The Code of the Arctic regions
Автор: Nesterenko M.Y., Koposov S.G., Portsel A.K., Shadrina O.N.
Журнал: Arctic and North @arctic-and-north
Рубрика: Management, economy, regionology
Статья в выпуске: 6, 2012 года.
Бесплатный доступ
In article materials of a round table “Code of Arctic regions”, spent are systematised on February, 29th, 2012.
Arctic regions, day of a cold, a code
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148320447
IDR: 148320447 | УДК: [332.14+338.2](985)
Текст научной статьи The Code of the Arctic regions
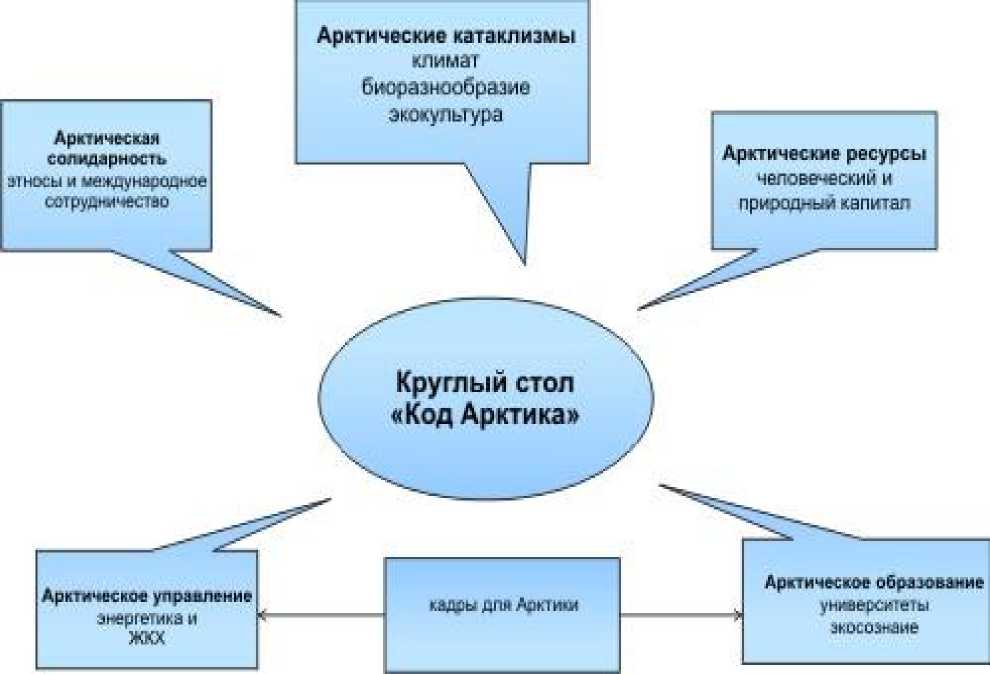
During the celebrating the Day of the Arctic, the Institute of Management and regional studies of the Northern (Arctic) Federal University named after M.V. Lomonosov on the February 29, 2012 hold a round table under the mysteriously named the "Code of the Arctic." The event should show what is included in the concept of the "Arctic", to decipher the code. The "Code of the Arctic" is understood by us as a latent, encrypted information, the system of certain knowledge, character, revealing the hidden meaning, the content of laminated the Arctic space. Advance, even 19 January 2012, employees of the center the "Arctic partnership" proposed for discussion at the round table a number of topics, including the "Code Arctic" [1].
Global climatic changes: myth or reality?
The rise of the sea level
«melting permafrost»
flood, rain, «new ice age»
Ecological problems of the Arctic the treat to the biodiversity of the Arctic
Arctic tourism (national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, scansens).
URL:
The life on the North: depletion of the resources or new perspectives?
4-
4-
4-
4-
SMP and the perspectives of the water transport Energetic and JKH in the North
Management experience in the Arctic region «human dimension» in the Arctic
4-
4-
4-
Ethnicity and identity in the Arctic, Nordmen, the Arctic solidarity
The space of the Arctic culture: the experience of the developing of the high -latitude
Ways and difficulties in forming eco knowledge in the Arctic, international Arctic cooperation in the Arctic1.
On the site of the center of the "Arctic partnership," we also publish material on the philosophy of the idea of celebrating the Day of the Cold, where it came from, as is discussed. Realizing that these materials has a historical interest for those who will be celebrating the Day of the Arctic in the coming years, we have systematized and publish them in the journal " Arctic and North", making appropriate references to authors and sources.
The aim of the round table, the "code in the Arctic" was to attract the attention of students and the scientific community to the problems and sensitive issues in the Arctic, to reveal the con- tents of the code in the Arctic, to deepen knowledge about the Arctic region, to study the impact of climatic changes on the polar regions of the world, socio-cultural convergence, the promotion of the Arctic thinking, learning and the development of the Arctic regions. After all, the Arctic - is not only an immense amount of resources that need to be mastered. This concept is much broader and deeper. The Arctic - is first of all the people who live and work in difficult conditions in the north, an area of more than 20 million square feet. miles.
29.02.2012 was held the Round Table, which brought together experts from different disciplines to discuss the geopolitical, economic, political, social, environmental and innovation issues in the Arctic. It was attended by: E. Antipin, the Senior Lecturer, the Department of the State and Municipal Management; Verteshin A.I., the Doctor of Political Sciences, Professor, Department of State Municipal Management; Dregalo A.A., Doctor of Philosophy, Professor, the Head of the Department of the State and Municipal Management; Koposov S.G., the director of the Center of Space Monitoring, V.S. Kuznetsov, Ph.D., Deputy, Director of the National Park "Russian Arctic", Lukin, Y, F., the doctor of the historical sciences, professor, director of the Institute of the management and Regional Studies of the NArFU, Lyakhov J. Y, the head of the sector of the electronic reading room library of the NarFU, A. Lavrentiev, a senior fellow at the Center, "Arctic partnership ", Michael A., the minister of the economic development of the Arkhangelsk region; Muzykin M., journalist of" True North "; Nasonova N.P., Senior Lecturer, the Department of the State and Municipal Management, Nesterenko, M. Yu, the director of the center "Arctic Partnership"; D. Nesterov, a journalist of the press center of the NArFU, Nikolaev A.V., the senior lecturer in marketing and trading business; S.S. Nikulin, a specialist department of the state and municipal management; P. Okunev, Ph.D., Professor, Department of State and Municipal Management; Portsel A.K., Ph.D., Associate Professor of Murmansk Technical University (Murmansk), Sokolov, V.P, the spokesman of the sea port of Arkhangelsk, Shadrina O.N., Ph.D. in Philosophy, Associate Professor, the Senior Researcher of the Center of the "Arctic Partnership", students 2, 3, 4 courses of the Institute of the management and the Regional Studies of the NarFU.
There were so many questions, as well as points of view on them, the discussion lasted over two hours. Among the main themes – were environmental issues, issues of geopolitics and socio-economic development of the Arctic zone of Russia.
The first question, which was discussed - the socio-economic development of the Arctic zone of Russia and the projects for inclusion in the federal program, announced by the Minister of the Economic Development of the Arkhangelsk region E. A. Mikhailovsky. In his speech, he talked

primarily about the consolidated union of all territories to address problems and issues of the development in the Arctic, the approval and adoption of the necessary documents on the state status of sub-Arctic zone of Russia HN, the discussion which took place in Moscow at a meeting of the Ministry of Regional Development in February 2012. There, together with representatives of the administration of the city of Naryan-Mar and the Institute of Management and regionologi of the NArFU, he announced proposals for inclusion in this program. It also identified some conceptual approaches:
The development of the activities in the Arctic region should have a systemic and, therefore, efficiency. Proposed to be reflected in the program complete system measures aimed at leveling the economic and social conditions in comparison with other regions of Russia.
The proposals to use the already found solutions to the broadcast on the positive experience of other actors in the Arctic;
The preparation of the standard solutions: it is necessary to seek solutions to common problems in areas such as new technologies on dirty roads, the construction of winter roads and the optimization of health services (telemedicine, mobile hospital), and new projects of vehicles - light domestic planes (no replacement AN-2) swamp buggies, etc E.A.Mihaylovsky designated spheres of the human activity in the North, which require the government support: energy and utilities, transportation, food security, housing, preservation of ecology of the North, support for indigenous peoples, etc. He listed key projects for the region, which in first need to pay attention to the development of the Arkhangelsk region:
The construction of a new deep-water region the "North" Arkhangelsk sea port;
participate in the projects to develop offshore fields;
the project "Mezen tidal electro – power station";
the construction of a highway of Onega - Severodvinsk;
the construction of a highway of Naryan-Mar - Mezen - Archangelsk;
NIR "Clusters of Arkhangelsk region": the construction, timber, Arctic tourism, science and education.
In conclusion, E.A.Mihaylovsky said that we need to work closely with academic and formation-cational institutions, especially with NArFU named after M.V. Lomonosov, because today it is this institution has the highest concentration of specialists in the Arctic.
The Speech by the Minister continued the director of the Institute of management and re-gionologii, Professor Y.F. Lukin . The key points, that he mentioned, it was the lack of strategy and the development of the program of the AZRF, the regulatory framework for the definition of the southern border of the Arctic zone of Russia. Need to adopt a federal law on the Arctic zone of Russia, to clarify its structure. Y.F. Lukin suggested that the author's model of "Arctic XXI», which includes: Administrative and legal, physical, geographical, spiritual and civilizational, geocultural, geopolitical, geo - economic space, ecology, arctic solidarity and partnership. He was told by the course of the preparation of the project "Russia in the Arctic: History, Present and Prospects" and others.
«Russia in the Arctic: history, present time, perspectives etc.
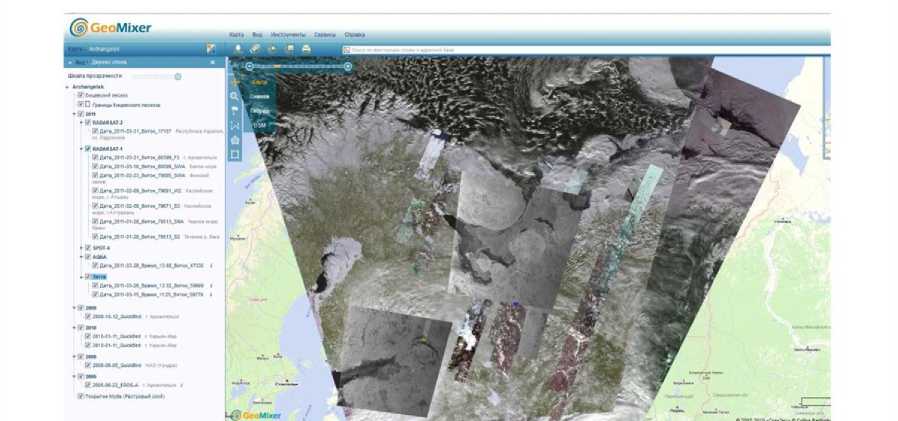
S. G.Koposov, the director of the Center of Space Monitoring of the Arctic NArFU reported the results of space activities in the Arctic and the use of innovative technologies. At the heart of the Centre - the domestic technology of reception and processing of images of Earth from Space "UniScan-36", which is the developer of Engineering and Technology Center "RDC" (Moscow). The Centre decided by a wide range of tasks, among which are essential: monitoring in near real time to meet the needs of the economy, carrying out research work, improvement of educational pro- grams.


СЕВЕРНЫЙ (АРКТИЧЕСКИЙ) ФЕДЕРАЛЬНЫЙ УНИВЕРСИТЕТ имени М.В. ЛОМОНОСОВА

Открытие
Центра космического мониторинга Арктики
With the help of «UniScan-36" in Arkhangelsk organized the direct reception of satellite da- ta f th i f i it T A U S EROS B I l RADARSAT 1 2 C da),
SPO per pix

Terra, Aqua, Radarsat-1 и 2, Spot 5 и Eros B



Центр космического мониторинга Арктики
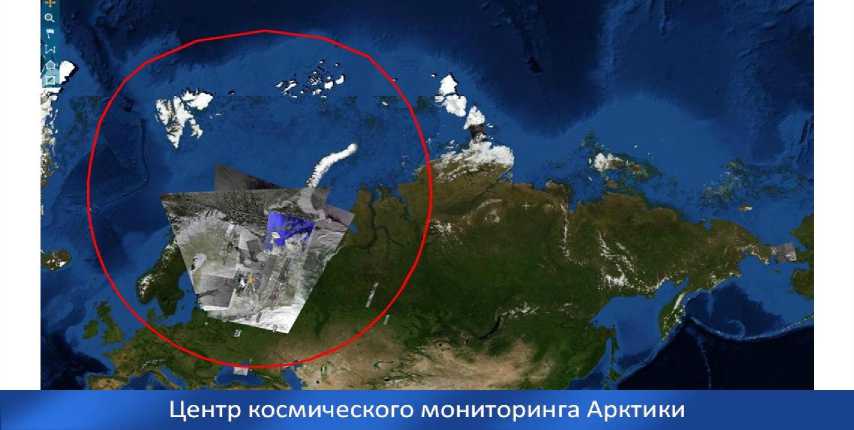
Actual satellite shooting makes it possible to monitor ice conditions in the waters, to organize information tracking and optimization of vessels, to monitor forestry, fisheries, mining, construction, emergencies (including forest fires and losses), weather, etc
Fields: Creating ZMR (with an accuracy 5-10 m in height): creating and updating of plans and maps (up to 1:25000 scale); monitoring of natural disasters
(Floods, moving of the icebergs, etc.), monitoring of the growing ecological processes (distribution of oil spills, forests pests and diseases, etc.), agricultural, forestry monitoring (updating of the maps, control of land use, illegal logging), tracking ice and snow environment, infrastructure monitoring, monitoring of the ship's environment, etc.
Центр космического мониторинга Арктики
The
Radius of the review station«UNI SCAN-36», which was set in the NArFU is approximately 3 500
In the year of the center has accumulated extensive data (over 16 thousand images) in the Arkhangelsk Oblast and neighboring regions, including highly detailed images with a resolution of 0.7 m major cities in the region. In the center are trained at seminars "Methods and practice of remote sensing (RS)" More than 150 students. Ongoing provision of information for scientific research. Powered geo portal with constant filling space images for use in the educational process and projects. Together with the support of the department web site is developing an online catalog of satellite images to automate the ordering process images for internal use at the university (the estimated date of implementation - March 2012).
Наличие снимков в каталоге ЦКМА
|
Наименование спутника |
Кол-во |
|
AQUA |
619 |
|
TERRA |
632 |
|
EROS-B |
14 |
|
RADARSAT-1 |
2 908 |
|
RADARSAT-2 |
47 |
|
SPOT-4 |
7 408 |
|
SPOT-5 |
4 485 |
|
ИТОГО: |
16 113 |
Центр космического мониторинга Арктики
In accordance with the agreements on cooperation established with the Northern interregional cooperation by the Federal Service for Hydrometeorology and Environmental Monitoring (Northern UGMS), St. Petersburg Institute for Informatics and Automation of RAS (SPIIRAS), "NC PE," Foundation "Nansen Center", etc. Under a contract with one of the enterprises of the Federal space Agency - JSC "SPC" REKOD "- carried out the developmental work" Monitoring of the Northern Territories. "Negotiations are under way to integrate the university to create a single geographically distributed information system for remote sensing (RS ETRIS). Initiated a project with the Office of Automation of the Arkhangelsk region to create the Atlas of the Arkhangelsk region.
Pilot projects initiated by the following companies: Arkhangelsk Branch of Roslesozash-chita - to monitor drying of the forests and windfalls, Arkhangelsk Sea Commercial Port - Monitoring of ice conditions and emergencies. Ongoing mapping of forest areas and the impact of industrial facilities, monitoring of field development, assessment of damage caused by illegal logging, evaluation of the impact of oil on natural landscapes, monitoring fires.
Центр космического мониторинга Арктики
In line there are several other projects with MGTU named after N. Bauman. Bauman, Found "Nansen Center", Kola Science Centre RAS, Greenpeace Russia, the number of departments of the university. Negotiations with OJSC "NK" Rosneft "", OAO "Gazprom Space Systems", Arkhangelsk and Murmansk sea trade ports, the great port of St. Petersburg, JSC "Norilsk Nickel", "Naryanmarneftegaz" Roshydromet (SRC "Planeta", JSC "NII TP "), MES (National Emergency Management Center, Arkhangelsk CMC), FSUE" Atomflot "PG" Center for nature and Environment ", FGBU" National park "Russian Arctic", OJSC "Rostelecom" and other organizations.
In addition, the university is a member of the consortium created "Universites geoportals (UNIGEO)", which will develop a joint strategy development and implementation of innovative technologies and methods of remote sensing data and to organize the interaction of universities on the use and the development of the modern geo information technologies in education, science, industry and development management regions.
УНИГЕО

Also, the university established a small innovative company "navigation service the" Arctic "" Implemen f mobile objects. The co NASS / GPS, installation a
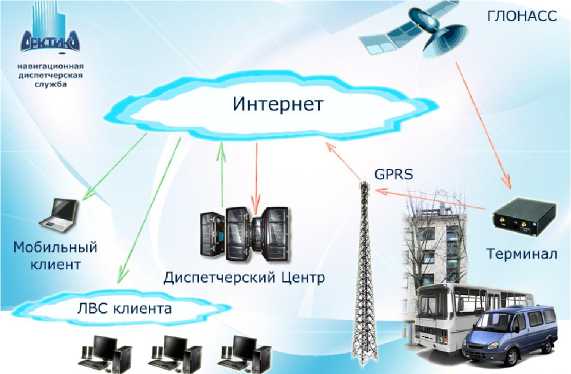
Компьютеры клиента ОСС Строения / Транспорт
Центр космического мониторинга Арктики
The participants at the roundtable suggested at the geoportal to designate the borders of the Arctic zone of Russia, from Archangelsk region, as well as articles and photographs relating to the Arctic.
Another part of the mysterious package in the Arctic is its territory, which should be especially protected. V.S. Kuznetsov, the deputy, the Director of the National Park "Russian Arctic," said the problems and current situation of these territories in the Arctic zone of Russia. Entrusted with the management of the park, "Russian Arctic." The main problem appears normative base, which in the present circumstances require revision and modification. The second problem is a global hit in the Arctic territory. Traditionally, a sea cruise, which is the most expensive way. And the air. Should be more than just economic regulation, as Russian law does not allow establishing a fee for entry to these areas in contrast to other countries in the Arctic zone. The center of the "Arctic partnership" was proposed to investigate the problem and the study of proposals for possi- ble solutions.
A.K. Portsel, Ph.D. in History, Associate Professor of Murmansk State Technical University has a long history of problems on the island of Spitsbergen. Areas such as Svalbard have military-

strategic and geopolitical importance, and only then - is the economic one. It was noted by the Council of the Ministers of the tzar Russia in the early twentieth century, when preparing for an international conference on the status of the archipelago. Concluded in the 1920 the agreement of Paris of the Svalbard archipelago passed under the sovereignty of Norway. But this is an agreement established the right of free economic activity in the Spitsbergen square (the archipelago and the adjacent waters of the ocean) and the neutral status of Spitsbergen. Norway is the part of NATO, and so we do not care whether saved demilitarized status of the archipelago. But the peculiarity of the situation lies in the fact that the only economic activity may ensure the presence of Russia in the Spitsbergen square and hence the possibility of effective enforcement of the neutral status of Spitsbergen.
In the twentieth century, the main economic activity in the archipelago was coal mining. Coal is mined in the mines of Spitsbergen, allowed to solve the fuel problem of the Kola Peninsula in the prewar and early postwar years. But after the collapse of the USSR Trust "Arktikugol" failed to preserve the old scale of production: now works only one of our three mines – is Barentsburg. The revival of the Russian coal mining in Svalbard in the Soviet scale is unlikely. It is important to keep it at least at current levels, because the main difficulty - where to sell the coal.
From the end of the twentieth century are increasingly deployed fishing in the waters of the archipelago. The agreement on the delimitation in the Barents Sea, signed in 2010, retains a 15-year effect of the Norwegian-Russian Fisheries Commission, which regulates fishing in Svalbard. But what will happen after the expiration of this period? Already, the Norwegian side is increasingly trying to prevent this kind of economic activity contracting parties, especially Russia. Detention of Russian ships in the Norwegian ryboohranoy these areas are not uncommon. To consolidate the Russian presence on Spitsbergen, the decision to build a fish processing plant. But this is not an easy task. Construct, of course, possible, but how realistic is it to provide work, and most importantly - sales of products?
Paris agreement left open the question of the exploitation of the shelf adjacent to Spitsbergen. The agreement on the delimitation in the Barents Sea (2010) says nothing about the special economic status of Spitsbergen square. The Norwegian side is trying to treat it as recognition of the shelf at the sole property of the archipelago of Norway. A production of hydrocarbons - is one of the main directions of the economic development in the Arctic in the nearest future.
The struggle for Svalbard - is an integral part of the unfolding struggle for "redistribution of the Arctic", which is aggravated in connection with the signing of the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea. Russia's accession to this instrument and the rejection of the principle of sectoral division of the polar domains have led to what is in the center of the Arctic Ocean have "no man's space." In 2006 the government adopted a Strategy for Norway's northern regions. In particular, it declares the goal to make Norway a leader of scientific investigations in the Arctic and a leading position in the world in the field of resource management of the North and its environment. Svalbard in this strategy plays a leading role.
The ruling circles in Norway is not the first decade of almost openly tried to oust from the zone of Svalbard of all foreign competitors. This is done under the guise of environmental protection and the protection of biological resources from predatory fishing. In the vast archipelago created protected areas, where almost impossible to conduct any business activity. Even archaeologists can conduct their work only under the strict control of the authorities on Svalbard.
But now to the archipelago aspire China, Germany, Poland and other countries. Through the participation in various activities, they are fixed on the islands and in coastal waters, where an active mining of biological resources, and in the future production of hydrocarbons is possible. Here, the interests of Russia and Norway, as major economic entities in the Spitsbergen square are the same: activation of the third competitor is hardly necessary, Oslo and Moscow.
The Treaty of Paris about Svalbard - is a unique document: it defines a unique status of the archipelago, which has no analogues. In fact, Norway is not the master of the archipelago, and the manager, who coordinates the activities of all participants in this contract. Many practical issues of economic, scientific and other activities on different interpretations of the Norwegians and the rest of the contract. But the accumulated historical experience shows that the Treaty of Paris, with all its faults, is so far a reliable basis on which it is possible to solve all arising from Spitsbergen square international disputes. So now put the question of revising the treaty would hardly be expedient for Russia: any such attempt will be actively used by Norway to secure its full sole rule over the archipelago2.
O.N. Shadrina, PhD in Philosophy, the Associate Professor, the Senior Researcher Center of the "Arctic Partnership", revealing the code of the Arctic, has focused on the problems of the human dimension in the Arctic, political and economic aspects of environmental conservation, climatic change impacts. "Human dimension" in the Arctic reflects the "double effect" on the nature of the Arctic in terms of politics and human activities in the region.
The first, to pay attention to the following policy considerations. 1) According to the monitoring of federal media at the end of 2011 the Ministry of Economic Development Ministry has sent to the Marine Board of the Government clarify the results of the baselines from which the breadth of the territorial sea, exclusive economic zone and continental shelf of Russia. Ministry of Economic Development proposes to use the method of straight baselines, which will push the limits of territorial waters, EEZ and continental shelf in the North Pole for a few

miles. Several new areas of the Arctic seas is proposed to include the historic waters. At the same time harmonize with the other Arctic countries do not need: the internal changes are consistent with international practice. 2) The strategic interest of Russia in the Arctic - the energy that is very "practical." When extending the boundaries of the total hydrocarbon resources of the continental shelf will exceed 100 billion of fuel. Russia has already carried out drilling in the vicinity of the Lomonosov Ridge to prove it. 3) To continue the militarization of the Arctic. Russian Defense Ministry announced the formation of the Arctic crews. Norway has just, in March 2012, conducted military exercises Golden Response (Cold Response), which was attended by about 16 thousand soldiers from 14 countries. The purpose was to rehearse maneuvers with NATO forces for high-intensity operations in winter conditions. During the exercise was lost Norwegian military transport aircraft Hercules C-130J. 4) The economic development of remote areas should be provided with security measures, so the MOE began to create a rescue infrastructure on the coast of the Northern Arctic Ocean, which is associated with the prospect of development of SMEs.
The activation of the external and internal political intentions in the Arctic region, in terms of different states, leading to increasing environmental problems. In this connection it should be noted that even the forecast of the further development of the Arctic climate. There is a high likelihood that in the years 2035-2040 the water of the Arctic basin will be ice-free for at least one month of the year. By the end of this century, this period may be increased to two - three months. Emerging environmental threats in the Arctic have a variety of consequences:
To change the position of indigenous peoples. It is possible to consider the expulsion of the peoples of the northern Canada (according to the Prime Minister of Canada, Anderson).
The Arctic has its own, a special ecosystem of which we know practically nothing. When laying new sea routes should be carefully considered set of questions (WWF). Particular importance is the irreversibility of the threat of oil spills in cold Arctic waters.
The remoteness of the region is extremely difficult to work search and rescue missions in the Arctic.
The peculiarity of climatic changes in the Arctic is that one of the most sensitive changes in the climate region of the world can have the opposite effect on global climate. The Arctic is an extremely difficult target for physical and mathematical modeling, prediction and construction of climatic scenarios. According to the observations of scientists, the signs of global warming visible everywhere in the Arctic. Already, there are visible changes that are increasingly attracting attention. "There is a darkening of the Arctic sea ice and snow-covered areas, usually with white. White snow and ice reflect solar radiation, but the darkening due to the melting Arctic in the summer it absorbs ... The air temperature over the Arctic territories as a whole is increased, and in such circumstances, the number of tundra vegetation to grow »(Arctic Report Card, 2006). Emerged over the Arctic in the winter - spring of 2010-2011, the ozone hole was the most "deep" for more than 20 years of observation and closer in size to the Antarctic ozone hole. Global warming has stopped for at least next thousand years even if a total ban on greenhouse emissions since 2100, and this will lead to melting of glaciers in western Antarctica to the year 3000. Members of the Russian-American expedition to the Eastern sector of the Arctic have discovered the new large fields of me- thane in the northern parts of the Laptev Sea and the Bering Sea. Enhanced seismic activity in the Arctic.
The negative effects of global warming are obvious: it's the offensive of the ocean, melting of glaciers, tsunamis, a violation of the ecosystem, burning and rotting forests, flooded the threat of the indigenous population, the ozone hole over the Arctic, the threat of oil spills, radiation, air migration, change of the magnetic poles of the earth, and so etc. But the most dangerous consequence of Russia's global warming is raising of the sea levels as a result of which will be flooded in the first place the city of St. Petersburg, the Yamal Peninsula. There are several climatic scenarios. In one of them a new peak of global glaciation will occur in 2055. In another, in 2055, our planet, "boil like a pot that is not removed in time from the fire." In any case, the disasters of this magnitude are accompanied by: epidemics, crop failures, mass migrations of peoples, the so-called "climate refugees.
Despite the recorded events, the Russian science and the political bomonde with optimistic view look at the consequences of global warming due to the possibility of extraction of energy and water resources, the opening of the Northern Sea Route and the new opportunities of cooperation with European and Asian countries. However, there is a very real danger of dilettantism and disorientation of the Russian leadership on climatic changes and prospects for development, taking into account natural risks caused by human activities, as well as not antropological factors. Reducing the risks and threats require specific action by the Russian state. See the necessity of the cooperation between the countries and regions of the Arctic zone to tackle global problems and reduce risks to human activity in the Arctic. Russia as Arctic Power, has become a leader in the formation of a favorable (excluding any risk from human impacts) style of interaction in the Arctic

Arctic solidarity. Even today, the International Mari time by the Organizationtime drafting the Polar
Code, mandatory for passenger and cargo vessels plying the Arctic (London,
NArFU named after M.V. Lomonosov in cooperation with other organizations, which are interested in the research and the development of the Arctic, should initialize the production of a single code, the
Arctic, including all areas of interaction between man and nature in the Arctic region to the global community, the Arctic as a "territory of dialogue," the space of human solidarity and tolerance.
Список литературы The Code of the Arctic regions
- Shadrina O. N. The Code of the Arctic. URL: http://narfu.ru/iuir/ arctic_ partnership/code_ arctic.php (date of access: 10.03.2012).


