Smoke priming, a potent protective agent against salinity: effect on proline accumulation, elemental uptake, pigmental attributes and protein banding patterns of rice ( Oryza sativa)
Автор: Jamil Muhammad, Malook Ijaz, Parveen Salma, Naz Tayybah, Ali Arshad, Ullah Jan Sami, Ur Rehman Shafiq
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 1 т.9, 2013 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The exogenous application of plant derived smoke solution through seed pre treatment is consider to create tolerance in the plant against salinity, for this purpose different dilution of plant derived smoke solution as 1:5000 Buhania, 1:1000 Buhania, 1:1000 Cymbopogon, 1:500 Cymbopogon were used against 0 mM, 50, 100 and 150mM NaCl solution in the medium. The effect was observed on total proline accumulation, heavy metals uptake, photosynthetic pigments and protein poly peptide bands intensity in two rice varieties as Basmati 385 (B-385) and Shaheen Basmati (S. Basmati). Proline concentration increases while chlorophyll “a” chlorophyll “b” and carotene level decreases with increasing salinity. On other hand zinc concentration increases while cadmium and lead concentration decrease in the crop under saline conditions. Intensity of protein polypeptides bands decreases gradually with increasing salinity level but plants from the seeds soaked with smoke solution alleviate the drastic affect of salinity, and intensity of bands is quite good by comparing with non primed seeds. It is concluded that seed priming with plant derived smoke solution show beneficial effect on crop to protect them from salinity.
Salinity, smoke priming, rice, proline rich proteins, heavy metals, sds-page
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14323710
IDR: 14323710
Текст научной статьи Smoke priming, a potent protective agent against salinity: effect on proline accumulation, elemental uptake, pigmental attributes and protein banding patterns of rice ( Oryza sativa)
Soil salinity is the burning issue for crop production around the globe, including Pakistan. More than half of the world depends upon on rice as a food. The amount of rice used in Asia is approximately 30-80% (Narciso and Hossain, 2002). Rice is the main food crop of Pakistan (Zia et al., 1998) and is consider as a salt sensitive crop (Mass and Hoffman, 1977). Reduction in rice yield is about 68% in salinity affected soil (Qayyum and Malik, 1988). Harmful effect of salinity on physiological, biochemical and molecular aspects of different crop was extensively investigated in Pakistan (Jamil et al., 2012a; Khan et al., 1995). Salinity affects every aspect of plant physiology and bio chemistry by reducing photosynthetic pigments (Jenifer and Franklin 2002) interfering with minerals uptake (Knight et al., 1992; Noraho and Gaur, 1995) proline accumulation (Shamseddin-Saeid and Farahbakhsh, 2003) and even on protein synthesis (Jamil et al., 2012). Different ways are used to overcome the drastic affect of salinity and Salinisation in which seed priming is the most economical and easy approach recently used (Iqbal and Ashraf, 2007). Priming with smoke solution is the cheep and economical way to stimulate the plant in the ecosystem to germinate (Brown and Botha, 2004). Plant derived smoke solution not only affect germination but also has value able affects on flowering and somatic embryogenesis (Kaley, 1993; Senaratna et al., 1999). A part from that so many studies on salinity and different priming agent which alleviate the adverse affect of salt stress; affect of smoke solution priming is a novel work and its affect on biochemical and molecular aspect on rice is limited. Therefore, this research work is initiated to used smoke solution as a priming agent to alleviate the salt stress and to analyzed their effect on various bio chemical attributes of the plants such as proline accumulation, uptake of different minerals, photosynthetic pigments and also on protein banding patterns under saline condition.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Plant Materials
Seeds of two rice ( Oryza Sativa ) varieties, Basmati-385 and Shaheen Basmati were procured from National Agriculture Research Center (NARC) Islamabad, Pakistan.
Preparation of Samples
Hypochlorite solution 3.5% was used for surface sterilization of the seeds. The sterilized seeds were soaked in priming solution of Cymbopogon jwarancusa and Buhania varegata (produces by burning of 333 grams of plants material and smoke were bubbled through one liter of distilled water) for 24 hours. Seeds were then germinated in Petri plates at control temperature for ten days. Seedlings were then grown in Hoagland’s solution for two weeks (Hoagland, s and Arnon 1950). The seedling was irrigated with renewed solution after each week. Salt treatment in this solution was started after two weeks of the experiment. The NaCl treatment used was 0 controls, 50, 100 and 150 mM. After harvesting, plant materials were divided in to two parts, half harvested part in liquid nitrogen for proline and SDS-PAGE analysis while other half was oven dried at 80oC.
Proline analysis
Proline was quantified as by Bates et al. (1973) with a slight modification. Fresh plant material (100 mg) was crush in liquid nitrogen and complete homogenized in 5 ml of 3% salfosalicylic acid and the residue was removed by centrifugation at 4000 rpm for 30 minutes. The homogenized tissue (~1 ml) react with I ml acid ninhydrin ( 1.25 g ninhydrin warmed in 30 ml of glacial acetic acid along with 20 ml of 6 M phosphoric acid with continue stirring at room temperature) for 1 hour at 1000C at oven. The reaction mixture was vigorously mixed with 2 ml of toluene and placed at room temperature for 30 minutes until separation of two phases. The upper aqueous color phase containing toluene was place in room temperature (250C) for 20 minutes and optical density was measured spectrophotometrically at 520 nm using toluene as a blank. D-Proline standard cure is used for concentration of Proline on a fresh weight basis, using formula (μmol Proline /g fw -1).
Photosynthetic pigment Analysis
Lichtenthaler and Wellburn (1985) method was used for the determination of chlorophyll and carotenoids contents. Dry plant sample (25 mg) along with 25 mg of MgO was taken in a test tube to neutralize the plant acid and prevent the formation of pheophytin. Add 5 ml of methanol and homogenized on shaker for 2 hrs. Transfer the turbid pigment extract to 5 ml graduated centrifuge tube. Centrifuge for 5 min at 4000 x g in an explosion-proof tabletop centrifuge at 250C. Transfer the supernatant into a cuvette and take an absorbance reading at three wavelengths as 666 nm, 653 nm and 470 nm, taking methanol as blank in a (UV-VIS) spectrophotometer. The chlorophyll “a”, chlorophyll “b” and total carotenes was calculated by the formula
C a = 15.65 A 666 – 7.340 A 653
n C b = 27.05 A 653 – 11.21 A 666
C x+c = 1000 A 470 – 2.860 C a – 129.2 C b / 245
SDS-PAGE Protein Analysis
Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) was used for protein analysis of control, salt treated and smoke primed plants as described by (Laemmle, 1970) with slight modifications. Leaves were crushed in liquid nitrogen to fine powder and 12 mg was weighed in 1.5 ml micro tube. Protein extraction buffer (Tris-HCL 0.5 M (pH 8), 2.5% SDS, 10% Glycerol, 5% 2-merceaptoethanol) of about 400ul was added to each micro tube. Kept it overnight at 40oC and then centrifuge at 13000 rpm for 10 minutes at room temperature. The supernatant was removed and store at 4 oC containing extracted protein. Electrophoresis was done at 80 V for 2 and half hours by using Standard Twin Mini Gel Unit (USA).
Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250 (Sigma) for 40 minutes was used for staining, and distained with 20% methanol, and 5% acetic acid. The molecular weight of protein subunits was measured by comparing sample bands to the standard protein molecular weight marker bands (Benchmark Protein Ladder 10 – 220 KDa) in the electrophorogram.
Micro elements analysis of plant Samples
Plant material (100 mg) was wet digested by acid mixture of nitric acid and sulfuric acid according to Garraud et al. (1996). The filtrate was suitably diluted with De ionized water to a constant volume for all samples. The diluted samples were used for Atomic absorption spectroscopy (Perkin ELMER, A Analyst 400) with air acetylene flame using hollow cathode lamps against the standard (Hanlon, 1992)
Statistical analysis
Analysis of variance was performed by using MS-Excel (statistics 9.1version) Statistical software. Each Petri plate was considered as a replicate and mean value was compared with Standard deviation.
RESULTS
Effect of Salt Stress and Smoke Priming On Proline Accumulation
Results of our study shows that under salt stress condition accumulation of proline was significantly increased as compared to control. As in control, proline amount was 0.405 mg/g which increased to 0.783mg/g at 150 mM salt concentration in Basmati – 385, while these values were 0.494 mg/g at control and 0.926 mg/g at 150 mM salt concentration in Shaheen Basmati (Fig. 1A and 1B). On other hand all smoke dilutions reduced the amount of proline as 1:500 Cymbopogon +150 mM salt solution had 0.596 mg/g of proline compared to non primed seeds (0.783 mg/g) in Basmati-385 (Fig. 1A) while in Shaheen Basmati, these values was 0.535 mg/g in 1:500 cymbopogan+150 mM salt solution and in non primed seeds, the value was 0.926 mg/g at 150 mM salt stress solution (Fig. 1B). Effect of Salt Stress and Smoke Priming on Photosynthetic Pigments
Chlorophyll and carotene contents decreased with increasing salt concentration in the medium. As in control with 0 mM salt, the chlorophyll a, b and carotene values were 8.42, 8.67, and 421.32 mg/g respectively, which reduced to 6.82, 5.87, 252.30 mg/g at 150 mM salt stress in Basmati-385 (Fig. 2). Similar pattern of result was seen in Shaheen Basmati as shown in Figure 3. On other hand smoke primed seedlings shows good response to salinity and alleviates the stress affect to a great extent (Figs. 2 and 3). As in 1:5000 Buhania+150 mM salt solution, the amount of chlorophyll “a” was noted 7.06 mg/g, which was high from 6.85 mg/g in plant treated with 150 mM salt solution. Similar pattern of results was shown by other smoke dilutions in chlorophyll b and carotene in both varieties (Figs. 2 and 3).
Effect of Salt Stress and Smoke priming on micro elements uptake
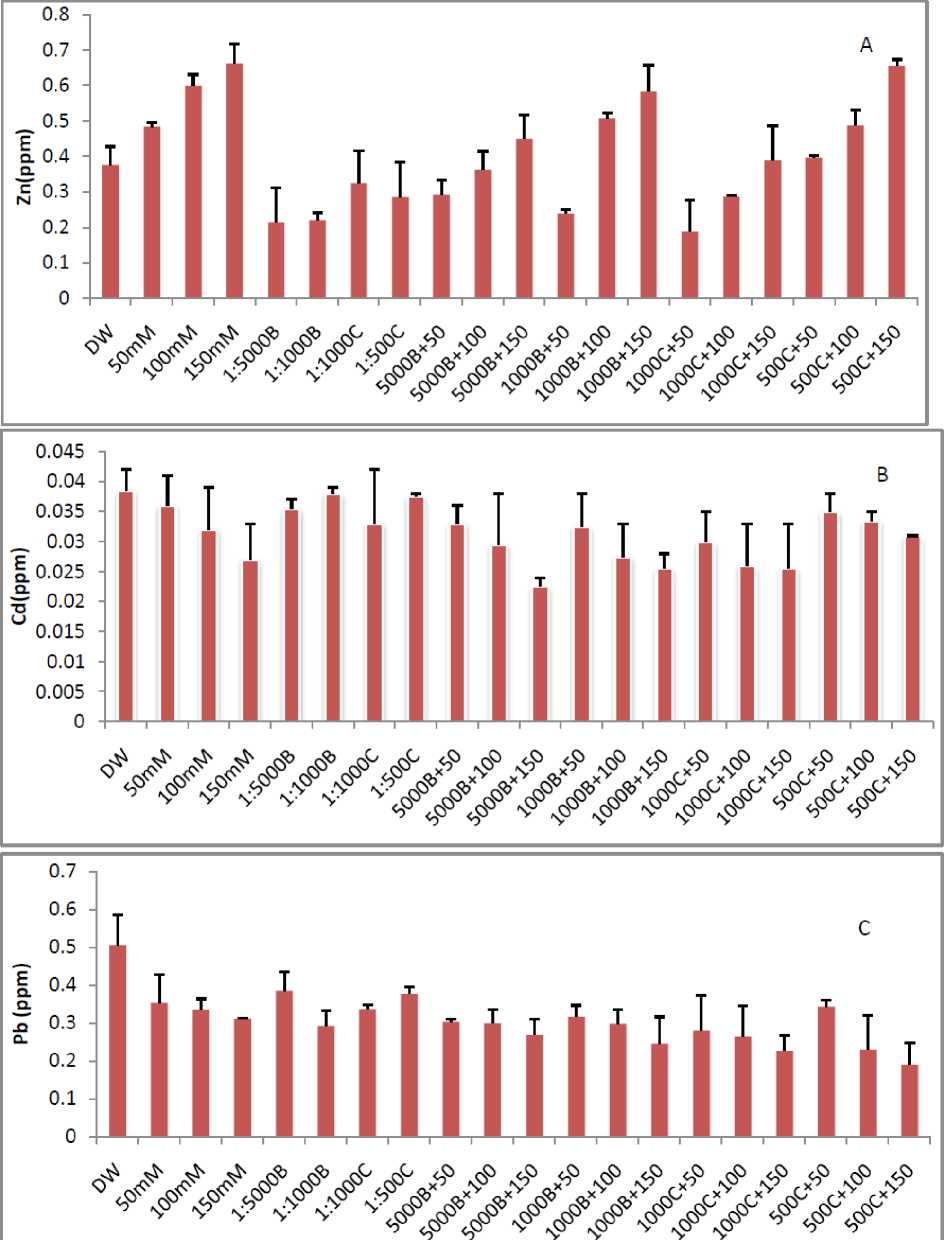
Zinc concentration increased in leaves with increasing salt concentration. As in control the zinc concentration was 0.298 ppm, which increase to 0.719 ppm under 150 mM salt stress in Basmati-385 (Fig. 4). In Shaheen Basmati, these values were 0.375 ppm in control and 0.662 ppm in 150 mM salt stress. In both varieties smoke priming effect uptake of the minerals by reducing the overall zinc concentration with alleviating salt stress condition. In Basmati – 385, zinc value was 0.291 ppm in 1:5000 Buhania+50 mM treatment compared to non primed seedling (0.482 ppm) at 50 mM (Fig. 4) while same situation was noted in Shaheen Basmati (Fig. 5). On the other hand cadmium and lead both were significantly reduced by increasing salt stress in the medium and show negative correlation with salinity (Fig. 4 and 5). At 150 mM NaCl stress cadmium reduced to 0.027 ppm as compared to control 0.038 ppm and lead reduced to 0.311 as compared to 0.505 ppm. Smoke primed significantly improved the amount of cadmium and lead as compared to non primed seed plants (Fig. 4 and 5).
Comparison of different concentration of salinity and smoke primed seedling by SDS- PAGE
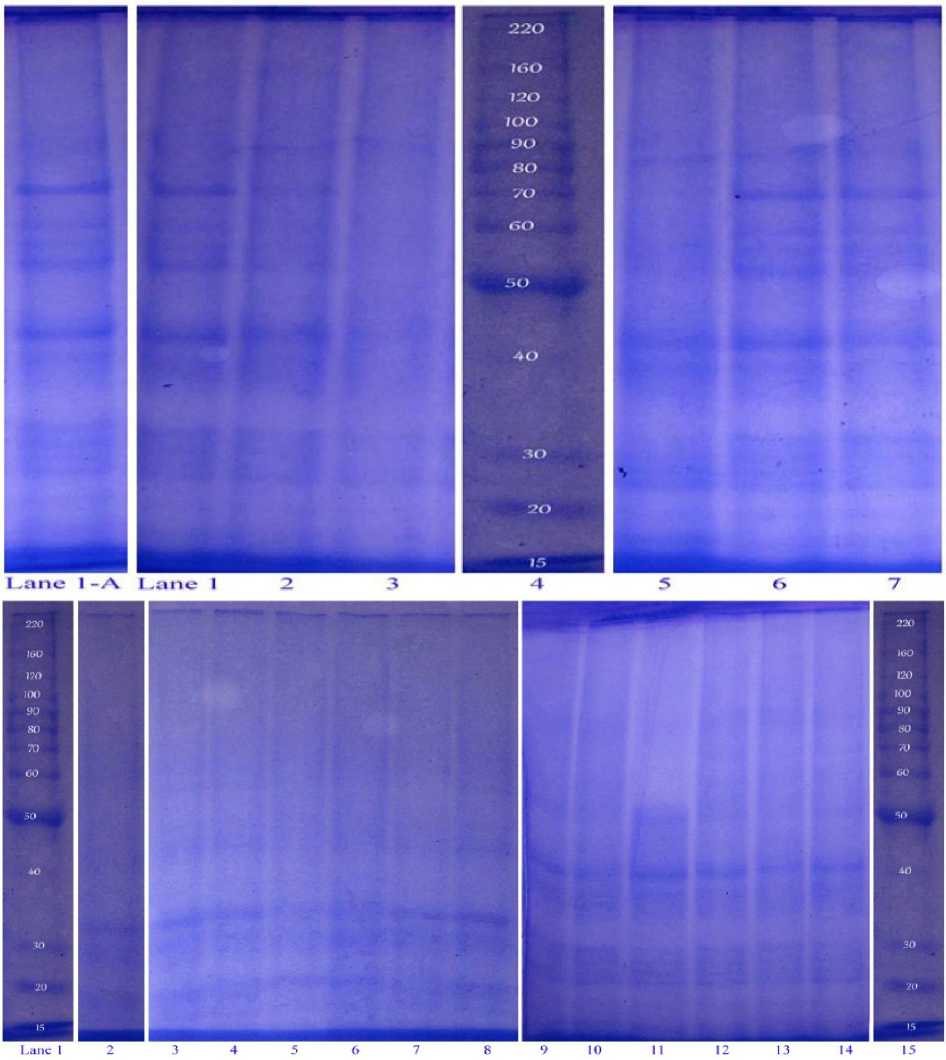
Total leaf extracted protein content were gradually decrease in both varieties as Basmati-385 and Shaheen basmati with increasing NaCl concentration in the medium (Fig. 6). On other hand the banding intensity of primed seed plants were high from that of salt stress plants (Fig. 6). The polypeptide bands between 40 KDa and 70 KDa was present in plant raised from smoke primed seeds but these bands were absent or of very low intensity in the salt treated plants (Fig. 6) Beside these, plants raised from primed seeds had good bands intensity between 40 KDa and 20 KDa from salt stress plants. In Basmati-385, the bands between 50 KDa and 70 KDa was absent at 150 mM salt concentration and the intensity of these bands were lower at 100 mM salt concentration by comparing with control. Bands between 40 KDa and 20 KDa was present at 100mM, and 150mM salt concentration but their intensity was quite low as compared to control while plant raised from smoke primed seeds had grater intensity of the polypeptides then that of the salt treated samples (Fig. 6A).
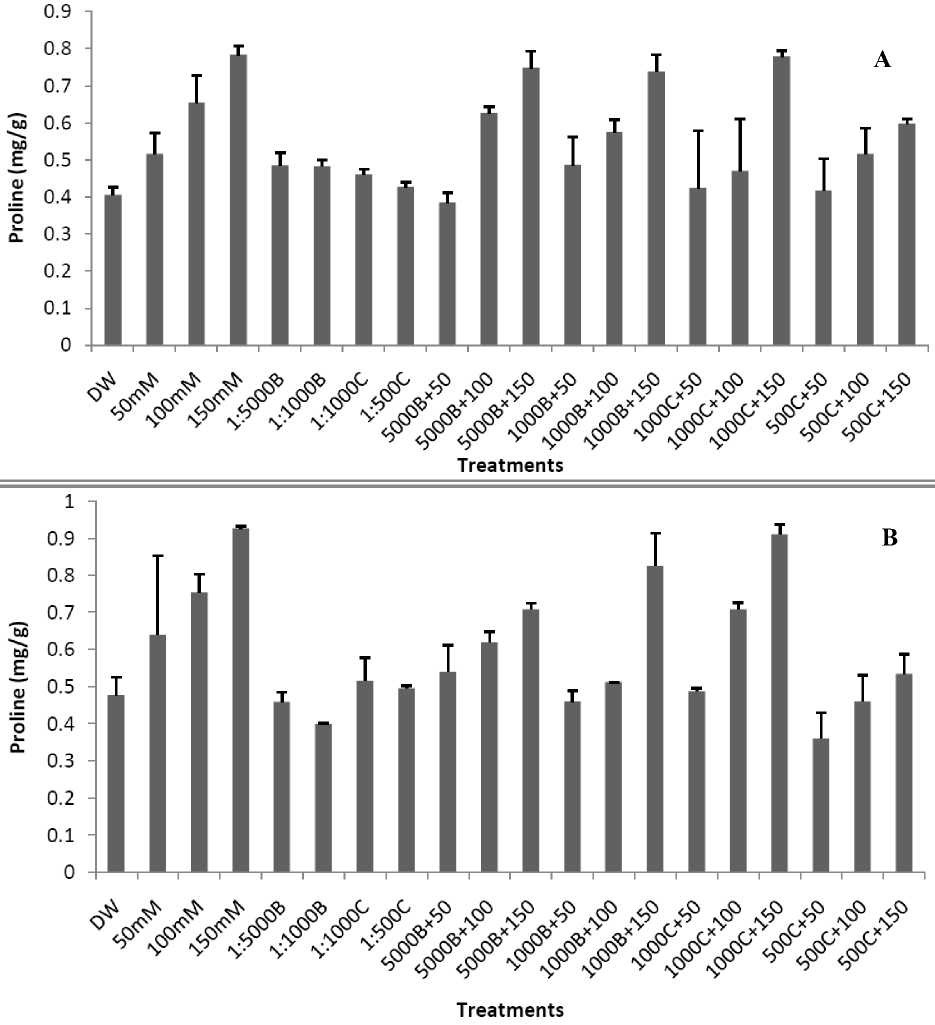
Figure 1: A. Effect of different concentration of salt stress and smoke priming on proline accumulation in Basmati- 385. (B-5000, B-1000, C-1000 and C-500 are smoke dilutions while B-1000+50 mM, B-1000+100 mM, B-1000+150 mM, B-5000+50 mM, B-5000+100 mM B-5000+150 mM, C-1000+50 mM, C-1000+100 mM, C-1000+150 mM, C-500+50 mM, C-500+100 mM and C-500+150 mM are alleviating solutions).
B. Effect of different concentration of salt stress and smoke priming on proline accumulation in Shaheen Basmati. (B-5000, B-1000, C-1000 and C-500 are smoke dilutions while B-1000+50 mM, B-1000+100 mM, B-1000+150 mM, B-5000+50 mM, B-5000+100 mM B-5000+150 mM, C-1000+50 mM, C-1000+100 mM, C-1000+150 mM, C-500+50 mM, C-500+100 mM and C-500+150 mM are alleviating solutions).
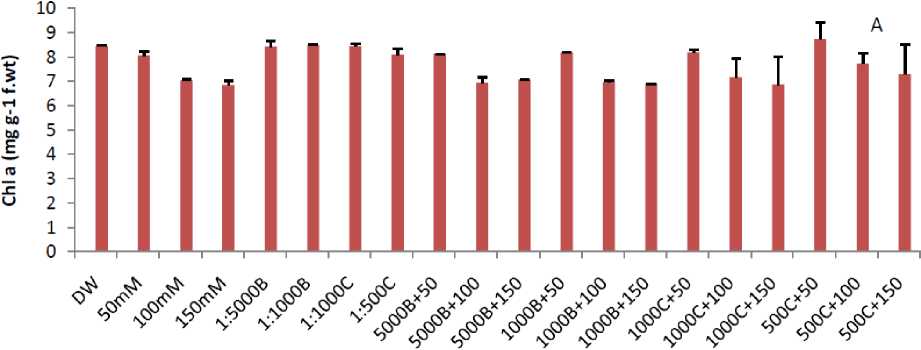
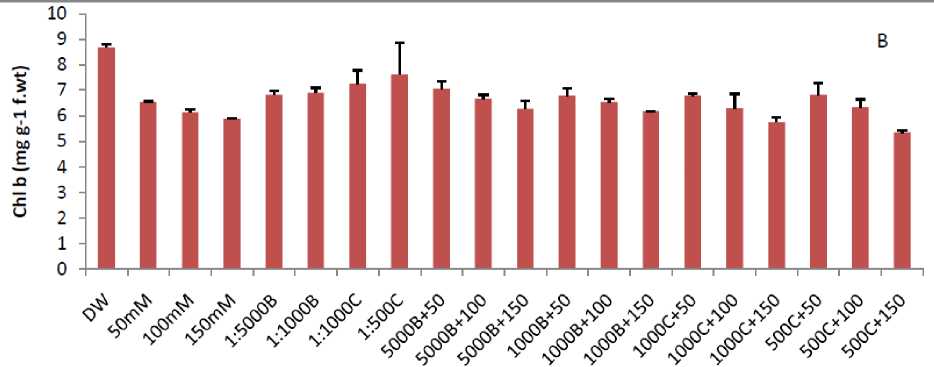
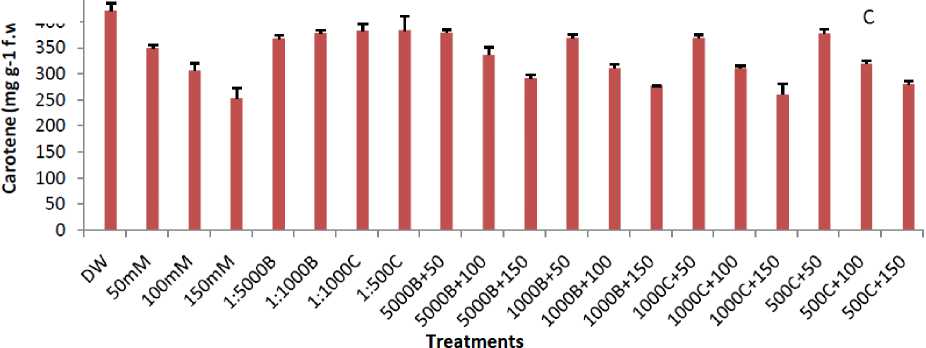
Figure 2: Effect of different concentration of salt stress and smoke priming on Chl a (A). Chl b (B) and Carotenoids (C) in Basmati – 385. (B-5000, B-1000, C-1000 and C-500 are smoke dilutions while B-1000+50 mM, B-1000+100 mM, B-1000+150 mM, B-5000+50 mM, B-5000+100 mM B-5000+150 mM, C-1000+50 mM, C-1000+100 mM, C-1000+150 mM, C-500+50 mM, C-500+100 mM and C-500+150 mM are alleviating solutions).
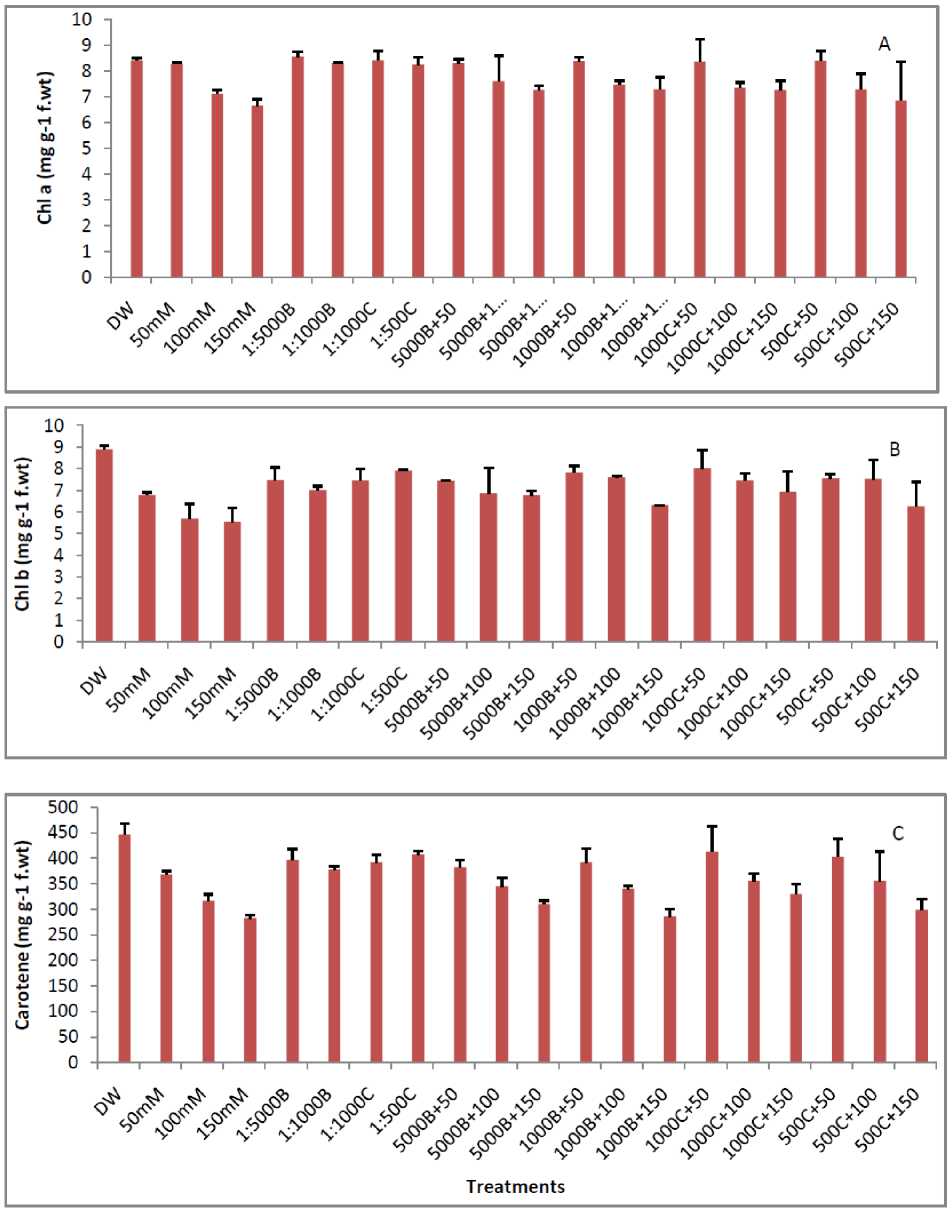
Figure 3: Effect of different concentration of salt stress and smoke priming on Chl a (A), Chl b (B) and Carotenoids (C) in Shaheen Basmati. (B-5000, B-1000, C-1000 and C-500 are smoke dilutions while B-1000+50 mM, B-1000+100 mM, B-1000+150 mM, B-5000+50 mM, B-5000+100 mM B-5000+150 mM, C-1000+50 mM, C-1000+100 mM, C-1000+150 mM, C-500+50 mM, C-500+100 mM and C-500+150 mM are alleviating solutions).
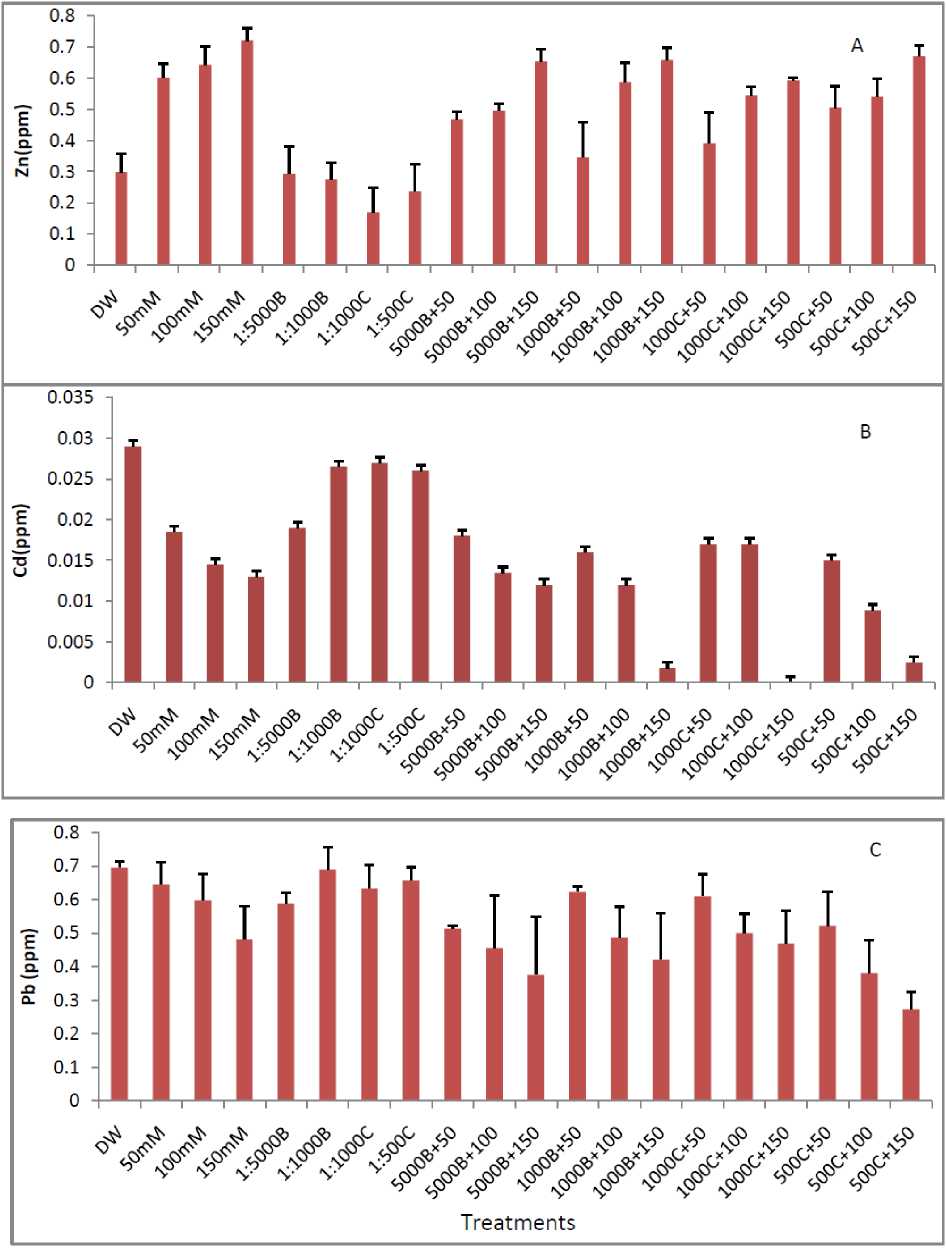
Figure 4: Effect of different concentration of salt stress and smoke priming on Zn (A), Cd (B) and Pb (C) contents of Basmati-385. (B-5000, B-1000, C-1000 and C-500 are smoke dilutions while B-1000+50 mM, B-1000+100 mM, B-1000+150 mM, B-5000+50 mM, B-5000+100 mM B-
5000+150 mM, C-1000+50 mM, C-1000+100 mM, C-1000+150 mM, C-500+50 mM, C-500+100 mM and C-500+150 mM are alleviating solutions).
Treatments
Figure 5: Effect of different concentration of salt stress and smoke priming on Zn (A), Cd (B) and Pb (C) contents of Shaheen Basmati. (B-5000, B-1000, C-1000 and C-500 are smoke dilutions while B-1000+50 mM, B-1000+100 mM, B-1000+150 mM, B-5000+50 mM, B-5000+100 mM B-5000+150 mM, C-1000+50 mM, C-1000+100 mM, C-1000+150 mM, C-500+50 mM, C-500+100 mM and C-500+150 mM are alleviating solutions).
A
B
Figure 6: A. Effect of different concentration of salt stress and smoke priming on polypeptide banding pattern of Basmati-385. Lane 1. Marker, 2. Control, 3. 50mM, 4. 100mM, 5. 150mM, 6. 5000B, 7. 1000B, 8. 1000C, 9. 1000B+50, 10. 1000B+100, 11 1000B+150, 12. 1000C+50, 13. 1000C+100, 14. 1000C+150, 15. Marker.
B. Effect of different concentration of salt stress and smoke priming on polypeptide banding pattern of ShaheenBasmati. Lane 1-A Control, 1. 50mM, 2. 100mM, 3. 150mM 4. Marker, 5. 1000B, 6. 1000C, 7. 500C.
DISCUSSION
Different types of changes occur within the plant during salt stress and there is a natural defense system presents against abiotic stresses in the form of secondary metabolites etc. Proline is one main component of this defense mechanism of plant to salt stress. As we know from previous studies that proline accumulation occurs in plant leaves in response to salt or other type of abiotic stresses (Shamseddin- saeid and Farahbakhsh, 2008). The result of our study shows that by increasing NaCl concentration in the medium, the proline accumulation increases as compared to control (Figs. 1A and 1B). According to Girija et al. (2002) that the accumulation of proline provide strength to the plant against abiotic stresses. Induction of cell wall protein (proline rich protein) occurs under salt stress (Ueda et al., 2007). In our result the seed primed had lower amount of proline amount than that of non primed seeds plants. This might be due to the long lasting ability of the smoke solution compounds that interfere with the expression of genes and produced less salt stress proteins. External application of osmoprotectant, plant hormones through seeds or any way is good and alternate way to reduce the salt stress (Ashraf et al., 2008). Smoke priming has a role to promote the post germination growth of the plant (Sparg et al., 2005). According to Crosti et al. (2006) that smoke treated seeds germinate earlier of Anus glutinosa, and so by this way rapid germination provide a chance to the seedling to escape a huge number of a biotic stress (Murungu et al., 2005).
Photosynthetic pigments like chlorophyll and carotene were also decreased with increasing salinity (Figs. 2 and 3). Ashraf and Rasul (1988) reported that the reduction in chlorophyll content under salinity is due to the suppression of enzymes required for chlorophyll synthesis under higher salinity. Salt stress may cause destruction of chloroplast and instability of pigment protein complex (El-Samad et al., 2011). These observations were similar to the results of El-Samad et al. (2011) that salinity inhibited growth and affected the content of chlorophyll and carotenoids in broad bean plants. Photosynthetic pigments were decreased in saline conditions thereby decrease in chlorophyll and carotene contents. It has been reported that salinity greatly influence chlorophyll content (Jamil et al., 2012). According to (Harris et al., 1999) that seed priming cause faster emergence of seedlings and has role in drought resistance. All smoke solutions priming alleviated the adverse effects of salinity on chlorophyll and carotene contents (Figs. 2 and 3) Seedling from smoke treated seed show vigours growth compare with un treated seeds (Baxter and Van staden, 1994) and vigours growth shows strong photosynthetic activity of the plant, so it may concluded from the present study that smoke might have some role with enzyme pool responsible for the process of photosynthesis which give the plant a strength to overcome the stress.
There was a significant increase in the concentration of zinc with increasing salinity (Fig. 4 and 5) while cadmium and lead contents reduced in leaves of the plant expose to higher salinity in the medium (Fig. 4 and 5), because the concentration of the sodium ion was high and this may reduced the intra cellular and extra cellular up take of cadmium and lead. Other work also indicates that a higher level of salinity cause a decrease in the concentration of elements by the plants ( Fritioff et al ., 2005). Our result is strongly correlated with the work of Hirpara et al. (2005); Knight et al. (1992); Hassan et al. (1970); Mass et al. (1972); Noraho and Gaur (1995). Smoke priming alleviates the salt stress in case of heavy metals uptake (Fig. 4 and 5 ); it shows us that smoke might have some role in reducing the accumulation of toxic elements like Na which help the plant in the accumulation of other useful compounds.
Effect of salt stress in protein changes in rice is rarely been studied (Kongngern et al., 2005).
Protein and intensity of poly peptide was decreases with increase in salt concentration in plant medium (Fig. 6). According to (Kumar et al., 2009) that salt stress markedly changes in protein profile of root and shoot of rice seedlings. Our result is with line with Jamil et al. (2012) and Kumar et al. (2009) that salinity gradually affects the banding pattern and intensity of proteins. Other side priming with plant derived smoke solution influence good and notable effect on the intensity of protein polypeptide bands (Fig. 6). Expression of specific stress proteins is a main indication in maintaining the reliability, native configuration and topology of cellular membranes components to make certain their normal performance under salt stress (Wahid et al., 2007).
CONCLUSIONS
Since smoke priming was more affective in alleviating the drastic effect of salinity in biochemical and molecular level, but the answer to the question is still pending that how the smoke alleviate the salt stress to such a notable extent. Beside these, Smoke priming is proved to be a potent protective agent against salinisation and further research work is necessary to promote smoke priming in agriculture as a low cast agriculture practice.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Financial support for this study was provided by HEC through research grant no. 1348, Pakistan
REFRENCES
Ashraf, M. and Rasul, E. (1988) Salt tolerance of mungbean (Vigna radiata) at two growth stages. Plant Soil , 110 , 63-67.
Ashraf, M., Athar, H.R., Harris, P.J.C. and Kwon, T.R. (2008) Some prospective strategies for improving crop salt tolerance. Adv. Agron., 97 , 45-110.
Bates, L.S., Waldren, R.P. and Teare, I.D. (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water studies. Plant Soil, 39, 205–208.
Baxter, B.J.M., Van Staden, J., Granger, J.E. and Brown, N.A.C. (1994) Plant-derived smoke and smoke extracts stimulate seed germination of the fire-climax grass Themeda triandra . Environ. Exp. Bot., 34 , 217–223.
Brown, N.A.C. and Botha, P.A. (2004) Smoke seed germination studies and a guide to seed propagation of plants from the major families of the Cape Floristic Region. South Afri. J. Bot ., 70 , 559-581.
Crosti, R., Ladd, P.G., Dixon, K.W., Piotto, B. (2006) Post-fire germination: The effect of smoke on seeds of selected species from the central Mediterranean basin. Forest Ecol. Manage. , 221 , 306–312.
El-Samad, Abd. H.M., Shaddad, M.A.K. and Barakat, N. (2011) Improvement of plants salt tolerance by exogenous application of amino acids . J. Med. Plants Res., 5(24) , 5692-5699.
Fritioff, A., Kautsky, L., Greger, M. (2005) Influence of temperature and salinity on heavy metal uptake by submersed plants. Environ. Pollut., 133 , 265-274
Garraud, H., Robert, M, Quetel C.R., Szpunar, J. and Donoard, O.F.X. (1996) At. Spectr ., 17(5) , 183.
Girija, C., Smith, B.N. and Swamy, P.M. (2002) Interactive effects ofsodium chloride and calcium chloride on the accumulation ofproline and glycinebetaine in Peanut ( Arachis hypogaea L.). Environ. Exp. Bot. , 47 , 1–10.
Hanlon, E.A (1992). Determination of potassium, calcium, and magnesium in plants by Atomic Absorption Techniques. In Plank, C.O. (ed.), Plant analysis reference procedures for the southern region of the UnitedStates. Southern Cooperative Series Bulletin #368, Athens, pp: 30-33.
Hassan, H.A.K., Drew, J.V., Knudsen, D. and Olson, R.A. (1970) Influence of soil salinity on production of dry matter and uptake and distribution of nutrients in barley and corn. I. Barley ( Hordeum vulgare L.). Agron., J. , 62 , 4345.
Hirpara, K.D., Ramoliya P.J., Patel A.D and Pandey A.N. (2005) Effect of salinisation of soil on growth and macro- and micro-nutrient accumulation in seedlings of Butea monosperma (Fabaceae). Anales de Biología, 27 , 3-14.
Hoagland, D.R. and Arnon, D.I. (1950) The water culture method for growing plants without soil. Calif. Agric. Exp. Stn. Cir., 347 , 32.
Iqbal, M. and Ashraf, M. (2007) Seed preconditioning modulates growth, ionic relations, and photosynthetic capacity in adult plants of hexaploid wheat under salt stress. J. Plant. Nutr. 30 , 381–396.
Jamil, M., Bashir, S., Anwar, S., Bibi, S., Bangash, A., Ullah, F. and Rha, E.S. (2012) Effect of salinity on physiological and biochemical characteristics of different varieties of rice. Pak. J. Bot ., 44 , 7-13.
Jenifer, A. and Franklin- Janus, J. (2002) Growth and elemental composition of Jak pine seedlings treated with sodium chloride and sodium sulfate. Trees structure and function, 16(4-5) , 325-330.
Keeley, J.E. (1993) Smoke-induced flowering in the fire-lily Cyrtanthus ventricosus. South Afri. J. Bot., 59, 638.
Khan, A.H.M., Ashraf, Y., Naqvi, S.S.M., Khanzada, B. and Ali, M. (1995) Growth ion and solutecontents of sorghum grown under NaCl andNa2SO4 salinity stress. Acta Physiol. Plant., 17, 261-268.
Knight, S. L., Rogers, R. B., Smith, M. A. L. and Spomer, L. A. (1992) Effects of NaCl salinity on miniature dwarf tomato Micro-Tom: Growth analysis and nutrient composition. J. Plant Nutr. 15 :, 2315-2327.
Kong-ngern, K., Daduang, S., Wongkham, C., Bunnag, S., Kosittrakuna, M. and Theerakulpisuta, P. (2005) Protein profiles in response to salt stress in leaf sheaths of rice seedlings Sci. Asia, 31 , 403-408
Kumar, V., Shriram, V., Nikam, T.D., Jawali, N. and Shitole, M.G. (2009) Antioxidant enzyme activities and protein profiling under salts tress in indica rice genotypes differing in salt tolerance. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci., 55(4) , 379394.
Laemmli, U.K. (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature , 227, 680-685.
Lichtenthaler, H.K. and Wellburn, A.R. (1985) Determination of total carotenoids and chlorophylls A and B of leaf in different solvents. Biol. Soc. Trans ., 11 , 591-592.
Mass, E.V. and Hoffman, G.J. (1977) Crop salt tolerance – Current assessment. J. Irrig ., Drain. Div., ASCE., 103 (IR2) , 115-134.
Mass, E.V., Ogata, G. and Garber, M.J. (1972) Influence of salinity on Fe, Mn, and Zn uptake by plants. Agron. J., 64 , 793-795.
Murungu, F.S., Nyamugafata, P., Chiduza, C., Clark, L.J., Whalley, W.R. (2005) Effects of seed priming and water potential on germination of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) and maize (Zea mays L.) in laboratory assays. S outh Afri. J. Plant Soil, 22 , 64–70.
Narciso, J. and Hossain, M. (2002) World rice statistics. IRRI,
Noraho, N. and Gaur, J.P. (1995) Effect of cations, including heavy metals,on cadmium uptake by Lemna polyrhiza L. Biometals, 8 , 95-98.
Qayyum, M.A. and Malik, M.D. (1988) Farm production losses in salt-affected soils. Proc. 1st Nat. Congr. Soil Sci., lahore, Pakistan, pp. 356-364.
Senaratna, T., Dixon, K., Bunn, E., Touchell, D. (1999) Smoke-saturated water promotes somatic embryogenesis in geranium. Plant Growth Regul., 28, 95–99.
Shamseddin-Saeid, M. and Farahbakhsh H. (2008) Investigation of quantitative and qualitative parameters of canola under salty conditions for determining the best tolerance index. J. Sci. Technol. Agri. Nature Resource , 12 , 65-78.
Sparg S.G., Kulkarni, Light and Van Staden, J. (2005) Improving seedling vigour of indigenous medicinal plants with smoke. Biores. Technol ., 96 , 1323–1330
Ueda, A., Yamamoto-Yamane, Y. and Takabe T. (2007) Salt stress enhances proline utilization in the apical region of barley roots. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Communi., 355, 61–66.
Wahid, A., Perveen, M., Gelani, S. and Basra, S.M.A. (2007) Pretreatment of seed with H2O2 improves salt tolerance of wheat seedlings by alleviation of oxidative damage and expression of stress proteins. J. Plant Physiol. , 164 , 28394.
Zia, M.S., Aslam, M., Rehmatullah, M.B., Khan, M., Baig, B. and Ali, A. (1998) Assessment Of nitrogen availability in calcareous soil under rice based cropping system. Pak. J. Soil Sci ., 15 , 166-73.
Список литературы Smoke priming, a potent protective agent against salinity: effect on proline accumulation, elemental uptake, pigmental attributes and protein banding patterns of rice ( Oryza sativa)
- Ashraf, M. and Rasul, E. (1988) Salt tolerance of mungbean (Vigna radiata) at two growth stages. Plant Soil, 110, 63-67.
- Ashraf, M., Athar, H.R., Harris, P.J.C. and Kwon, T.R. (2008) Some prospective strategies for improving crop salt tolerance. Adv. Agron., 97, 45-110.
- Bates, L.S., Waldren, R.P. and Teare, I.D. (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water studies. Plant Soil, 39, 205-208.
- Baxter, B.J.M., Van Staden, J., Granger, J.E. and Brown, N.A.C. (1994) Plant-derived smoke and smoke extracts stimulate seed germination of the fire-climax grass Themeda triandra. Environ. Exp. Bot., 34, 217-223.
- Brown, N.A.C. and Botha, P.A. (2004) Smoke seed germination studies and a guide to seed propagation of plants from the major families of the Cape Floristic Region. South Afri. J. Bot., 70, 559-581.
- Crosti, R., Ladd, P.G., Dixon, K.W., Piotto, B. (2006) Post-fire germination: The effect of smoke on seeds of selected species from the central Mediterranean basin. Forest Ecol. Manage., 221, 306-312.
- El-Samad, Abd. H.M., Shaddad, M.A.K. and Barakat, N. (2011) Improvement of plants salt tolerance by exogenous application of amino acids. J. Med. Plants Res., 5(24), 5692-5699.
- Fritioff, A., Kautsky, L., Greger, M. (2005) Influence of temperature and salinity on heavy metal uptake by submersed plants. Environ. Pollut., 133, 265-274
- Garraud, H., Robert, M, Quetel C.R., Szpunar, J. and Donoard, O.F.X. (1996) At. Spectr., 17(5), 183.
- Girija, C., Smith, B.N. and Swamy, P.M. (2002) Interactive effects ofsodium chloride and calcium chloride on the accumulation ofproline and glycinebetaine in Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Environ. Exp. Bot., 47, 1-10.
- Hanlon, E.A (1992). Determination of potassium, calcium, and magnesium in plants by Atomic Absorption Techniques. In Plank, C.O. (ed.), Plant analysis reference procedures for the southern region of the UnitedStates. Southern Cooperative Series Bulletin #368, Athens, pp: 30-33.
- Hassan, H.A.K., Drew, J.V., Knudsen, D. and Olson, R.A. (1970) Influence of soil salinity on production of dry matter and uptake and distribution of nutrients in barley and corn. I. Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Agron., J., 62, 43-45.
- Hirpara, K.D., Ramoliya P.J., Patel A.D and Pandey A.N. (2005) Effect of salinisation of soil on growth and macro-and micro-nutrient accumulation in seedlings of Butea monosperma (Fabaceae). Anales de Biología, 27, 3-14.
- Hoagland, D.R. and Arnon, D.I. (1950) The water culture method for growing plants without soil. Calif. Agric. Exp. Stn. Cir., 347, 32.
- Iqbal, M. and Ashraf, M. (2007) Seed preconditioning modulates growth, ionic relations, and photosynthetic capacity in adult plants of hexaploid wheat under salt stress. J. Plant. Nutr. 30, 381-396.
- Jamil, M., Bashir, S., Anwar, S., Bibi, S., Bangash, A., Ullah, F. and Rha, E.S. (2012) Effect of salinity on physiological and biochemical characteristics of different varieties of rice. Pak. J. Bot., 44, 7-13.
- Jenifer, A. and Franklin-Janus, J. (2002) Growth and elemental composition of Jak pine seedlings treated with sodium chloride and sodium sulfate. Trees structure and function, 16(4-5), 325-330.
- Keeley, J.E. (1993) Smoke-induced flowering in the fire-lily Cyrtanthus ventricosus. South Afri. J. Bot., 59, 638.
- Khan, A.H.M., Ashraf, Y., Naqvi, S.S.M., Khanzada, B. and Ali, M. (1995) Growth ion and solutecontents of sorghum grown under NaCl and Na2SO4 salinity stress. Acta Physiol. Plant., 17, 261-268.
- Knight, S. L., Rogers, R. B., Smith, M. A. L. and Spomer, L. A. (1992) Effects of NaCl salinity on miniature dwarf tomato Micro-Tom: Growth analysis and nutrient composition. J. Plant Nutr. 15:, 2315-2327.
- Kong-ngern, K., Daduang, S., Wongkham, C., Bunnag, S., Kosittrakuna, M. and Theerakulpisuta, P. (2005) Protein profiles in response to salt stress in leaf sheaths of rice seedlings Sci. Asia, 31, 403-408
- Kumar, V., Shriram, V., Nikam, T.D., Jawali, N. and Shitole, M.G. (2009) Antioxidant enzyme activities and protein profiling under salts tress in indica rice genotypes differing in salt tolerance. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci., 55(4), 379-394.
- Laemmli, U.K. (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature, 227, 680-685.
- Lichtenthaler, H.K. and Wellburn, A.R. (1985) Determination of total carotenoids and chlorophylls A and B of leaf in different solvents. Biol. Soc. Trans., 11, 591-592.
- Mass, E.V. and Hoffman, G.J. (1977) Crop salt tolerance -Current assessment. J. Irrig., Drain. Div., ASCE., 103 (IR2), 115-134.
- Mass, E.V., Ogata, G. and Garber, M.J. (1972) Influence of salinity on Fe, Mn, and Zn uptake by plants. Agron. J., 64, 793-795.
- Murungu, F.S., Nyamugafata, P., Chiduza, C., Clark, L.J., Whalley, W.R. (2005) Effects of seed priming and water potential on germination of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) and maize (Zea mays L.) in laboratory assays. South Afri. J. Plant Soil, 22, 64-70.
- Narciso, J. and Hossain, M. (2002) World rice statistics. IRRI, http://www.irri.org/science/ricestat.
- Noraho, N. and Gaur, J.P. (1995) Effect of cations, including heavy metals,on cadmium uptake by Lemna polyrhiza L. Biometals, 8, 95-98.
- Qayyum, M.A. and Malik, M.D. (1988) Farm production losses in salt-affected soils. Proc. 1st Nat. Congr. Soil Sci., lahore, Pakistan, pp. 356-364.
- Senaratna, T., Dixon, K., Bunn, E., Touchell, D. (1999) Smoke-saturated water promotes somatic embryogenesis in geranium. Plant Growth Regul., 28, 95-99.
- Shamseddin-Saeid, M. and Farahbakhsh H. (2008) Investigation of quantitative and qualitative parameters of canola under salty conditions for determining the best tolerance index. J. Sci. Technol. Agri. Nature Resource, 12, 65-78.
- Sparg S.G., Kulkarni, Light and Van Staden, J. (2005) Improving seedling vigour of indigenous medicinal plants with smoke. Biores. Technol., 96, 1323-1330
- Ueda, A., Yamamoto-Yamane, Y. and Takabe T. (2007) Salt stress enhances proline utilization in the apical region of barley roots. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Communi., 355, 61-66.
- Wahid, A., Perveen, M., Gelani, S. and Basra, S.M.A. (2007) Pretreatment of seed with H2O2 improves salt tolerance of wheat seedlings by alleviation of oxidative damage and expression of stress proteins. J. Plant Physiol., 164, 283-94.
- Zia, M.S., Aslam, M., Rehmatullah, M.B., Khan, M., Baig, B. and Ali, A. (1998) Assessment Of nitrogen availability in calcareous soil under rice based cropping system. Pak. J. Soil Sci., 15, 166-73.


