The application of cloud point extraction in food industries
Автор: Saman Azizizadeh, Mohammadyar Hosseini, Somayeh Aziznia
Журнал: Биология в сельском хозяйстве @biology-in-agriculture
Рубрика: Биологические проблемы переработки и производства продуктов питания
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.4, 2014 года.
Бесплатный доступ
This article is a brief introduction of theoretical results of cloud point extraction in food science. In this article, we present a collection of introductions on cloud point extraction, besides the advantages and its functionality have been studied and described the way this method demanded. This easy and simple method is affordable and has a wide range of application in determination of different samples and the ability of evaluating analyte in ng levels is possible in this method.
Extraction, surfactant, micelle, cloud point
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14770280
IDR: 14770280 | УДК: 664
Текст научной статьи The application of cloud point extraction in food industries
Extraction of a chemical variety from natural or lab samples in order to analyze or pharmaceutical, edible or industrials goals require removing of other varieties in sample. All the treatment and process in this was called extraction where micelle systems are of the most functional methods (1). In recent decades, extraction and concentration stages in order to determine trace amount of some compounds in water solutions have been considered. Requirement of really low amount products of contaminants in water, soil and other biological samples revealed that high sensitive analyzing method and appropriate separation needs to be employed. Commonly applied methods in extraction and ion concentration in water solutions are liquid-liquid extraction (LLE) and solid phase extraction (SDP) therefore more tendency to replace solvent extraction methods in order to reduce sample manipulation, analyte loss and prevent using toxic solvents required (1).
The problem in both LLE and SPE is prolongation of extraction time and high manipulation. Other developed methods may reduce organic solvent applications and finally removed them. Solid phase micro extraction (SPME) is a method in organic compounds extraction from biological samples. SPME is base on analyte balance between polymeric stationary phases and sample matrix. In this method we need more than 1hr to extract sample (1).
In this method, surfactants used where their high capacity in dissolving different materials that permits an insoluble or negligible solubility readily dissolve in water.
A low volume of concentrated surfactant allows adjusting of analyte in 1 stage, then determining by atomic absorption, GC, and HPLC. It is a non toxic cheap method (2).
Surfactants
Surfactants are a collection of words including surface, active and agent. Surfactants are organic compounds containing hydrophobic groups in tails and hydrophilic groups in head. A surface active material has R-X structure in which hydrocarbon chain(R) with 8-18 carbon atoms and X is polar hydrophilic ion (4).
Micelle
In recent 76 years, an interesting relationship between physiochemical properties of surface active materials solution and their concentration proposed that quotes sudden changes in physiochemical properties these solution in a low range of concentration. These properties attributed to the aggregation of two character molecules and concepts such as micelle and critical concentration. Surface activating molecules in highly diluted solutions are in monomer form. However sometimes they find in dimer and trimer forms. When concentration of surfactant comes to a suitable amount, spontaneous aggregation and micelle forming occur (5).In this aggregation, hydrophobic part is in center of micelle, while polar groups interact with water surface and hydrated with lots of water molecules. Regarding chemical structures of micelles, they can be cationic, anionic, double ionic and non ionic (4).
Micelles types
Micelles categorized in two groups, common micelles and reverse micelles. In polar solvents, the hydrophobic groups in tail of surfactant molecules direct to the center while hydrophilic groups direct to polar solvent resulting in create micelle aggregates. This status called common micelle. The process of aggregation in non polar solvent is so that end groups of surfactant molecules direct to the center and create hydrophilic core of micelles while non polar groups interact with solvent. These micelles called reverse (7).The size of micelles depends on temperature. For double characters non ionic in aqua medium, reduction of temperature led to enlarge the micelles diameter as a result of exothermic monomer into micelle structure in low temperature. Studies revealed that for Light scattering of double characters non ionic in non aqua medium, between temperature and the size of micelles is a direct relation (7).
Cloud point extraction
Surfactants used in this method of analyte extraction where they add to sample solution and do pre concentration treatment.
Could point extraction stages
First, surfactants add to sample, if required some salt adds as well, and then keeps in special temperature up to when the solution become turbid and give critical temperature. Solution centrifuged and extraction finished. Therefore sample gathers on the aqua phase and supernatant separated. This method is as scattering as liquid-liquid extraction (2).
Overall:
-
• First surfactant added to the sample.
-
• Adding salt to increase extraction
-
• Keeping in certain time up to becoming turbid of solution (cloudy point)
-
• Centrifuge
-
• Separation sample in aqua phase and collection of supernatant in order to separation
The advantages of cloudy point extraction methods
-
1. High concentration factor is available.
-
2. Surfactants are cheap and non environment contamination.
-
3. Surfactants use in low volumes.
-
4. The possibility of processing with sensitive compounds in low temperature is available.
The different types of analytes are separable with different properties.
The function of cloudy point extraction (1):
-
1. Separation of metal cations such as, aluminum, chrome, …
-
2. Separation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
-
3. Separation polychlorinated compounds.
-
4. Separation of biological molecules like proteins (casein, α lactalbomine).
-
5. Separation of pesticides
-
6. Separation of Lantids and metals mixture from water samples.
-
7. Separation of fat soluble vitamins.
-
8. Separation of choloro phenols, phenols, benzyl alcohol from water samples.
Examples of cloudy point extraction in food science
Application of cloudy point extraction in protein separation from cow milk and separation with mass spectrometry
Poly oxy ethylene and iso actyle phenyl ether (Triton X-114) are non ionic surfactant. In a research study parameters including the concentration of Triton X- 114, NaCl concentration, pH as effective parameters on extraction efficiency investigated, finally after using cloud point extraction method in order to separate, matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization – time off flight mass spectrophotometry (MALDI-TOF MS) used to conduct (11).
Applying of cloud point in separation of antioxidant (phenols) from olive oil wastes
In this study the application of Triton X-114 which has proved being efficient in extraction of phenolic compounds. The use of Triton X-114 as an effective surfactant in phenol compounds extraction has been researched. The affection of surfactant concentration on phenol compounds individually and total phenol compounds as well studied. In this study olive mill wastewater purchased from Argos Co, Greek. Before adding of surfactant, fat compounds extracted with hexane 20 min kept in water bath 20 min at 55-65 ° C and centrifuged with 3500 rpm for 5 min (12).
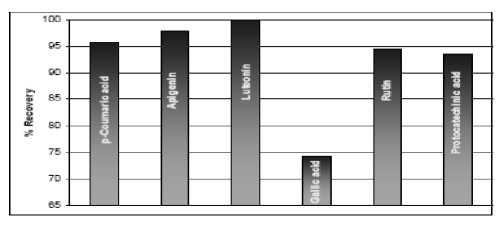
Figure 1. The investigation of surfactant affection in constant concentration of 4% on the efficiency of extraction 12)
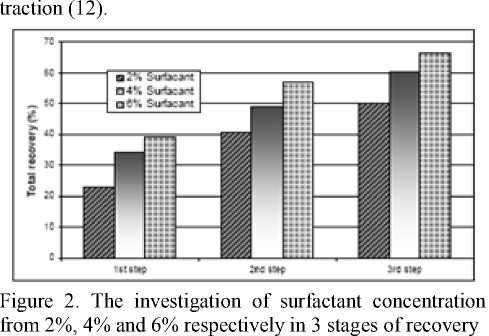
In determination of surfactant affection in constant concentration of 4 % on extraction efficiency (figure 1), all of the surfactant had the efficacy of more than 90% except Gallic acid with 74.2%. In next stage of surfactant concentration from 2% to 4% and then 6 % (figure 2), the amount of efficiency has been increased in 3 stages ex-
The application of Triton X-114 can successively use for phenol compounds extraction in aqua medium and even can extract Luteonin, Apigenin and p-Coumaric acid with 96% efficiency (12).
Conclusion
Cloud point extraction is a strong analyzing method in improving of determination level and detection of met- als analyzing, contaminants, and biological molecules. Applying micell system cause concentration factor thus resulting in increasing of efficiency. This method is also affordable with wide range of demanding and the possibility of metal evaluation in ng levels like determination of ions in water.
Список литературы The application of cloud point extraction in food industries
- R. C. Mart´ınez, E. R.Gonzalo, B. Cordero, J.L. Pavo´n, C. Pinto, E. Laespada, Surfactant cloud point extraction and preconcentration of organic compounds prior to chromatography and capillary electrophoresis, Journal of Chromatography A, 902 (2000) 251-265.
- H.Filik, S,Cekiç (2011). Cloud Point Extraction of Pesticide Residues, Pesticides in the Modern World -Trends in Pesticides Analysis, Dr. Margarita Stoytcheva (Ed.), ISBN: 978-953-307-437-5.
- M. S. Noorashikin, S. Mohamad & M. R. B. Abas (2013): Cloud Point Extraction (CPE) of Parabens Using Nonionic Surfactant Phase Separation, Separation Science and Technology, DOI: DOI: 10.1080/01496395.2012.756034
- Y.C. Liao, O. A. Basaran, E. I. Franses, Micellar Dissolution and Diffusion Effects on Adsorption Dynamics of Surfactants, AIChE Journal, 49 (2003) 3239-3240
- M. Moradi, Y. Yamini. Surfactant roles in modern sample preparation techniques: A review, J. Sep. Sci. 2012, 35, 2319-2340
- T. Dwars, E. Paetzold, G. Oehme, Reactions in Micellar Systems, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 7174-7199.
- P. G. Mazzola, A. M. Lopes, F. A. Hasmann, A. F. Jozala, T. Penna, P. O. Magalhaes, C. O. Yagui, A. Pessoa, Liquid-liquid extraction of biomolecules: an overview and update of the main techniques, J Chem Technol Biotechnol 83, 2008; 143-157 (2008).
- M. F. Silva, E. S. Cerutti, L D. Martinez, Coupling Cloud Point Extraction to Instrumental Detection Systems for Metal Analysis, Microchim Acta (2006)155, 349-364.
- B, Ojeda, F. S, Rojas, Separation and preconcentration by a cloud point extraction procedure for determination of metals: an overview, Anal Bioanal Chem 2009; 394:759-782.
- T. Ingram, S. Storm, P. Glembin, S. Bendt, D. Huber, T. Mehling, I. Smirnova, Aqueous Surfactant Two-Phase Systems for the Continuous Countercurrent Cloud Point Extraction, Chemie Ingenieur Technik, 84, 2012; 840-848.
- A.Lopes, J.Garcia, R.Catharin, L.Santos, M.Eberlin, M.Arruda, Cloud point extraction applied to casein proteins of cow milk and their identification by mass spectrometry, Analytica Chimica Acta 590 (2007); 166-172.
- E. Katsoyannos, A. Chatzilazarou, O. Gortzi, S. Lalas, S. Konteles, Pa Tataridis, Application of cloud point extraction using surfactants in the isolation of physical antioxidants (phenols) from olive mill wastewater, Fresenius Environmental Bulletin, 15 (2006); 1122-1125.


