Sustainable municipal solid waste incineration fly ash (MSWIFA) alkali-activated materials in construction: fabrication and performance
Автор: Peng Dong, Jingyi Liu, Huiru Wang, Hongyan Yuan, Quan Wang
Журнал: Нанотехнологии в строительстве: научный интернет-журнал @nanobuild
Рубрика: Системные решения технологических проблем
Статья в выпуске: 1 т.14, 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Introduction. Recent years have seen a pressing need to dispose of municipal solid waste due to rapid urbanization. The municipal solid waste incineration fly ash (MSWIFA) produced from solid waste incineration power plant exhibits pozzolanic properties and poses concern of toxicity leaching when used directly as building materials. This paper presents an alkali-activation method to produce sustainable alkali-activated MSWIFA materials (AAFMs) with various MSWIFA dosages and investigate the corresponding fabrication and performance. Materials and Methods. Composited alkali activators activate the MSWIFA with constant alkalinity of 5% and the molar ratio of Si/Na = 0.86. The resulting geopolymers' bulk densities, mineral composites, morphology, and compression strength are thoroughly examined. Results and discussions. Results show that the use of MSWIFA may lead to more loose structures because the bubbles are generated from metallic aluminum and alkali activators. Additionally, the production of multiple crystals also accounts for increasing porosity. The generated multi-crystals such as Sylvite, Halite, Hydrocalumite, Calcium Hydroxide, and Ettringite are further detected from the morphology and mineral analysis. Furthermore, compression tests and toxicity characteristic leaching procedures (TCLP) are conducted to investigate the mechanical performance and heavy metals solidification performance of AAFMs, with an optimal compression strength of 19.99MPa at 28 days for AAFM-10 while toxicity leaching is subject to regularity limits. Conclusions. This study shows that great potential of using the alkali-activation method to recycle hazardous municipal solid fly ash into construction materials with both ecological safety and high performance.
Municipal solid waste fly ash, alkali-activation, mineral analysis, morphography, compression strength, toxicity leaching
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142231840
IDR: 142231840 | УДК: 62 | DOI: 10.15828/2075-8545-2022-14-1-43-52
Текст научной статьи Sustainable municipal solid waste incineration fly ash (MSWIFA) alkali-activated materials in construction: fabrication and performance
Original article
methods, incineration is considered as a great alternative due to its effective mass/volume reduction of waste by 70/90%, respectively, and its more straightforward treatment process, low cost and even the potential of powergeneration [4]. Besides, the incineration waste residue shows excellent potential as a source of construction materials that may help mitigate carbon emissions caused by cement production and further elevate the resource utilisation and revolution of green materials and construction.
The municipal solid waste incineration residuals are generally composed of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash (MSWIFA) and municipal solid waste incineration
SYSTEM SOLUTIONS FOR TECHNOLOGICAL PROBLEMS bottom ash (MSWIBA) [5]. Containing similarly fundamental chemicals such as Al2O3, CaO, and SiO2 with OPC, MSWIFA is expected as raw materials to agglomerate and burn clinker or play a role as supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs) to produce other construction materials such as Strain hardening cementitious composites (SHCC) [6]. The MSWIFA also feature high heavy metal leaching and high concentration chlorides, which may have risks in contaminating groundwater and soil if leached, although only approximately 20% of total residual volume. Consequently, wise strategies are necessary to solidify the heavy metals before direct using MSWIFA as the ideal SCM. Various chelating agents are well developed for heavy metal immobilisation, while the MSWIFA after processing may still end up in landfill sites rather than used as construction materials. It has been reported that cement solidification/immobilisation can effectively reduce the potential of heavy metal leaching [7]. However, the extra consumption of cement may run counter to reducing carbon emissions [8]. Conversely, from current research, heavy metal solidification/im-mobilisation of MSWIFA by the alkali-activation method may present a possible solution to considering service performance and environmental effects.
Alkali activation (Geopolymerization) is defined as the reaction of a solid aluminosilicate precursor under alkaline conditions or induced by the alkali activator to produce a hardened binder based on a combination of hydrous alkali-aluminosilicate and alkali-alkali earth-aluminosilicate phases [9]. The general mechanism of geopolymerization involves the dissolution, migration, gelation, reorganization, polymerization, and hardening of aluminosilicate precursors [10]. The final products mainly contain various disordered, high-molecular, and well-connected sodium-aluminate-silicate-hydrate (N-A-S-H) gels networks in which basic metal cations (e.g., K+, Na+ and Pb+) are incorporated to balance the charge in these structures. The most common precursors used to produce alkali-activated materials (geopolymers) are wastes or industrial by-products, which may be derived from various resources and industrial activities such as Coal Fly Ash (CFA), Ground-granulated Blast Furnace Slag (GGBS), Red Mud (RM) [11, 12] and Municipal Solid Waste Ash (MSWA). The utilisation and transformation of industrial by-products as renewed raw materials significantly control emission footprint and are promoted as an environmentally beneficial option in engineering practice.
While alkali activation of high-pozzolanic solids such as CFA and GGBS has received considerable attention, the fabrication and performance of AAFMs, especially in terms of mechanical performance and environmental safety (heavy metal leaching behaviours), have not been well-studied. Recently, some studies on AAFMs have been conducted in conjunction with using MSWIFA as an aluminosilicate precursor. The dehydrated cementitious waste (DCW) is employed as a binder substitute to produce a DCW-IFA paste that exhibits the anticipated solidification/immobilization action on heavy metals such as Pb [13]. AAFMs can also be synthesized using a ternary binder composed of MSWIFA, OPC, and Metakaolin (MK). The presence of metakaolin significantly reduced the amount of heavy metals released from the binder matrix [14]. A composite binder comprising 50% wt. MSWIFA, and 50% wt. OPC is intended to fabricate AAFMs with a compression strength of more than 18.8 MPa at 28 days [15]. Moreover, existing metallic aluminum in MSWIFA/MSWIBA has also garnered considerable interest owing to its rapid burning of aluminum waste and formation of a protective oxidized coating [16,17]. Aluminum may result in a porous structure, lowering the mechanical property. Additionally, the microstructure is discovered using a visual approach, which reveals crystals with various forms and porous morphog-raphy [18].
This research aims to investigate the alkali-activated fabrication procedures and performance, which help reuse the MSWIFA as sustainable construction materials with high performance. In this study, the geopolymers made by proper activators and gradient MSWIFA dosage are firstly fabricated. Subsequently, the tests of morphology and mineral analysis of pastes are conducted to show the physical and chemical properties of AAFMs. Furthermore, the mechanical property is of primary concern and determined by compression tests to examine the fundamental loading capacity as construction materials. Heavy metal leaching tests are finally conducted to simulate solidification performance in complex natural environments for the sake of environmental safety.
-
2. MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1. Materials
The municipal solid waste incineration fly ash is collected from a waste incineration power station in Weifang, Shandong Province, China. The solid precursors may also contain Coal Fly Ash (CFA), Ground-granulated Blast Furnace Slag (GGBS) and 42.5 MPa Ordinary Poland Cement (OPC) as significant aluminosilicate resources produced from a thermal power plant (Meizhou, China), Wuxin Materials Company (Wuhan, China) and Huaxin Cement Corporation (Wuhan, China), respectively. Fig. 1 presents particle distributions of MSWIFA. From the figure, most MSWIFA particles range from 0.93–103 µm with the average particle size of 9.87 µm, while the mean size of CFA and GGBS particles are 18.3 and 13.7 µm, respectively. The chemical compositions of these raw materials are then determined by an X-ray fluorescence spectrometer (XRF), as shown in Table 1. The alkaline
SYSTEM SOLUTIONS FOR TECHNOLOGICAL PROBLEMS
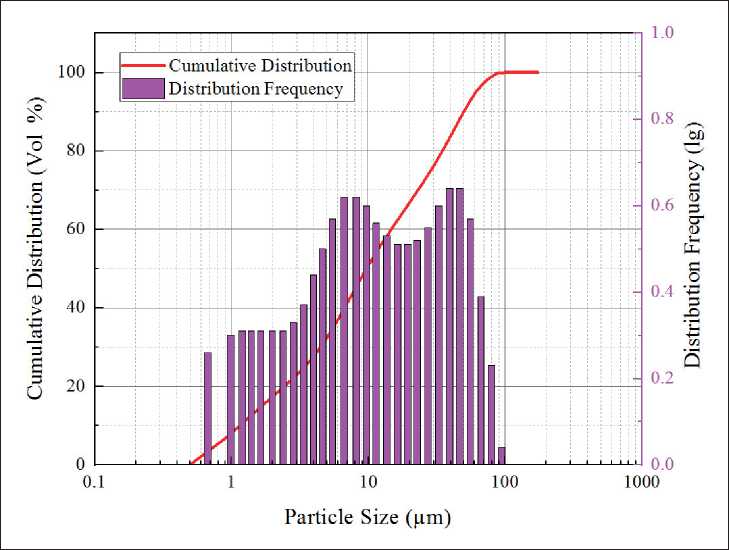
Fig. 1. Particle size distribution of MSWIFA
Table 1
Chemical compositions of MSWIFA (wt. %)
2.2. Mixture design
The mix design in this work contains a total of 12 groups of mixtures, as shown in Table 2. The alkali activators are configured from the table by adjusting the relative amounts of Sodium Hydroxide, Sodium Metasilicate, and deionised water. The solutions for all mixtures are set as constant alkalinity of 5% with the same molar ratio of Si/Na = 0.86. In binders, the dosage of GGBS accounts for 50% weight of the binder (MSWIFA + CFA + GGBS) in each group, while CFA replaces the IFA from 0% to 50%. This water/solid ratio also keeps constant as W/S = 0.39.
2.3. Preparation process
The binder powders and corresponding solid alkaline pellets (NaOH + Na2SiO3•5H2O) are firstly dry-mixed for 2 mins to reach a homogeneous state. Subsequently, the deionised water is poured into the homogeneous mixtures and blended in a low speed for the 30 s, high speed for 1min, and finally 30s at a low rate. After mixing, the fresh geopolymers are finally pro-
SYSTEM SOLUTIONS FOR TECHNOLOGICAL PROBLEMS
Table 2
Mixture proportions of AAFMs
|
Proportion by weight |
||||
|
MSWIFA |
CFA |
Slag |
Cement |
|
|
AAFM-0 |
0 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
0 |
|
AAFM-10 |
0.1 |
0.4 |
0.5 |
0 |
|
AAFM-20 |
0.2 |
0.3 |
0.5 |
0 |
|
AAFM-30 |
0.3 |
0.2 |
0.5 |
0 |
|
AAFM-40 |
0.4 |
0.1 |
0.5 |
0 |
|
AAFM-50 |
0.5 |
0 |
0.5 |
0 |
|
CS-50 |
0.5 |
0 |
0 |
0.5 |
Water/Solid Ratio = 0.39; Si/Na = 0.86 in activators.
duced with proper workability and fluidity. The above geopolymer pastes are then cast in molds with the size of 50×50×50 mm and cured under the lab conditions for 7 and 28 days after demolding.
-
2.3.1. Tests and Characterization
-
2.3.1.1. Bulk Density
-
-
2.3.1.2. Morphography
-
2.3.1.3. Mineral analysis
X-ray diffraction (XRD) is carried out to reveal the crystalline phases of MSWIFA-based geopolymers via diffractometer (Bruker D8 Powder). The diffraction is operated at 40 kV and 40 mA with a Cu Kβ of 1.54056 Å. The diffraction range is set from 6.25 deg to 90 deg with an interval of 0.02 deg per step. Powder samples for XRD tests are crushed and sieved under 45µm-sized sieves and evenly laid on the slides.
-
2.3.2. Compression tests
-
2.3.3. Toxicity characteristic leaching procedure (TCLP)
-
3. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1. Bulk Density
Bulk density is a sufficient index of structure compactness. A micrometer scale directly weights the mass of geopolymers, while the volume can be measured by the Archimedes drainage method. The bulk density is finally calculated by dividing the mass of the sample by the volume of displaced water.
The microtopography of geopolymers is obtained by a Zeiss Merlin scanning electron microscope (SEM). After pre-heating at 60oC to evaporate the inner water, the specimens are cut into dimensions under 0.5 cm and coated with Pt by a coating machine to enhance surface charging. The accelerating voltage and current are 5 kV and 5 mA under the SE2 channel pattern. Coupled with SEM, element analysis is also conducted to characterize the elementary composites of specific areas and points in the images by an Apollo X energy dispersive system (EDS).
The compression strength of MSWIFA-based geopolymers is determined by an unconfined uniaxial compression test according to ASTM C109 [19]. The dimension of samples is set as 50×50×50 mm. The prepared specimens are then loaded in a multi-function mechanical testing machine (Weeping brand, China) with a rate of 50 N/s. An automation software records the loading force and the displacements until failure. The compression tests are performed at curing age of 7 day and 28 day, respectively.
The leaching test is conducted by the horizontal oscillation method to determine the toxicity of samples in accordance with GB 16889-2008 [20]. The solid samples are firstly broken down and crushed into fragments (< 9 mm). After that, the crushed chippings were dissolved and emerged in 5% glacial acetic acid at liquid-solid ratio (L/kg) 20:1. Then all the suspensions are set into conical flasks and shook at a vibration frequency of 110 ± 10 times/min and an amplitude of 40mm under a horizontal oscillation shaker. The mixtures were firstly shaken for 8 hours under laboratory conditions and then kept steady for another 16 hours. After filtering by a 0.45 µm filter in a Buchner funnel, the leachate was collected and tested via an Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES, Perkin Elmer). The regular limit of concentrations of leached heavy metals including Zn, Pb, Cu, Ba, Cr, and Cd are 100, 0.25, 40, 25, 4.5, and 0.15 mg•L–1, respectively.
Fig. 2 shows the bulk density of AAFMs. From the result, the AAFMs’ bulk density is inversely related to
SYSTEM SOLUTIONS FOR TECHNOLOGICAL PROBLEMS
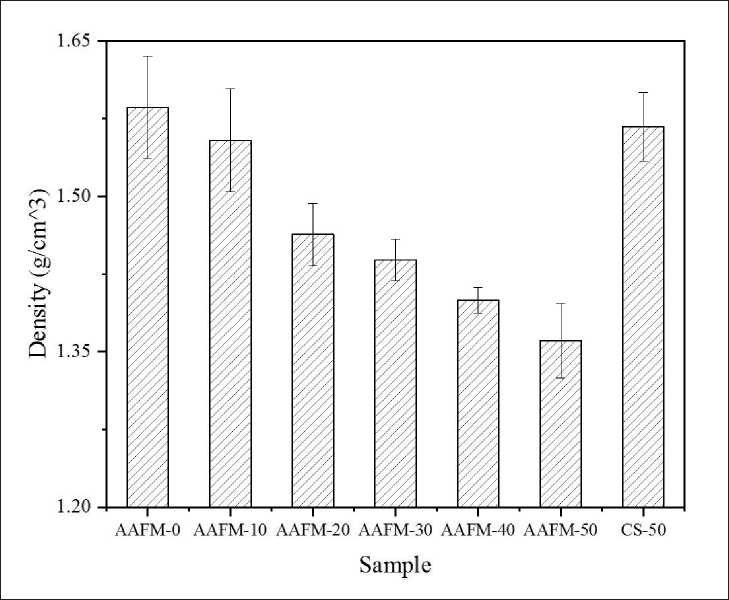
Fig. 2. Bulk density of AAFMs
the MSWIFA dosage in precursors. As indicated, the bulk density of AAFM-10 reaches around 1.55 g/cm3, whereas it drops to 1.36 g/cm3 at sample AAFM-50. The decreased compactness of AAFMs may be attributed to two main reasons. First, the bubbles generated in paste lead to high porosities of AAFMs. The hydrogen releases because of the reaction between the residual metallic aluminum in MSWIFA and alkali [16,21], thus decreasing the bulk density. The other reason is that more loose interior structures are produced due to the generation of multiple crystals. This point can be verified in Sections 3.2 and 3.3.
-
3.2. Morphography
-
3.3. Mineral analysis
-
3.4. Compression Strength
The morphology of each AAFM sample at 28 days is shown in Fig. 3, which consists of some typical shapes of crystal such as needle-like crystals (Fig. 3(a)), flakes (Fig. 3(b)) and fluffy-like crystals(Fig. 3(c)) [13, 15, 22]. Fig. 3 shows the morphology difference of AAFMs caused by MSWIFA dosage in the same fabrication method. It is easy to identify that Fig. 3 (d) has more unreacted particles while less amorphous C-(N)-A-S-H gel due to more unreactive contents in MSWIFA than replaced CFA, indicating that the alkali-activation reaction is almost inadequate. From the chemical composites of MSWIFA Fig. 4, the insufficient contents of silicate and aluminum may help explain less geopolymerization production, microcracks, and low compressive strength.
The XRD spectrum of original MSIWFA powder and AAFMs are presented in Fig. 4. The main crystal phases of AAFMs are Calcite, Portlandite, Hydrocalumite, Ettringite and Anhydrite. For the control group without MWSIFA(ASTM-0), typical crystal phase hydration products such as Calcium Hydroxide (Ca(OH)2), Hydrocalumite, and Ettringite (Ca6Al2(SO4)3(OH)12•26H2O) are detected (Fig. 4). Additionally, the presence of Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) may be attributed to the carbonation of calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2) during sample preparation. New crystals such as Portlandite and Hydrocalumite are detected because MSWIFA was added in [13], which is also identified in the original MSWIFA in Fig. 4. Contrarily, the peak of Calcite and Hydrocalumite tends to increase. Specifically, it is already reported that the Hydrocalumite existed in the form of a chloridebearing phase, that is, C1H43Al4Ca8Cl2O36 [23]. The extra chloride was introduced with high contents in MSWIFA, and Hydrocalumite is one of the main crystalline chlo-ride-aluminium-calcium products after geopolymerization [24].
Fig. 5 illustrates the compressive strength of specimens at 7th days and 28th days, respectively. As shown in Fig. 5, the dosage of MSWIFA used in raw materials has a negative effect on the compression strength of geopolymers
SYSTEM SOLUTIONS FOR TECHNOLOGICAL PROBLEMS
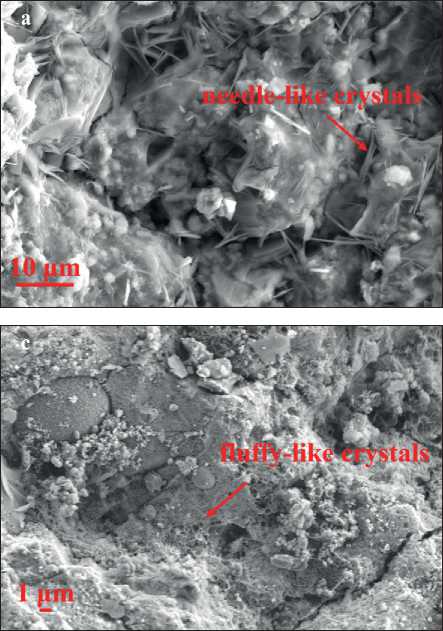

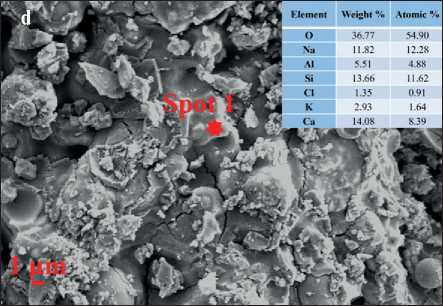
Fig. 3. Morphology of (a) Needle-like crystals (b) Flakes (c) Fluffy-like crystals (d) C(N)-A-S-H gels
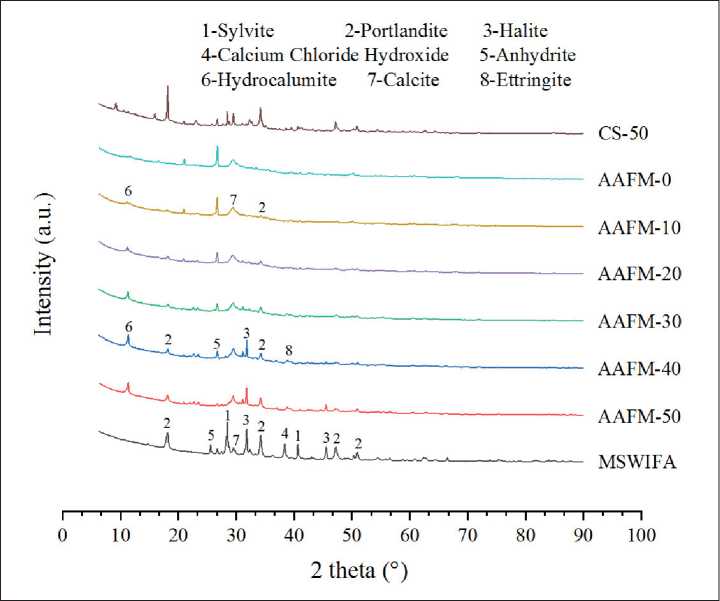
Fig. 4. Mineral analysis of MWIFA and AAFMs
SYSTEM SOLUTIONS FOR TECHNOLOGICAL PROBLEMS
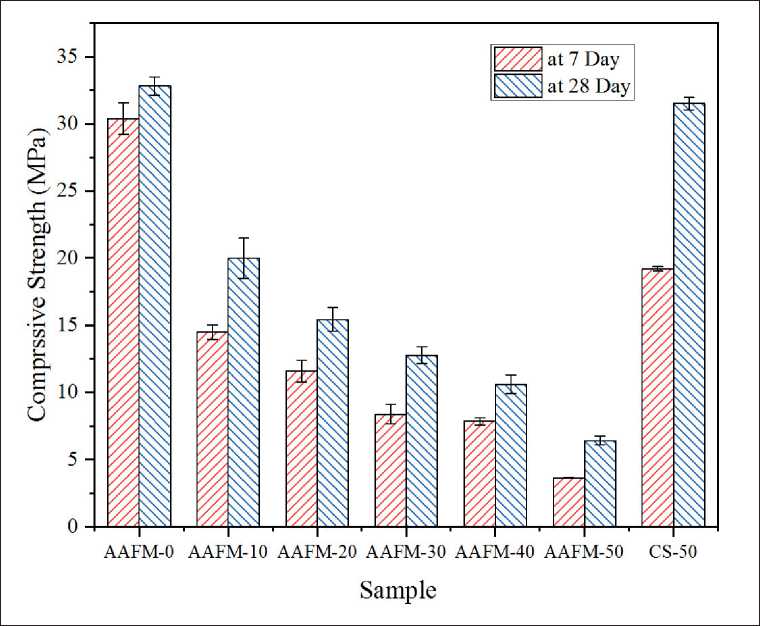
Fig. 5. Compression strength of AAFMs
[6, 25]. The sample (AAFM-0) made without MSWIFA gains the highest compressive strength at 28 days at around 32.8 MPa while decreasing to 6.0 MPa at Sample AAFM-50 with a mass fraction of 50% MSWIFA. There are two primary explanations for the adverse effects, first the quantity of active aluminosilicate in MSWIFA reduces in comparison with the amount of CFA substituted in the precursor, indicating that less N(C)-A-S-H gel is generated; the oher cause is that more residual aluminum in high dosage MSWIFA reacts with alkali during geopolymerization, generating hydrogen gas and reducing the compactness of geopolymers, hence lowering compression strength.
3.5. Toxicity Leaching Performance
4. CONCLUSION AND FUTURE RESEARCH
The toxicity leaching performance of raw MSWIFA and AAFMs synthesised by different MSWIFA dosages is shown in Table 3. The quantity of MSWIFA utilised in AAFMs seems to be growing as the concentration of hazardous heavy metals in AAFMs rises. Furthermore, samples generated using alkali-activated techniques (AAFM-50) had a more significant solidification impact on all heavy metals leaching behaviours than cement-solidified samples (CS-50), indicating that alkali-activation is a more effective way for heavy metals solidification [26, 27]. Alkali-activated technologies improve solidification efficiency and expand the applica- tion scope of AAFMs while lower emissions and cost as structural materials.
In particular, the concentrations of Zn, Cu, Ba, and Cr in AAFMs and original MSWIFA are lower than the GB 16889-2008 standard limitations [20]. Conversely, Pb content fails to meet the standard criteria for samples with MSWIFA dosages greater than 10% wt. Moreover, the concentration of leached Cd in AAFM-50 exceeds the limit of 0.15 mg/L in standard. When the MSWIFA dose reaches 10% wt. in binders, the toxicity leaching performance of AAFM-10 proves to be a sustainable building material because of excellent environmental safety.
This paper has reported the fabrication and performance of sustainable municipal solid waste incineration fly ash alkali-activated materials (AAFMs) in construction. The following conclusions can be drawn from this research.
-
• The feasibility of synthesizing AAFMs with composited activators of sodium hydroxide and sodium metasilicate has been experimentally validated in this study. The inner structure of AAFMs containing MSWIFA is proved to be loose, and the bulk density tends to be inversely proportional to MSWIFA dosage. The bulk density of
SYSTEM SOLUTIONS FOR TECHNOLOGICAL PROBLEMS
AAFM-10 is around 1.55 g/cm3 and falls to 1.36 g/cm3 when the MSWIFA dose reaches 50%.
-
• Multiple polymerization products have been explored in detail. According to mineral analysis and tomography, many crystal phases and amorphous N(C)-A-S-H gels are detected. In hardened AAFMs, KCl, Ettringite, Ca (OH)2 and CaCO3 are recognized from an XRD pattern, while needle-like crystals, fluffy-like crystals and flakes are observed using SEM.
-
• The AAFMs obtained a relatively high mechanical performance. The compression strength of AAFM-10 reaches 19.99 MPa, whereas it decreases to 6.43 MPa at the 28th day in the case of AAFM-50, which allows the possible application as structural materials. In addition, the MSWIFA dosage has detrimental influence on the compression strength of AAFMs.
-
• AAFMs have greater efficiency than cement in so-lidifying/immobilising heavy metals and increasing environmental safety. The sample AAFM-10 demonstrates toxicity leaching performance within regulatory limits, with a dosage of MSWIFA of 10% wt.
Although the fabrication techniques and performance of AAFMs are thoroughly examined in this research, the workability and durability are not thoroughly examined. Setting time, fluidity, and cost may influence the implementation of MSWIFA-based AAFMs. Moreover, longterm leaching behaviours and treatment on additional harmful compounds should be explored before the engineering use of the MSWIFA. Furthermore, some innovative methods including nano technologies [28–32] could be incorporated to better dispose MSWIFA in a sustainable way.
Table 3
Heavy metals concentrations in the TCLP leachates at 28 days
|
TCLP (mg • L–1) |
||||||
|
Zn |
Pb |
Cu |
Ba |
Cr |
Cd |
|
|
GB16889-2008 |
100 |
0.25 |
40 |
25 |
4.5 |
0.15 |
|
AAFM-0 |
0.068 |
0.02 |
0.041 |
1.82 |
0.044 |
0.001 |
|
AAFM-10 |
0.511 |
0.032 |
0.048 |
1.505 |
0.046 |
0.007 |
|
AAFM-20 |
1.601 |
0.364 |
0.064 |
0.779 |
0.053 |
0.011 |
|
AAFM-30 |
2.54 |
0.512 |
0.072 |
0.787 |
0.061 |
0.014 |
|
AAFM-40 |
5.159 |
0.756 |
0.097 |
0.851 |
0.062 |
0.036 |
|
AAFM-50 |
7.996 |
0.992 |
0.202 |
0.869 |
0.064 |
0.138 |
|
CS-50 |
9.645 |
1.298 |
0.594 |
1.007 |
0.091 |
0.428 |
|
MSWIFA |
12.87 |
1.588 |
1.17 |
1.113 |
0.113 |
0.798 |
Список литературы Sustainable municipal solid waste incineration fly ash (MSWIFA) alkali-activated materials in construction: fabrication and performance
- X. Sun, J. Li, X. Zhao, B. Zhu, G. Zhang, A Review on the Management of Municipal Solid Waste Fly Ash in American, Procedia Environmental Sciences. 31 (2016) 535–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2016.02.079.
- S. Ma, C. Zhou, J. Pan, G. Yang, C. Sun, Y. Liu, X. Chen, Z. Zhao, Leachate from municipal solid waste landfills in a global perspective: Characteristics, influential factors and environmental risks, Journal of Cleaner Production. 333 (2022) 130234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.130234.
- L.F. Pearse, J.P.A. Hettiaratchi, D. Da Costa, A new biochemical methane potential assay for landfilled waste using the organic fraction of municipal solid waste, Bioresource Technology Reports. 12 (2020) 100579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2020.100579.
- L. Makarichi, W. Jutidamrongphan, K. Techato, The evolution of waste-to-energy incineration: A review, Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. 91 (2018) 812–821. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.04.088.
- X. Gao, B. Yuan, Q.L. Yu, H.J.H. Brouwers, Characterization and application of municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) bottom ash and waste granite powder in alkali activated slag, Journal of Cleaner Production. 164 (2017) 410–419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.06.218.
- J. Li, Z. Dong, E.-H. Yang, Strain hardening cementitious composites incorporating high volumes of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash, Construction and Building Materials. 146 (2017) 183–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.04.098.
- K. Yan, F. Gao, H. Sun, D. Ge, S. Yang, Effects of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash on the characterization of cement-stabilized macadam, Construction and Building Materials. 207 (2019) 181–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.02.048.
- A. Assi, F. Bilo, A. Zanoletti, J. Ponti, A. Valsesia, R. La Spina, A. Zacco, E. Bontempi, Zero-waste approach in municipal solid waste incineration: Reuse of bottom ash to stabilize fly ash, Journal of Cleaner Production. 245 (2020) 118779. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118779.
- J.L. Provis, Alkali-activated materials, Cement and Concrete Research. 114 (2018) 40–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2017.02.009.
- Z. Tang, W. Li, Y. Hu, J.L. Zhou, V.W.Y. Tam, Review on designs and properties of multifunctional alkaliactivated materials (AAMs), Construction and Building Materials. 200 (2019) 474–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.12.157.
- K. Tian, Y. Wang, S. Hong, J. Zhang, D. Hou, B. Dong, F. Xing, Alkali-activated artificial aggregates fabricated by red mud and fly ash: Performance and microstructure, Construction and Building Materials. 281 (2021) 122552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.122552.
- D. Hou, D. Wu, X. Wang, S. Gao, R. Yu, M. Li, P. Wang, Y. Wang, Sustainable use of red mud in ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC): Design and performance evaluation, Cement and Concrete Composites. 115 (2021) 103862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2020.103862.
- P. Tang, W. Chen, D. Xuan, H. Cheng, C.S. Poon, D.C.W. Tsang, Immobilization of hazardous municipal solid waste incineration fly ash by novel alternative binders derived from cementitious waste, Journal of Hazardous Materials. 393 (2020) 122386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122386.
- M. Cyr, R. Idir, G. Escadeillas, Use of metakaolin to stabilize sewage sludge ash and municipal solid waste incineration fly ash in cement-based materials, Journal of Hazardous Materials. 243 (2012) 193–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.10.019.
- L. Chen, L. Wang, D.-W. Cho, D.C.W. Tsang, L. Tong, Y. Zhou, J. Yang, Q. Hu, C.S. Poon, Sustainable stabilization/solidification of municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash by incorporation of green materials, Journal of Cleaner Production. 222 (2019) 335–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.03.057.
- W. Zhu, X.H. Rao, Y. Liu, E.-H. Yang, Lightweight aerated metakaolin-based geopolymer incorporating municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash as gas-forming agent, Journal of Cleaner Production. 177 (2018) 775–781. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.12.267.
- A. Maldonado-Alameda, J. Giro-Paloma, A. Svobodova-Sedlackova, J. Formosa, J.M. Chimenos, Municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash as alkali-activated cement precursor depending on particle size, Journal of Cleaner Production. 242 (2020) 118443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118443.
- D. Xuan, P. Tang, C.S. Poon, MSWIBA-based cellular alkali-activated concrete incorporating waste glass powder, Cement and Concrete Composites. 95 (2019) 128–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2018.10.018.
- Standard for Pollution Control on the Landfill Site of Municipal Solid Waste.Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China, 2008.
- X. Tian, F. Rao, C.A. León-Patiño, S. Song, Effects of aluminum on the expansion and microstructure of alkali-activated MSWI fly ash-based pastes, Chemosphere. 240 (2020) 124986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124986.
- Y. Mao, H. Wu, W. Wang, M. Jia, X. Che, Pretreatment of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash and preparation of solid waste source sulphoaluminate cementitious material, Journal of Hazardous Materials. 385 (2020) 121580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121580.
- W.-J. Long, J. Peng, Y. Gu, J. Li, B. Dong, F. Xing, Y. Fang, Recycled use of municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash and ferronickel slag for eco-friendly mortar through geopolymer technology, Journal of Cleaner Production. 307 (2021) 127281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127281.
- Y. Jun, T. Kim, J.H. Kim, Chloride-bearing characteristics of alkali-activated slag mixed with seawater: Effect of different salinity levels, Cement and Concrete Composites. 112 (2020) 103680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2020.103680.
- L. Kan, R. Shi, Y. Zhao, X. Duan, M. Wu, Feasibility study on using incineration fly ash from municipal solid waste to develop high ductile alkali-activated composites, Journal of Cleaner Production. 254 (2020) 120168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120168.
- K. Yin, X. Dou, W.-P. Chan, V.W.-C. Chang, Comparative leaching characteristics of fly/bottom ashes from municipal solid waste incineration under various environmental stresses, J Mater Cycles Waste Manag. 22 (2020) 46–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-019-00915-4.
- G. Weibel, U. Eggenberger, S. Schlumberger, U.K. Mäder, Chemical associations and mobilization of heavy metals in fly ash from municipal solid waste incineration, Waste Management. 62 (2017) 147–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2016.12.004.
- Ivanov L.A., Bokova E.S., Muminova S.R., Katuhin L.F. Nanotechnologies: a review of inventions and utility models. Part I. Nanotechnologies in Construction. 2020, Vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 27–33. DOI: 10.15828/2075-8545-2020-12-1-27-33.
- Ivanov LA., Kapustin I.A., Borisova O.N., Pisarenko Zh.V. Nanotechnologies: a review of inventions and utility models. Part II. Nanotechnologies in Construction. 2020, Vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 71–76. DOI: 10.15828/2075-8545-2020-12-2-71-76.
- Ivanov LA., Demenev A.V., Pisarenko Zh.V., Wang Q., Nanotechnologies: a review of inventions and utility models. Part III. Nanotechnologies in Construction. 2020, Vol. 12, no. 3, pp. 140–146. DOI: 10.15828/2075-8545-2020-12-3-140-146.
- Ivanov L.A., Ishkov A.D., Pisarenko Zh.V., Wang Q., Prokopiev P.S. Nanotechnologies: a review of inventions and utility models. Part IV. Nanotechnologies in Construction. 2020;12(5): 275–284. Available from: doi: 10.15828/2075-8545-2020-12-5-275-284.
- Ivanov L.A., Xu L.D., Bokova E.S., Ishkov A.D., Muminova S.R. Nanotechnologies: are view of inventions and utility models. Part V. Nanotechnologies in Construction. 2020; 12(6): 331–338. Available from: doi: 10.15828/2075-8545-2020-12-6-331-338.


