Synthesis and structure of osmium complex [Ph 4P] 2[OsBr 6]
Автор: Sharutin V.V., Sharutina O.K., Senchurin V.S.
Журнал: Вестник Южно-Уральского государственного университета. Серия: Химия @vestnik-susu-chemistry
Рубрика: Металлоорганическая химия
Статья в выпуске: 4 т.7, 2015 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Tetraphenylphosphonium hexabromoosmate, [Ph 4P] 2[OsBr 6] (I), has been structurally characterized after synthesis by interaction of sodium hexabromoosmate with tetraphenylphosphonium bromide in dimethyl sulfoxide. The phosphorus atoms of [Ph 4P] + cations have distorted tetrahedral coordination geometry (СPС angles are 106.23(11)°-113.23(10)°), the P-С bond lengths are 1.791(2)-1.801(2) Å). In octahedral [OsBr 6] 2- anions the Os-Br bond lengths equal 2.4752(2)-2.5020(3) Å, trаns-BrOsBr angles are 180°.
Sodium hexabromoosmate, tetraphenylphosphonium bromide, dimethyl sulfoxide, комплекс [ph 4p] 2[osbr 6], complex [ph 4p] 2[osbr 6], crystal structure, x-ray diffraction analysis
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147160324
IDR: 147160324 | УДК: 546.97+546.185+547.53.024+548.312.5 | DOI: 10.14529/chem150402
Текст научной статьи Synthesis and structure of osmium complex [Ph 4P] 2[OsBr 6]
Complexes containing [OsBr6]2 - anions are some of the least structurally characterized ionic osmium complexes [1]; among them there is only one complex with phosphonium cations, [Ph 3 PH] +2 [OsBr 6 ]2 - [2].
In the present paper the synthesis and structure of osmium complex [Ph4P] + 2[OsBr6]2 - ( 1 ) has been described.
Experimental
Synthesis of [Ph 4 P]+ 2 [OsBr 6 ]2– (1). A mixture of 0.035 g (0.08 mmol) of tetraphenylphosphonium bromide and 0.030 g (0.04 mmol) of sodium hexabromoosmate was dissolved by stirring in 2 mL of dimethyl sulfoxide. After evaporation of the solvent, formation of dark brown crystals was observed; they were filtered off and dried. 0.046 g (82%) of the complex was obtained, m.p. 320 ° C. IR (v, cm-1): 3053, 1583, 1482, 1437, 1313, 1186, 1107, 1025, 995, 761, 752, 721, 690, 663, 531, 522. Found, %: С 42.49, Н 3.06. Anal. calc. for C 48 H 40 P 2 Br 6 Os (M = 1348.37), %: С 42.74, Н 2.97.
IR-spectrum was recorded on a Bruker Tensor 27 IR spectrometer in KBr pellet.
The X-ray diffraction experiment for crystal 1 was carried out on a Bruker D8 Quest diffractometer (Mo K α radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å, graphite monochromator). Data collection, their editing, and refinement of the unit cell parameters, as well as accounting for absorption, were carried out using the SMART and SAINT-Plus programs [3]. All calculations for structure determination and refinement were carried out using the SHELXL/PC program [4]. Structure 1 was determined by the direct method and refined by the least-squares method in anisotropic approximation for non-hydrogen atoms. The main crystallographic data and structure refinement details are given in Table 1. The main bond lengths and bond angles are listed in Table 2.
The full tables of atomic coordinates, bond lengths, and bond angles were deposited with the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre (№ 1000138; ; .
Table 1
Crystallographic data, the experimental and structure refinement parameters for compound 1
|
Parameter |
Value |
|
Formula |
C 48 H 40 P 2 Br 6 Os |
|
М |
1348.37 |
|
Т , К |
296(2) |
|
Crystal system |
Triclinic |
|
Space group |
P-1 |
Table 1 (end)
|
Parameter |
Value |
|
a , Å |
10.2879(4) |
|
b, Å |
10.5331(4) |
|
c, Å |
12.1824(5) |
|
α, deg |
92.7640(10) |
|
β, deg |
99.9850(10) |
|
γ, deg |
116.3110(10) |
|
V , Å3 |
1153.68(8) |
|
Z |
1 |
|
ρ (calc.), g/cm3 |
1.941 |
|
- 1 µ , mm |
8.061 |
|
F (000) |
644.0 |
|
Crystal size, mm |
0.32 × 0.26 × 0.13 |
|
9 Range of data collection, deg |
5.92 - 52.86 |
|
Range of refraction indices |
- 12 < h < 12, - 13 < k < 13, - 15 < l < 15 |
|
Measured reflections |
36441 |
|
Independent reflections |
4730 (R int = 0.0245) |
|
Refinement variables |
259 |
|
GOOF |
1.105 |
|
R factors for F2> 2 g (F2) |
R 1 = 0.0171, wR 2 = 0.0416 |
|
R factors for all reflections |
R 1 = 0.0195, wR 2 = 0.0426 |
|
Residual electron density (min/max), e/A3 |
0.35/ - 0.66 |
Table 2
Selected bond lengths (d) and bond angles ( ω ) in the structure of compound 1
|
Bond |
d , Å |
Angle |
ω , deg |
|
Os(1) - Br(1 1 ) |
2.4985(2) |
Br(11)Os(1)Br1 |
180.0 |
|
Os(1) - Br(1) |
2.4986(2) |
Br(2)Os(1)Br1 |
91.620(8) |
|
Os(1) - Br(2) |
2.4752(2) |
Br(21)Os(1)Br1 |
88.380(8) |
|
Os(1) - Br(3) |
2.5019(3) |
C(1)P(1)C31 |
106.23(11) |
|
Os(1) - Br(3 1 ) |
2.5020(3) |
C(1)P(1)C11 |
109.65(11) |
|
P(1) - C(1) |
1.798(2) |
C(31)P(1)C11 |
109.57(11) |
|
P(1) - C(31) |
1.800(2) |
C(21)P(1)C1 |
113.23(10) |
|
P(1) - C(21) |
1.791(2) |
C(21)P(1)C31 |
108.47(10) |
|
P(1) - C(11) |
1.801(2) |
C(21)P(1)C11 |
109.60(11) |
|
Symmetry transformation: 1 |
-x, 1-y, 1-z |
Results and Discussion
It is known that the synthesis of osmium complex [Ph3PH] + 2[OsBr6]2 - was carried out by consecutive addition of triphenylphosphine, glacial acetic acid and acetic anhydride to the dichloromethane solution of tetrabutylammonium hexabromoosmate, and heating of the reaction mixture for 3 days at 55–60 ° С, with the yield equaling 29% [2].
We have ascertained that the reaction of sodium hexabromoosmate with tetraphenylphosphonium bromide in dimethyl sulfoxide leads to formation of air-stable dark brown crystals of tetraphenylphosphonium hexabromoosmate ( 1 ), isolated from the reaction mixture with the yield equaling 82 %:
DMSO
2 Ph 4 PBr + Na 2 OsBr 6 → [Ph 4 P]+ 2 [OsBr 6 ]2– + 2 NaBr
Sharutin V.V. , Sharutina O.K., Senchurin V.S.
Synthesis and structure of osmium complex [Ph 4 P] 2 [OsBr 6 ]
According to the X-ray diffraction data, phosphorus atoms in tetraphenylphosphonium cations have slightly distorted tetrahedral coordination geometry: СPС angles lie within the range 106.23(11) °- 113.23(10) ° , P - С distances are 1.791(2) - 1.801(2) A) (Fig. 1).
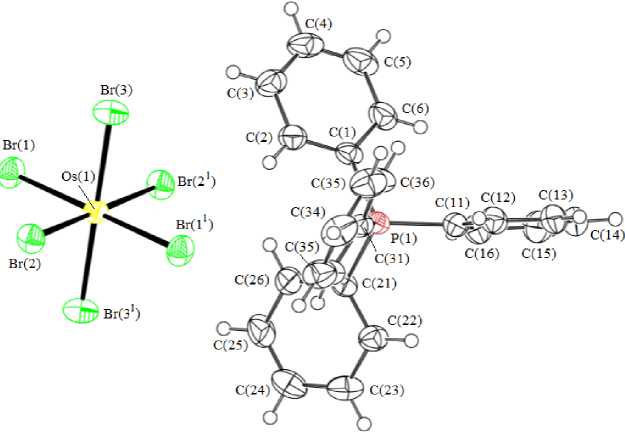
Fig. 1. Structure of complex 1
In centrosymmetric octahedral [OsBr6]2 - anions, the Os - Br bond lengths equal 2.4752(2) - 2.5020(3) A, trans -BrOsBr angles are 180 ° . Two tetraphenylphosphonium cations are bonded with hexabromoosmate anion by intermolecular H --- Br hydrogen bonds (2.90 and 3.01 A) (Fig. 2).
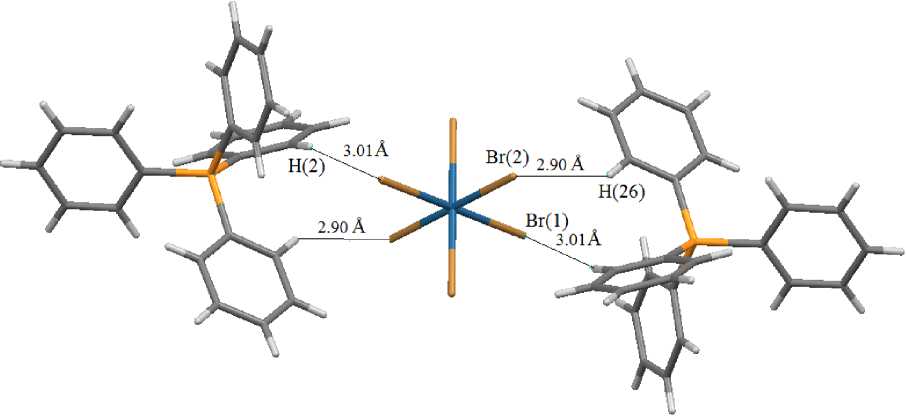
Fig. 2. The system of hydrogen bonds in the crystal of complex 1
Conclusions
Thus, the osmium complex with the tetrahedral tetraphenylphosphonium cation and the centrosymmetric octahedral Os-,Br-containing [OsBr6]2 - anion has been synthesized and structurally characterized for the first time. Formation of crystal structure occurs due to intermolecular H --- Br hydrogen bonds between tetraphenylphosphonium cations and hexabromoosmate anions.
Список литературы Synthesis and structure of osmium complex [Ph 4P] 2[OsBr 6]
- Cambridge Crystallografic Database. Release 2015. Cambridge.
- Robinson P.D., Hinckley C.C., Matusz M., Kibala P.A. Acta Cryst. 1988. Vol. C44. P. 619-621.
- Bruker (1998). SMART and SAINT-Plus.Versions 5.0.Data Collection and Processing Software for the SMART System.Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker (1998). SHELXTL/PC.Versions 5.10. An Integrated System for Solving, Refining and Displaying Crystal Structures From Diffraction Data. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.

![Synthesis and structure of osmium complex [Ph 4P] 2[OsBr 6] Synthesis and structure of osmium complex [Ph 4P] 2[OsBr 6]](/file/cover/147160324/synthesis-and-structure-of-osmium-complex-ph-4p-2-osbr-6.png)
