Spatiotemporal patterns and trends of the Mongolian plateau wildfires
Автор: Yushan , Chi Wenfeng , Duwala , Zhang Hongyan , Wulantuya , Xu Kunpeng , Bao Yuhai
Журнал: Природа Внутренней Азии @nature-inner-asia
Рубрика: Внутренняя Азия
Статья в выпуске: 4 (5), 2017 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Based on the long-time series MODIS Fire Product, the spatiotemporal distributional patterns of the Mongolian Plateau wildfires were analyzed using ArcGIS. The future trend of the Mongolian Plateau wildfires was also examined with Hurst index. The study provided a scientific basis and reference for aspects such as the development of a secure ecological environment and the international ecological security. Results included: (1) The occurrence of Mongolian Plateau wildfires shows an upward trend in recent years, with alternating peaks and bottoms annually, and seasonal feature is that high occurrence in spring and autumn, low occurrence in summer and winter. (2) The wildfires of the Mongolian Plateau were also found to have a concentrate distribution, indicating that such behavior was not in a random process. Instead, certain factors may have contributed to their occurrence. (3) About 2/3 of the total burned area were in Mongolia, which located mainly in the grassland region near the eastern border, and in the forest and grassland region in the north. (4) The wildfires at the forest-grassland boundary area between eastem Mongolia and Inner Mongolia were found to be more persistent, while those at the area between the central north Mongolia and the Greater Khingan Mountains area in Inner Mongolia were found to be less persistent.
Satellite remote sensing, trend analysis, mongolian plateau
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148317991
IDR: 148317991 | УДК: 504.06(517.3) | DOI: 10.18101/2542-0623-2017-4-13-25
Текст научной статьи Spatiotemporal patterns and trends of the Mongolian plateau wildfires
Globally, more than 30000 ha of forest and grasslands were destroyed by wildfire annually, creating significant impacts on the ecological environment and economic development [Giglio, Randerson, & Werf, 2013; van der Werf et al ., 2010]. China is one of the countries that is affected severely by grassland wildfire. Worldwide forest and grassland fire increase sharply with the damage it caused in past years. It is difficult to prevent because the dispersity and enormous type of fire. Additionally, a large amount of fire point can not be control in time and eventually cause catastrophes due to out of date equipment [Duwala, 2012]. The Mongolian Plateau is an important ecological barrier for China. However, its arid to semi-arid climate and the delicate ecological condition make it a high-risk area for wildfire. So, studies on the wildfire risk at the Mongolian Plateau were considered to be one of the strategic components for the «Belt and Road, B&R» policy.
Forest fires have a relatively strong spatiotemporal pattern. Hence, identifying the spatial and temporal difference between forest and grassland fire are important in understanding and monitoring the characteristics of the wildfire changes, as well as finding out their spatiotemporal distribution. This can provide the scientific basis for reducing the wildfire risk [Zhang et al ., 2008]. The occurrence of forest and grassland fires was found to be determined by climate conditions, topographic elements and meteorological factors [Yu et al ., 2009]. Forest and grassland fires were also closely associated with anthropogenic factors. Areas with a higher population density were found to be corresponding to a higher frequency of wildfire occurrence [Zhang et al ., 2011]. At the northern border of Inner Mongolia, many potential fire hazards for wildfire were found. About 95% of the fire events were caused by human-related ignitions [Zhang et al., 2010], indicating the driving mechanism for the fire occurrence has important significance for the prevention and control of the forest and grassland fires.
With the development of the remote sensing technology in the 20th Century since the 1980s, researches on large-scale monitoring techniques have become more and more sophisticated [Zhang et al ., 2007]. Studies of the monitoring of fire events based on the remote sensing technology mainly focused on (1) monitoring of the fire sources and the evaluation of the fire events [Wang et al ., 2011]; (2) estimation of the burned area [Chuvieco et al ., 1989]; (3) monitoring of the fire risks [Paltridge et al ., 1988]; and (4) analysis of the spatiotemporal patterns for fire events [Csiszar et al ., 2005].
2. Data and method2.1 Study area
Mongolian plateau, located along with Qilian, Helan and Yin mountain as its south border, Tangnu, Kente as its north border, Altai in the west and Daxinganling in the east. Generalized Mongolian plateau also include a part of Ordos where on the south of Yin mountain and Yellow river, makes it become to a relatively closed inland ecological geographic unit in Eurasian continent [Batunacun,2015]. The study area of this paper, located at 87°50'~ 126°15'N, 37°17~ 53°22E and with an area of 2,720,000 km2, covers the main part of the Mongolian Plateau which includes the whole of Mongolia and the Inner Mongolian Autonomous Region, China (Fig. 1). The topography of the plateau generally experiences a gradual decrease from the west to east, where the hilly areas are dominated in the northwest, Gobi Desert in the southwest and hilly grassland in the central and east. The average altitude of the plateau is around 1580 m. The study area is also located at the mid-latitudes and is characterized by a significant change in the altitude of the sun throughout the year. Differences in temperature around the year are also drastic, typically with a long and cold winter and a short and warm summer. The climate changes from a humid to sub-humid climate in the cold-temperate mountainous zone in the north, to a sub-humid to sub-arid climate in the cool-temperate zone in the central area, and then an arid climate in the cool-temperate zone at the center, and to a semi-humid to semi-arid climate at mountainous and plain areas of the cool-temperate zone in the south. Being affected by the water vapor from the Arctic Ocean in the north and the Pacific Ocean in the east, the annual precipitation of the Mongolian Plateau is around 300-400 mm. A gradual decrease in precipitation is also observed from north to south and from east to west. The annual precipitation in the Gobi Desert area to the southwest of the Mongolian Plateau is around 100 mm. Due to the effect of the climate and the soil properties, grassland types of the Mongolian Plateau are found to exhibit the following sequence from northeast to southwest: forest, meadow steppes, typical steppes, desert steppes, stepped deserts and deserts. Further, the ecosystem is delicate, and the occurrence of fire hazards is recurrent. The state of the Mongolian Plateau ecosystem can seriously influence the environment of the entire North China and Northeast Asia.
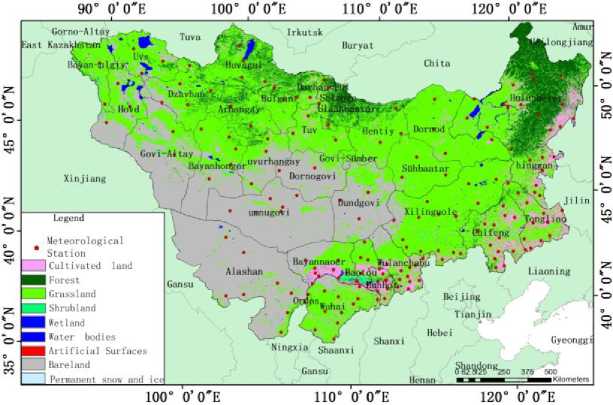
Fig. 1. Location map of study area and the meteorological stations
2.2 Preparation of data
This study involved the usage of specialized data such as fire source, land use/cover information and basic geographic information etc. obtained through data requests and network download. In particular, the data for fire source were obtained from the 6260 images from the Level-3 MODIS standard product — MOD14A1 (Terra) and MYD14A1 (Aqua) during 2000–2015. The spatial resolution of the product is 1 km, while its temporal resolution is 1 day. Firstly, a set of pretreatment of the MODIS data was performed, i.e. the Fire Mask dataset MOD14A1 (Terra) and MYD14A1 (Aqua) was being divided into 10 levels (Table 1) and the pixels with value 7, 8, and 9 were extracted. Then, the MOD13A3 product, which had the same monitoring period as that of the fire source dataset, was downloaded from the NASA website . Finally, land use/cover data was obtained through the global 30 m surface coverage dataset provided by the National Geomatics Center of China .
Tab. 1. Pixel classification of the Fire Mask (MOD14A1/MYD14A1)
|
Digital Number |
MOD14A1/MYD14A1 |
|
0-2 |
Untreated (input error or other reasons) |
|
3 |
Water |
|
4 |
Cloud |
|
5 |
Burned area |
|
6 |
Unknown |
|
7 |
Low-confidence fire |
|
8 |
Medium-confidence fire |
|
9 |
High-confidence fire |
2.3 Methodology
Hurst Index is an index for determining whether the time series data are random walks or biased random walks [Chen et al ., 2005]. The index was first introduced by an English hydrologist, Hurst, and was soon widely applied in hydrology, economy, meteorology, and geology, etc. [Xu, 2002]. This study focused on the aeolian soil erosion and vegetation change through constructing a long time series dataset. The equations are as follow:
For the long time series dataset:
§(t)g§(1), §(2), ••■§(n) (1)
Defining the mean sequence:
Т
§ > т = - £ § ( t ) т = 1,2,..., n (2)
Т t = 1
Process parameters such as cumulative deviation, range and standard deviation were involved in obtaining the index. The equations are as follow (Xu, 2002):
t
X ( t ,т ) = £ ( § ( u ) - § > т ) 1 < t < Т (3)
u = 1
R ( т ) = max X ( t , т ) - min X ( t , т ) т = 1,2,..., n 1< t <Т 1< t <Т
Т
5 ( т ) = - £ ( § ( u ) -§\ )2
L t u = 1 J
R (т ) ^ R = Д у R (t ) .
5 ( t ) 5 Т u ^1 5 ( t )J
t = 1,2,
n
H = slope (In T ,ln )
0.5 < H < Irefers to the persistence of the series;
0 < H < 0.5, refers to anti — persistence of the time series.
where , X ( t,T ) is the cumulative deviation ; R ( t ) the range ; 5 ( t ) the standard deviation ; slope (In t , In R15 ) the least square fitting ; H the Hurst index 0
3. Characteristics of the spatiotemporal changes of the Mongolian Plateau wildfire 3.1 Analysis of the characteristics of the spatial changes of the Mongolian Plateau wildfire
By performing an overlay analysis by superimposing the spatial distribution map of the Mongolian Plateau fire sources onto the land use map and administrative map from 2000–2015, it is found that: (1) The fires of the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region were distributed in the eastern and southern parts of the region. The fire at the cultivated land in the east and in the south was caused by the stubble burning practices during spring and autumn. Large area of grasslands such as meadow steppes, typical steppes, and desert steppes was common at the Xilingol League and Hulunbuir city Inner Mongolia. Grassland fires were mainly found in the meadow steppes at the eastern
3.2 Characteristics of the temporal changes of the Mongolian Plateau wildfire
Inner Mongolia and at the typical steppes at the central Inner Mongolia, while forest fires were found at the forest area of Greater Hinggan mountains at the Central Hulun-buir and Western Hinggan League. (2) The fires of Mongolia were mainly distributed at the eastern Mongolia grassland area at the Chinese-Mongolia border and in the grassland and forest area at the northern part of Mongolia.
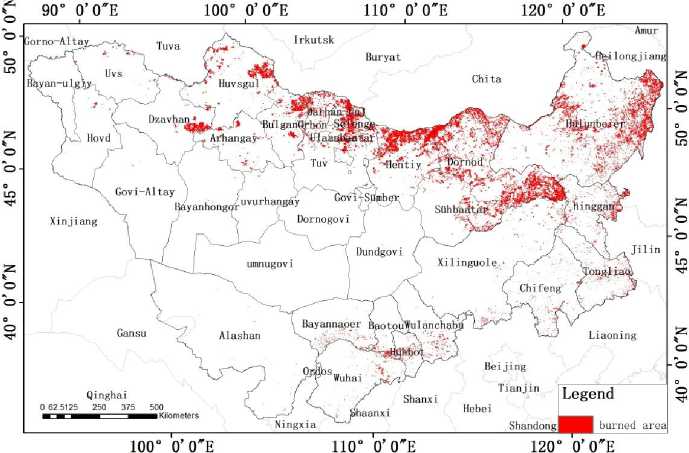
Fig. 2. Spatial pattern of the burned area from 2000–2015
By processing the burned area products derived from remotely sensed data in the period of from 2000–2015 using the grid computation method, the burn frequency map of the Mongolian Plateau was obtained (Fig. 3). Results indicated that (1) the area with a lower burn frequency (burn frequency ≤2) in the past 16 years was around 120, 130 km2, where 37,62% of the burned area was distributed in the eastern and southern part of the Inner Mongolian Autonomous Region, and 62,38% was distributed in the grassland area of eastern Mongolia and in the forest and grassland area of northern Mongolia; (2) the area with medium burn frequency (burn frequency = 3–5) was around 17,712 km2, where 31,92% of the burned area was distributed at the Inner Mongolian Autonomous Region, and 68.08% in the grassland area of eastern Mongolia and in the forest and grassland area of northern Mongolia; (3) the area with high burn frequency (burn fre-quency≥6) was around 1,738 km2, where 41,6% of the burned area was distributed at the Hulunbuir, Hinggan League and Xilingol League of the Inner Mongolian Autonomous Region, and 58,4% in the grassland area of the Dornod Province of Mongolia and in the forest area of the Zavkhan Province, Arkhangai Province, Bulgan Province, Selenge Province, Khentii Province, Töv Province and the Khövsgöl Province of north Mongolia.
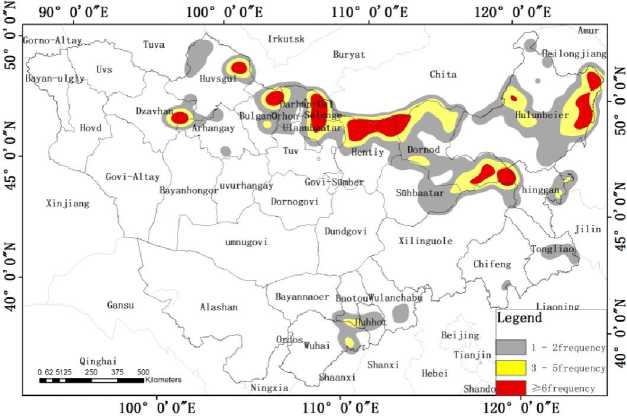
Fig. 3. Distribution map of burn frequency at the Mongolian Plateau from 2000–2015
By overlaying the fire source data and land use data, the following characteristics of the temporal distribution of the Mongolian Plateau fire sources were found (Fig. 4): (1) The largest burned areas for the different land use types were found to be occurring in spring every year, while the smallest burned areas were found in winter; (2) There exhibits a significant increase in agricultural burned area after 2013. The largest burned area was found in March, 2015 with an area of 1799 km2; (3) A significant increase in the forest burned area was found in spring 2003, 2006, 2007, 2008, 2009, 2012 and autumn 2002. The burned area in May, 2009 was found to be up to 2850 km2; Grassland fires were mainly found in March, April, May and June every year. Relatively high frequency of grassland fires was also found in October. In April, 2015, the burned area for the Mongolian Plateau grassland was up to 7260 km2, which is the largest monthly record for grassland burned area in the recent 16 years.
From Fig. 5, it is found that: (1) There exhibited an increasing trend for the burned area in the Inner Mongolian Autonomous Region in the recent five years. From 2011 – 2015, the burned area increased from 25709 km2 to 70950 km2. Of which, the agricultural fire area increased three-fold from 9757 km2 to 37579 km2 during 2011–2015, while that of the grassland fire increased from 9691 km2 to 27542 km2 from 2011–2014 before experiencing a slight decrease of 4290 km2 in 2015. (2) In 2003, the fire area for grassland fire and forest fire was around 25611 km2 and 25545 km2 respectively, which arethe largest values obtained in 16 years. (3) Year 2003, 2006 and 2008 were the years with the relatively larger area of forest fire in the Inner Mongolian Autonomous Region, where the burned area was found to be 25545 km2, 15016 km2 and17105 km2 respectively .
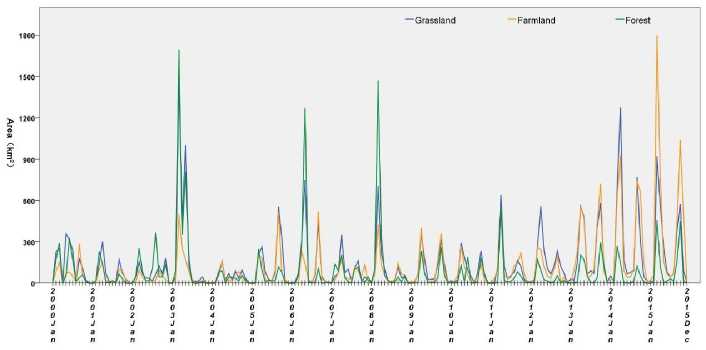
Fig. 4. Burned area for the agricultural fire, forest fire, and grassland fire in the Mongolian Plateau from 2000–2015
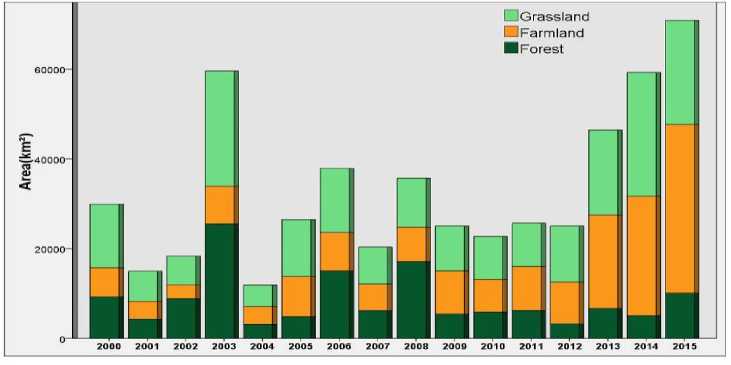
Fig. 5. Burned area for the agricultural fire, forest fire, and grassland fire in Inner Mongoliafrom 2000–2015
Fig. 6 illustrated the annual change of fire in Mongolia from 2000–2015. (1) The burned area in Mongolia was the largest in 2015 (106132 km2) and smallest in 2010 (15362 km2). (2) The wildfires in Mongolia mainly occurred in grassland, with an average annual burned area of 42441 km2. In 2002, 2007 and 2012, the burned area for grassland was significantly higher than the average value, where the burned area of 59299 km2, 57288 km2, and 67224 km2 was recorded respectively. In 2015, the burned area for grassland in Mongolia was around 91076 km2, which doubled the average area. (3) The burned area by forest fire in Mongolia was relatively larger during the three-consecutive years from 2007–2009, where a burned area of 23115 km2, 35455 km2 and 31136 km2 was recorded respectively.
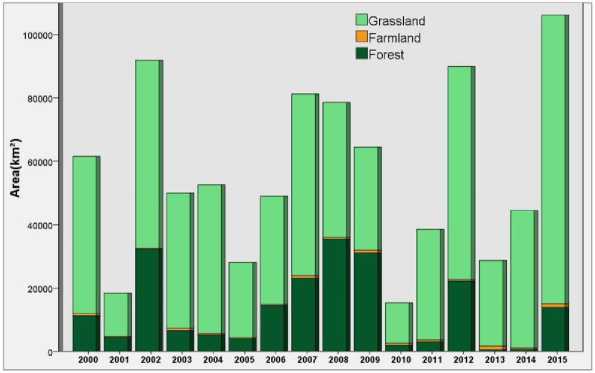
Fig. 6. Statistics of the burned area for the agricultural fire, forest fire, and grassland fire in Mongolia from 2000–2015
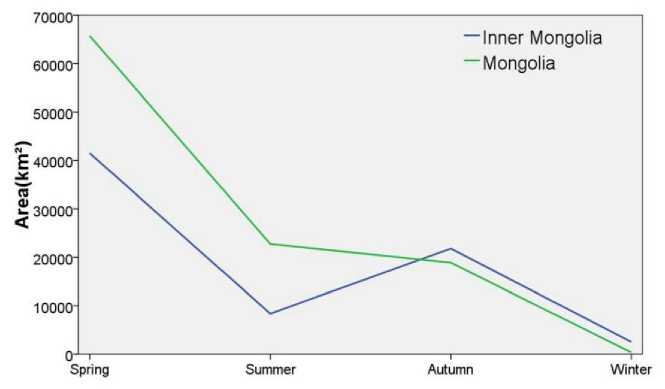
Fig. 7. Average seasonal value for the Mongolian Plateau wildfire from 2000–2015
Fire management in the Mongolian Plateau in spring was relatively difficult due to its characterized dry and windy climate with low precipitation, the production practices of wasteland burning and stubble burning, and the inconvenient transportation and low population density in the grassland and forest area. Hence, most of the fire occurring at the Mongolian Plateau was in spring. The average burned area in the Inner Mongolian Autonomous Region in spring was 41471 km2, while the average burned area in Mongolia in spring was 1,5 times of that the average burned area in the Inner Mongolia. In summer, the increase in precipitation in the Inner Mongolian Autonomous Region lead to a higher humidity of the combustibles and in the air. It is therefore not easy for a wildfire to happen. The burned area also decreased to below 10000 km2. The burned area in Mongolia in summer was around 23000 km2, which is a lot smaller than in spring. In autumn, due to the increase in the amount of combustibles after plant defoliation, a lower water content in the combustibles, a lower humidity and the practice of stubble burning, the burned area in the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region increased again to 20000 km2. In winter, due to the presence of snow on the surface of the Mongolian Plateau, the wildfire in the region was basically absent.
4. Characteristics of the future trend
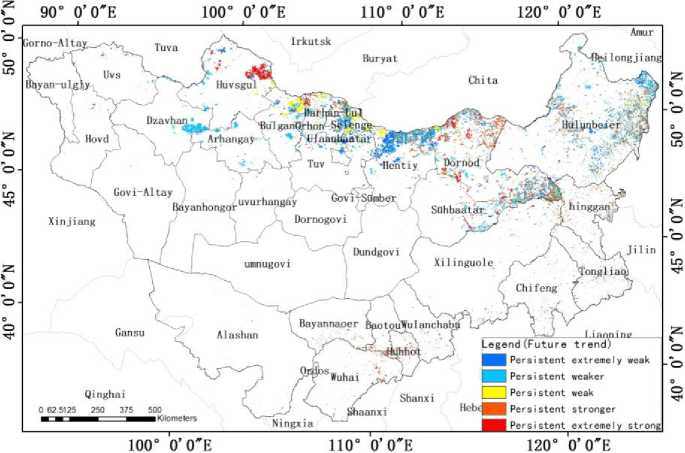
Fig. 8. Distribution map of the probability for wildfire occurrence in Mongolian Plateau represented by the Hurst index
The probability index (Hurst index) for the forest and grassland wildfire in Mongolian Plateau was around 0,0001–0.9, with an average value of 0,39. The percentage of the burned area with a strong persistent future trend was around 32,68%, while that with a weak persistence was around 67,32%. Due to the interaction between the human factors and the natural factors, and the fact that the wildfires occurrence affected by human factors (e. g. stubble burning in cultivated lands) had a stronger persistence, the probability of wildfire occurrence in the future was found to be higher in the transition zone between the forest and grassland. From the spatial structure point of view, a higher ratio of Mongolian Plateau wildfire was found to occur within Mongolia. The border area between eastern Mongolia and Inner Mongolia that lay within the forest — grassland transition zone was found to have a higher wildfire persistence, while the area at the central north Mongolia and at the Greater Khingan Mountainous region in Inner Mongolia that was dominated by forest was found to have a lower wildfire persistence. The probability for forest and grassland wildfire in Mongolia was around 1,5 times of that for Inner Mongolia.
5. Discussion and conclusion
The following conclusion was obtained from this study:
( 1 ) There exhibits a significant temporal dynamic pattern for the Mongolian Plateau wildfires. The peak and trough of the burned area were found to exhibit a significant alternating pattern every year, with a corresponding increasing trend also observed. This is especially true as the agricultural burned area in Inner Mongolia had significantly increased after 2013, and a peak burned area of 106132 km2 was found in 2015 in Mongolia. There is also a clear seasonal change for the Mongolian Plateau wildfire, where a higher frequency of wildfire occurrence was observed in spring and autumn, and a lower frequency for summer and winter. Most of the wildfires for the Inner Mongolian Autonomous Region and that of Mongolia occurred in spring. Due to an increase in precipitation and a high humidity of the atmosphere, soil and combustibles in summer, the number of wildfires in the Inner Mongolian Autonomous Region decreased. In autumn, as there w ere stubble burning practices and decrease in water content in the combustibles, the number of wildfire events increased. In winter, the condition for the wildfire occurrence cannot be met due to the presence of the snow coverage. On the other hand, the number of wildfires in Mongolia did not exhibit such a big difference between summer and autumn. There were also basically no wildfire in winter in Mongolia.
( 2 ) From the analysis of wildfire spatial distribution and burned frequency using the ArcGIS software, aggregate distribution was found to be the mode of distribution for the wildfire in the Mongolian Plateau in the recent 16 years. This indicated that the grassland wildfire occurrence was not in a random process. Certain factors may have contributed to the occurrence. The burned rate for the grassland in the Inner Mongolian Autonomous Region of China was found to be much lower than that of the Mongolia. The burned area in Mongolia constituted of 2/3 of the total burned area. The fires of Mongolia were mainly distributed in the eastern Mongolia grassland area at the Chinese-Mongolia border and in the grassland and forest area at the northern part of Mongolia. The fires of the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region were distributed in the eastern and southern parts of the region. From the view of location points, the largest burned area was the Dornod Province of Mongolia, where it constituted 24,4% of the total burned area. This is followed by that of Hulunbuir in the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, where it constituted 23,88% of the total burned area.
( 3 ) From the analysis of the future trend of the Mongolian Plateau fire using the Hurst index, it is found that the wildfires at the forest-grassland boundary area between the Inner Mongolia and Mongolia were found to be more persistent, while those at the area between the central north Mongolia and Greater Khingan Mountains area in Inner Mongolia were found to be less persistent.
This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China
(No. 41461102), and Science and technology plan projects in Inner Mongolia multi-scale Mongolia plateau grassland fire risk comprehensive evaluation technology research based on 3S(No. 201502113), and Arxan forest disasters monitoring and early warning and emergency management system research
Список литературы Spatiotemporal patterns and trends of the Mongolian plateau wildfires
- Giglio L., J.T. Randerson and G.R.V.D. Werf, analysis of daily, monthly, and annual burned area using the fourth-generation global fire emissions database (GFED4). Journal of Geophysical Research Bio-geosciences, 2013. 118(1): 317-328.
- ZHANG Ji-quan, ZHANG Hui, TONG Zhi-jun, SONG Zhong-shan, WU Xiao-tian. Loss assessment and grade partition of grassland fire disaster in Northern China [J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2007. 16(6): 121-128.
- YU Wen-ying, ZHOU Guang-sheng, ZHAO Xian-li, XIE Yan-bing, JIA Qing-yu. Characteristics of forest fire and its controls in Daxing'anling Mountains, Heilongjiang province [J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2009. 25(4): 1-5.
- Zhang Dongyou, Feng Zhongke, Li Yiqiu, Zhang. Remote Sensing Estimation of Forest Net Primary Productivity in Heilongjiang Province with C-FIX Model [ J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2011. 47(7):34-37.
- Zhang Yanping, Hu Haiqing. Climatic Change and Its Impact on Forest Fire in Daxing anling


