Study of estimation and variation of alpha-amyrin content among individuals of Suaeda maritima (L.) Dumort. growing along the south-east coast of India
Автор: Pati Maniklal, Nandi Asis Kumar
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.20, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Suaeda maritima (L.) Dumort. of the family Chenopodiaceae, is an annual succulent herb growing on salty marshy habitat as one of the dominant mangrove associate species and also as pure vegetation of that. It is regularly harnessed by the local people for use as food as well as for alleviating different maladies. Alpha-amyrin, a triterpenoid, is a remarkable biomolecule available in S. maritima . It is reported to have cardioprotective, anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant properties. A survey of the amount of alpha-amyrin content available in the individuals of S. maritima, collected from eight different regions of the sea coast of the bay of Bengal like, Digha, Sankarpur, Tajpur, Dadanpatrabarh, Shoula, Bankiput and Petuaghat, was conducted with normal phase high performance thin layer chromatography (HPTLC) in this study. It also portrayed variation in the amount of alpha-amyrin among the plant individuals of the species growing in the said zones. The existence of variation in the amount of alpha-amyrin seems to be prospective for selecting the best producer out of them.
Alpha-amyrin, hptlc, suaeda maritima
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143182805
IDR: 143182805
Текст научной статьи Study of estimation and variation of alpha-amyrin content among individuals of Suaeda maritima (L.) Dumort. growing along the south-east coast of India
Alpha-amyrin, a pentacyclic triterpenoid of medicinal importance has been reported to occur in different mangrove plants and mangrove associate species in earlier literatures (Pant and Rastogr, 1979; Ghosh et al ., 1985; erreira, 2022). This active biomolecule possesses a wide spectrum of pharmaceutical and biological functions like, anti-microbial, insecticidal (Ekalu et al ., 2019; Viet et al ., 2021; Oliveria, 2022), antioxidant, anti-arthritic, anti-inflamatory, anti-nociceptive, anti-depressant, anti-hyperglycemic (Oliveira et al ., 2005; Pinto et al ., 2007; olanda et al ., 2008; Barros et al ., 2011; Melo et al ., 2011; Santos et al ., 2012; Aragao et al ., 2015; Beulah, 2021; Lakhmi, 2023), and antiulcer, gastroprotective properties (Oliveira et al ., 2004; Prabhakar et al ., 2017).
Suaeda maritima (L.) Dumort., the annual sea-blite, a herb of the family Chenopodiaceae is locally known as ‘Giria Shak’ in West Bengal. It is used by the village folks as vegetable and also for curing maladies of various nature (Trease and Evans, 2002; Singh et al ., 2013; an and Bakovic, 2015; Roy et al ., 2021).
This species is generally found to grow along the coastal belts of Indian subcontinent as well as grow luxuriantly in the coastal belt of Purba Medinipur district of West Bengal in India (Das et al ., 2015) and the present authors published a report (Pati and Nandi, 2022) on the morphological and phytochemical accounts of the species growing in the coast of Bay of Bengal in Purba Medinipur district.
Estimation of the quantity of alpha-amyrin among different individuals of this species, collected from distantly placed sites of the studied area, were carried out under this program in search of variation in the content, if any, among the individuals of different sites. The biomolecule having medicinal importance any variation in the amount thereof was expected to be worthwhile for sorting out the best producer from amongst the locally growing individuals of the species.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Collection and identification of plant material
Plant samples were collected at their flowering and fruiting stage from eight regions of the cost of the district
Preparation of Sample Solution
The well cleaned aerial parts of the plant materials were chopped into pieces and dried in shade at room temperature and was pounded to powder in mechanical grinder. Twenty grams of the dried aerial parts of different groups of individuals taken as different samples were weighed and poured in 150 mL of methanol solvent. The mixture was stirred on every 30 minutes for 3 hour and thereafter kept as such for two days. The plant extracts were filtered separately using Whatman No 1 filter paper at room temperature. The obtained extracts were concentrated to one third of its original volume by rotary evaporator. The concentrates were dissolved in 2 mL of solvent of methanol: chloroform (1: 1, v/v) in a 10 mL volumetric flask and stored in a refrigerator for PTLC analysis. Thereafter 0.50 mL of this solution was diluted up to 10 mL by methanol to obtain working standard solution of alpha-amyrin (Stahl, 1969).
Preparation of Standard solution
Standard alpha-amyrin (purity 99.3%), from Sigma-Aldrich Chemie Gmb (Aldrich Division, Steinbeim, Germany) was used as reference. Ten mg of alpha-amyrin was accurately weighed and transferred to 10 mL volumetric flask. ive mL of methanol solution was added into the volumetric flask and sonicated in an ultrasonic bath at a frequency 50 z for 5 minutes for complete dissolution of alpha-amyrin. The volume was then made up to 10 mL with methanol. Thus, a stock solution of this standard chemical 1000 μg/mL was prepared (Martelanc et al., 2009).
Preparation of mobile phase
The mobile phase used in the present analysis was prepared by mixing petroleum ether, ethyl acetate, and acetonitrile in the volume ratio of 8.2: 1.2: 0.1 (v/v/v). During development of each plate, a fresh mobile phase was prepared.
High Performance Liquid Chromatography
Chromatography was carried out on 20 cm × 10 cm TLC aluminum pre-coated silica gel 60 254 plate, with 200 μm layer thickness (E. Merck, Mumbai, India). Standard and sample solutions were applied on the plates as 8 mm bands, 13 mm apart from each other and 10 mm from bottom edge of the plate, under a continuous spray of inert gas by means of a Camag Linomat 5 TLC sample applicator with a 100μL syringe ( amilton, Bonaduz, Switzerland). After the application, pre-derivatization was performed by exposing the plate to iodine vapour for 10 minutes. The pre-derivatized plate was developed vertically ascending in a twintrough glass chamber (Camag, Switzerland) saturated with mobile phase and the optimized chamber saturation time for the mobile phase was 20 minutes at room temperature. After development, the plate was air dried and derivatized by dipping in anisaldehyde-sulphuric acid reagent for 2 seconds. The plate was then air-dried for complete removal of anisaldehyde-sulphuric acid and heated at 110°C for 3 minutes. The slit dimension used was 5.00 × 0.45 mm with scanning speed of 20 mm/sec, throughout the analysis and the flow rate of 150 nL/s was used (Martelanc et al ., 2009). Densitometric scanning was then performed at 580 nm for alpha-amyrin using Camag TLC scanner 4 with winCATS software version 1.4.6.
The applied chromatographic conditions permitted a well separation of alpha-amyrin from the plant extract of 8 samples without any decomposition of alpha-amyrin.
Linearity
Determination of linear dynamic range concentration of alpha-amyrin was done by applying 5µL and 6µL of working standard containing alpha-amyrin on TLC plate. The peak area obtained from densitograms for each applied concentration of alpha-amyrin were noted. The calibration curves of the standard were obtained by plotting graphs of mean peak area of the standard versus corresponding concentration.
System suitability
The chromatographic separation was performed by injecting 5µL and 6µL standard solution of alpha-amyrin on TLC plate in two replicates under specified chromatographic conditions (Table 1). The values of percent relative standard deviations of peak area from the chromatogram and retention factor of standards were taken as an indicator of system suitability.
Specificity
Assay
The developed and validated PTLC method was used to quantify the amount of alpha-amyrin from the extract of dried whole plant powder of S. maritima . Twenty microliters (20µL) of each extract of plant materials of 8 zones was applied on the same TLC plate. The plate was developed and scanned under the specified chromatographic conditions ( igure 7). Identity of the bands of alpha-amyrin in the sample solutions was confirmed by comparing the value of retention factor in samples with that of the reference standard. The value of retention factor (Rf) for alpha-amyrin was 0.49.
Estimation of Alpha-amyrin
The amount of alpha-amyrin present in each sample solution was determined from the calibration curve, by using the peak areas of alpha-amyrin in the sample.
RESULTS
The amount of alpha-amyrin was found to vary from 0.03 mg/g to 0.22 mg/g in the populations of the plant species S. maritima growing in different patches along the coastal area of Purba Medinipur district of West
Bengal in India (Table 2). The greater amount of alpha-amyrin was found to occur in the plants growing at Digha, Tajpur, Shoula and Petuaghat regions. The highest amount was noticed in the plants from Digha ( igure 3), shown in TLC plate as track DG ( igure 7) and the lowest in the community from Dadanpatrabarh ( igure 4), shown in TLC plate as Track DP ( igure 7).
Table 1. PTLCperformance of Standard alpha-amyrin.
|
Sample |
Applied volume |
Start Rf |
Max Rf |
End Rf |
Area |
Amount (mg/g) |
|
Standard (S1) |
5 µL |
0.46 |
0.51 |
0.56 |
4197.9 |
0.05 |
|
Standard (S2) |
6 µL |
0.44 |
0.49 |
0.54 |
5079.6 |
0.06 |
Table 2. PTLCperformance of alpha-amyrin from eight populations of S. maritima .
|
Sample No |
Sample |
Applied volume |
Start Rf |
Max Rf |
End Rf |
Area |
Amount (mg/g) |
|
1. |
DG |
20 µL |
0.47 |
0.51 |
0.54 |
12397.1 |
0.22 |
|
2. |
SN |
20 µL |
0.45 |
0.48 |
0.52 |
5167.6 |
0.06 |
|
3. |
TJ |
20 µL |
0.46 |
0.49 |
0.54 |
8972.9 |
0.15 |
|
4. |
DP |
20 µL |
0.48 |
0.51 |
0.55 |
3750.7 |
0.03 |
|
5. |
S |
20 µL |
0.45 |
0.48 |
0.52 |
8731.4 |
0.14 |
|
6. |
JN |
20 µL |
0.49 |
0.52 |
0.56 |
4399.3 |
0.05 |
|
7. |
BN |
20 µL |
0.45 |
0.48 |
0.51 |
5817.2 |
0.08 |
|
8. |
PG |
20 µL |
0.44 |
0.48 |
0.51 |
7309.5 |
0.11 |
[DG- Sample of Digha; SN- Sankarpur; TJ- Tajpur; DP- Dadanpatrabarh; S - Shoula; JN- Junput; BN- Bankiput; PG-Petuaghat].
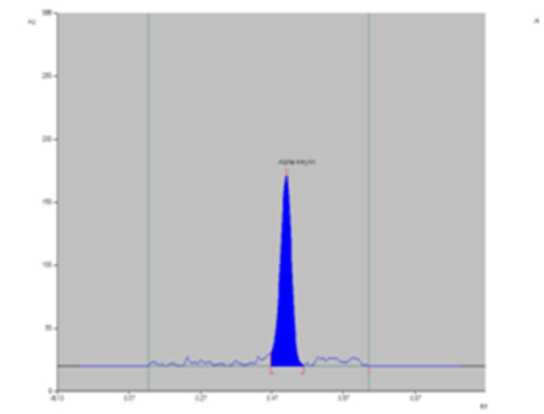
Figure 1. PTLCchromatogram of standard of alpha-amyrin.
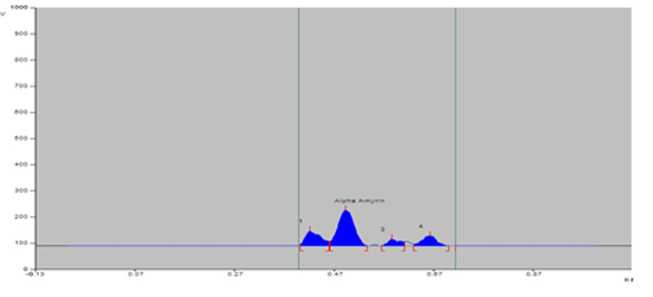
Figure 2. PTLCchromatogram of sample of S. maritima from Tajpur (TJ).
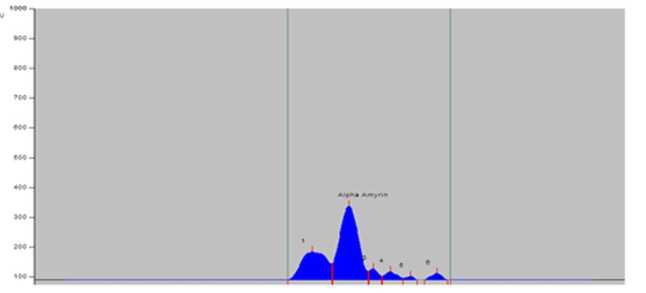
Figure 3. PTLCchromatogram of sample of S. maritima from Digha (DG).
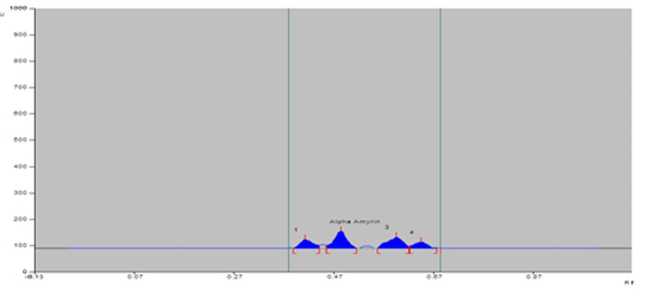
Figure 4. PTLCchromatogram of sample of S. maritima at Dadanpatrabarh (DP).
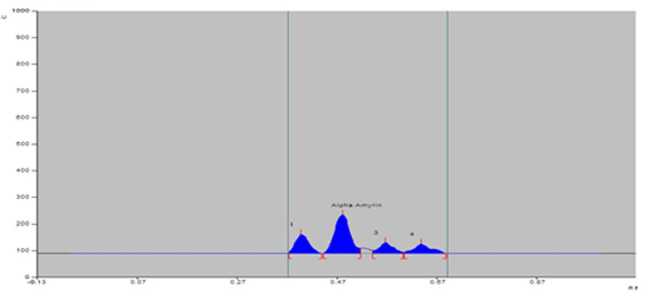
Figure 5. PTLCchromatogram of sample of S. maritima from Petuaghat (PG).
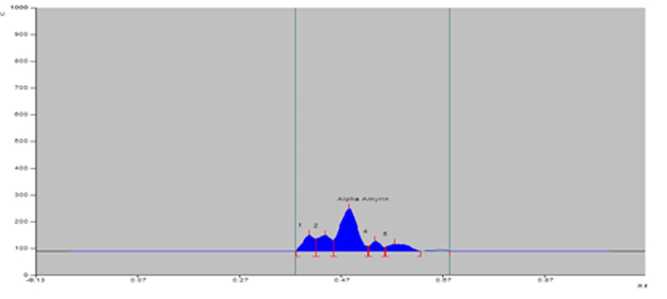
Figure 6. PTLCchromatogram of sample of S. maritima from Shoula (S ).
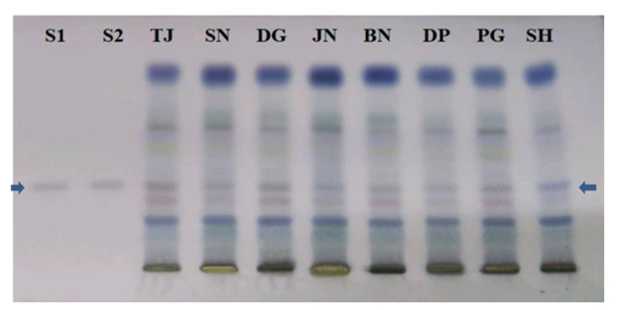
Figure 7. TLC of alpha-amyrin (band marked with arrows) of the standards and from the samples of S. maritima from different sites [S1-Standard; S2- Standard; DG- Digha; SN- Sankarpur; TJ- Tajpur; DP- Dadanpatrabarh; S - Shoula; JN- Junput; BN- Bankiput; PG- Petuaghat].
DISCUSSION
The study showed considerable difference in the amount of alpha-amyrin content among the individuals collected from different spots of the studied area. owever, the cause of such variation can hardly be attributed to their genetic difference, as even the plants being grown at different locations situated far apart from one another, they grow quite contiguously and under the regular influence of tidal waves, which always disseminate the seed propagules indiscriminately leaving least scope for growing of populations with different genetic makeups at different sites.
Earlier works on different plants have shown that the physical factors like heat (Gill and Tuteja, 2010; Pucciariello et al., 2012; ortunato, 2023) or salt stress ( ossain and Dietz, 2016; Yang and Guo, 2018; Behera, 2021; Zang, 2021; Yu B, 2022; Mondal et al., 2023) can lead to the production of greater amount of reactive oxygen species and also the increased production of the biochemicals like, proline, glycine betaine, a host of secondary metabolites including amyrins, to maintain the osmotic balance, to combat the ROS (Reactive oxygen species) and damage due to salt stress. Choi et al. (2012) recorded higher proline content in S. maritima, as a measure to control salt stress, a feature which also relate to the occurrence of amyrin along with other phenolic contents in the plant. Changes in biomolecules under the influence of salinity has been documented in different experiments, as the activity of Superoxide dismutase was recorded to get increased (Wang, 2004; Guan et al., 2011; Sachdev, 2021) and the gene for Glutathione transferase was found to be upregulated (Sahu and Shaw, 2009) in S. maritima tissues with the increase of salinity. So, the changes in metabolite content have been claimed (Yu et al., 2022) to play vital role in maintaining cell osmotic potential, cell membrane structure, as well as in destructing ROS. In consideration of these facts and Digha being situated on the bank of the ocean, Bay of Bengal, in comparison to other sites, taken in the survey, and consequently having greater concentration of salt, the occurrence of greater amount of alpha-amyrin in the plants growing at this site seems to be quite up to the expectation. So, the difference in the amount of alpha-amyrin recorded in the studied populations of S. maritima is least likely due to any genetic difference between them, instead, due to the difference in micro-environmental factors the plants are subjected to.
CONCLUSION
The present work expressed the potentiality of S. maritima as a source of the medicinally important compound alpha amyrin by PTLC. Difference in the amount of alpha amyrin content recorded amongst the individuals of Suaeda maritima growing in the studied area represents intraspecific diversity in respect of that medicinally important biomolecule. The difference in the amount of alpha-amyrin among the contiguously growing individuals might be due to the difference in micro-environmental factors of the growing sites rather than the difference in their genetic content. A further indepth study may confirm the reason behind it. Regular intake of it as food by the local people is expected to be beneficial for them. Proper exploitation of the best producer individuals by pharmaceutical industries may be useful for human welfare in a bigger way.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors are grateful to RKM Quality Testing Laboratory, Narendrapur, Kolkata, India, for providing lab facility. The authors wish to thank to the Director of Central National erbarium, owrah, India for identification and authentication of the species and special thanks go to the local people for their kind cooperation during sample collection.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest.
Список литературы Study of estimation and variation of alpha-amyrin content among individuals of Suaeda maritima (L.) Dumort. growing along the south-east coast of India
- Aragao G.F., Carneiro L.M. and Rota-Junior A.P. (2015). Alterations in brain amino acid metabolism and inhibitory effects on PK are possibly correlated with anticonvulsant effects of the isomeric mixture alpha and beta-amyrin from Protium heptaphyllum. Pharm. Biol, 53(3), 407- 413.
- Barros F.W.A., Bandeira P.N. and Lima D.J.B. (2011). Amyrin esters induce cell death by apoptosis in HL-60 leukemia cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 19, 1268-1276.
- Behera L.M. and Hembram P. (2021). Advances on plant salinity stress responses in the post-genomic era: A review. J. Crop Sci. Biotech., 24, 117-126.
- Beulah G., Divya D., Kumar N.S.S., Sravya M.V.N., Govinda R.K., Chintagunta A.D., Divya G., Hari-Chandana S., Blessy B. D. and Simhachalam G. (2021). Purification and characterization of bioactive compounds extracted from Suaeda maritima leaf and its impact on pathogenicity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Catla catla fingerlings. AMB Expr., 11, 135.
- Choi S.C., Lim S.H. and Kim S.H. (2012). Growth and solute pattern of Suaeda maritima and Suaeda asparagoides in an abandoned salt field. J. Ecol. Field Biol., 35(4), 351-358.
- Das D.C., Pati M. and Mahato G. (2015). Study of the tidal vegetation of Purba Medinipur district of West Bengal, India. Int. J. Bioassays., 4 (5), 3915-3921.
- Ekalu A., Ayo R.G. and Habila J.D. (2019). Bioactivities of Phaeophytin a, a-Amyrin, and lupeol from Brachystelma togoense Schltr. J. Turkish chem. soc., 6(3), 411-418.
- Ferreira M.J., Diana C.G.A., Pinto A.C. and Silva H. (2022). Halophytes as Medicinal Plants against Human Infectious Diseases. Appl. Sci., 12(15), 7493.
- Fortunato S., Lasorella C., Dipierro N., Vita F. and de Pinto M.C. (2023). Redox Signaling in Plant Heat Stress Response. Antioxidants, 12(3), 605.
- Ghosh A., Misra S. and Dutta A.K. (1985). Pentacyclic triterpenoids and sterols from seven species of mangrove. Phytochem., 24(8), 1725-1727.
- Gill S.S. and Tuteja N. (2010). Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem., 48, 909-930.
- Guan B., Yu J., Lu Z., Zhang Y. and Wang X. (2011). Effects of water-salt stresses on seedling growth and activities of antioxidative enzyme of Suaeda salsa in coastal wetlands of the Yellow River Delta. Environ. Sci., 32, 2422-2429.
- Han N. and Bakovic M. (2015). Biologically Active Tri-terpenoids and Their Cardio protective and Anti-Inflammatory Effects. J. Bioanal. Biomed., 12, 005.
- Holanda P.S.A., Pinto L.M.S. and Guedes M.A. (2008). Antinoceptive effect of triterpenoid a, p-amyrin in rats onorofacial pain induced by formalin and capsaicin. Phytomedicine, 15, 630-634.
- Hossain M.S. and Dietz K.J. (2016). Tuning of Redox Regulatory Mechanisms, Reactive Oxygen Species and Redox Homeostasis under Salinity Stress. Front. Plant Sci., 7, 548.
- Lakshmi K.P. and Rao N.G.M. (2023). Antimicrobial Screening of the Solvent Extracts of Halophytic Plant Suaeda maritima (L.) Dumort. Against Selected Pathogens. Sch. Acad. J. Biosci., 11, 315-322.
- Martelanc M., Vovk I. and Simonovska B. (2009). Separation and identification of some common isomeric plant triterpenoids by thin-layer chromatography and high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr., 1216(38), 66626670.
- Melo C.M., Morais T.C. and Tome A.R. (2011). Anti-inflammatory effect of a, b-amyrin, a triterpene from Protium heptaphyllum on cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis in mice. J. Inflamm. Res., 60(7), 673681.
- Mondal S., Burgert S., Asch J., Rahaman E. H. M. S. and Asch F. (2023). Salinity effects on the activities of ROS scavenging enzymes in leaves of two sweet potato clones. J. Agron. Crop Sci., 209, 841853.
- Oliveira F.A., Costa C.L. and Chaves M.H. (2005). Attenuation of capsaicin-induced acute and visceral nociceptive pain by alpha-and beta-amyrin, a triterpene mixture isolated from Protium heptaphyllum resin in mice. Life Sci., 77, 29422952.
- Oliveira F.A., Vieira-Junior G.M. and Chaves M.H. (2004). Gastro protective effect of the mixture of alpha- and beta-amyrin from Protium heptaphyllum: role of capsaicin-sensitive primary afferent neurons. Planta Med., 70, 780-782.
- Oliveira R.C., Bandeira P.N., Lemos T.L.G., Dos Santos H.S., Scherf J.R., Rocha J.E., Pereira R.L.S., Freitas T.S., Freitas P.R., Pereira-Junior F.N., Marinho M.M., Marinho E.M., Marinho E.S., Nogueira C.E.S., Coutinho H.D.M. and Teixeira A.M.R. (2022). In silico and in vitro evaluation of efflux pumps inhibition of a, p-amyrin. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn., 40(23), 12785-12799.
- Pant P. and Rastogr R.P. (1979). The terpenoids. Phytochem., 18(7), 1095-1108.
- Pati M. and Nandi A.K. (2022). Morphological and phytochemical studies of Suaeda maritima (L.) Dumort. growing along the coastal belt of Purba Medinipur District, West Bengal, India in search of the prospective variation. Curr. Bot., 13, 34-39.
- Pinto S.A.H., Pinto L.M.S. and Cunha G.M.A. (2007). Anti-inflammatory effect of a, b-Amyrin, a pentacyclic triterpene from Protium heptaphyllum in rat model of acute periodontitis. Inflammopharmacology, 15, 1-5.
- Prabhakar P., Reeta K.H. and Maulik S.K. (2017). a-Amyrin attenuates high fructose diet-induced metabolic syndrome in rats. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab., 42, 23-32.
- Pucciariello C., Banti V. and Perata P. (2012). ROS signaling as common element in low oxygen and heat stresses. Plant Physiol. Biochem., 59, 3-10.
- Roy M. and Dutta T.K. (2021). Evaluation of Phytochemicals and Bioactive Properties in Mangrove Associate Suaeda monoica Forssk. ex J.F.Gmel. of Indian Sundarbans. Front Pharmacol., 12, 584019,
- Sachdev S., Ansari S.A., Ansari M.I., Fujita M. and Hasanuzzaman M. (2021). Abiotic Stress and Reactive Oxygen Species: Generation, Signaling, and Defense Mechanisms. Antioxidants, 10(2), 277.
- Sahu B.B. and Shaw B.P. (2009). Isolation, identification and expression analysis of salt induced genes in Suaeda maritima, a natural halophyte, using PCR-based suppression subtractive hybridization. BMC Plant Biol., 9, 69.
- Santos F.A., Frota J.T. and Arruda B.R. (2012). Antihyperglycemic and hypolipidemic effects of a, ß-amyrin, a triterpenoid mixture from Protium heptaphyllum in mice. Lipids Health Dis., 11, 98.
- Singh S., Mann R. and Sharma S.K. (2013). Antihyperlipidemic activity of Suaeda maritima (L.) Dumortier Stem in Triton induced hyperlipidemic rat. Int J Ayurveda Pharma Res., 4(2), 203-206.
- Stahl E. (1969). Thin Layer Chromatography Handbook", (2nd ed.). Springer-Verlage, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, pp.873.
- Trease and Evans (2002). Pharmacognosy, (15th ed.). University of Nottingham, Nottingham, UK, pp.22.
- Viet T.D., Xuan T.D. and Anh H. (2021). a-Amyrin and ß-Amyrin isolated from Celastrus hindsii leaves and their antioxidant, anti-xanthine oxidase, and antityrosinase potentials. Molecules, 26(23), 7248.
- Wang B., Luttge U. and Ratajczak R. (2004). Specific regulation of SOD isoforms by NaCl and osmotic stress in leaves of the C3 halophyte Suaeda salsa L. J. Plant Physiol., 161(3), 285-293.
- Yang Y. and Guo Y. (2018). Elucidating the molecular mechanisms mediating plant salt-stress responses. New Phytol., 217(2), 523-539.
- Yu B., Zheng W. and Xing L. (2022). Root twisting drives halotropism via stress-induced microtubule reorientation. Dev. Cell., 57, 2412-2425.
- Yu W., Wu W., Zhang N., Wang L., Wang Y., Wang B., Lan Q. and Wang Y. (2022). Research Advances on Molecular Mechanism of Salt Tolerance in Suaeda. Biology, 11(9),1273.
- Zang W., Miao R., Zhang Y., Yuan Y., Pang Q. and Zhou Z. (2021). Metabolic and molecular basis for the salt and alkali responses of Suaeda corniculate. Environ. Exp. Bot., 192, 104643.


