The development of Yakutia in the context of modeling the development of the North of Russia
Автор: Prisyazhny M.Y.
Журнал: Arctic and North @arctic-and-north
Рубрика: Management, Economy
Статья в выпуске: 7, 2012 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Taking into account the specific development of the North on the basis of economic-geographical approach of nordifikation of economic activity and regional policy is based in the same space a variety of factors, environment and development tools. In Yakutia, realized long-term specific geopolitical goals of the state. The article describes the approaches to the selection of management strategies for the development of the northern territories of the country.
North, Yakutia, economic develop-ment, types of territories, regional policy, and the development model
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148320434
IDR: 148320434 | УДК: 911.3(571.56)
Текст научной статьи The development of Yakutia in the context of modeling the development of the North of Russia
The socio--‐economic development of Yakutia and of other northern regions of Russia is complicated by a number of the negative factors and conditions of the development. Given the nature of the development of the North on the basis of the economic--‐geographical approach nor--‐ dification economic activity and regional policy is based in the same space a variety of conditions, factors and tools development (Figure 1).
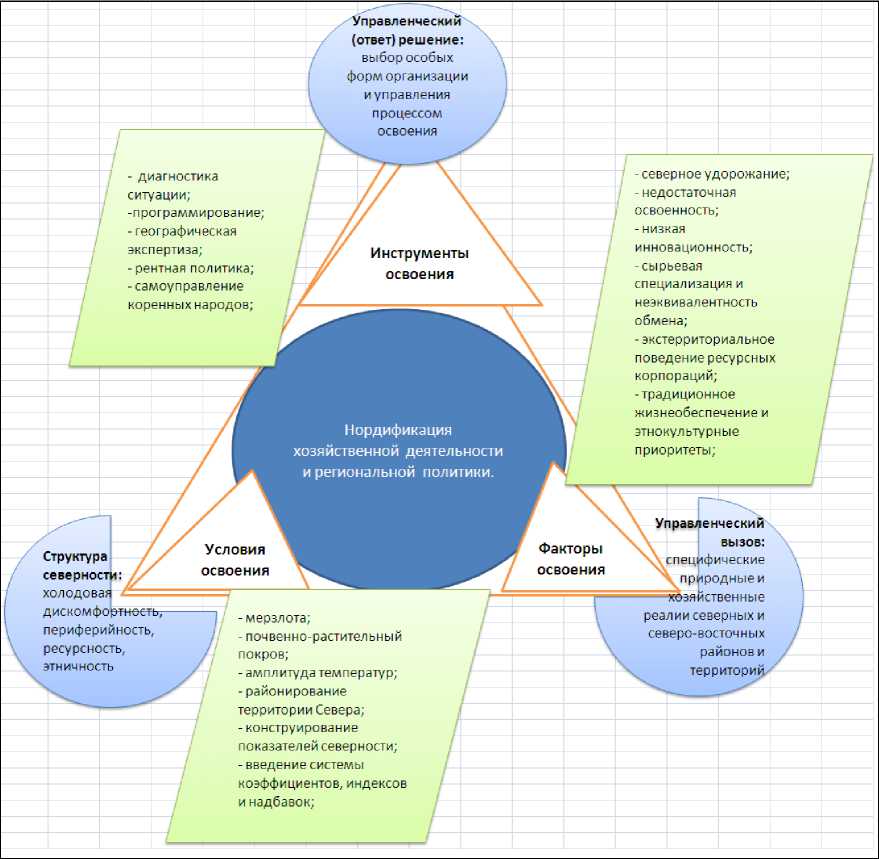
Picture 1. The specific of the development of th North (Economic –geographical approach)
Today we need a new general line of the North that can be called "From subsidies --‐ to self development." To understand the fundamental differences between the prevailing current of the Russian North and the new models both qualitatively and quantitatively a set of models for the North of Russia at present and in the next 50--‐60 years present their characteristics (Table 1).
Table 1
Features of existing and emerging development model of the Russian North
|
Industrial model |
The sustainable development |
|
1. North, as a colonial suburb resource type to the more southern parts of the country, was not formed as a con--‐ nected social and economic space for type and operated in the "North --‐ South --‐ North" |
1. Increasingly evolving in the "North --‐ South --‐ North" Arctic becomes an arena of the actions of the regional governments for the creation of transnational associa--‐ tions |
|
2.Russia is positioned as one of the superpowers or as insignificant part of the Great Eight Geoeconomic |
2. For Russia, it is important to consider the develop--‐ ment of the North and the general area in the Big Eight Arctic |
-
3. Predominant principle of the uniqueness of the natu--‐ ral resources of the North and his personification of a system of internal government regulation (the regional factor and northern allowances northern delivery, etc.)
-
3. Principle of the "North" is supplemented with the use of the principle of Circumpolar non--‐market goals of the northern policy
Industrial model
-
4. Costly mechanism of the state support, unequal ex--‐ change of financial and material resources between North and mainland
-
5. The centralization of the entire political, economic, business, social and cultural activities exclusively in the hands of the state and its authorized agencies
-
6. Indigenous peoples' rights in the traditional laws of Nature (the distribution of quotas, licenses, traditional craft, etc.)
-
7. Pre--‐emptive rights of indigenous peoples over other groups of resident population of the North in most areas of life
-
8. Planned or transition economy with a focus on mar--‐ ket--‐based mechanisms of production and non--‐ production areas, including statutory funding
-
9. Highly specialized employment of permanent and migrant populations in disjoint sectors of the economy, low involvement of indigenous people in the industrial activities
-
10. The state regulates the amount and nature of the use of natural resources
-
11. During the Cold War, the Arctic region looked con--‐ frontation, if not merit consideration as a separate re--‐ gion of the world
-
12. Use of the North and its resources with foreign capi--‐ tal is predominantly prohibitive
-
13. Development of the economy of northern regions mostly tied to availability of resources, providing oppor--‐ tunities for people to earn the main area of settlement "big money" and go to the "mainland"
-
14. Control of the Arctic based on a sectoral approach. Preferential involvement in the research and develop--‐ ment of the North of the small number of the world
-
15. Globalization is ever--‐increasing impact on the eco--‐ nomic processes in the Arctic and the North
-
4. It is important for Russia through positioning as the northern countries makro territories legitimately secure special treatment of the state in a single economic space of the world market by type of WTO
-
5. Decentralization, the shift of regional policy on the transfer of a significant part of the authority by the northern regions, which will be a modern manifestation of the "centralization" in the tradition of Russian gov--‐ ernance Siberia
-
6. The federal government passes the indigenous organ--‐ izations responsible for the distribution of acceptable ranges of resources and the introduction of appropriate regulation
-
7. Orderly equity modern legal practices of indigenous populations and deep--‐seated
-
8. Non--‐market nature northern policy goals with indi--‐ vidual personal "north" of Russia advanced experience of foreign "north"
-
9. Synthesis, the combination of seasonally ordered multizanyatosti permanent residents and seasonal or--‐ dered monozanyatosti temporary population
-
10. Public ownership of the resources is dominated, in some jurisdictions allow the privatization process with fixing majority of the state through regional and local authorities
-
11. Arctic is the region building. Simultaneously create governance structures at the national and sub--‐national levels
-
12. International project in the field of transport, ener--‐ gy, mining, education, science, etc.
-
13. Priority for the economic development is to raise the quality of life of the Northerners. The North as a "house" of the stable long--‐term permanent residence of the population based on the implementation of the principles of equal opportunities for people in both the North and other regions
-
14. Entry into the competition for a wide range of the Arctic states, including non--‐Arctic. Free access to the Arctic Ocean trade and research vessels of all countries
-
15. Promote the exchange of knowledge in the Arctic by strengthening international cooperation at the level of communities, municipalities and indigenous peoples
Territorial model of the sustainable development
In Yakutia (as in any other region of the country) are sold long--‐term specific geopolitical goals of the state. Geostrategic problem which is solved by means of exploration and development of the North--‐East of the country for nearly 400 years, is to provide military, political and economic influence of Russia in the Arctic Ocean and the Pacific, the control over the most important re--‐ serves of natural resources and benefit from the effective inclusion based on their use in the sys--‐ tem of international economic relations. It is the development of Yakutia as a key player in the North--‐East of the country can support and strengthen Russia's status as a world power (Figure 2).
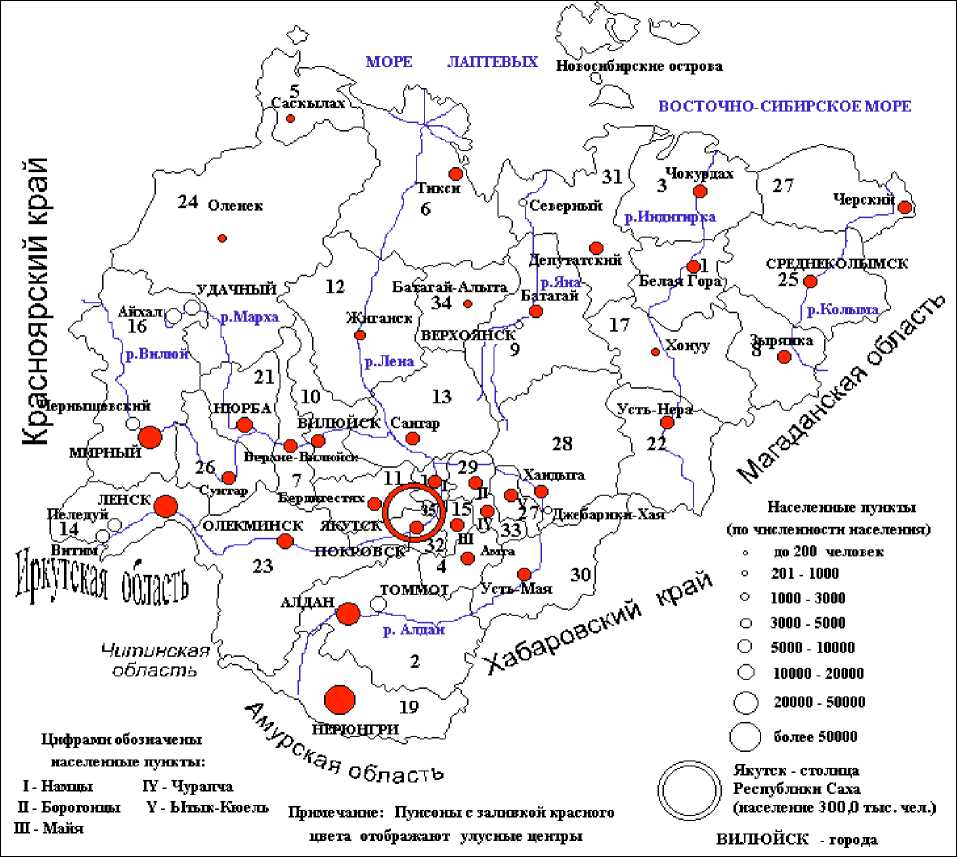
Picture 2. Ulsi (administrative regions) Republic Saha (Yakutia)
Ulus sequence number corresponds to the number on it placed in the schematic map, a list of ulus is presented in Table 2. Applied to one of the ways of Yakutia regulation is a structural shift, aimed at smoothing vertical hierarchy "republican government --‐ ulus power --‐ power naslega --‐ sep--‐ arate household" and a gradual transition to a more horizontal forms of partnership work and the public authorities, government and individual household. Modernization of the previously estab--‐ lished multi--‐level hierarchies in the management and direction of the republican economy may have been due to the formation of self--‐organized associations of cooperatives, miners, farmers, indigenous communities, national corporations, small businesses.
Table 2
Ulusi (Adminastrative regionsof the republic Saha Yakutia
|
1. Abiiskiy |
11.Gorniy |
20.Nijnekolimskiy |
29. Yst Aldanskiy |
|
2. Aldanskiy |
12. Jiganskiy |
21. Nurbinskiy |
30. Yst Maiskiy |
|
3. Allaihovskiy |
13. Kobiyaskiy |
22. Oimyakonskiy |
31. Yst Yanskiy |
|
4. Amginskiy |
14. Lenskiy |
23. Olekminskiy |
32. Hangalasskiy |
|
5. Anabarskiy |
15.Megino--‐kangalsskiy |
24. Olenekskiy |
33. Churapchinskiy |
|
6. Bulunskiy |
16. Mirniyskiy |
25.Srednekolimskiy |
34. Eveno--‐Bitantaiskiy |
9Verhoyanskiy 10. Viluyskiy |
17. Momskiy 18. Namskiy 19. City Nurengri |
26. Suntarskiy 27. Tattinskiy 28. Tomponskiy |
35. City Yakutsk |
Recognition of the growing importance of the regional economy for the country means the need to look at the outputs of innovation. Interests of the residents of Yakutia must necessarily be taken into account when forming the overall balance of the interests of participants in the devel--‐ opment and distribution of productive forces of Yakutia --‐ the federal government, the Far Eastern Federal District of the Republic, a major Russian and foreign companies, the local business com--‐ munity, civil society / public and local territorial communities .
Created in Yakutia production capacity, the available mineral resources, adapted to the conditions of the northern population, the experience of resource development and management in the new market conditions are the necessary prerequisites for economic and social progress of the country. Binding offers to realize the potential of the individual levels of the administrative re--‐ gion and a single scenario of the region would make an adequate choice for the conditions of management strategies.
Adminastrative organization of the territory
Administrative--‐territorial division performed for comfort and control area of the existing state power. Such a breakdown trying to take into account the history of the territorial cohesion of settlements, a unity of economic, convenient geographical proximity. The latter can be seen in the village Hani (in the south of Yakutia). Previously, this strip of land was the territory Olyokminsky ulus was, except for a few Evenki nomads, almost deserted. District authorities and other services reach these places in such exceptional cases, such as election, a serious illness of some nomad re--‐ quires calling a doctor from the center. The link was just a helicopter, and the high water could swim the river Olyokma. Now, some of these sites laid the Baikal--‐Amur Railway, built a railway sta--‐ tion Hani. The area has in correcting the economic situation in the country of the great prospects of the absorptive capacity of many mineral deposits, including mainly high--‐grade iron ore. There--‐ fore, the territory was transferred the Neryengeri area, where you can get up to Hani railway. Fi--‐ nally Neryungrinsky area since 1987 has to the west of its main array stretched latitudinally wedge territory.
We proceed from the principle of methodological review of the core area of contradiction: between the relatively stable areas and the natural environment is extremely dynamic economic activity of man. The natural environment as a natural landscape average (terrain, areas, swimming pools) and higher (zones and belts, mountains, plains) the level of dimensions to be persistent for thousands of years, and the economic activity is changing not only in the scale of decades, and sometimes even faster.
Resolution of the contradiction between the stability and dynamics of the territory is seen in the change of the administrative--‐territorial division (hereinafter --‐ ADT) as needed. It should be more than just touch the unit level ulus territory. Now existing uluses mainly formed intuitively. At ADT republic there is another line of contradictions. The specificity of the interaction of economic and administrative--‐territorial structure is in varying degrees of stability: the first structure is more dynamic, the latter --‐ more inertial.
Until the 1930s, all of Yakutia has been divided into seven districts: Bulunsky Vilyuisk, Verkhoyansk, Yakutia, Lena, Aldan and Kolyma. The backbone of the modern division was formed in 1930--‐1931. Then ADT at ulus reshapes seven times (excluding short--‐term consolidation area in the late 1950s) were organized later Verkhnevilyuisk, Kobyaysky, Verkhnekolymsk, Verkhoyansk, Ust--‐Jansky, Mirny, Eveno Bytantaysky--‐city areas and Neryungri. They were created by the transfer of territories adjacent ulus. So Kobyaysky ulus was formed in 1937 by land Namsky, Mountain, Vil--‐ yui ulus, later withdrew him half liquidated Sakkyryrskogo area on the right bank of the Lena River and in the basin of the Yana River. In this case there are no grounds for the geographical expan--‐ sion of the territory of the ulus, other than being a simple administrative consolidation, was not. As a result, with adjoining lowland pastoral areas annexed mountain, reindeer territory, from which no transport except aviation relations was not a long time, probably will not. As well the ar--‐ ea can be sent and Namsky ulus, with whom, at least, could be related to winter road through the valley Tumars. So something eternal and objective in the current ADT Yakutia at ulus not. Another thing --‐ naslezhny level. In education naslega reflected a legacy of the tribal population of Yakutia device.
Birth within a certain area first by blood and family ties were subject to elders of the clan, which in some circumstances exercised razbiratelskuyu, military, and other features that were to some extent desired in quarrels with Rodowicz, robbery of the other genera, etc. where there was no taxation, no major public works, such as, for example, irrigation in China, the large military--‐ political conflicts, needs a constant regulation.
Of course, in today's extreme mobility of the population base is largely lost. However, as the nature of land conflicts, naslezhnoe division still plays a role. At the same time, apparently, there is no need to touch this level of administrative division.
Nasleg as a unit of the grassroots civil division is only in Yakutia. Until recently, the country was dominated by the term "village council", now in government, called a Western--‐style "munici--‐ pality." Rarely in other parts of the country there are other names. The word "naslega" --‐ a corrup--‐ tion of the Yakut way Russian "B". In recent years a grassroots identification of territorial division of the concepts of "territorial community", "community", etc.
The currently, the country is divided into 34 regional divisions ulus level and one urban metropolitan area. These divisions may be called by any of either "heartland" or "district." "Ulus" --‐ is outdated Yakut may ancient Turkic word meaning a large genus. Until 1930, that is to split the republic into districts, these words refer to a territorial division largely on traditional tribal territo--‐ ries: Boturussky (boturutsy) Khorinsk (horintsy) Bolugursky (bolugurtsy), etc. The word was re--‐ turned to denote areas in the early 1990s. Now the area named them Moma, Neryungrinsky and Mirny. As long as the rest of the term "heartland." This is determined by the decision of the As--‐ sembly of Deputies of the territorial entities.
At 17 ulus, the encampments of Yakut population prevails, and in six encampments --‐ abso--‐ lutely, representing more than 90% of the total population. Champion in this respect is Churapcha --‐ 98.5%. The remaining share of descending Saha is Ust--‐Aldan, Tattinsky, Upper Viluiskaya, Moun--‐ tain, Suntarsky.
In the remaining 18 encampments, including the territory of the city of Yakutsk is dominat--‐ ed by Russian speakers. In Neryungri the figure is 98%, followed by Mirny, Aldan and Lena, which also more than 90% of the population is Russian--‐speaking.
The only national heartland --‐ Eveno--‐Bytantaysky located Bytantay River, a tributary of the Yana, where the indigenous population is 96.7%. The remaining uluses vary greatly in ethnic com--‐ position. There is no need to create special Yakut or Russian ulus, as these people are the largest in the country. And Evensky ulus held a special policy to revive the language, culture and tradition--‐ al economy. In any case, as it was intended, although the economic and geographical analysis of the consequences of such a step turns its low efficiency.
In recent years there have been significant changes in the number of population of the cri--‐ sis that engulfed the entire country and all areas of human existence. The total number of the population has decreased by about 15%. In all the major cities of the country, except for the capi--‐ tal, there was a significant population decline. Especially landslide was a reduction in population in the Ust--‐Yanskiy Ulus, where the population dropped by 80%. Significantly reduced the population in Oimyakon (63%), Bulun (40%), Verkhoyansk (by 48%) and Aldan (19%) districts. With the revival of the economy after a long crisis in population can once again begin to grow.
In coming years, the territory of the republic did not change, but there may be qualitative and quantitative changes in the republic. We can expect consolidation ulus that redkozaselennoy territory is quite real. But until we have what we have. Thus, of all the administrative units only Yakutsk has an area of up to 10 thousand square meters. km. Five ulus have an area 11--‐20 thou--‐ sand square meters. km, four --‐ 21--‐50 thousand square meters. km twelve --‐ 51--‐100 thousand square meters. km, eight --‐ 101--‐150 thousand square meters. km, three --‐ 151--‐200 thousand square meters. miles, two --‐ more than 200 thousand square meters. km, and this is an area of a large Eu--‐ ropean country. The administrative center is 10 cities, 11 towns and 14 villages.
Number of the administrative units is subject to constant change. Separate settlements are recognized as naslega or create their municipalities. Now the country self--‐accepted at ulus, but that does not mean that large towns, especially in the industrial ulus can not declare in his gov--‐ ernment. There are several large settlements, which are many times greater than the population some ulus. Among naslega has 31 national, three of which are nomadic. If they are in the Yakut and Russian--‐ulus, it may, for the national development, to announce their municipalities.
In the natural attitude may be based on the geological and geomorphological framework territory. Here the territory of Yakutia is divided into three parts: Western lowland, upland South and East Mountains. A further stage of division can be performed on large river basins: the differ--‐ ent parts of the Lena, Anabar, Olenka, Viljui, Olekma, Aldan, Yana, Indigirka and Kolyma. Other reason of the natural divisions – is the geographical landscape. In this respect the territory of Ya--‐ kutia is divided into tundra, northern and middle taiga zone and mountainous area with high--‐rise landscape differentiation. In the future these areas and mountainous region can be divided again, the river basin, but almost all of these rivers, except Viljui, Aldan and Olekma are straddling.
So, the most real, relevant sustainable environment, it is the division of the territory of the basins of major rivers [3]. Most of all, the trend expressed basin organizations in environmental policy. Methodological and methodical approaches allow to widely implement this method in the practice of physical and economic geography, as well as geopolitical and many other areas of re--‐ search. However, the current dynamic of the territory --‐ the socio--‐economic activities of the people
-
--‐ not the same river basin, and the river itself are disproportionate in terms of pools populate their population, economic specialization.
In the modern administrative--‐economic regionalization of Yakutia, in our view, we should look at the eclectic division, which is based on rather put a natural division. However, it should al--‐ so take into account the proportionality of the population and economy in order to ulus had about equal political and economic responsibility, social and natural load [4]. In light of the comments offered are six units of the integrated management of Yakutia (the names are out of the question --‐ it may be ulus, areas, districts, and anything else) (Figure 4).
-
1. The North, which includes Anabar ulus, most Olenek ulus, the flat part of Bulun and Zhi--‐ gansky ulus, lowland Ust--‐Yana ulus Allaihovsky, Nizhnekolymskiy and Srednekolymskiy Dis--‐ trict. There basins Anabar, Olga, Lena, Yana, Indigirka and Kolyma mainly in the lower reaches of each of them within the tundra and northern taiga zones. Here are engaged in fishing, hunting, herding, and mining. However, for some time (until the new technological solutions) should refrain from the accelerated development of the mining industry, envi--‐ ronmental hazards to the area. The small nation can create the basins average rivers their tribal administration.
-
2. The North--‐East Mountain, including The Upper, Abyysky, Moma, Oymyakon, Eveno--‐ Bytantaysky, Verkhoyansk ulus and mountainous part of Ust--‐Yana, Bulun, Zhigansk, Kobyayskogo, Tomponsky, Ust--‐Maya ulus. It develops mining, people are engaged in horse breeding, reindeer herding, hunting. The few people can have their administration, while not going into prirodopolzovatelskie sectoral conflicts.
-
3. Vilyuisk, which includes all uluses Vilyui pool, in this case from Olenek ulus are Markha riv--‐ er basins and the Upper Tyunga. Residing population is engaged in agriculture, cattle breeding, in the developing industry and energy.
-
4. Srednelensky – is the area along the Lena River from Lena to Namsky ulus, including min--‐ ing. Of the types of economic activity, the most important breeding, agriculture, manufac--‐ turing and energy.
-
5. The East, including beyond the river and the plain of the ulus Tomponsky and Ust--‐Maya ulus. Corresponds mainly Aldan River Basin in its middle and lower reaches. People are en--‐ gaged in cattle breeding, agriculture and processing of agricultural products.
-
6. The South, which includes the city Neryungri Aldan ulus, mountainous part of southern Olyokminsky district. Had developed a diverse industry, hunting, herding. The few people
in the area of residence exercise governmental power through its administration, but un--‐ der the control of the subjects of industrial and transport of natural resources.
This division allows for the spread of the mountains and plains, landscapes, watersheds, and, in some ways, a modern specialty services. As in the territory, and the number of people (maybe with the exception of Srednelenskogo and Southern regions), they are quite proportion--‐ ate. Of course, the area is huge, but in terms of modern communications is not a major problem for the management and organization of access to a number of social functions. Such restructuring is intended as an ADT optimization of the socio--‐economic and political governance, will keep the gradual process of the land development.
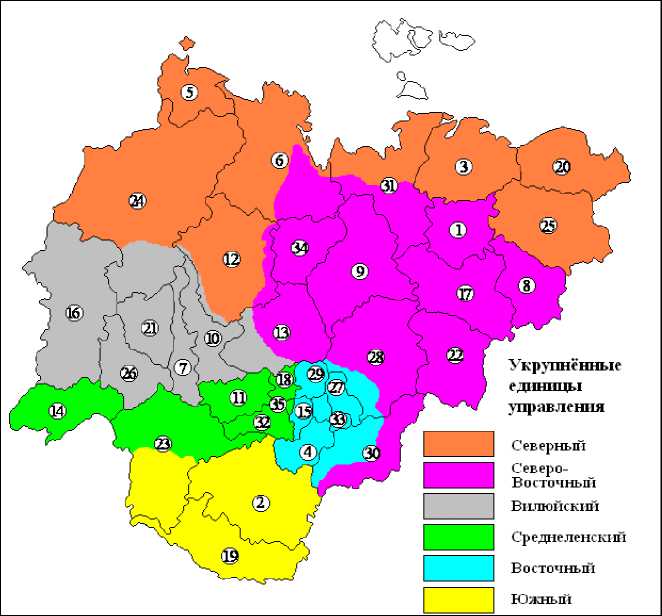
Picture 4. An example of the marking of onsolidated units of Yakutiya
* * *
Globalization is increasingly expanding impact on the course of the economic and social processes in the country. Further development of the territory of Yakutia is defined by a growing focus on the northern areas as the resource and biosphere reserve. Due to the challenges of the globalization, Russia needs to reform the entire system of the organization of life in the North. We must shift the focus of regional policy on the transfer of a significant part of the authority by the northern regions. The multiplicity of scenarios considered and typologies --‐ base for Arctic re--‐ gionostroitelstva regional, intraregional and local levels, is not contrary to previously stressed nor--‐ difikatsii aspects of the business and the regional policy.
The territory of the North of Russia is of the great interest to the economic and geograph--‐ ical analysis of the interrelated issues of the territory development encourages scientists to the further research [5]. Both in the methodological and practical terms, this involves the solution of problems, not only of the region, but it is important from the standpoint of the development of principles and measures of regional policy for the northern, eastern and the north--‐eastern regions of Russia.
Список литературы The development of Yakutia in the context of modeling the development of the North of Russia
- Prisyajnii M. Y. Problems of improving the forms of the development of the northern regions in the transition period and in the future // Regional problems of economic transformation. 2010. Number 3. Pp. 4246.
- Prisyajnii M. Y. The territorial organization of the economy Yakutia // Spatial Economics. 2011. Number 2. Pp. 3353.
- Korytnyi L.V. The Basin concept in the wildlife management. Irkutsk: Institute of Geography of the Russian Academy of Sciences, 2001. 163 p.
- Maksimov G.N. Juror M. Yu geography, history and philosophy of selfsustaining development of Yakutia // Geographical bases of Yakutia in the brief descriptions uluses naslega and populated areas of the country. Yakutsk Sahapoligrafizdat, 2003. Pp. 1926.
- Lukin Y.F. The great redistribution of the Arctic. Arkhangelsk: Northern (Arctic) Federal University, 2010. 400 p .


