Сортовая специфичность эффектов ризобактерий в отношении азотфиксирующего симбиоза и минерального питания сои в условиях агроценоза
Автор: Береговая Ю.В., Тычинская И.Л., Петрова С.Н., Парахин Н.В., Пухальский Я.В., Макарова Н.М., Шапошников А.И., Белимов А.А.
Журнал: Сельскохозяйственная биология @agrobiology
Рубрика: Агросистемы будущего растение и почва
Статья в выпуске: 5 т.53, 2018 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Для бобовых растений важным механизмом взаимодействия с ризобактериями служит их способность стимулировать формирование азотфиксирующего симбиоза с клубеньковыми бактериями. В то же время мало известно о внутривидовой (сортовой) изменчивости бобовых растений в реакциях на инокуляцию ризобактериями. Наши недавние модельные исследования с проростками сои на гидропонике показали способность ризобактерии Pseudomonas oryzihabitans Ep4, продуцирующей ауксины и содержащей АЦК дезаминазу, активнее стимулировать рост и колонизировать корни у сортов Красивая Меча и Свапа, чем у сорта Бара. Целью настоящей работы было изучение сортоспецифичных ответных реакций растений сои Glycine max (L.) Merr. на инокуляцию ризосферными бактериями при различном минеральном питании в условиях агроценоза. Исследования выполняли на трех раннеспелых районированных сортах сои северных экотипов - Красивая Меча, Свапа и Бара. Использовали штаммы ризобактерий Ps. oryzihabitans Ep4 и Variovorax paradoxus 3-P4...
Внутривидовая изменчивость, минеральное питание, ризосфера, симбиотическая азотфиксация, фитогормоны, агроценоз
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142216604
IDR: 142216604 | УДК: 633.34:579.64:631.847.211:631.811 | DOI: 10.15389/agrobiology.2018.5.977rus
Текст научной статьи Сортовая специфичность эффектов ризобактерий в отношении азотфиксирующего симбиоза и минерального питания сои в условиях агроценоза
Работа выполнена при поддержке РНФ (подготовка и проверка чистоты бактериальных инокулюмов и биопрепаратов — грант ¹ 16-16-00080; постановка полевых опытов — грант ¹ 14-16-00137; элементный анализ растений — грант ¹ 17-76-10039) и РФФИ (изучение образования клубеньков и азотфиксации — грант ¹ 15-04-09023). Депонирование штаммов выполнено в рамках Программы ФАНО России по развитию и инвентаризации биоресурсных коллекций научными организациями.
В настоящее время накоплен значительный экспериментальный материал о положительном действии ассоциативных ризосферных бактерий (ризобактерий) на рост, питание и адаптацию сельскохозяйственных растений к неблагоприятным климатическим и почвенным факторам с помощью фиксации атмосферного азота, продукции или утилизации биологически активных веществ, мобилизации питательных элементов в ризосфере, индукции системной устойчивости и биоконтроля фитопатогенов (1-5). Для бобовых растений важным механизмом взаимодействия с ризобактериями служит их способность стимулировать формирование азотфиксирующего симбиоза с клубеньковыми бактериями (6-8). Так, число клубеньков на корнях сои увеличивается при совместной инокуляции клубеньковыми бактериями Bradyrhizobium japonicum и ризобактериями Pseudomonas fluorescens (911), Azospirillum brasilense (12), Bacillus subtilis (13-17), B. thuringiensis (13, 14, 18), B. megaterium (19), Paenibacillus lautus (19), а также неидентифицирован-ными фосфатмобилизующими бактериями (20). Действие ризобактерий может быть связано со снижением биосинтеза стрессового фитогормона этилена (к которому очень чувствительно клубенькообразование) за счет утилизации ризобактериями его предшественника 1-аминоциклопропан-1-карбокси-лата (АЦК) с помощью фермента АЦК дезаминазы (19, 21-23). Предполагается, что продукция ризобактериями ауксинов, стимулирующих рост корней и клубенькообразование, вовлечена в активацию азотфиксирующего симбиоза (4, 8, 24). Однако в большинстве перечисленных работ механизмы положительного действия ризобактерий на симбиоз сои с ризобиями не изучали.
Так же мало известно о внутривидовой (сортовой) изменчивости бобовых растений в реакциях на инокуляцию ризобактериями. У четырех сортов гороха Показаны значительные различия эффектов Ps. brassicacearum Am3 при поглощении питательных веществ (N, P, K, Ca, S, Fe) из загрязненной тяжелыми металлами почвы (25). Влияние ризобактерии Az. brasil-ense , которая фиксирует азот и продуцирует ауксины, на рост сорго (26), пшеницы (27) и фасоли (28) существенно варьировало в зависимости от сорта. Похожие результаты получены для близкого к ней вида Az. lipoferum в опытах с сортами кукурузы (29). Выявлена сортовая специфичность в эффектах ризобактерий на бобово-ризобиальный симбиоз у сои (15, 30), гороха (31-32) и нута (33). Различия в экспрессии генов, связанных с сигналин-гом ауксинов и этилена, описаны у двух сортов риса при инокуляции Az. li-poferum (34). Варьирование способности интродуцируемых популяций ризо-бактерий колонизировать корни растений в зависимости от сорта описано и в других работах (27, 35). Однако причины внутривидовой изменчивости взаимодействий растений и ризобактерий пока не изучены, что существенно сдерживает применение последних в качестве биопрепаратов (36).
Основная бобовая культура в России — соя. Ее рост и питание в значительной степени зависят от симбиоза с клубеньковыми бактериями и ризобактериями. Для расширения ареала этой культуры нужны сорта, устойчивые к низким температурам и адаптированные к бедным почвам. Для самого северного района возделывания сои в России — Орловской области созданы раннеспелые сорта северных экотипов Красивая Меча, Свапа и Бара. Однако об их симбиотических особенностях и потенциале известно мало. Можно предположить, что ризобактерии, продуцирующие ауксины и содержащие АЦК дезаминазу, должны способствовать лучшей адаптации растений к неблагоприятным для сои почвенно-климатическим условиям.
Ранее в модельных опытах с проростками сои на гидропонике мы показали, что ризобактерия Ps. oryzihabitans Ep4, продуцирующая ауксины и содержащая АЦК дезаминазу, активнее стимулирует рост и колонизирует 978
корни у сортов Красивая Меча и Свапа, чем у сорта Бара. Это связано с интенсивной корневой экссудацией органических кислот, сахаров и аминокислот и их эффективной утилизацией и трансформацией ризобактериями (32). Тесную интеграцию штамма Ps. oryzihabitans Ep4 с сортами Красивая Меча и Свапа частично подтвердили результаты полевого опыта при совместной инокуляции растений клубеньковыми бактериями (37).
В этом сообщении мы впервые описываем положительное влияние ризосферных бактерий, содержащих АЦК дезаминазу, на разные сорта сои северных экотипов и их симбиоз с клубеньковыми бактериями.
Цель работы — выявление зависимости сортоспецифичных ответных реакций растений сои от штамма ризобактерий и минерального питания в условиях агроценоза.
Методика. Семена суперэлиты раннеспелых районированных сортов сои Glycine max (L.) Merr. Красивая Меча и Свапа получены во Всероссийском НИИ бобовых и крупяных культур (г. Орел,), сорта Бара — в ООО «Соевый комплекс» (г. Краснодар).
При инокуляции использовали штаммы ассоциативных бактерий, содержащих АЦК дезаминазу и продуцирующих ауксины: Pseudomonas ory-zihabitans Ep4 (38) и Variovorax paradoxus 3-P4 (39). Для приготовления инокулюма ассоциативные бактерии культивировали в разработанной ранее жидкой питательной среде (40) в течение 4 сут при 28 ° С и 180 об/мин. Полученную суспензию разбавляли стерильной водопроводной водой до конечной концентрации 107 кл/мл. Для образования азотфиксирующего симбиоза использовали биопрепарат ризоторфин («ЭКОС», г. Санкт-Петербург), содержащий клубеньковую бактерию Bradyrhizobium japonicum 634b в стерилизованном торфе в качестве носителя (109 кл/г торфа). Чистоту инокулюмов и биопрепарата проверяли микробиологическими методами. Все штаммы были депонированы в Ведомственную коллекцию полезных микроорганизмов сельскохозяйственного назначения (Всероссийский НИИ сельскохозяйственной микробиологии, г. Санкт-Петербург).
Почва участков, на которых проводили полевые опыты (НОПЦ «Интеграция» Орловского ГАУ, п. Лаврово, Орловский р-н, 2013-2015 годы), темно-серая лесная среднесуглинистая, содержание гумуса — 3,4±0,1 %, подвижного азота — 57±8 мг /кг, подвижного фосфора — 100±8 мг/кг, подвижного калия — 136±9 мг/кг, рН 5,0±0,06 (средние данные за 3 года). Почвенные характеристики определяли стандартными методами (41).
Растения выращивали в семипольном севообороте зернового типа с полной рендомизацией делянок (площадь делянки 10 м2) в 4-кратной повторности для каждого варианта, предшественник — черный пар. Минеральное удобрение (диаммофоска) вносили за 7 сут до посева в дозах N30P81K81 и N44P11 6 K11 6 (соответственно 70 и 100 % из расчета на планируемый урожай 3 т/га). Непосредственно перед посевом семена протравливали фунгицидом Максим КС (флудиоксонил, 2 мл/кг семян; ООО «Сингента», Россия) в рабочей концентрации (изучаемые штаммы, по данным предварительных экспериментов, к ней устойчивы), часть семян обработали ризоторфином (штамм B. japonicum 634b, 2 г/кг семян). Норма высева для всех семян — 70 шт/м2 (селекционная сеялка Plotseed XL, «Wintersteiger», Австрия). Инокулюм Ps. oryzihabitans Ep4 и V. paradoxus 3-P4 (200 мл/м2) вносили прикорневой обработкой на 10-е и 27-е сут после посева (соответственно в фазы проростков и 2-3 настоящих листьев), контроль — варианты без инокуляции (для оценки эффектов ризобактерий по интегральным параметрам при коинокуляции контролем служил вариант с ризоторфином). Во всех вариантах перед посевом применяли почвенный препарат Дуал
Голд, КЭ (1,6 л/га; ООО «Сингента», Россия), в фазу 3 настоящих листьев — Базагран, ВР (2 л/га; ООО «БАСФ», Россия). Для борьбы с вредителями использовали инсектицид Карате Зеон, МКС (0,4 л/га; ООО «Сингента», Россия). За 2 нед до уборки проводили десикацию препаратом Реглон Супер, ВР (1,5 л/га; ООО «Сингента», Россия). Семена собирали объединителем TERRION-SAMPO SR2010 («Агротехмаш», Россия).
В фазу цветения оценивали нитрогеназную (азотфиксирующую) активность на корнях ацетиленовым методом (42). Для этого у 5 растений с каждой делянки корни промывали водопроводной водой, подсчитывали число клубеньков, помещали корни в герметичные флаконы (250 мл) и инкубировали в атмосфере 10 % ацетилена 1 ч при 25 ° C. Реакцию останавливали раствором формалина (2,5 %), содержание этилена определяли на газовом хроматографе ФГХ-1 (ООО НПП «ЭКАН», Россия). Затем клубеньки отделяли от корней, высушивали и взвешивали. Листья растений с каждого участка высушивали и использовали для элементного анализа.
В семенах измеряли содержание белка и жира, используя инфракрасный анализатор зерна Infratec™ 1241 («FOSS», Дания) в соответствии с инструкциями производителя. Количество B, Ca, Co, Cu, Fe, K, Mg, Mn, Mo, Ni, P, S, Zn в листьях оценивали на эмиссионном спектрометре ICPE-9000 («Shimadzu», Япония). Для этого сухие листья измельчали и сжигали в смеси концентрированной HNO 3 и 38 % H2O2 (1:1) при 70 ° C (система DigiBlock, «LabTech», Италия). Общий азот в листьях определяли на автоматическом анализаторе Kjeltec 2300 («FOSS Analytical», Дания).
Статистическую обработку данных проводили в программе STATIS-TICA 10 («StatSoft, Inc.», США). Использовали дисперсионный анализ (тест наименьшей средней разницы Фишера), t -критерий Стьюдента и корреляционный анализ. Рассчитывали средние ( М ) и ошибки средних (±SEM).
Результаты. При применении ризоторфина в варианте с N30P81K81 число клубеньков увеличивалось по сравнению с контролем у всех сортов, с N44P11 6 K11 6 — у сортов Красивая Меча и Свапа (табл. 1). Совместная инокуляция со ризобактериями также приводила к более интенсивному образованию клубеньков, при этом у сорта Свапа их число было достоверно выше (p < 0,001), чем в варианте с моноинокуляцией ризоторфином (см. табл. 1). Во всех вариантах с ризоторфином повышалась масса клубеньков. У сорта Свапа совместная обработка ризоторфином и Ps. oryzihabitans Ep4 увеличивала массу клубеньков на обоих фонах минерального питания и активность азотфиксации при N30P81K81 по сравнению с контролем и применением ризоторфина. При использовании V. paradoxus 3-P4 на 70 % фоне минерального питания у инокулированных ризоторфином растений сортов Свапа и Бара достоверно возрастала масса клубеньков (соответственно p < 0,001 и p = 0,044). Повышенную азотфиксацию у всех сортов на 100 % фоне минерального питания отмечали только при совместной инокуляции клубеньковыми и ассоциативными бактериями (см. табл. 1).
При N30P81K81 в фазу цветения увеличилась надземная масса растений у сортов Красивая Меча и Свапа как в случае монокультур бактерий, так и при сочетании штаммов с ризоторфином, но сорт Бара положительно отреагировал только на моноинокуляцию ризоторфином (табл. 2). При N 44 P 116 K 1 1 6 ризоторфин повышал надземную массу только у сортов Красивая Меча и Свапа. Для сорта Бара совместная инокуляция со штаммом Ps. oryzihabitans Ep4, а для сорта Красивая Меча — с V. paradoxus 3-P4 оказалась достоверно эффективнее (соответственно p = 0,015 и p = 0,039) (см. табл. 2), чем моноинокуляция ризоторфином. Штаммы Ps. oryzihabit-ans Ep4 и V. paradoxus 3-P4 достоверно (p от 0,045 до 0,0012) повысили мас-980
1. Симбиотические показатели растений в фазу цветения у сортов сои Glycine max (L.) Merr. под влиянием клубеньковой бактерии Bradyrhizobium japonicum 634b (ризоторфин) и ассоциативных бактерий Pseudomonas oryzihabitans Ep4 и Variovorax paradoxus 3-P4 при разном минеральном питании (М±SEM, НОПЦ «Интеграция» Орловскиого ГАУ, п. Лаврово, Орловский р-н, 2013-2015 годы)
2. Биомасса растений в фазу цветения у сортов сои Glycine max (L.) Merr. под влиянием клубеньковой бактерии Bradyrhizobium japonicum 634b (ризоторфин) и ассоциативных бактерий Pseudomonas oryzihabitans Ep4 и Variovorax paradoxus 3-P4 при разном минеральном питании ( М ±SEM, НОПЦ «Интеграция» ФГБОУ ВО Орловский ГАУ, п. Лаврово, Орловский р-н, 2013-2015 годы)
|
Вариант |
Сухая масса, г/растение |
|||||
|
надземная часть |
корни |
|||||
|
Красивая Меча |
Свапа |
Бара |
Красивая Меча |
Свапа |
Бара |
|
|
Без инокуляции |
N 30 P 81 K 81 (70 %) 39±2a 35±4a 44±2a |
3,5±0,1a |
3,9±0,2a |
3,8±0,3a |
||
|
B. japonicum 634b |
45±2b |
46±3b |
55±4b |
4,1±0,3ab |
5,1±0,4ab |
4,1±0,2ab |
|
Ps. oryzihabitans Ep4 |
49±3bc |
45±2ab |
43±2a |
4,3±0,2bc |
5,1±0,4ab |
4,6±0,5b |
|
V. paradoxus 3P-4 |
48±1bc |
47±5b |
44±4a |
4,5±0,1bc |
5,8±0,6b |
4,3±0,4ab |
|
B. japonicum 634b + Ps. oryzihabitans Ep4 |
48±2bc |
46±5b |
47±4ab |
4,1±0,3b |
6,1±0,5b |
4,2±0,2ab |
|
B. japonicum 634b + V. paradoxus 3P-4 |
52±1c |
50±3b |
41±4a |
4,8±0,2c |
5,0±0,3ab |
4,7±0,4b |
|
Без инокуляции |
N 44 P 116 K 116 (100 %) 27±3a 46±1a 47±2a |
3,5±0,1a |
4,8±0,3a |
3,7±0,2a |
||
|
B. japonicum 634b |
36±1b |
57±3b |
49±3ab |
3,9±0,3ab |
6,1±0,6ab |
4,0±0,2ab |
|
Ps. oryzihabitans Ep4 |
35±1b |
48±4ab |
59±4bc |
4,2±0,2b |
5,5±0,5ab |
3,9±0,2ab |
|
V. paradoxus 3P-4 |
33±1ab |
52±4ab |
53±5abc |
4,5±0,2b |
5,2±0,4ab |
3,8±0,2ab |
|
B. japonicum 634b + Ps. oryzihabitans Ep4 |
39±0bc |
57±5b |
61±3c |
4,2±0,2b |
6,4±0,8b |
4,5±0,1b |
|
B. japonicum 634b + V. paradoxus 3P-4 |
42±1c |
52±4ab |
58±5bc |
4,1±0,1b |
6,3±0,8b |
4,0±0,2ab |
П р и м еч а ни е. Для каждой дозы удобрений разными латинскими буквами обозначены статистически значимо различающиеся варианты (тест НСР Фишера, p < 0,05, n = 12).
Во всех вариантах с ризоторфином содержание N в листьях увеличивалось (табл. 3). На фоне 70 % минерального питания оба штамма ри-зобактерий при моно- и смешанной инокуляции с ризоторфином повышали содержание Р в листьях у сорта Красивая Меча (см. табл. 3). У сорта Свапа этот показатель возрастал при инокуляции смесью ризоторфина и Ps. oryzihabitans Ep4 на обоих фонах удобрений, у сорта Бара — только на 70 % фоне. Содержание Mg, Ca, B, Fe, Zn и Mo (см. табл. 3) в листьях у растений сортов Красивая Меча и Свапа при использовании смеси ризо-торфина и Ps. oryzihabitans Ep4 на обоих фонах, как правило, было выше. Похожий, но менее выраженный результат для этих двух сортов получили при инокуляции смесью ризоторфина и V. paradoxus 3-P4: при N30P81K81 бактерии не влияли на содержание Mg, Ca, B и Zn, а при N44P11 6 K11 6 не повышалось количество Р. У сорта Бара (в отличие от двух других) контрольные и инокулированные растения по элементному составу листьев часто различались несущественно что проявилось для Mg, B, Zn, Mo на 70 % фоне и для P, Fe и Zn — на 100 % фоне (см. табл. 3, 4). Положительное влияние совместной инокуляции на содержание макро- и микроэлементов во многих случаях было достоверным по отношению как к контролю без инокуляции, так и к варианту с применением ризоторфина (см. табл. 3, 4).
Ризоторфин и ризобактерии не повышали содержание Co, Cu, K, Mn, Ni и S в листьях. Исключением был рост количества Со у сортов Красивая Меча (на 15 %, p = 0,015, n = 12) и Свапа (на 26 %, p = 0,015, n = 12), а также S — у сорта Свапа (на 23 %, p = 0,016, n = 12) при инокуляции смесью ризоторфина и Ps. oryzihabitans (данные не представлены).
На обоих фонах минерального питания ризоторфин повысил урожай семян у всех сортов (максимально — при смешанных инокуляциях с ризобактериями) (табл. 5). На сорте Свапа достоверный рост урожайности
-
3. Содержание макроэлементов в листьях в фазу цветения у сортов сои Glycine max (L.) Merr. под влиянием клубеньковой бактерии Bradyrhizobium japonicum 634b (ризоторфин) и ассоциативных бактерий Pseudomonas oryzihabitans Ep4 и Variovorax paradoxus 3-P4 при разном минеральном питании ( М ±SEM, НОПЦ «Интеграция» Орловского ГАУ, п. Лаврово, Орловский р-н, 2013-2015 годы)
Вариант
N, мг/г
P, мг/г
Mg, мг/г
Ca, мг/г
Красивая Меча
Свапа
Бара
Красивая Меча
Свапа
Бара
Красивая Меча
Свапа
Бара
Красивая Меча
Свапа
Бара
Без инокуляции
25,5±0,6a
26,3±0,6a
26,3±1,0a
N 30 P 81 K 81 (70 %)
10,1±0,4a 10,7±0,4a 10,3±0,3a
5,0±0,4ab
4,0±0,2a
4,2±0,2a
18,0±0,9a
16,2±0,9a
17,6±0,8a
B. japonicum 634b
29,4±07c
31,2±1,0bc
30,9±1,1b
10,8±0,3a
11,8±0,3ab
10,4±0,3a
4,9±0,4a
4,4±0,2ab
4,7±0,2a
19,0±0,9a
16,6±1,0a
19,1±0,4ab
Ps. oryzihabitans Ep4
27,6±0,8bc
27,8±1,0a
27,6±0,9a
11,3±0,5b
11,7±0,5ab
11,0±0,6ab
5,2±0,4ab
4,5±0,3ab
4,5±0,3a
20,2±0,8ab
17,2±1,3a
17,8±0,8ab
V. paradoxus 3P-4
27,1±0,7ab
28,1±0,8ab
27,6±0,9a
11,1±0,4b
11,2±0,5ab
10,7±0,3a
5,3±0,4ab
4,4±0,2ab
4,2±0,2a
18,5±0,8a
16,0±0,5a
18,5±0,8ab
B. japonicum 634b + Ps. oryzihabitans Ep4
30,7±0,6c
32,6±1,0c
32,6±0,9b
11,8±0,4b
12,5±0,4b
12,0±0,5b
5,9±0,4b
5,0±0,3c
4,7±0,2a
21,7±1,1b
20,1±1,3b
19,6±0,7b
B. japonicum 634b + V. paradoxus 3P-4
29,9±0,9c
31,2±1,2bc
31,3±1,2b
11,7±0,3b
12,0±0,6ab
10,7±0,5a
5,1±0,4ab
4,9±0,2bc
4,7±0,2a
19,3±1,0ab
17,2±1,0a
19,2±0,5ab
Без инокуляции
28,9±0,7a
30,4±1,3a
29,4± 1,3a
N 44 P 116 K 116 (100 %) 11,7±0,2a 12,3±0,5a 11,6±0,4a
4,4±0,1a
4,7±0,3ab
4,2±0,1a
17,9±1,0a
16,1±0,6a
15,8±0,3a
B. japonicum 634b
32,5±0,8bc
33,9±1,2bc
32,2±1,0b
12,1±0,2a
12,2±0,4a
11,8±0,4a
4,9±0,1ab
4,6±0,3a
4,1±0,2a
21,6±0,9bc
16,9±0,6a
17,3±0,6ab
Ps. oryzihabitans Ep4
30,0±1,1a
32,2±1,5ab
31,3±1,1a
12,6±0,3ab
13,2±0,6ab
11,8±0,5a
5,3±0,2ab
4,6±0,2a
4,3±0,2ab
22,7±1,1c
17,1±0,6a
16,4±0,8a
V. paradoxus 3P-4
30,5±1,1ab
31,7±1,7a
30,1±1,1a
12,1±0,5a
12,4±0,6a
11,9±0,4a
4,9±0,2ab
4,7±0,2ab
4,1±0,2a
19,5±0,9ab
16,8±0,4a
17,0±0,7ab
B. japonicum 634b + Ps. oryzihabitans Ep4
33,5±0,6c
35,4±1,1c
34,1±0,9b
13,4±0,1b
14,5±0,6b
12,8±0,6a
5,5±0,3b
5,3±0,2bc
5,1±0,4c
24,1±1,4c
21,7±1,7b
18,9±0,7b
B. japonicum 634b + V. paradoxus 3P-4
32,0±0,6bc
35,2±1,2bc
33,5±0,9b
12,0±0,4a
13,1±0,6ab
12,0±0,6a
5,4±0,5ab
5,5±0,2c
4,9±0,5bc
22,4±1,3bc
17,3±1,1a
18,6±0,7b
П р и м е ч а н и е. Для каждой дозы удобрений разными латинскими буквами обозначены статистически значимо различающиеся варианты (тест НСР Фишера,
p < 0,05, n =
12).
-
4. Содержание микроэлементов в листьях в фазу цветения у сортов сои Glycine max (L.) Merr. под влиянием клубеньковой бактерии Bradyrhizobium japonicum 634b (ризоторфин) и ассоциативных бактерий Pseudomonas oryzihabitans Ep4 и Variovorax paradoxus 3-P4 при разном минеральном питании ( М ±SEM, НОПЦ «Интеграция» Орловского ГАУ, п. Лаврово, Орловский р-н, 2013-2015 годы)
Вариант
B, мкг/г
Fe, мкг/г
Zn, мкг/г
Mo, мкг/г
Красивая Меча
Свапа
Бара
Красивая Меча
Свапа
Бара
Красивая Меча
Свапа
Бара
Красивая Меча
Свапа
Бара
Без инокуляции
45±2a
39±2a
50±5a
N 30 P 81 K 81 (70 %) 109±3ab 112±4a 108±7a
30±3a
35±3a
39±3a
9,3±0,4a
8,7±0,2a
9,4±0,3a
B. japonicum 634b
54±4ab
45±3a
52±5a
102±5a
112±5a
122±11a
31±3a
41±3ab
37±2a
9,6±0,3a
9,1±0,3a
9,7±0,2a
Ps. oryzihabitans Ep4
49±5ab
46±4a
50±4a
125±8b
137±17b
130±10ab
35±2ab
40±3a
37±3a
10,1±0,3ab
8,8±0,3a
9,7±0,3a
V. paradoxus 3P-4
55±4b
46±4a
52±4a
123±13b
126±13ab
112±7a
34±2ab
37±3a
35±3a
9,8±0,3ab
8,9±0,3a
9,4±0,3a
B. japonicum 634b + Ps. oryzihabitans Ep4
53±3ab
58±4b
56±5a
143±8b
137±7b
145±12b
39±3b
49±4b
38±3a
10,6±0,3b
10,3±0,5b
10,0±0,4a
B. japonicum 634b + V. paradoxus 3P-4
54±5ab
48±4a
51±4a
126±8b
126±4ab
139±12b
34±3ab
36±3a
36±3a
10,2±0,4b
9,3±0,4a
9,6±0,2a
Без инокуляции
55±1a
42±1a
42±2a
N 44 P 116 K 116 (100
121±4a 103±5a
%)
112±6a
42±1a
34±3a
39±2a
9,7±0,1a
8,6±0,3a
9,0±0,2a
B. japonicum 634b
55±2a
44±2ab
55±5b
130±8ab
117±8ab
118±10a
45±2a
45±3b
40±2a
10,7±0,2b
9,1±0,3ab
8,7±0,3a
Ps. oryzihabitans Ep4
57±3a
47±3ab
55±4b
132±6ab
116±5ab
114±5a
42±3a
39±3ab
37±2a
11,1±0,2bc
9,0±0,2ab
8,6±0,2a
V. paradoxus 3P-4
56±2a
50±2ab
55±3b
123±4a
128±6bc
115±5a
41±2a
41±2ab
41±3a
10,2±0,3ab
9,2±0,1ab
9,0±0,2a
B. japonicum 634b + Ps. oryzihabitans Ep4
62±5a
60±5c
74±6c
164±8c
144±12c
133±4a
47±2a
47±3b
43±2a
11,9±0,4c
9,3±0,2ab
10,1±0,4b
B. japonicum 634b + V. paradoxus 3P-4
61±4a
53±4bc
52±3b
150±9bc
130±6bc
131±5a
45±2a
43±3b
40±2a
11,6±0,4c
9,5±0,4b
10,0±0,4b
П р и м еч а ни е. Для каждой дозы удобрений разными латинскими буквами обозначены статистически значимо различающиеся варианты (тест НСР Фишера, Р < 0,05, n
= 12).
-
5. Продуктивные показатели у сортов сои Glycine max (L.) Merr. под влиянием клубеньковой бактерии Bradyrhizobium japonicum 634b (ризотор-фин) и ассоциативных бактерий Pseudomonas oryzihabitans Ep4 и Variovorax paradoxus 3-P4 при разном минеральном питании ( М ±SEM; НОПЦ «Интеграция» ФГБОУ ВО Орловский ГАУ, п. Лаврово, Орловский р-н; 2013-2015 годы)
Вариант
Урожайность, г/м2
Содержание белка в семенах, %
Содержание жира в семенах, %
Красивая Меча
Свапа
Бара
Красивая Меча
Свапа
Бара
Красивая Меча
Свапа
Бара
Без инокуляции
217±10a
200±14a
204±6a
N 30 P 81 K 81 (70 %)
34,2±2,0a 31,6±0,7a
33,0±0,8a
21,0±0,8a
23,2±0,9a
23,7±1,2a
B. japonicum 634b
262±8b
264±16b
258±9bc
38,1±0,7b
34,4±0,4b
34,6±1,0a
22,8±0,4b
24,5±0,8b
24,0±0,8ab
Ps. oryzihabitans Ep4
250±11ab
258±10b
240±10bc
38,1±0,9b
33,7±0,9a
34,5±1,7a
21,8±0,5ab
24,7±0,6ab
23,3±0,9a
V. paradoxus 3P-4
260±14b
229±6ab
226±11ab
38,2±0,6b
35,9±0,3b
34,6±0,3a
21,7±0,7ab
23,9±0,8ab
24,3±1,1ab
B. japonicum 634b + Ps. oryzihabitans Ep4
249±12ab
313±15c
251±10c
39,0±1,0b
41,1±0,7c
35,1±0,8ab
23,2±0,7b
23,9±0,3ab
25,9±1,1b
B. japonicum 634b + V. paradoxus 3P-4
270±14b
280±17bc
270±15c
38,3±0,6b
36,4±0,9b
37,8±0,9b
21,8±0,9ab
24,9±0,6b
22,5±0,3a
Без инокуляции
204±26a
237±11a
N 44 P 116 K 116 (100 %) 266±21a 34,6±2,4a 32,7±1,3a
33,3±0,8a
19,8±0,5a
23,0±0,3a
22,6±0,4a
B. japonicum 634b
249±12b
299±10b
312±6bc
39,3±1,2b
35,4±1,1bc
35,8±1,4ab
21,8±0,7b
22,5±0,3a
22,7±0,9a
Ps. oryzihabitans Ep4
219±26ab
267±12ab
290±13a
40,1±1,1b
35,6±0,9c
35,0±0,8a
21,4±0,7ab
23,3±0,3ab
23,0±0,2a
V. paradoxus 3P-4
235±18ab
272±17ab
293±15a
40,3±0,3b
33,2±1,3ab
35,7±0,7ab
21,8±0,3b
24,7±0,4b
23,2±0,2a
B. japonicum 634b + Ps. oryzihabitans Ep4
251±13b
277±9b
343±7c
39,7±0,8b
37,9±0,5d
36,9±1,8b
22,0±0,5b
23,9±0,5ab
24,2±1,0a
B. japonicum 634b + V. paradoxus 3P-4
253±10b
301±12b
313±15c
38,1±1,0b
36,3±0,6c
36,9±0,5b
22,9±0,3b
24,8±0,5b
23,4±0,4a
П р и м е ч а н и е. Для каждой дозы удобрений разными латинскими буквами обозначены статистически значимо различающиеся варианты (тест НСР Фишера, p <
0,05, n = 12).
(p = 0,008) относительно варианта с ризоторфином получили при его комбинации с Ps. oryzihabitans Ep4 при 100 % минерального питания. Содержание белка в семенах повышалось во всех вариантах инокуляции у сорта Красивая Меча, а также во всех вариантах у сорта Свапа (кроме моноинокуляций Ps. oryzihabitans Ep4 и V. paradoxus 3-P4 на фоне соответственно N30P81K81 и N44P11 6 K11 6 ) (табл. 5). У сорта Бара этот эффект наблюдали только для комбинаций ризоторфина с V. paradoxus 3-P4 при N30P81K81 и с обоими ризосферными штаммами при N44P11 6 K11 6 . Содержание жира в семенах инокулированных растений тоже чаще было выше у сорта Красивая Меча, реже — у сорта Свапа и только в одном случае (смесь ризофор-фина и Ps. oryzihabitans Ep4 на 70 % фоне) — у сорта Бара (см. табл. 5).
Проведенные нами полевые опыты показали, что ризобактерии положительно влияют на азотфиксирующий симбиоз, рост и питание раннеспелых сортов сои северных экотипов. Это расширяет имеющиеся представления о взаимодействиях ризобактерий с бобовыми растениями при коинокуляции (11, 12, 14, 16), сравнении других сортов (15-19), разном азотном и фосфорном питании (20) в традиционных районах возделывания сои. Подтвердились данные о специфичности реакций изучаемых сортов на инокуляцию ризобактериями, которые указывали на более эффективную интеграцию штамма Ps. oryzihabitans Ep4 с сортами Красивая Меча и Свапа, обусловленную особенностями корневой экссудации (37). У этих сортов корни растений более интенсивно выделяют органические кислоты и сахара, которые служат питательным субстратом для ризобактерий и способствуют колонизации ризосферы. Ризобактерии, в свою очередь, хуже используют корневые экссудаты у сорта Бара (вероятно, из-за присутствия антибактериальных веществ). Еще один важный компонент экссудатов — триптофан (предшественник при биосинтезе ауксинов бактериями) (34) не усваивается в ризосфере у растений сорта Бара (37). Полученные результаты согласуется с данными о важной роли корневых экссудатов в сортовой специфичности эффектов ризобактерий, описанной для роста растений гороха (32), бобово-ризобиального симбиоза сои (15, 30), а также роста у Arabidopsis thaliana (45) и сорго (46).
Более эффективные взаимодействия между изучаемыми ризобакте-риями и сортами Красивая Меча и Свапа по сравнению с сортом Бара также подтверждается оценкой бактериальных эффектов по интегрированным параметрам (рис. 1). Они позволяют суммировать показатели, относящиеся к определенным аспектам реакции растений на инокуляцию, но не зависят от эффекта использования ризоторфина. Во всех случаях (за исключением влияния V. paradoxus 3-P4 на симбиоз) минимальные значения эффектов ризобактерий наблюдались для сорта Бара (см. рис. 1). При этом эффекты обоих штаммов на минеральное питании и штамма V. paradoxus 3-P4 — на биомассу растений у сорта Свапа оказались достоверно выше, чем для сорта Бара. Отметим, что максимальные относительные величины ризобактериальных эффектов получены для параметров азотфикси-рующего симбиоза (см. табл. 1, рис. 1). Это указывает на важность взаимодействий микроорганизмов в ризосфере не только для обеспечения активного роста за счет эффективного функционирования симбиоза, но и для интенсивного минерального питания растений. Действительно, по содержанию питательных элементов в листьях при совместной инокуляции ризобактери-ями и ризоторфином наблюдались аддитивные и синергические эффекты .
Положительное действие ризобактерий на азотфиксирующий симбиоз сои (повышение образования клубеньков и ацетилен-редуктазной активности) могло быть связано с наличием фермента АЦК дезаминазы 986
(38, 39). Известно, что АЦК-утилизирующие ризобактерии уменьшают количество АЦК в корнях, способствуя снижению биосинтеза растениями фитогормона этилена, который служит ингибитором образования симбиотических клубеньков (23, 48). В наших экспериментах ранее описана стимуляция клубенькообразования у гороха штаммом V. paradoxus 5C-2 (21), а также у сои сорта Свапа штаммом Ps. oryzihabitans Ep4 (37).
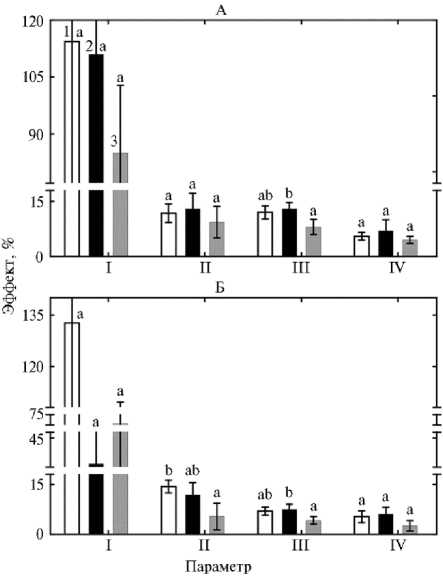
Рис. 1. Зависимость эффекта ризобак-терий Pseudomonas oryzihabitans Ep4 (А) и Variovorax paradoxus 3P-4 (Б) от сорта сои Glycine max (L.) Merr., оцененная по интегрированным параметрам: I — cимбиоз (число клубеньков, масса клубеньков, нитрогеназная активность), II — биомасса (надземная масса, масса корней в фазу цветения, урожайность), III — питание (содержание N, P, K, Mg, Ca, B, Fe, Zn и Mo в листьях), IV — качество (содержание белка и жира в семенах); 1 — Красивая Меча, 2 — Свапа, 3 — Бара. Эффект ризобактерий рассчитан как среднее значение эффектов компонентов параметра относительно соответствующего контролю (без инокуляции или с инокуляцией B. japonicum 634b) на каждом из двух фонов удобрений (N 30 P 81 K 81 или N 44 P 116 K 116 ) . Вертикальными отрезками обозначены ошибки средних (±SEM). Статистически значимые различия между сортами для каждого параметра обозначены разными латинскими буквами ( t -тест Стьюдента, р < 0,05) (НОПЦ «Интеграция» Орловского ГАУ, п. Лаврово, Орловский р-н, 2013-2015 годы).
Полученные результаты согласуются с данными исследователей, изучавших влияние совместной инокуляции клубеньковыми и ризосферными бактериями на азотфиксирующий симбиоз у различных бобовых культур. Так, показано, что инокуляция нута ризобиями Mesorhizobium ciceri и ризобактериями Ps. fluorescens (49) или Bacillus sp. (50) приводила к увеличению числа и массы клубеньков. Эти показатели повышались также при совместной инокуляции фасоли ризобиями R. leguminosarum bv. phaseoli с разными видами ризобактерий рода Bacillus (51-52), Ps. fluorescens или Az. lipoferum (53). Ризобактерии Az. brasilense , Azotobacter chroococcum , B. ce-reus , Ps. putida и Ps. fluorescens стимулировали образование клубеньков и азотфиксирующую активность у голубиного гороха ( Cajanus cajan ) при применении биопрепарата клубеньковых бактерий Rhizobium sp. (54). Похожие результаты получены при использовании ризобактерий и ризобий для инокуляции гороха (55, 56), чечевицы (56), маша (57) и люценры (58). Как правило, в этих экспериментах стимуляция образования клубеньков приводила к повышению биомассы надземной части растений и урожая семян.
Влияние изучаемых штаммов ризобактерий на растения сои было во многом сходно, о чем свидетельствовала положительная корреляция между эффектами Ps. oryzihabitans Ep4 и V. paradoxus 3-P4 на измеряемые параметры на фоне N30P81K81 (r = +0,60, p < 0,001, n = 48) и N44P116K116 (r = +0,70, p < 0,001, n = 48). Это могло быть связано с общностью механизмов их взаимодействия с растениями, поскольку оба штамма обладают высокой активностью АЦК дезаминазы и продуцируют ауксины и сидерофоры (37-39). Но Ps. oryzihabitans Ep4 в большей степени, чем V. paradoxus 3-P4, повышал содержание питательных элементов в листьях, особенно при совместной инокуляции с клубеньковыми бактериями (см. табл. 3, 4, рис. 1). Известно, что ризобактерии рода Pseudomonas мобилизуют питательные элементы в почве и их положительное действие на минеральное питание служит важным механизмом улучшения роста растений (4, 25, 43, 44). Однако имеются лишь фрагментарные сведения о способности ризобактерий рода Variovorax влиять на потребление растениями питательных элементов. Так, ранее мы показали, что инокуляция штаммом V. paradoxus 5C-2 гороха повышала потребление N, P, K, Ca и Mg растениями (25, 59). Представленные в настоящей работе результаты указывают на то, что V. paradoxus усиливает потребление питательных элементов соей и этот эффект зависит от сорта и дозы минеральных удобрений.
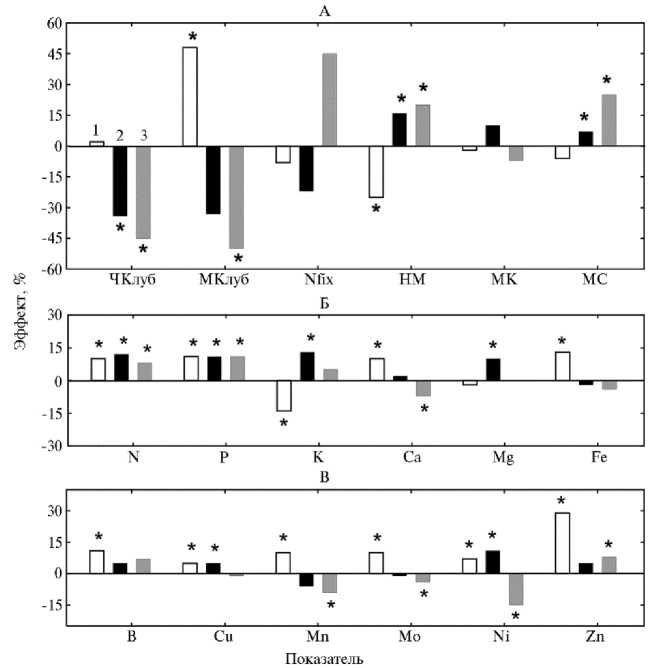
Рис. 2. Реакция сортов сои Glycine max (L.) Merr. Красная Меча (1) , Свапа (2) и Бара (3) на минеральные удобрения: ЧКлуб — число клубеньков, МКлуб — масса клубеньков, Nfix — ацетилен-редуктазная активность клубеньков, НМ — надземная масса сухих растений в фазу цветения, МК — масса сухих корней в фазу цветения, МС — масса семян в фазу полной спелости; N, P, K, Ca, Mg, Fe, B, Cu, Mn, Mo, Ni и Zn — содержание элементов в листьях в фазу цветения. Эффект фона удобрений представлен как отношение средних для всех вариантов инокуляции абсолютных величин показателя при N 30 P 81 K 81 к средней величине этого показателя при N 44 P 116 K 116 . Звездочками обозначены статистически значимые различия между фонами удобрений (тест НСР Фишера, р < 0,05, n = 72) (НОПЦ «Интеграция» Орловского ГАУ, п. Лаврово, Орловский р-н, 2013-2015 годы).
Наблюдаемые на растениях эффекты для каждого из двух штаммов ризобактерий также были схожи на обоих фонах минерального питания. Мы обнаружили положительную корреляцию эффектов на этих фонах по измеряемым параметрам для Ps. oryzihabitans Ep4 ( r = +0,61, p < 0,001, n = 48) и 988
V. paradoxus 3-P4 ( r = +0,49, p < 0,001, n = 48). Результаты свидетельствуют о способности изучаемых ризобактерий положительно и относительно стабильно влиять на ростовые и питательные характеристики растений сои при разных дозах минерального питания. В то же время в реакции сортов сои на минеральные удобрения обнаружены существенные различия, которые показаны как усредненные эффекты фактора удобрений для всех вариантов инокуляции (рис. 2). Во-первых, на 100 % фоне минерального питания у сортов Свапа и Бара число и масса клубеньков были меньше, а у сорта Красивая Меча второй показатель повышался. То есть оптимальная доза удобрений (наиболее вероятно, азотных) для образования азот-фиксирующего симбиоза индивидуальна для сорта. Во-вторых, положительная ростовая реакция на повышение дозы минеральных удобрений была в большей степени характерна для сорта Бара с относительно низким симбиотическим потенциалом в отношении ризобактерий, что привело к наибольшему увеличению надземной массы и массы семян (см. рис. 1). Отзывчивость на минеральные удобрения и эффективность симбиоза могут быть взаимосвязаны, поскольку у растений существует эволюционная детерминанта, направленная на компенсацию низкой адаптации к неблагоприятным почвенным условиям за счет интенсификации симбиотических взаимодействий с микроорганизмами. Этот феномен впервые был описан нами при изучении корреляций между эффективностью взаимодействия 99 генотипов гороха с грибами арбускулярной микоризы и их устойчивостью к тяжелым металлам (60). В-третьих, при повышении дозы удобрений только у сорта Бара снижалось содержание питательных элементов (Ca, Mn, Mo, и Ni) в листьях, за исключением уменьшения количества К у сорта Красивая Меча (см. рис. 1). Это, вероятно, было связано с разбавлением элементов биомассой, которая наиболее значимо повышалась у сорта Бара на 100 % фоне минерального питания.
Таким образом, ризобактерии Pseudomonas oryzihabitans Ep4 и Vario-vorax paradoxus 3-P4, которые продуцируют ауксины и обладают АЦК-дезаминазной активностью, способны активизировать бобово-ризобиаль-ный симбиоз и потребление корнями питательных элементов из почвы, повышать продуктивность и улучшать качество семян раннеспелых сортов сои северного экотипа. Это указывает на стабильность и значимость наблюдаемых эффектов и, следовательно, на перспективность использования таких микроорганизмов в качестве биопрепаратов для улучшения адаптации сои к северным регионам возделывания. Существенные генотипические различия между сортами сои в реакциях на инокуляцию ризобактериями свидетельствуют о более высокой степени интеграции ризобактерий с сортами Красивая Меча и Свапа по сравнению с сортом Бара в условиях агроценоза. Возможно, недостаток симбиотического потенциала сорта Бара компенсируется его способностью более эффективно использовать минеральные удобрения. В этой связи представляет интерес изучение возможностей создания сортов и растительно-микробных систем, сочетающих высокую симбиотрофность и активную ассимиляцию питательных элементов из удобрений и почвы.
Список литературы Сортовая специфичность эффектов ризобактерий в отношении азотфиксирующего симбиоза и минерального питания сои в условиях агроценоза
- Vessey J.K. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria as biofertilizers. Plant Soil, 2003, 255(2): 571-586 ( ) DOI: 10.1023/A:1026037216893
- Bashan Y., Holguin G., de-Bashan L.E. Azospirillum-plant relationships: physiological, molecular, agricultural, and environmental advances (1997-2003). Can. J. Microbiol., 2004, 50(8): 521-577 ( ) DOI: 10.1139/w04-035
- Glick B.R., Cheng Z., Czarny J., Duan J. Promotion of plant growth by ACC deaminase-producing soil bacteria. Eur. J. Plant Pathol., 2007, 119(3): 329-339 ( ) DOI: 10.1007/s10658-007-9162-4
- Plant growth and health promoting bacteria/D.K. Maheshwari (ed.). Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2010 ( ) DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-13612-2
- Nascimento F.X., Rossi M.J., Soares C.R.F.S., McConkey B.J., Glick B.R. New insights into 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate (ACC) deaminase phylogeny, evolution and ecological significance. PLoS ONE, 2014, 9(6): e99168 ( ) DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099168
- Korir H., Mungai N.W., Thuita M., Hamba Y., Masso C. Co-inoculation effect of rhizobia and plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on common bean growth in a low phosphorus soil. Front. Plant Sci., 2017, 8: 141 ( ) DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00141
- Medeot D.B., Paulucci N.S., Albornoz A.I., Fumero M.V., Bueno M.A., Garcia M.B., Woel-ke V.R., Okon Y., Dardanelli M.S. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria improving the legume-rhizobia symbiosis. In: Microbes for legume improvement/M.S. Khan, A. Zaidi, J. Musarrat (eds.). Springer-Verlag, Vienna, 2010: 473-494 ( ) DOI: 10.1007/978-3-211-99753-6_19
- Pérez-Montaño F., Alías-Villegas C., Bellogín R.A., del Cerro P., Espuny M.R., Jiménez-Guerrero I., López-Baena F.J., Ollero F.J., Cubo T. Plant growth promotion in cereal and leguminous agricultural important plants: from microorganism capacities to crop production. Microbiol. Res., 2014, 169(5-6): 325-336 ( ) DOI: 10.1016/j.micres.2013.09.011
- Polonenko D.R., Scher F.M., Kloepper J.W., Singgleton C.A., Laliberte M., Zaleska I. Effects of roots colonizing bacteria on nodulation of soybean roots by Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Can. J. Microbiol., 1987, 33(6): 498-503 ( ) DOI: 10.1139/m87-083
- Zhang F., Dashti N., Hynes R.K., Smith D.L. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and soybean nodulation and nitrogen fixation at suboptimal root zone temperatures. Annals of Botany, 1996, 77(5): 453-460 ( ) DOI: 10.1006/anbo.1996.0055
- Chebotar V.K., Asis C.A., Akao S. Production of growth-promoting substances and high colonization ability of rhizobacteria enhance the nitrogen fixation of soybean when coinoculated with Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Biol. Fert. Soils, 2001, 34(6): 427-432 ( ) DOI: 10.1007/s00374-001-0426-4
- Hungria M., Nogueira M., Araujo R. Co-inoculation of soybeans and common beans with rhizobia and azospirilla: strategies to improve sustainability. Biol. Fert. Soils, 2013, 49(7): 791-801 ( ) DOI: 10.1007/s00374-012-0771-5
- Bai Y., D'Aoust F., Smith D.L., Driscoll B.T. Isolation of plant-growth-promoting Bacillus strains from soybean root nodules. Can. J. Microbiol., 2002, 48(3): 230-238 ( ) DOI: 10.1139/w02-014
- Bai Y., Zhou-Xiao M., Smith D.L. Enhanced soybean plant growth resulting from coinoculation of Bacillus strains with Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Crop Sci., 2003, 43(5): 1774-1781 ( ) DOI: 10.2135/cropsci2003.1774
- Atieno M., Herrmann L., Okalebo R., Lesueur D. Efficiency of different formulations of Bradyrhizobium japonicum and effect of co-inoculation of Bacillus subtilis with two different strains of Bradyrhizobium japonicum. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2012, 28(7): 2541-2550 ( ) DOI: 10.1007/s11274-012-1062-x
- Tsigie A., Tilak K.V.B.R., Anil K.S. Field response of legumes to inoculation with plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Biol. Fert. Soils, 2012, 47: 971-974 ( ) DOI: 10.1007/s00374-011-0573-1
- Masciarelli O., Llanes A., Luna V. A new PGPR co-inoculated with Bradyrhizobium japonicum enhances soybean nodulation. Microbiol. Res., 2014, 169: 609-615 ( ) DOI: 10.1016/j.micres.2013.10.001
- Mishra P.K., Mishra S., Selvakumar G., Kundu S., Gupta H.S. Enhanced soybean (Glycine max L.) plant growth and nodulation by Bradyrhizobium japonicum-SB1 in presence of Bacillus thuringiensis-KR1. Acta Agr. Scand. B-S. P., 2009, 59(2): 189-196 ( ) DOI: 10.1080/09064710802040558
- Diep C.N., My N.T.X., Nhu V.T.P. Isolation and characterization of endophytic bacteria in soybean root nodules. World Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2016, 5(6): 222-241.
- Shiri-Janagard M., Raei Y., Gasemi-Golezani G., Aliasgarzad N. Influence of Bradyrhizobium japonicum and phosphate solubilizing bacteria on soybean yield at different levels of nitrogen and phosphorus. International Journal of Agronomy and Plant Production, 2012, 3(11): 544-549.
- Belimov A.A., Dodd I.C., Hontzeas N., Theobald J.C., Safronova V.I., Davies W.J. Rhizosphere bacteria containing ACC deaminase increase yield of plants grown in drying soil via both local and systemic hormone signaling. New Phytol., 2009, 181: 413-423 ( ) DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2008.02657.x
- Gamalero E., Glick B.R. Bacterial modulation of plant ethylene levels. Plant Physiol., 2015, 169: 13-22 ( ) DOI: 10.1104/pp.15.00284
- Nascimento F.X., Brígido C., Glick B.R., Rossi M.J. The role of rhizobial ACC deaminase in the nodulation process of leguminous plants. International Journal of Agronomy, 2016, 2016: Article ID 1369472 ( ) DOI: 10.1155/2016/1369472
- Remans R., Beebe S., Blair M., Manrique G., Tovar E., Rao I., Croonenborghs A., Torres-Gutierrez R., El-Howeity M., Michiels J., Vanderleyden J. Physiological and genetic analysis of root responsiveness to auxin-producing plant growth-promoting bacteria in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Plant Soil, 2008, 302(1-2): 149-161 ( ) DOI: 10.1007/s11104-007-9462-7
- Safronova V.I., Stepanok V.V., Engqvist G.L., Alekseyev Y.V., Belimov A.A. Root-associated bacteria containing 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase improve growth and nutrient uptake by pea genotypes cultivated in cadmium supplemented soil. Biol. Fert. Soils, 2006, 42(3): 267-272 ( ) DOI: 10.1007/s00374-005-0024-y
- Das S.K., Sharma K.L., Neelam S., Srinivas K. Effect of cultivars, nitrogen sources and soil types on response of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L.) to Azospirillum inoculation. Ann. Agric. Sci., 1997, 18(3): 313-317.
- Saubidet M.I., Barneix A.J. Growth stimulation and nitrogen supply to wheat plants inoculated with Azospirillum brasilense. J. Plant Nutr., 1998, 21(12): 2565-2577 ( ) DOI: 10.1080/01904169809365588
- Burdman S., Kigel J., Okon Y. Effects of Azospirillum brasilense on nodulation and growth of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Soil Biol. Biochem., 1997, 29(5-6): 923-929 ( ) DOI: 10.1016/S0038-0717(96)00222-2
- Walker V., Bertrand C., Bellvert F., Mënne-Loccoz Y., Bally R., Comte G. Host plant secondary metabolite profiling shows a complex, strain-dependent response of maize to plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria of the genus Azospirillum. New Phytol., 2011, 189(2): 494-506 ( ) DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03484.x
- Dashti N., Zhang F., Hynes R., Smith D.L. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria accelerate nodulation and increase nitrogen fixation activity by field grown soybean under short season conditions. Plant Soil, 1998, 200(2): 205-213 ( ) DOI: 10.1023/A:1004358100856
- Белимов А.А., Демчинская С.В., Сафронова В.И. Реакция гороха на инокуляцию ризосферными АЦК-утилизирующими бактериями в присутствии эндомикоризного гриба Glomus intraradices. Сельскохозяйственная биология, 2012, 3: 90-97.
- Кузмичева Ю.В., Шапошников А.И., Азарова Т.С., Петрова С.Н., Наумкина Т.С., Борисов А.Ю., Белимов А.А., Кравченко Л.В., Парахин Н.В., Тихонович И.А. Состав корневых экзометаболитов высокосимбиотрофного сорта гороха Триумф и его родительских форм. Физиология растений, 2014, 61(1): 121-128.
- Imran A., Mirza M.S., Shah T.M., Malik K.A., Hafeez F.Y. Differential response of kabuli and desi chickpea genotypes toward inoculation with PGPR in different soils. Front. Microbiol., 2015, 6: 859 ( ) DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00859
- Drogue B., Sanguin H., Chamam A., Mozar M., Llauro C., Panaud O., Prigent-Combaret C., Picault N., Wisniewski-Dye F. Plant root transcriptome profiling reveals a strain-dependent response during Azospirillum-rice cooperation. Front. Plant. Sci., 2014, 5: 607 ( ) DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00607
- Okubara P.A., Kornoely J.P., Landa B.B. Rhizosphere colonization of hexaploid wheat by Pseudomonas fluorescens strains Q8rl-96 and Q2-87 is cultivar-variable and associated with changes in gross root morphology. Biol. Control, 2004, 30(2): 392-403 ( ) DOI: 10.1016/j.biocontrol.2003.11.003
- Smith K.P., Goodman R.M. Host variation for interactions with beneficial plant-associated microbes. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol., 1999, 37: 473-491 ( ) DOI: 10.1146/annurev.phyto.37.1.473
- Kuzmicheva Y.V., Shaposhnikov A.I., Petrova S.N., Makarova N.M., Tychinskaya I.L., Puhalsky J.V., Parahin N.V., Tikhonovich I.A., Belimov A.A. Variety specific relationships between effects of rhizobacteria on root exudation, growth and nutrient uptake of soybean. Plant Soil, 2017, 419(1-2): 83-96 ( ) DOI: 10.1007/s11104-017-3320-z
- Belimov A.A., Safronova V.I., Sergeyeva T.A., Egorova T.N., Matveyeva V.A., Tsyganov V.E., Borisov A.Y., Tikhonovich I.A., Kluge C., Preisfeld A., Dietz K.J., Stepanok V.V. Characterisation of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria isolated from polluted soils and containing 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase. Can. J. Microbiol., 2001, 47(7): 642-652 ( ) DOI: 10.1139/cjm-47-7-642
- Belimov A.A., Hontzeas N., Safronova V.I., Demchinskaya S.V., Piluzza G., Bullitta S., Glick B.R. Cadmium-tolerant plant growth-promoting bacteria associated with the roots of Indian mustard (Brassica juncea L. Czern.). Soil Biol. Biochem., 2005, 37(2): 241-250 ( ) DOI: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2004.07.033
- Лактионов Ю.В., Попова Т.А., Андреев О.А., Ибатуллина Р.П., Кожемяков А.П. Создание стабильной формы ростстимулирующих микробиологических препаратов и их эффективность. Сельскохозяйственная биология, 2011, 3: 116-118.
- Arinushkina E.V. Guidelines for the chemical analysis of soils. Moscow State University Press, Moscow, 1970.
- Hardy R.W.F., Bums R.C., Holsten R.D. Application of the C2H2-C2H4 assay for measurement of nitrogen fixation. Soil Biol. Biochem., 1973, 5(1): 47-82 ( ) DOI: 10.1016/0038-0717(73)90093-X
- Preston G.M. Plant perceptions of plant growth-promoting Pseudomonas. Philos. T. Roy. Soc. B, 2004, 359(1446): 907-918 ( ) DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2003.1384
- Patten C.L., Glick B.R. Bacterial biosynthesis of indole-3-acetic acid. Can. J. Microbiol., 1996, 42(3): 207-220 ( ) DOI: 10.1139/m96-032
- Spaepen S., Vanderleyden J., Remans R. Indole-3-acetic acid in microbial and microorganism-plant signaling. FEMS Microbiol. Rev., 2007, 31(4): 425-448 ( ) DOI: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2007.00072.x
- Badri D.V., Quintana N., El-Kassis E.G., Kim H.K., Choi Y.H., Sugiyama A., Verpoorte R., Martinoia E., Manter D.K., Vivanco J.M. An ABC transporter mutation alters root exudation of phytochemicals that provoke an overhaul of natural soil microbiota. Plant Physiol., 2009, 151: 2006-2017 ( ) DOI: 10.1104/pp.109.147462
- Saleem M., Arshad M., Hussain S., Bhatti A.S. Perspective of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) containing ACC deaminase in stress agriculture. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biot., 2007, 34(10): 635-648 ( ) DOI: 10.1007/s10295-007-0240-6
- Krotzky A., Bergold R., Werner D. Plant characteristics limiting associative N2 fixation with two cultivars of sorghum mutants. Soil Biol. Biochem., 1988, 20(2): 157-162 ( ) DOI: 10.1016/0038-0717(88)90032-6
- Verma J.P., Yadav J., Tiwari K.N. Enhancement of nodulation and yield of chickpea by co-inoculation of indigenous Mesorhizobium spp. and plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria in Eastern Uttar Pradesh. Commun. Soil Sci. Plan., 2012, 43(3): 605-621 ( ) DOI: 10.1080/00103624.2012.639110
- Wani P.A., Khan M.S., Zaidi A. Co-inoculation of nitrogen fixing and phosphate solubilizing bacteria to promote growth, yield and nutrient uptake in chickpea. Acta Agron. Hung., 2007, 55(3): 315-323 ( ) DOI: 10.1556/AAgr.55.2007.3.7
- Elkoca E., Turan M., Donmez M.F. Effects of single, dual and triple inoculations with Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus megaterium and Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. phaseoli on nodulation, nutrient uptake, yield and yield parameters of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L. cv. ‘ELKOCA-05'). J. Plant Nutr., 2010, 33(14): 2104-2119 ( ) DOI: 10.1080/01904167.2010.519084
- Figueiredo M.V.B., Martinez C.R., Burity H.A., Chanway C.P. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria for improving nodulation and nitrogen fixation in the common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). World J. Microb. Biot., 2008, 24(7): 1187-1193 ( ) DOI: 10.1007/s11274-007-9591-4
- Yadegari M., Asadi Rahmani H., Noormohammadi G., Ayneband A. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria increase growth, yield and nitrogen fixation in Phaseolus vulgaris. J. Plant Nutr., 2010, 33(12): 1733-1743 ( ) DOI: 10.1080/01904167.2010.503776
- Tilak K.V.B.R., Ranganayaki N., Manoharachari C. Synergistic effects of plant-growth promoting rhizobacteria and Rhizobium on nodulation and nitrogen fixation by pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan). Eur. J. Soil Sci., 2006, 57(1): 67-71 ( ) DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2389.2006.00771.x
- Dileep Kumar B.S., Berggren I., Mårtensson A.M. Potential for improving pea production by co-inoculation with fluorescent Pseudomonas and Rhizobium. Plant Soil, 2001, 229(1): 25-34 ( ) DOI: 10.1023/A:1004896118286
- Mishra P.K., Mishra S., Selvakumar G., Bisht J. K., Kundu S., Gupta H.S. Co-inoculation of Bacillus thuringeinsis-KR1 with Rhizobium leguminosarum enhances plant growth and nodulation of pea (Pisum sativum L.) and lentil (Lens culinaris L.). World J. Microb. Biot., 2009, 25(5): 753-761 ( ) DOI: 10.1007/s11274-009-9963-z
- Qureshi M.A., Shakir M.A., Iqbal A., Akhtar N., Khan A. Co-inoculation of phosphate solubilizing bacteria and rhizobia for improving growth and yield of mungbean (Vigna radiata L.). J. Anim. Plant Sci., 2012, 21(3): 491-497.
- Guinazu L.B., Andres J.A., Del Papa M.F., Pistorio M., Rosas S.B. Response of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) to single and mixed inoculation with phosphate-solubilising bacteria and Sinorhizobium meliloti. Biol. Fert. Soils, 2010, 46(2): 185-190 ( ) DOI: 10.1007/s00374-009-0408-5
- Wang Q., Dodd I.C., Belimov A.A., Jiang F. Rhizosphere bacteria containing 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase increase growth and photosynthesis of pea plants under salt stress by limiting Na+ accumulation. Funct. Plant Biol., 2016, 43(2): 161-172.
- Belimov A.A., Puhalsky I.V., Safronova V.I., Shaposhnikov A.I., Vishnyakova M.A., Semenova E.V., Zinovkina N.Y., Makarova N.M., Wenzel W., Tikhonovich I.A. Role of plant genotype and soil conditions in symbiotic plant-microbe interactions for adaptation of plants to cadmium polluted soils. Water Air Soil Poll., 2015, 226(8): 1-15 ( ) DOI: 10.1007/s11270-015-2537-9


