The assessment of liquefaction and lateral spreading effects on bridges
Автор: Murashev A.K., Kirkcaldie D.K., Keepa C., Cubrinovski M., Orense R., Lloyd J.N.
Рубрика: Теория расчета строительных конструкций
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.14, 2014 года.
Бесплатный доступ
This paper presents a summary of the outcomes from a research project commissioned by the NZ Transport Agency to develop design guidance for bridges in New Zealand for liquefaction and lateral spreading effects. The purpose of this research is to prepare design guidelines that will give clear design methodology and enable cost-efficient design of bridges, reducing the need for costly ground improvements on sites subject to these hazards. The current stage of the project is a review of the available design methods and the development of design principles and methods for liquefaction and lateral spreading effects on bridges appropriate for New Zealand conditions. Once finalised, the proposed design requirements and guidelines will be incorporated in the NZ Transport Agency’s Bridge Manual and disseminated to the wider New Zealand engineering community.
Design guidance for bridges, liquefaction and lateral spreading effects, groundimprovements, requirements and guidelines
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147154384
IDR: 147154384 | УДК: 627.514
Текст научной статьи The assessment of liquefaction and lateral spreading effects on bridges
Bridges and highway structures located on sites with shallow groundwater tables or close to bodies of water can be susceptible to earthquake damage. Liquefaction of saturated sand-like materials (sands, sandy gravels, non-plastic silts), cyclic softening or cyclic failure of clay-like materials (plastic silts and clays) and lateral spreading can result in significant damage to bridges and highway structures. Earthquake damage to bridge abutment slopes on sites prone to liquefaction and lateral spreading may include ground failures, excessive lateral displacements and settlements. A large number of recorded cases of damage to bridge foundations due to the lateral displacements and settlements associated with liquefaction have been reported worldwide. There are also recent examples of earthquake damage to bridge structures caused by liquefaction and lateral spreading in Christchurch as a result of 2010 the Darfield earthquake and 2011 Christchurch earthquakes.
Soil deformation caused by liquefaction and lateral spreading can result in damage to bridge abutment and pier foundations and structural elements of bridges. A detailed report on the performance of highway structures during the Darfield and Christchurch earthquakes of 4 September 2010 and 22 February 2011 has been prepared by Wood et al. (2012). Conservative design approach quite often results in the need for costly ground improvement to fully mitigate against liquefaction, cyclic softening and lateral spreading at bridge sites. Regular review and improvement of design methods for bridges located on sites prone to liquefaction and lateral spreading is critical for the development of costeffective bridge designs.
The design of bridges on sites prone to liquefaction and lateral spreading is a complex process that requires consideration of a large number of issues:
-
• Issues relating to geotechnical investigations: geotechnical investigation techniques for field and laboratory testing, determination of site subsoil class, development of a reliable ground model.
-
• Issues relating to the evaluation of liquefaction and lateral spreading: determination of seismic demand, triggering of liquefaction, liquefaction-induced ground displacements, evolution of liquefaction and associated loads with time, settlement and lateral spreading including their uncertainties and outstanding issues, issues of practical concern (liquefaction of low plasticity silts, probabilistic vs. deterministic liquefaction evaluation, effect of groundwater conditions and artesian water heads, liquefaction at depth and maximum depth of liquefaction, cyclic mobility, partial liquefaction and limited shear strain), assessment of reduced bearing and pull out capacity of the foundation piles and of the effect of negative skin friction.
-
• Issues relating to ground improvement: available methods of ground improvement, effectiveness and cost of ground improvement work, reliability and resilience of the adopted ground improvement.
-
• Issues relating to the detailed analysis of the effect of liquefaction and lateral spreading on the bridge structure: methods of analysis, determination of model parameters, boundary conditions and pile-group effects, key uncertainties and the need for sensitivity analysis, soil – structure interaction, P-Δ effects, performance criteria (displacements, plastic deformation in piles and piers, need for postearthquake repair or replacement of the bridge).
-
• Structural design issues: interaction between structural and geotechnical designers, definition of
acceptable damage states and design for adopted damage states, structural detailing of bridges to reduce damage and increase repairability.
-
• Construction issues: confirmation of ground conditions and design assumptions, control of ground improvement quality.
-
• Post-construction monitoring issues: equipment / systems for monitoring post-earthquake performance of bridges (e.g. inclinometers in piles and/or ShapeAccelArrayTM that consists of a chain of sensor elements / segments joined together in such a manner that they can move in relation to each other in all directions except for twisting, each segment contains a multi‐axial MEMS-chip accelerometer which makes the segment act as an extremely accurate inclinometer), post-earthquake inspections and assessment.
All of the above issues affect the design process, the quality of the developed design solution and finally the seismic behaviour of bridges as well as the ability of the bridge and geotechnical engineers to assess the post-earthquake condition of bridges.
In 2013 NZ Transport Agency commissioned a research project to develop design guidelines for design of bridges on sites prone to liquefaction and lateral spreading in New Zealand. The research project includes a review of seismic behaviour of bridges on sites prone to liquefaction and lateral spreading in New Zealand and overseas, review of available design methods for bridges against liquefaction and lateral spreading effects as well as detailed consideration of the bridge design framework in New Zealand and development of appropriate design methodology for New Zealand conditions (Murashev et al., 2013). It was not possible to address all of the design issues in detail within the first stage of the research project. Therefore areas where supporting information is not available and further research work is required have been identified.
Phases of response
When evaluating the effects of liquefaction and lateral spreading on the performance of the bridge pile foundations using equivalent static analyses, it is necessary to conduct separate analyses for different phases of the response (Cubrinovski et al., 2009). The following analyses corresponding to different phases of the response should be carried out:
-
• Cyclic analysis without liquefaction, in which inertial loads that would occur in the absence of liquefaction are considered.
-
• Cyclic liquefaction analysis, estimating the potential and consequences of liquefaction, and considering simultaneous kinematic loads (due to cyclic ground displacements) and structural inertial loads while accounting for stiffness and strength degradation due to excess pore water pressures.
-
• Lateral spreading analysis, estimating the potential for liquefaction and consequences of lateral spreading including large stiffness and strength
degradation, and kinematic loads due to large displacements associated with lateral spreading. Inertial loads may be considered in this analysis, but such loads are of secondary importance in the spreading phase, and can be ignored in many cases.
Classification of design methods
Methods of analysis for bridges and piles in liquefied soils range from simplified methods using an equivalent static analysis approach to a rigorous time history analysis based on the effective stress principle. These analysis methods can be classified into three different categories:
-
• Pseudo-static analysis (PSA) or equivalent static analysis.
-
• Direct dynamic time history analysis: (a) -effective stress analysis (ESA) considering effects of excess pore pressures and liquefaction through detailed constitutive modelling, and (b) - total stress analysis (TSA), dynamic analysis using total stresses or equivalent stresses (either ignoring excess pore pressures or considering them in a simplified manner). In the direct method of analysis (ESA and TSA), the response of the soil-pile-pier-abutment-deck system can be considered over the entire period of time from the initiation of shaking to the final stage of postearthquake equilibrium and residual deformation of the bridge in a single analysis.
-
• Substructure analysis methods which use some features of PSA, ESA or TSA but are essentially hybrid approaches tailored to address specific aspects in the performance assessment. For example, the well-known Newmark-type analysis (which is a simplified, user-defined time history analysis) would be a typical representative of this group of methods. The substructure method, uses a set of separate but related analyses to assess the performance of a bridge subsystem.
Effect of liquefaction and lateral spreading can be evaluated by considering a single member (e.g. a single pile), a subsystem of the bridge (pile group, pier piles or piled abutment), or the whole bridge. Each of these models is acceptable in the evaluation of the bridge performance provided that proper boundary conditions and modelling assumptions are used, and that there is a clear understanding of the analysis objectives and limitations. The cyclic response should be considered both in the transverse and longitudinal directions, whereas the lateral spreading response is commonly considered in the longitudinal direction of the bridge.
Pseudo-Static Analysis
In the PSA approach, a relatively simple beamspring model is used for the soil-pile-bridge system to perform a nonlinear equivalent static analysis. This approach is also referred to as the beam on Winkler foundation or static pushover analysis.
Based on our review of available PSA methods, the following design methods would be appropriate for New Zealand conditions:
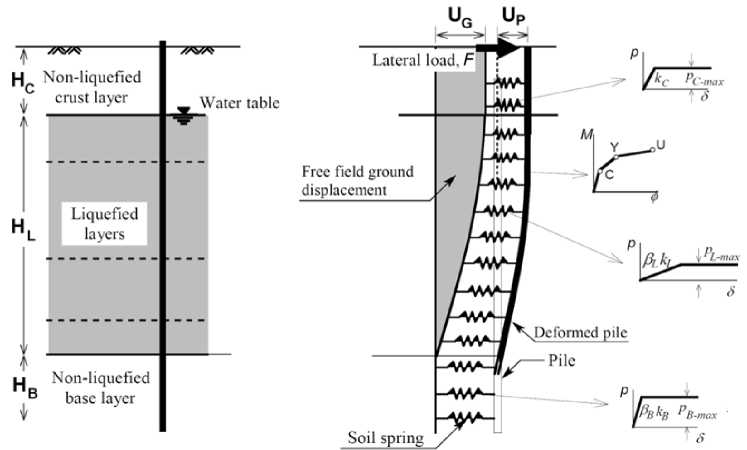
Fig. 1. Beam-spring model for pseudo-static analysis of piles in liquefying soils: model parameters and characterization of nonlinear behaviour (Cubrinovski et al., 2009)
-
• Cubrinovski method (Cubrinovski et al., 2009)
-
• Pacific Earthquake Engineering Research Centre (PEER) method (Ashford et al., 2011)
The main features of these methods are briefly described below.
Cubrinovski method
This PSA method can be applied either to a single-pile, pile group or the whole bridge. We will use the single pile model to describe the method.
The typical beam-spring model representing the soil-pile system in the analysis is shown in Figure 1. The model can incorporate a multi-layered deposit with liquefied layers of different thickness and different depths, a crust of non-liquefiable soil at the ground surface, and deeper non-liquefiable layers including base layers at the tip of the pile. Parameters of the model are shown in Fig. 1.
Given that the key requirement of the analysis is to estimate the inelastic deformation and damage to the pile, the proposed model incorporates simple but non-linear load-deformation relationships for the soil and the pile. The soil is represented by bilinear (elastic-plastic) springs, the stiffness and strength of which can be degraded to account for effects of nonlinear behaviour and liquefaction. The pile is modelled with a series of beam elements each having a tri-linear moment-curvature relationship. Commonly available software and finite element programs can be employed for the beam-spring model and analysis. Two equivalent static loads can be applied to the pile: a lateral force at the pile head (F) representing the inertial load on the pile due to vibration of the superstructure, and a horizontal ground displacement (UG) applied at the free end of the soil springs representing the kinematic load on the pile due to lateral ground movement (cyclic or spreading) in the free field. As indicated in Fig. 1, it is assumed that all of the ground surface displacement is accommodated within the liquefied layer, that the non-liquefied crust at the ground surface moves as a rigid body and undergoes the same ground displacement as the top of the liquefied layer, and that the non-liquefying base layer is not moving. Deformed shapes of piles and bending moment distribution in the piles can be obtained from the analysis. If the pinning effect of the bridge deck needs to be included, a full bridge model including the bridge deck should be developed.
PEER Method
The PEER method of analysis (Ashford et al., 2011) is very similar in concept to Cubrinovski method. A beam-spring model is used (Fig. 2) in which non-linear soil springs and nonlinear (tri-linear or bi-linear) moment-curvature relationships are employed for the soil and the pile respectively. Lateral, vertical and bearing soil springs are defined
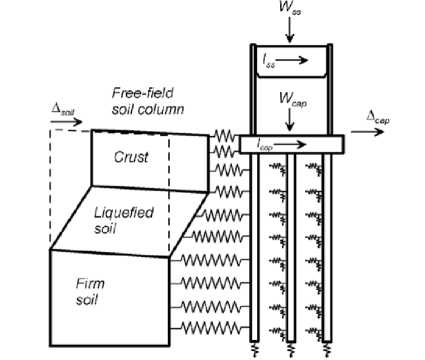
Fig. 2. Pile-group model in the PEER equivalent static analysis with imposed soil displacements in the model, however it is stated that guidance for the vertical springs and bearing springs cannot be provided. For the liquefied soil, reduction factors (or so-called p-multipliers) are applied to the nonliquefied soil spring (p-y) resistance.
The method can be used for the analysis of a single pile, pile group or whole bridge. Analyses in both transverse and longitudinal directions, and separate analyses for non-liquefaction and liquefaction cases are recommended.
The displacement based approach is adopted as the best method for lateral spreading analysis using the equivalent static approach, in which free field ground displacements are applied at the base of the soil springs. A number of methods are recommended for estimating the free field displacements (Ashford et al., 2011). However, considering the uncertainties in estimating lateral spreading displacements, it is recommended to employ several different methods and to use a range of anticipated displacements in the analysis.
The PEER method suggests that for design purposes it is prudent to assume that sufficient lateral spreading displacement occurs during strong ground shaking, and therefore analyses should be performed in which lateral spreading displacements and inertial loads are applied simultaneously.
In addition to the above PSA methods, the report (Murashev et al., 2013) provides a summary of the following two Japanese design methods:
-
• Architectural Institute of Japan (AIJ) Method (Tokimatsu and Asaka, 1998).
-
• Japan Road Association (JRA) Method (JRA, 1996).
AIJ Method
The AIJ method was developed for the design of piles for building foundations. It is one of the most developed and widely used methods for the analysis of pile foundations in Japan. The key features of the AIJ method are as follows.
The displacement-based approach using a beamspring model is adopted with bi-linear soil springs and tri-linear moment-curvature relationships for the pile. Free field ground displacements are applied at the base of the soil springs to simulate effects of transient ground displacement and spreading displacements.
Stiffness of soil springs is defined using the subgrade reaction approach. Recommendations are given on the reduction factor for liquefied soil springs; the reduction factor is given as a function of the SPT blow count and depth. Three separate analyses are recommended for the pile foundations: no-liquefaction analysis (Case I), liquefaction analysis (Case II) and ground displacement analysis without liquefaction (Case IIIa) and with liquefaction, i.e. under lateral spreading conditions (Case IIIb) as illustrated in Fig. 3 (Tokimatsu and Asaka, 1998).
Effects of ground displacements are neglected in no-liquefaction analysis (Case I ) with the inertia force being the only applied load in this analysis. In the liquefaction analysis (Case II), the effects of inertia and ground displacement demands are combined.
JRA Method
The JRA method was developed specifically for highway bridges. Highway bridges in Japan are very large and massive structures and large diameter piles in a group are typically used for the bridge foundations. The piles are very stiff and strong and this is reflected in the design and analysis philosophy of the JRA Method.
The JRA method also considers three cases using separate analyses for: no-liquefaction case, liquefied soil case and laterally spreading soil case. The JRA analytical model for a pier-pile structure using a beam-spring model is shown on Fig. 4. Bi-linear springs and tri-linear relationships are used for the soil and pile respectively. Effects of liquefaction are accounted for by multiplying the stiffness (subgrade reaction coefficient), ultimate soil reaction and skin friction capacity by a degradation coefficient which is defined as a function of the factor of safety against liquefaction triggering and depth.
Force-based approach (with prescribed lateral loads equal to the ultimate passive soil pressures applied to the pile) is used for lateral spreading analysis. Rankine passive pressures are specified for the non-liquefied layers, while lateral pressures applied by the underlying liquefied layer are assumed to be equal to 30 % of the overburden effective stress. Strictly speaking, force-based methods should be discouraged from use since they quite often produce incompatible soil loads and pile displacements.
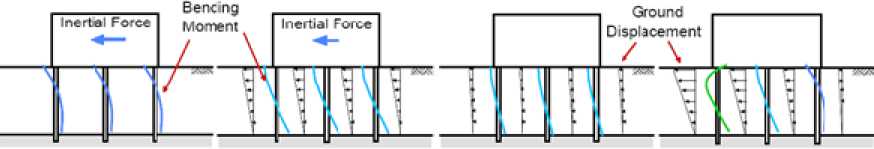
I) During shaking without liquefaction
II) During shaking after liquefaction lll-a) Residual ground displacement after earthquake lll-b) Lateral ground displacement after earthquake
Fig. 3. Separate analyses and loading conditions (inertia and kinematic loads) for three different stages of the response
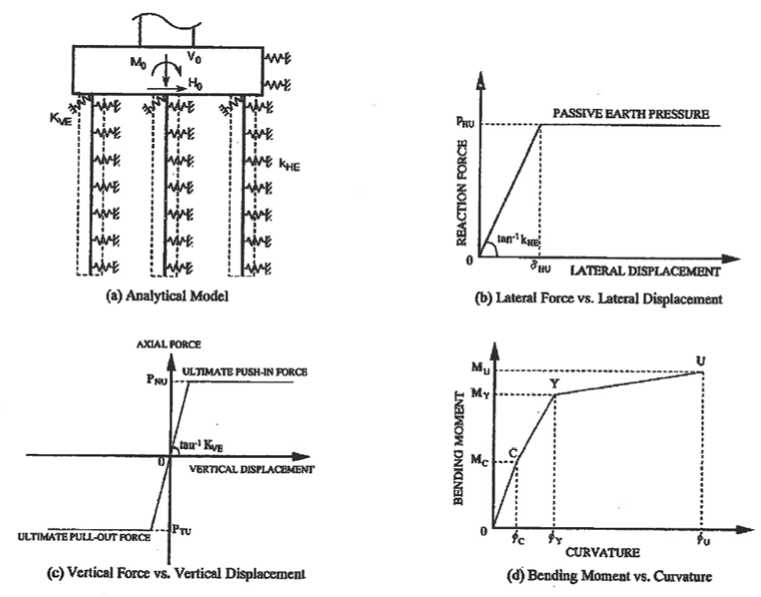
Fig. 4. JRA analytical model and load deformation relationships for liquefaction analysis of a pier pile foundation
Time history analysis
The dynamic response of the bridge is highly nonlinear and changes dramatically as it goes through the different transient stages from the initiation of strong shaking, through rapid build-up of excess pore pressures and consequent reduction in stiffness and strength of soils, development of liquefaction and post-liquefaction large ground deformation associated with earthquake-induced but gravity driven spreading. A non-linear time history analysis allows to investigate the dynamic response of the bridge while accounting for the complex soil-pile-pier-abutment-deck interaction or response of the bridge system in liquefying and laterally spreading soils. There is no doubt that a sound numerical analysis that is well calibrated and executed provides the most realistic simulation of the actual bridge behaviour. Two types of such analysis are commonly carried out:
-
• Effective stress analysis (ESA) which permits evaluation of seismic soil-pile interaction while considering the effect of excess pore pressure and eventual soil liquefaction on the pile response.
-
• Total stress dynamic analysis that has the same attributes as ESA but cannot simulate effects of the excess pore pressures and liquefaction with the same level of accuracy as ESA.
Substructure analysis
-
• Identify the soil layers that are likely to liquefy.
-
• Assign undrained residual strengths to the layers that will liquefy.
-
• Perform pseudo static seismic stability analysis to calculate the yield coefficient ky for the critical potential sliding mass.
-
• Estimate the maximum lateral ground displacement.
-
• If the assessment indicates that movement of the foundation is likely to occur in concert with the soil, then the structure should be evaluated for adequacy at the maximum expected displacement. This is the mechanism illustrated in Fig. 5.
-
• The structural remediation alternative makes use of the pinning action of the piles
-
• Identify the plastic mechanism in the pile that is likely to develop as the ground displaces laterally.
-
• From an analysis of the pile response to a liquefaction induced ground displacement field, the likely shear resistance of the foundation is estimated.
-
• This increased resistance is then incorporated into the stability analysis, which increases ky. If appropriate, this lateral shear resistance should be reduced to account for P-Δ effects.
-
• Recalculate the overall system displacement on the basis of the revised resistance levels and iterate until the resistance is consistent with the level of displacement estimated. Once a realistic displacement is calculated, the system can be assessed for this level of movement.
-
• If necessary, additional piles can be installed or ground improvement carried out to reduce the seismic displacement further.
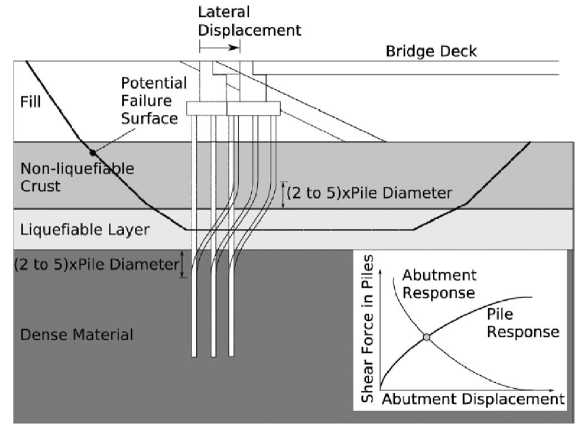
Fig. 5. “Pile-pinning” effect for the case of a pile that is locked into to both the soils above and below the liquefied soil layer
Conclusion
An extensive review of the design methods for bridges located on sites prone to liquefaction and lateral spreading has been carried out. There is no consensus amongst the geotechnical engineering community on the preferred design methodology. Therefore, geotechnical engineers should choose one of the described design methods based on the consideration of the importance level of the bridge, client’s requirements and available time and project budget. The design is highly dependent not only on the design methodology for the bridge, but also on the quality of geotechnical investigations, assessment of seismic demand and triggering of liquefaction. It is therefore recommended that a number of different methods are used and sensitivity analyses are carried out at each stage of the design process. Irrespective of the adopted design method, it is always important to address uncertainties associated with the assessment of liquefaction potential of soils and the magnitude of lateral spreading, and evaluate the effect these uncertainties on the predicted response / performance of the bridge structures. Additional research work will be carried out to further refine design recommendations for bridges located on sites prone to liquefaction and lateral spreading and to incorporate those into the Bridge Manual (NZ Transport Agency, 2013).
Список литературы The assessment of liquefaction and lateral spreading effects on bridges
- Architectural Institute of Japan, AIJ. (2001). Recommendations for Design of Building Foundations, p. 65 (in Japanese).
- Ashford S.A., Boulanger R.W., and Brandenberg S.J. (2011). Recommended Design Practice for Pile Foundations in Laterally Spreading Ground. Pacific Earthquake Engineering Center, Berkeley, California.
- Cubrinovski M., Ishihara K. and Poulos H. (2009). Pseudostatic analysis of piles subjected to lateral spreading. Special Issue, Bulletin of NZ Society for Earthquake Engineering, 42(1), 28-38.
- Japan Road Association, JRA (1996). Part V, Seismic Design, Specifications for Highway Bridges (in Japanese).
- Ledezma C. and Bray J. (2010). Probabilistic Performance-Based Procedure to Evaluate Pile Foundations at Sites with Liquefaction-Induced Lateral Displacement. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng., 136(3), 464-476.
- MCEER (2003) Liquefaction Study Report -Recommended LRFD Guidelines for the Seismic Design of Highway Bridges. MCEER/ATC-49-1 report, Applied Technology Council & Multidisciplinary Centre for Earthquake Engineering Research, American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials, Washington D.C.
- Murashev A.K., Kirkcaldie D.K., Keepa C., Cubrinovski M., Orense R. (2013). Development of the design guidance for bridges in New Zealand for liquefaction and lateral spreading effects, draft report for NZ Transport Agency’ research project TAR 12/09
- NZ Transport Agency (2013) SP/M/022 Bridge manual, Wellington.
- Tokimatsu K. and Asaka Y. (1998). Effects of liquefaction-induced ground displacements on pile performance in the 1995 Hyogoken-Nambu earthquake, Special Issue on Geotechnical Aspects of the January 15, 1995 Hyogoken-Nambu Earthquake, No. 2, Soils and Foundations, 163-177.
- Wood J.H., Chapman H.E., Prabhaharan P. (2012). Performance of highway structures during the Darfield and Christchurch Earthquakes of 4 September 2010 and 22 February 2011, Report for NZ Transport Agency.


