Small business as the basis of municipal economy: problems and support forms (by way of Petrosavodsk example)
Автор: Savelyev Yuri Vladimirovich, Mazurovsky Maxim Andreevich, Zhirnel Evgeniy Viktorovich
Журнал: Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast @volnc-esc-en
Рубрика: Regional economy the issue theme: small entrepreneurship development
Статья в выпуске: 2 (6) т.2, 2009 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The article considers the role and function of small businesses in the development of the municipality on the example of the city of Petrozavodsk. Results of entrepreneurs’ questioning are given, the main problems of small businesses and forms of its support at the municipal level are considered.
Small businesses, municipal economy, small businesses state support, municipal economic policy
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147223134
IDR: 147223134 | УДК: 334.012.64(470.22)
Текст научной статьи Small business as the basis of municipal economy: problems and support forms (by way of Petrosavodsk example)
Yuri V.
SAVELYEV
Ph.D. in Economics, Acting Chief Scientific Secretary of the Presidium of Russian Academy of Sciences of KSC
Maxim A.
MAZUROVSKY
Chairman of the State Committee of the Republic of Karelia on youth affairs, postgraduate student, Institute of Economics, KSC RAS
Evgeniy V.
ZHIRNEL
Ph.D. in Economics
Scientific Secretary, Institute of Economics, KSC RAS
In the socio-economic development of the municipality a special role is played by small businesses. It is this form of business which allows meeting the rapidly changing demand for various goods and services more effectively. Small businesses are complementary activities of large and medium-sized enterprises oriented to the most extensive and capacious markets. Small business creates jobs, develops and implements new technology, most tailored to local conditions. In the current economic conditions related to the crises, special attention is paid to small business and enterprise support occupies an important place in the set of anti-crisis measures of the Russian Government. This is primarily connected to the fact that small business is able to compensate for the reduction of jobs in large enterprises, to meet domestic demand, curbing inflation, as well as provide revenue to the budgets of all levels.
Of particular importance is the development of small businesses, primarily at the municipal level, because of its functions, among which the most important are the following:
-
• Focus on local markets , meeting various and changing demand for goods and services (often these are rather specific goods and services that can not be made by large enterprises).
-
• Promote competition in local markets , resulting in their more efficient operation and generation of competitive advantages of the municipal economy in general.
-
• Diversifying the local economy and encourage the development of foreign economic relations . The activity of small businesses allows expanding market specialization of municipal economy, small business partnerships allow local economy integrating into the external value chain.
-
• Changing the mode of the territory’s development . The development of small business allows for more efficient use of the territory, more evenly distribute the work and human resources of the territory, optimize the deployment of productive forces.
-
• Provision of employment . This factor becomes of particular importance for municipalities, development of which depends on a single or a number of enterprises.
-
• A significant contribution of small businesses in the formation of a profitable part of the municipal budget . In some countries with market economies (USA, UK, Germany, France, Netherlands, Finland and others) the contribution of small enterprises in the formation of both national and local budgets is determined (up to 35 – 40% of all tax revenues). In Russia this figure is lower by more than 2 times – about 15%.
-
• Building the necessary infrastructure for the production of large enterprises . It is extremely difficult to overestimate the value of small businesses for large enterprises find. Any large company signed a large number of contracts, outsourcing, retail and wholesale sales, distribution to small businesses, through which big business is embedded in a system of partnerships and international inter-corporative network.
-
• Ensuring the implementation of new technologies and techniques . In developed countries,
small businesses produce more than 60% of all services, half of all industrial output and nearly half of all innovative ideas and innovations. In addition, small businesses, seeking to adapt to changes in demand in the consumer market, are more receptive to innovation.
-
• Formation of incomes, provision of labor mobility, poverty reduction and the formation of the middle class . At the local level, small businesses are the main source of income generation of most of the economically active population; the proportion of the middle class is also directly dependent on the level of small business development, and consequently, the level of social tension in society.
The special role of small businesses in the socio-economic development of the municipality determines the importance of the study and taking into account current trends in this sector of the economy in the design and implementation of strategic planning documents. The main research objective is the analysis of existing problems and making recommendations on improving the forms and tools for small business support by public authorities and local self-government [2]. From this perspective, this article presents some results of studies in the field of small business conducted by the Institute of Economics KSC RAS, on the example of the Petrozavodsk urban district.
More than half of all small businesses and individual entrepreneurs of Karelia are located in Petrozavodsk. Generally recognized index of development of small businesses in the region, or municipality is the density of small businesses (the number of small businesses per 1000 inhabitants). Number of small businesses in the city of Petrozavodsk per 1000 people is to 1,9 times higher than the average for the Republic of Karelia and the Russian Federation (for details: in the Russian Federation per 1000 residents there are 7 small businesses, in the city of Petrozavodsk – 13). The number of employed in small businesses in the city is presented in table 1 . The sector employs about 25% of the total employed in the municipal economy for today.
Table 1. The number of employed in small businesses in Petrozavodsk, pers.
|
Indicator |
2006 |
2007 |
2008 |
Forecast 2009 |
Forecast 2010 |
|
Number of individual entrepreneurs |
8 200 |
8 500 |
8 950 |
9 050 |
9 300 |
|
Number of workers hired by individual entrepreneurs |
6 200 |
6 350 |
6 400 |
6 500 |
6 600 |
|
Number of employees in small enterprises in the city |
22 800 |
23 400 |
24 400 |
25 400 |
26 400 |
|
Total in small businesses |
37 200 |
38 250 |
39 750 |
40 950 |
42 300 |
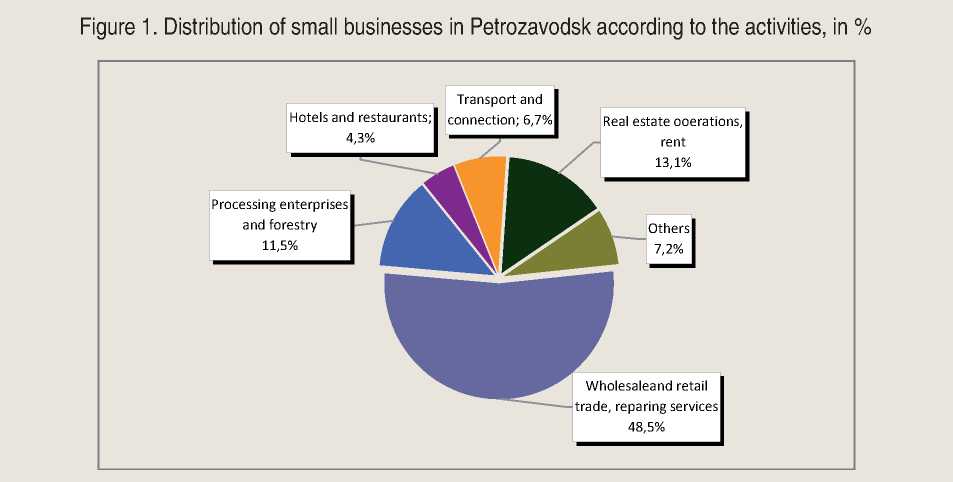
According to available data the largest share of small enterprises in their total number, as in the whole of the Republic of Karelia, and in Petrozavodsk, accounts for such kind of economic activities as “wholesale and retail trade, repair of motor vehicles, household goods and personal utilities”, and is 48,5% (fig. 1) .
The greatest concern for small organizations is the sphere of trade, in which nearly half the total number of small businesses operates. This is due to the fact that the average profitability of business in trade is significantly higher than in industry and other sectors. In addition, the trade is characterized by short period of capital turnover, thus reducing business risks, and that is a critical factor when choosing the type of economic activity for many small businesses.
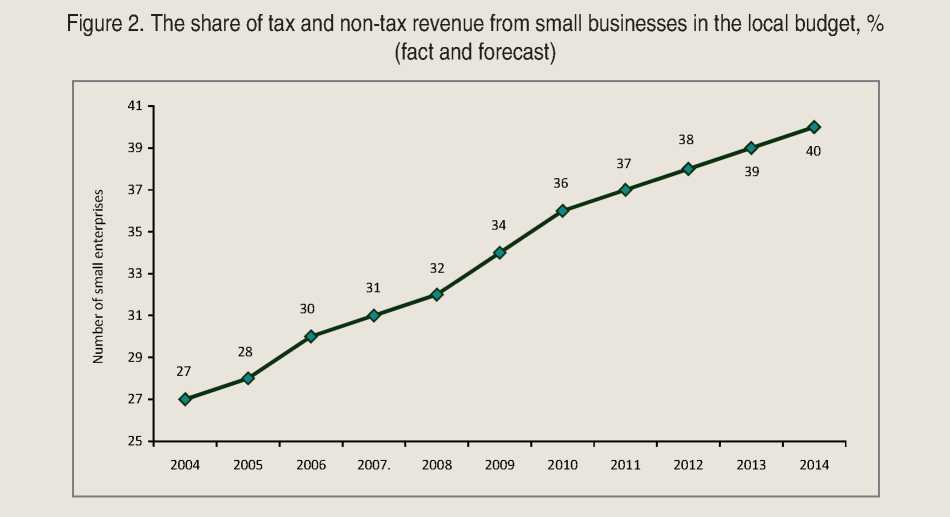
Currently, small business is a major source of revenue in the local budget (about 30%), with the projected increase in the proportion of tax and non-tax revenues of small businesses in the city budget of up to 40% by 2014 (fig. 2) .
However, these positive trends are accompanied by a number of negative phenomena. Despite the fact that the role of small businesses in the economic development of the municipality in recent years is increasing, yet small businesses much more frequently use “gray” and “shadow” patterns of economic activities and use various tax avoidance schemes. This is corroborated by official information on the performance of small businesses. For example, the profitability of products of this sector of the economy is about 2%, while return on assets is less than 4%. In terms of attracting investment, this figure is extremely low, and first of all it is explained by its under-side with entrepreneurs. It is estimated by Rosstat, that 70% of small businesses real rates significantly differ from the official reporting indicators. According to experts, the share of “shadow” companies in small business is higher than in the general economy, although in recent years there has been a reduction of “shadow” and “gray”
economy sectors [5]. Of particular interest is the cost-benefit analysis (according to official statistics) in the context of the major industries in which small firms operate (fig. 3) [4].
According to official data, the profitability of production (works, services) of small enterprises in agriculture, is almost 3 times higher than in trade. The profitability of small businesses in the area of health, physical education and social security was the highest (18,1%), while in the field of transportation and real estate transactions profitability has negative values (-10,2% and -2,8% respectively).
These circumstances determine the need for sources of information adequate to existing realities in the analysis of small business development and evaluation of its potential. The following results of small business study
Figure 3. Profitability of products (works, services) of small businesses in several sectors of the economy of Karelia (according to the data of Kareliyastat)
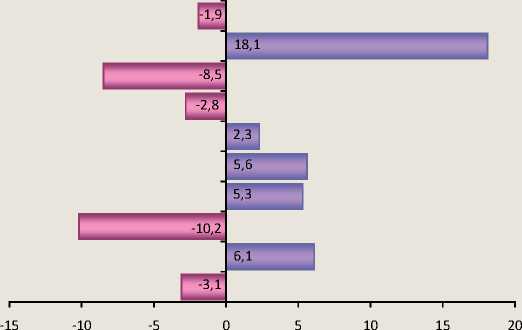
Education
Health and social welfair
Housing and communal services
Real estate operatios
Trade and nutrition
Construction
Connection
Transport
Agriculture
Industry
Profitability, %
are based on the survey of entrepreneurs in Petrozavodsk, which was held in November – December 2007. In the process of questioning 80 small and medium-sized enterprises in Petrozavodsk were interviewed, working in different industries and economic activities. Most of the companies – 64 out of 80 surveyed – are working in industry, services and construction. Companies operating in the market in different times participated in the survey: 5 – 8 years – 22% of the companies surveyed; from 10 to 15 years – 21,3%; from 1 to 3 years old – 17,6%, these are quite young companies; from 3 to 5 years – 16%.
A special place in the study was given to an analysis of the problems faced by entrepreneurs. First, this analysis allows correct understanding the “gaps“ in the development of small businesses and making decisions in its support. There is a need for analysis and designing interventions to improve the local economic policies in general.
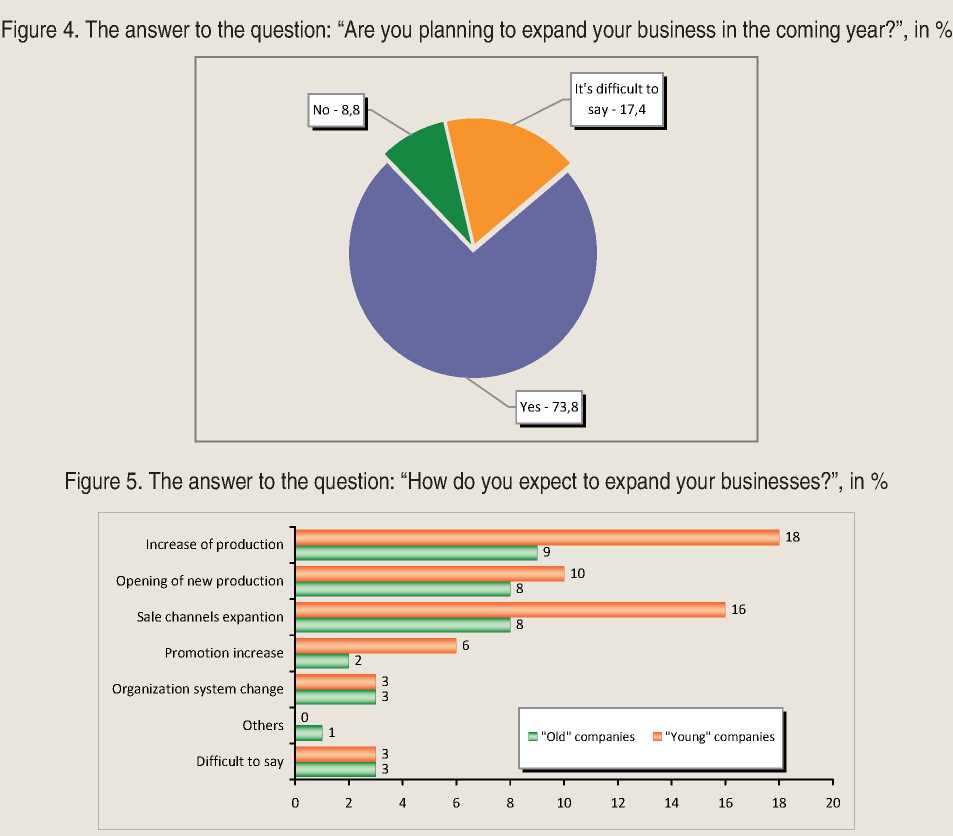
ity areas of business expansion for “young” companies are increasing production, expanding sales channels and the organization of the production of new products. “Old” companies are more conservative and less likely to support production of new products, as established in the “niche” of mature markets and have fear of stability reducing in the established production development and organization. However, “old” companies are more actively in favor of changing the organizational structure of the company, which indicates a shift to quality growth.
In summary, the characteristics and problems of small businesses, depending on the period of their operation are presented in table 2 . The results of questionnaires show that “young” companies are more mobile, more flexible and quickly adapt to changes of environmental factors; “old” companies tend to occupy a stable market niche and have lower mobility and volatility.
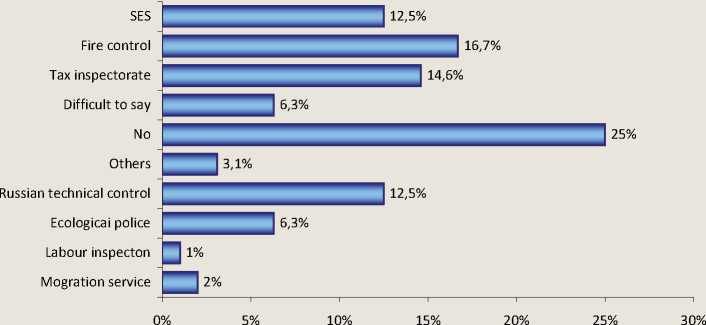
Based on these questionnaires, small businesses have some difficulties in relationship with the following regulatory agencies: fire control (20% of respondents), the tax inspectorate (14,6%), Russian technical control (12,5%), sanitary-epidemiological service (12,5%). Thus 25% of respondents stated that they have no problems in relations with the supervisory services (fig. 8) .
Summarizing the views of small businesses representatives in Petrozavodsk on problems
Table 2. The main characteristics and problems of small businesses, depending on the period of their operation
|
“Young” companies |
“Old” companies |
|
|
|
Conclusion . More mobile companies are characterized by more rapid adaptation to changing conditions; they have more experience of interacting with foreign partners. |
Conclusion . More stable companies with stable market niche are characterized by less mobility and greater need for funding at the expense of larger scale production. |
Figure 6. The answer to the question: “Do you plan to expand the geography of your business?”, in %
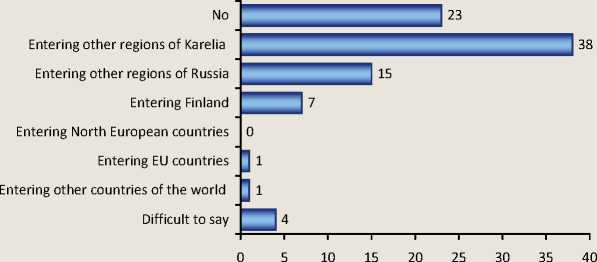
Figure 7. The answer to the question: “What problems in your business do you encounter most often?”, in%
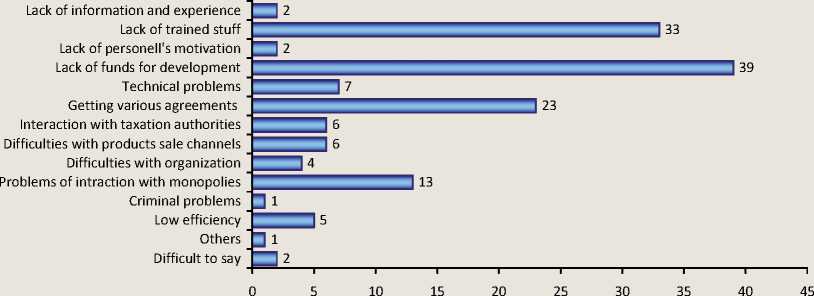
Figure 8. The answer to the question: “What controlling services bring you the most difficulties?”
and prospects of development, administrative, economic and other barriers the following conclusions can be made:
-
1. The state of small business in Petrozavodsk is quite stable and is characterized by a high entrepreneurial activity.
-
2. The companies operating in the market during different time have different strategies of behavior. “Young” companies tend to overlook the growing markets with strong marketing, “old” companies are established in “niche” mature markets and are therefore characterized only by supporting marketing.
-
3. Most small businesses in Petrozavodsk see possibilities for expanding their business by increasing production, expanding distribution channels and production of new products.
-
4. Plans to expand the geography of small businesses business were connected mainly with areas of the republic, which proves that small businesses are targeted primarily at the regional market.
-
5. Small business representatives do not connect Difficulties and problems concerning market expansion with the internal capabilities of business but the economic and administrative barriers, the growth rates of natural monopolies, the instability of legislation.
In the face of world financial and economic crisis, which the negative effects have become increasingly felt by representatives of Russian businesses in the autumn of 2008, the problem of small business support has become even more urgent. It is clear that currently a significant number of entrepreneurs in the new environment had to revise their plans to expand business and to refrain from increasing the production or release of new products. On the one hand, the crisis will help to improve the efficiency of enterprises, optimize costs, finding new options. On the other hand, a significant portion of these businesses has serious problems and needs the support of both the public and municipal authorities.
Despite the fact that the crisis has not seriously affected at small businesses, in contrast to the large export-oriented companies, some of its implications in the near future may adversely affect the competitiveness of small enterprises. This directly relates to those small businesses which work with large companies or guided by them in their activities. With regard to small businesses, working with the end user, this is due to the decline in sales resulting from a decline in purchasing power of population, and with a sharp increase in costs. For example, the devaluation of the ruble led to higher prices of imported products and components manufacturing, which will undoubtedly affect the profitability of manufacturing enterprises, which are the consumers of such products. Moreover, without total solution of the problem of cross-subsidization and the deteriorating financial condition of large enterprises electricity tariffs for small and medium-sized businesses have increased.
In this regard, the task of small business supporting is becoming a priority in the implementation of local economic policy. Under the new circumstances, this task will require and implement previously planned activities and the development of new anti-crisis measures, taking into account the changed conditions. At the present time in Petrozavodsk a longterm municipal program “Development and municipal support for small and medium-sized businesses in the territory of Petrozavodsk city district for 2009 – 2014“ is developed. The total projected amount of the Program funding is 22,5 million rubles; its implementation involves activities such as [1]:
-
1. Financial support for small and medium entrepreneurship (including the subsidized interest rate on investment loans).
-
2. Property support (transfer of possession or use of municipal property).
-
3. Information and consultancy support (an Internet-representation “Small and Medium Business in Petrozavodsk“, information and reference materials issue, business consulting).
-
4. Training, retraining and skills development.
-
5. Support for innovation and industrial production (subcontracting conclusion, development of business incubators industry, etc.).
-
6. Support for entrepreneurs engaged in foreign economic activities.
With the implementation of policies to support small and medium-sized businesses in the territory of the municipality the new challenges that entrepreneurs face now must be taken into account. Solving these problems will require, above all, building a constructive dialogue between business and power. The effectiveness of this policy will be mainly determined by the speed of decisions, as well as efficiency of tools for coordinating the interests.
Список литературы Small business as the basis of municipal economy: problems and support forms (by way of Petrosavodsk example)
- Development and municipal support for small and medium-sized businesses in the territory of Petrozavodsk city district for 2009 -2014: long-term municipal program . -Access mode: http://g2b.ptz.ru/msb/development/
- Ivanov, V.V. Municipal management: a handbook/V.V. Ivanov, A.N. Korobova. -M.: INFRA-M, 2002. -718 p.
- Assessment and research of small and medium-sized businesses’ needs in the city of Petrozavodsk and Karelia. Analysis of Administrative Barriers: A Report on R&D/Institute of Economics, Karelian Scientific Center, Russian Academy of Sciences, 2007.
- The results of the small sector of the economy of Karelia: analytical note/Kareliyastat. -Petrozavodsk, 2005, 2006.
- Yasin, E.G. The shadow response of business/E.G. Yasin//Rossiyskaya Gazeta. -2007. -№ 4305.


