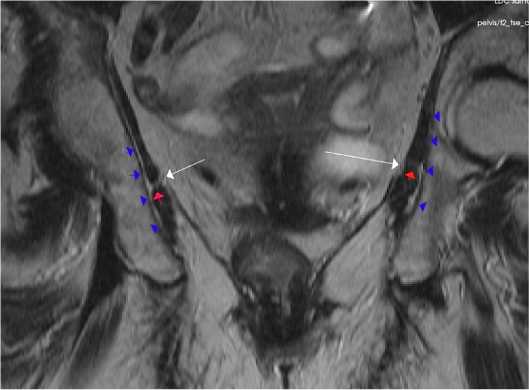
Рисунок 4. Корональная проекция таза на уровне анального канала женщин эктоморфного типа телосложения старческого возраста. Белая стрелка - сухожильная дуга мышцы, поднимающей задний проход; красные стрелки - продолжение фиброзных волокон от сухожильной дуги в толщу внутренней запирательной мышцы до уровня запирательной мембраны (синие стрелки) Figure 4. Coronal projection of the pelvis at the level of the anal canal of ectomorphic type of body build in elderly women. White arrow -tendon arch of the muscle elevating the anus; red arrows - continuation of fibrous fibers from the tendon arch into the thickness of the internal constrictor muscle up to the level of the constrictor membrane (blue arrows)
В сагиттальной проекции таза на серии снимков можно проследить ход оптически неоднородных по плотности волокон от уровня основания подвздошно-копчиковой мышцы до запирательной мембраны. Ниже приведена серия МВТ снимков мужчины эндоморфного типа телосложения второго возрастного периода с формированием сухожильной дуги мышцы, поднимающей задний проход, взаимоотношение со внутренней запирательной мышцей и проксимальный отдел подвздошно-копчиковой мышцы (рис. 5А, Б, В).
Полученные данные показывают тесное морфологическое взаимодействие мышцы, поднимающей задний проход, внутренней запирательной мышцы и запирательной мембраны.
Прикрепление к прямой кишке
Мышца, поднимающая задний проход, прикрепляется к прямой кишке порциями волокон, которые получили название «лобково-прямокишечная мышца» и «лобково-анальная мышца». На поперечных томограммах прямой кишки хорошо визуализируются «вплетение» волокон лобково-копчиковой мышцы в прямую кишку с формированием лобково-ректальной и лобково-анальной порций, лобково-простатической - у мужчин, лобково-влагалищной - у женщин (рис. 6).
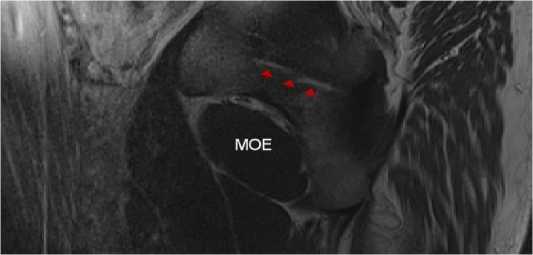
Рисунок 5А. Сагиттальная проекция таза мужчины эндоморфного типа телосложения второго возрастного периода. Фиброзные волокна сухожильной дуги в толще внутренней запирательной мышцы на уровне запирательной мембраны (красные стрелки). МОЕ - наружная запирательная мышца
Figure 5А. Sagittal projection of the pelvis of a male endomorphic body type of the second age period. Fibrous fibers of the tendon arch in the thickness of the internal hock muscle at the level of the hock membrane (red arrows). MOE is the external constrictor muscle
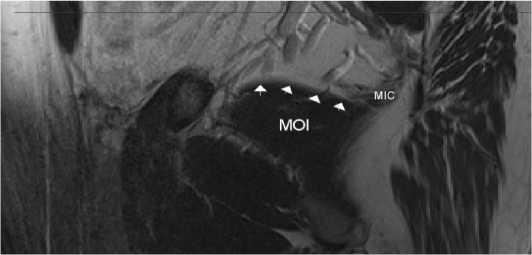
Рисунок 5Б. Сагиттальная проекция таза мужчины эндоморфного типа телосложения второго возрастного периода на уровне основания внутренней запирательной мышцы (MCI). Формирование сухожильной дуги мышцы, поднимающей задний проход (белые стрелки). В срезе представлен фрагмент уже сформированной подвздошнокопчиковой мышцы (MIC)
Figure 5Б. Sagittal projection of the pelvis of a man of endomorphic type of physique of the second age period at the level of the base of the internal obturator muscle (MOI). Formation of the tendinous arch of the muscle elevating the anus (white arrows). The slice shows a fragment of the already formed iliopsoas muscle (MIC)
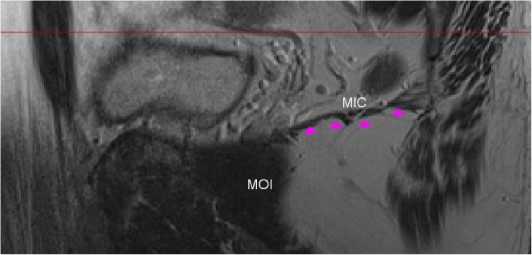
Рисунок 5B. Сагиттальная проекция таза мужчины эндоморфного типа телосложения второго возрастного периода на уровне основания подвздошно-копчиковой мышцы (MIC). Плато сформированной подвздошно-копчиковой мышцы MIC (розовые стрелки). MCI - внутренняя запирательная мышца
Figure 5В. Sagittal projection of the pelvis of a male of endomorphic type of physique of the second age period at the level of the base of the iliopsoas muscle (MIC). Plateau of the formed iliopsoas muscle MIC (pink arrows). MOI is the internal obturator muscle
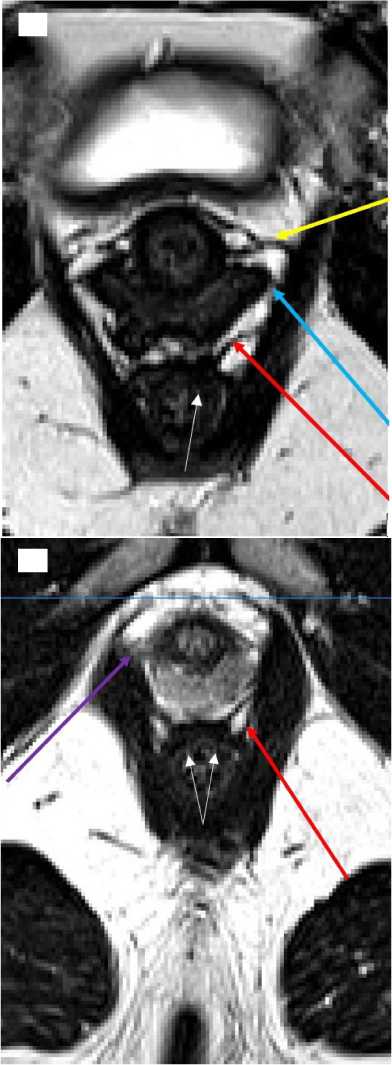
Рисунок 6. Аксиальная (поперечная) проекция области выхода из малого таза на уровне наружного анального сфинктера женщины второго возрастного периода мезоморфного типа телосложения (А) и мужчины эктоморфного типа телосложения первого возрастного периода (Б). Красная стрелка - лобково-анальная мышца; голубая стрелка - лобково-влагалищная мышца; желтая стрелка - мышца-сжиматель уретры; фиолетовая стрелка - лобково-простатическая мышца. Белые стрелки - указывают на оптически разреженные участки стенки прямой кишки в области «вплетения» волокон лобково-прямокишечной мышцы
Figure 6. Axial (transverse) projection of the pelvic outlet area at the level of the external anal sphincter of a woman of the second age period of the mesomorphic body type (A) and a man of the ectomorphic body type of the first age period (Б). Red arrow - pubo-anal muscle; blue arrow - pubo-vaginal muscle; yellow arrow - urethral constrictor muscle; purple arrow - puboprostatic muscle. White arrows - indicate optically sparse areas of the rectus wall in the area of "intertwined" fibers of the pubo-prostatic muscle
При детальном рассмотрении области прикрепления лобково-ректальной (анальной) мышцы к прямой кишке выявлены оптически плотные и разреженные области продольного мышечного слоя прямой кишки. Область «вплетения» m. levator ani соответствует разрежённой (с меньшей плотностью мышечной ткани) (рис. 7).
Морфологическое исследование синтопических особенностей мышцы, поднимающей задний проход, проведены на препаратах плодов человека среднего триместра беременности. Исследование взаимоотношения m. levator ani с прямой кишкой у плодов оказалось удобным с точки зрения визуализации структур тазового дна на небольших увеличениях (хЮ, х15). С одной стороны, структуры малого таза и мышцы, поднимающей задний проход, в этом периоде сформированы, с другой - полученные данные могут иметь клинический интерес в неонатологических исследованиях при родах глубоко недоношенным плодом.
Полученные нами данные подтверждают наличие морфологически и функционально различных зон в прямой кишке человека (рис. 8). Формируя отдельные пучки, продольный гладкомышечный слой прямой кишки группируется в более плотные мышечные структуры. При этом скелетные мышечные волокна лобково-прямокишечной мышцы с эндомизием заполняют пространства (разреженные зоны) между пучками, простираясь до внутреннего циркулярного гладкомышечного слоя.
Такое тесное морфофункциональное взаимодействие скелетной и гладкой мышечной ткани позволяет осуществлять тонкую регуляцию процессов удержания прямой кишки в состоянии покоя за счёт мышечного тонуса, с одной стороны, с другой - осуществлять изменение положения органа и размера просвета для осуществления акта дефекации.
Таким образом, область прикрепления мышцы, поднимающий задний проход, на прямой кишке функционально менее подвижна и наиболее адаптирована к прикреплению и передаче усилия со скелетной мышцы.
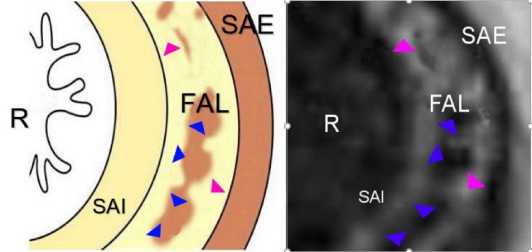
Рисунок 7. Аксиальная (поперечная) томограмма прямой кишки женщины мезоморфного типа телосложения второго возрастного периода: R - прямая кишка; SAI - внутренний сфинктер (циркулярные мышечные пучки), FAL- продольные анальные волокна; SAE - наружный анальный сфинктер; розовые треугольники -разреженные участки продольного анального мышечного слоя, фиолетовые - плотные
Figure 7. Axial (transverse) tomogram of the rectum of a woman of mesomorphic type of body build of the second age period: R- rectum; SAI - internal sphincter (circular muscle bundles), FAL - longitudinal anal fibers; SAE - external anal sphincter; pink triangles - sparse areas of the longitudinal anal muscle layer, violet - dense ones
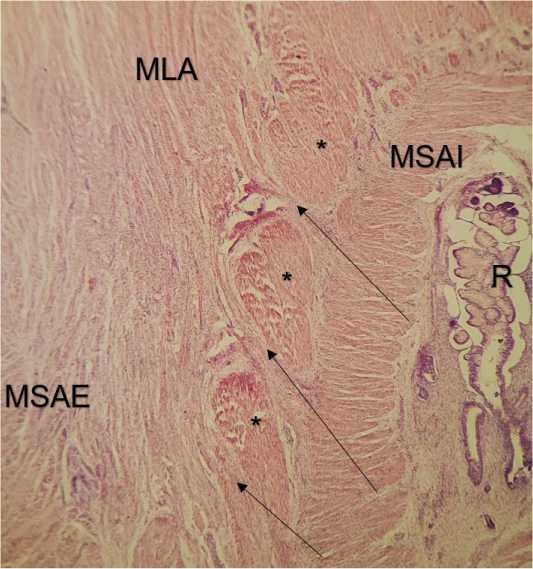
Рисунок 8. Тазовое дно плода Ж. 20 нед. Окр. гематоксилин-эозин. Ув. х15. MSAI - внутренний анальный сфинктер, MSAE -наружный анальный сфинктер; MLA- мышца, поднимающая задний проход; R - прямая кишка; * - продольные гладкомышечные волокна прямой кишки; стрелки - входящие волокна леватора между порциями продольных пучков
Figure 8. Pelvic floor of fetus W. 20 weeks. Hematoxylin-eosin staining. Eq. х15. MSAI - internal anal sphincter, MSAE - external anal sphincter; MLA - muscle elevating the anus; R - rectum; * - longitudinal smooth muscle fibers of the rectum; arrows - incoming levator fibers between the portions of the longitudinal bundles
Список литературы Синтопические взаимоотношения мышцы, поднимающей задний проход, с прямой кишкой и стенкой таза человека по данным классических и цифровых морфологических методов исследования
- Shafik A. A new concept of the anatomy of the anal sphincter mechanism and the physiology of defecation. Levator hiatus and tunnel: anatomy and function. Dis Colon Rectum. 1979; 22:539-549.
- Shafik A. Levator ani muscle: new physioanatomical aspects and role in the micturition mechanism. World J Urol. 1999; 17:266-273.
- Shafik A., Ahmed I., Shafik A.A. et al. Surgical anatomy of the perineal muscles and their role in perineal disorders. AnatSci Int. 2005; 80:167-171.
- Thompson P. The myology of the pelvic floor: a contribution to human and comparative anatomy. 1899. Mc Corquodale, London.
- Shafik A. New concept of the anatomy of the anal sphincter mechanism and the physiology of defecation. II. Anatomy of the levator ani muscle with special reference to puborectalis. Invest Urol. 1975; 13:175—182.
- Shafik A. A new concept of the anatomy of the anal sphincter mechanism and the physiology of defecation. III. The longitudinal anal muscle: anatomy and role in anal sphincter mechanism. Invest Urol. 1976;13:271-277.
- Shafik A., Sibai O.E., Shafik A.A. et al. A novel concept for the surgical anatomy of the perineal body. Dis Colon Rectum. 2007;50:2120-2125.
- Muro S., Nimura A., IbaraT. et al. Anatomical basis for contribution of hip joint motion by the obturator internus to defaecation/urinary functions by the levator ani via the obturator fascia. J Anat. 2022. https://doi.org/10. 1111/joa.13810
- Tuttle L.J., Delozier E.R., Harter K.A. et al. The role of the obturator internus muscle in pelvic floor function. J Womens Health Phys Ther.
- BabaT., HommaY., Takazawa N. et al. Is urinary incontinence the hidden secret complications after total hip arthroplasty? Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014;24:1455-1460.
- Okumura K., Yamaguchi K., Tamaki T. et al. Prospective analyses of female urinary incontinence symptoms following total hip arthroplasty. Int
- Tamaki Т., Oinuma K., Shiratsuchi H. et al. Hip dysfunctionrelated urinary incontinence: a prospective analysis of 189 female patients undergoing total hip arthroplasty. Int J Urol. 2014;21:729-731.
- Ashton-Miller J.A., Delancey J.O. Functional anatomy of the female pelvic floor. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2007;1101:266-296.
- Smith W. The levator ani muscle; its structure in man, and its comparative relationships. Anat Rec. 2001;26:175-203.
- Netter F. Human anatomy atlas. Transl. in russ. L.L. Kolesnikov guid. 6th ed Moscow: GEOTAR-Media 2018:624.
- Лысов H.A., Гелашвили П.А., Супильников A.A. Методологические основы объективизации морфологических исследований. Вестник медицинского института «РЕАВИЗ»: реабилитация, врач и здоровье. 2011;2:53-65. [Lysov N.A., Gelashvili Р.А., Supilnikov A.A. Methodological foundations of objectification of morphological research. Bulletin of the medical Institute "REAVIZ": rehabilitation, doctor and health.
- Torsten B. Moeller Atlas of Sectional Anatomy 2 vol. ed second revised. New York, 2011:213.
- Супильников A.A., Девяткин A.A., Павлова O.H., Гуленко О.Н. Морфологические и физиологические аспекты течения раневого процесса (литературный обзор). Вестник медицинского института «РЕАВИЗ»: реабилитация, врач и здоровье. 2016;2(23):144-151. [Supilnikov А.А., Devyatkin А.А., Pavlova O.N., Gulenko O.N. Morphological and physiological aspects of the course of the wound process (literary review). Bulletin of the medical Institute "REAVIZ": rehabilitation, doctor and health. 2016;2(23):144-151. (In Russ)]


