Synthesis and structure of tri(meta-tolyl)antimony bis(benzenesulfonate)
Автор: Sharutin V.V., Sharutina O.K., Senchurin V.S.
Журнал: Вестник Южно-Уральского государственного университета. Серия: Химия @vestnik-susu-chemistry
Рубрика: Металлоорганическая химия
Статья в выпуске: 4 т.7, 2015 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Tri( meta-tolyl)antimony bis(benzenesulfonate) m-Tol 3Sb(OSO 2C 6H 5) 2 (1) has been synthesized by interaction of tri( meta-tolyl)antimony with benzenesulfonic acid in the presence of tert-butyl hydroperoxide (mole ratio 1:2:1) in ether solution. Antimony atoms in 1 have trigonal-bipyramidal coordination with arenesulfonate substituents in axial positions (OSbO 171.05(11)°, CSbC 116.21(19)°, 117.38(18)°, 126.40(15)°). The Sb-C and Sb-O distances equal 2.091(4), 2.098(4), 2.115(4) and 2.105(2), 2.116(3) Å. Intermolecular contact (Sb•••O 3.421(3) Å) occurs between the central atom and the oxygen atom of sulfonate group.
Tri(meta-tolyl)antimony, benzenesulfonic acid, tert-butyl hydroperoxide, molecular structure, x-ray diffraction analysis
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147160337
IDR: 147160337 | УДК: 547.53.024+549.242+548.312.5 | DOI: 10.14529/chem150412
Синтез и строение бис(бензолсульфоната) три(мета-толил)сурьмы
Взаимодействием три( мета-толил)сурьмы с бензолсульфоновой кислотой в присутствии третбутилгидропероксида (1:2:1 мольн.) в растворе эфира синтезирован бис(бензолсульфонат) три( мета-толил)сурьмы ( m-Tol 3Sb(OSO 2C 6H 5) 2 (1). Атомы сурьмы в 1 имеют тригонально-бипирамидальную координацию с аренсульфонатными заместителями в аксиальных положениях (OSbO 171,05(11)°, CSbC 116,21(19)°, 117,38(18)°, 126,40(15)°). Расстояния Sb-C и Sb-O равны 2,091(4), 2,098(4), 2,115(4) и 2,105(2), 2,116(3) Å. Между центральным атомом и атомом кислорода сульфонатной группы имеет место внутримолекулярный контакт (Sb•••O 3.421(3) Å).
Текст научной статьи Synthesis and structure of tri(meta-tolyl)antimony bis(benzenesulfonate)
In the course of research on the synthesis and structure of quinqevalent antimony arenesulfonates [1–4] we have studied the reaction of tri( meta -tolyl)antimony with benzenesulfonic acid in the presence of tert- butyl hydroperoxide in ether. The structure of the obtained product has been established by X-ray diffraction analysis.
Experimental
Tri( meta -tolyl)antimony bis (benzenesulfonate) synthesis. The mixture of 0.250 g (0.63 mmol) tri( meta -tolyl)antimony, 0.200 g (1.26 mmol) benzenesulfonic acid and 0.057 g 70% aqueous solution of tert -butyl hydroperoxide in 10 mL ether stood for 24 h at room temperature. The obtained crystals were recrystallized from toluene. The yield is 0.386 g (86%) of colorless crystals 1 with decomposition temperature 152 ° C. Found, %: C 55.23, Н 4.34. Calculated for C33H3 i O6S2Sb, %: C 55.87, H 4.37. IR spectrum, ( v , cm ’1 ): 1320, 1140, 1140 (SO 2 ).
IR spectra were recorded on the Fourier-transform spectrometer Bruker Tensor 27 in KBr pellets.
The X-ray diffraction analyses of crystal 1 were performed on the Bruker D8 Quest diffractometer (Mo K „ -emission, X = 0.71073 A, graphite monochromator). The data were collected and analyzed, the unit cell parameters were refined, and the absorption correction was applied using the SMART and SAINT-Plus programs [5]. All calculations for structure determination and refinement were performed using the SHELXL/PC [6] and OLEX2 programs [7]. The structures were determined by the direct method and refined by the least-squares method in the anisotropic approximation for non-hydrogen atoms. The main crystallographic data and refinement results for the structures are listed in Table 1, the selected bond lengths and bond angles are given in Table 2.
The full tables of atomic coordinates, bond lengths, and bond angles were deposited with the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre (CCDC 1057589, ; .
Table 1
Crystallographic data and the experimental and structure refinement parameters for compound 1
|
Parameter |
Value |
|
Empirical formula |
C 33 H 31 O 6 S 2 Sb |
|
Formula weight |
709.45 |
|
Т , К |
296 |
|
Crystal system |
Monoclinic |
|
Space group |
P2 1 /c |
|
a , Å |
14.4831(6) |
Table 1 (end)
|
Parameter |
Value |
|
b , Å |
12.7730(5) |
|
c, Å |
17.7157(7) |
|
α , deg |
90.00 |
|
β, deg |
99.4680(10) |
|
γ , deg |
90.00 |
|
V , Å3 |
3232.6(2) |
|
Z |
4 |
|
ρ (calcd.), g/сm3 |
1.458 |
|
- 1 µ , mm |
1.024 |
|
F (000) |
1440.0 |
|
Crystal size, mm |
0.68 × 0.38 × 0.26 |
|
2 θ Range of data collection, deg |
6.54 - 51.4° |
|
Range of refraction indices |
-17 ≤ h ≤ 17, -15 ≤ k ≤ 15, -21 ≤ l ≤ 21 |
|
Measured reflections |
40302 |
|
Independent reflections |
6147 |
|
R int |
0.0288 |
|
Refinement variables |
382 |
|
GOOF |
1.081 |
|
R factors for F2 > 2 σ (F2) |
R 1 = 0.0387, wR 2 = 0.0866 |
|
R factors for all reflections |
R 1 = 0.0513, wR 2 = 0.0973 |
|
Residual electron density (min/max), e /Å3 |
0.80/-0.49 |
Table 2
Selected bond lengths and bond angles in the structure of compound 1
|
Bond |
d , Å |
Angle |
ω , deg |
|
Sb(1) - O(1) |
2.116(3) |
C(11)Sb(1)O(1) |
94.96(14) |
|
Sb(1) - C(11) |
2.091(4) |
C(11)Sb(1)C(1) |
117.38(18) |
|
Sb(1) - C(1) |
2.098(4) |
C(11)Sb(1)O(4) |
93.68(14) |
|
Sb(1) - O(4) |
2.105(2) |
C(11)Sb(1)C(21) |
116.21(19) |
|
Sb(1) - C(21) |
2.115(4) |
C(1)Sb(1)O(1) |
85.33(13) |
|
S(1) - O(1) |
1.499(3) |
C(1)Sb(1)O(4) |
92.74(12) |
|
S(1) - O(2) |
1.402(4) |
C(1)Sb(1)C(21) |
126.40(15) |
|
S(1) - O(3) |
1.407(4) |
O(4)Sb(1)O(1) |
171.05(11) |
|
S(1) - C(31) |
1.772(4) |
O(4)Sb(1)C(21) |
85.13(14) |
|
S(2) - O(5) |
1.411(3) |
C(21)Sb(1)O(1) |
88.98(15) |
|
S(2) - O(6) |
1.425(3) |
O(1)S(1)C(31) |
100.53(19) |
|
S(2) - O(4) |
1.523(3) |
O(2)S(1)O(1) |
109.9(2) |
|
S(2) - C(41) |
1.765(4) |
O(2)S(1)O(3) |
118.3(3) |
|
C(11) - C(12) |
1.371(7) |
O(2)S(1)C(31) |
108.9(2) |
|
C(11) - C(16) |
1.377(7) |
O(3)S(1)O(1) |
109.1(2) |
|
C(12) - C(13) |
1.393(8) |
O(3)S(1)C(31) |
108.7(2) |
|
C(13) - C(14) |
1.394(14) |
O(5)S(2)O(6) |
118.2(2) |
|
C(13) - C(17) |
1.489(12) |
O(5)S(2)O(4) |
107.14(18) |
|
C(14) - C(15) |
1.339(14) |
O(5)S(2)C(41) |
108.9(2) |
|
C(15) - C(16) |
1.391(9) |
O(6)S(2)O(4) |
109.74(17) |
|
C(31) - C(32) |
1.362(6) |
O(6)S(2)C(41) |
108.1(2) |
|
C(31) - C(36) |
1.367(7) |
O(4)S(2)C(41) |
103.88(17) |
Results and Discussion
It is known that oxidation of tri( meta -tolyl)antimony by hydrogen peroxide in the presence of benzenesulfonic acid leads to formation of tri( meta -tolyl)antimony bis (benzenesulfonate) with 72% yield [4].
We have established that the oxidative addition reaction with the use of tri( meta -tolyl) antimony, benzenesulfonic acid and tert -butyl hydroperoxide leads to formation of the target product with 86% yeild:
Et2O m-To^Sb + 2 HOSO2C6H5 + t-BuOOH ^ m-TohSb(OSO2Ph)2 + H2O + t-BuOOH
Note that compound 1 , obtained by this reaction, has higher melting point (152 ° C), than that according to the procedure with the use of hydrogen peroxide (145 ° C [4]).
From the X-ray analysis data it follows that the antimony atoms in tri( meta -tolyl)antimony bis (benzenesulfonate) have trigonal-bipyramidal coordination with arenesulfonate substituents in axial positions (Fig. 1).
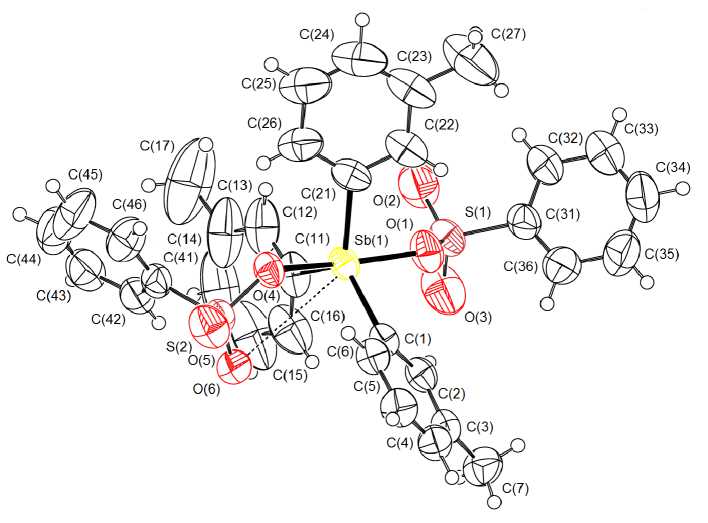
Fig. 1. The structure of compound 1
The value of axial angle OSbO equals 171.05(11) ° , the angles between equatorial phenyl substituents are unequivalent: 116.21(19) ° , 117.38(18) ° , 126.40(15) ° (Table 2). Their sum (359.99 ° ) is practically consistent with the theoretical value. This fact testifies that the antimony atoms and three carbon atoms, bonded to them, are coplanar. The distances Sb–C equal 2.091(4), 2.098(4), 2.115(4) Å, the bonds Sb - O (2.105(2), 2.116(3) A) are of covalent character.
As viewed from the maximal equatorial angle CSbC the close intermolecular contact between the central atom and the oxygen atom O(6) of the sulfonate group is observed (Sb···O 3.421(3) Å), which is less than the sum of Van der Waals radii of antimony and oxygen atoms (3.7 Å [8]). The structural organization of the crystal is formed with the participation of weak hydrogen bonds of the type O···H (2.525, 2.650 Å).
Conclusions
Thus, tri( meta -tolyl)antimony is oxidized by tert -butyl hydroperoxide in the presence of benzenesulfonic acid in ether to obtain tri( meta -tolyl)antimony bis (benzenesulfonate). In its molecule one sulfonate group is characterized by monodentate bonding type, the other one is of bidentate type.
Список литературы Synthesis and structure of tri(meta-tolyl)antimony bis(benzenesulfonate)
- Аренсульфонаты тетрафенилстибония. Синтез и строение/В.В. Шарутин, О.К. Шарутина, Л.П. Панова и др.//Журнал коорд. химии. -1997. -Т. 23, № 7. -С. 513-519.
- Сульфонаты тетра-и триарилсурьмы/В.В. Шарутин, О.К. Шарутина, Л.П. Панова, В.К. Бельский//Журн. общ. химии. -1997. -Т. 67, № 9. -С. 1531-1535.
- Синтез и строение дитозилата три-п-толилсурьмы/В.В. Шарутин, О.К. Шарутина, Л.П. Панова и др.//Журн. общ. химии. -2002. -Т. 72, Вып. 2. -С. 249-251.
- Синтез и строение бис(аренсульфонатов) триарилсурьмы/В.В. Шарутин, О.К. Шарутина, Т.П. Платонова и др.//Журн. общ. химии. -2003. -Т. 73, Вып. 3. -С. 380-384.
- Bruker (1998). SMART and SAINT-Plus. Versions 5.0. Data Collection and Processing Software for the SMART System. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker (1998). SHELXTL/PC. Versions 5.10. An Integrated System for Solving, Refining and Displaying Crystal Structures From Diffraction Data. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program/O.V. Dolomanov, L.J. Bourhis, R.J. Gildea et al.//J. Appl. Cryst. -2009. -V. 42. -P. 339-341.
- Бацанов, С.С. Атомные радиусы элементов/С.С. Бацанов//Журн. неорган. химии. -1991. -Т. 36, Вып. 12. -С. 3015-3037.


