Somatic embryogenesis and plantlet regeneration under salinity stress conditions in mature caryopsis culture of Indian red rice (Oryza sativa L.) and assessment of genetic fidelity in regenerants
Автор: Girija D., Vikrant
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.21, 2025 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The main objective of this study was to establish the stable and efficient protocol for somatic embryogenesis and plantlet regeneration under NaCl-salt stress conditions in traditional Indian red rice (cv. Poongar) using mature caryopsis as explant and also to assess the genetic fidelity in regenerated plantlets. High frequency (98.88±1.33%) of callogenesis was recorded in MS (Murashige and Skoog, 1962) medium fortified with 10µM of 2,4-D (2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid) while maximum percentage (95.0±3.9%) of somatic embryogenesis and also maximum number (47.3±3.9) of somatic embryo per callus was recorded in presence of 5µM of 2,4-D alone. Furthermore, maximum frequency (85.33±2.02%) of germination of somatic embryos into plantlets was found in MS medium supplemented with 2.0mg/L of IAA (Indole-3-acetic acid), 3.0mg/L of BAP (6-Benzylaminopurine) and 1.0mg/L of Kn (Kinetin). During the salinity stress treatments, various concentrations (10mM, 25mM, 50mM and 100mM) of NaCl were used in this study in order to induce somatic embryogenesis and plantlets regeneration. Significantly, 100mM of NaCl shows the strong inhibitions for callus induction (26.67±0.63%)and somatic embryogenesis (31.3±1.8%),moreover, weight of the callus was also found to get decreased (94±0.5mg) than control (156±4.3mg) treatment. Interestingly, the highest concentration 150mM of NaCl was proved to be completely inhibitory and function show_abstract() { $('#abstract1').hide(); $('#abstract2').show(); $('#abstract_expand').hide(); }
Genetic fidelity, mature caryopsis, red rice, salinity, somatic embryogenesis
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143184742
IDR: 143184742
Текст научной статьи Somatic embryogenesis and plantlet regeneration under salinity stress conditions in mature caryopsis culture of Indian red rice (Oryza sativa L.) and assessment of genetic fidelity in regenerants
During the process of soaking, the nutrient from the husk gets absorbed by rice grain which increases the nutrient value and anti-oxidant property of rice (Komatsuzaki et al., 2007; ahman, 2019). Some of the indica and japonica varieties have been considered as recalcitrant rice crops in terms of callogenesis (Sahoo et al., 2011). Large number of plantlets could be produced by using PG s through callogenesis and plantlet regeneration. These PG s play vital role in cell division and differentiation during somatic embryogenesis (Kumar, 2016; Mostafiz et al., 2018).
Previous studies also reveal on in vitro regeneration in different pigmented rice using mature caryopsis culture (Diawuoh et al., 2016, Thi Linh et al., 2017, Sedeek et al., 2024), anther culture of Indonesian indica black rice (Maharani et al., 2020), mature embryo culture (Artadana et al., 2017).
Due to biotic and abiotic stresses, the productivity of rice gets decreased which causes the significant deficit in required supply (Sankar et al., 2011). Salinity is one of the major factors which affects the productivity of rice in saline prone areas throughout the world (Lee et al., 2003). In order to increase the yield of rice crops around saline prone areas especially coastal areas, in vitro regenerated stress tolerant crops have been produced. Many literatures are available on production of salinity tolerant plant through tissue culture techniques on white rice cultivar (Binh et al., 1992, Htwe et al., 2011; Siddique et al., 2014; Taratima et al., 2022).
Since literature on establishment of somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration under salinity stress conditions in Indian red rice is lacking completely, so present study was aimed to optimize an efficient and stable protocols for the induction of somatic embryo and plantlet regeneration in Indian red rice (Poongar) using mature caryopsis explant tissues under salinity stress conditions.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Source of Explant and Sterilization
Dry and healthy mature caryopses of Poongar, Indian red rice were collected from Perunthalaivar Kamaraj Krishi Vigyan Kendra (PKKVK), Puducherry (India) These seeds of red rice were de-husked manually after drying and washed to remove dust from the de-husked seeds. Washed seeds were further treated with tween 20 (teepol) for 10 mins followed by proper wash under running tap water to remove the detergent traces. Seeds were later surface sterilized with 70% ethyl alcohol (V/V) for 30 sec under laminar air flow to remove the microbes from the caryopsis explant tissues.
Finally, the seeds were treated with 0.1% of HgCl 2 (W/V) about 10mins to remove endophytes from the seeds followed by washing with sterilized distilled water for 2 times under aseptic conditions (under laminar air flow chamber). The sterilized seeds were finally dried on sterile filter paper to remove the excess water on the surface of the seeds to avoid water born contaminations.
Callus Induction Medium
For induction of callus, the sterilized mature caryopsis was inoculated on the MS Medium (Murashige and Skoog, 1962) supplemented with 30g/L of sucrose (W/V), 8g/L of agar as gelling agent in presence of various concentrations of auxin 2,4 D (5 µM, 10 µM, 20 µM, 30 µM and 40 µM). Finally, the pH of the nutrient media was adjusted to 5.5-5.8 and were autoclaved at 121°C at 15 psi for 20 min.
After sterilization of nutrient medium, the sterilized explants were transferred into the fresh medium under laminar air flow. The inoculated seeds were incubated for 21-days at 28±2°C under dark condition for induction of callus from the explant.
Determination of Fresh Callus Weight
After 21-days of culture initiation, incubated calli from the callogenic media were used to determine the fresh weight of the calli and 10 identical calli from different treatments were used to calculate the mean fresh weight of the callus.
Embryogenic Induction Medium
The callus from the explant was removed and inoculated into the MS medium which contains 30g/L of sucrose as carbon sucrose and 0.8% of agar included with various concentrations of PG s (2.5 µM and 5µM of 2,4-D alone, 5µM of 2,4-D with 1.0µM of Kn and 10µM of 2,4-D with 2.0µM of Kn). Furthermore, sub-cultured calli were incubated under dark conditions for 14 days at 28±2°C for proliferation of embryogenic callus.
Plantlet Regeneration Medium
Healthy embryogenic calli were transferred into regeneration medium which contains MS-salts, 30gm/L of sucrose, 8.0gm/L of agar and various combinations of plant growth regulators (P M1-P M6) Further, cultures were incubated at 28±2°C and light intensity of 15001600 lux 16 hours light for 30-days.
Salinity Stress Treatment
To understand the effects of salinity stress on callogenesis, the sterilized explant was inoculated into the nutrient medium with optimal concentrations of nutrient medium with sucrose, agar and 2,4-D along with different concentrations of sodium chloride (10mM, 25mM, 50mM, and 100mM) and without NaCl as control which were inoculated under dark conditions for 21-days.
The calli from the explants were transferred into the optimal concentration of embryogenesis induction medium and regeneration medium with corresponding stress conditions of NaCl for embryogenesis and regeneration of plantlets from the embryogenic callus.
Acclimatization
In vitro plantlets were removed from the medium and washed thoroughly using sterilized water to remove the adhering medium on the root which were transferred into the pot which contains autoclaved soil and vermiculite at the ratio of 3:1 and covered with polyethylene bags followed by irrigation with the same salt solutions regularly.
Isolation of DNA
The genomic DNA of in vitro regenerated plantlets of Poongar ( ed ice) was isolated from the leaf tissues which were grown with and without NaCl stress treatments by using CTAB method (Doyle and Doyle, 1990). Moreover, agarose (0.8%) gel electrophoresis was later used to identify the quality of isolated DNA.
RAPD, ISSR- PCR Analysis
To identify the homogeneity of stress tolerant plant and in vitro regenerated control plantlets, APD (OPA 1, OPA 4 and OPA 5) and ISS (UBC 823) primers were employed for PC amplification that were carried out in PC Thermal Cycler (GeneAmp PC ).
Gel loading dye (6X) added to the PC products were analyzed by 1.2% agarose gel electrophoresis in 0.5 X TBE buffer which contains ethidium bromide (0.5µg/ml). The PC products were loaded into the well and the electrophoresis was completed at 75V for 1 hour. Moreover, 2-log DNA ladder (NEB) was used as molecular standard. Electrophorized gel was visualized under UV transilluminator (Genei) and the image was captured under UV light using gel documentation system (Bio- ad).
Statistical Analysis
The experiments were repeated for three times each with 10 replicates. During the entire experiments, various traits in terms of percentage of explants showing callogenesis, percentage of callus shows somatic embryogenesis, frequency of plantlets regeneration, mean number of plantlets per callus and callus morphology with browning percentage were calculated.
Statistical data were performed by IBM SPSS Statistics 22, Duncan’s Multiple ange Test (DM T) and ANOVA were performed at 5% level of significance.
RESULTS
Induction of Callus
In the present study, among all the concentrations of 2,4-D, the maximum amount of callus was found with the lower concentration of 2,4-D (10µM), which shows the highest percentage of callogenesis (98.88±1.33%)
exhibited creamy, white and compact callus formation (Fig. 1B & Table 1) . Significantly, the maximum callus weight (156±4.3mg) was also recorded with the same treatment containing lower concentration of 2,4-D (10µM) whereas with the control experiment in basal medium, mature caryopsis was failed to show callus induction instead simple germination of mature caryopsis (Fig. 1A) was observed and thus, nutrient medium without 2,4-D was found to be non-responsive in terms of callogenesis even after 21-days of culture initiation.
Similarly, fresh weight of the calli were also decreased (103±1.7mg and 93±0.4mg) respectively with the increase in 2,4-D concentrations in the nutrient media. The nature of the callus was also observed to be affected and turns to pale yellow after 21-days of incubation.
Induction of Somatic embryogenesis
Healthy calli were sub-cultured into the embryogenic induction medium, the maximum percentage (95.0±3.9%) of somatic embryogenesis was found with 5µM of 2,4-D alone (Fig. 2 B) and the mean no. (47.3±3.9%) of somatic embryos per callus (Table 3) while it was followed by 10µM of 2,4-D in combination with 1.0µM of Kn (Fig. 2C) in terms of percentage of somatic embryogenesis (51.33±3.1%) and mean number of somatic embryos (13.7±0.6) per callus (Table 3) after 14-days of incubation. Moreover, reduction in frequency of somatic embryogenesis was obtained with the increase in Kinetin (2.0µM) concentration with 2,4-D (10µM) and therefore, 31.67±2.9% of somatic embryogenesis was recorded at 10µM of 2,4-D with
-
2 .0µM of Kn and number of somatic embryos per callus (11.2±0.51) was also reduced (Fig. 2D) .
In contrast, basal medium shows the minimum percentage of somatic embryogenesis and no. of somatic embryos per callus (27.9±2.3% and 7.3±0.31%) (Fig. 2A & Table 3) respectively.
Effects of Salt Stress on Callogenesis and Embryogenesis
There is significant difference between control and salt treated callus. At lower concentration of NaCl (10mM), induced callus was white and compact. A significant reduction in percentage of callogenesis (91.1±2.33%) (Fig.1F & Table 2) and mean callus weight (145±0.8mg) was recorded after 21-days of incubation. The salt -treated calli were embryogenic and shows small, white nodular structure and maximum percentage of embryogenesis was recoded as 67.5±2.33% (Fig. 2E & Table 4) whereas control shows somatic embryogenesis (95.0±3.9%) after 15-days of sub-culture.
However, the higher concentration (100mM) of NaCl is lethal and shows least percentage of callogenesis (26.67±0.63%) (Fig. 1I & Table 2) and somatic embryogenesis (31.3±1.8%) (Fig. 2H &Table 4) . Significantly, further increase in concentration of NaCl (150mM) was proved to be completely lethal and the calli were necrosed, whereas lower concentrations (25mM and 50mM) of NaCl could show relatively high (76.67±3.36% and 62.23±1.09%) percentage of callogenesis (Fig. 1G & H) respectively (Table 2) and also for somatic embryogenesis (52.9±1.8% and 45.6±2.3%) respectively after 15-days of sub-culture (Fig. 2F & G) respectively (Table 4) .
There is significant difference between control and salt-stress treated cultures at 5% level of significance (p=0.05). the mean percentage of callogenesis, callus weight and somatic embryogenesis was affected to (91.1±2.33%, 145±0.8mg and 67.5±2.33) in control treatments (98.88±1.33%, 156±4.3mg and 95.0±3.9) respectively (Tables 2 & 4) .
Plantlet Regeneration
There is significant difference between these two different combinations of nutrient media in terms of frequency of plantlet regeneration and percentage of callus necrosis. 57.0±1.67% of plantlet regeneration was recorded with P M4 and mean number of regenerated plantlets (12.3±0.3) per embryogenic callus (Table 5) was recorded.
Significantly, with the medium containing 2.0mg/L of IAA, 3.0mg/L of BAP, and 1.0mg/L of Kn (P M6), mean number of plantlets (34.3±1.3) per callus was obtained after 4-weeks of incubation (Fig. 3B) .
Effect of Salt Stress on Plantlet Regeneration
Embryogenic calli were sub-cultured into the respective (P M6) plantlet regeneration medium (2.0mg/L of IAA, 3.0mg/L of BAP, and 1.0mg/L of Kn) with and without various concentrations of NaCl. Lower concentration of NaCl (10mM) shows 74.52±1.2% of plantlet regeneration and 23.3±1.8 tolerant plantlets per embryogenic callus (Fig. 3C & Table 6). It was followed by 25mM and 50mM of NaCl (65.5±1.5 & 16.67±1.18) and (49.3±0.97% & 12.33±0.67) respectively (Fig. 3D & Table 6) .
Genetic Fidelity analysis using ISSR and RAPD markers
The APD primers OPA-1, OPA-4, and OPA-5) and ISS primer (UBC 823) each was seen to amplify in forms of several bands in NaCl (100mM) treated samples and in control regenerants as well (Table 7). Every APD amplified band was evident in between the ranges from 100bp-3Kb while ISS bands were visible in range of <3Kb and also exhibit polymorphisms leading to genetic dissimilarities (Fig. 4A-D ). The APD primer OPA-1 could amplify overall 10 scorable bands. Significantly, 7 among 10 were observed to be polymorphic and shows 70% of polymorphism rate (Fig. 4A) . The maximum rate of polymorphism (86%) was exhibited by the primer OPA 4 in which the numbers of amplicons were 7 and 6 showing the genetic heterogeneity (Fig. 4B) .
Similarly, the OPA 5 band produces around 6 amplicons among 5 are polymorphic bands and rate of genetic dissimilarities was observed to be 83% (Fig. 4C & Table 7). Moreover, the ISS Primer UBC 823 shows 4 polymorphic band among 5 shows 80% genetic dissimilarity (Fig. 4D & Table 7) Hence, the salinity tolerant plantlet was treated as genetically altered and exhibits the polymorphism in order to overcome the salinity stress condition compared with control plantlet. Moreover, probably in order to adapt the NaCl stress the regenerated plantlet exhibits genetic differences and shows polygenic in nature.
regeneration and 34.3±1.3 plantlet per callus was
Table 1 : Poongar- ed rice ( Oryza sativa L.); effects of various concentrations of auxin 2,4-D on callus induction in mature caryopsis culture after 21-days of culture initiation. Significant at 5% level of significance. Table indicates the same letters in a column, don’t differ significantly as per Duncan Multiple ange Test (DM T) calculation.
|
Concentration of 2,4-D (µM) |
Callogenesis (% Mean±SE) |
Callus Weight (mg) (Mean±SE) |
Callus Morphology |
|
0 |
0 |
0 |
Seedling germination |
|
5.0 |
9.13±0.86 a |
20±0.19a |
Seed germination with little callus |
|
10 |
98.88±1.33e |
156±4.3e |
Compact, Creamy, White |
|
20 |
70.0±1.88d |
120±2.6d |
Friable, Creamy, White |
|
30 |
46.67±1.96c |
103±1.7c |
Pale Yellow |
|
40 |
23.3±1.01b |
93±0.4b |
Pale Yellow |
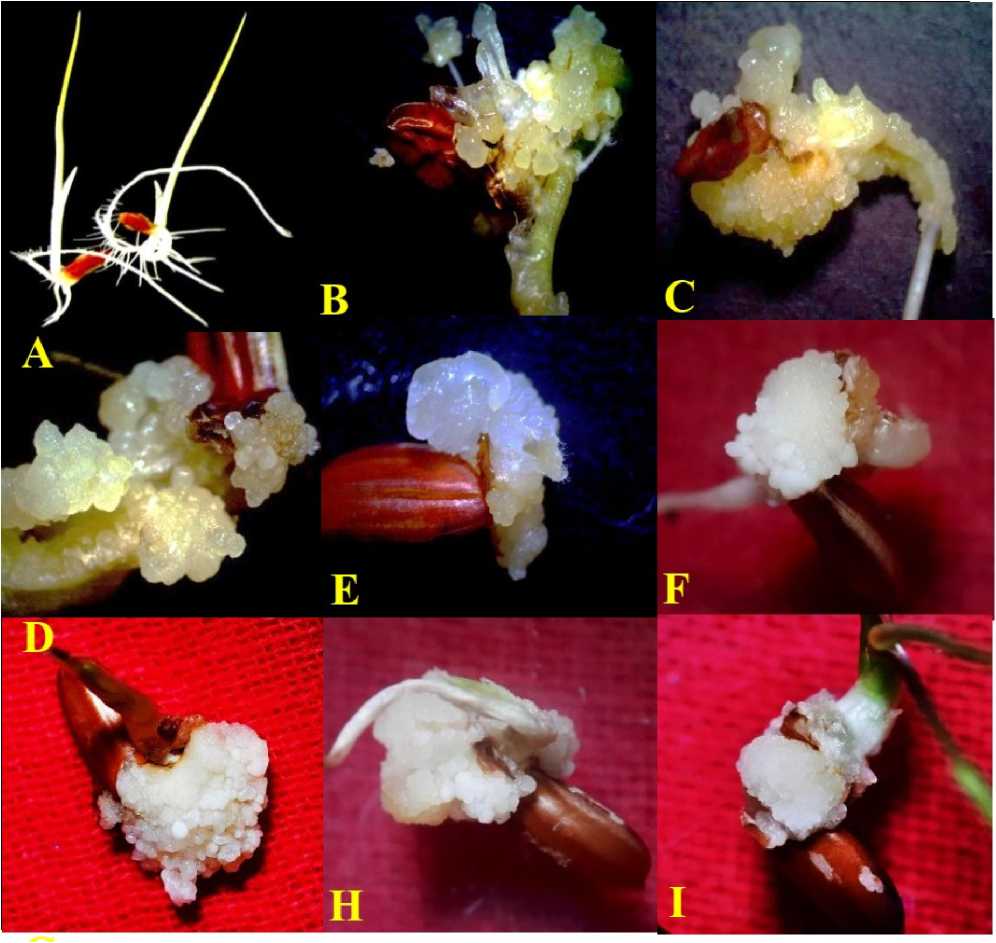
Figure 1. Poongar - ed rice ( Oryza sativa L.) ; Mature caryopsis culture showing effects of NaCl (salinity stress) on callogenesis; (A) Control (B) 2,4-D (10µM) (C) 2,4-D (20µM) (D ) 2,4-D (30µM) (E ) 2,4-D (40µM) (F ) 2,4-D (10µM) + 10mM of NaCl (G) 2,4-D (10µM) + 25mM of NaCl (H) 2,4-D (10µM) + 50mM of NaCl (I) 2,4-D (10µM) + 100mM of NaCl salt treatments (after 21-days of culture initiation).
Table-2: Poongar- ed rice ( Oryza sativa L.), effects of salinity stress (NaCl) on frequency of callogenesis and mean weight of the callus in mature caryopsis culture after 21-days of culture initiation. Significant at 5% level of significance. Table indicates the same letters in a column, don’t differ significantly as per Duncan Multiple ange Test (DM T) calculation.
|
Concentration of NaCl |
Concentration of |
Callogenesis (%Mean±SE) |
Callus Weight (mg) |
|
(mM) |
2,4-D |
(Mean±SE) |
|
|
0 |
10μM |
98.88±1.33 e |
156±4.3 e |
|
10 |
91.1±2.33d |
145±0.8 d |
|
|
25 |
76.67±3.36c |
120±0.1 c |
|
|
50 |
62.23±1.09b |
118±0.8 b |
|
|
100 |
26.67±0.63a |
94±0.5 a |
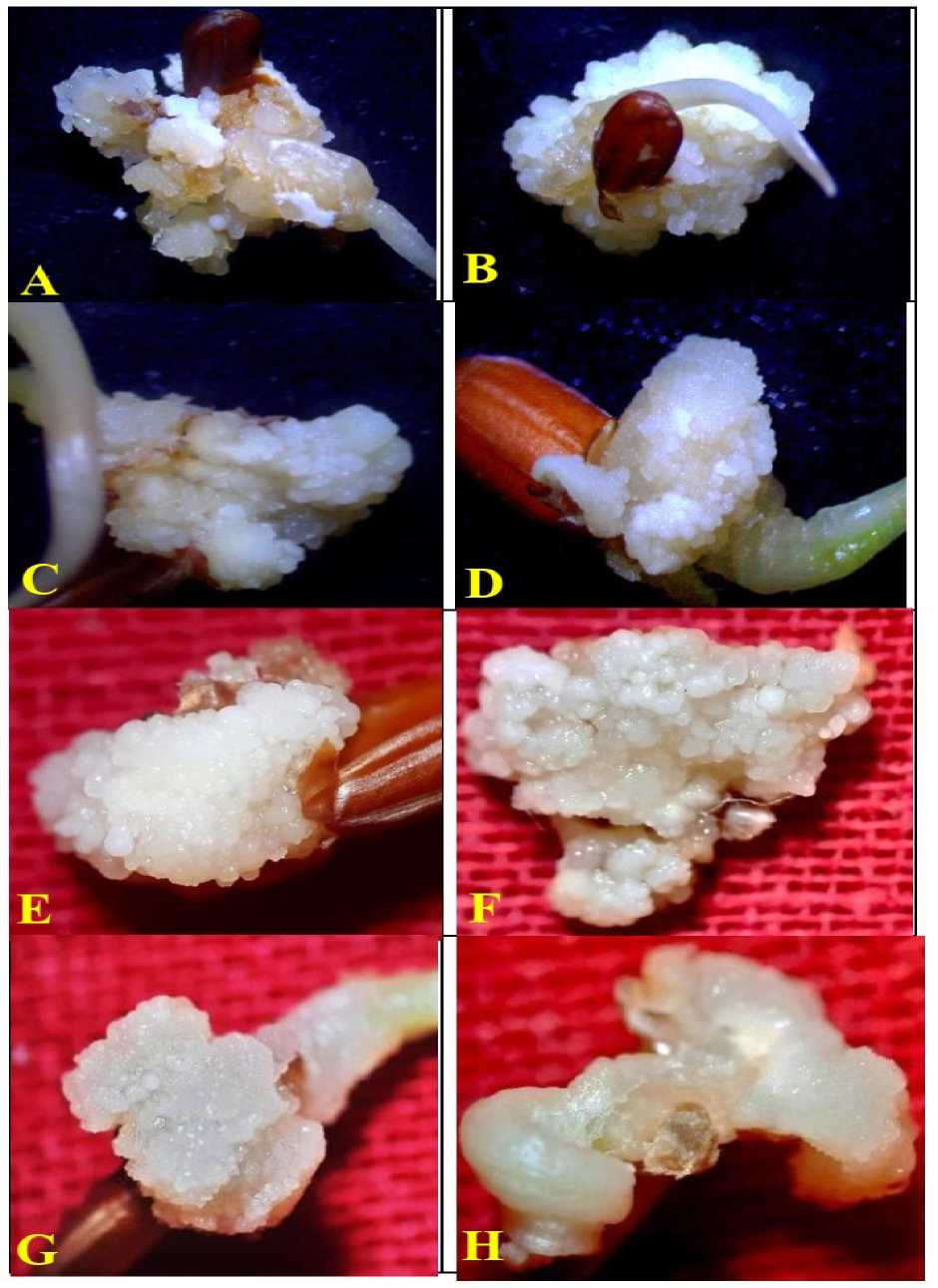
Figure 2. Poongar - ed rice ( Oryza sativa L.) ; Mature caryopsis culture showing effects of NaCl (salinity stress) on callogenesis; (A) Control (B) 2,4-D (10µM) (C) 2,4-D (20µM) (D ) 2,4-D (30µM) (E ) 2,4-D (40µM) (F ) 2,4-D (10µM) + 10mM of NaCl (G) 2,4-D (10µM) + 25mM of NaCl (H) 2,4-D (10µM) + 50mM of NaCl (I) 2,4-D (10µM) + 100mM of NaCl salt treatments (after 21-days of culture initiation).
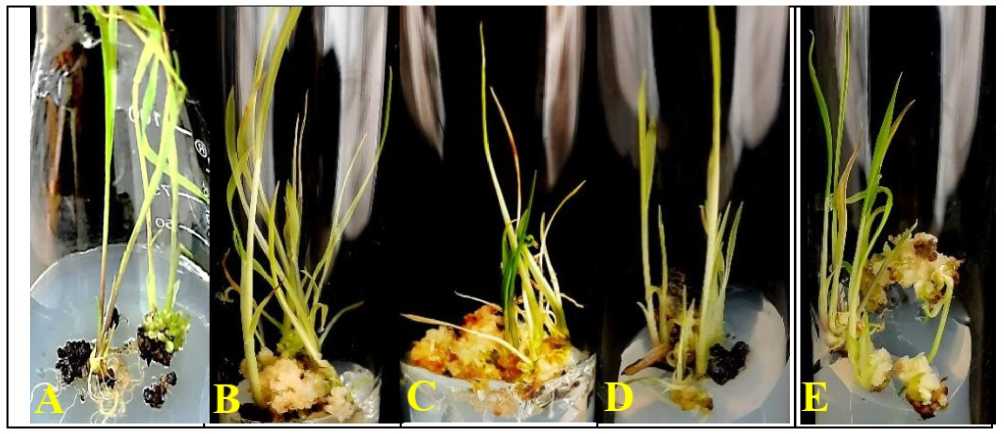

Figure 3. Poongar - ed rice ( Oryza sativa L.) ; Mature caryopsis culture showing effects of NaCl (salinity stress) on plantlet regeneration; (A) P M5 (B) P M6 (C ) P M6 +10mM of NaCl (D ) P M6 + 50mM of NaCl (E ) P M6 + 100mM of NaCl salt treatments (after 30-days of culture initiation).
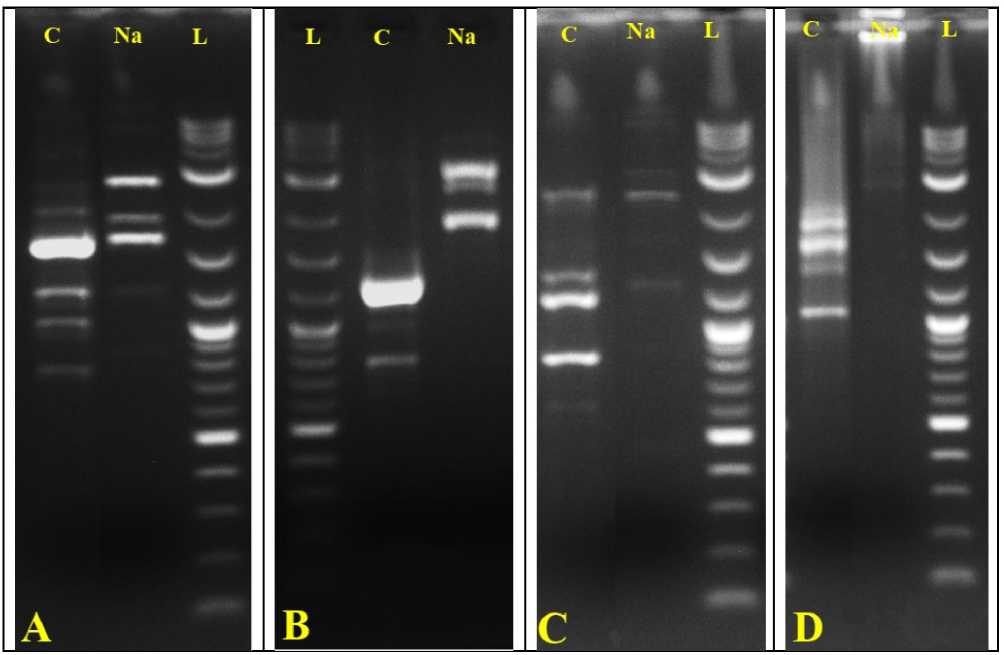
Figure 4. Poongar - ed rice ( Oryza sativa L.) ; APD and ISS amplification profile of in vitro regenerated plantlets
Control (C), NaCl (Na), Ladder (L) using four different primers; (A) OPA-1 (B) OPA-4 (C) OPA-5 (D) UBC-823.
Table-3: Poongar- ed rice ( Oryza sativa L.), effects of various concentrations of auxin (2,4-D) with various concentrations of cytokinin (Kn) on somatic embryogenesis after 14-days of sub-culture. Significant at 5% level of significance. Table indicates the same letters in a column, don’t differ significantly as per Duncan Multiple ange Test (DM T) calculation.
|
Combination of Auxin with Cytokinin |
Somatic Embryogenesis (%±SE) |
No. of Somatic Embryos/Callus (Mean±SE) |
|
|
2,4-D (µM) |
Kn (μM) |
||
|
0 |
0 |
27.9±2.3a |
7.3±0.31a |
|
2.5 |
0 |
40.21±3.5c |
11.9±1.9c |
|
5.0 |
0 |
95.0±3.9e |
47.3±3.9e |
|
10 |
1.0 |
51.33±3.1d |
13.7±0.6d |
|
10 |
2.0 |
31.67±2.9b |
11.2±0.51b |
Table-4: Poongar- ed rice ( Oryza sativa L.), Exhibiting the impacts of salinity stress (NaCl) on frequency of somatic embryogenesis and number of somatic embryos per callus in mature caryopsis culture after 14-days subculture of embryogenic callus. Significant at 5% level of significance. Table indicates the same letters in a column, don’t differ significantly as per Duncan Multiple ange Test (DM T) calculation.
|
Concentration of NaCl (mM) |
Concentration of 2,4-D |
Somatic Embryogenesis (%Mean ± SE) |
No. of Somatic Embryos/ Callus (Mean ± SE) |
|
0 |
5µM |
95.0±3.9e |
47.3±3.9e |
|
10 |
67.5±2.33d |
31.2±2.5 d |
|
|
25 |
52.9±1.8c |
22.9±1.9 c |
|
|
50 |
45.6±2.3b |
18.6±1.5 b |
|
|
100 |
31.3±1.8a |
12.7±0.9 a |
Table-5 : Poongar- ed rice ( Oryza sativa L.), effects of various concentrations of auxin (IAA) with various concentrations of cytokinins (BAP and Kn) on germination of somatic embryo and plantlet regeneration in mature caryopsis culture after 30-days sub-culture of embryogenic callus. Significant at 5% level of significance. Table indicates the same letters in a column don’t differ significantly as per Duncan Multiple ange Test (DM T) calculation.
|
Combination of Auxin with Cytokinins (µM) |
Plantlet egeneration (%Mean±SE) |
No. of egenerated Plantlets/Callus (Mean±SE) |
Necrosed Callus (%) |
|||
|
IAA |
BAP |
Kinetin |
||||
|
PRM1 |
0 |
2.0 |
0.5 |
10.7±1.2a |
4±0.6a |
70 |
|
PRM2 |
0 |
3.0 |
1.0 |
45.0±2.87 b |
7.3±0.3b |
44 |
|
PRM3 |
1.0 |
2.0 |
0.5 |
52.0±2.30c |
10±0.6bc |
45 |
|
PRM4 |
1.0 |
3.0 |
1.0 |
57.0±1.67d |
12.3±0.3c |
39 |
|
PRM5 |
2.0 |
2.0 |
0.5 |
63.3±1.76 e |
27.7±0.3d |
35 |
|
PRM6 |
2.0 |
3.0 |
1.0 |
85.33±2.03f |
34.3±1.3e |
10 |
Table-6: Poongar- ed rice ( Oryza sativa L.), Exhibiting the impact of salinity stress (NaCl) on percentage of callus showing regeneration of plantlets, number of plantlets per embryogenic callus and frequency of necrosed callus after 30-days sub-culture of embryogenic callus. Significant at 5% level of significance. Table indicates the same letters in a column don’t differ significantly as per Duncan Multiple ange Test (DM T) calculation.
|
Concentration of NaCl (mM) + P M6 |
Plantlet egeneration (%Mean ± SE) |
No. of egenerated Plantlets/ Callus (%Mean ± SE) |
Necrosed Callus (%) |
|
0 |
85.33±2.02e |
34.3±1.3e |
10 |
|
10 |
74.52±1.2d |
23.3±1.8d |
19 |
|
25 |
65.5±1.5c |
16.67±1.18c |
23 |
|
50 |
49.3±0.97b |
12.33±0.67b |
45 |
|
100 |
20.7±0.6a |
8.2±0.89a |
64 |
Table-7: Poongar- ed rice (Oryza sativa L.), effects of APD and ISS primers used for amplification for genetic fidelity assessment in control and salinity (100mM NaCl) tolerant plantlets.
|
Primers |
OPA 1 |
OPA 4 |
OPA 5 |
UBC 823 |
|
Primer Sequence (5′-3′) |
AATCGGGCTG |
AATCGGGCTG |
AGGGGTCTTG |
AGGGGTCTTG |
|
Total No. of Amplicons |
10 |
7 |
6 |
5 |
|
Band length of Amplicons (bp) |
100bp-3KB |
100bp-3KB |
100bp-3KB |
<3KB |
|
Monomorphic Bands |
3 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
Polymorphic bands |
7 |
6 |
5 |
4 |
|
Frequency of Polymorphism (%) |
70% |
86% |
83% |
80% |
DISCUSSION
Approximate duration of Poongar red rice crop is 7090 days suitable to grow in all seasons but most common period for cultivation is December to March. An average height of the crop is 129.9cm and produces 80 grains per ear head. Average yields of this crop are 600Kgs/acre grows in alluvial and clay soil (Karpagalakshmi et al., 2021) mostly cultivated in southern part of India.
Effects of NaCl-Salt on Callogenesis
Callus is considered as an unorganized and undifferentiated mass of parenchymatous cells (Bhatia, 2015). Most commonly used synthetic hormone for callus induction is 2,4-D alone (Castillo et al., 1998; Shahsavari, 2010), however, some of the other studies reveal that the combination of 2,4-D (3.0mg/L) with NAA (2.0mg/L) causes high percentage (up to 90%) of callogenesis (Trejo-Tapia et al., 2002; Ali et al., 2004; Din et al., 2016). Since the variation in genotypes between different variety of rice is common, therefore, some of the hormonal combinations have been proved to be not suitable.
Significantly, in this study 2,4-D alone (10µM) is turned out to be more effective and thus, shows maximum mean frequency of callogenesis (98.88%) and fresh weight of the induced callus (156mg). In parallel, there is decrease in frequency of callus induction if the concentration of 2,4-D gets increased ( amesh et al., 2009). Depends on explants used, the nature of the callus differs and callus induction can also be affected due to pH, PG s’ light intensity etc. (Barman et al., 2016),
The most commonly used medium for induction of callus and regeneration of callus are MS, LS, and N 6 (Pandey et al., 1994) but MS medium shows the maximum frequency of callus induction and regeneration of embryogenic callus (Khanna and aina, 1998). Simultaneously, mature de-husked seed has been emerged as a good source of explant for callogenesis (Ge et al., 2006; Khaleda and Al-Forkan 2006). Callus from scutellum of the mature caryopsis is also proved as a suitable source of explant for in vitro regeneration (Dina et al., 2016). Significantly, due to the availability of mature caryopsis throughout the year, mature caryopsis was used during present study in red rice.
In previously available report based on mature caryopsis culture, the mean weight of the callus was recorded to be lower (84.0mg) during 100mM of NaCl treatment in the cultivar B I38 whereas the control treatment shows relatively higher mean callus weight (97.0mg) while with further increase in concentration of NaCl (150mM), the weight of the callus was reduced to half of the weight (34.0mg) of callus that induced with 100mM of NaCl-treatment (Zinnah, 2013). With the increase in concentration of NaCl in nutrient medium, fresh weight of the callus decreases which indicates the negative effect of salinity stress (Shankhdhar et al., 2000; Priya et al., 2011).
Similarly, in case of the cv. Chinikanai, the weight of the callus without salt stress was reported as 240mg which was later decreased to 129mg during the treatment with 100mM of NaCl stress. Significantly, in terms of callogenesis, the rice cv. Chinikanai tolerates up to 200mM of NaCl and produces the least callus weight (35.0mg) after one month of incubation (Zinnah et al., 2013).
In presence of medium level of salt-stress, the yield gets decreased up to 60% (Zeng et al., 2002). Furthermore, previous studies also indicate that addition of salt into the medium decreases the frequency of somatic embryogenesis and plantlet regeneration (Ping et al., 2006, Tariq et al., 2008). By ionic and osmotic mechanisms, the plant cell gets damaged through the ions Na+ and Cl- which are present in NaCl (Chinnusamy et al., 2005).
Morphology of the calli at nutrient medium without stress were globular, creamy and friable which were getting worst when the concentration of NaCl getting increased ( attana and Bunnag, 2015; Sidek et al., 2024). Effects of salinity on callus induction were observed in terms of decreased size of callus, callus necrosis, and presence of large vacuoles cause unorganized meristematic zone (Atabaki et al., 2018). In the Malaysian variety MA DI Siraj 297, the viability of callus was decreased and led to necrosis of callus at the concentration of 150mM. Hence, 100mM of NaCl was considered to be threshold level for callogenesis (Sidek et al., 2024).
Additionally, previous studies reveal that 11.7g/L of NaCl shows reduced frequency of cell viability (45.33%) where control shows 85.33% in the cultivar B I dhan47 while the frequency get less viability (10.67%) in the B 10 cultivar. Moreover, B I dhan32 was completely affected and shows 0% of viable calli after 4-weeks of incubation (Siddique et al., 2014).
Moreover, during this study in red rice cv. Poongar, lower concentration of 2,4-D (10µM) alone proves to be enough for induction of callus from mature caryopsis culture and shows 98.88± 0.86 percentage of callogenesis, while even concentration of NaCl (50mM) in presence of 2,4-D (10µM) was found to be inhibitory and shows significantly reduced percentage of callogenesis (62.23±1.09%). Interestingly, increase in further higher concentration 100mM of NaCl, frequency of callogenesis (26.67±0.63%) was sharply declined and the callus appeared to be pale yellow even after 2-days of incubation.
Effects of NaCl- Salt on Somatic Embryogenesis
Several reports are available indicating the high concentration of NaCl strongly affects both the embryogenesis and regeneration in rice (Subhashini and eddy,1989; Vajrabhaya et al., 1989). Studies reported that most of the embryogenic calli were yellow and show similar morphological structures (Sahoo et al., 2011). Due to genotypic variation between the rice, composition of medium, and plant growth regulator used, considerable differences in embryogenesis could be observed in the induced callus like size, colour, number and morphology (Lee et al., 2003).
In another study, embryogenic callus was distinguished into 4 types Type-I (white or cream colour and compact organized callus), Type-II (yellow and organized callus), Type-III (yellow or brown unorganized callus), and Type-IV ( hizogenic callus) (Visarada et al., 2002). Furthermore, during previous study to increase the embryogenesis and regeneration of calli, small amount of Kn could be used among the indica rice varieties (Nhut et al., 2000; Afrasiab and Jafar, 2011) while this study in Poongar rice, low concentration of 2,4-D (5µM) alone was proved to be effective to induce higher rate of embryogenesis.
Among all the different concentrations, very low concentration of 2,4-D (5µM) alone without addition of NaCl salt shows highest percentage of somatic embryogenesis (95.0±3.9%) and also the maximum number (47.3±3.9) of somatic embryos per callus. Significantly, among all the concentrations of NaCl treated callus, 100mM of NaCl in presence of 2,4-D (5µM) treatment shows the lowest frequency of embryogenesis (31.67±2.9%) and also the minimum number (11.2±0.51) of somatic embryos per callus. In contrast, the lower concentration of NaCl (10mM) in presence of 2,4-D (5µM) shows the highest (67.5±2.33) percentage of somatic embryogenesis after 14-days of salinity treatment.
Effects of NaCl-Salt on Plant Regeneration
Factors like explants source, genotype, culture conditions and combinations of plant growth regulators, osmotic pressure, and partial desiccation affect the frequency of shooting (Vennapusa et al., 2015). eports are available on addition of proline into the culture medium gives positive impact on regeneration of rice varieties (Ge et al., 2006; Shahsavari, 2011).
Addition of Kn into the regeneration medium increases the frequency of regeneration of plantlet from the somatic embryos (Nhut et al., 2000; Afrasiab and Jafar, 2011). Some reports suggest that Kn is more effective compared to BAP in terms of regeneration (Lee et al., 2003, Barman et al., 2016).
Addition of auxin plays vital role during plantlets regeneration (Prodhan et al., 2001; Mostafiz et al., 2018). Many reports suggest that composition of medium, source of explant and culture environment can affect the potential of regeneration (Khatun et al., 2003; Hoque and Mansfield 2004). Moreover, appearance of green spots on the embryogenic callus indicates the initiation of regeneration and these green spots later form adventitious shoots (Artadana et al., 2017).
Earlier studies reveal that the concentration of BAP in regeneration medium influences the regeneration of plantlet (Shaheenuzzaman et al., 2001 and Malek et al., 2007). However, MS-medium alone is enough for formation of root from the shoot after 2-weeks of incubation (Kumar et al., 2016).
Although, there is regeneration in NaCl-treated calli but there will be physiological and molecular changes (ionic, osmotic, and tissue tolerance) due to the stress conditions ( oy et al ., 2014; Bhatia, 2015; Isayenkov et al., 2019). Highest frequency of regeneration in terms of rooting japonica is better than indica (Mikami and Kinoshita, 1988). Addition of NaCl to the medium helps to study the effect of salinity stress on different stages of regeneration (Priya et al., 2011).
Significantly, high level of NaCl affects the frequency of regeneration in general and rice in particular. Moreover, in previous study, 128mM of NaCl was found to be inhibitory in terms of regeneration (Basu et al., 1997). NaCl inhibits in vitro plant regeneration more than other salt stress like Na 2 So 4 which indicates that Cl-containing salts are more inhibitory for in vitro plant regeneration (Arefin, 2018).
Previous study reports that the percentage of regeneration without stress was recorded as 80% but higher concentration of NaCl 100mM shows the maximum inhibitory response and thus, minimum percentage of regeneration (20%) was recorded. With further increase in concentration of NaCl (150mM), there was no regeneration of plantlet from the embryogenic calli in the cultivar cv. B I 38 (Zinnah et al., 2013).
In contrast, cv. Chinikanai shows 20% of plantlet regeneration with the concentration of 150mM of NaCl into the regeneration medium, which was further decreased to 0% when increases the concentration of NaCl to 200mM in comparison to control treatment where the frequency of regeneration was obtained 60% (Zinnah et al., 2013).
During present study, the lowest concentration of NaCl (10mM) treatment could show the maximum frequency (74.52±1.2%) of plantlet regeneration and also number of regenerated plantlets (23.3±1.8) per callus while in contrast, the highest concentration of NaCl (100mM) resulted the minimum frequency (20.7±0.6%) of plantlet regeneration and also the minimum number (8.2±0.89) of regenerants per callus regeneration were obtained in comparison to the control (P M6) treatment where 85.33±2.02% of plantlets regeneration and 34.5±1.3 plantlet per callus were noted.
Assessment of Genetic Fidelity analysis in Regenerants
Among the in vitro regenerated plantlets, the genetic variability or dissimilarity can be assessed through different ISS , and APD primers which are DNA based molecular markers ( awat et al., 2013). It is the technique used to find the homogeneity or to find the difference among in vitro regenerated plantlets and in vitro stress tolerant plantlets. Four APD and ISS primers (OPA1, OPA4, OPA5 and UBC 823) were used in present study and all the primers could show dissimilarities in terms of generation of polymorphic bands. Among all the four primers tested, APD primer (OPA 4) shows the maximum frequency of polymorphism (86%) and the polymorphic bands were positioned in between 100bp-3Kb.
CONCLUSION
In this study, an efficient and stable protocol for high frequency of somatic embryogenesis and plantlet regeneration from mature caryopsis in red rice (Poongar) could be established. The induction of callus and differentiation of somatic embryos along with the production of salinity (NaCl) tolerant plants could be also successfully achieved in red rice cv. Poongar. Further, genetic homogeneity of in vitro regenerated control plantlets and in vitro regenerated stress tolerant plantlets were assessed by using APD and ISS markers resulted in generation of polymorphic DNA bands.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS


