Some aspects of the social life in the estimates and beliefs of the residents of the Russian Arctic (Based on polls of the Murmansk region)
Автор: Gushina I.A., Polojenzova O.A.
Журнал: Arctic and North @arctic-and-north
Рубрика: Social Sciences
Статья в выпуске: 14, 2014 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The article presents some results of sociological surveys of the population of a region of the Russian Arctic − Murmansk region in recent years. Emphasis is placed on the estimates of financial position, purchasing power, identity , social mood and expectations.
Case studies, self‐identification, evaluation, оpinions, social stratification, social mood, purchasing power, the territorial society, ranking problems
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148319870
IDR: 148319870 | УДК: 332.143
Текст научной статьи Some aspects of the social life in the estimates and beliefs of the residents of the Russian Arctic (Based on polls of the Murmansk region)
The Zone of the Russian Arctic, to which the Murmansk region, is currently the object of at--‐ tention of the world because of contact in the region geo--‐economic interests of many countries.
Numerous promises speedy prosperity and well--‐being of the region and even some steps in this direction by the Russian authorities so far no tangible results were not given. Exploration of the natural resources in the Arctic is impossible without augmentation of human potential, without the " long--‐standing problem solving people for a long time living and working in the Arctic land --‐ Lyakh, ensuring a decent life to those who will lead them further development "[1, p.67].
The research methods of the sociology of the social reality allows you to organize and summarize the phenomena of the social life, and results--‐based management at all levels. The so--‐ cio--‐economic situation in the Russian society in recent decades is not facilitated the development of balance and social justice in the areas of public life. Instability in the economy and politics, changing the structure of the social stratification of the population does not have added confi--‐ dence in the present and the future.
The research of the representations of the inhabitants of a region of the Russian Arctic, Murmansk region on various aspects of their lives helps to identify patterns and trends of social mood, the most acute problems of life. This article presents some of the results of the sociological research in recent years, the emphasis is on material condition assessments, identity, social mood and expectations.
The level of life of the population
Basis for assessing the standard of living in the region are indicators such as revenues, cost structure, the consumption of products and services. According to opinion polls since 2007 marked increase in actual revenue in the Murmansk region, including in 2012, thanks to the index--‐ ing public sector wages and pensions. This corresponds to the official statistics, which recorded growth of per capita income (Table 1).
Table 1
Income dynamics of the population in Murmansk region in 2007 - 2012 [2]
|
Indicators |
2007 |
2008 |
2009 |
2010 |
2011 |
2012 |
|
Per capita income of the population, per month |
15859 |
19615 |
22333 |
24047 |
25303 |
27854 |
|
Average nominal monthly wages of workers organi--‐ zations rub. |
18581 |
23763 |
26592 |
29303 |
32304 |
36259 |
|
Subsistence minimuma4) (average per capita) per month |
5676 |
6743 |
7582 |
8215 |
8878 |
9044 |
In addition to assessing the current financial situation, respondents were asked to indicate how much income would be sufficient for them. Throughout the years of the study, the difference between the received and expected income was approximately 1.4 times: in 2009 the average revenue generated was estimated at 12.4 thousand rubles, in 2012 --‐ 17.3 thousand rubles, and the desired respectively 32.9 and 43.4 thousand rubles. Thus, despite some positive developments, the current level of material well--‐being is clearly not satisfied majority.
In this regard, an interesting assessment identity of the respondents categorized as "rich", "middle--‐income" and "poor" (Table 2). Submitted indicators show very little difference in the amounts of money between "poor" and "rich": just 2,5 - 3,5 times. Of course, it should be borne in mind that the wealthiest representatives of the regional society available for this kind of the so--‐ ciological information, but, nevertheless, we can conclude that the claims in the sample of the re--‐ spondents who consider themselves "rich", quite small: in 2011 this amounted to 38.8 thousand rubles, in 2012 --‐ 40.6 thousand rubles.
Table 2
Identity of the respondents in the terme of the income in 2009 - 2011.,rubles
|
Indicators |
2009 |
2010 |
2011 |
2012 |
|
Income "rich", rubles per month. |
25250,0 |
30646, 8 |
38800,0 |
40571,2 |
|
Income people of moderate means, rubles per month. |
14140,7 |
16354,8 |
16198,6 |
17466,6 |
|
Income of the "poor and needy" |
9330,2 |
10784,9 |
10801,9 |
13448,4 |
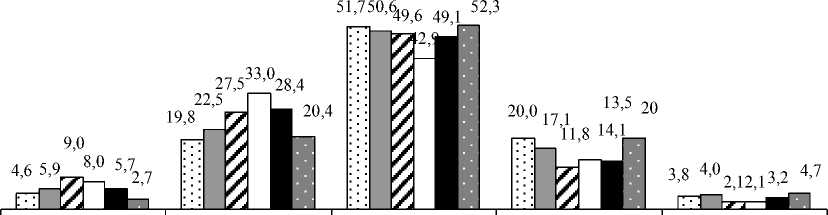
As we know, based on people has a direct impact on their purchasing power. Fig. 1 pre--‐ sents estimates of purchasing power in the last six years. Their fluctuations appear logical and consistent: positive changes in consumption patterns, formed in 2007 - 2008. Were violated sig--‐ nificant impact of the financial crisis.
In May 2009, about half of the respondents (47.5%) indicated that their crisis noticeably touched, which was manifested in the increase in expenditures on consumer goods and services, delays and / or cuts in wages and social benefits. These phenomena are largely affected by public sector employees and middle managers. In the crisis of 2008 and the following two years have in--‐ creased the proportion of those who "only had enough money for food" and "do not even have enough food," the bulk of these are representatives of the lower social strata. Richer also felt the "breath" of the crisis, pointing out that the purchase of durable goods has become difficult. In 2012, the purchasing power of the indicators have returned to pre--‐crisis levels, which indicates a certain stabilization of the purchasing power of the population.
At the same time, an adaptation of the population to speak crises preferred strategy of be--‐ havior during the crisis. If a decade ago, the prevailing mood of social dependency, and the bulk of the population counted on the help of the state, but now more than half are trying to find addi--‐ tional sources of income, while 17% of respondents chose austerity.
□ 2007
□ 2008
и 2009
□ 2010
■ 2011
□ 2012
Денег не хватает даже на приобретение пр оду ктов питания
Денег хватает только на пр иобр етение продуктов питания
Денег достаточно для пр иобр етения необходимых пр оду ктов и одежды
Поку пка большинства товар ов длительного пользования не вызывает у нас тр у дностей
Денег вполне достаточно, чтобы ни в чем себе не отказывать
Pic. 1. Respondents' assessment of their ability to purchase in 2077-2012, %
Thus, in general, the assessment of the current personal financial situation of the urban population of the Murmansk region changed slightly, despite some revenue growth, while there was an increase in self--‐assessments of bad financial position and deteriorating purchasing power of the population of the region.
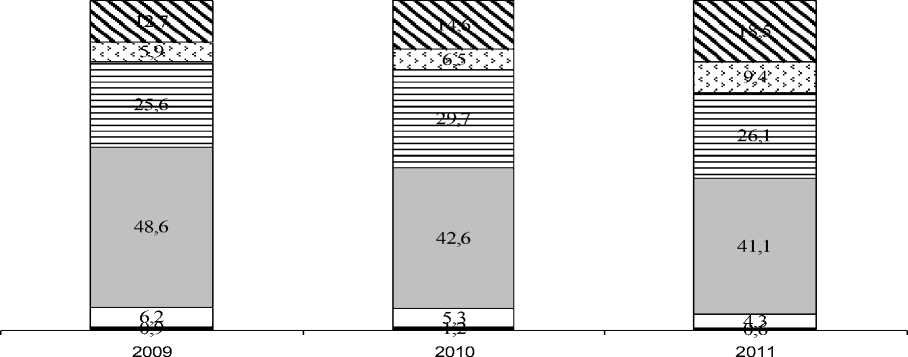
■ Верхний слой □ Слой выше среднего □ Средний слой в Слой ниже среднего □ Нижний слой ы Не знаю
Pic. 2. Identity of the respondents belonging to a social group in 2009-2011, %
Self--‐esteem of belonging to a particular social class is important for everyone, because de--‐ pending on her form attitudes, values, aspirations, level of social protest and more. During 2003 -2009. social identity is characterized by a certain constancy. But in 2010, recorded negative trends:: decreased the percentage of those who identify themselves as layers "upper", "above av--‐ erage" and "average" in favor of layers "below average" and "low", as well as those who found it difficult to self--‐esteem (Fig. 2). This period coincides with the seemingly overcome the first wave mirovogoekonomicheskogo crisis significantly affected in the mood of uncertainty, stratification vibrations fall in the level of positivity in the current mood.[3]
The role of the problem of the region
Among the most significant problems in the region traditionally respondents indicate un--‐ doubtedly interconnected inflation and low living standards (Fig. 3). However, in the 2012 version of "Low Life" has moved into fifth place (28.1%), "skipping" forward issues such as the poor quality of infrastructure (public utilities and state highways) --‐ 35.9%.
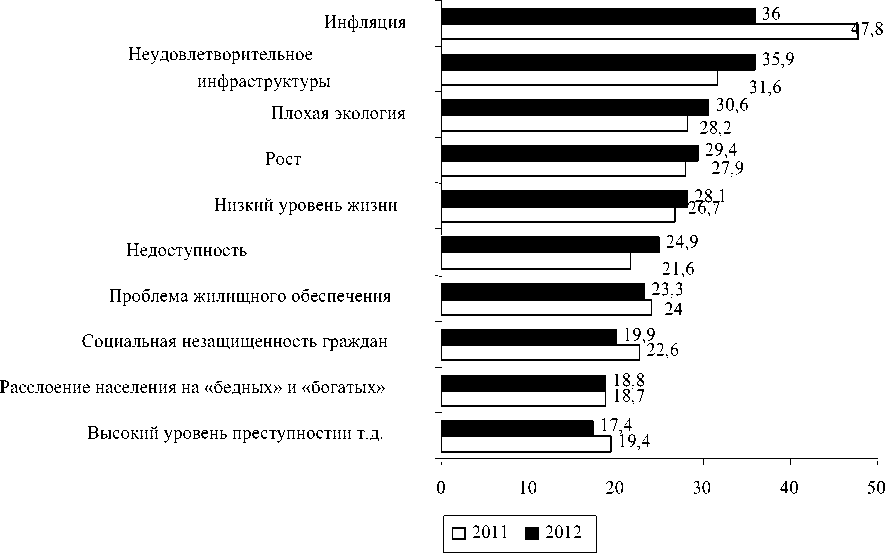
Pic. 3. Dynamics of urgent problems of the region in the respondents' assessments in 2011-2012 гг., %
Sphere Utilities – is a subject for a separate discussion, we need only note that from the outset of its reform fixed high level of distrust of this undertaking. Quality of housing and commu--‐ nal services in all the years of observation are evaluated by respondents as very low fees --‐ unrea--‐ sonably inflated. Many payment for utilities significantly affects the level of life, primarily concerns the socially disadvantaged and low--‐income citizens and persons in working age, as they relate to the category of people with the lowest incomes.
In addition, the residents critically assess the condition of the road network in the region. Also move the inconvenience, this most negative impact on the economy of the Murmansk region overstated cost structure of goods, works and con--‐meadow; created obstacles in attracting foreign investment.
The third most important people in the region is isolated complex ecological situation (30.6%) due to a serious burden on the environment by industrial enterprises, the irrational use of this resource, as well as increased environmental awareness.
Problem of low availability and quality of health care is largely worried residents. Hailed as the modernization of this sector while not brought tangible results, rather the opposite: the so--‐ called optimization of the network of health facilities, according to the respondents of the cities of Apatity, Kandalaksha Olenegorska, reduced them to the level of accessibility of health care. Health care remains one of the most socially sensitive areas as the need for health--‐care concerns of each person. Poor quality and inaccessibility (it was pointed out 24.9% of the respondents) care is ad--‐ versely affected by the level of health in the Murmansk region. The distribution of responses on the degree of the satisfaction with the quality of health care in 2012 on a scale of 5 (completely satisfied) to 1 point (completely dissatisfied) revealed extremely low average --‐ 2.6 points, which indicates the existence of the serious problems in improving health effective treatment and pre--‐ vention of diseases.
Traditionally sharp remain problems such as alcoholism (29.4%), housing (23.3%), lack of the social protection of citizens (19.9 %), stratification of the population into rich and poor (18.8%), high levels of crime (17.4 %). At the same time representatives of the lower strata are more concerned about the problems of inflation, layoffs, unemployment, delays in the payment of pensions and benefits. Those who consider themselves to upper social strata, are more concerned with the poor state of roads, poor quality of health services, engineering infrastructure utilities, environmental problems.
Regional level of the social adaptation, life satisfaction
To assess the regional level of the social adaptation used sociological information about the degree of confidence in the future of the respondents (Figure 4). Sustainability of the current situation, positive or negative evaluation of the various aspects of their lives form the level of the positive perception of the future. The last three years have seen a situation of uncertainty: the constant group of respondents (25%) "completely confident" and "somewhat confident " in their future. Unfortunately, this figure does not characterizes the situation in the region as stable.
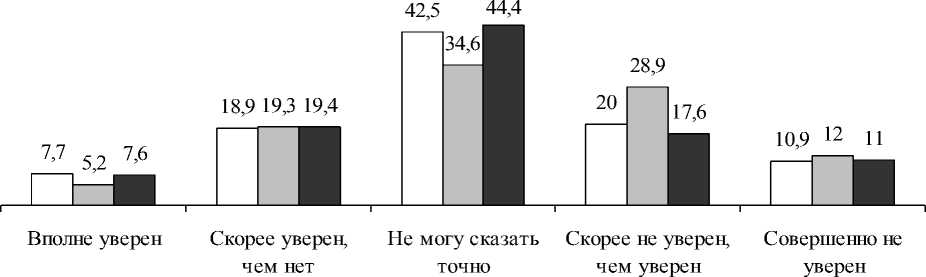
□ 2010 □ 2011 □ 2012
Pic. 4. Respondents' assessments of the degree of confidence in the future in 2010-2012, %
In 2011, 9% increase in the share of those who "rather than confident" in their future, while reducing the proportion of "very confident". In 2012 almost 45 % of the respondents could not determine the choice of the options, indicating that low mood adaptation to the current social situation. Thus, the instability of the socio--‐economic situation, the lack of clear, consistent policy implementation proclaimed reform course formed a third of northerners fairly low level of confi--‐ dence in their future. This category includes the majority of the respondents who identified them--‐ selves as "poor", as well as workers in industry, transport, the service sector, trade and pension--‐ ers.
Preponderance of the opinion public uncertainty about the future development of the country for the next five years raises questions about the reasons for the following estimates: in 2012 over 40% of respondents did not answer this question, and 38.7% believe that these years are "neither good nor bad". Most likely, based on these evaluations --‐ and the lack of awareness of the population in disbelief prospects for industrial production, economic and social policy, em--‐ ployment. To a certain extent, these ideas about the future of the country indicate a predomi--‐ nance of social sentiment social apathy.
Satisfaction with their own life is an important indicator of the condition and social stability in the territorial society and society as a whole (Fig. 5). Held us sociological monitoring revealed the following trends: in recent years dominated partial satisfaction assessment (40 - 45%), about one third of respondents were mostly satisfied (a significant share of this category of youth, which is inherent optimism) and almost 20 % in whole or in generally not satisfied with their life situa--‐ tion, and a trend towards worsening satisfaction ratings.
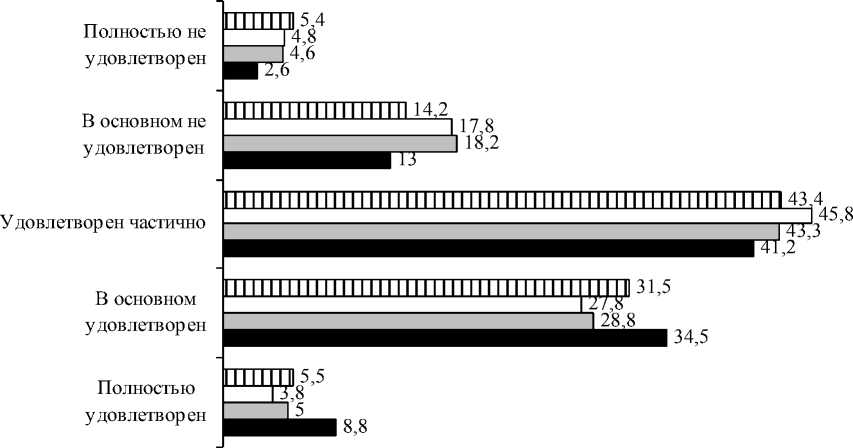
ш 2012
□ 2011
□ 2010
■ 2008
Pic. 5. Respondents' assessments of the level of the satisfaction with their lives as a whole in 2008-2012., %
Conclusion
Population representation of the social reality is largely dependent on the nature of the in--‐ teraction between society and the authorities of the existence of the effective mechanisms of in--‐ fluence on individual public authority. On the other hand, it is important how seriously the author--‐ ities perceive public opinion about the implemented socio--‐economic policies as an important source of information to make good decisions.[4]
Sociological information contributes to understanding the public perception of social policy and implemented evidence--‐based conclusions and generalizations about its effectiveness and pro--‐ spects for improvement. Possibility of structuring, synthesis and analysis represents a significant resource for improving the effectiveness of social control. It identifies the need for greater use of sociological methods in management.
Список литературы Some aspects of the social life in the estimates and beliefs of the residents of the Russian Arctic (Based on polls of the Murmansk region)
- Рябова Л. А. О неотложных мерах по повышению уровня качества жизни населения Арктической зоны РФ // Север и рынок: формирование экономического порядка. 2012. № 1. С. 67−71.
- Мурманской области — 75 лет: стат. сб. / Территориальный орган Федеральной службы государственной статистики по Мурманской области (Мурманскстат). Мурманск, 2013. 113 с.
- Гущина И. А., Довиденко А. В. Влияние кризиса на уровень социальной стабильности в Мурманской области // Север и рынок: формирование экономического порядка. 2011. № 2. С. 83−87.
- Кондратович Д. Л. Возможности исследования институциональной эффективности социальной организации и управления в северном регионе на основе социологической информации //Север и рынок: формирование экономического порядка. 2011. № 2. С. 94−99.


