The comparative analysis of experimental researches of the physical and physico-chemical indicators of the fulfilled and cleared oils received by selective clearing
Автор: Tagberlieva G.K., Adyrova G.M., Almagambetova M.Zh.
Журнал: Мировая наука @science-j
Рубрика: Основной раздел
Статья в выпуске: 2 (11), 2018 года.
Бесплатный доступ
As a result of theoretical analysis and experimental studies of the topical issue of waste oil purification, a new solution has been obtained, consisting in the development of a laboratory method and installation using an extraction component in laboratory conditions. Thus, the development of a selective purification method allows partial coagulation and sedimentation of contaminants contained in the oil, and It has also been experimentally confirmed that the use of centrifugation using the extracting component o leuma significantly improves the quality of cleaning.
Selective cleaning, motor oil, oleum, extractant, centrifugation
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/140289132
IDR: 140289132
Текст научной статьи The comparative analysis of experimental researches of the physical and physico-chemical indicators of the fulfilled and cleared oils received by selective clearing
Determine physico-chemical parameters of oils: kinematic viscosity (dynamic), the content of insoluble residue, water content, acid number, oil color was used on GOST methods.
As a result of experimental studies carried out in the laboratory on small quantities of oils, the optimal concentration of the injected extractive component and the temperature regime for the most intensive coagulation process and subsequent deposition of contaminants were determined.
As a result of the experiment it was determined that after introduction of oleum and intensive mixing of oil with it there was enlargement of particles which were removed by centrifugation [1].
Considering the data of the analysis of physical and chemical parameters of oils it is established that the content of insoluble sediment in the purification of oil according to the developed method is reduced by 3-4 times in the refined oil compared to the original, the acidity decreases by 2-3 times, the viscosity of the oil and the oil flash point during its purification changes slightly and is 3 – 5% of the level of the original contaminated oil.
Analyzing the color of the oil, it can be stated that during the purification of waste engine oils, the color score decreases from 8 to 6.
It is advisable to evaluate the suitability of the oil for reuse by acid number.
This approach allows us to estimate the life of the refined waste oil, given the acid number of fresh and purified oil.
For example, a batch of refined oil meets all the requirements for use in the engine, but its neutralizing properties are not close enough to the limit values. (0.9 mg/Koh/g). If this oil is mixed with fresh oil in the proportion of 50: 50, then as a result all its physical and chemical parameters will improve and it can be used repeatedly for a certain time [1].
Table 1 - Used physics-chemicals methods of analysis
|
Characteristics |
Method name |
Normative document |
|
|
1 |
Physical and chemical characteristics |
Determination of density by hydrometer |
ГОСТ 3900-85 |
|
2 |
Determination of dynamic viscosity and calculation of kinematic |
ГОСТ 33-2000 |
|
|
3 |
Determination of the freezing temperature |
ГОСТ 20287-91 |
|
|
4 |
Composition |
Determination of water content |
ГОСТ 2477-65 |
|
5 |
Determination of mechanical impurities content |
ГОСТ 10577-78 |
-
3.1 Analysis of values for determination of kinematic viscosity of waste and refined oils. The statement is made in accordance with GOST 33-2000.
-
3.2 Analysis of determination of the acid number of used and purified motor oils. The statement is made in accordance with GOST 5985-79. (fig.2).
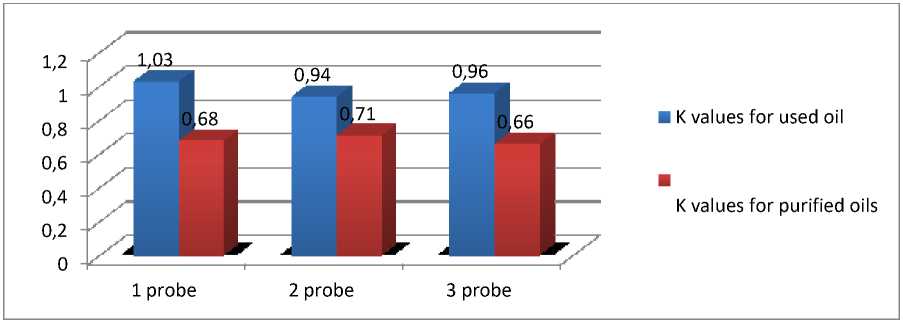
Figure 2-Comparison chart of the acid number (K) of used and refined
-
3.3 Determination of the optical density of refined engine oils.
(fig.1)
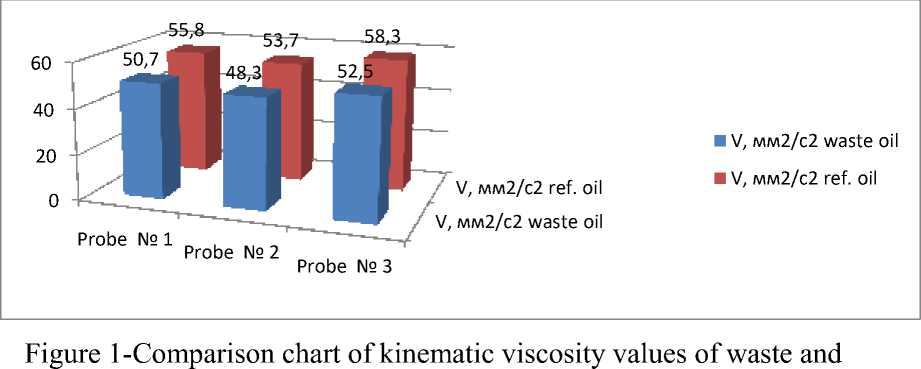
refined oils
oils
Determination of the optical density of used motor oils was carried out on a concentration photovoltaic colorimeter type КФК-2МП (fig. 3).
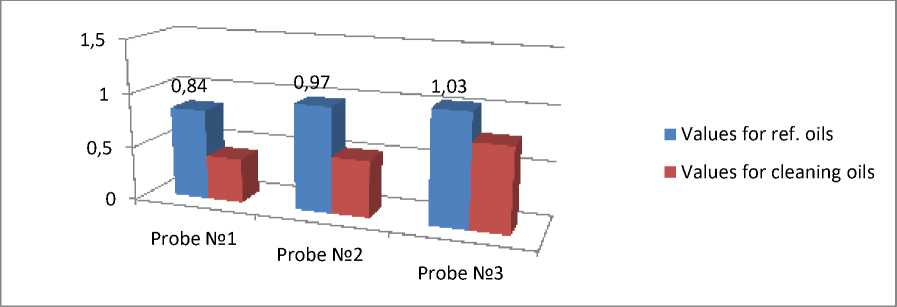
Figure 3-Comparison chart of the optical density of oils
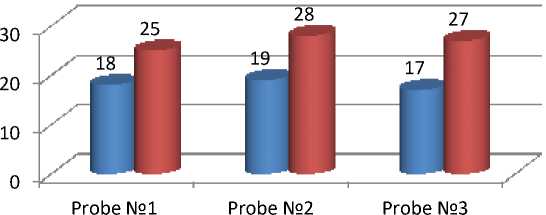
3.4 Analysis of determining the color of waste and refined engine oils on the colorimeter CNT. The statement is made in accordance with GOST 20284-
74 (fig.4)
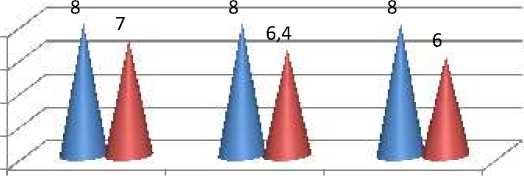
Probe №1
Probe №2
Probe №3
-
■ ЦНТ for waste oil
-
■ ЦНТ for ref. oil
-
3.5 The analysis of the definition of the freezing temperature of the exhaust and cleaned the motor oil. The statement is made in accordance with
GOST 20287-91 (fig.5).
Figure 4 - Comparison chart of the color values of used and refined oils
-
■ Values for weaste oil
-
■ Values for ref. oil
-
4. Brief analysis of the developed method of selective purification of waste oil and calculation of the material balance.
Figure 5 – Comparative chart of the values of the freezing temperature of the exhaust and refined oils
As the main extractive component selected oleum company scat, which is a Smoking liquid, at a concentration of SO2 20% by weight melting point 11,0°C, boiling point 166,5 °C. for purification were taken 3 samples of waste engine oils from three oil change stations.
The laboratory process of selective purification consists of the following stages: preparation of raw materials, heating (up to 45±5 ENC), introduction of extractant, intensive mixing in the extractor, centrifugation, delivery and storage of oil [2].
Equipment and reagents: extractor with mechanical mixing device; thermostat type it-2; drying Cabinet; laboratory autotransformer; cone-shaped funnel with a volume of 50-100 cm3; flask with a capacity of 250 cm3; filter paper; solvent oleum (table 5).
Then calculated the material balance of the process (table.6) [3].
Table 6 – Material balance for selective purification of waste oils with oleum
|
Source data |
Weight |
Raw Material, % |
Content, % |
|
Starting material: |
100 |
100 |
100 |
|
120 |
120 |
100 |
|
|
Raw Material (PR) |
220 |
220 |
|
|
The Solvent (PD) |
88 |
88 |
100 |
|
57 |
57 |
67,0 |
|
|
31 |
31 |
16,47 |
|
|
Just: |
132 |
132 |
100 |
|
43 |
43 |
25,9 |
|
|
89 |
136 |
53,94 |
|
|
Taken: |
220 |
220 |
- |
From this it follows that when cleaning the waste oil with oleum, the mass amount of the resulting refined product from the total mixture is 57 g per 120 g of the extractive component of oleum. The percentage is 32% by weight of raffinate and 68% of the extract.
Studies performed in the laboratory on small volumes of waste oils, is allowed to justify the possibility of applying exagerado component of oleum.
The oleum introduced into the oil is evenly distributed throughout the volume. As a result of mixing, coagulation of impurities dispersed in the waste oil occurs [3].
When cleaning the oil with the use of this agent, it is clarified due to the activity of oleum ions in relation to resins contained in the waste oil.
As a result of theoretical analysis and experimental studies of the actual problem – purification of waste oils, a new solution is obtained, which consists in the development of a laboratory method and installation using an extractive component in the laboratory. As a result of the development of a selective cleaning method, a pathway has been found for the possibility of partial coagulation and deposition of oil-containing contaminants. It has been experimentally confirmed that the application of centrifugation using an extractive component significantly improves the quality of cleaning. High quality of cleaning is achieved by intensive mixing with the extractor rotor from 200 to 300 rpm, the temperature of the cleaned oil is 45 \ ±50 º C, cleaning time T = 60-80 minutes. Physical and chemical methods of research of raw materials established the advantages of the purification process using oleum compared with conventional centrifugation. During the cleaning of the oil according to the proposed method, the content of insoluble precipitate decreases by 3-4 times, the color score decreases from 8 to 6 points.
Список литературы The comparative analysis of experimental researches of the physical and physico-chemical indicators of the fulfilled and cleared oils received by selective clearing
- Остриков В.В. Топливо, смазочные материалы и технические жидкости. - Ульяновск, 2009. - 575 с
- Большаков Г.Ф. Физико-химические основы прмененния топлив и масел. - Новосибирск: Наука, 1987. - 208 с.
- Годунова, Л.Н. Обоснование нормативов срока службы восстановленных моторных масел в тракторных двигателях [Текст]: дис. канд. техн.наук - Зер-ноград 2005. - 100 с


