Strategic management as a factor of small and medium-sized entrepreneurship functioning enhancing
Автор: Dorogovtsev Anatoly Pavlovich, Zargaryan Arshak Mesropovich
Журнал: Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast @volnc-esc-en
Рубрика: Regional economy the issue theme: small entrepreneurship development
Статья в выпуске: 2 (6) т.2, 2009 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The article is devoted to actual problems of small and medium-sized entrepreneurship’s development. Characteristics of the main directions of small and medium-sized businesses at the federal and regional levels development is given, the strategic management of small and medium-sized businesses features are identified.
Strategic management, small and medium entrepreneurship, efficiency
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147223131
IDR: 147223131 | УДК: 334.012.63/.64(470.12)
Текст научной статьи Strategic management as a factor of small and medium-sized entrepreneurship functioning enhancing
UDC 334.012.63/.64(470.12)
Strategic management as a factor of small and medium-sized entrepreneurship functioning enhancing
The article is devoted to actual problems of small and medium-sized entrepreneurship’s development. Characteristics of the main directions of small and medium-sized businesses at the federal and regional levels development is given, the strategic management of small and medium-sized businesses features are identified.
Strategic management, small and medium entrepreneurship, efficiency.
Anatoly P.
DOROGOVTSEV
Technical University
Arshak M.
ZARGARYAN postgraduate student of Vologda State Technical University
Academic research in the field of small and medium-sized businesses have begun to develop recognizing the importance of this sector as a major source of job creation and economic growth, which was especially pronounced in the 90s years of the twentieth century. Progress in the theoretical development of the strategic management concept in small and medium enterprises is largely attributable to a significant contribution of this sector in the maintenance of the economy and the welfare of the population in most countries of the world.
While a substantial amount of research related to strategic management, and strategies analysis was done for large corporations, strategic management concerning small and medium business almost has not been developed until recently. Traditional strategic management researchers have faced the need to define this concept in terms of the formation of plans, as the main objective was to develop an optimal strategy for large organization parameters.
Meanwhile, economically developed countries’ statistics shows that each year tens of thousands of small and medium-sized enterprises go to “self swimming”. However, almost as many enterprises curtail their business with an enviable constancy, and the only a few are able to stay on the market for more than a few years [1].
There are quite simple ideas and concepts that can greatly increase the chances of success of any enterprise. The concept of small and medium enterprise has come to Russia from Western countries, where it has begun to emerge as the main pillar of the economy. Presumably, massive lay-offs in large corporations could be one reason for this phenomenon, when their redundant workers were subsequently employed in small and medium enterprises [3].
In the Russian Federation Small and Medium Business began developing relatively recently. If in the middle of 1980s there were about 40 thousand enterprises and they were all public, by 1994 the number of registered companies has reached 900 thousand, 90% of which were private. In 1991 – 1992 with the advent of the Russian Federation laws “On property in the Russian Federation” and “On enterprises and entrepreneurial activity” procedure for registration simplified.
If the process of formation and development of small and medium-sized businesses in foreign countries was held for decades, in Russia the million-strong class of businessmen-owners who have the desire and ability to work has been formed just for a few years (table 1).
The data of table 1 shows that in 2007 compared with 2000 the number of small businesses has increased by 255 thousand; average number of people employed in them has increased by 2 million people. An important factor in enhancing the role of small enterprises in the economy is the sharp increase in fixed assets investment, indicating an increase of material and technical base of small businesses as an essential condition for their further development. Thus, investment in fixed assets of small businesses in 2007 compared to 2000 increased 5 times and amounted to 22,7 mln. rubles per one small enterprise.
In the past few years, small and medium businesses the Vologda region is developing quite stable. Comparison of the Vologda region to other NWFD regions (excluding St.-Petersburg) by the number of small and medium-sized enterprises shows that it takes a middle position in the overall ranking table – 5th place out of 9. The size of small businesses in the region is larger than in the NWFD regions. One such enterprise in the Vologda region employs, on average, 15 people, in St.-Petersburg – 6 people. Major indicators of small and medium-sized businesses is shown in table 2 .
Table 1. Basic indicators of small enterprises activities in Russia
|
Indicators |
Year |
||||||
|
2002 |
2003 |
2004 |
2005 |
2006 |
2007 |
2007 to 2002 |
|
|
The number of small businesses (at the end of the year), thousands |
882,3 |
893,0 |
953,1 |
979,3 |
1 032,8 |
1 137,4 |
28,9% |
|
The average number of employees (excluding external workers), thousands of people |
7 220,3 |
7 458,9 |
7 815,1 |
8 045,2 |
8 582,8 |
9 239,2 |
28% |
|
Average number of external workers, thousands of people |
502,9 |
546,9 |
608,6 |
630,4 |
656,5 |
640,2 |
27% |
|
Average number of employees who performed work on contracts of civil law, thousands of people |
252,9 |
249,0 |
243,5 |
258,1 |
229,3 |
277,9 |
9% |
|
Investment in fixed capital, bln. rubles |
51,0 |
67,3 |
99,2 |
120,5 |
171,3 |
259,1 |
5 times |
|
Small businesses turnover, bln. rubles |
– |
– |
– |
9 612,6 |
12 099,2 |
15 468,9 |
100% |
|
The number of small enterprises per 10 thousand people |
61 |
62 |
66 |
69 |
73 |
80 |
31% |
Source: Small business in Russia 2008: a statistical digest / Rosstat.
Table 2. Major indicators of small and medium-sized businesses in the Vologda region
|
Indicator |
2005 |
2006 |
2007 |
2008 |
2008 to 2005, % |
|
Number of employees in small and medium-sized businesses, thousands of people |
145,0 |
156,0 |
160,0 |
169,2 |
16 |
|
The turnover of small and medium-sized businesses, bln rubles |
55,5 |
69,8 |
79,6 |
72 |
29 |
|
Source: Business and power: regional business magazine. – 2009. – № 2 (17). |
|||||
Being inferior to other NWFD subjects by the number of small and medium-sized businesses the Vologda region holds a leading position in terms of number of employees at one company.
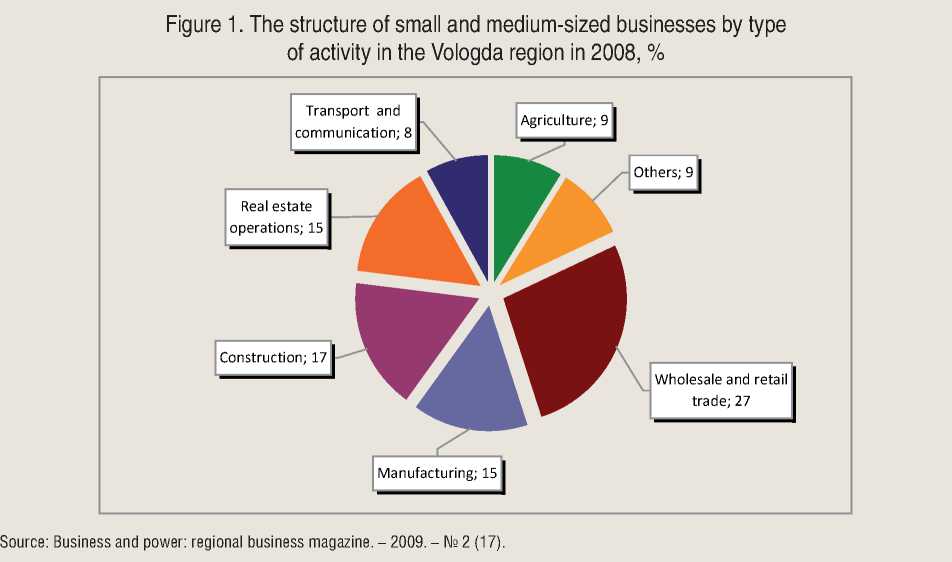
Sectoral distribution of main activities in the Vologda region has a slight difference from the distribution in the Russian Federation. Small and medium-sized businesses in the region mainly focus on wholesale and retail trade (the region – 27%, Russia – 32,1%), real estate, rental and service delivery (the region – 15%, Russia – 13,7%; fig. 1 ).
Another feature of the small and mediumsized businesses in the Vologda region is the dominance of individual entrepreneurs (58% in the structure of employment) over small and medium-sized enterprises (42%). The average number of individual entrepreneurs in the region is 32,7 people per 1 thousand inhabitants. This is higher than in Russia (24,1) and St.-Petersburg (14,3), which is connected with the taxation peculiarities and registration simplification. Individual entrepreneurs specialize in wholesale and retail trade (45%). Their share in transport and communication is 16,5%, in the provision of public utilities, social and personal services – 10%. Employment of individual entrepreneurs in manufacturing and agriculture is fixed at 7,2 and 6% respectively. Individual entrepreneurs, in contrast to the small and medium-sized enterprises have already mastered the provision of public utilities, social and personal services.
The issue of strategic development of these enterprises, as claimed by some researchers, is that the formal procedures of strategic management are inappropriate in the context
of small and medium-sized enterprises. They have neither the management nor the financial resources that could be used for strategic management techniques (Cragg and King, 1988; Shrader, 1989; Watts and Ormsby, 1990). A number of studies have concluded very little relationship of strategic planning and operations of small and medium-sized enterprises (Unni, 1981; Robinson; 1984; Orpen, 1985). These studies indicate the dual relationship of planning and operation of small and medium-sized enterprises. It is anticipated that planning value is reduced by such factors as uncertain activities, management competence and companies’ development stage.
Small and medium enterprises is a relatively new area of research within the framework of strategic management (Chell, 2001). According to Hanlon and Scott (1995), the model of rational planning is the most promising in the development of small businesses strategies. Planning is often viewed as the company’s key to the success, since it reduces uncertainty, warrants alternatives consideration and helps managers to interact with investors. Thompson argues that entrepreneurs should have the ability to think and act strategically. Strategic management is seen as a necessity, it is recognized that the development and implementation of business strategies in small and medium-sized firms are different from similar processes in large companies.
In our opinion, the publications devoted to small businesses interpret strategic management without reflection of its essence. The concept of strategic management is applicable to small and medium-sized businesses. However, it is necessary to take into account a number of specific characteristics of this sector of the economy, which should leave their mark on the development strategy of such organizations.
So, what is the difference between the process of strategic management in small and medium enterprises and a similar process in large companies? The process of strategy forming in large companies comprises four main stages: 1) strategic analysis, 2) identification of strategic alternatives, 3) strategies developing and 4) strategy implementation [3, 5].
At the stage of strategic analysis both external and internal factors to development of the company or hindering it are taken into account. A comprehensive analysis of the company is made: its strengths and weaknesses, potential and internal reserves, the financial situation. The analysis allows presenting the company’s present situation, and drawing the line, following which it will be able to use its capabilities. This phase is needed to determine the company’s readiness to strategic action.
“Strategic alternatives” stage includes the definition of the mission and the goals, finding ways and means to achieve them. This stage is crucial, because by defining the goals of development, the company is focusing its resources on the implementation of those operations, which correspond to a given direction. Alternative strategies and primary economic rationale for the effectiveness of each of the proposed alternatives are also made here.
The strategy development is the development of the most appropriate choice, formulating strategies and developing business projects, plans and programs for its implementation. Stage of the strategy implementation is carried out using previously developed plans, linked to each other and corresponding to the strategy content in all major functional areas of business enterprise.
After completion of the strategy implementation a monitoring mechanism to assess the impact of implemented strategies in the enterprise is established. This mechanism should include a definition of criteria for results evaluating, comparing actual performance with targeted, analysis of variances between actual and targeted rates, adjustments to the strategy if necessary [2].
Logical framework of strategy development for small and medium-sized businesses and
Figure 2. The scheme of strategic management for small and medium business
1.Development of main business idea

2а. Business environment study
2б. Possible opportunities and threats detection

4. SWOT-analysis

3а. Internal factors evaluation
3б. Personal goals evaluation

No
8. Comparing actual and targeted activities
7. Business plan realization
6. Mission, goals Yes and business plan ^---- development
5. Is business possible?
its implementation is as follows (fig. 2). Small and medium-sized businesses do not fit into the strategic management process including the study of the surrounding business environment, building, strategy implementing and its results evaluating. These companies must have a new mission, goals and new strategies and policies which reflect the correlation of external opportunities and threats to internal strengths and weaknesses. Differences in procedures for the development strategy for small and medium-sized businesses from a similar procedure for the large business is that the process of strategy development for small and medium businesses requires a definition of the principal possibility of business constructing in the initial stage. While for large companies strategic management is one of the components of the controlling mechanism and there are no questions concerning the possibility of the organization’s functioning as a whole. In other words, the strategic management in small and medium enterprises should react to more quickly to changes in the external environment, i.e. to be more detailed. Therefore a modi- fied version of strategic management model is proposed, which is more in line with the “new entrepreneurial business”.
The “new entrepreneurial businesses” is understood as a new level of development of business relationships that are taking place in Russia today. These relationships are different from those that were in the country in mid-1990's.
The model of strategic management for small and medium-sized businesses in every industry has specific characteristics. However, the proposed universal model, with certain adjustments fits for all small and medium-sized businesses.
In the stage phase the basic idea of business is developed. In the second and third stages organization’s internal and external environment is studied, both the possibility and threats from the external environment are identified. The fourth stage is devoted to an analysis of strategic factors to the application of SWOTanalysis. At the fifth stage, it is decided whether or not to proceed. If it seems that the main idea of the business can be carried out effectively, it should be continued to operate. Otherwise, it is necessary to abandon further development of ideas, until there is no change in strategic factors. In case the feasibility of the main ideas of the business is assessed as achievable, a mission, objectives, strategies and policies are developed at the sixth stage. At the seventh stage the implementation of business plan using the plans and actions is taking place. Finally, at the eighth stage the actual performance is compared to the planned. Dependent to the extent that the actual results differ from the planned one should revise the mission, its objectives and strategies.
A distinctive feature of the proposed model of the strategic management system in small and medium enterprises is the clarity and specificity of action, which increases their efficiency.
Thus, the system of strategic management is a key element of successful operation, not only large corporations but also small and mediumsized enterprises. The presence of a strategic approach helps small and medium enterprises to build competence in a continually changing external environment, which will undoubtedly have a positive effect on activity.
The proposed model of strategic management in small and medium-sized enterprises is more adapted to the realities of this sector of the economy and serves as a universal, simplified model, by means of which one can start to build a system of strategic management.
Список литературы Strategic management as a factor of small and medium-sized entrepreneurship functioning enhancing
- Analoui, F. Strategic management in small and medium enterprises: a textbook for university students/transl. from English. F. Analoui, A. Karami. -Moscow: UNITY-DANA, 2005. -400 p.
- Barinov, V.A. Strategic management: training manual/V.A. Barinov, V.L. Harchenko. -M.: INFRA-M, 2006. -285 p.
- Karpov, A.E. Strategic management and effective development of business/A.E. Karpov. -M.: Outcome and Quality, 2005. -512 p.
- Lapusta, M.G. Small business: a textbook/M.G. Lapusta. -M.: INFRA-M, 2008. -685 p.
- Thompson, A.A. Strategic Management: Concepts and situations for analysis/A.A. Thompson, A.J. Strickland: transl from English. -12th edition. -M.: Williams, 2006. -928 p.
- Business and power: regional business magazine. -2009. -№ 2 (17)


