Study of photosynthesis process in the presence of low concentrations of clomazone herbicide in tobacco ( Nicotiana tabacum)
Автор: Darwish Majd, Lopez-Lauri Flicie, Sallanon Huguette
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 1 т.9, 2013 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The effect of chemical residues of clomazone on photosynthetic processes has been studied by using several low concentrations of the herbicide (0, 1, 0.1, 0.01, 0.001, 0.0001 and 0.00001) µM and seedlings of two varieties of tobacco ( Nicotiana tabacum L.cv.Virginie vk51, Nicotiana tabacum, L.cv. Xanthi ). The content of photosynthetic pigments, the parameters of the chlorophyll-a fluorescence and the JIP-test were performed on an adult leaf (AL) and a young leaf (YL), that gave a complementary design to know the action's mode of clomazone on the plant physiological processes. Clomazone reduced the total chlorophyll (a+b), carotenoids pigments (reduction in size antenna pigments judged by an increase in the chlorophyll a/b ratio) in young leaves more than adults leaves. The maximal photochemical efficiency (Fv/Fm) of photosystem II (PSII) decreased significantly in young leaves compared to adult leaves and in (Virginie) variety than (Xanthi) variety. Among the parameters calculated of the JIP-test most affected by the treatment, PIabs, 1-VJ, ABS/RC, DI0/RC, TR0/RC, ET0/RC, ET0/ABS, which indicated a comparable effects of clomazone(1μM, 0.1µM, 0.01µM) between the two types of leaves and the varieties used. More, the results showed that the concentration (1μM) was the most effective among the other low concentrations used and the (Virginie) variety is more sensitive than the (Xanthi) variety. We conclude that clomazone has probably two combined functions (physiological, toxic) judged by the different behavior of both types of leaves in the presence of the herbicide.
Chlorophyll fluorescence, jip-test, photosynthesis, photosystem ii, tobacco
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14323713
IDR: 14323713
Текст научной статьи Study of photosynthesis process in the presence of low concentrations of clomazone herbicide in tobacco ( Nicotiana tabacum)
The plant uses light energy to synthesize organic compounds. The light reactions of photosynthesis in higher plants are conducted through the cooperation of two photosystems, PSI and PSII which are physically distinct in the stroma and grana of the thylakoid membrane, respectively (Whitmarsh and Govindjee, 1999; Dekker and Boekema, 2005). Today, because of the current development in agricultural production. Pesticides and herbicides that are named plant protection products have become a major environmental danger which menaces the plants on earth's life. Herbicides are chemicals commonly used to control weeds in agriculture and most of them are continually discharged into aquatic environments through surface runoff (Kloeppel et al., 1997). Many studies have been performed to determine the action's mode of herbicides in the production of singlet oxygen (¹O 2 ) and the three intermediate redox states (superoxide, peroxide and hydroxyl radical) which are more reactive (Wong, 2000; Frankart et al., 2003). Other studies have been conducted in particular to elucidate the action's mechanism of herbicides on plant physiology (growth rate, pigment content and chlorophyll fluorescence) and vegetable production (Waldhoff et al., 2002; Kaňa et al., 2004; Walters and young, 2010; Souza et al., 2012). In the case of plants exposed to herbicides, and under a continuous light, electron transport will be blocked and QA will stay in reduced state, promoting the formation of reactive oxygen species, such as (¹O2), via chlorophyll triplet (³Ch*) (Rutherford and Krieger-Liszkay, 2001; Fufezan et al., 2002).
During recent years, an intensive use of herbicides has raised increasing concern mainly because of their massive pollution of the environment. Glyphosate, Clomazone and Paraquat are the most widely used broad-spectrum herbicides (Rosso et al., 2010). Clomazone [2 -(2-chlorobenzyl)-4, 4 dimethyl -1, 2-oxazolidin -3-one] is a pre-emergence herbicide used against broad-leafed and grassy weeds (Chang and Konz, 1984; Warfield et al., 1985). It is widely used to control weeds in canopies of soybean, cotton, sugar cane, maize, rice, tobacco (Chang et al., 1997). Clomazone is used in 78% of the planted area. Before flooding the fields for cultivation of the rice, clomazone alone or in combination with other herbicides is applied for control of weeds (Saldain and Deambrosi, 2009). Clomazone is absorbed by roots and emerging shoots, and transported with the transpiration stream in the xylem (Senseman 2007). It is generally accepted that clomazone prevents the accumulation of chloroplast pigments and plastidic isoprene evolution (Duke and Kenyon 1986; Zeidler et al., 2000). All results showed that the impact of clomazone on carotenoids and chlorophyll biosynthesis leads to bleaching of leaves (photoxidation of chlorophylls). Recently it was shown that the toxicity of clomazone is not induced by clomazone itself, but rather by its break down product, 5- ketoclomazone that blocks 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate (DXP) synthase, the first enzyme of the plastidic isopentenyl diphosphate(IPP) synthesis pathway (Mueller et al. 2000; Ferhatoglu et al., 2001). More, (Souza et al. 2012) indicated that combined clomazone with ametryn herbicide had caused an oxidative stress in the Emilia coccinea plants. In reality, most the experiments which have used high concentrations of clomazone indicate the toxic effect of clomazone on plastid enzymes (DXP, MEP, IPP) and therefore on the biosynthesis of photosynthetic pigments (chlorophyll (a, b) and carotenoids). Limited reports have been published on the effects of low concentrations of clomazone on photosynthesis using chlorophyll-a fluorescence parameters and particularly in cultivar tobacco.
The aim of this work was to study the low concentrations' effects (chemical residues which may exist in the environment) on the physiological process by using several low concentrations of the clomazone. And also if the herbicide lead to an oxidative stress by special regard to changes in photosynthetic pigments, parameters of the chlorophyll-a fluorescence, and by using the JIP-test as a method to evaluate the photosynthesis in adult leaves and young leaves of tobacco's seedling growing in the medium containing clomazone.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Plant material and chemical treatment
Seeds of two varieties of tobacco ( Nicotiana tabacum L.cv.Virgenie vk51, Nicotiana tabacum, L.cv. Xanthi ) were cultivated in soil for two weeks. Germination was carried out in sterile conditions. Tobacco seedlings were obtained in three leaves stage after 5 weeks of the germination. Then, seedlings were placed for 14 days in a nutrient solution of Auckland 1M KNO3 (101g/L) 1M Ca (NO3)2.H2O (236g/L) 1M MgSO4.7H2O (246.5 g/L) 1M KH2PO4 (136.08g/L), 0.01 M FeEDDHA (4.352 g/L) ) with low concentrations (0, 1, 0.1, 0.01, 0. 001, 0.0001, 0.00001) µM of the clomazone herbicide (Sigma-Aldrich, USA) in tubes (15mL). The culture solution was refreshed two times a week. The plants were grown in a growth chamber with temperature of 17° C, humidity60%, 16 h light/8 h dark cycle and the flux of photons (PAR) 70 μ mol. m -².s-¹, to minimize the effect of light and its role in the phenomenon of bleaching, (Duke and Kenyon 1986 ) shown that the use of the light intensity 150μmol photons PAR m-². s-¹ caused the photobleaching in seedlings of cowpea primary.
Determination of chlorophyll and carotenoids content
Total chlorophyll (a+b) and the total carotenoids were determined by extraction using pure acetone (100%) as solvent. Samples were incubated 15 min on ice. Then the samples were centrifuged 5 min at 15000g and 4°C. Quantification of chlorophyll and carotenoids was performed immediately after extraction. Absorbance readings were made at 662
and 645 nm for chlorophyll pigments and 470 nm for carotenoids. The content was calculated using the formula of Lichtenthaler (1987).
Chlorophyll fluorescence and the JIP-test.
The behavior of photosystem II (PSII) can be evaluated using a rapid kinetics of the chlorophyll-a fluorescence emitted by the leaves of plants adapted to darkness. The Chlorophyll-a fluorescence was used to evaluate the state of seedlings in two different varieties of tobacco. The chlorophyll-a fluorescence was determined in the dark, seedlings are adapted for 20 minutes in the dark, an adult (AL) and a young leaf (YL) was taken from each seedling for the measurement. The chlorophyll-a fluorescence (expressed in relative units) was measured using a portable Handy (PEA Hansatech, UK). A strong pulse of light (3000 µmol. m -². s -¹) is used to determine the chlorophyll-a fluorescence. The fluorescence parameters were calculated automatically, Фp0 = Fv /Fm = (Fm-F0) /Fm, which represents the maximal quantum yield photochemical of PSII (Kitajama and Butler, 1975) and the quantum yield of open centers of PSII (Maxwell and Johnson, 2000). The JIP-test was performed on all measures of fluorescence transient and is based on a simple model, how the flux of photons absorbed by photosynthetic pigments antenna (ABS) is dissipated as heat (DI) and fluorescence or transported as the trapped flux (TR) of reaction centers to be converted into energy redox by reducing the plastoquinone (QA) to (QA-). Then (QA-) is reoxidized to (QA), therefore the creation of an electron transport (ET) that leads to CO2 fixation (Heerden et al., 2004). These fluxes are expressed in specific energy flux (per reaction center) or as proportions of other flux (ratios or yields). The values of fluorescence are corresponding to time intervals, the steps O-J-I-P were recorded and used as data origins in the JIP-test (Strasser et al., 2000). Including: the fluorescence intensity maximum (Fm), the fluorescence intensity at 50 ms (F0), 300 µ seconds (F300), and 2 ms (FJ). The calculation of energy flux and ratios of specific flux was fully explained by Strasser and coworkers (Strasser and Strasser, 1995; Tsimilli-Michael et al., 1995; Strasser et al., 2000; Hermans et al., 2003).
Flux of specific energy expressed by the reaction center (RC)
Slope at the origin of the of normalized fluorescence rise
M0 = (F300 – F0) / (Fm – F0) /0, 25 ms
Observed rate of QA reduction
TR0/RC = (M0/Vj) = (ABS/ RC) (Fv/Fm)
Rate of electron transport beyond QA ˉ
ET0/RC = (TR0/RC) (1 - Vj) = (TR0/RC) (ET0/ TR0)
Rate of photon absorption
ABS/RC = (TR0/RC) / [(Fm – F0) /Fm]
Rate of heat dissipation
DI0/RC = (ABS/RC) - (TR0/RC)
Relative variable fluorescence at 2 ms
Vj = (F2ms – F0) / (Fm – F0)
Efficiencies (or flux ratios)
Maximum efficiency with which an absorbed photon results in QA reduction
TR0 /ABS = (TR0/RC) / (ABS/RC) = (Fm- F0) / Fm
Efficiency with which an absorbed photon results in electron transport beyond QA ˉ
ET0/ABS = (ET0/RC) / (ABS/ RC)
Density of reaction centers per the chlorophyll Functional reaction centers per cross-sectional leaf area
RC/ABS = (RC/TR 0 ) (TR 0 /ABS)
Efficiency with which a trapped exciton can move an electron into the electron transport chain further than QA ˉ
ET0/TR0 = (ET0/RC) (TR0/RC) = 1-VJ
Performance index
Compound function of light energy absorption, efficiency of QA reduced and conversion energy to electron transport
PIABS = [RC/ABS] [(TR0/ABS)/(F0/Fm)] [(ET0/TR0)/Vj] ______________________________________________________________________
The subscript " 0 " indicates the quantification of PSII behavior at the onset of fluorescence induction.
ABS is proportional to the concentration of photosynthetic pigments of chlorophyll antenna Chlant ______________________________________________________________________
Statistical analysis
Differences between treatment means were compared using the Wilcoxon test with R statistical software at the 95% probability. Data are presented for values ±S.E. The Significance levels are represented by letters (a, b, c, d) to determine significant differences between treatments.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
For a long time, carotenoids have been given a central role in photoprotection of the photosynthetic apparatus by limiting the destructive reactions (¹O2) or by quenching the triplet state of chl (Chl*), which is sensitive to the formation of reactive oxygen species (Cogdell et al ., 1992; Telfer et al ., 1994; Bartley and Scolnik, 1995). Levels of chlorophyll (Chla, Chlb) and total carotenoids were significantly reduced in leaves of the both tobacco's varieties at the highest concentration of clomazone (1μM) used (Fig. 1C, D, G and H). Agrees with previous results showing that the photosynthetic pigments (Chls, carotenoids) decreased with increasing the concentration of clomazone (Lutzow et al ., 1990; Weimer et al .,
1992; Kaňa et al ., 2004). But we find that the decrease in chlorophyll and carotenoids is more significant in young leaves of the (Virginie) variety (Chls 55.77% (Xanthi), 77.91% (Virginie), Carotenoids 51.09% (Xanthi), 73.61 % (Virginie)) than adult leaves of the variety Xanthi (Chls 5.78% (Xanthi), 38.88% (Virginie ), Carotenoids 3.08% (Xanthi), 33.82% (Virginie)). Clomazone caused a significant increase in ratio (chl a/b) in young leaves at the concentration (1μM) in (Xanthi) variety and (1, 0.1 µM) in (Virginie) variety (Fig. 1B and F). The increase in ratio (chl a/b) indicates that the amount of pigments antenna (LHCII) reduced in the PSII of the thylakoid membrane (Lichtenthaler et al ., 1982; Anderson et al ., 1998; Kaňa et al ., 2004). In addition, with (1μM) of clomazone, there is a significant reduction in the ratio (chl (a+ b)/car) in both type of leaves in (Virginie), compared with ( Xanthi ) which shows a reduction not significant in the young leaves (Fig. 1A and E). This reduction expresses that carotenoids are more affected than Chls by the herbicide.
Chlorophyll fluorescence has been widely used in research of photosynthesis, such as studying the effect of several herbicides on the photosynthetic performance (Frankart et al ., 2003; Kaňa et al ., 2004; Vaillant-Gaveau et al ., 2007). A significant decrease in (Fv/Fm) was observed at the (1μM) treatment in adult leaves of the (Virginie) variety and it was not significant in (Xanthi) variety,( Fig. 2C and F). Related to young leaves, Fv/Fm decreased significantly at the concentration (1μM) ( Fv/Fm= 0.279 (Virginie); Fv/Fm =0.454 (Xanthi). This result don’t corresponds with result of (Kaňa et al ., 2004) showing that clomazone cause a small reduction not significant in Fv/Fm, and with results of (Duke and Kenyon, 1986), who observed no direct effect of clomazone on electron transport in PSII.
In addition, the performance index (PIabs) had provided information on the seedlings tobacco's state treated with clomazone. We notice that clomazone (1μM, 0.1μM) affected both types of leaves, and the young leaves were the most affected. We found that there is a large reduction compared to the control for this parameter ( (1μM) of clomazone PIabs = 0.054 for (Virginie) and PIabs = 0.163 for (Xanthi)) ( Fig. 2B and E). This parameter is related to one hand with the density of reaction centers per chlorophyll, and the other hand with the maximum quantum yield (TR0/ABS) and the efficiency with which a trapped electron can go beyond AQ- in chain electron transport (1-VJ =ET0/TR0) (Strasser et al ., 2000). The J step considered to be associated with an accumulation of QA¯ QB¯ from as demonstrated by experimental results and theoretical simulations. Therefore it is necessary to follow the JIP-test to determine whether the effect of the herbicide on the photosynthetic apparatus is limited on the toxicity of clomazone, which inhibits the synthesis of (Chls carotenoids), or there is an another effect on the process of photosynthesis (the status of electron transport) accordingly.
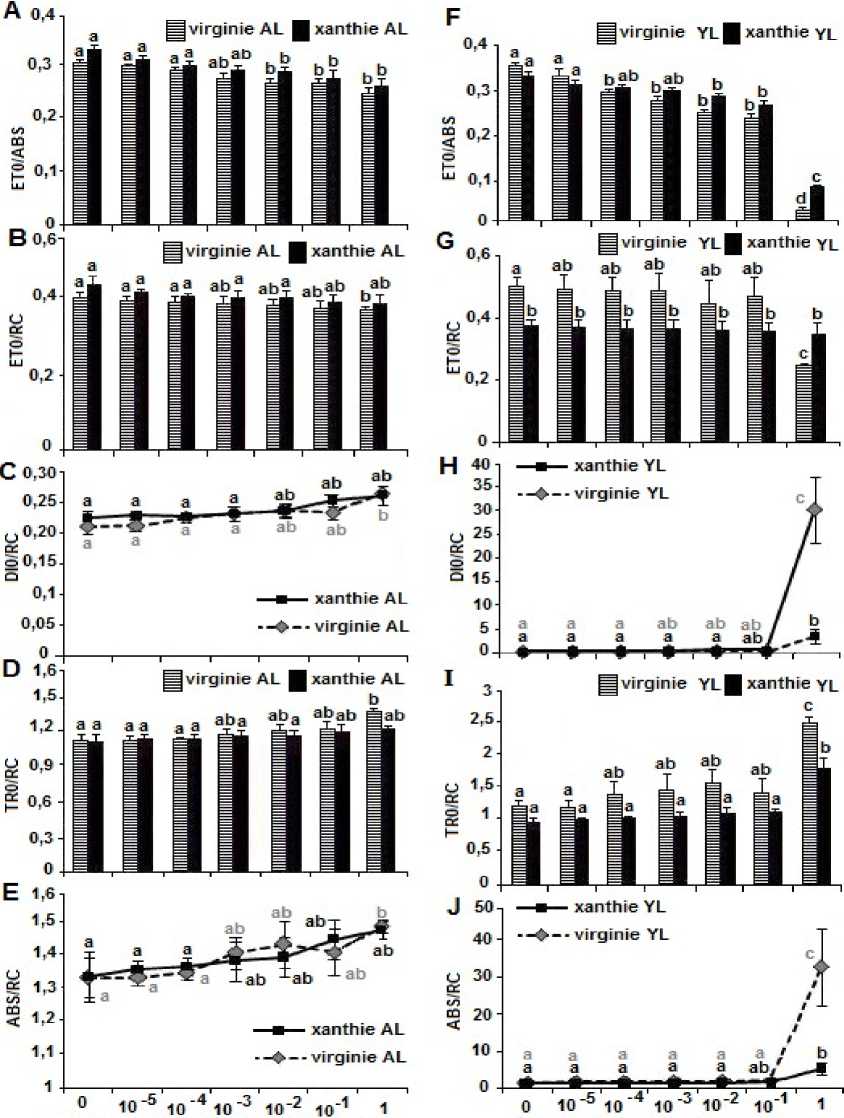
The JIP-test has been used to access the sensitivity of plants to different environmental conditions, (Tsimilli-Michael et al., 1995; Krüger et al., 1997; Ripley et al., 2004; Appenorth et al., 2001; Strauss et al., 2006;Bussotti et al., 2007). Our study confirmed that electron transport at the acceptor side of PSII was a clomazone-induced inhibitory site when tobacco's seedlings exposed to clomazone. A decrease value in the efficiency with which a trapped exciton can move an electron into the electron transport chain further than QA¯ (1-VJ=ET0/TR0) in exposure to (1µM) clomazone in both young and adult leaves. But, the decrease was more pronounced in the young leaves and the (Virginie) variety ( Fig. 2A and D). A significant increase in photons absorbed by the reaction center (ABS/RC) was observed in adult leaves of (Virginie) variety at the concentration (1μM) compared to (Xanthi) variety and other concentrations of the herbicide. In the young leaves, effect of clomazone (1μM) touched the two varieties with a greater increase of (ABS/RC) in (Virginie) variety (Fig. 3E and J), agrees with (Hermans et al., 2003), who noted that the total flux of photon absorbance of PSII by the number reaction center (ABS/RC) was decreased in plants collected, which have a poor performance, and with (Xia and Tian, 2009), who reported that(ABS/RC) increased in Chlorella pyrenoidosa exposed to excess Cu. The parameter (TR0/RC) is proportional to the excitation flux trapped by the reaction center (RC) (Strasser et al., 2000). A significant increase (TR0/RC) was only observed in adult leaves of the variety (Virginie) with clomazone treatment (1μM) (Fig. 3D). In the young leaves, (1μM) of clomazone increased the energy trapped by the reaction center in both varieties, but the increase was greater in (Virginie) than (Xanthi) (Fig.3I). This result is contradictory with (Hermans et al., 2003) indicating that the excitation flux trapped by reaction centers of the PSII reduced with a poor performance of the plants collected. Our result corresponds to results obtained by (Kaňa et al., 2004), who found that the (TR0/RC) parameter increased (30%) for barley plants cultivated in the presence of 500 µM clomazone compared to the control, that can be due to the increase in yield of light in the leaves, this may caused the acceleration of supply and excitation to the reaction center. In our case, this increase (TR0/RC) is due to the increase in photons absorbance (ABS) flux compared with number of reaction centers (RC).
Energy dissipated into heat by the reaction center was only significantly increased in adult leaves treated with (1μM) of clomazone in (Virginie) (Fig. 3C). In young leaves, (1μM) clomazone leads to increase levels of energy dissipation (DI0) by the reaction center (RC), and the more increase was in Virginie (DI0 = 30.272) compared to Xanthi (DI0 = 3.59) (Fig. 3H). We find nevertheless an increase in the energy trapped by the reaction center. There is an important amount of energy that was dissipated as heat and this corresponds to (Hermans et al. 2003) who reported the increase of energy dissipated into heat for plants of poor performance compared with control, agrees with (Khamis et al. 1990; Verhoeven et al., 1997), who indicated that the increase of dissipation into heat of the excited energy is probably due to the intervention of the xanthophyll cycle under conditions of treatment (a deficiency of nitrogen and light intensive). In addition, it is possible that the dissipation of energy into heat by the reaction center has increased with the reduction of carotenoids (LHCs), and therefore it has reduced the ability of pigments to protect the xanthophyll cycle (Kaňa et al., 2004). The electrons transported (ET0) by the reaction center (RC) were significantly reduced for adult leaves in (Virginie) at (1μM) of clomazone and no difference was found in (Xanthi) (Fig. 3B). In young leaves, clomazone (1μM) decreased the electrons transported beyond QA- in both varieties, but the high decrease was in Virginie (50.79% compared with control) compared to Xanthi (7.21% compared with control) (Fig. 3G).Even though, there is a good capture of energy excited by the reaction center (TR0/RC was increased), but still the number of electrons transported by the reaction center has been reduced, according to (Hermans et al., 2003) who showed that the parameter (ET0/RC) was decreased in the leaves of plants that have a low performance (PIabs).
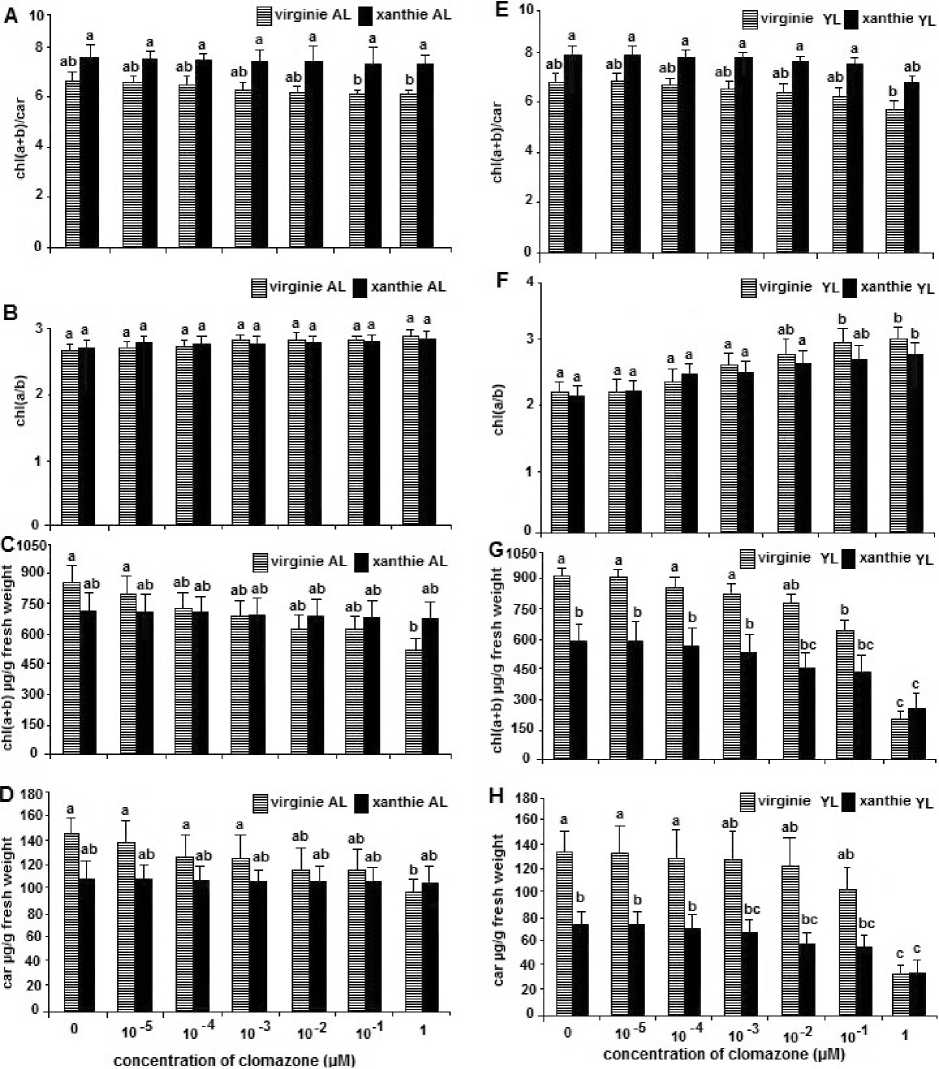
Fig 1. Influence of several low concentrations of clomazone on pigment content in leaves of two varietes of tobacco. All data represent means. SE for n=8 and different letters (a. b. c. d) to determine significant differences between the treatments.
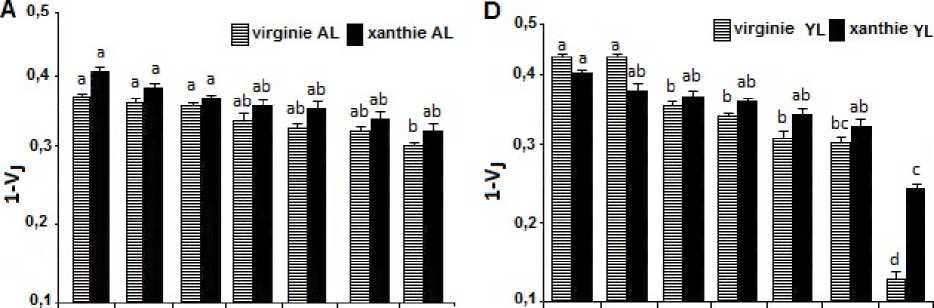
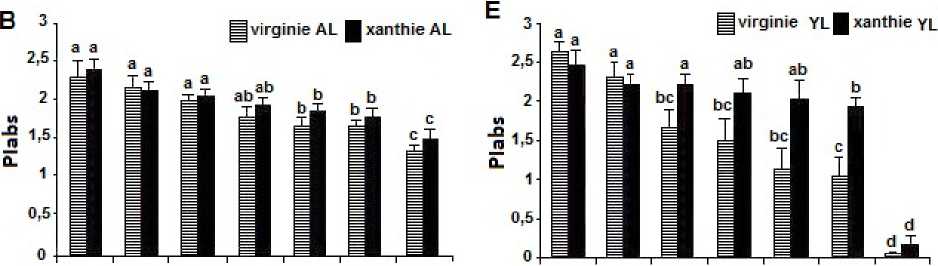
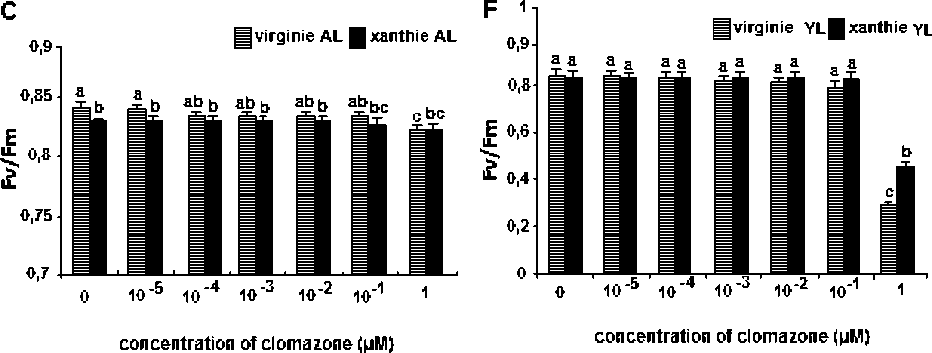
Fig 2. Effect of clomazone treatments in leaves of two varieties of tobacco on Chi fluorescence intensity (Fv/Fm. maximal efficiency photochemical of PSII) and on the performance index (Plabs) in the J step of fluorescence rise.
concentration of clomazone (pM) concentration of clomazone (pM)
Fig 3. ABS/RC, TRO/RC, DIO/RC, ETO/RC and ETO/ABS in the seedling leaves of two varieties of tobacco, which are treated by several low concentrations of clomazone. All datat represent means, SE for n=8 and different letters to detrmine the significant differences between the treatments
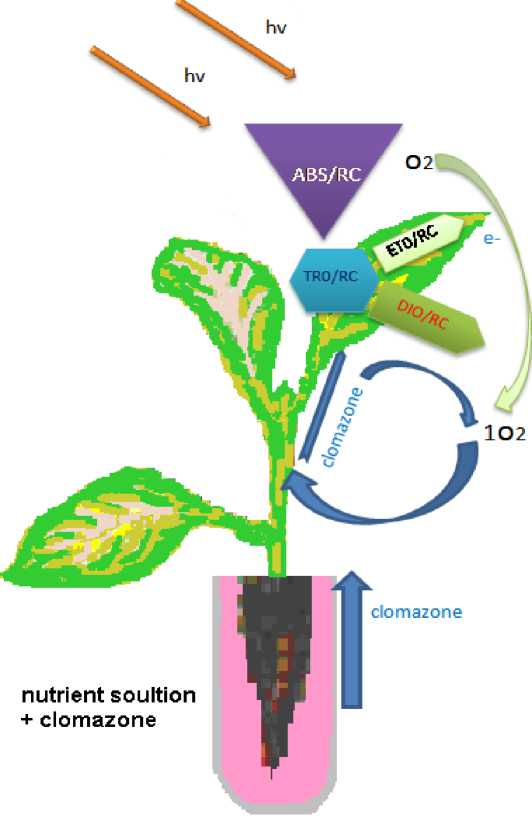
Fig 4. Energy pipeline models of the performance of tobacco seedlings treated with clomazone herbicide. The leaf models show the phenomenological fluctuations which are expressed as total absorbation flux of PSII antenna chlorophyll (ABS), energy flux trapping (TRO), energy dissipated into heat (DIO) and electron transport flux (ETO) divided by the number of active (in the sense of QA reduction) reaction centres (RC).
In addition, the large excited energy dissipation heat can explain the reduction in the transfer of electrons from the reaction center (ET0/RC). The electrons transported (ET0 ) beyond the QA- by photons flux (ABS absorbed by photosynthetic pigments antenna Chls) were reduced more significantly in young leaves than adults leaves. This decrease was found at clomazone treatments (1 0.1, and 0.01) µM in both varieties (Virginie and
Xanthi) (Fig. 3A). In the young leaves, (Virginie) was affected more than (Xanthi) with the concentration (1μM) of clomazone, and there is a significant difference between the two varieties with this treatment (Fig. 3F). As (ET0/ABS) is related to the density of chlorophyll per reaction center (RC/ABS) and the electrons transported by the reaction center (ET0/RC). It is normal that the number of electrons transported (ET0) by the flux of photons absorbed (ABS) decrease, with a decrease found in number of electrons transported (ET0), the increase in the dissipation into heat (DI0/RC) (Appenorth et al., 2001), and the decrease in total chlorophyll. Hermans et al., (2003) found a good relationship between the relative performance of the electron transferred (ET0/ABS ) and the amount of chlorophyll in the leaves of plants selected.
DISCUSSION
The effect of clomazone herbicide on the process of photosynthesis and photosynthetic pigments content has already been studied in barley seedlings by (Kaňa et al., 2004 ), who measured several fluorescence's parameters of chlorophyll-a accompanying with JIP-test (F0, Fm, Fv/Fm, Vj, 1-qp, qn, Rfd, TR0/RC). In this work, we used the content of pigments (carotenoids, chlorophyll (a+b), chl a/b, chl (a+b), the parameters of the fluorescence of chlorophyll-a (F0, Fm Fv/Fm ) and the parameters of the JIP-test (PIabs, 1-VJ,ABS /RC, TR0/RC, DI0/RC, ET0/RC, ET0/ABS) as highly relevant to well determine the effect of clomazone on photosynthesis in two varieties of tobacco. For this, all measurements were performed on an adult and a young leaves. Chlorophyll and carotenoids are strictly correlated with each other, because carotenoids have an important role in protecting chlorophyll from photo-oxidation during growth (Biswall, 1995).
Our work confirms that clomazone reduces the content in pigments of the leaves (total chlorophyll, carotenoids) with the highest concentration used (1μM) in young leaves for both varieties and in adult leaves for (Virginie) variety. A similar decrease was obtained with the high concentration of clomazone in adult leaves of tomato and tobacco (Scott et al., 1994) and seedlings' adult leaves of barley (Kaňa et al., 2004). But in our case, the difference between the two types of leaves means that clomazone probably affects photosynthesis. Especially we observed in (Xanthi) variety that clomazone had not any effect significant to decrease the pigments content in adult leaves, and its effect was significant in young leaves. It gives us an indication that clomazone probably retards the kinetics of photosynthesis, thus the biosynthesis of pigments in young leaves. The behavior of (Virginie)variety which more sensitive support this idea, there is an effect on adult leaves and the effect was multiplied on young leaves. It means that the efficiency of photosynthesis is reduced more with a first influence on photosynthesis. The second influence comes from the reduction in the biosynthesis of photosynthetic pigments, and this probably related to the inhibition of enzymes which synthesize the chlorophyll and carotenoids. After reduced the levels of pigments in the leaves the efficiency of photosynthesis decreases through the reduction of photons absorbed. The correlation between changes in the ability to absorb of photons and parameters of photosynthesis was also observed for leaves growing with different irradiation conditions (Kurasová et al., 2002). Although the parameters of chlorophyll fluorescence-a, as F0, Fm, Fv/Fm, none gives often satisfactory results. The Fv/Fm is often not correlated with the chlorophyll content of leaves (Maxwell and Johnson, 2000; Lazár, 2006). This parameter is an indicator of stress (Maxwell and Johnson, 2000). A decrease in Fv/Fm could be due to an increase in protection by increasing non-radiative energy dissipation or damages of photoinhibition of the reaction center of PSII (Maxwell and Johnson, 2000). In our work, the Fv/Fm is a good indicator that the seedlings are under stress.
Especially, to follow this parameter in an adult and a young leaves, where we find that (Virginie) was more affected for both type of leaves. But the decline in Fv/Fm was higher in young leaves. This also supports our idea, that the effect of clomazone is not limited to its toxic effect, but also it has another function, which affects the PSII reaction center.
In addition, to study the effect of clomazone on the transfer of electrons from the acceptor side of PSII, the JIP-test was used to explain the progressive flux of energy through the reaction center's level of PSII. This test was used for a wide range of physiological processes, such as evaluation of the quality of urban trees in a comparative study of physiological processes by following the flux of energy by the JIP-test (Hermans et al., 2003), the quantification of photosynthetic performance of phosphorus deficiency with the kinetics of fluorescence of chlorophyll-a in sorghum (Ripley et al., 2004), and measurements of chlorophyll florescence to evaluate the time and storage temperature of the leaves of vegetables Valeriana (Ferrante and Magiore, 2007). Among several indices that can be calculated with JIP-test, PIabs,1-VJ, ABS/RC, TR0/RC, DI0/RC, ET0/RC, ET0/ABS, they are the best parameters that showed differences between tobacco's seedlings for the two varieties (Virginie; Xanthi) and both types of leaves (Fig. 2,3). PIabs encompasses fluorescence transient changes associated with changes in antenna conformation and energy fluctuations, therefore PIabs helps to estimate plant vitality with high resolution (Hermans et al., 2003). PIabs indicated a difference response of PSII in the adult and the young leaves treated with clomazone (1, 0.1, 0.01) μM. The (Virginie) variety was the most affected according to this parameter, and the decline in (PIabs) was higher in young leaves than adult leaves, but for another variety (Xanthi), this parameter was reduced only in young leaves. This gives an indicator that the seedlings of tobacco were in the state stressed. In addition, it is normal to find the (PIabs) decreases as a result of the reduction in the maximum efficiency of PSII (Fv/Fm = TR0/ABS) and efficiency with which a trapped exciton can move an electron into the electron transport chain further than QA¯ (1-VJ). The flux of absorbance energy (ABS) and energy dissipation (DI0) by the reaction center increased at the concentration (1μM) in both types of leaves in (Virginie) variety and in young leaves in (Xanthi) variety. These results suggest that Chl antenna size of PSII might decreased by clomazone treatments, agrees with (Kaňa et al., 2004), who confirmed that clomazone reduced the formation of pigment-protein complexes in the thylakoid membrane, and Dinç et al., (2012) reported that reduction of antenna size led to a lower chlorophyll content and the chlorophyll loss had little effect on the antenna size. Although, there is an increase in (TR0/RC), and reduction in (ET0/RC) and (ET0/TR0) in clomazone treatment (1μM), that may be a result of the inactivation of reaction centers (RCs), conversion of excitation energy absorbed into heat (DI0), and partially to the transfer of excitation energy with the PSII antenna. Dinç et al., (2012) indicated that the transfer excitation energy with the antenna does not impose a rate limitation on the trapping of energy(TR0).
CONCLUSION
Chlorophyll-a Fluorescence parameters followed by the JIP-test can be very useful in detecting the effects on the plant physiological processes caused by low concentration of clomazone (1 μM, 0.1 μM, 0.01 μM), and its gave us an alternative view on the action mechanism of clomazone on photosynthesis in seedlings of tobacco treated. Our work showed that there is a difference between the two varieties treated with clomazone, and (Virginie) variety was more sensitive than(Xanthi) variety. We find that the difference between the two types of leaves in response to clomazone treatments is probably due to effect of two functions of clomazone: the first function on the kinetics of photosynthesis and in particular the reaction center of PSII. It is probable that the clomazone blocks electron transfer beyond QA¯(see fig. 2A and D), hence the formation of chlorophyll triplet (³Chl*) is expected, leading to formation of singlet oxygen (¹O2). The accumulation of (¹O2) increasingly contributes to oxidative stress that touches photosynthesis and the biosynthesis of photosynthetic pigments, the adult leaves response in presence of clomazone supports this idea. In addition, through the time, accumulation of (¹O2) and the other (ROS) may help trigger the second toxic function of the herbicide. Ferhatoglu and Barrett, (2006) observed that clomazone was metabolized and oxidized in plants (clomazone → clomazone-OH→ keto-clomazone), then keto-clomazone inhibits synthesis of DXP the first enzyme in the chain of the isoprenoid biosynthesis of chloroplast, which can also confirms our idea Fig. 4.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by the French Ministry of Education and Research, and by laboratory of fruits and vegetables of university of Avignon and Vaucluse countries.
REFRENCES
Anderson, J.M., Chow, W.S and Goodchild, D.J (1998). Thylakoid membrane organization in sun shade acclimation. Aust. J. Plant. Physiol. 15, 11-26.
Appenorth, K.J., Stockel J; Srivastava, A and Strasser, R.J (2001). Multiple effects of chromate on the photosynthetic apparatus of Spirodela polyrhiza as probed by OJIP chlorophyll a fluorescence measurements. Environmental Pollution 115 , 49-64.
Biswall, B (1995). Carotenoids catabolism during leaf senescence and its control by light. Photochem. Photobiol. 30 , 3–14.
Bussotti, F., Strasser, R.J and Schaub, M (2007). Photosynthetic behavior of weedy species under high ozone exposure probed with the JIP-test: A review. Environmental Pollution 147 , 439-437.
Chang, J.H and Konz, M.J (1984). 3-
Isoxazolidinones. A new class of herbicides, ACS Abstract, 187th National Meeting. Pest. Chemistry Div 22.
Chang, J.H., Konz, M.J., Aly, E.A; Sticker, R.E., Wilson, K.R., Korg, N.E and Dickson, P.E (1997). 3-Isoxalidones and related compounds a new class of herbicides, in: Baker DR, Fenyes JG, Moberg WK, Cross B, (Eds.), Synthesis and Chemistry of Agrochemicals, ACS Symposium series 355, American chemical.society, Washington,. DC 10–23.
Cogdell, R.J., Andersson, P.O and Gillbro, T (1992). Singlet states of carotenoids and their involvement in photosynthesis and as pigments collectors of light. Photochimy and photobiology, B: Biologie 15 , 105-12.
Dekker, J.P and Boekema, E.J (2005). Supramolecular organization of thylakoid membrane proteins in green plants. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1706 , 12–39.
Duke, S.O., Kenyon, W.H (1986). Pigment synthesis and photosynthetic function in leaves of cowpea primary (Vigna unguiculata L). Pest. Biochem. Phys. 25: 11-18.
Dinç, E., Ceppi, G.M., Tóth, S.Z., Bottka, S and Schansker, G (2012). The chl a fluorescence intensity is remarkably insensitive to changes in the chlorophyll content of the leaf as long as the chl a/b ratio remains unaffected, Biochim. Biophys. Acta . 1817(5) :770-779
Ferhatoglu, Y., Barret, M and Chapell, J (2001). 5-Ketoclomazone Inhibits 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase of non-.melavonate pathway of isoprenoids biosynthesis, In Proceeding of 2001 National Meeting-Expert Committee on Weeds, Quebec City, Canada, pp 52–53.
Ferhatoglu, Y., Barrett, M and Avduishko, S (2005). The basis for the safening of clomazone by phorate insecticide in cotton and inhibitors of cytochrome P450s. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 81 , 59–70.
Ferrante, A and Maggiore, T (2007). Chlorophyll a fluorescence measurements to evaluate storage time and temperature of Valeriana leafy vegetables. Postharvest. Biology and
Technology 45 , 73-80.
Frankart, C., Eullaffory, P and Vernet, G (2003). Comparative.effects of four herbicides on nonphotochemical fluorescence quenching in. Lema minor. Environmental and Experimental Botany 49 , 159-168.
Fufezan, C., Rutherford, A.W and Liszkay, A.K (2002). Singlet oxygen production in herbicide-treated photosystem II. FEBS letters 532 , 407410.
Khamis, S., Lamaze, T., Lemoine, Y and Foyer, C (1990). Adaptation of the photosynthetic apparatus in maize leaves as a result of nitrogen limitation. Plant Physiol. 94 , 14361443.
Kitajama, M and Butler, W.L (1975). Quenching of chlorophyll fluorescence and primary photochemistry in chloroplasts by dibromothymoquinone. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 376 , 105-115.
Kloeppel, H., Koerdel, W and Stein, B (1997). Transport of herbicides in runoff and retention of herbicides in a band filter rainfall and runoff simulation studies. Chemosphere 35 , 129-141.
Krüger, G.H.J., Tsimilli-Michael, M and Strasser, R.J (1997). Light stress provokes plastic and elastic modifications in structure and function of photosystem II in camellia leaves. Physiol. Plant. 101 , 65–277.
Kurasová, I., Čajánek, M., Kalina, J., Urban, O and Špunda, V (2002). Characterization of acclimation of Hordeum vulgare to high irradiation based on different responses of photosynthetic activity and pigment composition. Photosynth. 72 , 71-83.
Lazár, D (2006). The polyphasic chlorophyll a fluorescence rise measured under high intensity of exciting light. Funct. Plant. Biol. 133 , 9–30.
Lichtenthaler, H.K., Kuhn, G., Prenzel, U., Buschmann, C and Meier, D. (1982). Adaptation of chloroplast-ultrastructure and of chlorophyll protein levels to high-light and lowlight growth conditions. Z. Naturforsch. 37 , 464475.
Lutzow, M., Beyer, P., and Kleinig, H. (1990). The herbicide command does not inhibit the prenyl diphosphate-forming enzymes in plastids, Z. Naturforsch. 45 , 856-858.
Maxwell, K and Johnson, G.N (2000). Fluorescence of chlorophyll-a,. a practical guide. J. Exp. Bot. 51 , 659–668.
Mueller, C., Schwender, J., Zeidler, J and Lichtenthaler, H.K (2000). Properties and inhibition of the first two enzymes of the nonmevalonate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthetic. Biochem. Soc. 28 , 792–793.
Rosso, J.A., Mártire D.O., Gonzalez, M.C and Diaz Kirmser, E.M (2010). Degradation of the herbicides clomazone, paraquat, and glyphosate by thermally activated peroxydisulfate. Agric. and Food Chem. 58, 12858-12862.
Rutherford, A.W and Liszkay, A.K (2001). Oxidative stress induced by herbicides in the photosystem II. Trends in Biochemical Science 26 , 648-653.
Saldain, N and Deambrosi, E (2009). Selectividad del Command en preemergencia en El Paso 144. In: Alvarez O, editor. Arroz Resultados Experimentales 2008- 2009- Instituto Nacional de Investigación Agropecuaria. INIA; Treinta y Tres, Uruguay, pp 7–12.
Scott, J.E., Weston L.A., Chappell, J and Hanley, K (1994). Effect of.clomazone on IPP isomerase and prenyl transferase activities in cell suspension cultures and cotyledons of solanaceous species, Weed Sci. 42, 509–516.
Senseman, S.A (2007). Herbicide Handbook, Ed 9, Weed Science Society of America, Lawrence, KS, pp 224–226.
Souza, R.C., Rocha Gomes Ferreira D.T., Vitorino H.S., Souza Barbosa G.V., Endres, L and Ferreira, V.M (2012). Oxidative stress in Emilia coccinea (Asteraceae) caused by a mixture of Clomazone+ Ametryn. International Research Journal of Plant Science 3 ( 5 ), 80-87.
Strauss, A.J., Kruger, G.H.J., Strasser, R.J and Van Heerden, P.D.R (2006). Ranking of dark chilling tolerance in soybean genotypes probed by the chlorophyll a fluorescence transient O-J-I-P. Environmental and Experimental Botany 56 , 147-157.
Telfer, A., Dhami, S., Bishop, S.M., Phillips, D and Barber, J (1994)..B Carotene quenches singlet oxygen formed by isolated Photosystem II reaction centres. Biochimie 33 , 14469-74
Tsimilli-Michael, M., Kruger, G.H.J and Strasser, R.J (1995). Suboptimality as driving force for adaptation: a study about the. correlation of excitation light intensity and the dynamic fluorescence emission in plants. In Photosynthesis:.From Light to Biosphere, eds, P Mathis, Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, pp. 981–984.
Vaillant-Gaveau, N., Bigot, A., Fontaine, F and Clément, C (2007). Effect of the herbicide flumioxazin on photosynthetic performance of grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.). Chemosphere 67, 1243–1251.
Verhoeven, A.S., Demming-Adams, B and Adams, W.W (1997). Enhanced employment of the xanthophyll cycle and thermal energy dissipation in spinach exposed to high light and N stress. Plant Physiol. 113:817-824.
Waldhoff, D., Furch, B and Junk, W.J (2002). Fluorescence parameters, chlorophyll concentration, and anatomical features as indicators for flood adaptation of an abundant tree species in Central Amazonia: Symmeria paniculata . Environ. Exp. Bot. 48 , 225-235.
Walters, S.A and Young, B.G (2010). Effect of herbicide and cover crop on weed control in notillage jack-o-lantern pumpkin ( Cucurbita pepo L.) production. Crop protection 29 , 30-33.
Warfield, T.R., Carlson, D.B; Bellmann, S.K and Guscar, H.L (1985). Weed control in soybeans using command, Weed Sci. Abstr . 25 , 105.
Weimer, M.R., Balke, N.E and Buhler, D.D (1992). Herbicide.clomazone does not inhibit in vitro geranylgeranyl synthesis from mevalonates. Plant Physiol. 98, 427-432.
Whitmarsh, J. and Govindjee (1999) The Photosynthetic Process. Concepts in Photobiology: Photosynthesis and
Photomorphogenesis. Edited by G.S. Singhal, G. Renger, K-D. Irrgang, S. Sopory and Govindjee. Narosa Publishers/Kluwer Academic Publishers, pp. 11-51.
Wong, P.K (2000). Effect of 2,4-D, glyphosate and paraquat on growth, photosynthesis and chlorophyll-a synthesis of Scenedesmus quadricauta. Berb. 614. Chemosphere 41 , 177182.
Xia, J and Tian, Q (2009). Early stage toxicity of excess copper to photosystem II of Chlorella pyrenoidosa-OJIP chlorophyll a fluorescence analysis. Journal of Environmental Science 21 , 1569-1574.
Zeidler, J., Schwender, J., Mueller, C and Lichtenthaler, H.K. (2000). The non-mevalonate isoprenoid biosynthesis of plants as a test system for drugs against malaria and pathogenic bacteria. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 28 , 796–797.
Список литературы Study of photosynthesis process in the presence of low concentrations of clomazone herbicide in tobacco ( Nicotiana tabacum)
- Anderson, J.M., Chow, W.S and Goodchild, D.J (1998). Thylakoid membrane organization in sun shade acclimation. Aust J Plant Physiol 15, 11-26.
- Appenorth, K.J., Stockel J; Srivastava, A and Strasser, R.J (2001). Multiple effects of chromate on the photosynthetic apparatus of Spirodela polyrhiza as probed by OJIP chlorophyll a fluorescence measurements. Environmental Pollution 115, 49-64.
- Bartley, G.E and Scolnik, P.A (1995). Plant carotenoids: pigment.for photoprotection, visual attraction, and human health. Plant Cell 7, 1027-1038.
- Biswall, B (1995). Carotenoids catabolism during leaf senescence and its control by light. Photochem. Photobiol 30, 3-14.
- Bussotti, F., Strasser, R.J and Schaub, M (2007). Photosynthetic behavior of weedy species under high ozone exposure probed with the JIP-test: A review. Environmental Pollution 147, 439-437.
- Chang, J.H and Konz, M.J (1984). 3-Isoxazolidinones. A new class of herbicides, ACS Abstract, 187th National Meeting. Pest. Chemistry Div 22.
- Chang, J.H., Konz, M.J., Aly, E.A; Sticker, R.E., Wilson, K.R., Korg, N.E and Dickson, P.E (1997). 3-Isoxalidones and related compounds a new class of herbicides, in: Baker DR, Fenyes JG, Moberg WK, Cross B, (Eds.), Synthesis and Chemistry of.Agrochemicals, ACS Symposium series 355,.American chemical.society, Washington,. DC 10-23.
- Cogdell, R.J., Andersson, P.O and Gillbro, T (1992). Singlet states.of carotenoids and their involvement in photosynthesis and as pigments collectors of light. Photochimy and photobiology, B: Biologie 15, 105-12.
- Dekker, J.P and Boekema, E.J (2005). Supramolecular organization of thylakoid membrane proteins in green plants. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1706, 12-39.
- Duke, S.O., Kenyon, W.H (1986). Pigment synthesis and photosynthetic function in leaves of cowpea primary (Vigna unguiculata L). Pest. Biochem. Phys 25: 11-18.
- Dinç, E., Ceppi, G.M., Tóth, S.Z., Bottka, S and Schansker, G (2012). The chl a fluorescence intensity is remarkably insensitive to changes in the chlorophyll content of the leaf as long as the chl a/b ratio remains unaffected, Biochima et Biophysica Acta. 1817(5):770-779
- Ferhatoglu, Y., Barret, M and Chapell, J (2001). 5-Ketoclomazone Inhibits 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate synthase of non-.melavonate pathway of isoprenoids biosynthesis, In Proceeding of 2001 National Meeting-Expert Committee on Weeds, Quebec City, Canada, pp 52-53.
- Ferhatoglu, Y., Barrett, M and Avduishko, S (2005). The basis for the safening of clomazone by phorate insecticide in cotton and inhibitors of cytochrome P450s. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol 81, 59-70.
- Ferrante, A and Maggiore, T (2007). Chlorophyll a fluorescence measurements to evaluate storage time and temperature of Valeriana leafy vegetables. Postharvest. Biology and Technology 45, 73-80.
- Frankart, C., Eullaffory, P and Vernet, G (2003). Comparative.effects of four herbicides on non-photochemical fluorescence quenching in. Lema minor. Environmental and Experimental.Botany 49, 159-168.
- Fufezan, C., Rutherford, A.W and Liszkay, A.K (2002). Singlet oxygen production in herbicide-treated photosystem II. FEBS letters 532, 407-410.
- Heerden, P.D.R., Strasser, R.J and Stress, G.H.J (2004). Reduction in.dark chilling N2-fixation in soybean by nitrate indicated by the kinetics of the florescence of chlorophyll-a. Physiol. Plant 121, 239-249.
- Hermans, C., Smeyers, M., Rodriguez R.M., Eyletters, M., Strasser, R.J and Delhaye, J.P (2003). Quality assessment of urban. Trees: a comparative study of physiological processes by.following the website of the fluorescence by the test-OJIP, Plant Physiol 160, 81-90.
- Kaňa, R., Šponduvá, M., Ilík, P., Lazár, D., Klem, K; Tomek, P., Nauš, J and Prášil, O (2004). Effect of herbicide clomazone.on.photosynthetic processes in primary barley (Hordeum.Vulgare). Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology 78, 161-170.
- Khamis, S., Lamaze, T., Lemoine, Y and Foyer, C (1990). Adaptation of the photosynthetic apparatus in maize leaves as a result of nitrogen limitation. Plant Physiol 94, 1436-1443.
- Kitajama, M and Butler, W.L (1975). Quenching of chlorophyll fluorescence and primary photochemistry in chloroplasts by dibromothymoquinone. Biochim Biophys. Acta 376, 105-115.
- Kloeppel, H., Koerdel, W and Stein, B (1997). Transport of herbicides in runoff and retention of herbicides in a band filter rainfall and runoff simulation studies. Chemosphere 35, 129-141.
- Krüger, G.H.J., Tsimilli-Michael, M and Strasser, R.J (1997). Light stress provokes plastic and elastic modifications in structure and function of photosystem II in camellia leaves. Physiol. Plant 101, 65-277.
- Kurasová, I., Čajánek, M., Kalina, J., Urban, O and Špunda, V (2002). Characterization of acclimation of Hordeum vulgare to high irradiation based on different responses of photosynthetic.activity.and pigment composition. Photosynth 72, 71-83.
- Lazár, D (2006). The polyphasic chlorophyll a fluorescence rise measured under high intensity of exciting light. Funct Plant. Biol. 133, 9-30.
- Lichtenthaler, H.K., Kuhn, G., Prenzel, U., Buschmann, C and Meier, D. (1982). Adaptation of chloroplast-ultrastructure and of chlorophyll protein levels to high-light and low-light growth conditions. Z. Naturforsch 37, 464-475.
- Lichtenthaler, H.K (1987). Chlorophylls and carotenoids-pigments.of photosynthesis biomebranes, in: Colowick SP, Kaplan,.N.O,.(Eds.), Methods in Enzymology, Vol 148. Academic Press, New York, pp 350-382.
- Lutzow, M., Beyer, P and Kleinig, H (1990). The herbicide command does not inhibit the prenyl diphosphate-forming enzymes in plastids, Z. Naturforsch 45, 856-858.
- Maxwell, K and Johnson, G.N (2000). Fluorescence of chlorophyll-a,. a practical guide. J. Exp. Bot 51, 659-668.
- Mueller, C., Schwender, J., Zeidler, J and Lichtenthaler, H.K (2000). Properties and inhibition of the first two enzymes of the non-mevalonate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthetic, Biochem. Soc 28, 792-793.
- Ripley, B.S., Redfern, S.P and Dames, J (2004). Quantification.of the photosynthetic performance of phosphorus-deficient Sorghum by means of chlorophyll-a fluorescence kinetics. South African Journal of Science 100, 615-618.
- Rosso, J.A., Mártire D.O., Gonzalez, M.C and Diaz Kirmser, E.M (2010). Degradation of the herbicides clomazone, paraquat, and glyphosate by thermally activated peroxydisulfate. Agric and Food Chem 58, 12858-12862.
- Rutherford, A.W and Liszkay, A.K (2001). Oxidative stress induced by herbicides in the photosystem II. Trends in Biochemical Science 26, 648-653.
- Saldain, N and Deambrosi, E (2009). Selectividad del Command en preemergencia en El Paso 144. In: Alvarez O, editor. Arroz Resultados Experimentales 2008-2009-Instituto Nacional de Investigación Agropecuaria. INIA; Treinta y Tres, Uruguay, pp 7-12.
- Souza, R.C., Rocha Gomes Ferreira D.T., Vitorino H.S., Souza Barbosa G.V., Endres, L and Ferreira, V.M (2012). Oxidative stress in Emilia coccinea (Asteraceae) caused by a mixture of Clomazone+ Ametryn. International Research Journal of Plant Science 3(5), 80-87.
- Strauss, A.J., Kruger, G.H.J., Strasser, R.J and Van Heerden, P.D.R (2006). Ranking of dark chilling tolerance in soybean genotypes probed by the chlorophyll a fluorescence transient O-J-I-P. Environmental and Experimental Botany 56, 147-157.
- Strasser, R.J., Srivastava, A and Tsimilli-Michael, M (2000). The fluorescence transient as a tool to characterize the situation photosynthetic samples. In M Yunus, U Pathre, P Mohanty, eds, Probing photosynthesis: mechanisms, regulation and adaptation.Taylor & Francis, London, UK, pp 445-483.
- Telfer, A., Dhami, S., Bishop, S.M., Phillips, D and Barber, J (1994)..B Carotene quenches singlet oxygen formed by isolated Photosystem II reaction centres. Biochimie 33, 14469-74
- Tsimilli-Michael, M., Kruger, G.H.J and Strasser, R.J (1995). Suboptimality as driving force for adaptation: a study about the. correlation of excitation light intensity and the dynamic fluorescence emission in plants. In Photosynthesis:.From Light to Biosphere, eds, P Mathis, Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, pp 981-984.
- Vaillant-Gaveau, N., Bigot, A., Fontaine, F and Clément, C (2007). Effect of the herbicide flumioxazin on photosynthetic performance of grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.). Chemosphere 67, 1243-1251.
- Verhoeven, A.S., Demming-Adams, B and Adams, W.W (1997). Enhanced employment of the xanthophyll cycle and thermal energy dissipation in spinach exposed to high light and N stress. Plant Physiol 113:817-824.
- Waldhoff, D., Furch, B and Junk, W.J (2002). Fluorescence parameters, chlorophyll concentration, and anatomical features as indicators for flood adaptation of an abundant tree species in Central Amazonia: Symmeria paniculata. Environ. Exp. Bot. 48, 225-235.
- Walters, S.A and Young, B.G (2010). Effect of herbicide and cover crop on weed control in no-tillage jack-o-lantern pumpkin (Cucurbita pepo L.) production. Crop protection 29, 30-33.
- Warfield, T.R., Carlson, D.B; Bellmann, S.K and Guscar, H.L (1985). Weed control in soybeans using command, Weed Sci. Abstr. 25, 105.
- Weimer, M.R., Balke, N.E and Buhler, D.D (1992). Herbicide.clomazone does not inhibit in vitro geranylgeranyl synthesis from mevalonates. Plant Physiol 98, 427-432.
- Whitmarsh, J. and Govindjee (1999) The Photosynthetic Process. Concepts in Photobiology: Photosynthesis and Photomorphogenesis. Edited by G.S. Singhal, G. Renger, K-D. Irrgang, S. Sopory and Govindjee. Narosa Publishers/Kluwer Academic Publishers, pp 11-51.
- Wong, P.K (2000). Effect of 2,4-D, glyphosate and paraquat on growth, photosynthesis and chlorophyll-a synthesis of Scenedesmus quadricauta. Berb. 614. Chemosphere 41, 177-182.
- Xia, J and Tian, Q (2009). Early stage toxicity of excess copper to photosystem II of Chlorella pyrenoidosa-OJIP chlorophyll a fluorescence analysis. Journal of Environmental Science 21, 1569-1574.
- Zeidler, J., Schwender, J., Mueller, C and Lichtenthaler, H.K. (2000). The non-mevalonate isoprenoid biosynthesis of plants as a test system for drugs against malaria and pathogenic bacteria. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 28, 796-797


