The effect of plant defense elicitors on common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) growth and yield in absence or presence of spider mite (Tetranychus urticae Koch) infestation
Автор: Farouk S, Osman M.A.
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.7, 2011 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Background The common bean plants "Phaseolus vulgaris L." is frequently attacked by the two spotted spider mite (TSSM) Tetranychus urticae, causing a substantial decrease in bean plant growth and yield as well as leaflet structure. Therefore, for commercial bean cultivation in the field controlling TSSM infection is necessary. Results Foliar application of salicylic acid (SA) or methyl jasmonate (MeJA) on common bean plants before or after two spotted spider mite infestation proved to be effective in reducing infestations. In most concentrations these elicitors significantly improved common bean plant growth i.e. had a positive effect on plant height, number of branches, shoot dry weight and leaf area per plant and bean yield. SA at 100 mg/l had the strongest positive effect. Moreover, application of elicitors significantly altered leaflet anatomical characters i.e. increased thickness of leaflet blade, thickness of palisade and spongy parenchyma as well as thickness of midrib region of the leaflet and changed the dimension of vascular bundles. Alternatively, TSSM infestation had the opposite effect on these leaflet anatomical characters. Conclusion We conclude that SA or MeJA could be used for controlling TSSM infestation, to improve plant growth and to improve bean yield in the field.
Salicylic, methyl jasmonate, red mites, bean, leaf anatomy, yield
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14323538
IDR: 14323538
Текст научной статьи The effect of plant defense elicitors on common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) growth and yield in absence or presence of spider mite (Tetranychus urticae Koch) infestation
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
The effect of plant defense elicitors on common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) growth and yield in absence or presence of spider mite (Tetranychus urticae Koch) infestation
Farouk S.1* Osman M.A.2
-
1 Agric. Botany Department, Faulty of Agriculture, Mansoura University, Mansoura, Egypt
-
2 Agric. Zoology Department, Faulty of Agriculture, Mansoura University, Mansoura, Egypt
-
1 E-mail: gadalla@mans.edu.eg
-
2 E-mail: mesoma20@mans.edu.eg
Received April 12, 2011
Background
The common bean plants " Phaseolus vulgaris L . " is frequently attacked by the two spotted spider mite (TSSM) Tetranychus urticae , causing a substantial decrease in bean plant growth and yield as well as leaflet structure. Therefore, for commercial bean cultivation in the field controlling TSSM infection is necessary.
Results
Foliar application of salicylic acid (SA) or methyl jasmonate (MeJA) on common bean plants before or after two spotted spider mite infestation proved to be effective in reducing infestations. In most concentrations these elicitors significantly improved common bean plant growth i.e. had a positive effect on plant height, number of branches, shoot dry weight and leaf area per plant and bean yield. SA at 100 mg/l had the strongest positive effect. Moreover, application of elicitors significantly altered leaflet anatomical characters i.e. increased thickness of leaflet blade, thickness of palisade and spongy parenchyma as well as thickness of midrib region of the leaflet and changed the dimension of vascular bundles. Alternatively, TSSM infestation had the opposite effect on these leaflet anatomical characters.
Conclusion
Common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) is one of the most popular vegetable crops and hence a fundamental source of proteins for human consumption. For example, in Egypt, common bean export reached about 24704 tones in 2006 (FAO, 2009). The two spotted spider mite (TSSM),
Tetranychus urticae Koch (Acari: Tetranychidae) is considered a major pests on different agricultural crops including bean plants. Globally, around 1,200 species of spider mites are known (Zhang, 2003), but TSSM is the most polyphagous of all and has been reported over150 host plants of economic value (Zhang, 2003; Wilkerson et al., 2005). TSSM feeds by puncturing cells with its stylets and draining the contents, thereby producing a characteristics yellow specking of the leaf surface. This chlorotic damage reduces the plant's ability to build carbohydrates via photosynthesis which consequently results in reduction of the total yield of vegetable crops. Moreover, following TSSM infestation secondary infestation by pathogens often cause substantial additional damage while, finally, it has been reported that TSSM outbreaks cause occupational allergic disease in greenhouse workers (Jee et al., 2000).
A major obstacle in controlling TSSM is the fact that it rapidly evolves resistance to pesticides (Geoghiou, 1990). In horticulture, as in Egypt, the TSSM has been a priority pest. Greenhouse pest management of TSSM is still largely based on chemical control since biological control has limited efficacy against higher mite population densities. Taken together, TSSM control still a matter of urgency.
During the last few decades, the need for sustainable vegetable production has increased to minimize the damage to environment and health as a consequence of the use of acaricides. Moreover, pesticides may also interfere with biological control since natural enemies often are similarly sensitive to them as their herbivorous prey, while getting exposed to these products directly or indirectly after ingesting pesticide-contaminated prey (Picone and Tassel, 2002). Thus, it is important to develop pest control methods that are better compatible with biological control, like using agents that elicit at low concentrations natural inducible plant defenses, from heron referred to as 'elicitors' (Bi et al., 1997). Such elicitors often are plant hormones or synthetic analogs. Ozawa et al. (2000) reported that spider mite feeding on lima bean plants elevated the expression of acidic and basic pathogenesis-related genes which could also be induced by the salicylic acid derivative methyl salicylate (MeSA) and Jasmonic acid (JA) suggesting that the SA- and JA-related signaling pathway are induced by spider mite feeding. In addition they found that both pathways are involved in the regulation of TSSM-induced Lima been volatiles that are attractive to the carnivorous natural enemies’ i.e. predatory mites, of spider mite.
An elicitor can be any naturally occurring plant compound as well as synthetic substance that initiates induced plant defense responses in the tissue it is applied a fashion comparable to natural induction by herbivores or pathogens. Hence elicitors can be used to 'mimic' natural induction without causing (mechanical) damage while increasing the plant's resistance to real herbivores or pathogens. Before the discovery of chemical elicitors, induced resistance was not a practical tool for use in agriculture because pre-inducing plants with biotic elicitors (eg actual herbivores) to protect against future, possibly more harmful attackers was too complicated to be feasible (Karban et al., 1997). However, to use induced plant defense responses as an effective tool in pest management, it is necessary to carefully evaluate their effects on plant performance and yield in a horticultural and/or agricultural setting.
Jasmonic acid (JA) and Salicylic acid (SA) are two endogenous signaling molecules implicated in regulation of plant resistance to herbivores and pathogens. JA is found in many plant species and is involved in regulating diverse plant functions, not only herbivore and pathogen resistance but also e.g. senescence (Creelman and Mullet, 1997). JA can be used to elicit plant defense. In tomato, application of JA results in induction of proteinase inhibitors and polyphenol oxidase and in a decrease in the preference and abundance of many common herbivores in the field (Thaler et al., 1996, 1999). Induction of JA-related responses is often obtained via application of its methyl ester methyl jasmonate (MeJA).
Salicylic acid (SA) (o-hydroxybenzoic acid), is a plant phenolic, is widely distributed throughout the plant kingdom. It is a hormone-like substance, which plays an important role in the regulation many aspects of plant growth and development (Raskin, 1992). However, it is especially famous for its ability to induce systemic acquired resistance (SAR) in plants (Ryals et al, 1996) i.e. resistance in induced but also uninduced distal leaves of the same plant.
We investigated the effectiveness of the elicitors MeJA or SA for controlling TSSM infestation under field condition and also tested their effects on common bean growth and yield as well as leaflet structure. We conclude that some, but not all, concentrations of either compound had positive effects on plant growth and yield in absence or presence of TSSM infestation and hence could find roles to play in integrated pest management on beans.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Two field experiments were conducted in Faculty of Agriculture, Mansoura University in two successive seasons 2006/2007 to study the impact of MeJA and SA on TSSM infestation on common bean plants, and on plant growth, yield and leaflet structure.
Seeds of common bean cv. Bronco were sown on March 12 and 9 in the two consecutive seasons respectively. Seeds were sown in hills 10 cm apart on one side of ridges 3 m long and 60cm width. All agricultural practices were carried out according to the recommendation of Ministry of Agricultures, Egypt. The plants were divided into four treatment groups within a complete randomized block design consisting of four replicates per treatment. Treatment one consisted of infestation with 50 adult females of T. urticae per plant dispersed over the two trifoliate leaves of 15 days-old plants. The second group was infested the same way as treatment one but then sprayed with one of the following solutions; 50, 100 mg/l SA, and 5x10 -5 , 10 -5 M MeJA, two weeks after the infestation (35, 40 and 45 DFS). Spraying was conducted by first spraying the plants with elicitor solution until dripping after adding 1% tween 20 as a wetting agent. Spraying was repeated i.e. the first time 21 days post infestation (DPI), the second time 26 DPI and the third 31 DPI. The third group was sprayed the same way as the second treatment group and was then infested with mites after the third spray. Plants were covered with mite-proof mesh bag. The fourth group represented as control plants (Uninfested plants). The densities of all stages of TSSM were monitored each every 10 days starting when plants were 50 days old. At each sampling date, 25 leaflets were randomly selected from each of the treatments and counting was conducted using a stereobinocular microscope.
At full blooming stage (70 DFS) a random sample of 5 plants from each experimental plot was taken for determining morphological characters, photosynthetic pigments contents of the third upper leaves. Chlorophyll was extracted by methanol after adding traces of sodium carbonate for 24 hours at room temperature. Chlorophyll concentration was determined spectrophotometrically according to Lichtenthaler and Wellburn (1985).
At the stage green pods could be harvested (85 DFS) the following data were recorded; number of green pods per plant, green pod yield per plant as well as the fruit composition with respect to ascorbic acid, total protein, total carbohydrates, acidity and total soluble solid. In short, total carbohydrates and the ascorbic acid as well as total acidity and total soluble solid of fruit were estimated using the anthrone method and 2.6-Dichlorophenol indophenole as described by Sadasivam and Manickam (1996) and AOAC (1980) respectively. Protein was extracted from the fruit and estimated by the method of Bradford (1976). For potassium and phosphorus determination, dry common bean pods were digested with HClO3/H2SO4 until a sample has become clear cooled and made up to 50 ml using deionized water. Potassium was determined by flame photometer (Kalra, 1998), and phosphorous using ammonium molybdate and ascorbic acid (Cooper, 1977)
Leaflet structure: Small pieces from the midrib region of the 3 rd upper leaflet (second season) were taken when plants were 70 days old. The samples were fixed in formalin aceto alcohol for 48 h, then dehydrated via n-butanole series and embedded in paraffin wax (52-54 o C melting points). Sections were prepared using a rotary microtome at 15-17 µm thickness and stained with safranin/light green and finally mounted in Canada balsam (Johanson, 1940). Selected sections were examined using microscope to determining the anatomical changes in leaves
The data was evaluated using One-way ANOVA to compare the effectiveness of elicitors on the population of TSSM, and common bean growth as well as yield and its quality. Means were compared at P=0.05 to separate means (Norman and Streiner,
2003) using MSTAT-C v.1.2 software.
RESULTS
TSSM population per leaflet days:
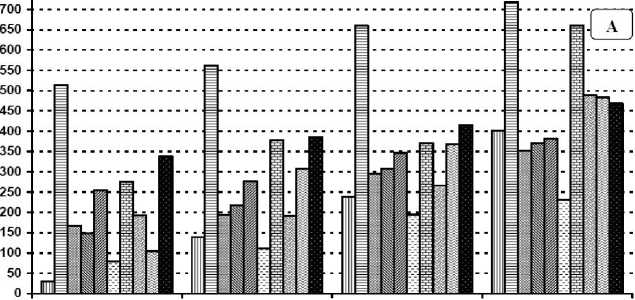
Figures (1 and 2) show that the mean number of eggs, nymph, larvae and adult of TSSM per one square inch of leaf surface in both seasons at 50, 60, 70 and 80 days of age. The mean number of eggs, nymph, larvae and adult of TSSM ranged between 145.66 to 817.00; 35.66 to 499.00; 39.66 to 390.00 and 30.66 to 718.33 per one square inch respectively. The data represented in the same figures revealed that after artificial infestation number of all TSSM stages increased significantly at 50, 60, 70 and 80 days of plant age compared to natural the infestation. In contrast, treatment with exogenous application of SA or MeJA at all tests concentration either before or after artificial infestation resulted in significant lower number of eggs, nymphs, larvae or adult TSSM compared to the artificial infestation. Notably in most cases application of 100 mg/l SA after artificial infestation significantly decreased the number of eggs, nymphs, larvae or adults compared to the same treatment on the naturally infested plants.
The highest rate of increase of T. urticae adults was 14.36 as observed after artificial infestation while the lowest rate of increase was 4.62 and was observed after application of 100 mg/l salicylic acid to artificially or naturally infested plants. The rates of increase after application of MeJA irrespective of the concentration or of 50 mg/l SA were 7.42, 7.04, and 7.64 respectively. However, when these same elicitor concentrations had been applied before the artificial infestation the rates of increase were 9.77, 13.2, 9.6 respectively and 9.39 after 100 mg/l salicylic acid
Growth Characteristics:
TSSM infestation caused chlorotic lesions at feeding sites and bronze-discoloration of infested leaves. Moreover, females TSSM produce webbing on the infested leaflet surface in which eggs are deposited. In these webs also dust aggregates hence affecting respiration and photosynthesis.
Plants infested with TSSM were significantly smaller, had significantly fewer branches and fewer leaves that were significantly smaller while shoot fresh and dry weight was significantly lower compared to uninfested plants (Table 1). In contrast, exogenous application of SA or MeJA prior to infestation had the exact opposite effect resulting in plants that were significantly bigger and heavier than the untreated infested plants but also than the untreated uninfested control plants. Here application of elicitors before infestation resulted in bigger plants than application after infestation with TSSM. SA at 100 mg/l was the most effective treatment for increasing plant growth and had the strongest effect when applied before infestation (Table 1).
Photosynthetic pigment:
Chlorosis is a typical symptom of plants infested with TSSM and may result from loss in chlorophyll due to mite feeding in combination with necrosislike cell death. Accordingly we observed a significant reduction in chlorophyll a, b, and total chlorophyll content as well as total carotenoids in the artificially infested common bean leaves compared to clean healthy leaves (figure, 4a). in contrast, these same pigments had increased significantly after exogenous application of SA or MeJA, either before or after infestation compared to infested or healthy plants with the strongest effect obtained by 100 mg/l SA (Figure 4a).
Finally the Chla:b ratio increased significantly by TSSM infestation but decreased significantly when also SA or MeJA had been applied as compared to healthy untreated control plants while application of SA at 100 mg/l prior to the infestation had the strongest effect.
Leaflet structure:
The leaves of the bean plant as shown in figure (5) are dorsiventral, that is, have a palisade parenchyma localized on the upper surface of the blade (adaxile) and a spongy parenchyma on the lower surface (abaxial). The palisade parenchyma is made up of elongated cells, densely packed and arranged perpendicularly to the epidermis. The spongy parenchyma cells show different forms and constitute the major part of the mesophyll cells arranged in an irregular fashion, with a smaller number of chloroplasts compared to the palisade cells, as well as large intercellular spaces
Application of SA or MeJA at all concentrations caused an increase in the thickness of midrib region of common bean leaflet with the strongest effect of SA at 100 mg/l (Table 2 and Figure 5). This increase is coincided with the increase in length and width of the main vascular bundle (Table 3). Application of the higher MeJA concentration (10 -5 M) decreased the width of vascular bundle specially when applied after infestation, meanwhile when used before infestation it gave the same width as healthy plants.
Application of SA or MeJA at all concentrations increased the thickness of leaflet blade in comparison to healthy or infested plants. This coincided with an increase in the thickness of the layers of palisade- and spongy-parenchyma as well as that of the upper and lower epidermis. In contrast, the higher concentration MeJA when applied after infestation caused the leaflet blade to become thinner. In most cases SA at 100 mg/l resulted in the stongest increase in leaflet blade thickness compared to natural or artificial infestation. Finally, leaflets infested with TSSM had thinner leaflet blades and a thinner main vascular bundle.
Yield and fruit quality
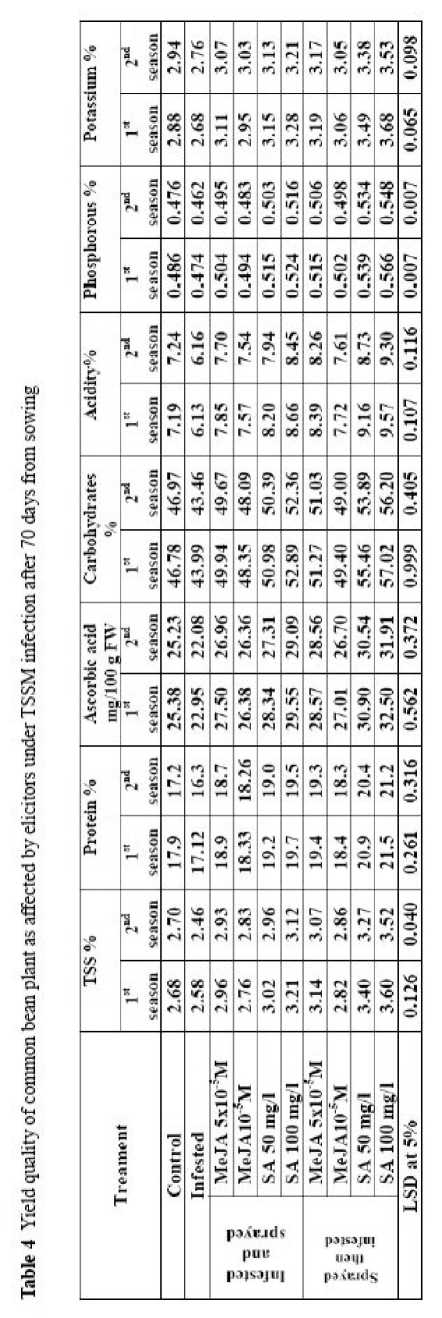
The bean yield and its components i.e. pod number per plant, pod yield/plant and pod length) as well as yield quality (expressed as total protein, ascorbic acid, total carbohydrates contents and the total percentage of soluble solid, total acidity percentage, phosphorous percentage and potassium percentage) was significantly lower after artificial TSSM infestation compared to unifested untreated controls. In contrast, application of SA or MeJA, especially 100 mg/l SA significantly increased yield and its components as well as yield quality compared to infested plants. The highest yield and good quality was obtained after application of elicitors especially after 100 mg/l SA when applied before infestation which increased pod number per plant, pod yield per plant, pod length, TSS%, protein, and ascorbic acid, carbohydrates, total acidity percentage, phosphorous percentage and potassium percentage compared to natural or artificial infestations (Table 4).
850 -
800 -
750 -
700 -
□ TSSM+MeJA 5x10-5 M
□ TSSM+SA100 mg/l QSA50 mg/l+TSSM
□ Artifical infection OTSSM+SA 50 mg/l □ MeJA 5x10-5+TSSM
□ control
QTSSM+MeJA 10-5M 0MeJA1O-5+TSSM ■ SA 100 mg/l+TSSM
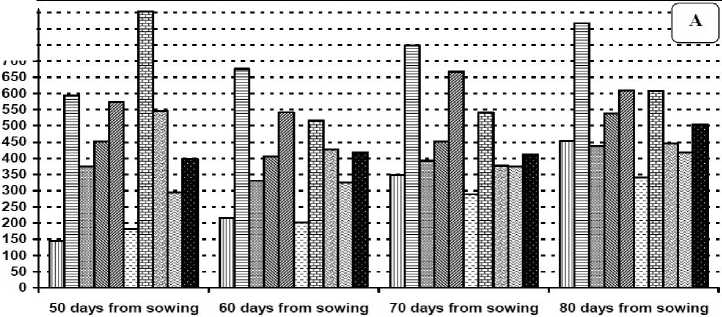
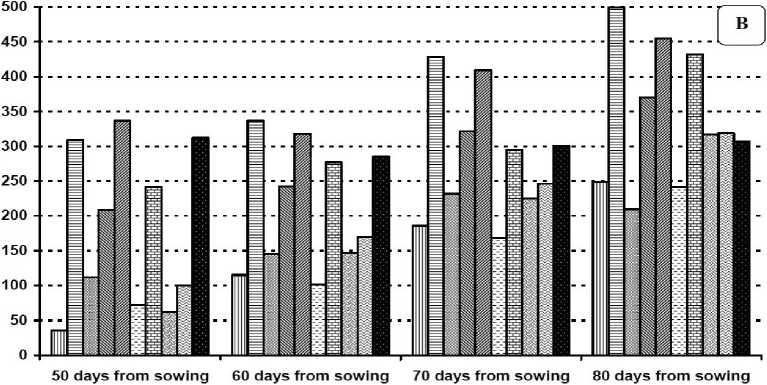
Figure 1 Average number of T. urticae eggs (A), nymph (B) per cm 2 on plants of 50, 60, 70 and 80 days of age respectively after elicitor treatments or artificial infestation in the second season
□ control В Artifical infection □ TSSM+MeJA5x10-5M OTSSM+MeJA 10-5M
0TSSM+SA5O mg/l 0TSSM+SA 100 mg/l 0 MeJA 5x10-5M+TSSM 0MeJA 10-5M+TSSM
0 SASO mg/l+TSSM ■ SA 100 mg/l+TSSM
50 days from sowing 60 days from sowing 70 days from sowing 80 days from sowing
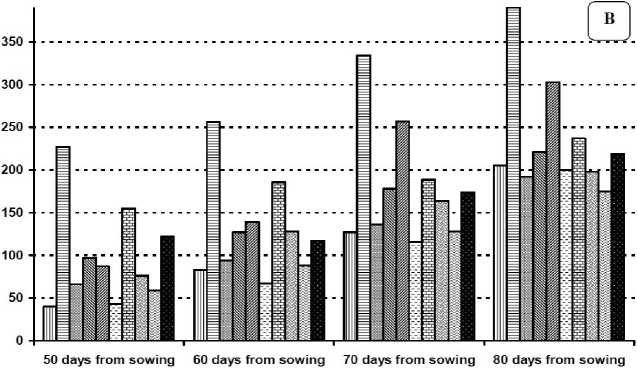
Figure 2 Average number of T. urticae adult (A), larvae (B) per cm 2 on plants of 50, 60, 70 and 80 days of age respectively after elicitor treatment or artificial infestation in the aecond season.
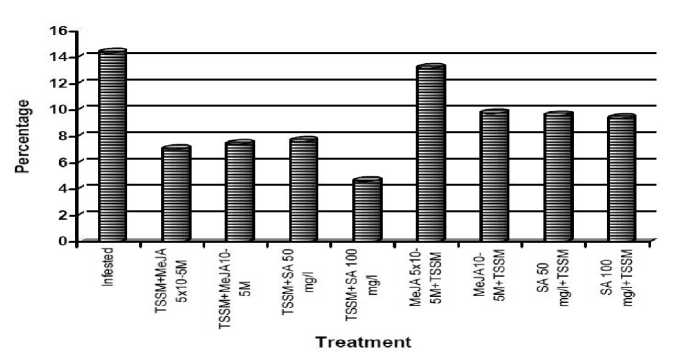
Figure 3 The total increase in TSSM adults on plants after treatment with exogenous SA or MeJA in two concentrations.
content mg/g FW content m
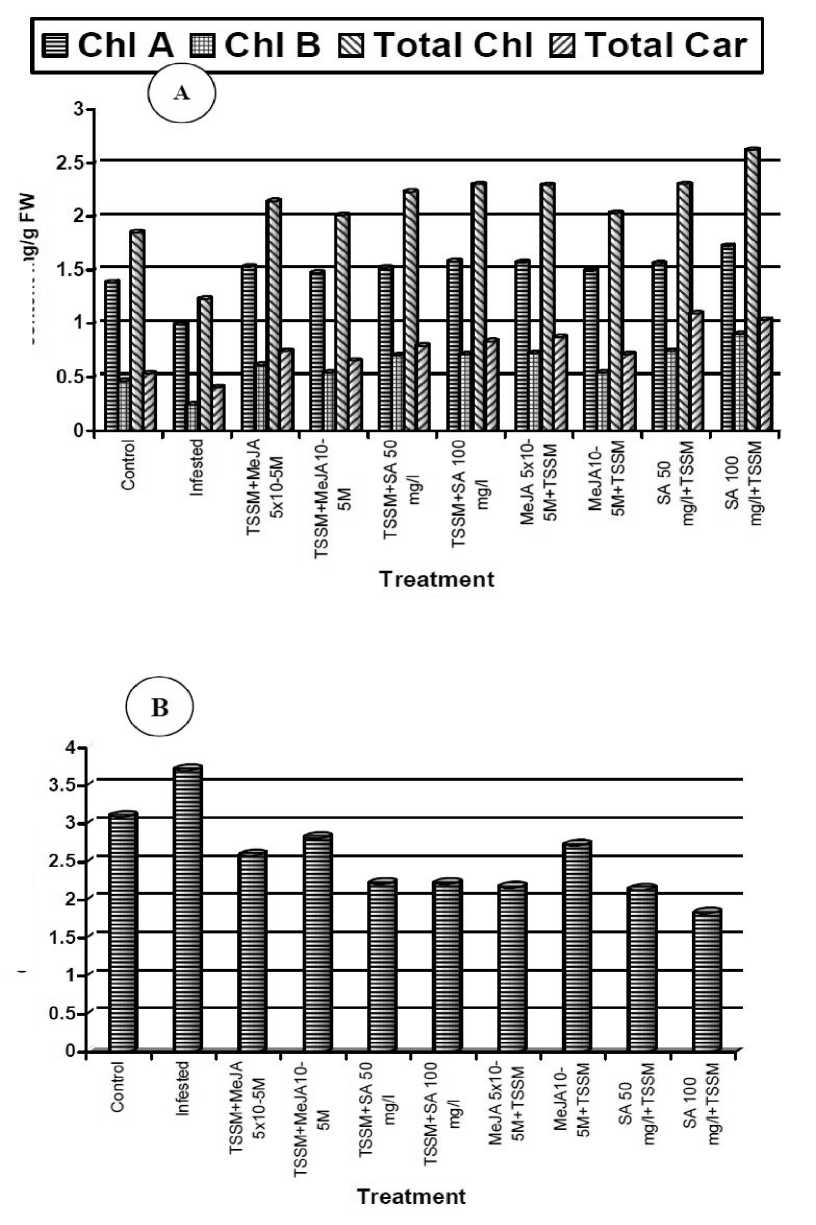
Figure 4 Photosynthetic pigments content (A) and chl a/b ratio (B) of 70 days old common bean leaves with or without T. urticae infection and with or without SA or MeJA treatment during second season
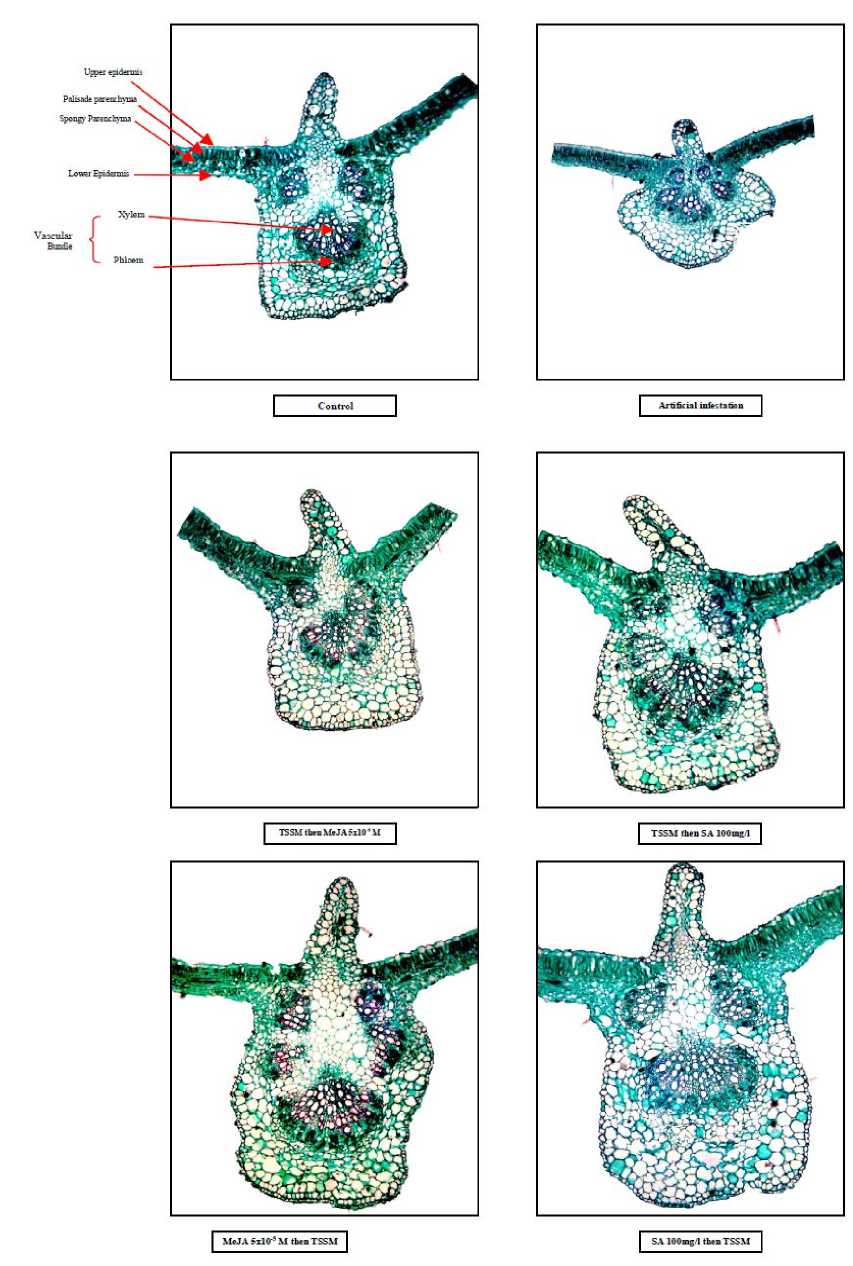
Figure 5 Common bean leaflet internal structure as affected by elicitors under T. urticae infection after 70 days from sowing during second season
Table 1 Growth characteristics of 70-days old common bean plants infested with TSSM and treated with or without SA or MeJA
|
L* <н Я Я ti ^ ^ i-l |
я ^ 2 |
о ri 3 |
oo 00 ri |
ri Oh XD |
z If |
to xg to |
c о ri |
у Ф о |
\o to to |
-r ■o oc |
DO |
g. Ct ^ |
|
|
я _ о ^" я % |
at F* tT |
-H |
■^ SO |
if, о If! |
00 to |
Oh* to |
if, at Z rl |
ri 2 |
oc о ОС |
i—l О ч\ 00 00 |
ГJ |
||
|
c « |
я •c - 5 |
P ri |
^ |
о r<, |
5 |
4. Ot tn |
о «*) |
т* ОС |
® ri |
m о |
|||
|
'— я |
□o ■O ri |
ф ri |
v4 ’T |
at ri |
1T |
o, —1 I" |
-O —1 *Tj |
in |
^ |
О |
|||
|
h о ^ |
Г1 " |
о |
ci T |
r*" 00 |
■30 |
rr. OS |
DO Э0 |
О W |
о |
ri |
|||
|
’— я |
sO |
to T |
to a: |
to r- |
.T. to oc |
OC о |
Ot 00 |
to 00 |
rr^ |
5*1 |
^ о ”T |
||
|
li Q ^ 6 G^ £ |
ri " |
M |
O\ |
м |
to 4—1 |
to |
ОС —-1 |
*o to ■—1 |
hC ■:>" i—i |
||||
|
^ я Ga |
•H |
to 00 |
ir |
гЧ |
■■^ to |
a ri |
at —। |
ri |
to r 1 |
V —1 |
|||
|
ti э § £ ^ ° Qi |
= 1 ri g |
to |
T |
xo |
-* |
in |
to in |
40 |
Ф |
||||
|
^ - |
XO |
"T |
-T |
-r |
№ |
-г |
-T |
iZ |
40 ч\ |
to о |
|||
|
Я '—’ 1^ |
я Q " Г| g |
In |
XO —i" |
to to |
to Z |
flj <** to |
О |
tq 2 |
f*> to |
oc to |
г |
to |
|
|
a w о v*i я a# |
SO |
3 |
f* |
d |
О |
to |
rr to |
to e |
*o
|
Ct ff$ |
|||
|
1 J— |
5 5 |
<2 Я |
о ч, < с |
о 5 |
E О <
|
= e о < iz |
1H lf< |
< о 3 |
g о ir, г |
I a 4 6Й |
s я A <7? >-1 |
||
|
paXiuds рис P»|S>JU| |
p»|S.yill uaqi paXiutl^ |
||||||||||||
Table 3 Yield of common bean plant as affected by elicitors under TSSM infection after 70 days from sowing.
|
E fib я 4 T 5 № |
Я 5 у « ® TD 5 I'M |
\о о |
so об |
ф ri |
© Г^ |
© |
■-' |
4 |
1Л о |
|||
|
1 Ф |
» о |
г^ об |
С rq ^ |
о |
© |
Ф rO |
о •Z |
z |
00 in © |
|||
|
a a T 4 ^ |
5 z ГМ |
ф fM \£ Оч |
ф о |
so |
Ф X О'" О' |
^ ri п |
re |
ГМ |
SO iZ © ^ |
ГД © iH |
X |
so |
|
f St 4 6 |
5 Ct ^ |
\с О'. О' |
о со >п 4? |
^ 00 *м |
5 ie О' |
О\ об еч |
0\ 00 |
X X |
ТГ ri ^и |
q |
•г! |
|
|
a 4 a 4 я т e a |
я о с ф ■о с |
с Z гч |
О о rj |
ф |
\с гм |
so го |
-1- |
'O 0< |
m об ri |
Q qi |
q w |
Os if) |
|
Я О я Ф Z* |
^t in гм |
г. Ох ■н |
© 0\ |
С -с r^J |
\D ^f |
so qj |
об r-i |
so qj |
Ф Tf |
00 ^t |
||
|
я » S 4 |
О с и |
о id ^ 1-5 |
7 ф н: 4 |
tu о ir< "^ V? |
о О tn |
? © V IT, 'f 1— 4 7 |
r* Ф 3 1-5 О s |
< w © ^ in |
о О < n |
xO f) ■я Q |
||
|
patpjds put’ p»isajui |
pajsajui uaqt pjAiuds |
|||||||||||
DISCUSSION
World wide crop losses without the use of pesticides and other non-chemical control strategies is estimated to be about 70% of crop production, amounting to 400 billion US Dollars. Moreover, pests often adapt to pesticides via natural selection just as they adapt to natural plant resistance. The use of chemical pesticides not only results in rapid build-up of resistance but their non-selectivity often affects the balance between pests and their natural predators which are also often used in biological control. Although using 'natural' plant elicitors can not abolish herbivores to become resistant they can be much more environmental friendly since they are active in relative low amounts and do not likely interfere with the well-being of carnivorous insects. We showed that treatment of bean plants in the field with SA or MeJA improved plant growth, yield and yield-quality profoundly and decreased natural and artificial spider mite infestations. In our hands these treatment did not have any negative effects on plant growth or productivity.
The effectiveness of the treatments for controlling TSSM may be due to the inhibition of photosynthesis of infested leaves and accelerated transpiration, leading to the drying out and premature fall of the leaves (Flechtman, 1979; Cheong et al., 2002). The decrease may be due to the inhibition of pigment biosynthesis which may results from the alteration in mineral nutrition or lack of assimilates which drain towards the TSSM or to the effect of ROS on these pigments (Stacey and Keen 1996). In damaged plant tissues there is an induction of ethylene biosynthesis that, in turn, has been associated with the induction and acceleration of abscission (Taiz and Zeiger, 1998). For this reasons, it would be important to vertify the effect of damages caused by the TSSM on ethylene production of common bean plants. Moreover, the infestation with T. urticae resulted in increasing the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) which destroy membrane permeability, and proteins as well as nucleic acid which decreased plant growth and yield. Moreover, the infestation leads to decreasing the content of nitrogen and phosphorous due to its effect of ion uptake which results from destroy membrane permeability (unpublished data). The stylet of mite penetrates the adaxial epidermis, reaching the palisade layer. They fed on the cell contents, destroying the chloroplast in the area restricted to where feeding takes place leading to the appearance of chlorotic areas (Flechtman, 1979).
In the present study the data indicate that application of elicitors decreased significantly TSSM population on the leaves. This reduction may be due to activation of plant induced systematic resistance (Repka, 2001). Generally elicitors may be served as a stimulatory effect on secondary metabolites production (Gundlach et al., 1992). Results indicate that elicitors especially SA stimulated the accumulation of soluble phenolic compounds in common bean leaves (unpublished data). This accumulation may be due to inhibition catalase activity (unpublished data), which in turn induces PAL gene expression and synthesis of phenolic compounds (Vermerris and Nicholson, 2006). Yet total phenols have long been considered as important defense-related compounds whose levels are naturally high in resistant varieties of many crops (Gogoi et al., 2001). Results also proved that application of both elicitors increased significantly ion contents i.e., N, P, K and Ca in common bean shoot which reflect to increasing plant growth and plant resistance to pests due to its role in plant metabolism, such as promote the development of thicker outer walls and stability of plant membrane in epidermal cells, thus preventing pests attack (Marschner, 1986). In this concern, increasing of nitrogen in plant stimulate synthesis of phenols and lignin content. All these are parts of the defense system of plant against infection (Marschner, 1986).
The application of both elicitors increased the total chlorophyll content of common bean leaves (Figure, 4a). This increment may be due to stimulating pigment formation and enhancing the efficacy of photosynthetic apparatus with a better potential for resistance and decrease in photophosphorylation rate usually occurring after infection (Amaresh and Bhatt, 1998). Elicitors was found to increase potassium content (Farouk et al., 2008), which may increase the number of chloroplast per cell, number of cell per leaf and consequently leaf area (Possingham, 1980). This result was supported by Farouk (2005) and Farouk et al (2008) on pea and cucumber plants respectively. The stimulating effect of elicitors on chlorophyll content may be due to stabilizing the active site of enzymes and photosynthetic reactions (Rahman et al., 2002), and increased nitrogen accumulation in plant shoot (unpublished data) which might have served in enhancing chlorophyll synthesis. Finally both elicitors activated the synthesis of carotenoids which protect chlorophyll from oxidation and finally increased chlorophyll content as reported in this study. Moreover, salicylic acid significantly increased chl. a, chl. b and carotenoids recording maximum values at 100 mg/l (Figure, 4a). In addition, the stimulating effect of elicitors on chlorophyll pigment may be due to enhancing cytokinin, auxin, GAs content. These results are in agreement with those obtained by Gharib (2006) on sweet basil and marjoram, Türkyılmaz et al. (2005) on bean, and El-Mergawi and Abdel-Wahed, 2007) on maize plants who found that salicylic acid caused significant increased in photosynthetic pigments content in leaves. In this study an increase in chlorophyll content were attained by MeJA at 70 Days old.
In addition, application of both elicitors decreased chl a:b ratio which play a curricular role in stabilizing photosynthetic processes which reflect to increasing photoassimilate and pod yield. The physiological significance of the decreased the ratio of Chl a:b during leaf infestation with TSSM, it is still unclear due to contradictive results from different studies. BjoЁrkman, (1981) suggested that the decrease in Chl a:b ratio can improve the capture of far-red radiation and helps to maintain an optimal energy balance between PSI and PSII. Therefore, the decrease in Chl a:b ratio may be required for TSSM infested plants to readjust their photosynthetic balance while under stress.
Foliar application with elicitors in both season showed in most cases a significant increase in common bean growth parameters, especially 100 mg/l SA. These increases may be attributed to elicitor's effect on physiological processes in plant such as ion uptake, cell elongation, cell division, enzymatic activation, and protein synthesis. In this concern, salicylic acid enhanced growth of wheat (Shakirova et al., 2003), pea (Farouk, 2005) and cucumber (Farouk et al., 2008) plants. Moreover El-Bahay (2002) reported that salicylic acid has the potentiality to exert a suppressive or simulative impact on various growth aspects of lupine seedlings through their direct interference with the enzymatic activities responsible for biosynthesis and/or catabolism of growth promoting and inhibiting substances.
The increase in common bean yield may be due to role of elicitors in stimulation of physiological processes which reflected on improving vegetative growth (Table, 1) that followed by active translocation of the photoassimilate from source to sink in common bean plant due to increasing leaf blade thickness as well as dimension of vascular bundles as a results of elicitors application (Table 2, Fig 5). In this concern, salicylic acid might be regulating plant growth by increasing enzyme activity as α-amylase and nitrate reductase, which accelerate the sugar translocation from the leaves to developing fruit (Sharma et al., 1986). Moreover, application of both elicitors lead to increased potassium content (unpublished data), which enhancing photosynthetic pigments and capacity, and subsequently dry matter accumulation (Umar and Bansal, 1995). In addition, application of salicylic acid inhibits ethylene production leading to increasing fruit number and consequently increased fruit yield per plant (Leslie and Romani, 1986). Generally, plants treated with salicylates or methyl jasmonate had higher yield in many plant species, cultivated either in greenhouse or in open conditions (Abdel-Wahed et al., 2006; Iqbal and Ashraf, 2006; Farouk et al., 2008).
Concerning yield quality, it is noted that application of both elicitors at both concentration improved yield quality as compared to infested or control plants, these results are agreement with those obtained by Sarangthem and Singh (2003) who found that the level of N, proteins and nitrate reductase activity were increased in Phaseolus vulgaris by foliar application of SA at 0.1%. Similarly, Haroun et al. (1998) found that low dose of salicylic acid (2.5 mM) significantly increased total carbohydrate content in seed lupine. Moreover, Farouk (2005) and Farouk et al., (2008) indicated that, under greenhouse and open field conditions, application of both SA or MeJA increased significantly pea and cucumber fruit quality respectively as regard to the content of ascorbic acid, protein, carbohydrates and some ions.
In conclusion, it may be possible to replace conventional chemical pesticides with any of the tested elicitor's specially Salicylic acid at 100 mg/l due to its safety for human and environment and thus provided both economical and ecological efficacy. In addition to the effectiveness using elicitors in controlling TSSM population and increase yield and quality of common bean under field conditions.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
We are grateful to Prof Dr. I. Fedina (Bulgaria) for providing methyl jasmonate. Also we thank Prof Dr. Merijn R. Kant (Institute for Biodiversity and Ecosystem Dynamics, the Netherlands) and Prof Dr M. A Zaher (Agric. Zoology and Entomology Dept., Cairo University) for useful comments on an earlier version of this manuscript.
Список литературы The effect of plant defense elicitors on common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) growth and yield in absence or presence of spider mite (Tetranychus urticae Koch) infestation
- Abdel-Wahed M.S.A., Amin A.A. and El-Rashad S.M. (2006) Physiological effect of some bioregulators on vegetative growth, yield and chemical constituents of yellow maize plants. World J. Agric. Sci., 2(2), 149-155.
- Amaresh C. and Bhatt R.K. (1998) Biochemical and physiological response to salicylic acid in reaction to systemic acquired resistance. Photosynthetica, 35(2), 255-258.
- AOAC (1980) Official Methods of Analysis of Association of official Analytical Chemists. 12th Ed. Washington, D.C.
- Bi J.L., Murphy J.P. and Felton G.W. (1997) Antinutritive and oxidative components as mechanisms of induced resistance in cotton to Helicoverpa zea. J. Chem. Ecol., 23, 97-128.
- Bjorkman O. (1981) Responses to different quantum flux densities. In: Lange O.L., Nobel P.S., Osmond C.B. and Ziegler H. (eds.). Physiological Plant Ecology, Spring-Verlag, Berlin, pp 57-107.
- Bradford M.M. (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the antification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem., 72, 248-254.
- Cheong Y.H., Chang H.S., Grupta R., Wang Zhu T. and Luan S. (2002) Transcriptional profiling reveals novel interactions between wounding, pathogen, abiotic stress and hormonal responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology, 129, 661-677.
- Cooper T.G. (1977) The tools of biochemistry. A Wiley-Interscience Pub. John Wiley and Sons, New York.
- Creelman R. A. and Mullet J. E. (1997) Oligosaccharins, brassinolides, and jasmonate: nontraditional regulators of plant growth, development, and gene expression. Plant Cell, 9, 1211-1223.
- El-Bahay M.M. (2002) Metabolic changes, phytohormonal level and activities of certain related enzymes associated with growth of presoaked lupine seeds in salicylic acid and gallic acid Bull. Fac. Sci., Assiut Univ., 31, 259-270.
- El-Mergawi R and Abdel-Wahed M. (2007) Diversity in salicylic acid effects on growth criteria and different indole acetic acid forms among faba bean and maize. International Plant Growth Substances Association.19th Annual meeting, Puerto Vallarta, Mexico, July 21-25.
- Fahl J.I., Queiroz-Voltan R.B, Maria Carelli L.C., Chiavinato M.A., Ana Prado K.S. and Souza J.C. (2007) Alteration in leaf anatomy and physiology caused by the red mite (Oligonychus ilicis) in plants of Coffea arabica. Braz. J. Plant Physiol., 19(1), 61-68.
- Farouk S., Ghoneem K.M. and Abeer A. Ali (2008) Induction and Expression of systematic resistance to downy mildew disease in cucumber plant by elicitors. Egyptian Journal of Phytopathology, (1-2): 95-111.
- Farouk S. (2005) Response of Pisum sativum L. to some osmoregulators and plant rowth substances under salt stress Ph.D Thesis, Faculty of Agriculture, Mansoura University, Egypt.
- Flechtmann C.H.W. (1979) Acaros de Importânćia Agricola. Livraria Nobel, San Paulo. (C.F. Fahl et al., 2007)
- Food Agriculture Organization (FAO) production year book, 2009.
- Geoghiou G.P. (1990) Overview of insecticide resistance. In Green M.B.; LeBaron HM and Moberg WK (eds). Managing. Resistance to Agrochemicals, American Chemical society symposium Series 421, pp 18-41.
- Gharib F.A. (2006) Effect of salicylic acid on the growth, metabolic activities and oil content of basil and marjoram. International J. Agric. Biology, 4, 485-492.
- Gogoi R., Singh D.V. and Srivastava K.D. (2001) Phenols as a biochemical basis of resistance in wheat against karnal bunt. Plant Pathology, 50(4), 470-476.
- Gundlach H., Muller M.J.; Kutchan T.M. and Zenk M.H. (1992) Jasmonic acid is a signal transducer in elicitor-induced plant cell cultures. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 89, 2389-2393.
- Haroun S.A., Aldesuqy H.S., Shukry W.M. and Gaber A.M., (1998) Regulation of growth and metabolism in Lupinus termis plant by sodium salicylate. Egypt J. Physiol. Sci., 22, 75.
- Iqbal M. and Ashraf M. (2006) Wheat seed priming in relation to salt tolerance, growth, yield and level of free salicylic acid and polyamines. Ann. Bot. Fennici., 43(4), 250-259.
- Jee Y.K., Park H.S., Kim H.Y., Park J.S., Lee K.Y., Kim K.Y., Kim Y.K., Cho S.H., Minand K.U. and Kim Y.Y. (2000) Two-spotted spider mite Tetranychus urticae: An important allergen in asthmatic non-farmers symtomatic in summer and fall months. Ann. Allergy. Asthma. Immunol., 84, 543-548.
- Johanson D.A. (1940) Plant Microtechnique. McGraw-Hill. Inc New York and London.
- Kalra Y.P. (1998) Handbook of reference method for plant analysis. CRC Press, Washington, DC.
- Karban R., English-Loeb G. and Hougen-Eitzman D. (1997) Mite vaccinations for sustainable management of spider mites in vineyards. Ecological Appl., 7, 183-193.
- Leslie C.A. and Romani R.J. (1986) Salicylic acid a new inhibitor of ethylene biosynthesis. Plant Cell Rep., 5(2), 144-146.
- Lichtenthaler H.K. and Wellbun A.R. (1985) Determination of total carotenoids and chlorophylls A and B of leaf in Different Solvents. Biol. Soc. Trans., 11, 591-592.
- Marschner H. (1986) Mineral nutrition of higher plants. Acad. Press. London.
- Norman G.R. and Streiner D.L. (2003) PDQ Statistics, 3rd Ed. BC Deckker Inc, London.
- Ozawa R., Arimura G., Takabayashi J., Shimoda T. and Nishioka T. (2000) Involvement of jasmonate-and salicylate-related signaling pathways for the production of specific herbivore-induced volatiles in plants. Plant Cell Physiol., 41, 391-398.
- Picone C. and Tassel D.V. (2002) Agriculture and biodiversity loss: Industrial Agiculture. IN: Niles Eldredge (ed.), Life on Earth: An Encyclopedia of Biodiversity, Ecology and Evolution, pp 99-105.
- Possingham J.V. (1980) Plastid replication and development in the life cycle of higher plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol., 31, 113-129.
- Rahman M.S., Miyake H. and Takeoka Y. (2002) Effects of exogenous glycinebetaine on growth and ultrastructure of salt-stressed rice seedlings (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Production Sci., 5, 33-44.
- Raskin K. (1992) Role of salicylic acid in plants. Ann. Rew. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol., 43, 439.
- Repka V. (2001) Elicitor-stimulated induction of defense mechanisms and defense gene activation in grapevine cell suspension cultures. Biologia Plantarum, 44, 555-65.
- Ryals J.A., Neuenschwander U.H., Willits M.G., Molina A., Steiner H.Y. and Hunt M.D. (1996) Systemic acquired resistance. Plant Cell, 8, 1809-1819.
- Sadasivam S. and Manickam A. (1996) Biochemical Methods, Second Eddition, New Age International. India.
- Sarangthem K. and Singh T.H.N. (2003) Efficacy of salicylic acid on growth, nitrogen metabolism and flowering of Phaseolus vulgaris. Crop Res., 26, 355-360.
- Shakirova F.M., Sakhabutdinova A.R., Bezrukova M.V., Fatkhutdinova R.A. and Fatkhutdinova D.R. (2003) Changes in the hormonal status of wheat seedlings induced by salicylic acid and salinity. Plant Sci., 164, 317-322.
- Sharma S., Sharma S.S. and Rau V.K. (1986) Reversal by phoenolic compounds of abscussic acid-induced inhibition of in vitro activity of amylase from seeds of Triticum aestivum L. New Phytol., 103(2), 293-297.
- Stacey G. and Keen N.T. (1996) Plant microbe interactions. APS Press. Minnesota.
- Taiz L. and Zeiger E. (1998) Plant Physiology. Sinauer Associates Inc., Publishers. Sunderland, Massachusetts.
- Thaler J.S, Stout M J., Karban R and Duffey S.S. (1996) Exogenous jasmonates stimulate insect wounding in tomato plants (Lycopersicon esculentum) in the laboratory and field. J. Chem. Ecology, 22, 1767-1781.
- Thaler J.S., Fidantsef A.L., Duffey S.S. and Bostock R.M. (1999) Trade-offs in plant defense against pathogens and herbivores: a field demonstration of chemical elicitors of induced resistance. J. Chem. Ecol., 25, 1597-1609.
- Türkyılmaz B., Aktas L.Y., Güven A. (2005) Salicylic acid induced some biochemical and physiological changes in Phaseolus vulgaris L. Science and Engineering Journal of Firat Univ., 17(2), 319-326.
- Umar S. and Bansad S.K. (1995) Potassium requirement of mustard (Brassica juncea L.) under moisture stress conditions. Plant Physiol. and Biochem., New Delhi, 22(2), 130-135.
- Vermerris W., and Nicholson R. (2006) Phenolic compounds Biochemistry. Springer, Netherlands.
- Wilkerson J.L., Webb S.E. and Capinera J.L. (2005) Vegetable pests II. Acari-Hemiptera-Orthoptera-Thysanoptera. UF/IFAS CD-Rom. SW 181.
- Zhang Z.Q. (2003) Mites of greenhouse. Identifcation, biology and control. CABI Pub.


