Strategy of sustainable development for the forestry complex as a subsystem of the regional economy
Автор: Letovaltseva Marina A.
Журнал: Arctic and North @arctic-and-north
Рубрика: Economics of the Northern communities. Politology
Статья в выпуске: 20, 2015 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Using the method of the SWOT-analysis, the article reveals the conceptual problems of the forest industry in the region, inertial and innovative strategic scenarios, two phases of the program activities of the timber industry: 2015—2020 and 2021—2030 years. The method of management, interaction between government and business. Developed the project of the regional cluster timber industry and of model its creation. It is noted that the cluster "PomorInnovaLes" created in the Arkhangelsk Region (2014), allows you to solve a number of practical problems. Interaction of the state, regions, municipalities and businesses will attract investment, and the development of infrastructure and social issues.
Timber industry, region, strategy, scenarios, program of development, cluster, "PomorInnovaLes", investments
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148318709
IDR: 148318709 | УДК: 332.1/332.025
Текст научной статьи Strategy of sustainable development for the forestry complex as a subsystem of the regional economy
The relevance of this topic is related to the fact that after a proper selection and successful implementation of the forestry strategy, the regional socio-economic system is effectively developing and changing. The development strategy of the timber industry is becoming a part of the regional policy, contributing to the socio-economic development of the region, preserving the environment that determines the purpose and objectives of this study.
The algorithm of development and implementation of the region’s timber industry development strategy could be conceptualized as follows: 1) Identification of strategic alternatives. 2) Choosing a strategy, basic directions of the forestry development. 3) A program of forestry development as tool for the implementation of the strategy. 4) Identification of tasks and their comparison with the problems of development. 5) Measures to implement the tasks: a) Evaluation of resources: raw materials, personnel and investments; b) Creation and development of regional forest industry cluster. 6) Development of a timber cluster model in the region. 7) Evaluation of the results of activities, monitoring and correction.
The effective implementation of the national forest industry development strategy is the introduction of the best international practices: 1) the strategic objectives at the federal, regional and local levels; each level has a certain authority in the field of forest management, supervision and control of private forest users and state forests (the USA); 2) encouraging the owners to change the forest management in order to balance private and public interests; the use of state mechanisms for economic compensation of costs (Finland); 3) adoption of the document, aimed at the implementation of individual plans, covering all levels — national, regional and local, different forms of ownership of land and forests (“Forest Planning”, UK); 4) management, conservation and sustainable development of forests and continuous development of forest-based industries (Sweden). Solving this kind of problems, it is important to take into account the huge number of factors that have a direct impact on the forest industry development.
Analysis of strategic alternatives for the development of the regional forest industry
In order to define strategic development alternatives of the Arkhangelsk regional forestry, SWOT-analysis is used.
SWOT-analysis of the forest industry and its activities in the Arkhangelsk region
S — strengths
O — opportunities
-
1) The convenient geographical location of the region, 1) the functioning of transport infrastructure (rail, sea and river ports) for the export of products.
Keeping the high role of the forest in the livelihood of the people; potentially capacious market for forest products in Russia and abroad.
The increase in demand for secondary resources (biofuels, pellets).
Development and implementation of modern technologies of specialized production and marketing of forestry products.
Improving the skills of workers in accordance with the international standards.
Regional integration with companies in other industries, research institutes, NArFU and creation of a regional timber industry cluster.
Creation of an effective set of deep processing of wood to meet external demand.
-
2) The presence of forest resources to increase the2)
volume of wood harvesting and processing.
-
3) The capacity for wood processing, production of3)
major forest products, including exports.
-
4) Sufficient amounts of manpower.
-
5) The presence of educational institutions that train4)
professionals (NArFU).
-
6) Availability of scientific, technical and industrial5)
capital, banking institutions.
W — weaknesses T — threats
1) Remote areas for forest development, poor 1) The volatility of world prices for forestry products, development of transport and infrastructure for harvesting and transportation of wood.
-
2) Irrational use of forest resources and their inefficient recovery affects the ecological, climatic component of the region; the presence of large amounts of dead
pulp and paper.
-
2) Reduction in exports and domestic consumption by reducing production and falling prices; job cuts.
-
3) Non-compliance of production quality standards; decrease in quality of wood in remote areas, in case
dry plants.
of its non-use.
The deficit of investment in terms of financial and economic crisis; the lack of readiness of banking institutions to lend to small and medium-sized businesses; difficulties in attracting foreign capital for the development of hard-to-forest areas.
Slow down the implementation of new production technologies, modernization of equipment for export-oriented and certified products.
Improvement of federal legislation on the use of hard and dead plants to produce biofuels; need to ensure the needs of the population in wood, housing, as well as the tax cut for small and medium-sized businesses.
-
3) Decrease of production funds; a high level of energy 4) consumption and slow modernization.
-
4) The lack of reliable sources of investment in primary production forestry and the attractiveness of the region.
-
5) Poorly functioning system of standardization and 5) certification of products and production processes.
-
6) Low level of management, marketing and logistics, slow process of integration of forestry enterprises, 6) including the one based on the cluster approach.
-
7) Inefficient state tax and financial policies in the forestry sector; instability of the federal legislation.
Effective use of development opportunities and minimizing risks involves overcoming the crisis in the industry, not only by cutting, but also creating jobs in order to improve product quality and control over its distribution system. It should be noted that specific natural factors affecting the activity of forestry, such as: degradation of natural resources, changing climatic conditions, resulting in a change of coniferous trees for deciduous trees and increasing the risk of forest fires in the dry forests.
Any area holds a special place in the geopolitical and national space, representing the territories with developing economic entities and economic links, or vice versa, requiring a state support through the creation of “points of growth” for industrial production. As a rule, each region has its leading industry, which is the economic base of its development.
Currently, as a result of the decrease of the resource base and increased tax rates associated with the use of resources, many regions of the North and their leading industries have undergone a crisis. The Arkhangelsk region is not an exception. It is situated on the territory with the powerful timber industry and there is a number of problems related to the depreciation of equipment and reduced production volumes. There is a need to create an economic mechanism that reflects the entire spectrum of cooperation between the parties of the forest industry of Russia interested in the rational use and reproduction of forests: foresters, environmentalists, loggers, lumbermen, exporters and consumers.
It is appropriate to examine two scenarios of strategic development of the Arkhangelsk region forestry: inertial and innovation. Both scenarios are based on the analysis of opportunities and threats of the timber industry, the study of modern legislation in terms of the existing shortcomings in the legal regulation of the forest industry of the Russian Federation.
The inertial scenario presents the preservation of the prevailing trends in the development of the regional forest complex where remains the possibility of implementing new projects in the logging, sawmilling, woodworking and pulp and paper industry. However, the inertial scenario is based on the forecast of a low growth of macroeconomic indicators and the development of forestry enterprises at the expense of their own capabilities. At the moment the timber industry needs state support and reducing the tax benefits, in particular. State support for this scenario should be implemented in accordance with the RF Governmental statement, June 30, 2007 № 419, which provides state support through the privileges on rent paid to the federal budget.
Under this scenario, the strategic development aimed at preserving the principles of industrial activity, raw timber supplies to the world market without taking into account the reproduction of forest resources.
The innovative scenario allows to make fundamental changes in the structure of the timber industry at the expense of a priority development of the pulp and paper industry through the creation of large forest complexes (centers of growth) and the introduction of facilities for production of completely new types of products, for the production of sawmill glued beam in order to ensure the domestic market with local products and strengthen its position in the international market.
Production of laminated veneer lumber will ensure the development of wooden housing construction in accordance with the national project “Available and Comfortable Housing — to Russian citizens”. The project aims at introduction of housing in the amount of 140 mln m2 per year, i.e. 1 m2 per resident of Russia. Also some more environmental projects could be introduced. The use of new waste processing technologies for the production of biofuels and the use of secondary resources contribute to the conservation and restoration of forest areas.
Under this scenario, it is advisable to develop public-private partnerships through the development of PPP-projects. As a result, the growth rate will be determined by the investment attractiveness of housing projects; favorability of credit conditions; availability and rates for the lease of sawmill and woodworking machinery; and amounts of state support aimed at developing national production, taking into account environmental parameters of the areas. Perhaps it will be done from the standpoint of “green economy”.
For the study and implementation of the proposed scenarios and strategies and in order to develop the investment policy, a number of problems and challenges of the forestry reveals (Table 1).
Table1
Interconnection of aims and challenges of the forestry development
Aims of the forestry development economic manag- production social ment


Reduce of the unemployment
Decrease of the forests’ quality
Use of the old technologies and equipment with a high degree of the manual labor and low productivity, which reduce competitiveness of the products
Low innovation activity and attractiveness for investors, caused by reduce in amount of scientific centers working for production
High level of tension in forest settlements, unclear lease regulations
Limits for forestry when introducing new types of products, demanded at national and international markets Unclear structure of production and export
Reduced growth of the timber industry
Poor developed infrastructure
Lack of qualified workers, low salaries and low productivity
Low level of ecological responsibility of the timber industry
Lack of effective state strategy for the forestry
** *
*** *
*** *
*
**
**
*
*
**
**
* *
* *
*
**
** *
****
****
* **
****
* *
* *
*
*
**
*
* *
*
*
**
*
* *
* *
**
*
* *
* *
**
**
One of the tools to address these challenges is the development of the forestry program, the aim of which is to ensure the progressive development of the territory of the forest complex on the principles of sustainable management. Forestry development program should include a phased implementation of the following measures.
Stage 1 (2015—2020)
-
V works on conservation, protection and reproduction of forest resources to ensure the stability and continuity of forest management;
-
V improvement of forest management on the principles of sound distribution between the forest users identified by the Forest Code of the Russian Federation in 2006;
-
V forestland transport development in the areas of active drying of forests;
-
V implementation of measures to stabilize the volumes of wood harvesting and processing in existing plants;
-
V improvement of forest resources to ensure wood processing;
-
V modernization of production capacities of wood-processing companies;
-
V introduction of facilities for the production of plywood and fibreboards,
-
V plants for wooden housing with domestic and foreign investments;
-
V creation of capacities for the biofuels production for the needs of municipal boiler houses in seven districts of the region.
Stage 2 (2021—2030)
-
V construction and modernization of forest seed and nursery based on co-financing of major leaseholders;
-
V new capacities for production of lumber and construction materials from wood for wooden houses; providing the needs of the regional building and construction complex;
-
V scientific research in order to improve the sustainability of forest management, reforestation and improved technology of cutting;
-
V creation of technologies and equipment for advanced mechanical, chemical and energy wood processing to reduce the environmental threats.
Forming a group of technological, economic and organizational interconnected industries, companies and organizations operating in the forestry sector, will contribute to the improvement of the existing mechanism of forestry at the federal and regional levels [1]. In this context and with a view to considering the possibility of cooperation between the state and business structures, it is advisable to organize not only the existing legal documents that define its activity (Pic. 1), but and forestry management practices as well (Table 2).
|
CD > CD 7u CD CD |
Forest Code of the Russian Federation, adopted on the 8 th of November 2006 |
& 5 * § m CD o 3 3 В ГО 5 2 О £ ” ф ГО un S 1 o tn -3 5 QJ Г0 3 C V) , 1 О ф |
|
Concept for the long term development of the Russian Federation for the period until 2020, adopted by the RF Government on the 17 th of November 2008, № 1662-р. |
||
|
Fundamentals of the state politics on security, protection and reproduction of forests in the Russian Federation for the period until 2030, adopted by the RF Government on the 26 th of September 2013 г. № 1724-р. |
||
|
Report on effectiveness and development of the forestry for the period until 2030, prepared for the meeting of the State council of the Russian Federation on the 11 th of April 2013. |
||
|
Forecast of development of the forest sector of the Russian Federation for the period until 2030, prepared by FAO and UNECE. |
||
|
State program of the Russian Federation "The development of industry and increase its competitiveness." |
||
|
State program of the Russian Federation "Development of forestry". |
||
|
"cd > CD 7u c о сю CD C£ |
The development strategy of timber industry complex of the Arkhangelsk region for the period up to 2030. |
QJ m 5. ro 73 о 2 00 r+ o' =5- d л 7Г 0> V) QJ О 00 |
|
Forest plan of the Arkhangelsk region 2009-2018. |
||
|
Policy documents on the development of roads, transport, infrastructure, housing, energy. |
||
|
The State Program "Development of shipbuilding 2013-2030 years" |
||
|
The state program "Development of transport system of the Arkhangelsk Region (2014 - 2020 years)» |
||
|
State program of the Arkhangelsk Region "Development of trade in the Arkhangelsk Region (2014 - 2020 years) |
||
|
The national project "Affordable and Comfortable Housing - to Russian citizens." |
|
Forestry industry |
Picture 1. Legal acts on forestry regulation in the Arkhangelsk region.
Table 2
Management of forestry in the Arkhangelsk region
Type of measures
Tools
Economic Administrative legal
Management
and
Social and psychological
Subventions, tax breaks, subsidies, public contracts, rates, fines
Programs of social and economic development. Forecasts. Concept. Strategy, regional programs, the Forest Plan, action plans, standards, regulation
Ministry of Natural Resources and Forestry Complex of Arkhangelsk region, the timber industry enterprises, the Agency for Transport of the Arkhangelsk region Auctions for loggers, state and regional prizes and awards
The current
management structure of the forestry is not perfect, since the methods are focused only on the sectoral tasks. Therefore, there is a need for a deeper coordination of activities of state, local authorities and business aimed at development of social and industrial infrastructure through the implementation of targeted programs and the use of the cluster approach. In this connection, it is an issue of management, aimed at the production of competitive products. Given the competitiveness of the products, we cannot forget about the limited resources: natural, financial and investments. Achievement of a multiplier effect may contribute to the formation of the technological chain, formed due to the interaction of related industries and the complementarity of products that will ensure the growth of the value added. The need to attract investments to create and modernize timber production and timber infrastructure and to create favorable conditions for forest management should be mentioned.
-
- to conclude a lease treaty without auctions;
Investment project № 1 (200 billion rub. — 3 billion rub.)
Investment project № 2 (3 billion rub. — 5 billion rub.)
Investment project № 3 (5 billion rub. — 10 billion rub.)
-
- establishing a minimum amount of rent;
-
- exemption from customs duties on products, and import — on equipment.
-
- lease prize amount is 50% of minimum;
-
- exemption from customs duties on raw materials.
-
- establishment of forestry cluster;
-
- introduction of new equipment and review of state support of business
Investments to the establishment of timber industry and wood processing
Picture 2. Forms of investments for forestry
In order to improve the interaction between the authorities and businesses, forestry complex needs a mechanism of public-private cooperation, operating through specific management practices, organizational structures and the rule of the law, which contributes to the manifestation of forms of public-state partnership. Financial and economic development of forestry practices and regulatory cooperation between the state, business and society include fiscal and monetary management. Forms of organization and management of calculations and payments should define specific rules and borders of cooperation. Also there is a need to monitor, to regulate and to systematize financial and investment resources that determine the development of plans and programs for forestry. It is advisable to use direct and indirect methods of state regulation and interaction to stimulate motivation to financing and investing the forestry [6].
The legislation of the Russian Federation and its subjects determines the implementation of administrative methods of state regulation and forms the legal basis of forestry and stateprivate partnership (SPP) using regulations and guidelines.
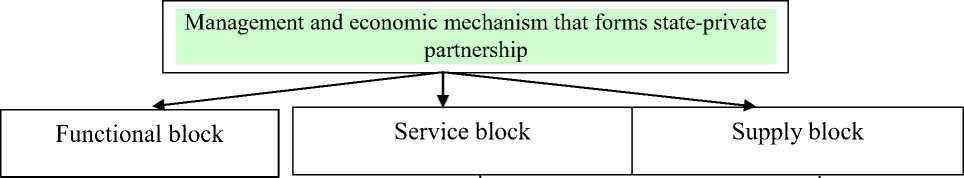
|
Budget expenses |
Economic regulation of the commercial sector |
|
Economic regulation of the state sector |
Uniform development policy for the forestry and SPP
|
Forms of the payment management |
Motivational activity related to funding |
|
Monitoring of the financial resources |
Sales programs
|
Federal and Regional legal Acts |
Managing the financial resources and investments |
|
Legal acts, |
|
|
instructions |
Improvement of the legislation on SPP and forestry management
Beneficial conditions for forestry
Administrative, legal, financial and economic methods for the development of forestry
Picture 3. Management and economic mechanism that forms state-private partnership
Forestry cluster
Creation and development of a timber industry cluster provides state support for large regional integrated self-developing market-oriented corporate structures; foreign and domestic investment in new forest enterprises; improving the competitiveness of forestry, woodworking, chemical, pulp and paper industry; strengthening the industry’s leadership in world production of high-tech wooden products; increasing the share of the region in the global market for timber products [3]. Participants of the regional cluster in the Arkhangelsk region are, for example, administration, business associations and business organization.
Table 3
Draft of the regional forestry cluster in the Arkhangelsk region
|
Elements of the cluster State and municipal authorities |
Participants of the regional cluster Ministry of Economic Development and Competition Policy of the AR, Ministry of Finance of the AR, AR Transport Agency, the Ministry of Fuel and Energy Complex and Housing and Public Utilities of the AR, Ministry of Natural Resources and Forestry Complex of the AR, Ministry of Industry and Construction of the AR, the Ministry of Labor, Employment and Social Development of the AR, the Agency of Architecture and Building of the AR, municipalities of the AR, Fund of development and support of small business of the AR. |
|
Associations of companies |
Association of enterprises and representatives of small and medium-sized businesses in the timber industry complex of the AR, the Association for Foreign Trade and the Association of oil and gas suppliers “Sozvesdie” of the AR. |
|
Cluster Council |
Representatives of the participants listed in the Table. |
|
Forestry |
Forest areas of the AR, logging enterprises of the AR. |
|
Forestry, wood processing, furniture production, production of wood and wood pellets |
Filial JSC “Gruppa Ilim” in the AR, JSC “Arkhangelsky CBK” (owner — Pulp Mill Holding GmbH (Austria), CJSC “Lesozavod № 25” (a part of the “Titan Group”), JSC “Onegsky LDK” (a part of the FIJ “Systema”), JSC “Arkhangelsky LDK № 3», CJSC “Arkhangelsk plywood plant”, LLC “Veslky DOK”, ULK Group. |
This cluster mechanism must take into account the full potential of the territory, to ensure the effective development of forestry enterprises as well as the integration of the regional economy in the world markets and the development of networking, possible due to the interaction of state, regional governments and municipal authorities, business and the local community. The mechanism for the creation and development of a timber industry cluster could be discussed in three stages. Preparations shall consider establishing a cluster by studies of economic, resource and organizational prerequisites, such as subsidies, co-financing, investors, bringing together different structures in the timber industry cluster. Main stage includes goals, objectives, establishment of the cluster, its composition, the feasibility study of cluster’s design: the financial plan, business plans of investment projects, tools to establish a cluster, including measures of the state support and financial forecast, which determines the effectiveness of the cluster. Concluding stage is aimed at creating a cluster management mechanism based on legal documents and a development plan, including: the legal framework, regulation and control; mechanism for stimulating investment activity; control over the business association, study of effective resource use; mechanism for the provision of public benefits and subsidies; co-financing of the RF regions; tax incentives and reduced customs duties.
Organizational-economic mechanism of creation and development of cluster and interdependence of development tasks and forestry problems contribute to the development of the model of a timber cluster (Pic. 4). In order to create and develop the regional cluster model, it is necessary: to improve the RF forestry legislation aimed at effectiveness of the forestry management and development; to attract foreign and domestic investment; to have closer cooperation between production and innovation infrastructures; to create the Cluster Council to unite the leaders of the cluster (manufacturing unit), representatives of small business, regional and municipal authorities and representatives of scientific institutions, who deal with the effect of cluster development in the region. High-tech parameter of the cluster and research intensity will be provided as a result of close cooperation between all patterns of production, transportation and an innovative infrastructure, which will positively affect the development of the region in terms of road transport network and IT-equipment [2].
The Arkhangelsk region has sufficient prerequisites for the implementation of cluster approach. In September 2014 a territorial timber cluster “PomorInnovaLes” was established. The cluster includes 24 participants: JSC “Arkhangelsk CBK”, JSC “Arkhbum”, CJSC "Lesozavod № 25”, timber enterprises group “Titan”, LLC "Belomorsky les”, PC Ltd. “Interstroy”, Ltd. “Priroda”, JSC “Plesetsky lespromhoz”, LLC “Niva”, JSC “Northern Shipping Company”, LLC “Nord-Wood”, JSC “Arkhangelsk Sea Commercial Port”, JSC “Arkhangelsky fanerny zavod", LLC “Arhbioenergo”, JSC “Solombalsky mashinostroitelny zavod”, JSC “Arkhangelskaya remontno-ekspluatacionnaya baza flota”, Northern (Arctic) Federal University named after MV Lomonosov, Moscow State University, Northern Scientific research Institute for Forestry Development (NSRIFD), Novodvinsk Industrial College, LLC “NordTehSad” and JSC “Arhgiprobum”. The cluster also includes representatives of small and medium business in the region: public organization “Regional Association for initiatives of small and medium-sized businesses” and LLC “Pomorsky lesnoy tekhnopark”. The initiative of the Arkhangelsk Pulp and Paper Mill to establish an innovative regional timber cluster was supported by the local Governor Igor Orlov, the Government of the region, the Arkhangelsk Regional Council of Deputies, the Arkhangelsk Chamber of Commerce, the regional office of the Russian public organization “Business Russia”. Chairman of the cluster Board is the GM of the JSC “Arkhangelsky CBK” Dmitry Igorevich Zylev. The cluster was established as non-commercial partnership1
|
Администрация Архангельской области |
Министерство природных ресурсов и ЛПК Архангельской области |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Строительство и введение в эксплуатацию безотходного лесоперерабатывающего комплекса. Экспорт готовой продукции (клееного бруса, пеллет). Малоэтажное домостроение. Снижение издержек производства. Привлечение инвестиций. |
Обеспечение населения древесиной по льготным тарифам, увеличение расчётной лесосеки, рациональное использование лесных фондов. Освоение труднодоступных лесных территорий. Экологизация производства. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Торгово-финансовый блок |
Блок инженерной инфраструктуры |
Нефтяные топливные компании (НТК) Роснефть - ООО «РН- |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
Маркетинговые и сбытовые компа- |
Банки |
Лизинговые компании |
Сервисные ремонтные организации |
Инжиниринговые компании |
Архангельскнефтепрод ОАО «Архангельскгеолдо ОАО «Татнефть». ООО Кластерный совет |
/кт», быча», «Лу- |
|||||||||||||||||
|
Научно-образо-ватель-ный блок |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
V |
Производственный блок |
Производственнологистический блок |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
' Лесное хозяйство |
Целлюлознобумажная промышленность |
Дерево-обрабатываю-щая промышленность |
Химическая про-мышлен лен-ность |
Энергетическая компания |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Судостроение,транспорт, связь Организации: ООО «Логистик», ОАО «Звездочка», ОАО «Се- взапдорстрой», логистические компании |
НИИ, ВУЗы Организации: САФУ, профессиональные училища №48. №35 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Новые технологии лесо-восстановитс льных работ (внедрение современных технологий сберегающих рубок, не требующих после себя больших лесовосстано- |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Производство легкомелованной бумаги; Полиграфическая и упаковочная промышленность |
Производство энергоресурсов, биотоп- |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Использование некондиционной древесины (сухостоя) для производства клееного бруса; Внедрения технологий деревооб- |
Производство смол, масел, спирта, биодизеля |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
з '| = з 5 х & ® - ^ II" О ° о 5 о х В. = 2 о :н £ м 5 " S а о и О |
* § 11 i д о" и О 5 = 5 g § о u Q ^ g о о а “ ч ° Ч u щ О К о с 1. I. 2 1 |
в i s у О О |! 1 1 и |
Созд отрасг |
евых |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
высших и средних образовательных учреждений |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Создание профильных школ |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Организации |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Лесничества Лесозаготовительные предприятия |
ОАО СЦБК, ОАО АЦБК |
ЗАО «Лесозавод №25», Лесозавод № 14, ООО «Даммере», СЛДК |
ОАО СЦБК, ОАО АЦБК |
ОАО«МРСК СевероЗап а-да«Архэнерг о» |
|||||||||||||||||||
Picture 4. Model of establishment of the regional cluster
At a press conference on the 27th of November 2014, Arkhangelsk Governor I. A. Orlov commented on the creation of the cluster in the "Interfax" central office and said that the forestry companies of the Arkhangelsk region had harvested 12mln m3 of wood per year, 6.5 mln m3 of this share had been harvested by small business. So, it seems to be important to stabilize the relationship between the participants of the cluster and to contribute to the dialog between them2. The GM of the JSC “Arkhangelsky CBK” D. I. Zylev supported the Governor: “Cluster-first of all, is a dialog and cooperation, it allows combining the interests of huge companies and small business. For example, our company is not involved in logging; we have contracts with small and medium-sized business. We are interested in high quality of wood and high quality companies in the cluster”3. Interaction within the cluster is based on an economic. At the same time, the conditions for the social development of the territories where the cluster exists get new industries and new jobs. Territories of the cluster discussed in this article is limited to the areas of Novodvinsk, Arkhangelsk, Plesetsk and Pinezhsky, Primorsky and Kholmogorsky Districts of the Arkhangelsk Region.
In practical terms, the interaction of governing bodies at the level of state, region, municipalities and businesses will undoubtedly contribute to the growth of forestry, investment and infrastructure development. Significant role is played by forestry enterprises and institutions of regional and municipal management. Also within the framework of public-private partnership, some measures are required: distribution of private investments in venture capital funds operating on the basis of public-private partnership, with government support through the tax benefits; attracting private capital to build the complex machine-building and house-building industries, focused on the use of innovative technologies needed for the construction of forest roads, harvesting of wood, its transport and processing; support for small and medium-sized business, active in specific forestry sector [9]. Development of the Russian economy and its northern regions in the context of improving the forestry management should be considered in terms of the transition from a state-private partnership to new forms of interaction. Large timber companies are the “points of growth” of the whole forest complex. So they should be considered as the main agents of the government, able to implement state and industrial policy in the forestry sector.
In general, the timber industry in the Arkhangelsk region has sufficient industrial and economic potential, which can be used for further growth and public policy, regulating its development, taking into account domestic and foreign experience. I think it is appropriate to introduce a limited extent to native forest settlements as a private property in order to create a small forest companies.
Conclusion
The growing importance of the North and the Arctic for Russia's economic development needs balanced solutions for the most important economic problems associated with the development of natural resources and social issues related to the life and interests of the population. The predominant economic activity is the production and its three main types (mining, manufacturing, production and distribution of electricity and water) have approximately the same specific importance. Areas of the North have different structures. As you know, in the Arkhangelsk Region and the Republic of Karelia more than a half volume of industrial production is manufacturing, and in the Komi Republic — mining. There is an interregional project “Belkomur” (White Sea — Komi — Ural). Three regions of Russia are involved in the project, focused on the creation of deep water port of the Arkhangelsk; construction of the railway, as well as construction and modernization of a number of industrial enterprises including forest proceeding. Energy resources generated as a result of the recycling of waste after harvesting and processing of wood could be used in other Arctic countries. The development of this type of production can be one of the tools for modernization of the country.
Northern territories play a key role in the national economy, in ensuring security and geopolitical interests of Russia [4]. We should agree with V.S. Selin and E.P. Bashmakova that the North and the Arctic have significant human potential adapted to living and working in extreme conditions, and qualified scientific and technical personnel. Natural resource potential of the northern territories, their production facilities contribute to their economic attractiveness and sustainable development [7]. But it should be noted that these regions have high level of migration caused by climatic conditions, low wages and lack of proper housing. Therefore, in the framework of the Northern Sea Route development project, it is advisable to consider the possibility of exports of wooden housing constructions to the other countries. Investments will contribute to the implementation of development projects of the forest areas through the creation of centralized systems and woodworking for the needs of the population of northern regions.
Western buyers impose ever more stringent environmental. Most of the forestry enterprises of the northern regions are far away from the “environmental” excellence. Existing problems of illegal logging, pollution of the atmosphere and water are acute for the forestry enterprises. Northern forestry products, including the one from the Arkhangelsk Region, are exported to European countries, to “environmentally sensitive” markets. So, the issue of ecological certification is very important. In this regard, the new Forest Code should take into account certificates that confirm environmentally responsible forest management [9].
In order to reduce the taxes for the forestry, there is a need to make changes to the tax legislation providing for a partial exemption of the payment for income tax, resulting from the sale of products manufactured within the investment projects; to remove or to reduce the import custom duties for imported equipment; review of value-added tax paid by suppliers (contractors).
It should be said that large regional forestry enterprises, in the Arkhangelsk region as well, are not fully provided with the raw materials because of the lease rights for the forest areas are not legally perfect. Only major tenants are involved in reforestation, fire-prevention measures, development of leased forest areas and forest villages. So, the state policy should include ensuring the long-term use of forest resources and control over their rational use, improvement of fee and tax system. In this regard, the need to develop a new forest policy provisions reveals as well as the securing the lease rights for forest resources.
The recovery of forestry enterprises needs innovative public policy providing the development of the forest sector. Investment development of the timber industry may be done by attracting new owners, effective functioning of a regional timber industry cluster associated with the intensive use of the rich forest potential and capable of stabilizing the economic development of the region, ensuring its stable future and strengthening the economic independence. In the current economic conditions the state's role in the implementation of innovative projects should be strengthened as long as own funds of the forestry companies and credits are extremely limited. The development of the forestry sector and the improvement of its socio-economic status may occur as a result of the public policy adjustment regulation of the timber cluster, taking into account the market situation; the development of a regional timber industry cluster; the interaction of timber, fuel and energy production, agriculture and etc.; projects on use of biofuels by introducing mini-CHP at the forestry enterprises; projects aimed at the use of dry trees for the production of laminated veneer lumber; development programs of affordable housing; attracting research institutions, researchers, professionals and practitioners for the development of applied programs designed to improve the forestry; attracting foreign investments for housing projects, forest roads projects and etc. and the public-private partnership.
It is the development of the forest industry that associated industries and infrastructure and leads to economic and social stability in North and is increasing the economic growth, improving the economy and demography, solving the problem of unemployment and improving living standards.
The practical significance of the study is in the fact that its research results may be used to develop and improve the state regulation of the timber industry, the development strategies and programs for the industry, aimed at solving problems of sustainable socio-economic development of the European North of Russia. In order to estimate key areas of forestry and address the main issues two variants of strategy, management and economic mechanism of establishment and development of the forestry cluster have been suggested and a model of its establishment has been developed.
The main conclusion is that the timber industry, on the one hand, is a city-forming factor for the northern regions and, on the other hand, it needs to develop a new and effective strategy based on the current situation. The policy in the field of forestry needs to be based on interaction of government and business and the development of effective forest management at the regional level, holding the optimal investment policy in order to improve the competitiveness of the North and other measures.
Список литературы Strategy of sustainable development for the forestry complex as a subsystem of the regional economy
- Kostyaev A.I. Territorialnaya differentsiatsiya uslovii hosyaistvovaniya [Terrotirial differesiation of the economic conditions]. Ekonomist, 2006, no. 9, pp. 23—30.
- Kostyaev A.I. Viravnivanie territorialnih socialno-ekonomicheskih razlichii [Improving territorial social and economic differences]. Ekonomika selskogog hozyaistva Rossii, 2006, no. 5, p.21.
- Kuzminov I.F. Lesnoi sector Kanadi i Rossii: perespektivi zaimstrovaniya zapadnih innovatsii I otechestvennom upravlenii lesami [Timber sector in Canada and Russia: perspectives of using the western experience in domestic forestry management]. Ekologicheskoe planirovanie i upravlenie, 2011, no.1, pp. 85—96.
- Lukin Y.F. Veliky peredel Arktiki [The great redistribution of the Arctic]. Arkhangelsk, 2010, 400p.
- Makar S.V. Osobennosti zarubezhnogo opyta s pozicij strategii razvitiya lesnogo potenciala Rossii [Features of foreign experience from the standpoint of the deve-lopment strategy of Russia's forest potential]. Vestnik finansovogo Universiteta, 2011, no.3 (63), pp. 66—75
- Nikonova G.N., Kriulina E.N. Neobhodimost, predposylki i nekotorye rezultaty tipologii selskih territorij (municipal'nyh obrazovanij) regiona [Necessary conditions and some results of the typology of rural areas (municipalities) of a region]. Vestnik APK Stavropolya, 2011, no 4, pp.100—104.
- Selin V.S., Bashmakova E.P. Znachenie severnyh i arkticheskih regionov v novyh geoekonomicheskih usloviyah razvitiya Rossii [Northern and Arctic regions in the new geoeconomic conditions of Russia]. Region: ekonomika i sociologiya, 2010, no. 3, pp. 23—39.
- Selin V.S. Severnye regioni Rossii: e'konomicheskaya dinamika i problemy razvitiya [Northern regions of Russia: economic dynamics and problems of development]. Region: ekonomika i sociologiya, 2011, no. 4, pp. 3—18.
- Suslov V.I. Strategiya ekonomicheskogo razvitiya regiona: podxody k razrabotke, struktura, modeli [The strategy of economic development of the region: the app-roaches to the development, structure model]. Region: ekonomika i sociologiya, 2009, no. 4, pp. 3—31.
- Cixan T.V. Klasternaya teoriya ekonomicheskogo razvitiya [The cluster theory of economic development]. Teoriya i praktika upravleniya. 2003, no. 5.


