The effect of substance abuse and smoking status on healing time of closed transverse femoral shaft fractures treated with open intramedullary nailing
Автор: Asadi Kamran, Mardani-Kivi Mohsen, Aris Arash
Журнал: Гений ортопедии @geniy-ortopedii
Рубрика: Оригинальные статьи
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.28, 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Introduction Nonunion or delayed union is a known postoperative complication in long bone fractures. Substance abuse may impair bone healing. In this paper, we investigated the effect of narcotics on healing time in femoral shaft transverse fractures and the effect of substance abuse and smoking on postoperative healing time. Material and methods This cohort study was conducted at the Orthopedic Clinic of Poursina Hospital, Rasht from 2017-2019. Patients with transverse fractures of the femoral shaft who underwent intramedullary rod insertion were followed for 6 months. Bone healing time based on substance abuse and smoking status was evaluated. Results There was a significant association between various groups (categorized based on cigarette smoking and using drugs) in terms of bone healing status (P = ы0.006). There was a statistically significant difference in healing status among the control group, smoker group, and addict and smoker group (P = 0.034 and P = 0.004, respectively). However, there was no statistically significant difference in healing status between control and addicts group (P = 0.517). Conclusions Treatment efficiency and performance in addicted and smoker patients are more unfavorable and hence which, in turn, requires more follow-up periods; therapies such as bone grafting and other methods are more frequently considered in addicted and smoker patients in case of lack of healing reaction. Therefore, prevention plans in high-risk groups can play a significant role in primary identification, treatment, and reducing the complications of fractures.
Femoral fracture, orthopedic methods, narcotics
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142235330
IDR: 142235330 | УДК: [615.015.6+613.84]:616.718.46-001.5-089.227.84 | DOI: 10.18019/1028-4427-2022-28-3-333-337
Текст научной статьи The effect of substance abuse and smoking status on healing time of closed transverse femoral shaft fractures treated with open intramedullary nailing
Original article
Road traffic accidents, one of the main causes of mortality and morbidity worldwide [1], are the major cause of bone fractures. Fractures of long bones, especially femoral shaft, resulting from high-energy trauma, are associated with unfavorable and lethal outcomes and are thus of great importance, especially in young patients [2]. Accordingly, appropriate management and early fixation of femoral shaft bone fractures are of great importance [3]. Internal fixation by intramedullary nails and rods are considered appropriate surgical methods for fixation of femoral shaft fractures, but are associated with several complications. Nonunion and delayed union are one of the main challenges after surgery, which can result in failure of the fixation and increase complications [4].
No evidence of bone healing is defined as nonunion and a slower progression than the anticipated duration is considered delayed union [5]. The importance of nonunion and delayed union has resulted in extensive search about their risk factors. According to the evidence, the mechanism of injury, severity of injury to soft tissues, and type of fracture are the main factors determining bone healing [6]. Patients with multitrauma are at the risk of impaired blood perfusion and altered inflammatory phase of bone regeneration, which can play a significant role in bone healing [7]. Several modifiable patient-related risk factors have also been identified to affect bone healing, such as diabetes and use of non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) [8]. Furthermore, a higher rate of nonunion has been observed in patients with daily tobacco use [9, 10] and cigarette smokers [11, 12]. An animal model has also suggested weaker bone healing and callus formation in rats receiving opioid analgesics after surgery [13]. Nevertheless, the effect of substance abuse with/without smoking on bone healing of femoral shaft fractures with intramedullary rods is not known, yet. Given the high frequency of trauma and fractures in Guilan province, particularly closed and transverse fractures of the femoral shaft, and unfortunately high frequency of substance abuse among its population, as well as insufficient information about the effect of substance abuse on bone healing of femoral shaft fractures, the present study aimed to investigate the effect of substance abuse and/or smoking on bone healing.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Ethics approval The protocol for this study was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB number: 1559). All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on studies with human participation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975 (in its most recently amended version). Informed consent was obtained from all patients included in the study.
In this cohort study, the effect of narcotics on healing of closed transverse fracture of the shaft was investigated in patients who referred to the orthopedic clinic, Poursina hospital, Rasht from 2017-2019. The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Guilan University of Medical Sciences.
After explaining the study objectives to the participants and obtaining a written informed consent from those who were willing to participate in the study. All adult patients (until 75 years of age) who referred to the study center during the study period with closed and transverse fracture of femoral shaft and were indicated for surgical fixation by intramedullary nailing, with similar income level, and gave consent to participate in the study were included into the study by convenient sampling method. Female patients who had a positive history of using hormonal or contraceptive drugs, or patients with diabetes, hyperthyroidism, renal disease, Cushing's syndrome, burn in fracture site, open or intra-articular fracture, rheumatic and metabolic bone diseases, malignant or benign tumors, bone atrophy following poliomyelitis, avascular necrosis following radiotherapy, congenital skeletal disorders, and those who used drugs affecting bone metabolism or required bone fixation with plate and screw materials, or received treatment later than 3 weeks after injury were not included into the study.
The sample size was calculated at 24 in each group, based on 95 % confidence interval (CI) and study power of 90 %; a final sample size of 32 was considered in each group considering 25 % chance of lost to followup. According to patients’ smoking status and substance abuse, patients were divided into four groups, each with 32 participants: only smoker (S group), both smoker and addict (SA group), neither smoker nor addict (control), and only addict (A group).
For data collection, the researcher designed a checklist that included demographic factors such as age, sex, underlying diseases, used medications, type of narcotics used, drug dosage per day and completed these data for all patients. Moreover, all patients were primarily assessed with rapid test and morphine test (opium, opium side products, heroine, crack, morphine, and narcotic pain medications) before entering the study. Consuming 6 cigarettes or more per day was considered as the being smoker in this study, in line with previous research [14]. Addiction was considered as “dependence on drugs in a way that it is completely harmful to the individual and the society” and “drug” refers to any kinds of chemical compound causing a change in brain function, including excitement, depression, abnormal behavior, anger, or impaired judgment.
All patients underwent intramedullary nailing by one surgeon. Starting point in priformis fossa was opened using a 5-cm oblique incision in trochanteric area. Using subvastus lateral approach, reduction at fracture site was achieved. After appropriate reaming, antegrade nail (Zimmer, United States) was used with two distal screws and one proximal locking screw after compression in fracture site. Patients were followed for 6 months and their clinical and radiological report were recorded at month 1, 3, 4, and 6 after surgery and the status and time of union in the patients were recorded. Clinical healing was defined as ability of weight-bearing and walking on the limb without feeling pain as well as no pain during the physician pressing the fracture site or when moving the limb along sagittal or coronal plane. Radiologic healing referred to at least 3 of 4 cortices improved in anteroposterior X-ray images. The physician and radiologist evaluating the healing process were unaware of the smoking and addiction status of patients.
Statistical analyses After data collection, they were input into the statistical software IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 19.0 (Released 2010. Armonk, NY: IBM Corp.), used for statistical analyses. Descriptive results were reported by number (percentage) for categorical variables and mean ± standard deviation (SD) or median for numeric variables, according to their normal distribution. To determine the mean time of healing, 95 % confidence interval was used to divide measuring times. Chi square test was used to examine the difference in categorical variables among the four study groups. Kolmogorov-Smirnov test was used to test the normal distribution of data, which showed that data related to the time of union (days) did not have normal distribution; therefore, Kruskal-Wallis test was used for comparing healing time among the four study groups. Multi-way analysis of variance (MANOVA) was used to compare the healing time based on main groups defined in the study with demographic variables (age and sex). Significance levels in tests and in two-way tests were considered p < 0.05.
RESULTS
Of 128 patients analyzed in four groups, 102 were male (79.7 %) and 26 were female (20.3 %). Mean ± SD of patients’ age was 45.78 ± 16.93 years (range: 18-69 years). There was no difference in demographic characteristics of the groups, as shown in table 1 (P > 0.05).
After 6 months, there were no cases of nonunion in the control group, 7 cases of nonunion (21.9 %) in S group, 4 cases of nonunion (12.5 %) in A group, and 10 cases of nonunion (31.2 %) in SA group with a statistically significant difference among the groups (P=0.006 with 99 % confidence and < 1 % error), according to the results of Chi-square test. The mean time of union was calculated for all patients with union at the end of 180
days. As demonstrated in table 2, there was no statistically significant difference in the time of union (days) among the four study groups (P = 0.759) (Table 2). Also, the results of Kruskal-Wallis did not reveal any significant difference between the time of non-union (day) among patients abusing different substances (P = 0.119) (Table 3).
The frequency of patients with union at month 1, 3, 4, and 6 after surgery are shown in table 4. As demonstrated, there was a significant difference in the frequency of cases with union at all intervals among the four study groups (P < 0.05); meanwhile the effect of time was only significant in A group (Table 4).
Table 1
Demographic characteristics of the study groups
|
Group |
Categories |
Non-addict non-smoker |
Only smoker |
Only addict |
Smoker and addict |
P-value* |
|
Sex |
Male |
25 (78.1 %) |
26 (81.2 %) |
25 (78.1 %) |
26 (81.2 %) |
0.979 |
|
Female |
7 (21.9 %) |
6 (18.8 %) |
7 (21.9 %) |
6 (18.8 %) |
||
|
Age category |
< 40 |
12 (37.5 %) |
13 (40.6 %) |
12 (37.5 %) |
13 (40.6 %) |
0.99 |
|
40–60 |
12 (37.5 %) |
12 (37.5 %) |
13 (40.6 %) |
12 (37.5 %) |
||
|
> 60 |
8 (25 %) |
7 (21.9 %) |
7 (21.9 %) |
7 (21.9 %) |
The results of chi square test, considered significant at <0.05, all values are reported as number (percentage)
Table 2
Comparison between the time of union (days) among the study groups
|
Group |
Number of patients with union |
Mean (days) |
Standard deviation |
95 %CI |
Z value |
p-value* |
|
Non-addict and non-smoker |
32 |
37.5 |
30.4 |
27.1-47.9 |
0.759 |
1.17 |
|
Only smoker |
25 |
43.75 |
38.5 |
28.4-59.2 |
||
|
Only addict |
28 |
45 |
38.7 |
30.7-59.3 |
||
|
Smoker and addict |
22 |
47.72 |
46.8 |
28.1-67.32 |
The results of Kruskal-Wallis test, considered significant at values < 0.05
Table 3
Comparing mean time of nonunion in patients with different substance abuse
|
Type of drug |
Number of patients |
Mean (days) |
Standard deviation |
Z value |
p-value |
|
Opium |
17 |
88.23 |
73.1 |
2.42 |
0.119 |
|
Opium concentrates (Shire) |
13 |
90 |
70.3 |
||
|
Heroine |
11 |
84.5 |
75.6 |
||
|
Crack |
6 |
30 |
0 |
||
|
Morphine |
4 |
30 |
0 |
||
|
Narcotic pain medications |
9 |
90 |
73.4 |
Table 4
Comparing the frequency of positive union among the study groups in each month
|
Group |
Month 1 |
Month 3 |
Month 4 |
Month 6 |
P-value |
|
Non-addict and non-smoker |
30 (93.8 %) |
30 (93.8 %) |
31 (96.9 %) |
32 (100 %) |
0.194 |
|
Only smoker |
21 (65.6 %) |
21 (65.6 %) |
23 (71.9 %) |
24 (75 %) |
0.061 |
|
Only addict |
24 (75 %) |
24 (75 %) |
27 (84.4 %) |
28 (87.5 %) |
0.017 |
|
Smoker and addict |
19 (59.4 %) |
19 (59.4 %) |
20 (62.5 %) |
22 (68.8 %) |
0.066 |
|
P-value |
0.011 |
0.011 |
0.005 |
0.005 |
All values are reported as number (percentage)
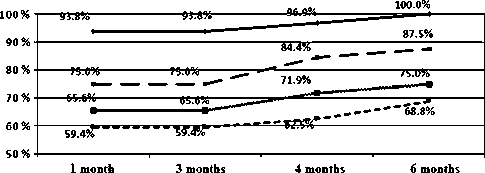
• control group
*~*~* Smoker
^^ Addict
Fig. 1 The frequency of patients with union at different time intervals
DISCUSSION
The present cohort on a population with male dominancy and mean age of 45.78 years showed that patients who did not smoke or abuse drugs had a 100 % union after 6 months, while a percentage of patients who smoked or abused drugs or both had nonunion during 6 months with significant difference among the groups. Furthermore, the difference in the frequency of patients with nonunion was significant in the previous intervals (1, 3, and 4 months). These results show that both smoking and narcotics have unfavorable results on bone healing of patients with closed and transverse fracture of femoral shaft and were indicated for surgical fixation by intramedullary nailing. The effect of smoking on impaired bone healing has been demonstrated in previous studies. In the study by Moghaddam et al., 85 patients with tibial shaft fractures were examined, of whom 39 never smoked and 45 were current or previous cigarette smokers. The results of this study showed that the smoker group, compared to nonsmokers, had an increased risk of nonunion (18 vs. 3 patients, respectively) and delayed union (21.5 vs. 16.1 weeks, respectively) [11]. These results are consistent with the results of the present study. Among several factors suggested as a risk factor of nonunion of long bone fractures, smoking status has been suggested as a significant factor [12]. In a review of 7110 articles, it was demonstrated that smokers had a higher rate of nonunion of tibial fractures and open fracture (OR ≈ 2) and a longer healing time (30.2 vs. 24.1 weeks) compared to nonsmokersС [15]. These results are consistent with the results of our study and indicate the unfavorable effect of smoking on bone healing after long bone fractures. The mechanism of this effect could be related to reduced serum levels of factors associated with bone healing, such as the lower serum levels of transforming growth factor (TGF- β 1) in smokers [16]. The lower serum level of testosterone, LH, and FSH in the smokers [17] could also play a role on the unfavorable effect of smoking on bone healing, as these sex-related hormones. Also, the negative outcome of smoking on bone healing is suggested to be related to the effect of its nicotine on the endogenous opioid system [18].
Narcotics are group of chemicals, which alter brain’s level of consciousness and reduce the body’s immune response [19]. Moreover, all narcotics negatively affect brain cells and other parts of body and alter the chemical balance in the body. Narcotics can include opium (concentrates) and side products (shire), heroin, crack, morphine, and narcotic pain medications. In the present study, the bone healing time was compared between patients with different substance abuse and the results showed no significant difference in any interval, which shows that all types of drugs abused can delay bone healing. Ezzatabadipour et al. investigated the effect of morphine dependence on bone healing in 56 rats divided randomly into two groups, maintained under similar laboratory condition, and followed for four weeks. The results showed that morphine-addicted rats had a different number of cells in the proliferative zone and thickness of cartilage growth, which confirmed the delayed bone healing in addicts [20], as suggested by the results of our study.
Studies have shown that chronic substance abuse and smoking can affect the endocrine system and the changes in this system can be attributed to delayed bone healing in patients with femoral fracture [21]; for instance, hyperprolactinemia induced by opioid can suppress osteoblast tissue growth, decrease serum levels of osteocalcin, and suppress the osteocalcin synthesis by osteoblasts [22]. Opioid addicts have also a lower bone concentration of Calcium, Phosphorus, Lithium and Potassium [23]. Furthermore, the lifestyle changes induced by substance abuse can decrease the calcium and phosphor intake and hence induce bone loss [24]. In the present study, we did not evaluate the cellular mechanism underlying the unfavorable effect of nicotine or narcotics on bone healing, but the clinical results showed that patients who smoked and abused drugs had the lowest percentage of bone healing after 6 months (68.8 %), which shows the synergistic effect of smoking and drugs on bone.
According the results of the present study, most patients with femoral shaft fracture were men (about 80 %), which is consistent with the results of previous studies, suggesting that men are the main victim of road accidents and hence long bone fractures [25]. In addition, sex-hormone levels were lower [24] and hypogonadism was more prevalent in male patients with chronic abuse of narcotics than females [26]. These may result in a higher rate of osteopenia in male. However, the results of our study did not show any difference in the bone healing status (percentage of nonunion) between male and female patients and the results of previous studies on the effect of sex on bone healing of long bone fractures are controversial [27]. Therefore, future studies are required to elucidate any difference in the bone healing of men and women. In the meantime, among several patient-related factors that affect nonunion after treatment of long bone fractures, age has been suggested as an important factor [27]. Then again, we found no difference in nonunion percentage of different age categories. All in all, there are several disease-related factors, such as fracture type and severity, type of tissue injury (open or closed), surgical details and techniques that can affect the results of nonunion, while in the present study, we excluded patients with severe head injury and included patients with similar severity of injury and type of fracture, as we only included patients with simple transverse femoral shaft fractures.
One of the strengths of the present study was objective assessment of smoking and substance abuse (rapid test and morphine test), which can report more accurate results compared to subjective assessment (patients’ report).
Furthermore, we evaluated four groups with similar demographics and disease-related variables, which improved the strength of the results. Nevertheless, this study could also have some limitations. One of the limitations of the present study was nonrandomized inclusion of patients into the study, which was not possible for us, as we considered several inclusion and exclusion criteria for reducing the effect of confounders, which in turn reduced the number of sample size. In addition, although we considered the sample size of each group more than the calculated sample size, with 25 % chance of lost to follow up, 32 patients were included in each group, which is statistically significant, but not clinically.
CONCLUSION
Generally, the results of our study showed significantly worse healing in patients who smoked or abused drugs or both, at all study intervals (1, 3, 4, and 6 months after surgery). As the group who smoked and abused drugs simultaneously had the highest rate of nonunion, nicotine and narcotics may have synergistic effects on bone healing. Although definite conclusion requires further studies with longer follow-ups, the results of our study suggesting the unfavorable effect of nicotine and narcotics on bone healing of femoral shaft fracture after intramedullary nailing infer the necessity of paying greater attention to bone healing of smokers and substance abusers and suggest that physicians should monitor addicts and smoker patients more closely for nonunion and consider further treatments such as bone grafting and other therapies or implement preventive plans for this high-risk group to reduce the risk of future complications.
Список литературы The effect of substance abuse and smoking status on healing time of closed transverse femoral shaft fractures treated with open intramedullary nailing
- Heron M. Deaths: Leading Causes for 2013 // Natl. Vital Stat. Rep. 2016. Vol. 65, No 2. P. 65-95.
- Kouris G., Hostiuc S., Negoi I. Femoral fractures in road traffic accidents // Rom. J. Leg. Med. 2012. Vol. 20, No 4. P. 279-282. DOI: 10.4323/ rjlm.2012.279.
- Timing of femoral shaft fracture fixation following major trauma: a retrospective cohort study of United States trauma centers / J.P. Byrne, A.B. Nathens, D. Gomez, D. Pincus, R.J. Jenkinson // PLoS Med. 2017. Vol. 14, No 7. P. e1002336. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002336.
- Somford M.P., van den Bekerom M.P., Kloen P. Operative treatment for femoral shaft nonunions, a systematic review of the literature // Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2013. Vol. 8, No 2. P. 77-88. DOI: 10.1007/s11751-013-0168-5.
- Non-unions / G.M. Calori, E.L. Mazza, S. Mazzola, A. Colombo, F. Giardina, F. Romano, M. Colombo // Clin. Cases Miner. Bone Metab. 2017. Vol. 14, No 2. P. 186-188. DOI: 10.11138/ccmbm/2017.14.1.186.
- Mirhadi S., Ashwood N., Karagkevrekis B. Factors influencing fracture healing // Trauma. 2013. Vol. 15, No 2. P. 140-155. DOI: 10.1177/1460408613486571.
- Impaired bone healing in multitrauma patients is associated with altered leukocyte kinetics after major trauma / O.W. Bastian, A. Kuijer, L. Koenderman, R.K. Stellato, W.W. van Solinge, L.P. Leenen, T.J. Blokhuis // J. Inflamm. Res. 2016. Vol. 9. P. 69-78. DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S101064.
- Patient-related risk factors for fracture-healing complications in the United Kingdom General Practice Research Database / R.K. Hernandez, T.P. Do, C.W. Critchlow, R.E. Dent, S.S. Jick // Acta Orthop. 2012. Vol. 83, No 6. P. 653-660. DOI: 10.3109/17453674.2012.747054.
- Green E., Lubahn J.D., Evans J. Risk factors, treatment, and outcomes associated with nonunion of the midshaft humerus fracture // J. Surg. Orthop. Adv. 2005. Vol. 14, No 2. P. 64-72.
- Asadi K. Effect of smoking on healing time of tibia fracture // J. Guil. Uni. Med. Sci. 2006. Vol. 15, No 57. P. 33-39. URL: http://journal.gums.ac.ir/ article-1-478-en.html.
- Cigarette smoking influences the clinical and occupational outcome of patients with tibial shaft fractures / A. Moghaddam-Alvandi, G. Zimmermann, K. Hammer, T. Bruckner, P.A. Grützner, J. von Recum // Injury. 2013. Vol. 44, No 11. P. 1670-1671. DOI: 10.1016/j.injury.2012.08.017.
- Predictors of patient reported pain after lower extremity nonunion surgery: the nicotine effect / A.V. Christiano, C.A. Pean, S.R. Konda, K.A. Egol // Iowa Orthop. J. 2016. Vol. 36. P. 53-58.
- Postoperative opioid administration inhibits bone healing in an animal model / J. Chrastil, C. Sampson, K.B. Jones, T.F. Higgins // Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2013. Vol. 471, No 12. P. 4076-4081. DOI: 10.1007/s11999-013-3232-z.
- Husten C.G. How should we define light or intermittent smoking? Does it matter? // Nicotin Tob. Res. 2009. Vol. 11, No 2. P. 111-121. DOI: 10.1093/ ntr/ntp010.
- Cigarette smoking increases complications following fracture: a systematic review / J.A. Scolaro, M.L. Schenker, S. Yannascoli, K. Baldwin, S. Mehta, J. Ahn // J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2014. Vol. 96, No 8. P. 674-681. DOI: 10.2106/JBJS.M.00081.
- Cigarette smoking decreases TGF-ß1 serum concentrations after long bone fracture / A. Moghaddam, S. Weiss, C. Wölfl, K. Schmeckenbecher, A. Wentzensen, P.A. Grützner, G. Zimmermann // Injury. 2010. Vol. 41, No 10. P. 1020-1025. DOI: 10.1016/j.injury.2010.03.014.
- Comparing the effects of cigarette and waterpipe smoke on serum levels of Lh, Fsh, estradiol and progesterone in female rats / R. Ahmadi, M.J. Lotfizadeh, F. Heidari, M. Mafi // FEYZ. 2013. Vol. 17, No 3. P. 232-238.
- Smoking modulation of mu-opioid and dopamine D2 receptor-mediated neurotransmission in humans / D.J. Scott, E.F. Domino, M.M. Heitzeg, R.A. Koeppe, L. Ni, S. Guthrie, J.K. Zubieta // Neuropsychopharmacology. 2007. Vol. 32, No 2. P. 450-457. DOI: 10.1038/sj.npp.1301238.
- Sacerdote P. Opioids and the immune system // Palliat. Med. 2006. Vol. 20, No Suppl. 1. P. S9-S15.
- The effects of morphine on tissue structure of the growth plate in male rats / M. Ezzatabadipour, M. Majidi, R. Malekpour-Afshar, S.H. Eftekharvaghefi, S.N. Nematollahi-Mahani // Iran J. Basic Med. Sci. 2011. Vol. 14, No 6. P. 514-520.
- Accelerated bone healing and excessive callus formation in patients with femoral fracture and head injury / P. Giannoudis, S. Mushtaq, P. Harwood, S. Kambhampati, M. Dimoutsos, Z. Stavrou, H.C. Pape // Injury. 2006. Vol. 37, No Suppl 3. P. S18-S24. DOI: 10.1016/j.injury.2006.08.020.
- Elevated plasma prolactin in abstinent methamphetamine-dependent subjects / T. Zorick, M.A. Mandelkern, B. Lee, M.L. Wong, K. Miotto, J. Shahbazian, E.D. London // Am. J. Drug Alcohol Abuse. 2011. Vol. 37, No 1. P. 62-67. DOI: 10.3109/00952990.2010.538945.
- Concentration profiling of minerals in iliac crest bone tissue of opium addicted humans using inductively coupled plasma and discriminant analysis techniques / A. Mani-Varnosfaderani, M. Jamshidi, A. Yeganeh, M. Mahmoudi // J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016. Vol. 120. P. 92-99. DOI: 10.1016/j. jpba.2015.12.005.
- Gozashti M.H., Shahesmaeili A., Zadeh N.A. Is opium addiction a risk factor for bone loss? // Iran Red Crescent Med. J. 2011. Vol. 13, No 7. P. 464-468.
- Epidemiological profile of extremity fractures and dislocations in road traffic accidents in Kashan, Iran: a glance at the related disabilities / M. Mahdian, M.R. Fazel, M. Sehat, G. Khosravi, M. Mohammadzadeh // Arch. Bone Jt. Surg. 2017. Vol. 5, No 3. P. 186-192.
- Katz N., Mazer N.A. The impact of opioids on the endocrine system // Clin. J. Pain. 2009. Vol. 25, No 2. P. 170-175. DOI: 10.1097/ AJP.0b013e3181850df6.
- Do Systemic Factors Influence the Fate of Nonunions to Become Atrophic? A Retrospective Analysis of 162 Cases / M. Rupp, S. Kern, T. El Khassawna, A. Ismat, D. Malhan, V. Alt, C. Heiss, M.J. Raschke // Biomed. Res. Int. 2019. 6407098. DOI: 10.1155/2019/6407098.


