Study of Serum Magnesium Levels and Its Relation to Glycemic Control in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Автор: Ashok V., Padmini P.J.
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 4 т.16, 2020 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Background and objectives: Diabetes mellitus is the most common endocrine disorder and the leading cause of death and disability in the world. Magnesium is the most common intracellular cation involved in insulin mediated glucose uptake. This study was conducted in type 2 diabetic patients to assess fasting blood glucose (FBS), HbA1c and serum magnesium levels and compare it with normal controls. Materials and Methods: This was a case control study which included 50 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and 50 healthy controls. Serum magnesium was estimated by calmagite endpoint method. HbA1c was estimated by immunoturbidimetry method. Statistical analysis was done using SPSS. Results and discussion: Decrease in mean level of serum magnesium were observed among diabetic patients. A negative correlation was observed between serum magnesium and HbA1c. A linear regression analysis showed an inverse relationship between serum magnesium and glycemic control among patients with diabetes mellitus. Conclusion: We concluded that type 2 diabetic patients who are at risk of developing microvascular complications with poor glycemic control must be regularly monitored for serum magnesium levels.
HbA1C, diabetes mellitus, magnesium, glycemic control
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143173866
IDR: 143173866
Текст научной статьи Study of Serum Magnesium Levels and Its Relation to Glycemic Control in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus is a major endocrine disorder of the world because of its increase in prevalence rate globally. The International Diabetes Federation (IDF) shows the total number of diabetic patients to be around 40.9 million in India and this is further going to rise to 69.9 million by the year 2025 (Sicree, 2006).
High concentration of glucose in the serum can increase the glycation of hemoglobin, forming Glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c). It is a simple and economical way for assessment of long term glycemic control (6-8 weeks) (Sacks et al. , 2002). Type 2 diabetes mellitus is associated with significant morbidity and mortality mainly due to microvascular complications which is related to poor glycemic control.
The present study was conducted to evaluate serum magnesium levels and its relation to glycemic control among the type 2 diabetic patients
OBJECTIVES
This study was carried out with the following objectives
-
1 To evaluate the serum magnesium levels in patients with Type 2 Diabetes mellitus and compare it with normal controls
-
2 To find the correlation between serum magnesium and HbA1C and FBS in patients with diabetes mellitus
MATERIALS AND METHODS
This study was conducted in the Department of Biochemistry at Karpagam faculty of medical sciences and research. This study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee, Karpagam faculty of medical sciences and research, Coimbatore
Study design: Hospital based case control study Sample size : 100 (calculated by 4pq/d2; where p is prevalence)
Study group: 50 Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and 50 healthy controls.
INCLUSION CRITERIA: Patients with Type 2 Diabetes mellitus attending diabetic clinic at Karpagam faculty of medical sciences and research, Coimbatore.
EXCLUSION CRITERIA: Patients with c ardiovascular disorders, pulmonary disorders (like respiratory failure) , Infections (Urinary tract infection) & inflammatory states , febrile illness , cancers , pregnant women with diabetes mellitus, patients receiving magnesium supplements or magnesium containing antacids, patients on diuretics, patients with history of alcohol abuse, malabsorption or chronic diarrhoea, patients who refused to give informed consent for the study.
Subjects who fulfilled the inclusion and exclusion criteria were included in the study. After explaining the nature of the study, written consent was obtained from all subjects before collecting blood sample.
Biochemical analysisEstimation of Fasting Blood sugar
Fasting blood sugar (FBS) was measured by glucose oxidase – peroxidase method using autoanalyser (Trinder, 1969).
Estimation of HbA1c
HbA1c was estimated by turbidometric immunoassay method (Jeppsson et al. , 2002).
Estimation of serum magnesium
Statistical analysis
Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS, USA) was used to do the statistical analysis. All parameters were presented as mean ± standard deviation (mean ± SD). Student's t-test was used for comparing the means of continuous variables. The correlations between various variables were calculated using the Pearsons correlation analysis. A linear regression analysis was performed to evaluate interrelationship between serum magnesium and HbA1C and FBS. A p value of less than 0.05 was taken as statistically significant.
RESULTS
The mean concentration values of serum magnesium, HbA1C and FBS were 1.28 mg/dl, 7.3 %, and 121 mg/dl respectively in patients with diabetes mellitus.
HbA1C and FBS were significantly higher in diabetic patients when compared with controls (Table 1). Decrease in mean level of serum magnesium were observed among type 2 diabetic patients (Table 1). Pearson’s correlation analysis showed a negative correlation between serum magnesium and FBS (r=-0.801, P<0.00) and also between serum magnesium and HbA1C (r=-0.804, P<0.00) (Table 2).
A linear regression analysis showed an inverse relationship between serum magnesium and HbA1C in patients with Diabetes mellitus (Figure 1).
Table 1. Comparison of clinical parameters between diabetic group and control groups
|
Parameters |
Diabetic group |
Control group |
P value |
|
Serum Magnesium (mg/dl) |
1.28 ± 0.26 |
2.11 ± 0.24 |
0.001* |
|
HBA1C (%) |
7.36 ± 1.13 |
5.54 ± 0.33 |
0.001* |
|
FBS(mg/dl) |
121 ± 14.09 |
86 ± 8.74 |
0.001* |
Data are presented as Mean ±SD.*P value ≤0.05 is statistically significant. Student t test was used to analyse the data. FBS=Fasting Blood Sugar
Table 2. Correlation analysis of Magnesium with FBS and HbA1c in type 2 diabetic patients
|
Variables |
R value |
P value |
|
FBS |
-0.801 |
0.00* |
|
HbA1C |
-0.804 |
0.00* |
Pearson correlation analysis was performed to analyze the data. * p<0.05 is considered statistically significant. FBS=Fasting Blood Sugar
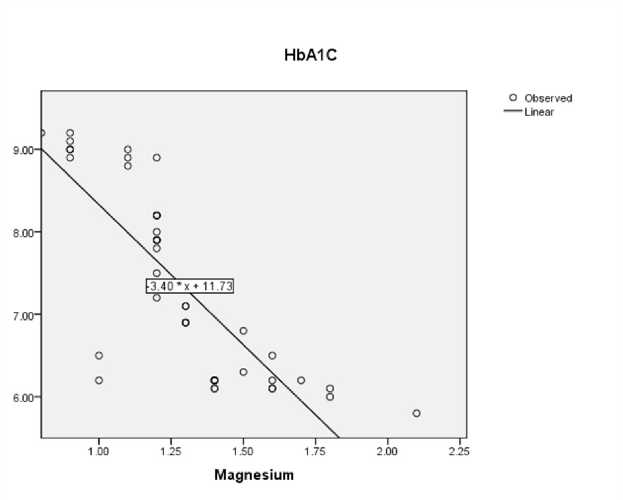
Figure 1. inearregression analysis between serum magnesium and HbA1c among the diabetic cases
DISCUSSION
Diabetes mellitus is a heterogeneous group of multifactorial, polygenic syndrome characterized by chronic hyperglycemia caused by a relative or absolute deficiency in insulin (Champe et al. , 2005). The chronic complications of diabetes mellitus affect many organ systems and it is the major cause of morbidity and mortality in patients with diabetes mellitus. The chronic complications are divided into macro vascular complications (coronary artery disease, peripheral arterial disease, and stroke) and micro vascular complications (diabetic nephropathy, neuropathy, and retinopathy) (Fowler, 2008).
Our study showed decreased level of magnesium in diabetic patients compared with the controls. This was in accordance with the results by Kundu et al. (2013) and Dasgupta et al. (2012). Serum magnesium was negatively correlated with FBS and HbA1C which is consistent to the results by Rao & Rao (2016). However a study by Saeed et al. (2019) showed no correlation between serum magnesium and HbA1C levels.
Magnesium depletion has a negative impact on glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity in diabetic patients. Hence prevention of hypomagnesemia in diabetic patients may therefore be beneficial in the management of the disease. The cause for the high prevalence of magnesium deficiency in diabetes are not clear, but may include increased urinary loss, lower dietary intake, or impaired absorption of Mg compared to healthy individuals. Patients with diabetes mellitus have altered metabolism of magnesium, probably due to hyperglycemia. Chronic hyperglycemia causes depression in the net tubular reabsorption of magnesium leading to hypomagnesaemia (Supriya et al. , 2013). ow levels of magnesium have shown to damage tyrosine kinase activity and receptors involved in insulin signaling (Sales & Pedrosa, 2006).
Diabetic patients with hypomagnesemia should be carefully monitored for glycemic control in order to prevent microvascular complications of diabetes mellitus. Hence screening should be done for the early detection of hypomagnesemia and to prevent complications in patients with diabetes mellitus. Further large scale studies are necessary to find the role of magnesium supplementation in Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
CONCLUSION ow serum magnesium is one of the additional risk factors for the development of microvascular complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Prevention of hypomagnesemia in diabetes mellitus by supplementing magnesium may be helpful in increasing insulin sensitivity and delaying the development of complications. Type 2 diabetic patients who are at risk of developing microvascular complications with poor glycemic control must be regularly monitored for serum magnesium levels.
Список литературы Study of Serum Magnesium Levels and Its Relation to Glycemic Control in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Champe P.C., Harvey R.A., Ferrier D.R. (2005) Illustrated Biochemitry, Diabetes Mellitus. 3rd ed. USA: Lippincott, Williams and Wilkins, P 342-351.
- Dasgupta, A., Sarma, D., & Saikia, U.K. (2012). Hypomagnesemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Indian journal of endocrinology and metabolism, 16(6), 1000.
- Fowler, M.J. (2008). Microvascular and macrovascular complications of diabetes. Clinical diabetes, 26(2), 77-82.
- Geiger, H., & Wanner, C. (2012). Magnesium in disease. Clin Kidney J. 5 (Suppl 1), i25–i38.
- Glindler, E.M., Hetti, D.A. (1971). Colorimetric determination with bound “Calmagite” of magnesium in human blood serum. Clin Chem, 17, 662.
- Jeppsson, J.O., Kobold, U., Barr, J., Finke, A., Hoelzel, W., Hoshino, T., Miedema, K., Mosca, A., Mauri, P., Paroni, R., Thienpont, L., Umemoto, M. & Weykamp C. (2002). Approved IFCC reference method for the measurement of HbA1c in human blood. Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine (CCLM), 40(1), 78-89.
- Kundu, D., Osta, M., Mandal, T., Bandyopadhyay, U., Ray, D., & Gautam, D. (2013). Serum magnesium levels in patients with diabetic retinopathy. Journal of natural science, biology, and medicine, 4(1), 113.
- Rao, Y.S., & Rao, V.D. (2016). Serum magnesium levels in type 2 diabetes. Int J Res Med Sci, 4, 991-994.
- Sacks, D.B., Bruns, D.E., Goldstein, D.E., Maclaren, N.K., McDonald, J.M., & Parrott, M. (2002). Guidelines and recommendations for laboratory analysis in the diagnosis and management of diabetes mellitus. Clinical chemistry, 48(3), 436-472.
- Saeed, H., Haj, S., & Qasim, B. (2019). Estimation of magnesium level in type 2 diabetes mellitus and its correlation with HbA1c level. Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism, 2(1), e00048.
- Sales, C.H., & Pedrosa, L.D.F.C. (2006). Magnesium and diabetes mellitus: their relation. Clinical nutrition, 25(4), 554-562.
- Saris, N.E.L., Mervaala, E., Karppanen, H., Khawaja, J. A., & Lewenstam, A. (2000). Magnesium: an update on physiological, clinical and analytical aspects. Clinica chimica acta, 294(1-2), 1-26.
- Sicree, R. (2006). Diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance. Diabetes atlas, 15-109.
- Supriya, M.S., Pinnelli, V.B., Murgod, R., & Raghavendra, D.S. (2013). Evaluation of serum copper, magnesium and glycated haemoglobin in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Asian J Pharm clin res, 6(2), 188-90.
- Trinder, P. (1969). Determination of glucose in blood using glucose oxidase with an alternative oxygen acceptor. Annals of clinical Biochemistry, 6(1), 24-27.


