The effects of leptin on gastric ulcer due to physical and psychological stress: involvement of nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2
Автор: Fallahi Soghra, Nabavizadeh Fatemeh, Sadr Seyed Shahabadin, Alizadeh Ali Mohammad, Adeli Soheila, Nahrevanian Hossein, Sadeghipour Hamid Reza, Hasanzadeh Gholamreza
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 4 т.7, 2011 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The present study aimed to assess the effects of Leptin on physical and psychological stresses inducing gastric ulcer. The potential role of endogenous nitric oxide (NO) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) in the effects of Leptin on the gastric ulcer in rats are also investigated. In this study, fifty-four male Wistar rats were equally divided into 9 groups and Leptin (10 µg/kg, s.c.) was administered twice a day for 14 days in advance of physical and psychological stress. Also, NG- nitro-l-arginine-methyl ester (L-NAME, 10 mg/kg, an inhibitor of NO synthase) and indomethtacin (5 mg/kg, in order to inhibit PG synthesis) were applied before Leptin administration. Ulcer index, gastric acid secretion, NO metabolites and PGE2 of stomach tissue suspension were all measured. Results indicated that ulcer index and gastric acid secretion were significantly decreased (p2 were increased (p2 pathways.
Leptin, gastric ulcer, nitric oxide, pge2, physical stress, psychological stress
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14323559
IDR: 14323559
Текст научной статьи The effects of leptin on gastric ulcer due to physical and psychological stress: involvement of nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2
Peptic ulcer is one of the common gastrointestinal diseases is caused by a break in the mucosal integrity close to the acid-secreting areas of the gastrointestinal tract (Kim et al., 2010).
Development of a peptic ulcer depends on the balance between the known aggressive factors such as gastric acid, pepsin, bile salts, abnormal motility, use of nonsteroidal ant-inflammatory drugs, infection with microorganisms and mucosal defense mechanisms. Also, physical and psychological stresses are widely accepted as triggers and or modifiers of the clinical course of diverse gastrointestinal disorders such as peptic ulcer. Growing experimental evidence from a variety of models such as immobilization, thermal injury or early maternal deprivation in laboratory animals uniformly supports the ability of stress to induce the development of gastric ulcers (Jiang et al., 2005; Caso et al., 2008).
Leptin is a key hormone that regulates food intake and energy expenditure via building to its corresponding receptor in the hypothalamus (Friedman et al., 1998). In the gastrointestinal tract, the stomach has been shown to produce Leptin, whose receptors are expressed in the stomach of rats and humans (Bado et al., 1998). In the stomach, Leptin has inhibitory effect on gastric acid secretion (Goiot et al., 2001)]. It also accelerates the gastric ulcer healing by mechanisms involving the upregulation of transforming growth factor and increases nitric oxide production due to upregulation of constitutive NO synthase (cNOS) and inducible NOS (iNOS) in the ulcer area ( konturek et al., 2001; Brzozowski et al., 1999). Another way of interpreting the presence of Leptin in the gastric mucosa is to invoke its ability to function as a mucosal defense factor in the stomach (Konturek et al., 2001). The present study aimed to assess the effects of Leptin on gastric ulcer induced by physical and psychological stresses, and the potential role of endogenous NO and prostaglandin E 2 (PGE 2 ) on the gastric ulcer formation in rat via Leptin pathway.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Material
Leptin was purchased from Amgen Inc, USA, L-
NAME, Indomethacin and pentagastrin obtained from Sigma Chemical Company, St. Louis, MO, USA. All solutions were freshly prepared and diluted in normal saline.
Animals and experimental protocols
Fifty-four male Wister rats (200-250 g) were housed in groups of 4 per cage and maintained in a temperature controlled room with a 12 h light/dark cycle. The procedure was in accordance with the guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animal of Tehran University of Medical Science. The animals were equally divided into nine groups (n=6) including Group (I) the control animals were not exposed to physical and psychological stresses. Animals of groups (II) and (III) were subjected to 1 h physical and psychological stresses (Phy + Psy groups) exposure for 14 days. In groups of (IV) and (V), Leptin (10 µg/kg, s.c) ( Adeymi et al., 2005) administered twice a day for 14 days 30 min before of physical and (v) psychological stress induction. Animals in (VI) and (VII) groups were injected by NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME, 10 mg/kg ip, a NOS inhibitor) twice a day 15 min before of Leptin with physical and psychological stresses induction. Animals in (VIII) and (IX) groups were received Indomethtacin (Indo, 5 mg/kg, in order to inhibit PG synthesis without gastric ulcer induction, twice a day, orally) 30 min before Leptin application and with physical and psychological stress.
Stress box and electrical shock instrument
Stress box consist of 9 compartments (50/16/16 cm) separated by transparent plastic boards (Ogqawa et al., 1990). The board prevents each animal from physical contact, but allows them to receive cues such as visual, auditory and olfactory sensations from the neighboring animal. Each compartment was equipped with a 5 mm diameter grid floor of stainless steel rods, placed 2.5 cm apart (Vincent et al., 2002). An electrical generator (current of 1 mA) (Borj Sanat Co. Iran, sensitivity 0.1-10 mA) was connected to the grid floor to generate an electric foot shock for 10 seconds with an interval of 60 s. The grid floor of 4 compartments were covered with plastic plates to prevent electric foot shock and served as non-foot-shock compartments for the psychological stress rats. From days 1 to 14, the electric foot shock was introduced to physical stress rats (stress responders) confined in the non-foot-shock compartments were then exposed to psychological cues, such as shrieks, smells of urine or stool, and jumping response from neighboring physical stress rats ( Vincent et al., 2002). Gastric lesion was found 14 days after physical and psychological stress.
Measurement of gastric acid secretion and plasma corticostrone level
The animals had free access to food and water except for the 24 h before the experiment when they were only deprived of food. Tracheostomy was performed under general anesthesia with sodium thiopental (50 mg/kg i.p) 30 min post stress exposure. To prevent gastric reflux, cervical esophagus was then ligated. Laparatomy was done and a polyethylene tube (2.5 mm O.D., 10 cm length) was placed into stomach via duodenal transverse incision gastric lavage was done several times with 1-2 ml of normal saline at 37єC. Animals were also allowed to have a 30 min recovery (Nabavizadeh et al., 2009). Basal acid secretion was measured with a digital titrator system (Basic Titrino, Metrohm, 794). Stimulated acid secretion was measured 15 min post pentagastrin (25 μg/kg i.p) injection (Nabavizadeh et al., 2009).
The stomach was removed and the ulcer scoring done. Then, body samples of stomach fixed formalin
(10%) for histological study and remnant of tissue immediately frizzed and kept at -70ºC for measurement of PGE 2 and NO metabolites. Also, a day before of gastric acid measuring, plasma corticostrone was determined using a commercially available ELISA kit (Cat. No. KT-510).
Measurement of ulcer score
The number of ulcers was counted. Ulcer scoring was done according to the method by Vogel (Vogel et al., 1997) as: The scores were: 0= no ulcer, 1= superficial ulcer, 2= deep ulcer, 3= perforation.
Ulcer index was measured by using following formula [25]: UI=UN+US+UP×10-1, UI= Ulcer Index, UN= Average number of ulcers per animal, US =Average number of severity score, UP=percentage of animals with ulcers
Percentage inhibition of ulceration was calculated as: % inhibition of ulceration = (Ulcer index Alcohol-Ulcer index Test) Ч100/Ulcer index Alcohol.
Preparation of gastric tissue homogenate for measurement of NO metabolites and PGE2
Weighed samples of gastric tissue (0.2 g) were placed in 1.5 ml microfuge tubes and homogenized using an electrical homogenizer (Model RS541-242, RS Components, Corby, UK) ( Golestan et al., 2010). Then homogenates tested for PGE 2 using a high sensitivity PGE 2 Chemiluminescence Enzyme Immunoassay (CEI) Kit (Assay Designs Inc., MI, USA) and NO metabolites with the Griess Micro Assay ( Nahrevanian et al., 2009).
Histopathological study
Statistical analysis
Data showed as Mean ± SE. Differences between two groups compared paired and unpaired t-test; more than two data series was compared with one way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s Test. P<0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
RESULTS
There were significantly differences in serum corticostrone between control group with Phy and Psy groups (237.7 ± 7.2, 435.2 ± 8.6 and 417. 4 ± 8.9 ng/ml, respectively, p<0.001). Also, serum corticostrone level was significantly more in other groups compared to control (p<0.001).
Effects of Leptin on physical and psychological stress-induced ulcer of gastric tissue
The number, score and index of ulcers were significantly decreased in response to Leptin together physical and psychological stress in comparison with Phy and Psy groups alone (p<0.05). Also, they were significantly increased in response to L-NAME and Indomethacin administration in comparison with Phy+Leptin and Psy+Leptin groups (p<0.05) (Table 1).
Effects of Leptin on physical and psychological stress-induced basal and stimulated gastric acid secretion
Basal and stimulated acid secretion were significantly decreased in response to Leptin+ physical/psychological stress in comparison with Phy and Psy groups alone (p<0.05). Also, they were significantly increased in response to L-NAME and Indomethacin administration before Leptin compared to Phy+Leptin and Psy+Leptin groups (p<0.05) (Table 2).
Effects of Leptin on NO metabolites level of gastric tissue
Our findings showed that the levels of NO metabolites of gastric tissue in Phy and Psy groups were significantly lower than control (p<0.05), but it was significantly increased by using Leptin (p<0.05). Also, NO metabolites level was significantly decreased in response to L-NAME in Phy+Leptin+L-NAME and Psy+Leptin+L-NAME groups compared to Phy+Leptin and Psy+Leptin groups, respectively (p<0.05) (Table 2).
Table1. Effects of Leptin on ulcer scoring due to physical and psychological stress of gastric tissue
|
Parameters Groups |
Number of ulcers |
Ulcer score |
Ulcer index |
Ulcer inhibition % |
|
Control |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
Phy |
4.2 ± 0.5 |
2.8 ± 0.3 |
17 ± 2.4 |
- |
|
Psy |
4 ± 0.6 |
2.6 ± 0.3 |
16.6 ± 2.2 |
- |
|
Phy+Leptin |
*1.6 ± 0.4 |
*0.9 ± 0.4 |
*7.5 ± 0.8 |
*55.9 |
|
Psy+Leptin |
#1.4 ± 0.3 |
#0.8 ± 0.3 |
#7.2 ± 2.7 |
#56.6 |
|
L-NAME+Leptin+Phy |
$3.8 ± 0.5 |
$2.4 ± 0.3 |
$16.2 ± 2.0 |
$4.8 |
|
L-NAME+Leptin+Psy |
†3.6 ± 0.5 |
†2.2 ± 0.4 |
†15.8 ± 2.1 |
†4.6 |
|
Indo+Leptin+Phy |
$3.9 ± 0.5 |
$2.6 ± 0.4 |
$16.5 ± 1.9 |
$3.5 |
|
Indo+Leptin+Psy |
†3.8 ± 0.4 |
†2.4 ± 0.3 |
†15.2 ± 2 |
†8.0 |
Data were expressed as mean±SE. n=6, *p<0.05 compared to Phy group, #p<0.05 compared to Psy group, $p<0.05 compared to Leptin+Phy group, †p<0.05 compared to Leptin+Psy group. Phy =
Physical stress group, Psy = Psychological stress group and Indo = Indomethacin.
Table2. Effects of Leptin on acid secretion, gastric tissue’s NO metabolite and PG E 2 levels due to physical and psychological stress-induced
|
Parameters Groups |
Basal acid output (mM/ml/15min) |
Stimulated acid output (mM/ml/15min) |
NO metabolite level (μM/g .wet weight tissue) |
PG E 2 level of gastric tissue (pg/mg) |
|
Control |
0.42 ± 0.02 |
0.84 ± 0.04 |
45.30± 0.82 |
118.3 ± 0.5 |
|
Phy |
*1.88 ± 0.3 |
*3.2 ± 0.3 |
*19.5 ± 4.4 |
*72.6 ± 1.1 |
|
Psy |
*1.9 ± 0.3 |
*3.3 ± 0.3 |
*21.7 ± 4.7 |
*83.7 ± 1.6 |
|
Phy+Leptin |
#0.4 ± 0.02 |
#0.8 ± 0.04 |
#42.7 ± 1 |
#117.1 ± 0.4 |
|
Psy+Leptin |
$0.38 ± 0.02 |
$0.78 ± 0.03 |
$45.2 ± 0.6 |
$117.4 ± 0.7 |
|
L-NAME+Leptin+Phy |
†1.03 ± 0.2 |
†2.2 ± 0.2 |
†15.8 ± 3.4 |
†115.5± 1 |
|
L-NAME+Leptin+Psy |
‡1.02 ± 0.2 |
‡2. 4 ± 0.2 |
‡18.6 ± 4 |
‡117 ± 0.5 |
|
Indo+Leptin+Phy |
†1.78 ± 0.3 |
†3 ± 0.3 |
†42.7 ± 1.1 |
†71.3± 0.5 |
|
Indo+Leptin+Psy |
‡1.8 ± 0.2 |
‡3.2 ± 0.3 |
‡45.8 ± 1 |
‡80.2 ± 0.5 |
Data were expressed as mean±SE. n=6, *p<0.05 compared to control group, #p<0.05 compared to Phy group, $p<0.05 compared to Phs group, †p<0.05 compared to Leptin+Phy group, ‡p<0.05 compared to Leptin+Phs group, Phy = Physical stress group. Psy = Psychological stress group and Indo = Indomethacin.
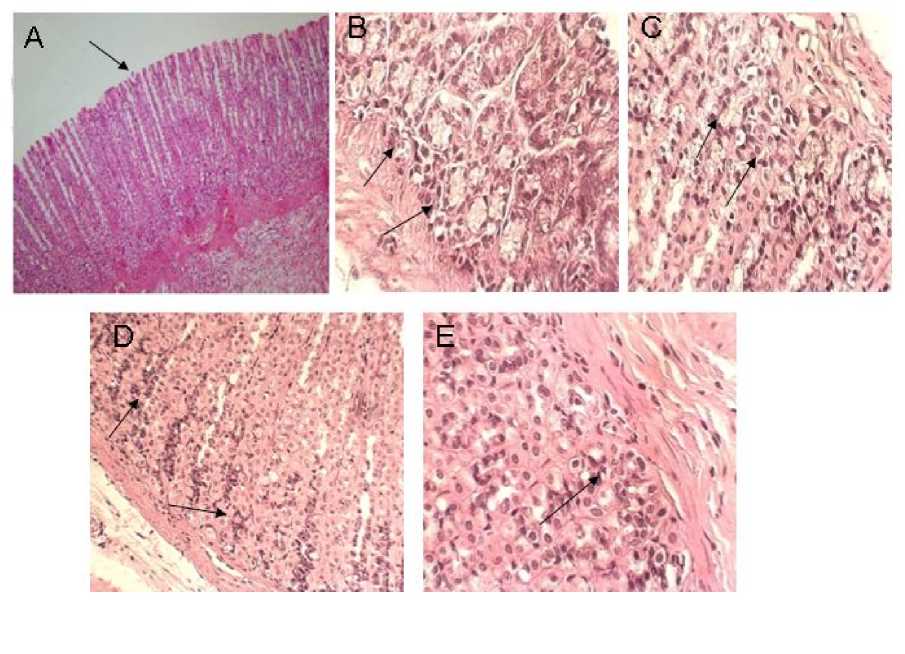
Figure1. Histological feature of gastric tissue due to physiology and psychological stress, Leptin, L-NAME and Indomethacin
A: Normal gastric mucosal (H & E staining, X100), B: Gastric mucosal ulcer due to physiology and psychological stress (H & E staining, X400), C: Healing gastric ulcer due to stresses using Leptin (H & E staining, X400), D and E: Impairing of gastric ulcer healing due to L-NAME and Indomethacin administration, respectively (H & E staining, X400); area of destruction parietal cell, decrease of oxyntic glands and also ulcers in the gastric tissue were detected.
Effects of Leptin on PGE2 level of gastric tissue
PGE 2 level of gastric tissue in Phy and Psy groups were significantly lower than control (p<0.05), but it was significantly increased by using Leptin (p<0.05). Also, PGE 2 level of gastric tissue was significantly decreased in response to Indomethacin in Phy+Leptin+Indo and Psy+Leptin+Indo groups compared to Phy+Leptin and Psy+Leptin groups, respectively (p<0.05) (Table 2).
Effects of Leptin with physical and psychological stress on histopathology of gastric tissue
Unlike Phy and Psy groups together Leptin and control, areas of destruction parietal cell, decrease of oxyntic cells and also ulcer in the stomach tissue were detected in Phy and Psy groups alone or in groups together L-NAME and Indomethacin (Fig. 1A-E).
DISCUSSION
This study has been carried out to investigate the therapeutic effects of Leptin on physical and psychological stress-induced gastric ulcer in rats, and the role of NO and PGE 2 in association with Leptin efficacy. We presented a significant difference in gastric ulcer index, gastric acid secretion, and gastric tissues NO metabolites and PGE 2 in stress groups than control. Using Leptin restored these changes. The protective effects of Leptin on stress-induced gastric ulcer can be abolished by L-NAME and Indomethacin as NO and PGE 2 inhibitors respectively. These findings emphasized the NO and PGE 2 involvement in the protective effects of Leptin in stress-induced gastric ulcer.
The physical and psychological stress exposure has been introduced as a model for induction of gastric ulcer. Stress has been a major antecedent in the pathogenesis of gastric ulcer (Ogiwara et al.,
1995). In this study, both physical and psychological stress elevated basal and stimulated gastric acid secretion, but a significant decrease was seen in stress +Leptin groups in comparison with only stress groups. The stress created remarkable gastric macroscopic and microscopic mucosal injuries. The lesions were long, hemorrhagic and glandular confined (Fig. 1C). Treatment with Leptin could reduce the ulcer index and promote gastric healing in phy+ Leptin and psy + Leptin groups (Table 1) (Fig. 1B).
It was showed that physical and psychological stress exposure increased gastric acid secretion that may be caused via activation of the vagus nerve (Shiriaishi et al., 1987). Shiraishi et al. have indicated neurons that are located in the lateral hypothalamic areas, and the paraventricular nucleus to affect gastric acid secretion ( Shiriaishi et al., 1987). Although ulcer etiology is idiopathic in most cases, it is generally accepted that an imbalance between acid production and mucosal integrity would be a causative factor (Vincent et al., 2002). Focal hyperemia, submucosal hemorrhage and circulatory disturbances seen followed by stress may be a clue of this imbalance manifestations acting via several gastric mechanisms.
In our study, NO metabolites of gastric tissue were significantly high in Leptin group than only stress groups; however it decreased by L-NAME in stress+Leptin groups. Several studies have demonstrated the importance of endogenous NO in the protection of gastric mucosa (Kim et al., 1998; Shiriaishi et al., 1987; Whittle et al., 1990). It is showed that about 50% of the nerves in the enteric nervous system contain nNOS (Dijkstra et al., 2004) and rat parietal cells are responsible for its expression. Also, endothelial NO plays an important role in the modulation of gastric mucosal integrity by interacting with sensory neuropeptides (Whittle et al., 1990; Tanaka et al., 2001). These findings suggest that endogenous NO may participate in the regulation of gastric secretion via an intracellular signaling (Dijkstra et al., 2004). In the present study, stresses significantly reduced gastric tissues NO together with increased mucosal injury compared to control group. These findings are in accordance with Trip and Tepperman study in which they reported decreased NO biosynthesis along with mucosal damage (Tripp et al., 1995). In the present study, it is assumed that NO release followed by Leptin administration can increase basal and stimulated vagus nerve tone and augment acetylcholine effects on gastric muscular cells. It has also been showed that NO can presynaptically facilitate vagal neurotransmission which ultimately leads to presynaptic L-type Ca+2 channels phosphorylation. This pathway causes increased presynaptic calcium influx and vesicular acetylcholine release (Herring et al., 2001).
In addition in our study, PGE2 level of gastric tissue was significantly high in Leptin groups than only stress groups, and it declined by addition of Indomethacin in stress+Leptin groups. These findings showed that Leptin may cause PGE2 induction. Several studies have demonstrated the importance of PGE2 in the protection of gastric mucosa and NSAID-induced gastropathy is an intricate process involving gastric mucus depletion, increased microvascular permeability, NO imbalance, as well as free radical production (Abdallah et al., 2010). But, it is indicated that Indomethacin at a low dose (< 5 mg/kg) did not cause any damage in both the stomach and small intestine, despite inhibiting PG production (Konaka et al., 1999). Adeymi et al. reported that Leptin prevention ability in rats when their gastric mucosa was exposed to ulcer inducing Indomethacin (Adeymi et al., 2005; Bastaki et al., 2004). Also, the vasodilatory function of PGE2 may cause increase blood flow and contributes to tissue repair (Bastaki et al., 2004). So, Leptin ulcer healing ability was decreased at result a lower tissue concentration of PGE2 that might Leptin act via activated cyclooxygenase pathway in preventing gastric ulcer and/or also Leptin stimulates mucus secretion by stimulated PGE2 that it can led to the healing of gastric ulcer. These findings thus support the results of earlier studies suggesting that the detrimental effects of Leptin gastric mucosa are associated with the NO synthesis and PGE2 generation. To our knowledge, physical and psychological stress has destructive effects on gastric epithelial layer. According to our histological findings, probably physical and psychological stresses decreased oxyntic cell and destruction parietal cell resulted in the increase gastric acid secretion (Vogel et al., 1997). Although, Leptin decreased in both basal and stimulated states, Leptin application caused a recovery cell structure. It is suggested that low acid secretion is resulting Leptin action by NO and PGE2 production.
CONCLUSION
The results of this study indicated the ulcer healing ability of Leptin in gastric ulcer induced by physical and psychological stresses. Moreover, Leptin functions may involve the NO and PGE 2 pathways.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was supported by the grant of Tehran University of Medical Science.
Список литературы The effects of leptin on gastric ulcer due to physical and psychological stress: involvement of nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2
- Abdallah D.M. (2010). Nicotinamide alleviates indomethacin-induced gastric ulcers: a novel antiulcer agent. Eur J Pharmacol. 627 (1-3): 276-280.
- Adeymi E.O., Bastaki S.A., Chandranath I.S., Hasan M.Y., Fahim M., Adem A. (2005). Mechanisms of action of leptin in preventing gastric ulcer. World J Gastroenterol. 11(27): 4154-4160.
- Bado A., Levasseur S., Attoub S., Kermorgant S., Laigneau J.P., Bortoluzzi M.N., et al. (1998). The stomach is a source of leptin. Nature. 394: 790-793.
- Bastaki S.M.A, Chandranath S.I., Adem A. (2004). The role of prostaglandin E2 in thelcer preventing ability of leptin. Gut. 53(suppl 3): A77.
- Brzozowski T., Konturek P.C., Konturek S.J., Pajdo R., Duda A., Pierzchalski P., et al. (1999). Leptin gastro-protection induced by cholesystokinin or by a meal. Role of vagal and sensory nerves and nitric oxide. Eur J Pharmacol 374:263-266.
- Caso J.R., Leza J.C., Mench N.L. (2008). The effects of physical and psychological stress on the gastrointestinal tract: lessons from animal models. Curr Mol Med. 8(4): 299-312.
- Dijkstra G, Van Goor H, Jansen PL, Moshage H. (2004). Targeting nitric oxide in the gastrointestinal tract. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 5(5):529-536.
- Friedman J.M., Halaas J.L. (1998). Leptin and regulation of body weight in mammals. Nature 395: 763-770.
- Goiot H., Attoub S., Kermorgant S., Laigneau J.P., Lardeux B., Lehy T., et al. (2001). Antral mucosa expresses functional leptin receptors coupled to STAT-3 signaling, which is involved in the control of gastric secretions in the rat. Gastroenterology.121: 1417-1427.
- Golestan Jahromi M., Nabavizadeh F., Vahedian J., Nahrevanian H., Dehpour A.R., Zare-Mehrjardi A. (2010). Protective effect of ghrelin on acetaminophen-induced liver injury in rat. Peptides. 31(11): 2114-2117.
- Herring N., Paterson D.J. (2001). Nitric oxide-cGMP pathway facilitates acetylcholine release and bradycardia during vagal nerve stimulation in the guinea-pig in vitro. J Physiol. 535(2): 507-518.
- Jiang P., Chang L., Pan C.S., Qi Y.F., Tang C.S. (2005). Protective role of metallothionein in stress-induced gastric ulcer in rats. World J Gastroenterol. 11(18): 2739-2743.
- Kim H., Kim K.H. (1998). Effect of nitric oxide on hydrogen peroxide-induced damage in isolated rabbit gastric glands. Pharmacology. 57(6): 323-330.
- Kim J.J., Kim N., Lee B.H., Kang J.M., Seo P., Lim M.K., et al. (2010). Risk factors for development and recurrence of peptic ulcer disease. Korean J Gastroenterol. 56(4): 220-228.
- Konaka A., Nishijima M., Tanaka A., Kunikata T., Kato S., Takeuchi K. (1999). Nitric oxide, superoxide radicals and mast cells in pathogenesis of indomethacin-induced small intestinal lesions in rats. J Physiol Pharmacol 50(1): 25-38.
- Konturek P.C., Brzozwoski T., Sulecuva Z., Brzozowska I., Dada A., Meixner H., et al. (2001). Role of leptin in ulcer healing. Eur J pharmacol. 414: 87-97.
- Nabavizadeh F., Salimi E., Sadroleslami Z., Vahedian J. (2009). Saffron (Crocus sativus) increases gastric acid and pepsin secretions in rats: Role of nitric oxide. Afr J Pharmacy Pharmacol. 3(5): 181-184.
- Nahrevanian H., Hajihosseini R., Arjmand M., Farahmand M., Ghasemi F. (2009). Evaluation of anti-leishmanial activity by induction of nitric oxide and inhibition of prostaglandin in Balb/c mice infected with Leishmania major. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health. 40(6): 1188-1198.
- Ogawa N., Hara C., ishilkawa M. (1990). Characteristics of socio-psychological stress induced by the communication box method in mice and rats. In: Manninen O (ed.) Environmental stress. ACESn Publishing Ltd, Tampele. 417-427.
- Ogiwara T., Sato N. (1995). Stress and etiology of peptic ulcer. Nippon Naika Gakkai Zasshi 84: 868-872.
- Shiriaishi T., Simpson S. (1987). Central control of gastric acid secretion by extra leteral hypothalamic nuclei. Brain Res Bull. 18(3):309-314.
- Tanaka A., Mizoguchi H., Kunikata T., Miyazawa T., Takeuchi K. (2001). Protection by constitutively formed nitric oxide of intestinal damage induced by indomethacin in rats. J Physiol Paris. 95(1-6): 35-41.
- Tepperman B.L., Whittle B.J. (1992). Endogenous nitric oxide and sensory neuropeptides interact in the modulation of the rat gastric microcirculation. Br J Pharmacol. 105(1): 171-175.
- Tripp M.A., Tepperman B.L. (1995). Effect of nitric oxide on integrity, blood flow and cyclic GMP levels in the rat gastric mucosa: modulation by sialoadenectomy. Br J Pharmacol. 115(2): 344-348.
- Vincent P.R., Koichi I., Hizaki K., Tetsurou N., Shinichi N. and Gakuji I. (2002). Emotional stress and brux-like activity of the masseter muscle in rats. European Journal of Orthodontics. 24: 107-117.
- Vogel H.G., Vogel W.H. (1997). Drug Discovery and Evaluation-Pharmacological Assays (ed. by H.G. Vogel and W.H. Vogel). Springer, Berlin, 1997, 757 pp.
- Wallace J.L., Granger D.N. (1996). The cellular and molecular basis of gastric mucosal defense. FASEB J. 10: 731-740.
- Whittle B.J., Lopez-Belmonte J., Moncada S. (1990). Regulation of gastric mucosal integrity by endogenous nitric oxide: interactions with prostanoids and sensory neuropeptides in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 99(3): 607-611.


