Studies on isolation, purification and inhibition of carboxylesterase from the midgut of fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda)
Автор: Shafia Hoor F., Puspha T.C., Nagesh Babu R.
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.20, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The fall army worm (FAW) ( Spodoptera frugiperda ) is a polyphagous pest which causes damage to commercially important cultivated crops such as maize, rice, sorghum, cotton and also different vegetable crops. Carboxyl esterases (CarE, EC.3.1.1.1) or esterases are enzymes in the carboxyl / cholinesterase gene family that catalyze the hydrolysis of carboxyl esters. The carboxylesterases enzyme are the detoxification enzymes in FAW. Therefore, the inhibition of carboxylesterases from FAW would help in pest management. In this scenario, Isolation, purification and inhibition studies were carried out on the midgut carboxylesterase enzyme of FAW. Through a combination of steps including centrifugation, ammonium sulfate gradient precipitation, DEAE-Cellulose ion exchange chromatography, the enzyme was purified from fifth instar larvae of FAW. The final purified carboxylesterase after ion exchange chromatography had a specific activity of 7282.22 units / mg protein, 5.6 - fold of crude homogenate, and a yield of 25%. The purity of esterase was established by PAGE and SDS-PAGE. The SDS-PAGE revealed a molecular weight of approximately 45kDa to 66kDa. Our studies on the purified midgut carboxylesterase showed complete inhibition by organophosphorous inhibitor (10-4 M). The enzyme was also inhibited by 1x concentration of Lizol (disinfectant) and by different natural extracts (1x) as well.
Fall armyworm (faw) (spodoptera frugiperda), fifth instar larvae, midgut, carboxylesterase, isolation, purification, centrifugation, deae-cellulose-ion-exchange chromatography, inhibition, dichlorvos, lizol, natural extracts
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143182817
IDR: 143182817
Текст научной статьи Studies on isolation, purification and inhibition of carboxylesterase from the midgut of fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda)
The fall armyworm (FAW) ( Spodoptera frugiperda ) is one of the devastating insect pests belonging to the family Noctuidae and falls in the Lepidoptera order. It is a polyphagous pest (Baudron et al. , 2019) causing damage to economically important cultivated cereal crops such as maize, rice, sorghum, cotton and various vegetable crops and eventually impacts on food security (FA , 2017; CABI, 2018; Bateman et al. , 2018). The FAW feeds on leaves, stem and reproductive parts of plant species (Tefera et al. , 2019). It is native to tropical and subtropical regions of the America. FAW, which was first found in America, is one of the common pests of maize in South and North America. In Africa, it was first reported in 2016 (Sisay et al. , 2018) and has become one of the major invasive pests reaching over 30 countries across tropical and southern Africa including Madagascar, Seychelles and Cabo Verde at the end of 2017 (Bateman et al. , 2018) which later reached over 44 countries (Sisay et al. , 2019). There are 353 plants reported as a host for this pest (Kansiime et al. , 2019).
Symptoms start with the larval stage making different sizes of papery windows in leaves leading to extensive defoliation of plants, occurrence of faecal materials and in later stage growth and development of plants is affected (Reddy, 2019). This insect has marching behaviour similar to that of the army causing havoc loss to the crops that come in its path (FA , 2019; CABI, 2019). The FAW is devastating in nature and CABI (2017) has predicted that the pest causes a possible loss of 6.1 billion US dollar only in African countries when control measures are not applied. The awareness programs regarding the symptoms, early detection and control measures of the pest along with the recommendation of effective pesticide and bio-pesticide can be effective to minimize the loss. Assessing suitable crop varieties that can tolerate the FAW needs to be initiated and in a longer run national policies should promote lower risk control options through short term subsidies and rapid assessment and registration of biopesticides and biological control products (CABI, 2017).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The Fall armyworm larvae, (S. frugiperda ) were
collected from the maize fields of Sungatta village, Devanahalli Taluk and reared in the Department of Biochemistry, Maharani Cluster University, Bangalore -560 001, by feeding with unlimited amounts of Zea mays leaves. Five-day old 5th instar larvae were used in the present investigation.
Isolation and enzyme activity
The larvae were dissected and the midgut slit open to remove the digestive juice and maize leaves. The midgut was rinsed with cold 0.1 M sodium phosphate buffer, pH 7.0, stored at 4°C until use. About 40 larvae yielded 13 g of midgut tissue. The tissue (13g) was homogenized using an mortar and pestle in two batches, taking 6.5 g at a time in 0.1 M sodium phosphate buffer, pH 7.0. The extract was centrifuged at 7500g for 20 min at 4°C. The supernatant from both two batches were pooled and used as the crude enzyme extract (Fig. 1).

Figure 1: Extraction of carboxyl esterase form midgut of fall armyworm.
Enzyme activity:
Assay was carried out by Gomori (Gomori G. 1941) and later modified by Van Asperen (Van Asperen. 1962). Enzyme reaction was initiated by adding 4ml of 60mM α-naphthyl acetate in phosphate assay buffer (pH 7.0) to 1ml tissue extract then incubated for 10 min at 27 ° C. Subsequently, the reaction was stopped by the addition of 1ml DBLS reagent and enzyme activity was measured at 600nm.
Staining for esterase activity.
Esterase activity was detected on PAGE and by the method of Hunter and Markert (1957). The electrophoresed gels were placed in 100 ml of 0.1 M sodium phosphate buffer, pH 7.0, containing a pinch of Fast Blue RR salt and 1-naphthyl acetate in 1 ml acetone, for 10 min at 37°C.
Purification
Ammonium sulphate precipitation:
Ammonium sulphate precipitation (0-80%) was carried out at 4 ° C and the precipitate obtained was centrifuged at 12000rpm for 12 min in the cold. The precipitate was then dissolved in 5 ml of 0.1 M sodium phosphate buffer, pH 7.0 and dialyzed with three changes of the same buffer. The precipitated proteins were removed by centrifugation at 12000rpm for 12 min in cold followed by determination of enzyme activity in both pellet and supernatant obtained (Fig. 2a and Fig. 2b).

Figure 2a: Ammonium sulphate precipitation at 4 ° C

Figure 2b: Dialysis of ammonium sulphate fraction at 4 ° C.
Ion-exchange chromatography on DEAE-cellulose
The 0-80% dialyzed ammonium sulphate fraction was’ applied onto DEAE-cellulose column equilibrated with 0.2M Tris HCl buffer, pH 8.3 (starting buffer). Usually, tris buffer is used with anion exchange chromatography. However, phosphate buffer is also preferred among other buffers. The column was washed with 60ml of starting buffer and collected into 40 Eppendorf tubes of unbound fractions, The washing was followed by elution with starting buffer, containing 0.4 M sodium chloride. ne peak of esterase activity was eluted in the washing and the second with 0.4 M sodium chloride. The peak fractions were designated as DEAE (Fig 3).

Figure 3: Ion-exchange chromatography on DEAE-cellulose
Preparative polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
Preparative polyacrylamide slab gel electrophoresis was carried out according to the method of Davis (1964) and rnstein (1964) in 16% gel. The concentrated and desalted DEAE fractions was loaded above the gel and electrophoresed at 4°C for 12h overnight at 30volts using 0.05 M glycine-tris base buffer, pH 8.3. After the completion of electrophoresis, the gel was stained for esterase activity using 1-naphthyl acetate as substrate containing phosphate buffer using fast blue RR as indicator. The stained portion of the gel containing esterase band was sliced and homogenized with 5 ml of cold 0.05 M sodium phosphate buffer, pH 7.0, containing 0.25 M sodium chloride. The homogenate was centrifuged in cold at 12000rpm for 12min. The residue was then resuspended (twice) in extraction buffer, homogenized and centrifuged. The pooled supernatant was concentrated using DEAE-cellulose as described above.
Molecular weight determination by SDS-PAGE
SDS-PAGE was carried out on 12% gels without using standard proteins. The molecular weight of the carboxylesterase enzyme of FAW was determined with reference to standard protein (Laemmli, 1970).
Effect of pH on carboxylesterase
The enzyme was incubated in different buffers of pH
4.0-9.5 for 10 min at room temperature and assayed for esterase activity at 27°C using 1-naphthyl acetate as substrate in different buffers of pH 4.0-9.5.
Effect of temperature on carboxylesterase
The enzyme was incubated at different temperatures between 5°C and 65°C for 10 min and assayed each time, at the same temperature, using 1-naphthyl acetate as substrate.
Inhibitors:
Synthetic inhibitors:
The enzyme was preincubated with different concentrations of inhibitor dichlorvos, (10-4 to 107M) for 20 min at 4°C. Then the enzyme was assayed using 1-naphthyl acetate as substrate. The enzyme was preincubated with other inhibitors like 1X Lizol, Surf excel and Tide detergents.
Natural Extracts:
The purified sample was loaded on polyacrylamide slab gel and electrophoresis was carried out and incubated in different 1% natural extracts of the following (Fig 4).
RESULTS
Enzyme activity:
Enzyme reaction was initiated by different dilutions (120ml, 1-50ml and 1-100ml) using 4ml of 60mM α-naphthyl acetate in phosphate assay buffer (pH 7.0) then incubated for 10 min at 27 ° C. Subsequently, the reaction was stopped by the addition of 1ml DBLS reagent and enzyme activity was measured at 600nm. (Fig 5)
Staining for esterase activity:
The esterase bands revealed when 1-naphthyl acetate was used as substrate. Hence, 1-naphthyl acetate was used as substrate for studies using PAGE. The gels were stored in 7.5% acetic acid (Fig. 6).
Enzyme purification
Table 1 summarizes the procedure for purification of an enzyme beginning with 13 g of midgut tissue. The average overall purification was 5.6-fold and the yield was 25%. The elution profile of ion-exchange chromatography on DEAE-cellulose. Ion-exchange chromatography of crude esterase preparation on
DEAE-cellulose at pH 7.0 esterase fractions, DEAE (Fig 7) and (Table-1).
Preparative polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis.
Preparative polyacrylamide slab gel electrophoresis was carried out according to the method of Davis (1964) and rnstein (1964) in 16% gel. The concentrated and desalted DEAE fractions was loaded above the gel and electrophoresed at 4°C for 12h overnight at 30volts using 0.05 M glycine-tris base buffer, pH 8.3 (Fig. 8a). After the completion of electrophoresis, the gel was stained for esterase activity using 1-naphthyl acetate as substrate containing phosphate buffer using fast blue RR as indicator (Fig. 8b)
Molecular weight determination by SDS-PAGE.
The bands obtained by SDS-PAGE was compared with standard protein (Laemmli, 1970). When compared to standard protein the molecular weight of the carboxylesterase enzyme of FAW was found to be approximately 45kDa to 66kDa (Fig 9).
Effect of pH
The esterase was found to be optimally active at pH 5.5 (Fig 10).
Effect of temperature:
The esterase was found to be optimally active at 40°C, with biphasic inactivation at higher temperatures (Fig 11).
Inhibitors: Synthetic inhibitors.
ne of the accepted classifications of esterases is by their inhibition properties (Meyers, 1960; Krisch, 1971; Walker and Mackness, 1983). Carboxylesterases are known to be serine hydrolases and therefore are strongly inhibited by organo phosphorus compounds.
Dichlorvos : The purified esterase, when incubated with different concentrations of dichlorvos , as illustrated for dichlorvos (Table 2, Fig. 12a,b). Maximum inhibition was noticed at 1x10-⁴ concentration. n the other hand, the esterase was found to be relatively resistant when treated with lower concentration of dichlorvos.
Surf excel detergent:
The purified esterase was incubated with 1x concentration of surf excel detergent for 20 minutes and tested for esterase activity using 1 naphthyl acetate as substrate. The enzyme was inhibited by detergent in enzyme assay. The bands were observed in NativePAGE indicating no inhibition (Fig 12c)
Tide detergent:
The purified esterase was incubated with 1x concentration of tide detergent for 20 minutes and tested for esterase activity using 1 naphthyl acetate as substrate. The enzyme was inhibited by detergent in enzyme assay. The bands were observed in NativePAGE indicating no inhibition (Fig. 12d).
Lizol
The purified esterase was incubated with 1x concentration of lizol disinfectant at different intervals of time and tested for esterase activity using 1 naphthyl acetate as substrate. The purified esterase was loaded on the gel Native-PAGE and the obtained gel was incubated with 1x concentration of lizol for 30 mins. Then stained for esterase activity. The band was not visible indicating that esterase has been inhibited (Fig 12e)

1. Vitex negundo (Chinese chaste tree) (Methanol)


4. Calotropis gigantea (crown flower) (Ethanol)

5. Azadiracta indica (Neem tree)(Distilled water)

9. Euphorbia heterophylla (Mexicon fire plant) (Distilled water)
Figure 4. Different natural plant extracts used for carboxylesterase inhibition studies.

8. Nigella sativa (Black jeera) (Distilled water)

10. Ficus carica (Distilled water)
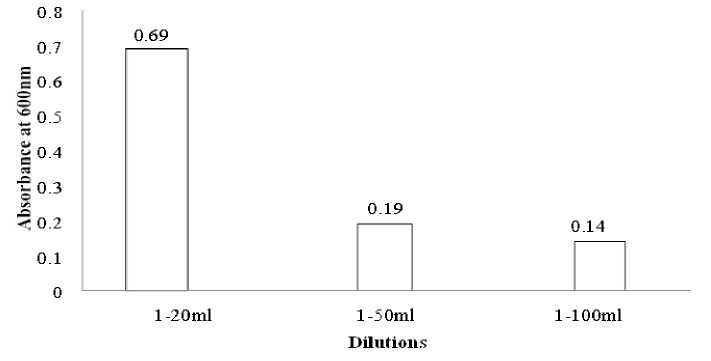
Figure 5. Enzyme activity at different dilutions.
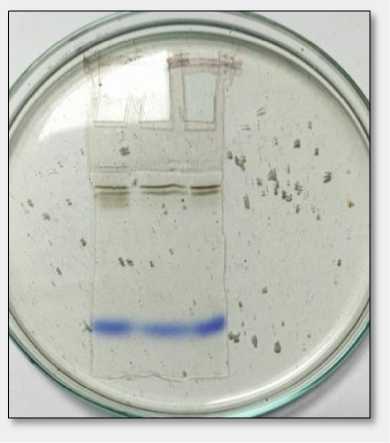
Figure 6. Enzyme activity observed on Native-PAGE.
Table 1 : Purification of carboxylesterase from the midgut of fall armyworm. ( S. frugiperda )
|
Purification step |
Total volume (ml) |
Total protein (mg) |
Total units (µmol/min) |
Specific activity (units/mg protein) |
Fold purification |
% yield |
|
Crude |
100 |
60 |
77970 |
1299.50 |
1.00 |
100.00 |
|
Ammonium sulphate (supernatant) |
28 |
133.6 |
27526.8 |
203.03 |
0.15 |
35.30 |
|
Ammonium sulphate (pellet) |
5 |
9.0 |
8079.5 |
897.72 |
0.69 |
10.36 |
|
DEAE |
1.5 |
2.7 |
19662 |
7282.22 |
5.60 |
25.21 |
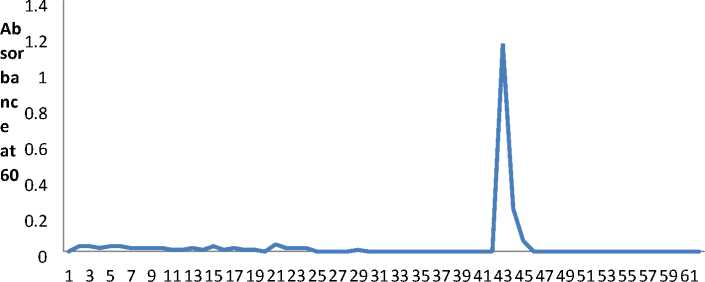
Fraction number
Figure 8a. Native-PAGE (Slab gel) Setup.
Figure 7. DEAE- Cellulose column chromatography of ammonium sulphate fraction of midgut carboxylesterase of FAW.
Figure 8b. After fraction, the stained portion of the gel containing esterase band of desalted DEAE fractions of midgut carboxylesterase from FAW.
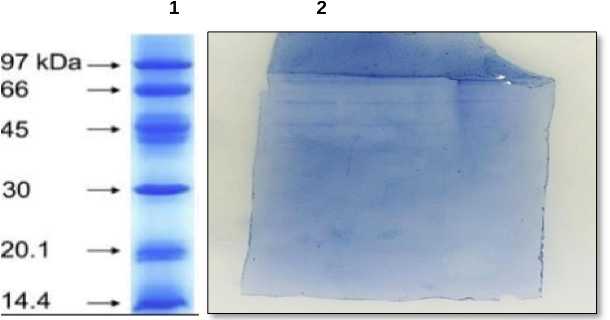
Figure 9. SDS-PAGE analysis (12%): (1) standards protein molecular weight (Gilles Caue, 2016), (2) The observed protein band of midgut carboxylesterase enzyme of FAW.
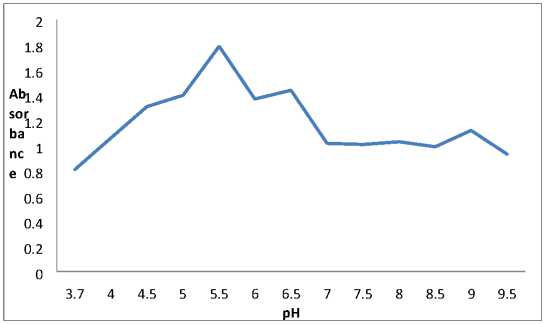
Figure 10. Effect of pH on carboxylesterase activity.
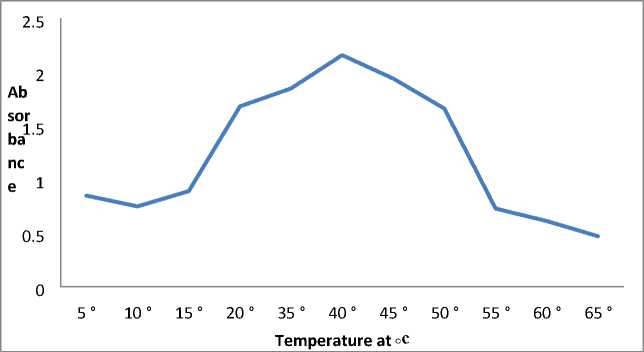
Figure 11. Effect of temperature on carboxylesterase.
Table 2: Esterase inhibition by different concentration of dichlorvos.
|
Concentration of dichlorvos (µM) |
D at 600nm in absence of inhibitor |
D at 600nm in presence of inhibitor |
% inhibition |
|
10-⁴ |
1.58 |
0.03 |
98.1 |
|
10-⁵ |
1.58 |
0.23 |
85.4 |
|
10- 6 |
1.58 |
0.34 |
78.4 |
|
10-⁷ |
1.58 |
0.56 |
64.5 |
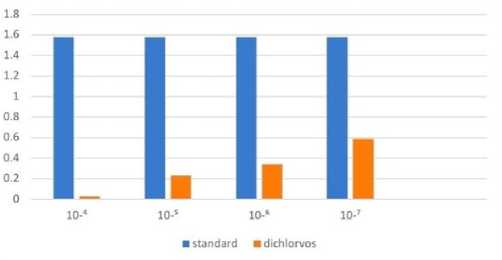

Figure 12b. Native-PAGE, Inhibition of carbo xylesterase by dichlorvos(10-4M)
Figure 12a. Inhibition bar graph for the hydrolysis of 1-naphthyl acetate by the midgut carboxylesterase with dichlorvos.
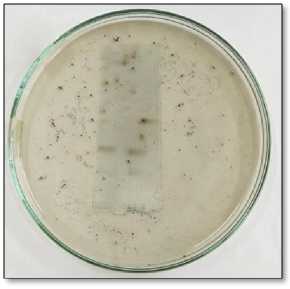

Figure 12c. Native-PAGE, Inhibition of carboxyl esterase by Figure 12d. Native-PAGE, Inhibition of carboxylesterase by
surf excel.
Tide.

Figure 12e. Native-PAGE, Inhibition of carboxylesterase by lizol
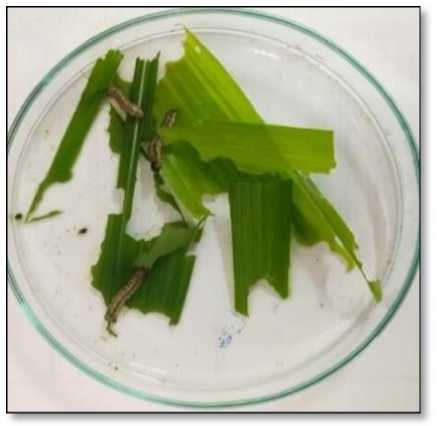

Before lizol
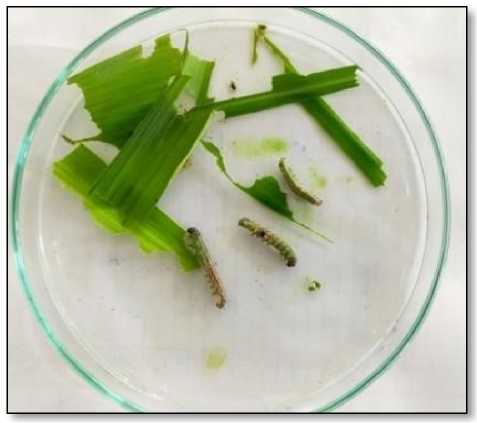

After lizol
Figure 13. The Fall armyworms which were fed with maize leaves sprayed with 1x concentration of lizol
Table 3. Enzyme activity results from natural extracts after 30 minutes incubation.
|
Sl no. |
Natural extract |
Result |
|
1. |
Vitex negundo ( Chinese chaste tree) |
No inhibition |
|
2. |
Melia dubia ( Malabar neem) |
Inhibited |
|
3. |
Ruta graveolens (Rue) |
No inhibition |
|
4. |
Calotropis gigantea (Crown flower) |
No inhibition |
|
5. |
Azadiracta indica (Neem tree) |
No inhibition |
|
6. |
Datura stramonium (Jimson weed) |
No inhibition |
|
7. |
Syzygium aromaticum (Clove) |
Inhibited |
|
8. |
Nigella sativa (Black jeera) |
No inhibition |
|
9. |
Euphorbia heterophylla (Mexicon fire plant) |
Inhibited |
|
10. |
Ficus carica (Fig) |
No inhibition |
1. Vitex negundo

2. Melia dubia
3. Ruta graveolens
4. Calotropis gigantea
5. Azadiracta indica

7. Syzygium aromaticum

8. Nigella sativa
9. Euphorbia heterophylla

10. Ficus carica
Figure 14. Native PAGE of natural extracts treated with midgut carboxylesterase of FAW.
Inhibition of reared fall armyworm
The reared Fall armyworms were fed with maize leaves (which was sprayed by 1x concentration of lizol) for 2 hours of interval. The maize leaves which were not treated with 1x concentration of lizol were fed to some fall armyworms which were used as control for the same interval of time (Fig 13)
The fall armyworms which were treated with 1x concentration of lizol were found dead within 1hour and 30 minutes.
Natural Extracts:
The obtained gel was incubated with natural extracts for 30 minutes duration of time. The portion of gel was stained for esterase band using 1-naphthyl acetate as substrate and fast RR blue as indicator (Table 3) and (Fig 14).
DISCUSSION
CONCLUSION
A Carboxylesterase has been isolated and purified from the midgut of the Fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) by a combination of ammonium sulphate fractionation, DEAE cellulose ion exchange chromatography. The homogeneity of the enzyme was established by PAGE and SDS-PAGE. ur study is mainly based on inhibitors for the carboxyl esterase, which is one of the enzymes involved in detoxification. Inhibiting the carboxylesterase enzyme will decrease the population of fall armyworm which helps in pest control management resulting in high yield of crops. Presently our agriculture system depends on synthetic insecticides which are harmful for environment. The disinfectant lizol, and detergents such as surf excel can be used as inhibitors of esterase at a lower concentration (1x). The different extracts (1x) of Melia dubia, Syzygium aromaticum, the latex of Euphorbia heterophylla are all natural extracts which inhibit the midgut carboxykesterase enzyme of FAW.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest.
Список литературы Studies on isolation, purification and inhibition of carboxylesterase from the midgut of fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda)
- Bateman, M. L., Day, R. K., Luke, B., Edgington, S., Kuhlmann, U., & Cock, M. J. (2018). Assessment of potential biopesticide options for managing fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) in Africa. Journal of applied entomology, 142(9), 805819.
- Baudron, F., Zaman-Allah, M. A., Chaipa, I., Chari, N., & Chinwada, P. (2019). Understanding the factors influencing fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda JE Smith) damage in African smallholder maize fields and quantifying its impact on yield. A case study in Eastern Zimbabwe. Crop protection, 120, 141-150.
- CABI. (2017). New report reveals cost of Fall Armyworm to farmers in Africa, provides recommendations forcontrol. Retrived from: https://www.cabi.org/news-article/new-report-reveals-cost-of-fall-armyworm-to-farmers-in-africa-provides-recommendations-for-control/
- CABI. (2018). Crop Protection Compendium. Retrived from: https://www.cabi.org/cpc/
- Davis, B. J. (1964). Disc electrophoresis. II. Method and application to human serum proteins. Ann. NY Acad. Sci, 121(2), 404-427.
- FAO, CABI. (2019). Community-Based Fall Armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) Monitoring, Early warning and Management, Training of Trainers Manual, First Edition. 112. Retrived from http://www.fao.org/37CA2924EN/ca2924en
- (FAW) in Africa. Food and agriculture Organization of theUnited Nations, 7 FAO, (2019). Regional Workshop for Asia Sustainable Management of Fall Armyworm. Retrived from: http://www.fao.org/3/ca7615en/ca7615en
- Hunter, R. L., & Markert, C. L. (1957). Histochemical demonstration of enzymes separated by zone electrophoresis in starch gels. Science, 125(3261), 1294-1295.
- Kansiime, M. K., Mugambi, I., Rwomushana, I., Nunda, W., Lamontagne-Godwin, J., Rware, H.....& Day, R. (2019). Farmer perception of fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiderda JE Smith) and farm-level management practices in Zambia. Pest management science, 75(10), 2840-2850.
- Krisch, K. (1971). 3 Carboxylic Ester Hydrolases. In The enzymes (Vol. 5,). Academic Press. pp. 43-69
- Ma, M., Jia, H., Cui, X., Zhai, N., Wang, H., Guo, X., & Xu, B. (2018). Isolation of carboxylesterase (esterase FE4) from Apis cerana cerana and its role in oxidative resistance during adverse environmental stress. Biochimie, 144, 85-97.
- Matova, P. M., Kamutando, C. N., Magorokosho, C., Kutywayo, D., Gutsa, F., & Labuschagne, M. (2020). Fall-armyworm invasion, control practices and resistance breeding in Sub-Saharan Africa. Crop science, 60(6), 2951-2970.
- Purification, characterization and properties of carboxylesterase from the midgut of the silkworm, Bombyx mori L. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 26(3), 287-296.
- Myers, D. K. (1960). Carboxyl ester cleavage (survey). In The Enzymes, Vol. IV. P. 1. Boyer, H. Lardy, and K. Myrback (eds.). New York: Academic Press, pp. 475-483.
- Ornstein, L. (1964). Disc electrophoresis. I. Background and theory. Ann. NY Acad. Sci, 121(2), 321-349.
- Reddy, T. S. K., Avinashe, H., & Dubey, N. (2021). Fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) attack on maize crop in India: A review. The Pharma Innovation Journal, SP-10(6): 173-176
- Satoh, T., Taylor, P., Bosron, W. F., Sanghani, S. P., Hosokawa, M. and La Du, B. N. (2002). Current progress on esterases: from molecular structure to function. Drug Metab. Dispos. 30, 488-493.
- Sisay, B., Simiyu, J., Malusi, P., Likhayo, P., Mendesil, E., Elibariki, N.....& Tefera, T. (2018). First report of the fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), natural enemies from Africa. Journal of Applied Entomology, 142(8), 800804.
- Sisay, B., Tefera, T., Wakgari, M., Ayalew, G., & Mendesil, E. (2019). The efficacy of selected synthetic insecticides and botanicals against fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda, in maize. Insects, 10(2), 45.
- Tefera, T., Goftishu, M., Ba, M., Muniappan, R.M. (2019). A Guide to Biological Control of Fall Armyworm in Africa Using Egg Parasitoids. First Edition, Nairobi, Kenya.
- Van Asperen, K. (1962). A study of housefly esterases by means of a sensitive colorimetric method. Journal of insect physiology, 8(4), 401416.
- Veerabhadrappa P.S., Sara Rani M. and Shadaksharaswamy M. (1980). Purification and properties of an esterase from Haltica caerulea. Ind. J. Biochem. Biophys. 17, 186-190.
- Walker, C. H., & Mackness, M. I. (1983). Esterases: problems of identification and classification. Biochemical pharmacology, 32(22), 3265-3269.


