Small business is an important reserve for development of a one company town
Автор: Tkachuk Stepan Nikolaevich
Журнал: Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast @volnc-esc-en
Рубрика: Regional economy
Статья в выпуске: 3 (11) т.3, 2010 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The small business development acquires strategic importance for sustained social and economic development of regions, especially for one company towns located on their territories. The composition of problems occurred in one company towns, the factors that create difficult situations in their economic and social and cultural life are considered in the article. The possibilities of using small business for sustainable growth of a one company towns and improving the quality of life of their people in times of crisis and during the post-crisis development are substantiated.
Vologda oblast, a one company towns, social and economic environment, diversification of a one company town economy, the role of small and medium businesses
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147223202
IDR: 147223202 | УДК: 334.012.64(470.12)
Текст научной статьи Small business is an important reserve for development of a one company town
The problems of the small business development and assessment of the situation
The small business development is one of the most important activities of government bodies at all levels within the framework of deciding questions of the social and economic development of territories and mitigating social problems.
In recent years, the small business development has gained increasingly in political, social and economic importance. This sector of the economy creates new jobs and maintains the bulk of consumers, producing complex of goods and services in accordance with the rapidly changing market demands. Small business contributes to increase tax revenues, most rapidly developing new products and economic niches and areas which are unattractive to large businesses.
On the one hand small and medium enterprises is a specific sector of the economy that creates wealth with minimal involvement of the material, natural and other resources and maxi- mum human capital, and on the other hand it is the sphere of self-realization and self-reliance of citizens within the rights granted by the Constitution of the Russian Federation (article 34).
Today small and medium business is characterized by high risk, low financial reserves, limited fixed assets, a significant amount of borrowed resources and other indicators that determine its “economic instability”.
The experience in implementing programs of small business development shows that only measures of integrated support can be effective. The system of integrated support at the local government level should include the following mandatory elements:
-
- necessary legal and regulatory framework, including the development program for small and medium enterprises;
-
- developed support infrastructure for small and medium-sized businesses, providing scientific and methodological, informational, educational and consulting support for beginners and existing entrepreneurs;
-
- protection of rights and legitimate interests of entrepreneurs;
-
- interaction between the business (as represented by associations of entrepreneurs and authorities);
-
- creating a favorable business climate.
Particular importance has the implementation of these requirements at the level of a one company towns.
Ministry of Regional Development of Russia approved the list of a one company towns, which in the crisis were in the most difficult economic situation and will receive government support.
Sokol is a one company town in the Vologda oblast. The city has several enterprises of forestry, wood processing and pulp and paper industries which are forming a company town. In 2008 the proportion of enterprises forming a company town was as follows: in the volume of dispatch of industrial products – nearly 63%, in the average number of employed people in the town – 27%, in the volume of the profit before taxing – 53%, in the town wide level of investment – 57%.
Sokol enterprises were among the first enterprises which felt the impact of the global financial crisis, the decline in both domestic and external demand.
In this regard, the development of small and medium business is defined in the beginning of one of the priorities of social and economic development.
Priority directions for small and medium enterprises should be determined on the existing social and economic situation in the town, financial capacities, the achieved results and with the main priorities of social and economic development of the municipality.
In recent years the structure of small enterprises of the city by economic activities remains virtually unchanged (fig. 1) . The main part belongs to the trade and catering companies (28%), industry (15%), construction (16%) and 11 – 15% organizations are engaged in operations with real estate, rent and rendering of services.
More than half of entrepreneurs (53%) employ in the retail and wholesale trade, 13% – in the service sector in transport and communications, 9% – in the sphere of consumer services. The share of workers employed in small business to the number of employees in general in the city is about one-third.
Until mid-2008 small business of the city was developing quite rapidly: the total number of small businesses, individual entrepreneurs, the proportion of people employed in this sector
Figure 1. Distribution of the number of small businesses the Sokol by the main economic activities for 2009, %
Wholesale and retail trade, cars and home appliances repairing; 28
AW
Processing productions; 15
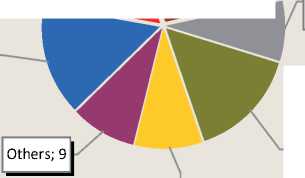
Real estate operations, rent and rendering of services; 15
Agriculture, hunting and forestry; 9
Transportation and communications; 8
was increasing, wages were raising; new objects of trade and catering were being opened.
To support small businesses in the city in 2009 the following measures were used:
-
1. The correction factor K2 of basic profitability K2 of a single tax on imputed income by all activities was not raised.
-
2. 5% tax rate under the simplified taxation system for socially important sectors (food and light industry, manufacturing of products of folk art crafts, housing and communal services, tourism) is run in.
-
3. A branch of the state institution “Business incubator” is created.
-
4. Nearly 4 million rubles of budgetary subsidies are sent on grants and compensation of the interest rate on loans. Due to this small businesses saved 398 work places and created 105 new ones, including in the manufacture of furniture – 46 places, in the wholesale and retail trade – 20, construction and production of building materials – 16, in food production – 8, in wood processing – 6, in the health services sector – 5, shoes production – 4.
-
5. A competitive placement of state orders for small businesses to produce products and render services for the public region and municipality needs was held.
Small and medium businesses of the city created in total 550 new jobs, including house building – 119, wood processing – 98, food production – 104, housing and communal services – 66, the sphere of transport services – 43, others (public services, environmental activities, IT-technologies, development of crafts, etc.) – 120.
However the negative consequences of the ongoing economic crisis significantly affect the activities of small businesses. The reduction in prices and demand for products, toughening of requirements by credit institutions, lack of liquidity led to late payment of wages, untimely tax payments and payments for delivered raw materials, materials and services.
Effect of crisis on the activities of small and medium-sized enterprises in various sectors has its own specifics.
Lumbering and wood processing. In 2009, the volume of products shipped by small businesses in forestry declined by 50%. Main problems of small enterprises in the industry related to “compression” of demand in export markets, a decline in demand in the building sector and, consequently, a significant reduction in production output, but with a sharp increase in competition. In addition, the industry lacks long-term price targets.
In food production the demand for food compared with other commodity groups declined slightly. However, in this sector, an increase of accounts receivable associated with the forced additional provision of delays of payments by manufacturers to wholesalers is observed. In addition, in food production sector small companies are extremely limited in the maneuver, as large players dominate the market who set the price limits, that is why smaller producers have to either work on the verge of profitability, or leave the market.
Wholesale trade in food products. A key problem for the wholesale companies is a violation of financial flows in the markets. An important factor in the existence of the wholesale level are the delays of major manufacturers and wholesale companies, formed, in particular, through bank loans, as well as own delays to retailers and other consumers. At the same time, many suppliers have increased direct sales and have access to end consumers, bypassing the wholesale level, what also contributed to the knock-out of the market for the weakest players.
Retail trade in manufactured goods. Demand remained in previous measure only for certain types of industrial consumer goods – clothing, textiles and footwear. Industrial goods are highly dependent on imports of finished products as well as of parts and separate elements. The devaluation caused a price increase that goes against the falling incomes. In addition, violation of financial ties led to supply disruptions of imported goods.
Retail trade in food products . Retail trade experienced the impact of the crisis less than other sectors of the economy. The falling of the demand does not exceed 15 – 20%, although there is a decrease in the amount of an average check and a change in the demand structure in favor of cheaper products. As in other industries, companies are experiencing a certain lack of financial resources to upgrade the range and development. There is an increase of a turnover time.
Repairing and maintenance of vehicles . The decline in demand for repair services was 30 – 40%. The volume of orders from corporate clients most dramatically reduced, many of which have significantly reduced activity. On the part of private clients “compression” of demand is not so much: because of limited demand for new cars, car owners pay more attention to repairing vehicles.
Building. This is the most affected industry: problems in it began in the spring of 2008, and the crisis has worsened the negative trend. So, in typical many-storied building companies recorded decrease in demand by 50 – 90%, in low-rise wooden building – slightly less – by 30 – 60%, in the design and installation of utilities – by 40 – 60%. Although a gradual decline in property prices is observed, but it is not yet able to revive demand. Resumption of growth in the cost of building materials, induced by increase in overhead costs of market participants, prevents resolution of problems in the industry. There was also a sharp increase in the cost of imported materials.
Transportation. The drop in orders, according to different estimates, is 60 – 80%. Financial problems of carriers were worsened by seasonal factor – the volume of traffic is reduced in winter. Prices for transport services fell by 30 – 50%. The specific problem of transportation companies, which profits are signifi- cantly dependent on the proportion of empty mileage, is a sharp drop in turnover of vehicles (50 – 60%). In connection with the decrease in the density of orders vehicles have to wait for return freight from the point of destination for several days or to return without freight.
Specialized map for business development based on the assessment of the impact of crises at various sectors of the economy was developed, which reflects the expectations of entrepreneurs about the attractiveness and competitiveness of business in different economic activities (fig. 2) .
This map allows to evaluate the condition and identify priority directions of businesses.
The broader study showed that Sokol has the following main problems hindering the development of small and medium businesses:
-
- inadequate legal and regulatory framework in the field of small and medium enterprises, the need to simplify and optimize the system of taxation, reduce tax pressure;
-
- lack of integrated support of the beginners, which allows, on the one hand, to have free access to resources, and on the other – to get basic knowledge;
-
- low potential to use bank loans for replenishing circulating capital due to their high cost and inadequacy of collateral securities for banks;
-
- low level of training of many managers of small and medium-sized businesses and individual entrepreneurs in matters of legal, financial, tax laws;
-
- limited access of entrepreneurs to information about available resources, including the surplus of production space and production equipment in large enterprises, which may be involved in market turnover by small and medium-enterprises;
-
- a weak attraction of small and mediumsized businesses to solve social problems, and in the first place of employment.
Conducting of effective, coherent policies for the support and business development, active solution of its problems will allow to diversify
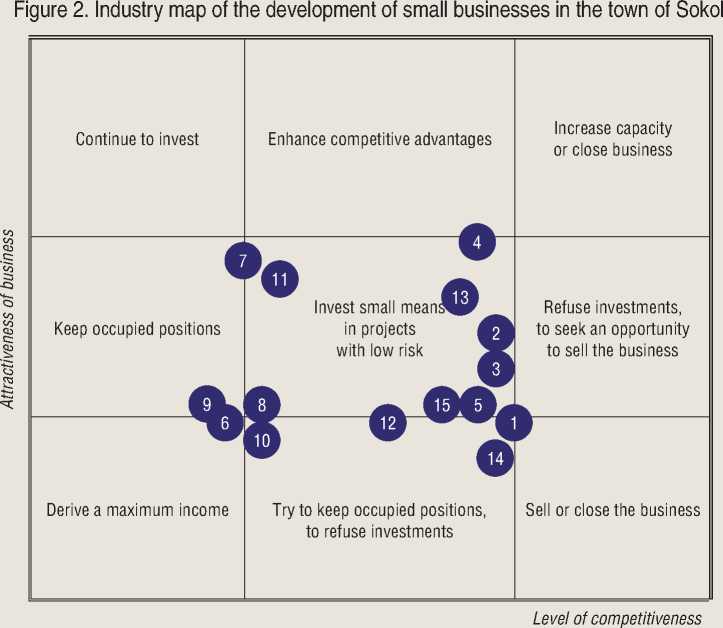
1 – wholesale trade in manufactured products; 2 – wholesale trade in food; 3 – retail trade in manufactured products; 4 – food retailing; 5 – repair of motor vehicles; 6 – repair of household appliances; 7 – manufacturing of food products; 8 – publishing and printing; 9 – manufacturing of machinery and equipment; 10 – manufacturing of metal, rolling and metal products; 11 – wood processing; 12 – textile and clothing industry; 13 – building; 14 – real estate operations; 15 – transportation.
the economy, create a new driving force for economic growth of the one company town.
Priorities for development of small and medium enterprises in the one company town
In consideration of the socio-economic situation and the existing structure of the city’s economy Sokol identifies priorities in the development of entrepreneurial activity:
-
• manufacture of food, industrial goods, consumer goods;
-
• building of housing, industrial and sociocultural objects;
-
• wood processing and recycling of secondary raw materials;
-
• public and social services (health, education and social welfare);
-
• housing and communal services, transport activities and introduction of energysaving technologies;
-
• innovation and environmental management;
-
• IT-technologies, development of traditional handicrafts and tourism.
The imbalance in the economy of Sokol, which is a one company town, can not be removed without the development of entrepreneurship.
The analysis showed that the development and support of small and medium businesses should be conducted in the following directions:
-
1. Improving the financial and credit support mechanisms to improve access to credit and investment resources (subsidization of a part of costs of small businesses in the payment of interest rate, the development of regional collateral mortgage-fund for small enterprises, promotion of the municipal district and the town to implement similar activities in the context of co-financing).
-
2. Creating a network of institutional infrastructure for small businesses (including a business incubator, marketing, subcontracting, information and consulting center, etc.). The solution of this problem will equalize the chances of small business with other groups of economic agents.
-
3. Promoting the competitiveness of local producers, supporting the export-oriented and innovative business (incentives to invest in modern equipment and training; incentives to implement quality management systems and develop cooperative ties with large enterprises).
-
4. Implementing measures to encourage the inflow of new labor force in small business (economic support for beginners, active promotion of small businesses, encouraging people, especially youth, to engage in business, training new entrepreneurs and personnel selection).
-
5. Enhancing the role of entrepreneurship in public life, its contribution to the solution of social problems of areas (promoting the establishment of business associations; attracting businessmen and their associations to develop regulatory legal acts in the sphere of economy and finance, development plans of the town and district, and various special programs, etc.).
Regulatory and legal support activities of small and medium-sized businesses and organizations that make up the infrastructure to support it, involves: a) examination of existing legal acts of local governments and legal act drafts within the scope of the interests of small and medium enterprises; b) the development and adoption of legal acts:
-
• defining a list of equipment intended for use by small and medium-sized businesses and organizations that make up the infrastructure to support it;
-
• regulating the provision of subsidies to compensate a part of expenses related to the payment of interest rate on loans obtained by small and medium-sized businesses and organizations that make up the infrastructure to support it in credit institutions of the city;
-
• establishing the procedure for transfer of property in the possession and use of small and medium businesses, organizations, forming the infrastructure to support it;
-
• other legal acts that determine the order of implementation of the Program.
Development of financial and credit support mechanism for small and medium-sized businesses includes the following measures:
-
a) subsidies for the payment of interest rates on loans obtained by small and medium enterprise from lending organizations, and the lease payments payable to leasing organizations;
-
b) provision of guarantees for the obligations of small and medium enterprises;
-
c) financing projects of small and medium entrepreneurship through the development of microcredit.
To support the new SME there is the assignment on the gratuitous and irrevocable basis of subsidies (grants) to establish their own business entities (except grants to state, municipal institutions, individual entrepreneurs, individuals-producers of goods, works and services for cost recovery in connection with the production of goods, works and services in part of the costs for state registration of legal entity or individual entrepreneur; acquisition of fixed assets and manufacturing equipment; rent).
Financial support for SMEs will also be maintained through the development of microfinance.
Microfinance is a non-profit organizations activity (foundations, consumer cooperatives, etc.) established to provide access of small and medium-sized enterprises and organizations of the support infrastructure to the financial resources through loans.
Target program “Development of small and medium businesses in Sokol in 2010 – 2012” provides support to about 50 investment projects of small and medium businesses:
-
- more than 10 projects in the manufacturing industry (tailoring shop and clothing factory, blacksmith and sewing workshops, workshops
for the production of corrugated sheets, building materials, furniture, window blocks, fuel briquettes) with the creation of 170 jobs;
-
- 8 projects in the field of production and distribution of electricity, gas and water with the creation of 390 jobs;
-
- 5 projects in the field of building (building of a tourist center, reconstruction of objects, building of economy class dwelling, country houses, the production of gypsum tiles) with the creation of 186 jobs;
-
- 4 projects in the trade and hotel services with the creation of 40 jobs;
-
- 4 companies to provide transportation services, of storage and processing of goods, leasing of logging equipment with the creation of 126 jobs;
-
- creation of ophthalmology center, wide-sports club, children’s art center;
-
- 6 projects to provide community, social and personal services;
-
- 10 projects to develop public services (laundry, car wash, renovation and restoration of furniture, road service, etc.) with the creation of 100 jobs.
It is planned to transform Vologda “Business incubator” into an independent businessincubator in Sokol (including marketing center and the center of subcontracts). Business incubator will provide support in the form of various consultations, seminars, external incubation and business training to small businesses. Each year the incubator will contain on favourable terms 20 small businesses, which will create about 200 jobs.
Informational and methodological support for SMEs, and organizations engaged in its support, include:
To resolve this issue the use of both traditional sources of media (radio and television programs, publications in the media on topical issues for small and medium enterprises) and interactive electronic resources and the Internet are provided for.
Advice and information support to SMEs is planned to be accomplished through an emergency legal and advice assistance to entrepreneurs, as well as consideration of their complaints on unauthorized checks conducted by law enforcement and regulatory agencies.
In this direction it is planned to establish hot lines in Sokol, the organization of mobile emergency legal assistance stations.
Preparation, training, skills development of small and medium enterprises and infrastructure to support it will be done through the implementation of such activities as:
-
• organization of seminars, conferences;
-
• organization and conducting training courses, retraining and skills;
-
• organization of “School for young entrepreneurs”;
-
• creation of circles of interest to older students.
When implementing measures in the field of general business regulation by the federal and regional government, it is safe to say that for the period 2010 – 2012 fairly high levels of development of small businesses will be reached in Sokol:
1) the number of small businesses and individual entrepreneurs will grow (2012 to 2009) half as much;
2)increase of the output volume of small enterprises (2012 to 2009) will be not less than 30% (or an average of 10% annually);
-
3) there will be a diversification of the structure of the urban economy, it will be less vulnerable to the emergence of new crises.
Список литературы Small business is an important reserve for development of a one company town
- Animitsa, E.G. Notes on the development of core (priority) directions of the economic restructuring of a one company towns /E.G. Animitsa. -Access mode: http://www.rosdeputat.ru/publications/view/19
- Egorsheva, N. In the most vulnerable situation a one company towns may find themselves/N. Egorsheva//Rossiyskaya Gazeta. The federal issue. -2009. -№ 4827. -15 January.
- Kryukov, O.G. The influence of the global financial crisis on the economy a one company towns/O.G. Kryukov, E.V. Arsenova//Effective crisis management. -2010. -№ 1. -Pp. 80-87.
- Kulakov, O. Diversification of the economy of a one company towns and production of a main enterprise /O. Kulakov//Materials of the All-Russian Conference “A one company towns: modern solutions”. -Access mode: http://www.monocityforum.ru/
- Lyubovny, V.Y. Monoprofile cities: state, problems, causes and possibilities of rehabilitation /V.Y. Lyubovny/Materials of the All-Russian Conference “A one company towns: modern solutions”. -Access mode: http://www.monocityforum.ru/
- Maslova, A.N. Features of including enterprises forming a company towns in the global economic exchange/A.N. Maslova//Bulletin of the Nizhny Novgorod University named after N.I. Lobachevsky (A series of “Social sciences”). -2009. -№ 1. -Pp. 30-34.


