Технологические основы переработки хвостов флотационного обогащения с применением комбинированных флотореагентов
Автор: Семушкина Л.В., Турысбеков Д.К., Тусупбаев Н.К., Котова О.Б.
Журнал: Вестник геонаук @vestnik-geo
Рубрика: Научные статьи
Статья в выпуске: 6 (258), 2016 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Апробированы технологии переработки хвостов флотационного обогащения с применением комбинированного флотореагента на примере Жезказганской фабрики и Тишинского месторождения (Казахстан). Комбинированный собиратель представляет собой смесь композиционного аэрофлота, ТС-1000 и бутилового ксантогената. Соотношение реагентов составляет 1:1:3. Преимуществом предлагаемого флотореагента является то, что он имеет в своем составе две полярные группы и длинный углеводородный радикал. Показано, что при флотации Жезказганских хвостов с применением меньшего, по сравнению с бутиловым ксантогенатом, расхода комбинированного собирателя получен черновой медный концентрат с содержанием меди 13.0 % при извлечении 80.22 %. По сравнению с базовой технологией содержание меди в черновом концентрате повышается на 5.1 %, извлечение на 31.4 %. При флотации Тишинских хвостов с применением комбинированного собирателя извлечение меди в коллективный концентрат повышается на 9.63 %; свинца на 8.41 %; цинка на 9.2 %.
Флотационные хвосты, доизмельчение, извлечение, комбинированный собиратель, флотация, концентрат
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/149129208
IDR: 149129208 | УДК: 622. | DOI: 10.19110/2221-1381-2016-6-28-32
Текст научной статьи Технологические основы переработки хвостов флотационного обогащения с применением комбинированных флотореагентов
The industry largely uses xanthates, dialkyldithiophosphates and mercaptans for the flotation of sulfides, oxidized minerals of heavy non-ferrous metals, native and noble metals. For the selective extraction of over 40 minerals of heavy non-ferrous and noble metals with different physical and chemical properties only 5 6 types of sulfhydryl collectors are used at flotation.
We tested several new reagents out of many combinations of three major donor atoms (S, N and O) in the main group of bonds, including several complexing agents, as collectors; and the received results were actively discussed in numerous books and papers [1—3].
The search and development of new more selective collecting reagents for the flotation process improvement is a priority when creating innovative technologies of flotation separation of substances and minerals. A large number of organic compounds were suggested as collectors, however, less 160 were used in practice [4]. The modern practice of application of collectors in the flotation of sulphide ores mainly involves xanthates and aerofloats. The additional application of aerofloats allows not only improving the quality of the sulphide concentrates due to a more selective action of the aerofloats, but also enhancing recovery of metals due to the ability of aerofloats to float fine particles efficiently.
The work [5] presented the results of laboratory researches and industrial tests on the use of hexyl xanthate of Hoechst company and mixtures with butyl and isopropyl xanthates at the flotation of sulfide copper minerals. The work showed technological and economic efficiency of application of hexyl and butyl xanthates mixture while reducing its consumption from 70 to 50 g/t. Copper recovery increased at 0.4 %.
As a more selective collector in the separation of pyrite and arsenopyrite it was suggested to use the reaction product of xanthate and propylene-chlorohydrin, which received the name of PROX reagent. The results of experimental studies of the collectors from the dialkyldithiophosphate class (aerofloats) indicate that their combined use with xanthates in many cases enhances the extraction of metals [6—9].
The application of mixtures of collectors is one of the methods to achieve the desired ratio in each case of amounts of chemically and physically adsorbed collector on the surface of floated mineral.
At present recycling involves rebellious ores and technogenic raw characterized by low content of valuable components, fine impregnation of mineral complexes and similar technological properties of the constituent minerals.
To achieve high technological results is important to prepare old tailings before enrichment operations. Preparations may include regrinding of tailings, fractionation, desliming and washing [10—12].
The development of effective technologies of extraction of minerals of non-ferrous and noble metals is one of the priorities for concentrating industry in Russia and Kazakhstan. These tasks are optimized within the framework of agreements on scientific cooperation, and the need for complete and integrated development of different deposits, ensuring high profitability of the enterprises, improving ecological environment in the mining regions determine relevance of scientific researches toward intensification of methods and ways of extraction of valuable components from rebellious and technogenic raw [13—14].
Experimental Procedure
We studied the possibility of processing flotation tailings from Zhezkazgan concentrating plant and flotation tailings from Tishinskoe deposit with the use of the combined collector. As the combined collector we selected a reagent mixture, which collective ability depends on pH. This allows selective separation of sulfide minerals with similar physical and chemical properties. Therefore the following initial reagents were used: butyl xanthate (BX), thionocarbamates TS-1000 and composite aerofloat.
The raw for the composite aerofloat was a composite mixture of Ñ3Í7-Ñ6Í13-ÎÍ alcohols extracted from the dried alcohol fraction of fusel oil. According to the fractional distillation of the fusel oil, the main component of dry fusel oil was isoamyl alcohol more than 80 %.
Our experiments presented that the fusel oil in the reaction with pentasulphide phosphorus behaved as isoamyl alcohol.
The production of composite aerofloat proceeded in two stages. The first step production of dialkyldithiophosphoric acid (so-called acid ester) by reaction of pentasulfide phosphorus with dried alcohol fraction Ñ3Í7-Ñ6Í13-ÎÍ. The second stage production of sodium salt of dialkyldithiophosphoric acid by alkali neutralization. The neutralization was carried out with excessive sodium hydroxide with production of the composite aerofloat.
The advantage of the suggested combined collector compared with other known reagents is that they contain two polar groups and a long hydrocarbon radical. We chose the opti- mal ratio of reagents in the composition of the combined collector, which made the composite aerofloat: thionocarbamates TC-1000: butyl sodium xanthate = 1: 1: 3.
We studied the possibility of processing flotation tailings from Zhezkazgan concentrating plant and flotation tailings from Tishinskoe deposit with the use of the combined collector [15]. We studied the mineral and granulometric composition of flotation tailings from Zhezkazgan concentrating plant and developed the flotation modes using basic flotation reagents. According to the results of chemical analysis the Zhezkazgan tailings contain 0.13 % copper; 0.01 % lead; 0.01 % Zn; 66.31 % SiO2; 2.3 % total iron; 11.8 % Al2O3; 5.96 % CaO; <0,0003 % Cd; 0.16 % sulfur.
The methods of study are mineralogical analysis , X-ray phase analysis ( X-ray diffractometer D 8 ADVANCE); X-ray fluorescence analysis (XRF spectrometer with wave dispersion Venus 200 PANalyical B. V. Holland) , chemical analysis , flotation ( at flotation machines FL-290, FM-1, FM-2 (Russia).
Results and Discussion
We conducted dispersion analysis of the tailings and studied the distribution of copper and iron by size class. The results of the analysis are presented in Table 1.
Table 1 shows that the main part of copper (72.43 %) is within —74 + 50 mcm size class, and in the smaller 10 mcm class (17.2 %).
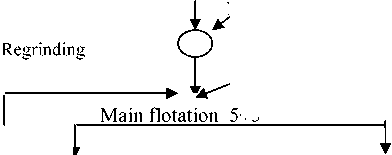
We conducted researches on improvement of technological modes of flotation of tailings from Zhezkazgan concentrating plant with the use of basic and combined collectors. The scheme of flotation of tailings from Zhezkazgan concentrating plant with production of draft copper concentrate is shown in Figure 1.
We improved the modes of regrinding of tailings from the plant and determined the optimum consumption of the reagents. The flotation was carried out with separate reagents and their various combinations.
The results of the flotation of tailings from Zhezkazgan copper plant with optimal consumption of the reagents are shown in Table 2.
Table 2 shows that the application of the combined collector (mixture of composite aerofloat, thionocarbamate TC-1000 and butyl xanthate in the ratio of 1:1:3) in the flotation cycle of tailings from Zhezkazgan copper plant allows to improve the technological characteristics of the enrichment compared to other reagents.
According to the base technology using only butyl xanthate (250 g/t) we obtained draft copper concentrate with the
Table 1. Results of dispersion analysis of flotation tailings from Zhezkazgan copper plant
Таблица 1. Результаты дисперсионного анализа хвостов флотационного обогащения Жезказганской медной фабрики
|
Size class, mcm |
Output, % |
Content, % |
Recovery, % |
|||
|
g |
% |
Си |
Fe |
Си |
Fe |
|
|
-74 +60 |
82.3 |
41.15 |
0.11 |
4.68 |
42.26 |
42.52 |
|
-60+50 |
10.1 |
5.05 |
0.64 |
3.96 |
30.17 |
4.41 |
|
-50+40 |
10.5 |
5.25 |
0.05 |
3.6 |
2.45 |
4.17 |
|
-40+30 |
14.5 |
7.25 |
0.04 |
3.6 |
2.71 |
5.76 |
|
-30+20 |
8.4 |
4.2 |
0.046 |
2.88 |
1.80 |
2.67 |
|
-20+10 |
13.8 |
6.9 |
0.053 |
4.68 |
3.41 |
7.13 |
|
-10+0 |
60.4 |
30.2 |
0.061 |
5.0 |
17.2 |
33.34 |
|
Исх. хвосты |
200 |
100 |
0.1071 |
4.53 |
100 |
100 |
Liquid glass — 200 g/t
Liquid glass — 100 g/t
Tailings of Zhezkazgan plant
Na2S — 700 g/t (34.7%)
BX — 400 g/t (150+150+100)
T —80-20+20 g/t
BX — 100 g/t
T —80-20 g/t
Test flotation 9'
I r ecfeaning 7'
II recleaning 5'

final tailings
III recleaning 5'
draft Cu concentrate
Fig. 1. Scheme of flotation of tailings from Zhezkazgan concentrating plant with production of draft copper concentrate
Рис. 1. Схема фёотациихвостов обогащения Жeзкaзгa^cкoй обогатите, щной фабрики с пoёyчe^иeм чернового медного концентрата
Table 2. Results of flotation processing of tailings from Zhezkazgan copper plant with different reagents
Таблица 2. Результаты флотационного обогащенияхвостов Жезказганской медной фабрики с различными реагентами
|
Note |
Output, % |
Content, % |
Recovery, % |
Note |
||
|
Cu |
Fe |
Cu |
Fe |
|||
|
Draft Си concentrate |
0.6 |
7.9 |
10.7 |
48.82 |
1.98 |
BX 250 g/t |
|
Resulted Tailings |
99.4 |
0.05 |
3.2 |
51.18 |
98.02 |
|
|
Initial flotation tailings |
100 |
0.097 |
3.25 |
100 |
100 |
|
|
Draft Cu concentrate |
0.8 |
5.2 |
9.8 |
45.61 |
2.49 |
Compositional aerofloat |
|
Resulted Tailings |
99.2 |
0.05 |
3.1 |
54.39 |
97.51 |
300 g/t |
|
Initial flotation tailings |
100 |
0.091 |
3.15 |
100 |
100 |
|
|
Draft Cu concentrate |
0.6 |
10.5 |
10.2 |
67.87 |
1.83 |
thionocarbamate |
|
Resulted Tailings |
99.4 |
0.03 |
3.3 |
32.13 |
98.17 |
60 g/t |
|
Initial flotation tailings |
100 |
0.093 |
3.34 |
100 |
100 |
|
|
Draft Cu concentrate |
0.65 |
8.6 |
10.9 |
58.45 |
2.18 |
BX + comp, aerofloat |
|
Resulted Tailings |
99.35 |
0.04 |
3.2 |
41.55 |
97.82 |
110 g/t |
|
Initial flotation tailings |
100 |
0.096 |
3.25 |
100 |
100 |
|
|
Draft Cu concentrate |
0.62 |
12.1 |
10.7 |
76.65 |
2.11 |
BX + |
|
Resulted Tailings |
99.38 |
0.023 |
3.1 |
23.35 |
97.89 |
thionocarbamate 60 g/t |
|
Initial flotation tailings |
100 |
0.098 |
3.15 |
100 |
100 |
|
|
Draft Cu concentrate |
0.68 |
10.9 |
11.5 |
74.91 |
2.48 |
Comp.aerofloat + |
|
Resulted Tailings |
99.32 |
0.025 |
3.1 |
25.09 |
97.52 |
thionocarbamate 90 g/t |
|
Initial flotation tailings |
100 |
0.099 |
3.16 |
100 |
100 |
|
|
Draft Cu concentrate |
0.62 |
13.0 |
9.6 |
80.22 |
1.78 |
Combined collector |
|
Resulted Tailings |
99.38 |
0.02 |
3.3 |
19.78 |
98.22 |
25 g/t |
|
Initial flotation tailings |
100 |
0.100 |
3.34 |
100 |
100 |
|
|
per content 7.9 % at recovery 48.82 %. Application of lower than the base reagent (25 g/t). This application resul |
||||||
thionocarbamate (60 g/t) and its combination with butyl xanthate can increase copper content in the draft copper concentrate to 12.1 % and copper recovery to 76.65 %.
The best results of the content and recovery of copper from the tailings of Zhezkazgan copper plant were achieved with the use of the combined collector, which consumption was much
in draft copper concentrate with the copper content 13.0 %, recovery 80.22 %.
The action of the combined collector was tested during flotation of tailings from Tishinskoe deposit. According to the results of chemical analysis the sample from the studied.
Tishinskoe tailings contained 0.05 % copper; 0.06 % lead;
-
1.1 % zinc; 52.3 % SiO2; 2.3 % iron; 8.1 % Al2O3; 2.5 % CaO; 8.7 % MgO. The dispersion analysis of tailings from Tishinskoe deposit showed that the most part of useful components — copper, lead and zinc were concentrated in the fraction 010 mcm.
The flotation scheme included regrinding of tailings, basic, control flotations and four recleanings of collective cop-per-lead-zinc concentrate.
We selected optimum mode of regrinding, consumption of collector and foaming agent in the cycle of collective cop-per-lead-zinc flotation of tailings from Tishinskoe deposit. At the optimum regrinding of tailings to 75.0 % of class — 0.040 mm, collector consumption 150 g/t, T-92 foaming agent — 80 g/t we obtained the collective copper-lead-zinc concentrate containing 2.5 % copper at recovery 61.7 %; 2.0 % lead at recovery 59.52 %; 4.3 % of zinc at recovery 59.41 %; 8.3 % of iron at recovery 40.4 %; 5.8 g/t of gold at recovery 53.41 %.
The application of the combined collector (mixture of composite aerofloat, TC-1000 thionocarbamate and butyl xanthate in ratio of 1:1:3) improves the extraction of useful components into the collective copper-lead-zinc concentrate produced from tailings of Tishinskoe deposit reducing the consumption of foaming agent T- 92 to 25 %, from 80 to 60 mg/kg (Table 3).
With the use of the combined collector we produced the collective copper-lead-zinc concentrate containing 2.2 % copper at recovery 76.74 %; 1.8 % lead at recovery 70.43 %; 3.3 % zinc at recovery 71.22 %. Extraction of copper increased at 9.63 %, lead — 8.41 %; zinc — 9.2 %.
At that the consumption of the combined collector was 50 g/t less than sodium butyl xanthate, the consumption of base foaming agent decreased at 25 %.
Conclusions
On the basis of complex studies we chose the selective combined collector consisting of mixture of composite aerofloat, TC-1000 and butyl xanthate. The reagent ratio was 1:1:3.
The advantage of the suggested flotation reagent is that it incorporates two polar groups and a long hydrocarbon radical.
The reagent action was studied with the flotation tailings from Zhezkazgan concentrating plant and tailings from Tishin-skoe deposit. It was shown that the flotation of tailings from Zhezkazgan plant with smaller, compared with butyl xanthate, consumption of combined collector resulted in the draft copper concentrate with copper content 13.0 % at recovery 80.22 %. Compared to the basic technology the copper content increased at 5.1 % in the draft concentrate, recovery at 31.4 %. The flotation of tailings from Tishinskoe deposit resulted in increasing extraction of copper at 9.63 %, lead — at 8.41 %; zinc — at 9.2 %.
Список литературы Технологические основы переработки хвостов флотационного обогащения с применением комбинированных флотореагентов
- AbramovA. A., Onal G. Requirements of theory and technology to the surface state of minerals to be floated // Proc. X IMPC. Izmir (Turkey), September 2004.
- Abramov A. A. // Proc. VI IMPS. Changing Scopes in Mineral Processing // ed. M. Kemal, V. Arslan, A. Akar, M. Canbazoglu. Rotterdam: Balkema, 1996. P. 181-186.
- Alan N. Buckley, Gregory A. Hope, Kenneth C. Lee, Eddie A. Petrovic, Ronald Woods Adsorption of O-isopropyl-N-ethyl thionocarbamate on Cu sulfide ore minerals // Minerals Engineering. 2014. Vol. 69. P. 120-132.
- Абрамов А. А. // Физ.-техн. пробл. разраб. полез. ископ. 2005. № 1. С. 4-14.
- Отрожденнова Л. А., Рябой В. И., Кучаев В. А., Малиновская Н. Д. Флотация медных сульфидных руд гексиловым ксатогенатом фирмы «Хёхст» // Обогащение руд. 2010. № 4.


