Состав и функции микробиома слепых отростков кишечника Oryctolagus dominis под влиянием комплексной кормовой добавки
Автор: Наркевич И.А., Йылдырым Е.А., Черных Т.Ф., Ильина Л.А., Ивкин Д.Ю., Филиппова В.А., Лаптев Г.Ю., Бражник Е.А., Пономарева Е.С., Дубровин А.В., Флисюк Е.В., Калиткина К.А., Скляров С.П., Морозов В.Ю., Новикова Н.И., Тюрина Д.Г.
Журнал: Сельскохозяйственная биология @agrobiology
Рубрика: Генетика, геномика, генетическая инженерия
Статья в выпуске: 6 т.57, 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
В современных условиях представляет интерес изучение эффективности натуральных комплексных кормовых добавок, которые позволят регулировать состав и метаболическую активность микробиома и улучшить иммунитет и физиологический статус кроликов. В настоящей работе впервые с применением биоинформатических методов обнаружено, что комплексный пробиотический биопрепарат оказывает влияние на изменение прогнозируемых метаболических путей в микробиоме кишечника кроликов. Целью работы было изучение совместного действия комплекса, содержащего минеральные вещества и пробиотик, на организм кроликов, их физиологические показатели, состав и функциональный потенциал микробиома. Исследование проводили в 2021 году на 10 кроликах породы советская шиншилла на базе вивария ФГБУ ВО СПХФУ Минздрава России. Возраст животных на начало эксперимента - 2,5 мес, живая масса - 5,37-5,53 кг. Животных разделили на две группы (по 5 гол. в каждой): I контрольная группа получала основной рацион (ОР) в соответствии с рекомендуемыми детализированными нормами РАСХН (2003 год), II опытная группа - ОР с добавлением комплексной кормовой добавки микроэлементов и пробиотического штамма бактерий в количестве 30 мг/гол. в сутки. Комплексная кормовая добавка включала микроэлементный препарат Silaccess (ООО «ТЕХНОЛОГ 2Д», Россия) в дозе 5 мг/кг живой массы. Кроме того, в добавку был включен пробиотический штамм микроорганизма Bacillus subtilis 1-85. На 30-е и 60-е сут после начала эксперимента животных взвешивали натощак перед утренним кормлением, а также брали кровь для анализа. Определяли естественную резистентность (бактерицидная активность, включая лизоцимную, фагоцитарная активность нейтрофилов). Образцы химуса слепых отростков кишечника для исследования микробиома отбирали в конце эксперимента с максимально возможным соблюдением условий асептики вручную и немедленно помещали в стерильные пластиковые пробирки. Тотальную ДНК выделяли с использованием набора Genomic DNA Purification Kit («Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.», США). Бактериальное сообщество оценивали методом NGS-секвенирования на автоматическом секвенаторе MiSeq («Illumina, Inc.», США) с праймерами для V3-V4 региона гена 16S рРНК: 5´-TCGTCGGCAGCGTCAGATGTGTATAAG-AGACAGCCTACGGGNGGCWGCAG-3´ (прямой праймер), 5´-GTCTCGTGGGCTCGGAGATGTG-TATAAGAGACAGGACTACHVGGGTATCTAATCC-3´ (обратный праймер). Реконструкцию и прогнозирование функционального содержания метагенома проводили при помощи программного комплекса PICRUSt2 (v.2.3.0) (https://github.com/picrust/picrust2). Математическую и статистическую обработку результатов осуществляли методом многофакторного дисперсионного анализа в программах Microsoft Excel XP/2003, R-Studio (Version 1.1.453) (https://rstudio.com). Фагоцитарный индекс был выше (p ≤ 0,05) во II опытной группе по сравнению с контрольной на 1,8, фагоцитарное число - на 32,3 % (p ≤ 0,05). С применением метода NGS-секвенирования во II группе были установлены более высокие значения индексов a-биоразнообразия Chao1, Shannon и Simpson (p £ 0,05) по сравнению с I группой. По данным исследований таксономического состава микроорганизмов слепых отростков кишечника кроликов выявили 12 филумов царства Bacteria , среди которых представители филума Firmicutes доминировали по численности (80,2±6,2 % в контрольной группе, 78,2±7,4 % в опытной группе). Во II группе происходило количественное увеличение филумов Verrucomicrobiota , Actinobacteriota , Patescibacteria , Proteobacteria , Desulfobacterota в 1,3-2,6 раза и снижение представленности филума Campilobacterota в 4,8 раза (p ≤ 0,05). В слепых отростках кишечника у кроликов из опытной группы наблюдалось возрастание численности бактерий рода Bacillus spp. в 2,82 раза по сравнению с контролем (p ≤ 0,05). В кишечнике животных из I контрольной группы присутствовал вид Staphylococcus sciuri (0,075±0,006 %), тогда как во II опытной группе его не обнаружили. В результате анализа, проведенного с использованием программного комплекса PICRUSt2 (v.2.3.0), у микробного сообщества кишечника кроликов мы выявили 370 прогнозируемых метаболических путей, при этом между экспериментальными группами наблюдались различия (p ≤ 0,05) по 36 путям. В кишечном микробиоме животных из II опытной группы по сравнению с I контрольной происходила активация (p ≤ 0,05) путей, которые относились к деградации ароматических соединений и ксенобиотиков, белковому, углеводному, энергетическому обмену, биосинтезу спиртов, фотодыханию, ассимиляции формальдегида, деградации мио-, хиро- и сцилло-инозитола, синтезу клеточной стенки и спорообразованию. Доминирующее число (15 путей) усиленных потенциальных метаболических путей было связано с деградацией ароматических соединений и ксенобиотиков.
Пробиотик, микроэлементы, резистентность, домашние кролики, микробиом, ngs-секвенирование, метаболические пути
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142237387
IDR: 142237387 | УДК: 636.92:636.085.22:579:577.21 | DOI: 10.15389/agrobiology.2022.6.1117rus
Текст научной статьи Состав и функции микробиома слепых отростков кишечника Oryctolagus dominis под влиянием комплексной кормовой добавки
В современных условиях представляет интерес изучение эффективности натуральных комплексных кормовых добавок, которые позволят регулировать состав и метаболическую активность микробиома и улучшить иммунитет и физиологический статус кроликов. В настоящей работе впервые с применением биоинформатических методов обнаружено, что комплексный пробиотический биопрепарат оказывает влияние на изменение прогнозируемых метаболических путей в микробиоме кишечника кроликов. Целью работы было изучение совместного действия комплекса, содержащего минеральные вещества и пробиотик, на организм кроликов, их физиологические показатели, состав и функциональный потенциал микробиома. Исследование проводили в 2021 году на 10 кроликах породы советская шиншилла на базе вивария ФГБУ ВО СПХФУ Минздрава России. Возраст животных на начало эксперимента — 2,5 мес, живая масса — 5,37-5,53 кг. Животных разделили на две группы (по 5 гол. в каждой): I контрольная группа получала основной рацион (ОР) в соответствии с рекомендуемыми детализированными нормами РАСХН (2003 год), II опытная группа — ОР с добавлением комплексной кормовой добавки микроэлементов и пробиотического штамма бактерий в количестве 30 мг/гол. в сутки. Комплексная кормовая добавка включала микроэлементный препарат Silaccess (ООО «ТЕХНОЛОГ 2Д», Россия) в дозе 5 мг/кг живой массы. Кроме того, в добавку был включен пробиотический штамм микроорганизма Bacillus subtilis 1-85. На 30-е и 60-е сут после начала эксперимента животных взвешивали натощак перед утренним кормлением, а также брали кровь для анализа. Определяли естественную резистентность (бактерицидная активность, включая лизоцимную, фагоцитарная активность нейтрофилов). Образцы химуса слепых отростков кишечника для исследования микробиома отбирали в конце эксперимента с максимально возможным соблюдением условий асептики вручную и немедленно помещали в стерильные пластиковые пробирки. Тотальную ДНК выделяли с использованием набора Genomic DNA Purification Kit («Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.», США). Бактериальное сообщество оценивали методом NGS-секвенирования на автоматическом секвенаторе MiSeq («Illumina, Inc.», США) с праймерами для V3-V4 региона гена 16S рРНК: 5´-TCGTCGGCAGCGTCAGATGTGTATAAG-AGACAGCCTACGGGNGGCWGCAG-3´ (прямой праймер), 5´-GTCTCGTGGGCTCGGAGATGTG-TATAAGAGACAGGACTACHVGGGTATCTAATCC-3´ (обратный праймер). Реконструкцию и прогнозирование функционального содержания метагенома проводили при помощи программного комплекса PICRUSt2 (v.2.3.0) . Математическую и статистическую обработку результатов осуществляли методом многофакторного дисперсионного анализа в программах Microsoft Excel XP/2003, R-Studio (Version 1.1.453) . Фагоцитарный индекс был выше (p ≤ 0,05) во II опытной группе по сравнению с контрольной на 1,8, фагоцитарное число — на 32,3 % (p ≤ 0,05). С применением метода NGS-секвенирования во II группе были установлены более высокие значения индексов α-биоразнообразия Chao1, Shannon и Simpson (p ≤ 0,05) по сравнению с I группой. По данным исследований таксономического состава микроорганизмов слепых отростков кишечника кроликов выявили 12 филумов царства Bacteria, среди которых представители филума Firmicutes доминировали по численности (80,2±6,2 % в контрольной группе, 78,2±7,4 % в опытной группе). Во II группе происходило количественное увеличение филумов Verrucomicrobiota, Actinobacteriota, Patescibacteria, Proteobacteria, Desulfobacterota в 1,32,6 раза и снижение представленности филума Campilobacterota в 4,8 раза (p ≤ 0,05). В слепых отростках кишечника у кроликов из опытной группы наблюдалось возрастание численности бактерий рода Bacillus spp. в 2,82 раза по сравнению с контролем (p ≤ 0,05). В кишечнике животных из I контрольной группы присутствовал вид Staphylococcus sciuri (0,075±0,006 %), тогда как во II опытной группе его не обнаружили. В результате анализа, проведенного с использованием программного комплекса PICRUSt2 (v.2.3.0), у микробного сообщества кишечника кроликов мы выявили 370 прогнозируемых метаболических путей, при этом между экспериментальными группами наблюдались различия (p ≤ 0,05) по 36 путям. В кишечном микробиоме животных из II опытной группы по сравнению с I контрольной происходила активация (p ≤ 0,05) путей, которые относились к деградации ароматических соединений и ксенобиотиков, белковому, углеводному, энергетическому обмену, биосинтезу спиртов, фотодыханию, ассимиляции формальдегида, деградации мио-, хиро- и сцилло-инозитола, синтезу клеточной стенки и спорообразованию. Доминирующее число
Кролики ( Oryctolagus dominis ) — ценные сельскохозяйственные животные с коротким периодом сукрольности, высокой плодовитостью, хорошей конверсией корма (1, 2). Мясо кроликов богато белком при низком содержании жира, холестерина и натрия и легко усваивается, что определяет его диетические свойства (3). Кроме того, эти животные часто используются в экспериментальных целях как модельные объекты.
Во многих странах кролиководство становится важной развивающийся подотраслью (4). Главными факторами, сдерживающими развитие кролиководства, остаются вирусные и бактериальные заболевания, приводящие к массовому падежу и существенным экономическим потерям (5).
Известно, что микробные популяции, населяющие желудочно-кишечный тракт животных, формируют микробиом — сложную экосистему, способную при благоприятных условиях авторегулировать свой гомеостаз. Кишечный микробиом млекопитающих играет важную роль в пищеварительных, метаболических, физиологических и иммунологических процессах, оказывает воздействие на восприимчивость хозяина ко многим имму-ноопосредованным заболеваниям и расстройствам (6), а также влияет на продуктивность (7, 8). Это подтверждено и на примере кроликов, хозяйственно ценные признаки которых также подвержены влиянию кишечной микробиоты (8).
Благодаря стремительному развитию технологий секвенирования, было проведено несколько интересных исследований по анализу микробных сообществ кишечника кроликов. В 2008 и 2012 годах исследовано бактериальное сообщество слепой кишки кроликов с использованием высокопроизводительного секвенирования ампликона V3-V4 гена 16S рРНК (9, 10). В 2018 году описаны изменения микробиоты кролика по отделам кишечного тракта с акцентом на микробиоту слепой кишки и фекалий (11). В 2019 году изучен состав микробиоты желчного пузыря кроликов разного возраста (12), в 2020 году исследована структура микробиоты кишечника у коммерческих кроликов в динамике от отъема до конца выращивания (13). Совсем недавно был охарактеризован состав бактериальной микробиоты на протяжении всего желудочно-кишечного тракта у новозеландских кроликов (5). Несмотря на существование микробных популяций в проксимальных и дистальных отделах желудочно-кишечного тракта кролика (14), слепая кишка служит основным органом, где происходят самые активные ферментативные процессы.
В современных условиях кролиководства такие факторы, как скученность значительного поголовья животных на ограниченной территории, нарушение принципов системы кормления и технологии содержания, смена рационов, недоброкачественные корма, бесконтрольное применение антибиотиков и другие стрессы, в разы увеличивают риск возникновения инфекционных заболеваний. Периоды отъема и доращивания, когда происходит переход с материнского молока на твердые корма, возникает стресс от отсутствия матери и перегруппировки, относятся к критическим (15). Это приводит возникновению энтеритов и желудочно-кишечных инфекций, в частности вызываемых бактериями Clostridia spp. и Escherichia coli, Lawsonia intracellularis, Salmonella spp. (5, 16). Одно из самых серьезных заболеваний сельскохозяйственных кроликов — эпизоотическая энтеропатия. Это многофакторный желудочно-кишечный синдром, летальность от которого достигает 30-95 % независимо от породы с возрастанием частоты встречаемости в период после отъема (17).
Кишечные заболевания часто проявляются как воспаление пищеварительной системы (18), которое приводит к нарушению целостности стенок (19). Воспаление и повреждение кишечника вызывают перераспределение питательных веществ, что приводит к снижению продуктивности животных и существенному увеличению экономических потерь (20). Исследования с применением хроматографических методов показали, что ряд дифференциальных метаболитов был вовлечен в пять метаболических путей, связанных с воспалением кишечника (метаболизм триптофана, метаболизм пиримидина, биосинтез фенилаланина, тирозина и триптофана, деградация лизина и секреция желчи) (21). В свою очередь, увеличение количества патогенных и условно-патогенных бактерий ( Escherichia coli , Clostridium spp., Bacteroides spp.) и снижение представленности полезных бактерий ( Lactobacillus casei , Bifidobacterium spp. и Lactobacillus spp.) связано с высвобождением провоспалительных сигнальных факторов (цитокинов, IL-6 и TNF- α ), а также повышенной секрецией иммуноглобулина А (IgA). Этот процесс имеет связь со снижением содержания короткоцепочечных жирных кислот, ингибированием всасывания кишечных ионов и воды и воспалением слизистой оболочки кишечника (22-24).
Стратегии регуляции микробиома и предотвращения расстройств пищеварения включают введение в рационы кормовых добавок, таких как пробиотики. В течение последнего десятилетия опубликовано несколько исследований о влиянии пробиотиков на продуктивные показатели кроликов (25-27). Некоторые авторы учитывали специфический и неспецифический иммунный ответ на пробиотические добавки в рационы. Были проанализированы различные гематологические параметры: общий белок, иммуноглобулины, лейкоциты и лимфоциты (28, 29). Установлено, что пробиотики оказывают позитивное действие на состав микробиома, снижая численность патогенов (30, 31).
Ранее мы провели исследование (32), основанное на биоинформа-тической обработке данных NGS-секвенирования гена 16S рРНК в микробиоме рубца молочных коров, которое продемонстрировало, что изменения в таксономической структуре микроорганизмов рубца под воздействием пробиотика Целлобактерин+ были связаны с метаболическими сдвигами функционального потенциала микроорганизмов, и подтвердило важную роль указанного пробиотика в поддержании метаболического гомеостаза. В 2021 году в работе на кроликах было продемонстрировано изменение потенциальных метаболических путей микробиома кишечника на основе секвенирования гена 16S рРНК в зависимости от генотипа, что позволило выявить потенциальные биомаркеры, важные для улучшения пород мясных кроликов (33).
Тем не менее экспериментов, связанных с оценкой влияния пробиотиков на состав и потенциальные метаболические пути кишечного микробиома кроликов, ранее не проводили. То есть механизм, с помощью которого микроорганизмы и пробиотики взаимодействуют на метаболическом уровне в кишечнике этих животных, неясен.
В отношении микроэлементов известно, что их введение в рацион оказывает позитивное воздействие на различные функции организма кроликов, такие как кислотно-щелочной баланс, метаболизм питательных ве- ществ и иммунитет. Дефицит железа у кроликов проявляется в снижении активности, потере аппетита, ухудшении состояния кожи и шерсти (34). Йод необходим для обеспечения правильного функционирования щитовидной железы, кобальт имеет прямую связь с усвоением организмом пушных зверей витаминов (35, 36).
Представляет интерес создание и изучение эффективности новых комплексных кормовых добавок, которые позволят получать экологически чистую продукцию кролиководства более высокого качества и снизить риск возникновения инфекционных заболеваний.
В настоящей работе впервые с применением биоинформатических методов обнаружено, что комплексный пробиотический биопрепарат оказывает влияние на изменение прогнозируемых метаболических путей микробиома кишечника кроликов.
Целью работы было изучение совместного действия комплекса, содержащего минеральные вещества и пробиотик, на организм кроликов, их физиологические показатели, состав и функциональный потенциал микробиома.
Методика. Исследование проводили в 2021 году на 10 кроликах породы советская шиншилла на базе вивария ФГБОУ ВО СПХФУ Минздрава России (г. Санкт-Петербург), имеющего государственную регистрацию в ГУ Санкт-Петербургская городская станция по борьбе с болезнями животных (ветеринарное регистрационное удостоверение на виварий ¹ 78-07132).
Экспериментальные группы формировали методом аналогов по возрасту и живой массе. Возраст животных на начало эксперимента — 2,5 мес, живая масса — 5,37-5,53 кг. Кормление и условия содержания кроликов соответствовали методическим указаниям (37).
Животных разделили на две группы (по 5 гол. в каждой): I контрольная группа получала основной рацион (ОР) в соответствии с рекомендуемыми детализированными нормами РАСХН (2003 год), II опытная группа — ОР с добавлением комплексной кормовой добавки (30 мг/гол. в сутки). Комплексная кормовая добавка включала микроэлементный препарат Si-laccess (ООО «ТЕХНОЛОГ 2Д», Россия) (38), состоящий из смеси минеральных компонентов кремния (35-42,7 %), железа (3,5-4,5 %), меди (0,080,12 %) и цинка (0,04-0,055 %) в стабилизирующем агенте (ГОСТ 12.1.007.76. М., 2007). Дозировка компонента Silaccess составляла 5 мг/кг живой массы. Кроме того, в добавку был включен водорастворимый пробиотик Ликвипро (ООО «БИОТРОФ», Россия) из соотношения 0,5 г/10 л воды. Введение пробиотического компонента осуществлялось круглосуточно в систему поения с помощью дозатора Dosatron D25RE5 («Dosatron», Франция). В основу препарата Ликвипро входит штамм Bacillus subtilis 1-85, препарат выпускается в сухом виде в форме порошка . Продолжительность эксперимента — 75 сут.
Интенсивность роста животных контролировали индивидуальным взвешиванием через 30 и 60 сут (в 3,5- и 4,5-месячном возрасте) после начала эксперимента натощак перед утренним кормлением. Живую массу подопытных кроликов определяли с использованием электронных весов для взвешивания животных Momert 6551 («MOMERT Co Ltd.», Венгрия) с погрешностью до 10 г, среднесуточные приросты за отмеченные периоды рассчитывали по общепринятой формуле:
. _ W1-W0
t , где А — среднесуточный прирост живой массы, г; W 0 — живая масса на начало эксперимента, кг; W 1 — живая масса на конец эксперимента, кг; t — число суток.
Клинико-физиологическое состояние кроликов оценивали при ежедневном осмотре. Обращали внимание на поведение, поедаемость корма, состояние шерстного покрова.
Через 30 сут после начала опыта и по окончании опыта (60 сут) у кроликов натощак брали кровь из хвостовой вены в вакуумные пробирки двух видов (с антикоагулянтом гепарином и с активатором свертывания). Определяли показатели естественной резистентности (бактерицидная активность, включая лизоцимную, фагоцитарная активность нейтрофилов). Фагоцитарную активность псевдоэозиноилов оценивали при подсчете фагоцитирующих клеток из 100 нейтрофилов. При определении бактерицидной активности сыворотки крови использовали методику И.М. Карпуть (39). Лизоцимную активность в сыворотке крови устанавливали нефелометрическим методом по В.Г. Дорофейчуку (40). Клинический (гематологический) анализ крови выполняли на аппарате ABXMICRO 60-OT18 («Roche», Франция).
Образцы химуса для исследования микробиома отбирали вручную из слепых отростков кишечника в конце эксперимента с максимально возможным соблюдением условий асептики и немедленно помещали в стерильные пластиковые пробирки. Все образцы замораживали при температуре - 20 ° C и отправляли в сухом льду в молекулярно-генетическую лабораторию научно-производственной компании ООО «БИОТРОФ» для выделения ДНК.
Тотальную ДНК из образцов выделяли с использованием набора Genomic DNA Purification Kit («Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.», США) согласно прилагаемой инструкции. Метод основан на селективном детергентно-опосредованном осаждении ДНК из субстрата с применением растворов для лизиса клеточных стенок и осаждения ДНК, 1,2 М хлорида натрия и хлороформа.
Бактериальное сообщество оценивали методом NGS-секвенирования, которое позволяет идентифицировать микроорганизмы до вида, на автоматическом секвенаторе MiSeq («Illumina, Inc.», США) с применением праймеров для V3-V4 региона гена 16S рРНК: 5´-TCGTCGGCAGCGTCA-GATGTGTATAAGAGACAGCCTACGGGNGGCWGCAG-3´ (прямой праймер), 5´-GTCTCGTGGGCTCGGAGATGTGTATAAGAGACAGGACTACH-VGGGTATCTAATCC-3´ (обратный праймер). Условия ПЦР были следующими: 3 мин при 95 ° С; 30 с при 95 ° С, 30 с при 55 ° С, 30 с при 72 ° С (необходимо для удлинения последовательности) (25 циклов); 5 мин при 72 ° С (окончательная элонгация). Секвенирование проводили при помощи реагентов для подготовки библиотек Nextera® XT IndexKit («Illumina, Inc.», США), для очистки ПЦР-продуктов Agencourt AMPure XP («Beckman Coulter, Inc.», США) и для проведения секвенирования MiSeq® ReagentKit v2 (500 cycle) («Illumina, Inc.», США). Максимальная длина полученных последовательностей составила 2½250 п.н.
Автоматический биоинформатический анализ выполняли с помощью программного обеспечения QIIME2 ver. 2020.8 . После импорта последовательностей в формате .fastq из секвенирующего прибора и создания необходимых для работы файлов сопоставления, содержащих метаданные изучаемых файлов, парные строки прочтений были выровнены. Далее последовательности фильтровали по качеству с использованием параметров настроек по умолчанию. Фильтрацию шумовых последовательностей проводили с помощью встроенного в программное обеспечение QIIME2 пакета DADA2, включающего информацию о качестве по- следовательностей в модель ошибок (фильтрацию химерных последовательностей, артефактов, адаптеров), что делает алгоритм устойчивым к последовательности более низкого качества. При этом использовали максимальную длину последовательности обрезки, равную 250 п.н. . Для построения филогении de novo выполнили множественное выравнивание последовательностей, применяя программный пакет MAFFT, далее проводили маскированное выравнивание, чтобы удалить позиции, которые значительно различались. Для назначения таксономии использовали программное обеспечение QIIME2, которое присваивает последовательности таксономическую идентификацию на основе данных ASV (методами BLAST, RDP, RTAX, mothur и uclust), используя базу данных по 16s rRNA Silva 138.1 .
На основании полученной таблицы оперативно-таксономических единиц (ОТЕ; оperational taxonomic unit, OTU) с использованием плагинов программного пакета QIIME2 были рассчитаны индексы биоразнообразия, а также построен график зависимости числа ОТЕ от числа прочтений. При статистическом анализе индексов разнообразия их дополнительное преобразование не проводили.
Реконструкцию и прогнозирование функционального содержания метагенома, семейств генов, ферментов проводили при помощи программного комплекса PICRUSt2 (v.2.3.0) (41). С программой работали согласно рекомендованному сценарию действий, все настройки использовали по умолчанию. ОТЕ каждого образца расположили в соответствии с его содержанием, от большего к меньшему, значения преобразовали с помощью логарифмического преобразования Log2. Для анализа метаболических путей и ферментов пользовались базой данных MetaCyc . Прогнозируемые профили метаболических путей MetaCyc оценивали по обилию ASV (Amplicon Sequence Variants) (42). Визуализацию данных и подсчет статистических показатели проводили с помощью веб-приложения Phantasus v1.11.0 , в котором, помимо основных методов визуализации и фильтрации, поддерживаются методы на основе R, такие как кластеризация k-средних, анализ основных компонент или анализ дифференциальных выражений с пакетом limma.
Математическую и статистическую обработку полученных результатов осуществляли методом многофакторного дисперсионного анализа (multifactor ANalysis Of VAriance, ANOVA) в программах Microsoft Excel XP/2003, R-Studio (Version 1.1.453) . Данные представлены как средние (M) и стандартные ошибки средних (±SEM). Достоверность различий устанавливали по t-критерию Стьюдента, различия считали статистически значимыми при p ≤ 0,05. Средние значения сравнивали с использованием теста достоверно значимой разницы Тьюки (HSD) и функции TukeyHSD в пакете R Stats Package.
Результаты. Показатели клинического анализа крови крайне чувствительны к различным физиологическим влияниям, в связи с чем профиль крови — это достаточно точное отражение подобных воздействий (4345). У животных контрольной и опытной групп содержание гемоглобина и эритроцитов соответствовали возрастным нормам, отмечались лишь некоторые незначительные отклонения: количество эритроцитов и гемоглобина во II опытной группе через 60 сут эксперимента (табл. 1). Кроме того, среднее содержание гемоглобина в эритроцитах в обеих группах превышало норму. В обеих группах наблюдались возрастные изменения показателей крови на разных этапах развития организма кроликов. Так, количество гемоглобина в крови у кроликов II опытной группы через 60 сут увеличилось на 8,2 % (p ≤ 0,05) по сравнению с началом эксперимента, а в крови у животных I контрольной группы — на 4,45 % (p ≤ 0,05). При этом между контрольной и опытной группами не наблюдалось статистически значимых различий по этим показателям (p > 0,05) (см. табл. 1).
-
1. Показатели клинического анализа крови кроликов ( Oryctolagus dominis ) породы советская шиншилла при применении комплексной кормовой добавки на основе пробиотического штамма бактерий Bacillus subtilis 1-85 и микроэлементов ( n = 5, M ±SEM; виварий ФГБОУ ВО СПХФУ Минздрава России, г. Санкт-Петербург, 2021 год)
-
2. Показатели естественной резистентности у кроликов ( Oryctolagus dominis ) породы советская шиншилла на 60-е сут эксперимента при применении комплексной кормовой добавки на основе пробиотического штамма бактерий Bacillus subtilis 1-85 и микроэлементов ( n = 5, M ±SEM; виварий ФГБУ ВО СПХФУ Минздрава России, г. Санкт-Петербург, 2021 год)
Показатель 1
I контрольная группа
1 II опытная группа
Лизоцим, %
36,18±1,04
46,29±1,36*
Бактерицидная активность сыворотки крови, %
38,45±1,09
46,68±1,27*
Фагоцитарная активность, %
43,45±1,19
63,27±1,33*
Фагоцитарный индекс
5,33±0,10
7,13±0,15**
Фагоцитарное число
2,88±0,10
3,81±0,11*
Фагоцитарная емкость, тыс. микробных тел
73,12±1,53
75,89±1,21
Примечани е. Описание групп см. в разделе «Методика».
* и ** Различия между опытной и контрольной группами на основании t -критерия Стьюдента статистиче-
ски значимы соответственно при p ≤ 0,05 и p ≤ 0,01
.
3. Среднесуточный прирост живой массы у кроликов (
Oryctolagus dominis
) породы советская шиншилла при применении комплексной кормовой добавки на основе пробиотического штамма бактерий
Bacillus subtilis
1-85 и микроэлементов
(
n
= 5,
M
±SEM; виварий ФГБОУ ВО СПХФУ Минздрава России, г. Санкт-Петербург, 2021 год)
|
Пока.за.те.ль |
Время после начало опыта |
I контрольная группа |
II опытная группа |
Возрастная норма |
|
Эритроциты, ½1012/л |
1-е сут |
7,01±0,43 |
7,24±0,31 |
5,2-7,8 |
|
30-е сут |
7,24±0,59 |
7,42±0,77 |
||
|
60-е сут |
7,28±0,33 |
8,20±0,93 |
||
|
Гемоглобин, ммоль/л |
1-е сут |
143,80±8,80 |
152,20±4,09 |
100,5-160,0 |
|
30-е сут |
143,80±4,30 |
152,00±7,31 |
||
|
60-е сут |
150,20±6,02 |
164,60±9,24 |
||
|
Среднее содержание гемогло- |
1-е сут |
19,72±1,80 |
21,06±0,71 |
9,3-15,3 |
|
бина в эритроцитах, пг/л |
30-е сут |
20,70±0,79 |
21,32±0,73 |
|
|
60-е сут |
20,44±0,58 |
22,14±2,34 |
Примечани е. Описание групп см. в разделе «Методика».
Учитывая тот факт, что у кроликов в раннем возрасте желудочно-кишечный тракт недостаточно подготовлен к перевариванию твердых кормов, а организм в период доращивания подвергается влиянию стресс-факторов, оказывающих воздействие на иммунитет, мы изучили показатели естественной резистентности у подопытных животных.
Судя по значениям показателей, которые косвенно отражают содержание врожденных иммунных медиаторов в крови (содержание лизоцима, бактерицидные характеристики крови, фагоцитарная активность, фагоцитарный индекс, фагоцитарное число), естественная резистентность у кроликов, получавших комплексную кормовую добавку, была выше контроля (p ≤ 0,05) (табл. 2). Так, фагоцитарный индекс (среднее число фагоцитированных микроорганизмов, приходящееся на один активный лейкоцит), отражающий интенсивность фагоцитоза, был выше во II опытной группе по сравнению с I группой на 1,8 (p ≤ 0,05), фагоцитарное число (отношение числа фагоцитировавших бактерии лейкоцитов к общему числу подсчитан- ных лейкоцитов) — выше на 32,3 % (p ≤ 0,05).
Усиление естественной резистентности у кроликов, получавших комплексную кормовую добавку, закономерно. Давно известно, что кровь содержит антимикробные компоненты, которые обеспечивают быстрые ответы на инфекцию (46). Врожденные ответы на микробные инфекции у млекопитающих опосредуются сигнальными молекулами, включая Toll-подобные рецепторы, цитозольные киназы, ядерный фактор (NF)-kB, факторы транскрипции (47). Проникновение патогенов индуцирует быструю экспрессию нескольких генов, кодирующих антимикробные белки и пептиды (48, 49). В свою очередь, существуют молекулярные механизмы, обеспечивающие перекрестную взаимосвязь между микробиомом и экспрессией генов хозяина, прежде всего генов иммунитета (50). Введение пробиотического штамма бактерии в совокупности с микроэлементами в кишечник кроликов могло оказать влияние на экспрессию генов хозяина, связанных с иммунитетом. Ранее было продемонстрировано увеличение содержания общего белка и глобулинов в сыворотке крови кроликов под влиянием пробиотика (28). Данные, полученные A.F. Mohamed с соавт. (51), свидетельствуют о том, что введение в рацион пробиотического штамма Lactobacillus acidophilus не оказало достоверного влияния на содержание глобулина, но привело к увеличению числа лейкоцитов и количества общего белка в сыворотке крови. Высказано мнение, что микроэлементы играют важную роль в различных физиологических процессах и имеют решающее значение для правильного функционирования иммунной системы (52).
|
Группа |
Экспериментальный период, сут |
Среднесуточный прирост массы, г |
|
I контрольная группа |
1-30 |
5,53±0,32 |
|
II опытная группа |
31-60 1-30 |
5,21±0,15 6,08±0,49 |
|
31-60 Примечани е. Описание групп см. в разделе «Методика». |
5,90±0,21 |
|
Исходя из результатов взвешивания кроликов, можно предположить отсутствие отрицательного влияния исследуемой комплексной кормовой добавки на основе микроэлементов и пробиотика на прирост живой массы (табл. 3). Однако следует отметить, что число животных в экспериментальных группах не обеспечивало достаточного уровня доказательности, поскольку группы формировались согласно основной цели нашего исследования — анализа состава и функций микробиома.
Ранее отмечалось позитивное действие пробиотиков и микроэлементов на показатели продуктивности кроликов. Так, A.A.A. Abdel-Wareth с со-авт. (25) исследовали комплексный препарат из смеси семян пажитника и пробиотика (AmPhi-Bact, «American Pharmaceutical Innovations Company, LLC» США), содержащего культуры Lactobacillus acidophilus , Lactobacillus plantarum , Bifidobacterium bifidum , метаболитов Bacillus subtilis и Aspergillus niger , на 45-суточных новозеландских белых кроликах в течение 6 нед. Авторы отмечали улучшение конверсии корма, более высокую усвояемость сырого протеина и увеличение мясной продуктивности в группах, получавших препарат. М. Lopez-Alonso с соавт. (53) высказали мнение, что микроэлементы координируют большое число биологических процессов и, следовательно, 1124
необходимы для поддержания продуктивности животных.
На следующем этапе работы мы изучили состав микробиома химуса из слепых отростков кишечника кроликов методом NGS-секвенирования. В общей сложности было сгенерировано 57,56 секвенированных последовательностей гена 16S рРНК (с медианой считываний 9,59 при min = 7,69 и max = 12,86). При сравнении I контрольной и II опытной групп по индексам Chao1, Шеннона и Симпсона оказалось, что их значения имели статистически значимые различия (p ≤ 0,05) (рис. 1). В опытной группе были отмечены более высокие значения индексов α -биоразнообразия. То есть комплексная кормовая добавка, включавшая пробиотический штамм и смесь микроэлементов, позитивно влияла на увеличение видового разнообразия микробиома в кишечнике кроликов. Эти результаты согласуются с данными других авторов (54, 55).
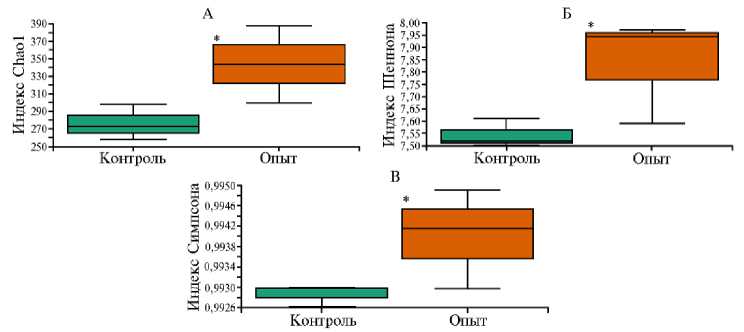
Рис. 1. Абсолютные значения индексов α -биоразнообразия Chao1 (А) , Шеннона (Б) и Симпсона (В) для микробиома слепых отростков кишечника кроликов ( Oryctolagus dominis ) породы советская шиншилла на 60-е сут эксперимента при применении комплексной кормовой добавки на основе пробиотического штамма бактерий Bacillus subtilis 1-85 и микроэлементов ( n = 3, M ±SEM; виварий ФГБОУ ВО СПХФУ Минздрава России, г. Санкт-Петербург, 2021 год). Рассчитано с использованием плагинов программного пакета Qiime2 ver. 2020.11. Описание групп см. в разделе «Методика».
* Различия между опытной и контрольной группами на основании t -критерия Стьюдента статистически значимы при р ≤ 0,05.
При исследовании состава микроорганизмов слепых отростков кишечника кроликов выявили 12 филумов царства Bacteria (рис. 2), среди которых представители филума Firmicutes доминировали по численности (80,2±6,2 % в I группе, 78,2±7,4 % во II группе), что указывает на их важное экологическое и функциональное значение в пищеварительном тракте. Основная функция Firmicutes — способность разлагать сложные полисахариды с последующим образованием короткоцепочечных жирных кислот (56). Судя по результатам исследований, проведенных ранее, доминирование представителей этого филума в содержимом слепых отростков достаточно типично для кроликов (11).
В нашем опыте филум Bacteroidetes оказался вторым по распространенности в кишечнике кроликов (13,3±1,2 % в I группе, 12,3±1,8 % во II группе). Ранее (9, 57) было доказано, что Bacteroidetes стимулируют развитие кишечно-ассоциированной иммунной ткани в пищеварительной системе. Результаты, аналогичные нашим, были получены и у диких кроликов, а также у домашних кроликов породы Rex (58, 59). В целом количественная представленность филумов в кишечнике кроликов соответствует таковой у других моногастричных травоядных (60, 61).
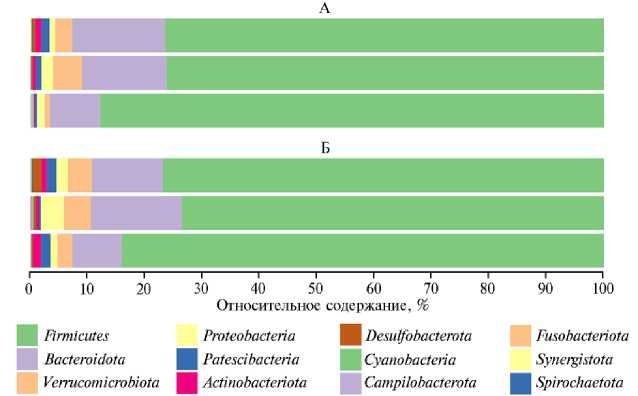
Рис. 2. Состав кишечного микробиома слепых отростков кишечника у кроликов ( Oryctolagus dominis ) породы советская шиншилла на уровне бактериальных филумов (по данным NGS-секвенирования ампликонов гена 16S рРНК) на 60-е сут эксперимента при применении комплексной кормовой добавки на основе пробиотического штамма бактерий Bacillus subtilis 1-85 и микроэлементов ( n = 3, M ±SEM; виварий ФГБОУ ВО СПХФУ Минздрава России, г. Санкт-Петербург, 2021 год). Описание групп см. в разделе «Методика».
В опытной группе по сравнению с контрольной происходило увеличение численности филумов Verrucomicrobiota , Actinobacteriota , Patescibacteria , Proteobacteria , Desulfobacterota в 1,3-2,6 раза и снижение представленности филума Campilobacterota в 4,8 раза (p ≤ 0,05). По всей вероятности, эти данные свидетельствуют о позитивном влиянии комплексной кормовой добавки на состав микробиома. Например, представители филума Verrucomicrobiota , такие как Akkermansia muciniphila , обладают пробиотической активностью, модулируя толщину слизи в кишечнике и повышая целостность кишечного барьера (62). Бактерии филума Actinobacteriota служат продуцентами антимикробных веществ, активных в отношении патогенов (63). При этом среди бактерий филума Campilobacterota , который был представлен единственным родом Campylobacter (рис. 3), встречаются патогенные формы, связанные с пролиферативной энтеропатией кроликов (64).
В слепых отростках кишечника кроликов II опытной группы наблюдалось возрастание количества бактерий рода Bacillus spp. в 2,82 раза по сравнению с контролем (p ≤ 0,05) (см. рис. 3), что может указывать на выживаемость и увеличение численности пробиотического микроорганизма, интродуцированного в составе комплексной кормовой добавки. Это важный вывод, поскольку интродуцированные штаммы микроорганизмов могут обладать разной способностью выживать в агрессивной среде кишечника хозяина (65). Ранее методом RAPD-PCR была доказана выживаемость пробиотических бактерий Bacillus clausii в желудочно-кишечном тракте в течение 12 сут (66).
Важно отметить, что в слепых отростках кишечника кроликов мы выявили значительное число родов, включая некультивируемые, относящиеся к целлюлозолитическим бактериям семейств Thermoanaerobacteraceae, Ruminococcaceae, Clostridiaceae, Eubacteriaceae, Lachnospiraceae, что согласуется с данными, полученными C. Bauerl с соавт. (67). Целлюлозолитические бактерии — наиболее релевантные микроорганизмы филума Firmicutes, способствующие расщеплению клетчатки растительных кормов. Так, S. Combes с соавт. установили (68), что бактерии рода Ruminococcus доминируют у здоровых кроликов, а при возникновении заболевания численность этих микроорганизмов снижается. E. Cotozzolo с соавт. (5) также показали, что обилие представителей семейств Ruminococcaceae и Lachnospiraceae служит важным показателям здоровья кишечника у кроликов. По мнению авторов, более высокая численность Lachnospiraceae характерны для здоровых животных, что связано со стимуляцией цекотрофного поведения. Цекотрофия — важная особенность отряда Lagomorpha, которая позволяет повышать усвояемость малопитательного растительного корма (69).
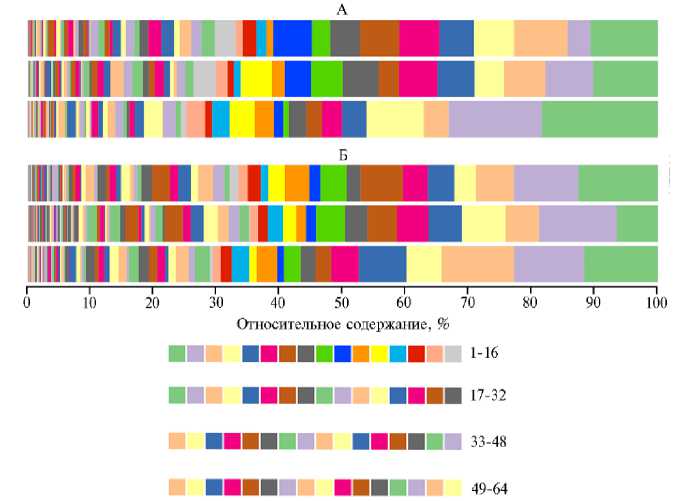
Рис. 3. Состав кишечного микробиома слепых отростков кишечника кроликов ( Oryctolagus dominis ) породы советская шиншилла на уровне бактериальных родов (по данным NGS-секвенирования ампликонов гена 16S рРНК) на 60-е сут эксперимента при применении комплексной кормовой добавки на основе пробиотического штамма бактерий Bacillus subtilis 1-85 и микроэлементов: 1 — f Lachnospiraceae g. unclassified, 2 — g. Clostridia UCG-014, 3 — g. Oscillospiraceae NK4A214, 4 — g. Ruminococcus , 5 — g. Monoglobus , 6 — g. Oscillospirales UCG-010, 7 — g. Clostridia vadinBB60, 8 — g. Bacteroides , 9 — g. Akkermansia , 10 — g. Rikenellaceae dgA-11 gut, 11 — f. Bacilli RF39 g. unclassified, 12 — g. Lachnospiraceae NK4A136, 13 — g. Christensenellaceae R-7, 14 — g. Eubacterium coprostanoligenes , 15 — g. Oscillospiraceae V9D2013, 16 — f. Lachnospiraceae g. unclassified, 17 — g. Ruminococcaceae Incertae Sedis, 18 — f. Oscillospiraceae g. unclassified, 19 — f. Eubacteriaceae g. unclassified, 20 — g. Eubacterium siraeum , 21 — f. Barnesiellaceae g. unclassified, 22 — g. Alistipes , 23 — g. Rikenellaceae RC9 gut, 24 — g. Candidatus Saccharimonas , 25 — g. Sub-doligranulum , 26 — g. Oscillospiraceae UCG-005, 27 — g. Tyzzerella , 28 — g. Campylobacter , 29 — f. Ruminococcaceae g. unclassified, 30 — g. Ruminiclostridium , 31 — g. Vibrionimonas , 32 — g. Muri-baculaceae , 33 — g. Desulfovibrio , 34 — g. Colidextribacter , 35 — f. Anaerovoracaceae g. unclassified, 36 — g. Pelomonas , 37 — g. Papillibacter , 38 — f. Atopobiaceae g. unclassified, 39 — g. Staphylococcus , 40 — f. Acidaminococcaceae g. unclassified, 41 — f. Peptococcaceae g. unclassified, 42 — g. Pseudomonas , 43 — g. Eubacterium nodatum , 44 — g. Anaerovoracaceae XIII AD3011, 45 — f. Sutterellaceae g. unclassified, 46 — g. Stenotrophomonas , 47 — g. Oscillospiraceae UCG-007, 48 — g. Ruminococca-ceae CAG-352, 49 — g. Prevotella , 50 — g. Lachnospiraceae NK4B4, 51 — g. Izemoplasmatales , 52 — f. Eggerthellaceae g. unclassified, 53 — g. Ruminococcaceae , 54 — g. Defluviitaleaceae UCG-011, 55 — g. Ruminococcaceae UCG-001, 56 — g. Holdemania , 57 — g. Oscillibacter, 58 — f. Erysipelatoclostridi-aceae g. unclassified, 59 — g. Escherichia - Shigella , 60 — g. Odoribacter , 61 — f. Xanthobacteraceae g. unclassified, 62 — g. Parabacteroides , 63 — g. Lachnospiraceae FCS020, 64 — g. Parasutterella ( n = 3, M ±SEM; виварий ФГБОУ ВО СПХФУ Минздрава России, г. Санкт-Петербург, 2021 год). Описание групп см. в разделе «Методика».
Дело в том, что в процессе пищеварения кроликов образуются фе- калии двух типов: твердые, бедные питательными веществами, и мягкие, состоящие из белка, витаминов, неорганических солей и содержащие значительное количество микроорганизмов. Последние носят название цекотро-фов и поедаются Lagomorpha в процессе цекотрофии. Поэтому существует предположение, что цекотрофия — это явление, которое обеспечивает формирование правильного состава кишечного микробиома. Однако в нашем исследовании не было обнаружено существенной разницы в содержании родов целлюлозолитических микроорганизмов между контрольной и опытной группами (р > 0,05).
Тем не менее позитивное влияние комплексной кормовой добавки на состав микробиома проявлялось в снижении численности ряда условнопатогенных и патогенных микроорганизмов в пищеварительной системе кроликов. Так, в кишечнике животных из контрольной группы присутствовал вид Staphylococcus sciuri (70) (0,075±0,006 %), тогда как в опытной он не был представлен. Стафилококкозы кроликов — опасные заболевания, которые приводят к возникновению пододерматитов, подкожных абсцессов, маститов, абсцессов внутренних органов, преимущественно легких, печени, матки. Также были описаны артрит, пародонтит, синусит и средний отит (71). Несмотря на большую значимость вида Staphylococcus aureus в возникновении стафилококкозов кроликов, клиническая значимость S. sciuri , по-видимому, возрастает, поскольку бактерия была связана с различными инфекциями, такими как эндокардит, перитонит, септический шок, инфекция мочевыводящих путей, эндофтальмит, воспалительные заболевания репродуктивной системы (72). Отсутствие Staphylococcus sciuri в опытной группе свидетельствует о позитивном эффекте кормовой добавки, включавшей пробиотический штамм и смесь микроэлементов, которые, вероятно, действуют в синергизме.
Метаболические пути
Описание Контроль Опыт р

PWY-1501
PWY-5430
PWY-181
DENITRIFICATION-PWY
PWY-6071
PWY-5647
P281-PWY
PWY-6107
PWY-6876
RL"MP PWY
PWY-1861
HOMOSER-METSYN-PWY
PWY-5180
PWY-5182
PWY-1541
PWY-6641
PWY-6505
PWY-5654
MET-SAM PWY
TEICHOICACID PWY
GLUCARDEG-PWY
PWY-5347
PWY-5420
PWY 5419
PWY 5655
PWY-6210
LACTOSECAT-PWY GALACTARDEG-PWY
Дегрздания миндальной кислоты
Путь мета-расщепления ароматических соединений Фотодыхание Снижение нитратов! Суперпуть деградации фенилтиамина
GLUCARGALACTSUPER-PWY
PWY 5747
P341-PWY
P621-PWY
PWYO-42
PWY 7431
PWY-7237
P125-PWY
Деградация 2-нитробснзоата I Деградация 3-фенилпропанояга Дырадация хлоросатициляга Биосинтез изопропанола Окисление формальдегидов I Ассимиляция формальдегидов II
Биосинтез L-метионина I Деградация толуола I
Деградация толуола II Супсрпуть деградации таурина Суперпуть деградации сульфолактагта Деградация Е-триптофана ХИ C7H7NO5 деградация до 2-оксопенденоата Суперпуть биосинтеза З-аденозил-Е-метионина Биосинтез тейхоевой кислоты (поли-глицерина) Деградация О-глюкората I Суперпуть биосинтеза Е-метионина Деградация катехола II Деградация катехола до 2-оксопент-4-еноата II Деградация Е тргппофана IX Деградация 2-аминофенола Деградация лактозы и галактозы I Деградация D-гадактарата I Деградация D-глюкарата. и D-галактрата 2-Метилцитратный цикл П
Гликолиз V
Деградация нейлон-6 олигомера 2-Метил цитратный цикл I Деградация ароматических биогенных аминов Деградация мио-., хиро- и цилло- инозитолов Суперпуть биосинтеза (Н,К)-бутанедиола
0,000121
0,001541
0,002282
0,003865
0,005563
0,006066 0,006662 0,007162 0,007374 0,008943 0,011012 0,011578 0,011710 0,011710 0,012648 0,013213 0,013377 0,014219 0,014324 0,014840 0,015503 0,019309 0,020692 0,025471 0,026437 0,027892 0,030183 0,030470 0,030470 0,032088
0,032733 0,033844 0,040726 0,041795 0,044955 0,048240
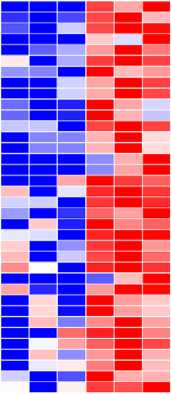
Рис. 4. Результаты функциональной аннотации прогнозируемых метаболических путей в микробиоме слепых отростков кишечника у кроликов (Oryctolagus dominis) породы советская шиншилла (по данным NGS-секвенирования ампликонов гена 16S рРНК) на 60-е сут эксперимента при применении комплексной кормовой добавки на основе пробиотического штамма бактерий Bacillus subtilis 1-85 и микроэлементов (n = 3, M±SEM; виварий ФГБОУ ВО СПХФУ Минздрава России, г. Санкт-Петербург, 2021 год). Данные получены при помощи программного комплекса PICRUSt2 (v.2.3.0) . Шкала отражает интенсивность потенциальных метаболических путей микробиома: синий цвет — наименьшая (минимальная) интенсивность, красный — наибольшая (максимальная). Описание групп см. в разделе «Методика».
В результате анализа, проведенного с использованием программного комплекса PICRUSt2 (v.2.3.0), у микробного сообщества кишечника кроликов исследованных групп мы обнаружили 370 прогнозируемых метаболических путей. Статистически значимые различия между экспериментальными группами (p ≤ 0,05) наблюдались по 36 путям (рис. 4). В кишечном микробиоме кроликов из II опытной группы по сравнению с I группой происходила активация (до 4-кратной, p ≤ 0,05) 8 путей, которые относились к белковому обмену (биосинтез и превращение аминокислот, азотистых соединений), 4 путей, относящихся к углеводному обмену (расщепление различных сахаров), 3 — к энергетическому обмену (метилцитратный цикл и гликолиз), 2 — к биосинтезу спиртов, 1 — к фотодыханию , 1 — к ассимиляции формальдегида, 1 — к деградации мио-, хиро- и сцилло-инозитола, 1 — к синтезу клеточной стенки и спорообразованию (путь биосинтеза тейховых кислот). Интересно, что доминирующее число потенциальных метаболических путей (15 путей) было связано с деградацией ароматических соединений и ксенобиотиков, включая деградацию таких токсикантов, как катехин, формальдегид, 3-фенилпропаноат, олигомер нейлона-6 (73, 74). Усиление потенциала деградации ксенобиотиков в кишечнике кроликов из опытной группы могло иметь связь с увеличением численности бактерий Bacillus spp . Bacillus spp . давно рассматриваются как потенциальные биодеструкторы и биоремедиаторы, способные разлагать разнообразные токсичные вещества благодаря синтезу различных ферментов (75, 76).
Усиление пути деградации мио-, хиро- и сцилло-инозитола (PWY-7237) во II опытной группе по сравнению с контролем (p ≤ 0,05) также могло иметь связь с увеличением содержания Bacillus spp . Предыдущие исследования выявили у Bacillus subtilis 1-85 ряд генов, необходимых для катаболизма мио-инозита, включая опероны iolABCDEFGHIJ и iolRS (77), а также ген iolT (78). Что касается усиления вовлеченных в белковый обмен потенциальных путей в опытной группе, то представляет интерес активация сразу трех путей (HOMOSER-METSYN-PWY, MET-SAM-PWY и PWY-5347), связанных с синтезом L-метионина. Это перекликается с выводами зарубежных исследователей (79), которые высказали предположение, что метионин и треонин продуцируются микроорганизмами слепой кишки и поступают в организм кроликов в процессе цекотрофии мягких фекалий.
Стоит отметить, что у растущих кроликов избыток белка рациона может приводить к более высокой частоте возникновения мукоидной энтеропатии (80, 81). Современные рекомендации по кормлению кроликов имеют тенденцию к снижению в рационе количества белка и увеличению содержания клетчатки с целью предотвращения расстройств пищеварения (82). Тем не менее промышленное кролиководство заинтересовано в выращивании высокопродуктивных животных. Согласно G.G. Partridge с соавт. (83), существует положительная связь между массой кроликов и потребностями в белке. Поэтому возможность снижения содержания белка в рационе при одновременной максимизации эффективности синтеза и усвоения аминокислот в пищеварительной системе в результате применения кормовых добавок представляется крайне актуальной.
Ранее было проведено исследование (33) по выявлению различий в функциональных возможностях микробиоты кишечника у двух коммерческих пород кроликов Elco и Ira на основе секвенирования гена 16S рРНК. Выявлено усиление функционального потенциала микробиома кишечника, связанного с бактериальным хемотаксисом, превращением пентозофосфата, фруктозы, маннозы и аминокислот с разветвленной цепью у кроликов Elco по сравнению с Ira. При этом влияние кормовых добавок на метабо- лический потенциал кроликов ранее не изучалось. Однако подобные работы проводились на других сельскохозяйственных животных — на крупном рогатом скоте (32), свиньях (84), птице (85). На примере несушек Hyline Brown было показано (85), что включение в рацион пробиотика на основе Bacillus subtilis DSM 32324, Bacillus subtilis DSM 32325 и Bacillus amyloliquifaciens DSM 25840 приводило к усилению путей, связанных с метаболизмом витамина В6, ретинола, фосфонатов и фосфинатов, тирозина, биосинтезом фенилпропа-ноидов, монобактамов, пантотенатов и КоА, деградацией РНК.
Таким образом, введение в рацион кроликов породы советская шиншилла комплексной кормовой добавки, включающей штамм бактерии Bacillus subtilis 1-85 и смесь минеральных компонентов кремния, железа, меди, способствовало изменению количества врожденных иммунных медиаторов в крови. Содержание лизоцима и другие бактерицидные характеристики крови, фагоцитарная активность, фагоцитарный индекс, фагоцитарное число у кроликов, получавших комплексную кормовую добавку (II опытная группа), были выше, чем в I контрольной группе (p ≤ 0,05). По результатам NGS-секвенирования в опытной группе выявлены более высокие значения индексов α -биоразнообразия Chao1, Шеннона и Симпсона (p ≤ 0,05), чем в контрольной. В составе микробиома слепых отростков кишечника кроликов обнаружено 12 филумов царства Bacteria , среди которых доминировали представители Firmicutes (80,2±6,2 % в контрольной группе, 78,2±7,4 % в опытной группе). В опытной группе увеличилось обилие Verrucomicrobiota , Actinobacteriota , Patescibacteria , Proteobacteria , Desulfobacterota и снизилась представленность Campilobacterota . У кроликов из опытной группы численность бактерий рода Bacillus возрастала в 2,82 раза по сравнению с контрольной (p ≤ 0,05), что, вероятно, свидетельствует о колонизации химуса кишечника штаммом пробиотического микроорганизма, введенного в рацион в составе комплексной кормовой добавки. В кишечнике контрольных животных обнаружен вид Staphylococcus sciuri (0,075±0,006 %). У микробного сообщества кишечника кроликов мы описали 370 прогнозируемых метаболических путей, по 36 из них наблюдались различия между экспериментальными группами (p ≤ 0,05). В кишечном микробиоме у кроликов из опытной группы по сравнению с контролем происходила активация (p ≤ 0,05) путей, которые относились к деградации ароматических соединений и ксенобиотиков, белковому, углеводному, энергетическому обмену, биосинтезу спиртов, фотодыханию, ассимиляции формальдегида, деградации мио-, хиро- и сцилло-инозитола, синтезу клеточной стенки и спорообразованию. Доминирующее число усиленных потенциальных метаболических путей ассоциировано с деградацией ароматических соединений и ксенобиотиков. Интересным представляется дальнейшее изучение других аспектов благоприятного воздействия интродуцированного штамма бактерии и комплекса микроэлементов на хозяина, в частности оценка продуктивных показателей и разработка технологий введения представленной кормовой добавки в пищеварительный тракт.
Список литературы Состав и функции микробиома слепых отростков кишечника Oryctolagus dominis под влиянием комплексной кормовой добавки
- Lebas F., Coudert P., de Rochambeau H., Thébault R.G. The rabbit: husbandry, health, and production. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome, 1997.
- Cullere M., Dalle Zotte A. Rabbit meat production and consumption: State of knowledge and future perspectives. Meat Science, 2018, 143: 137-146 (doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2018.04.029).
- Усачев И.И. Влияние бифидофлоры на энтеральный биоценоз и жизнеспособность животных. Вестник Бурятской государственной сельскохозяйственной академии им. В.Р. Филиппова, 2008, 1: 26-29.
- McNitt J.I., Lukefahr S.D., Cheeke P.R., Patton N.M. Rabbit production. CABI, Wallingford, UK, 2013.
- Cotozzolo E., Cremonesi P., Curone G., Menchetti L., Riva F., Biscarini F., Marongiu M.L., Castrica M., Castiglioni B., Miraglia D., Luridiana S., Brecchia G. Characterization of bacterial microbiota composition along the gastrointestinal tract in rabbits. Animals, 2020, 11(1): 31 (doi: 10.3390/ani11010031).
- Flint H.J., Scott K.P., Louis P., Duncan S.H. The role of the gut microbiota in nutrition and health. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 2012, 9(10): 577-589 (doi: 10.1038/nrgastro. 2012.156).
- Heinrichs J., Lesmeister K.E. Rumen development in the dairy calf. Advances in Dairy Technology, 2005, 17: 179-187.
- Drouilhet L., Achard C.S., Zemb O., Molette C., Gidenne T., Larzul C., Ruesche J., Tircazes A., Segura M., Bouchez T., Theau-Clément M., Joly T., Balmisse E., Garreau H., Gilbert H. Direct and correlated responses to selection in two lines of rabbits selected for feed efficiency under ad libitum and restricted feeding: I. Production traits and gut microbiota characteristics. Journal of Animal Science, 2016, 94(1): 38-48 (doi: 10.2527/jas.2015-9402).
- Monteils V., Cauquil L., Combes S., Godon J.J., Gidenne T. Potential core species and satellite species in the bacterial community within the rabbit caecum. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2008, 66(3): 620-629 (doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6941.2008.00611.x).
- Massip K., Combes S., Cauquil L., Zemb O., Gidenne T. High-throughput 16SDNA sequencing for phylogenetic affiliation of the caecal bacterial community in the rabbit: Impact of the hygiene of housing and of the intake level. Proc. VIIIth INRA-RRI Symposium on Gut Microbiology. Gut microbiota: friend or foe? Clermont-Ferrand, France, 2012: 57.
- Velasco-Galilea M., Piles M., Vinas M., Rafel O., González-Rodríguez O., Guivernau M., Sanchez J.P. Rabbit microbiota changes throughout the intestinal tract. Front. Microbiol., 2018, 9: 2144 (doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02144).
- Xing Y., Liu J., Lu F., Wang L., Li Y., Ouyang C. Dynamic distribution of gallbladder microbiota in rabbit at different ages and health states. PLoS ONE, 2019, 14(2): e0211828 (doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0211828).
- Fang S., Chen X., Pan J., Chen Q., Zhou L., Wang C., Xiao T., Gan Q. F. Dynamic distribution of gut microbiota in meat rabbits at different growth stages and relationship with average daily gain (ADG). BMC Microbiol., 2020, 20(1): 116 (doi: 10.1186/s12866-020-01797-5).
- Gouet P.H., Fonty G. Changes in the digestive microflora of holoxenic rabbits from birth until adulthood. Annales de Biologie Animale Biochimie Biophysique, 1979, 19(3A): 553-566.
- Carabaño R., Badiola I., Licois D., Gidenne T. The digestive ecosystem and its control through nutritional or feeding strategies. In: Recent advances in rabbit sciences /L. Maertens, P. Coudert (eds.). ILVO, Melle, Belgium, 2006: 211-228.
- Marlier D., Dewrée R., Lassence C., Licois D., Mainil J., Coudert P., Meulemans L., Ducatelle R., Vindevogel H. Infectious agents associated with epizootic rabbit enteropathy: isolation and attempts to reproduce the syndrome. Journal of Veterinary Diagnostic Investigation, 2006, 172(3): 493-500 (doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2005.07.011).
- Lebas F. Entérocolite: situation en juin 2001. Cuniculture, 2001, 28: 183-188.
- Lord B. Gastrointestinal disease in rabbits 2. Intestinal diseases. In Practice, 2012, 34(3): 156-162 (doi: 10.1136/inp.e973).
- Olkowski A.A., Wojnarowicz C., Chirino-Trejo M., Drew M.D. Responses of broiler chickens orally challenged with Clostridium perfringens isolated from field cases of necrotic enteritis. Research in Veterinary Science, 2006, 81(1): 99-108 (doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2005.10.006).
- Lu H., Adedokun S.A., Adeola L., Ajuwon K. Anti-inflammatory effects of non-antibiotic alternatives in Coccidia challenged broiler chickens. Journal of Poultry Science, 2014, 51(1): 14-21 (doi: 10.2141/jpsa.0120176).
- Tang T., Li Y., Wang J., Elzo M. A., Shao J., Li Y., Xia S., Fan H., Jia X., Lai S. Untargeted metabolomics reveals intestinal pathogenesis and self-repair in rabbits fed an antibiotic-free diet. Animals (Basel), 2021, 11(6): 1560 (doi: 10.3390/ani11061560).
- Deng Z., Han D., Wang Y., Wang Q., Yan X., Wang S., Liu X., Song W., Ma Y. Lactobacillus casei protects intestinal mucosa from damage in chicks caused by Salmonella pullorum via regulating immunity and the Wnt signaling pathway and maintaining the abundance of gut microbiota. Poultry Science, 2021, 100(8): 101283 (doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2021.101283).
- Liu B., Liu Q.-M., Li G.-L., Sun L.C., Gao Y.-Y., Zhang Y.-F., Liu H., Cao M.-J., Liu G.-M. The anti-diarrhea activity of red algae-originated sulphated polysaccharides on ETEC-K88 infected mice. RSC Advances, 2019, 9: 2360-2370 (doi: 10.1039/C8RA09247H).
- Karamzadeh-Dehaghani A., Towhidi A., Zhandi M., Mojgani N., Fouladi-Nashta A. Combined effect of probiotics and specific immunoglobulin Y directed against Escherichia coli on growth performance, diarrhea incidence, and immune system in calves. Animal, 2021, 15(2): 100124 (doi: 10.1016/j.animal.2020.100124).
- Abdel-Wareth A.A.A., Elkhateeb F.S.O., Ismail Z.S.H., Ghazalah A.A., Lohakare J. Combined effects of fenugreek seeds and probiotics on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, carcass criteria, and serum hormones in growing rabbits. Livestock Science, 2021, 251: 104616 (doi: 10.1016/j.livsci.2021.104616).
- Lam Phuoc T., Jamikorn U. Effects of probiotic supplement (Bacillus subtilis and Lactobacillus acidophilus) on feed efficiency, growth performance, and microbial population of weaning rabbits. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci., 2016, 30(2): 198-205 (doi: 10.5713/ajas.15.0823).
- Dimova N., Laleva S., Slavova P., Popova Y., Mihaylova M., Pacinovski N. Effect of probiotic “Zoovit” on productivity of rabbits. Macedonian Journal of Animal Scienc, 2017, 7: 123-127.
- Fathi M., Abdelsalam M., Al-Homidan I., Ebeid T., El-Zarei M., Abou-Emera O. Effect of probiotic supplementation and genotype on growth performance, carcass traits, hematological parameters and immunity of growing rabbits under hot environmental conditions. Anim. Sci. J., 2017, 88(10): 1644-1650 (doi: 10.1111/asj.12811).
- El-Shafei A.A., Younis T.M., Al-Gamal M.A., Hesham A.M. Impact of probiotic (Lactobacillus planterium L) supplementation on productive and physiological performance of growing rabbits under Egyptian conditions. Egyptian Journal of Rabbit Science, 2019, 29(1): 125-148 (doi: 10.21608/ejrs.2019.48188).
- Wlazło Ł., Kowalska D., Bielański P., Chmielowiec-Korzeniowska A., Ossowski M., Łukaszewicz M., Czech A., Nowakowicz-Dębek B. Effect of fermented rapeseed meal on the gastrointestinal microbiota and immune status of rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus). Animals (Basel), 2021, 11(3): 716 (doi: 10.3390/ani11030716).
- Shen X.M., Cui H.X., Xu X.R. Orally administered Lactobacillus casei exhibited several probiotic properties in artificially suckling rabbits. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci., 2020, 33: 1352-1359 (doi: 10.5713/ajas.18.0973).
- Йылдырым Е.А., Лаптев Г.Ю., Ильина Л.А., Дуняшев Т.П., Тюрина Д.Г., Филиппова В.А., Бражник Е.А., Тарлавин Н.В., Дубровин А.В., Новикова Н.И., Солдатова В.В., Зайцев С.Ю. Таксономическая и функциональная характеристика микробиоты рубца лактирующих коров под влиянием пробиотика Целлобактерина+. Сельскохозяйственная биология, 2020, 55(6): 1204-1219 (doi: 10.15389/agrobiology.2020.6.1204rus).
- Ye X., Zhou L., Zhang Y., Xue S., Gan Q. F., Fang S. Effect of host breeds on gut microbiome and serum metabolome in meat rabbits. BMC Vet. Res., 2021, 17(1): 24 (doi: 10.1186/s12917-020-02732-6).
- Алексеева Л.В., Арсанукаев Д.Л. Особенности микроэлементного метаболизма у животных. Мат. Межд. науч.-практ. конф. «Конкурентоспособность и инновационная активность АПК регионов». Тверь, 2018: 89-92.
- Алексеева Л.В., Макаревский А.А., Субботенко Т.В. Влияние препарата нанокремний на интенсивность роста норок. Мат. Межд. науч.-практ. конф. «Научные приоритеты в АПК». Тверь, 2019: 146-148.
- Алексеева Л.В., Лукьянов А.А., Белякова С.В. Применение антиоксидантных препаратов. Мат. Межд. науч.-практ. конф. «Конкурентоспособность и инновационная активность АПК регионов». Тверь, 2017: 132-134.
- Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. The National Academy press, Washington, D.C, 2011.
- Алексеева Л.В., Деменик Ф.Г., Савина А.С. Активность компонентов системы гомеостаза коров и их продуктивность под влиянием препарата нанокремний. Вестник тверского государственного университета. Серия: биология и экология, 2018, 2: 274-285.
- Карпуть И.М. Иммунология и иммунопатология болезней молодняка. Минск, 1993.
- Дорофейчук В.Г. Определение активности лизоцима нефелометрическим методом. Лабораторное дело, 1968, 1: 67.
- Douglas G.M., Maffei V.J., Zaneveld J.R. Yurgel S.N., Brown J.R., Taylor C.M., Huttenhower C., Langille M.G.I. PICRUSt2 for prediction of metagenome functions. Nature Biotechnology, 2020, 38: 685-688 (doi: 10.1038/s41587-020-0548-6).
- Tracey K.J., Wei H., Manogue K.R., Fong Y., Hesse D.G., Nguyen H.T., Kuo G.C., Beutler B., Cotran R.S., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor induces cachexia, anemia, and inflammation. The Journal of Experimental Medicine, 1988, 167(3): 1211-1227 (doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.1211).
- Овсянников А.Г. Анемия кроликов (этиопатогенез, диагностика, лечение). Канд. дис. СПб, 2019.
- Глаголева О.Н. Популяционная профилактика анемий, связанных с питанием. Вести МАНЭБ в Омской области, 2013, 2(2): 13-15.
- Kraemer K., Zimmermann B. Nutritional anemia. Sightand Life Press, Basel, Switzerland, 2007.
- Levy O. Antimicrobial proteins and peptides of blood: templates for novel antimicrobial agents. Blood, 2000, 96(8): 2664-2672.
- Modlin R.L., Brightbill H.D., Godowski P.J. The toll of innate immunity on microbial pathogens. N. Engl. J. Med., 1999, 340(23): 1834-1835 (doi: 10.1056/NEJM199906103402312).
- Hoffmann J.A. Innate immunity of insects. Current Opinion in Immunology, 1995, 7(1): 4-10 (doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(95)80022-0).
- Hoffmann J.A., Reichhart J.M., Hetru C. Innate immunity in higher insects. Current Opinion in Immunology, 1996, 8(1): 8-13 (doi: 10.1016/s0952-7915(96)80098-7).
- Nichols R.G., Davenport E.R. The relationship between the gut microbiome and host gene expression: a review. Human Genetics, 2021, 140(5): 747-760 (doi: 10.1007/s00439-020-02237-0).
- Mohamed A.F., El-Sayiad G.A., Reda F.M., Ashour E.A. Effects of breed, probiotic and their in-teraction on growth performance, carcass traits and blood profile of growing rabbits. Zagazig Journal of Agricultural Research, 2017, 44(1): 215-227 (doi: 10.21608/zjar.2017.53947).
- Lukác N., Massányi P. Vplyv stopoýtch prvkov na imunitný systém [Effects of trace elements on the immune system]. Epidemiol. Mikrobiol. Imunol., 2007, 56(1): 3-9.
- López-Alonso M. Trace minerals and livestock: not too much not too little. International Scholarly Research Notices, 2012, 2012: 704825 (doi: 10.5402/2012/704825).
- Kim H.B., Borewicz K., White B.A., Singer R.S., Sreevatsan S., Tu Z.J., Isaacsona R.E. Microbial shifts in the swine distal gut in response to the treatment with antimicrobial growth promoter, tylosin. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2012, 109(38): 15485-15490 (doi: 10.1073/pnas.1205147109).
- Pajarillo E.A., Chae J.P., Balolong M.P., Kim H.B., Seo K.-S., Kang D.-K. Characterization of the fecal microbial communities of duroc pigs using 16S rRNA gene pyrosequencing. Asian- Australas. J. Anim. Sci., 2015, 28(4): 584-591 (doi: 10.5713/ajas.14.0651).
- den Besten G., van Eunen K., Groen A.K., Venema K., Reijngoud D.-J., Bakker B.M. The role of short-chain fatty acids in the interplay between diet, gut microbiota, and host energy metabolism. Journal of Lipid Research, 2013, 54(9): 2325-2340 (doi: 10.1194/jlr.R036012).
- Abecia L., Rodríguez-Romero N., Yañez-Ruiz D.R., Fondevila M. Biodiversity and fermentative activity of caecal microbial communities in wild and farm rabbits from Spain. Anaerobe, 2012, 18(3): 344-349 (doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2012.04.004).
- Fu X., Zeng B., Wang P., Wang L., Wen B., Li Y., Liu H., Bai S., Jia G. Microbiome of total versus live bacteria in the gut of Rex rabbits. Front. Microbiol., 2018, 9: 733 (doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00733).
- Crowley E.J., King J.M., Wilkinson T., Worgan H.J., Huson K.M., Rose M.T., McEwan N.R. Comparison microbial population in rabbits and guinea pigs by next generation sequencing. PLoS ONE, 2017, 12(2): e0165779 (doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0165779).
- Bangsgaard Bendtsen K.M., Krych L., Sørensen D.B., Pang W., Nielsen D.S., Josefsen K., Hansen L.H., Sørensen S.J., Hansen A.K. Gut microbiota composition is correlated to grid floor induced stress and behavior in the BALB/c mouse. PLoS ONE, 2012, 7(10): e46231 (doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046231).
- An C., Kuda T., Yazaki T., Takahashi H., Kimura B. FLX pyrosequencing analysis of the effects of the brown-algal fermentable polysaccharides alginate and laminaran on rat cecal microbiotas. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2013, 79(3): 860-866 (doi: 10.1128/AEM.02354-12).
- Zhou K. Strategies to promote abundance of Akkermansia muciniphila, an emerging probiotics in the gut, evidence from dietary intervention studies. Journal of Functional Foods, 2017, 33: 194- 201 (doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2017.03.045).
- Glukhova A.A., Karabanova A.A., Yakushev A.V., Semenyuk I.I., Boykova Y.V., Malkina N.D., Efimenko T.A., Ivankova T.D., Terekhova L.P., Efremenkova O.V. Antibiotic activity of actinobacteria from the digestive tract of millipede Nedyopus dawydoffiae (Diplopoda). Antibiotics, 2018, 7(4): 94 (doi: 10.3390/antibiotics7040094).
- Hotchkiss C.E., Shames B., Perkins S.E., Fox J.G. Proliferative enteropathy of rabbits: the intracellular Campylobacter-like organism is closely related to Lawsonia intracellularis. Lab. Anim. Sci., 1996, 46(6): 623-627.
- Corcoran B.M., Stanton C., Fitzgerald G.F., Ross R.P. Survival of probiotic lactobacilli in acidic environments is enhanced in the presence of metabolizable sugars. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2005, 71(6): 3060-3067 (doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.6.3060-3067.2005).
- Ghelardi E., Celandroni F., Salvetti S., Gueye S.A., Lupetti A., Senesi S. Survival and persistence of Bacillus clausii in the human gastrointestinal tract following oral administration as spore-based probiotic formulation. J. Appl. Microbiol., 2015, 119(2): 552-559 (doi: 10.1111/jam.12848).
- Bäuerl C., Collado M.C., Zúñiga M., Blas E., Pérez Martínez G. Changes in cecal microbiota and mucosal gene expression revealed new aspects of epizootic rabbit enteropathy. PLoS ONE, 2014, 9(8): e105707 (doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0105707).
- Combes S., Gidenne T., Cauquil L., Bouchez O., Fortun-Lamothe L. Coprophagous behavior of rabbit pups affects implantation of cecal microbiota and health status. Journal of Animal Science, 2014, 92(2): 652-665 (doi: 10.2527/jas.2013-6394).
- Fekete S. Recent findings and future perspectives of digestive physiology in rabbits: a review. Acta Vet. Hung., 1989, 37(3): 265-279.
- Hu X., Zheng B., Jiang H., Kang Y., Cao Q., Ning H., Shang J. Draft genome sequence of Staphylococcus sciuri subsp. sciuri strain Z8, isolated from human skin. Genome Announcements, 2015, 3(4): e00714-15 (doi: 10.1128/genomeA.00714-15).
- Hermans K., Devriese L.A., Haesebrouck F. Rabbit staphylococcosis: difficult solutions for serious problems. Veterinary Microbiology, 2003, 91(1): 57-64 (doi: 10.1016/s0378-1135(02)00260-2).
- Dakić I., Morrison D., Vuković D., Savić B., Shittu A., Ježek P., Hauschild T., Stepanović S. Isolation and molecular characterization of Staphylococcus sciuri in the hospital environment. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 2005, 43(6): 2782-2785 (doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.6.2782-2785.2005).
- Mayer J., Huhn T., Habeck M., Denger K., Hollemeyer K., Cook A.M. 2,3-Dihydroxypropane 1-sulfonate degraded by Cupriavidus pinatubonensis JMP134: purification of dihydroxypropanesulfonate 3-dehydrogenase. Microbiology, 2010, 156(5): 1556-1564 (doi: 10.1099/mic.0.037580-0).
- Yurimoto H., Hirai R., Yasueda H., Mitsui R., Sakai Y., Kato N. The ribulose monophosphate pathway operon encoding formaldehyde fixation in a thermotolerant methylotroph, Bacillus brevis S1. FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 2002, 214(2): 189-193 (doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2002.tb11345.x).
- Arora P.K., Srivastava A., Singh V.P. Diversity of 4-chloro-2-nitrophenol-degrading bacteria in a waste water sample. Journal of Chemistry, 2016, 2016: 7589068 (doi: 10.1155/2016/7589068).
- Singh B., Singh K. Bacillus: as bioremediator agent of major environmental pollutants. In: Bacilli and agrobiotechnology /M. Islam, M. Rahman, P. Pandey, C. Jha, A. Aeron (eds.). Springer, Cham, 2016: 35-55 (doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-44409-3_2).
- Yoshida K.I., Aoyama D., Ishio I., Shibayama T., Fujita Y. Organization and transcription of the myo-inositol operon, iol, of Bacillus subtilis. Journal of Bacteriology, 1997, 179(14): 4591-4598 (doi: 10.1128/jb.179.14.4591-4598.1997).
- Yoshida K.-I., Yamamoto Y., Omae K., Yamamoto M., Fujita Y. Identification of two myoinositol transporter genes of Bacillus subtilis. Journal of Bacteriology, 2002, 184(4): 983-991 (doi: 10.1128/jb.184.4.983-991.2002).
- Abe Y., Sakoda T., Goto H., Ikeda S., Sukemori S. Cecotrophy contribute methionine and threonine requirements of rabbits. Journal of Pet Animal Nutrition, 2014, 17: 6-12 (doi: 10.11266/jpan.17.6).
- Gidenne T., Kerdiles V., Jehl N., Arveux P., Eckenfelder B., Briens C., Stephan S., Fortune H., Montessuy S., Muraz G. Protein replacement by digestible fibre in the diet of growing rabbits. 2: Impact on performances, digestive health and nitrogen output. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 2013, 183(3-4): 142-150 (doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2013.03.013).
- Martínez-Vallespín B., Martínez-Paredes E., Ródenas L., Moya V.J., Cervera C., Pascual J.J., Blas E. Partial replacement of starch with acid detergent fibre and/or neutral detergent soluble fibre at two protein levels: Effects on ileal apparent digestibility and caecal environment of growing rabbits. Livestock Science, 2013, 154(1-3): 123-130 (doi: 10.1016/j.livsci.2013.02.012).
- Trocino A., García J., Carabaño R., Xiccato G. A meta-analysis on the role of soluble fibre in diets for growing rabbits. World Rabbit Sci., 2013, 21(1): 1-15 (doi: 10.4995/wrs.2013.1285).
- Partridge G.G., Garthwaite P.H., Findlay M. Protein and energy retention by growing rabbits offered diets with increasing proportions of fibre. Journal of Agricultural Science, 1989, 112(2): 171-178 (doi: 10.1017/S0021859600085063).
- Shin D., Chang S.Y., Bogere P., Won K., Choi J.Y., Choi Y.J., Lee H.K., Hur J., Park B.Y., Kim Y., Heo J. Beneficial roles of probiotics on the modulation of gut microbiota and immune response in pigs. PLoS ONE, 2019, 14(8): e0220843 (doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0220843).
- Khan S., Chousalkar K.K. Functional enrichment of gut microbiome by early supplementation of Bacillus based probiotic in cage free hens: a field study. Animal Microbiome, 2021, 3(1): 50 (doi: 10.1186/s42523-021-00112-5).


