Strategic management of key development potential of split-level territorial socio-economic systems
Автор: Gainanov Damir Akhnafovich, Biglova Guzel Fatikhovna, Ataeva Aisylu Garifullovna
Журнал: Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast @volnc-esc-en
Рубрика: Socio-economic development strategy
Статья в выпуске: 2 (50) т.10, 2017 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The authors have elaborated methodological principles based on the nature of modern relations characterized by high degree of “financial” and “knowledge” economy integration, identified factors in the territory’s economic development capacity (financial, labor, innovation). The choice is explained by the fact that scientific innovations in all socio-economic systems set the dynamics of their development regardless of their level of functioning; financial capacity is regarded as a prerequisite for expanding the territory’s investment process which increases economic activity of business entities; employment potential of territorial social-economic systems (hereinafter TSES) is moderated by the level of innovation and investment which influence labor quality and efficiency. The authors also propose the idea defining the fundamental framework for strategic management of key development potential of split-level territorial socio-economic systems. The basic idea of the concept is that the development strategy of territorial socio-economic system is based on activation of key development potential of a particular territory, the transformation of which by using appropriate technology and competencies of new resources ensures the achievement of qualitative parameters of economic growth and the quality of life in terms of interest alignment of economic actors...
Strategic management, territorial socio-economic system, economic development, territory's development potential, interest alignment, national security
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147223936
IDR: 147223936 | УДК: 332.145 | DOI: 10.15838/esc.2017.2.50.4
Текст научной статьи Strategic management of key development potential of split-level territorial socio-economic systems
Over the past two decades, the role of strategic management in Russia, given the varied and multi-directional vectors of different socio-economic institutions, remains significant. However, despite the long period of its formation and development, the issue of strategic management such as its quality, still remains relevant. For this reason, the goals and objectives of strategies under development re main elusive and at times impossible to implement.
Currently, the system of strategic planning in Russia (including regional and municipal levels) is beginning to form on a new basis.
With the adoption of Federal law no. 172
resources”. E. Gorbunov and E. Fi
On strategic planning in the Russian consider it as “economic power”, “economic
Federation” in 2014 [9] the legal principles of strategic planning at the federal, regional and local levels were established together with the powers of the relevant federal and local authorities. However, practice shows that public authorities (mostly regional) and local governments have neither the expertise of quality strategic planning, nor technology for its implementation with the use of scientific techniques.
In the authors’ opinion, one of the most common bottlenecks in most policies is lack of coordination interests of the interested parties (stakeholders) and the issue of determination of key potentials for economic development of territorial socio-economic systems (TSES).
In domestic research studies, a significant number of works is devoted to studying economic potential. Thus, B.M. Mochalov, V.N. Mosin, D.M. Kruk, L.I. Lopatnikov, A.M. Rumyantsev [6] consider economic potential as the total capacity of industries to produce industrial and agricultural products, carry out capital construction, transport cargo, and provide services to the population. B. Plyshevskii, A. Todoseichuk, Y. Lychkin, and A. Tsygichko identify economic potential with categories such as “resources”, “investment”, “investment resources”, “national wealth”, “facilities and potential”; L. Samoukin, O. Kozlova consider it in relation to production relations characteristic of each socio-economic structure, which occur between individual employees, labor groups, and management authorities of an enterprise or an organization, economic sectors as a whole on the full use of their abilities to produce goods and services [6].
The authors consider economic potential as combined capabilities, capacities, unrealized hidden reserves of the economic system which amid the changing conditions can turn from opportunities to resources and be used for the purposes of the socioeconomic system.
In the authors’ view, the concept of TSES capacity development is closely connected with economic potential since the development of a territory without economy is impossible. Strategic management implies the selection of key components from all structural components of TSES development potential, the focus on which will help achieve maximum long-term results given the territory’s limited resources. For example, A.A. Auzan states that if the exhaustion of the country’s oil and gas resources takes place there will remain three basic possibilities of using competitive resources: military and technical, spatial, human potential [3]. From
,xxxdlar'9esx:?
the authors’ point of view, the key TSES potentials are innovative, financial, and labor which in modern conditions provide quality economic growth.
I.M. Tenyakov who studies economic growth provides the following classification: “By interpretation of correlation between economic growth and economic development in the variety of concepts and schools of economic thought it is possible to distinguish two approaches which are: quantitative (linear) and qualitative (cyclically discrete)” [7]. Within the first approach, growth and development do not differ much and are characterized by mainly quantitative indicators (income growth, life expectancy, literacy rate, mortality reduction, etc.). Development is characterized by certain indicators, and its complexity of formalization necessitates the use of a large number of assessment indicators. In turn, economic growth is reduced mainly to income growth (including per capita income) in the long term. The authors focus on the continuous process of economic development and, consequently, on the ability to quantitatively measure and compare economic development parameters over a long historical period. This approach aims at obtaining statistical description of the process of economic development and growth, starting from the industrial revolution or even earlier [1]. Real per capita GDP is normally used for these purposes. It implies data commensurability in both one country for a hundred years or more, and between different countries. Qualitative development parameters recede into the background [7].
The issue of quality economic growth is currently one of the most acute. “With the introduction of the concept quality “economic growth” the contradiction between economic growth (quantity) and economic development (quality) disappeared. National and civilizational development parameters can also be reflected in the indicators of quality economic growth” [7]. The authors agree with this approach; more extensive application of “quality economic growth” will remove the debatable application of economic growth and development indicators in the system of strategic planning.
1these theoretical positions the authors adhering to the concept of continuous development and quality economic growth highlight a number of capabilities which are the most crucial in the structure of modern economic relations. Thus, given the rapid global technological development over the past 30 years, it can be predicted that scientific and technological innovations in all socio-economic systems will define the dynamics of their development regardless of their performance level. Financial capacity of territorial social-economic systems predetermine the capabilities of investment process – the driver of economic activity potential and the indicators charac of economic entities. Innovation and its development are not used as indicators investment, in turn, are mediated by labor quality, its effectiveness is based on labor potential based on the quality of human capital.
Consideration of labor potential as the key one is explained by the fact that “the policy aimed at the development of regions and their inclusion in modernization processes hardly take into account the growth of human of public administration efficiency, the indicators of a viable state” [4].
The process of implementing these potentials, on the one hand, takes place within industrial relations and may be considered as resources; on the other hand, to ensure quality economic growth expanded reproduction is required, which in addition to the resources includes processes as regulators
Targets
Interest coordination
Development potentials
Figure 1. Concept of strategic management of key TSES development potentials
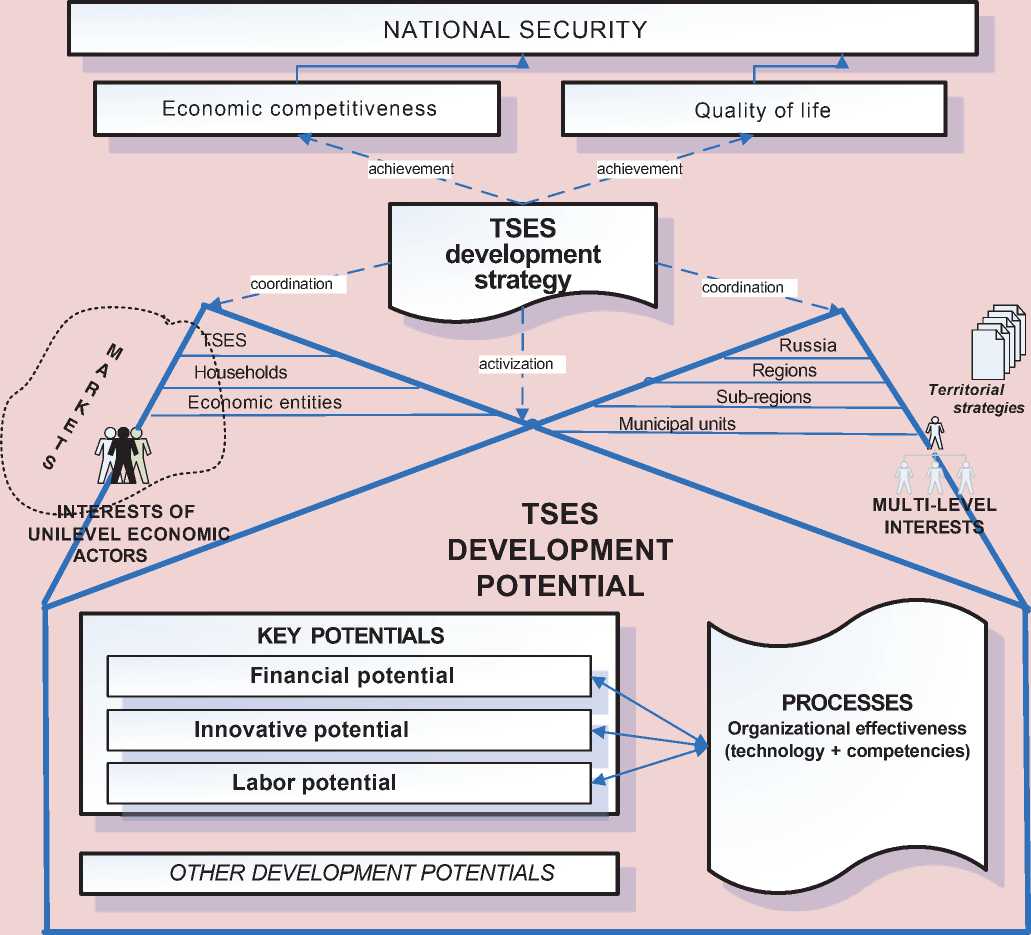
uction relations. In other words, a set into new resources ensures the achievement of financial, innovation and labor potential of qualitative parameters of economic growth forms production capacity, which in modern conditions determines the development of both production and territorial socioeconomic systems.
At the same time, the main scientific problem of strategic planning and management system formation at all economic levels is misunderstanding of the principles of strategic planning and its correlation with basic economic terms: market, potential, interests, resources etc. Quite often playing with economic terms takes place, confusion of definitions without systematic understanding of their correlation.
To solve this problem, the authors propose a concept of strategic management of key development potentials of multi-level TSES, which is a set of methodological principles about the nature of strategic management of TSES development processes, binding the territory’s potential as the basis for its development and the interests of economic actors as the basis for coordinated development aimed at TSES development ( Fig. 1 ).
The main idea of the concept: TSES development strategy is based on implementation of key development potentials of a particular territory, the transformation of which through the use of appropriate technology and competencies and the quality of life based on coordination of interests of TSES economic agents.
The methodological principles of the Concept of strategic management of key TSES development potentials are as follows.
Principle 1. The target of building the system TSES strategic management is to achieve parameters of the country’s national security and its regional projections.
From the standpoint of strategizing, basic subjectivity belongs to “the state” (Federation, region) and local authorities which create conditions for the territory’s sustainable development through a series of measures to ensure national security depending on the prevailing internal and external economic situation in the long term.
According to this, the main purpose of strategic planning is rational distribution of efforts and resources of a relevant TSES for ensuring sustainable socio-economic development and strengthening national security of both the country as a whole and its socio-economic parameters at the regional and local level.
The category of national security is defined by the National Security Strategy of the Russian Federation as the state of individual, social and state security from internal and external threats, which ensures the implementation of constitutional rights determine the ability of TSES to and freedoms of the Russian citizens, decent quality of life and standard of living, sovereignty, independence, government and territorial integrity, sustainable social and economic development [8]. Together with the concept of national interests of the Russian Federation, national security belongs to the country level of TSES organization. However, its structural components (social, informational, environmental, economic, transport, energy and personal security) are projected on sub-national and local levels of territorial organization of the population.
Since the National Security Strategy sets out parameters for assessing the state of national security (life expectancy; per capita GDP; decile ratio; inflation; unemployment, etc.), regional and municipal strategies should also be reflected (with the possibility of influencing determinants). In practice, if multi-level concepts/strategies/programs are compared, first, they do not explicitly reflect national security evaluation indicators, and, second, there is no coherent system reflecting the targets of socio-economic development of territories.
Principle 2. The basis for territory’s development is its capacity, which is a combination of tangible and intangible resources, unique technologies and competencies in the economic system which reproduction and ensure its competitiveness.
The basis of understanding the capacity of
TSES lies in the resource-based approach originally applied in the theory of firms in terms of formation of stable competitive advantages [2]. A significant advantage of the resource-based approach for TSES is the opportunity to link the territory’s potential with the principles of strategic management, namely, the selection and concentration of efforts on priority development areas which determine the project’s competitive advantages. From this point of view, the TSES capacity is a set of tangible and intangible resources, technologies and competencies in the economic system which determine the ability of TSES to expanded reproduction and ensure its competitiveness ( Fig. 2 ).
As can be seen, the basis of potential are basic resources, whish is a set of tangible and intangible assets used to meet social needs of the territory’s economic agents. They can be either explicit (recorded, controlled) or shadow (unrecorded and uncontrolled).
However, the set of resources does not determine its ability to self-development and competitiveness in the long term. It is obvious that in modern conditions the main role in the formation of competitive advantages of both economic actors and territorial systems belongs to the ability to exploit their resources
Figure 2. Logical model of TSES potential transformation in the results of development
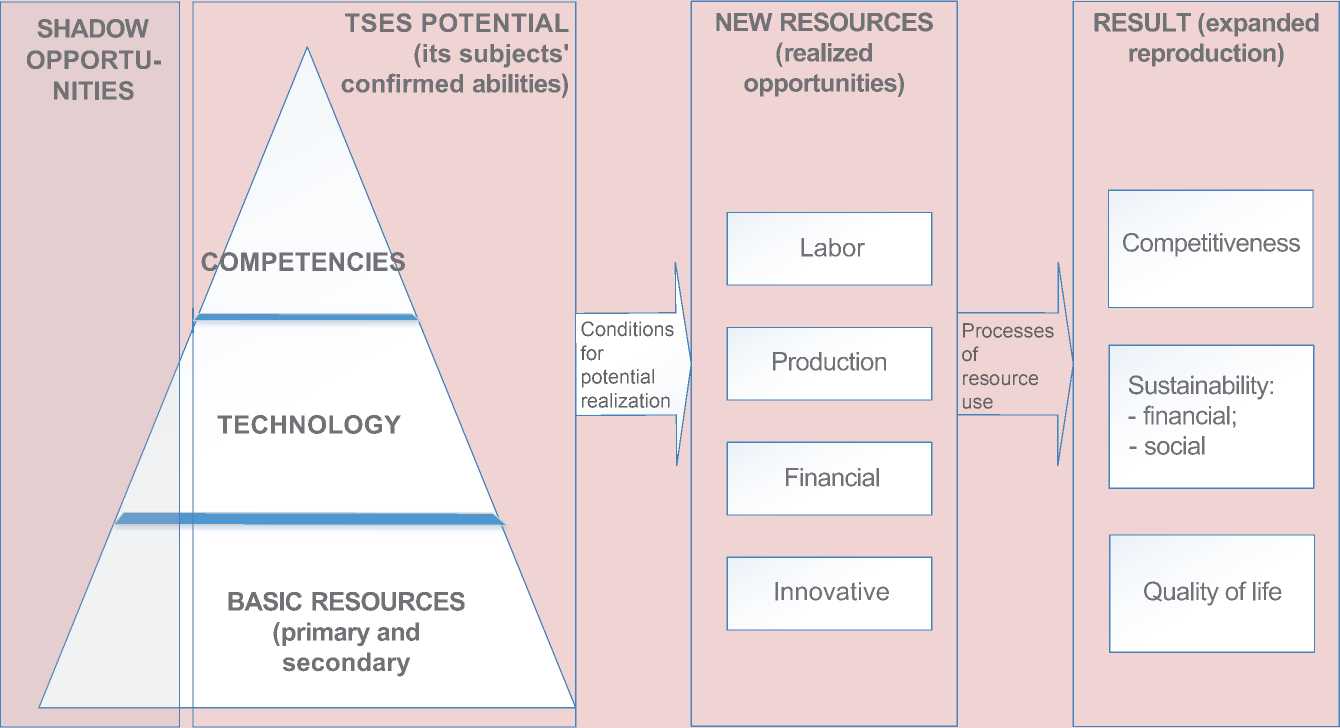
(availability of qualified personnel and high-performance equipment) rather than to the resources themselves (which in some cases do not even have much value).
Technology as a component of the system of TSES potential implementation is a set of organizational and production techniques and tools for transforming basic resources into new ones in their quantitative and qualitative terms. Competence is an important element of the system – is represents organizational and professional skills required to transform basic resources into new ones by using appropriate technologies.
In system interaction, all these elements are mediated by processes which influence the transformation of TSES potentials into qualitatively new resources.
The purpose for using resources is to ensure expanded reproduction of the system to achieve parameters of national security, social and financial sustainability and quality of life as an indicator of the territory’s social development.
Principle 3. The choice of the territory’s development vector is determined according to coordination of interests of economic actors and different TSES levels within a unified system of strategic planning in the Russian Federation.
Federal Law “On strategic planning in the Russian Federation” implies formation of a three-level system of strategic documents. At of coordination in the framework o the regional level, the following strategic private partnership strategies of major documents are being developed: strategy for socio-economic development (hereinafter SED) of the region; region’s SED forecast; long-term budget forecast of the region; region’s medium-term SED forecast; action plan for the implementation of the region’s SED strategy; regional state programs; regional scheme of territorial planning [9].
Such a large array of documents implies consideration of interests of various economic actors: enterprises, households, federal, regional and local authorities. Interests of economic agents are defined as formalized needs of economic actors for any good, which is the motivation for decisions and actions in economic or other activities. Interest realization is considered as satisfaction of interests through the use of goods, which leads to the change in the state as an actor itself and a TSES as a whole.
The main conflict of economic interests within the framework of all organizational and legal forms of management takes place in three areas: in property relations, management and income distribution.
It often happens that the set of municipal policies may in many positions be in conflict with the strategy of a constituent entity the Russian Federation, and the strategies of constituent entities – with federal strategies. Moreover, there are no effective mechanisms companies, including natural monopolies. They can act as strategic partners of various governance levels, and can focus on the use of certain resources, skills, and infrastructure, which is often not coordinated with the plans of other participants (stakeholders).
To solve the difficult problem of forming a unified system of strategic planning it is necessary to ensure the interaction of all levels of competitiveness of the national economy: macro-economic (management of economic system as a whole), meso- and microeconomic (interaction of enterprises, firms, and entire industries and households).
Meso- and micro-economic levels are focused on the market as the coordinator of interests of economic actors; long-term coordination of interests of different TSES levels is the main objective of territorial policies.
Such coordination is most effectively carried out through cooperation between regional and municipal executive authorities, representatives of business and expert community, where needs, interests and resources of the territory’s major actors are identified. This issue is of fundamental importance in the system of territorial development strategic management because the results of studying and coordinating interests and ranking needs influence the edjn20№
of goal setting, and, consequently, the direction of TSES socio-economic development.
Priority of the country’s national security parameters should become the main principle in this area with the greatest possible harmonization of interests within the country and individual economic actors. To develop interest coordination techniques it is important to understand that economic interests are implemented by setting goals and objectives which are expressed in performance indicators. Therefore, interaction between economic interests makes it possible to determine the extent and degree of their implementation for every participant in a particular program area.
Principle 4. Methodological techniques for the development and implementation of strategic documents at different governance levels are based on the program-project approach which ensures rational allocation of resources to achieve strategic objectives of territory’s development.
The traditional approach to the development and implementation of territorial and sectoral programs is the program-target approach. Lately there have been opinions that domestic experience of using the program-target approach to TSES development management has significantly discredited the effectiveness of this technique, the use of which has not solved any major regional problems or changed at least one adverse regional situation [11]. Development of “carbon copy” programs, misunderstanding the essence of strategic documents, complex program implementation without reference to specific projects have led to the ineffectiveness of a significant number of sectoral and territorial programs.
The highlighted shortcomings help eliminate the program-project approach which implements the “program-project-plan” chain. At the level of strategic planning, the basic territory’s development direction is specified, the level of objectives identifies the priorities for the territory’s development in specific areas, the level of specific projects determines the required resources and appoints the responsible actors; at the level of specific activities conditions for interaction of participants are set. The structure of programs and projects depends on the specific areas, as well as on the main stakeholders’ strategic documents at their disposal, which can be integrated into the strategy of a localized area if there is at least one point of intersection through priority functions.
Since 2016, the transition to project management has been formalized at the federal level. The Decision of the Russian Government adopted the Regulation on project activity in the Government of the
Russian Federation and approved the strategic management techniques.
functional structure of project activity potentials are innovative, financial, and management system. Accordingly, state labor, which ensure high-quality economic authorities of constituent entities of the Russian Federation are recommended to organize project activities following the
Regulation approved by the Government Decision [5].
The program-project approach can also be applied for developing urgent territories’ programs (programs of sub-regional development, inter-municipal development programs, etc.) which have different sources of financing projects.
Thus, the presented concept of development of key potentials of multi-level territorial systems has interconnected categories of economic theory, regional economy and territorial development growth in modern conditions. Activation of key potentials through using appropriate technology and competencies into new resources ensures achievement of qualitative parameters of economic growth taking into account coordination of interests of economic actors in TSES.
This helps create the methodological basis for the development of documents on the long-term prospects of territories’ development and develop a set of prompt tactical measures. Such documents must be linked to budget resources, specified in the action plan, be time-, performer- and fundbound and aimed at meet strategic priorities of territory’s development.
Список литературы Strategic management of key development potential of split-level territorial socio-economic systems
- Maddison A. Monitoring the World Economy: 1820-1922. P.: OECD, 1995.
- Wernerfelt B. The Resource-Based View of the Firm: Ten Years After. Strategic Management Journal, volume 16, no. 3 (March, 1995), pp. 171-174.
- Auzan A.A. Strategiya dolgosrochnogo razvitiya Rossii: novizna podkhoda . Nauchnye trudy Vol’nogo ekonomicheskogo obshchestva Rossii , 2015, volume 196, pp. 229-241..
- Ilyin V.A., Shabunova A.A. O nekotorykh tendentsiyakh v ekonomicheskom razvitii Rossii i regiona . Sotsiologicheskie issledovaniya , 2015, no. 8 (376), pp. 34-41..
- Postanovlenie Pravitel’stva RF ot 15.10.2016 № 1050 «Ob organizatsii proektnoi deyatel’nosti v Pravitel’stve Rossiiskoi Federatsii» (vmeste s «Polozheniem ob organizatsii proektnoi deyatel’nosti v Pravitel’stve Rossiiskoi Federatsii») . Spravochnaya pravovaya sistema «Konsul’tant plyus» (accessed: 17.02.2017)..
- Gainanov D.A. (Ed.) Strategicheskoe upravlenie potentsialom razvitiya territorial’nykh sotsial’no-ekonomicheskikh sistem: metodologicheskie podkhody i instrumental’noe obespechenie: monografiya . Ufa: ISEI UNTs RAN, 2016. 244 p..
- Tenyakov I.M. Natsional’noe razvitie i ekonomicheskii rost: teoriya i rossiiskaya spetsifika . Moscow, 2016, p. 52..
- Ukaz Prezidenta RF ot 31.12.2015 №683 «O Strategii natsional’noi bezopasnosti Rossiiskoi Federatsii» . Konsul’tant Plyus . Available at: http://www.consultant.ru..
- Federal’nyi zakon ot 28.06.2014 № 172-FZ (red. ot 03.07.2016) «O strategicheskom planirovanii v Rossiiskoi Federatsii» . Konsul’tant Plyus . Available at: http://www.consultant.ru..
- Khubiev K.A. Protivorechiya ekonomicheskogo rosta . Ekonomist , 2005, no. 8, p. 46..
- Shevtsov A. Novatsii v instrumentakh ekonomicheskogo ozhivleniya razvitiya territorii . Problemy teorii i praktiki upravleniya , 2015, no. 10, pp. 6-17..


