The features of state and municipal management of the development of single-industry settlements in the Arctic zone of the Russian Federation
Автор: Evgeniy E. Plisetskiy, Ekaterina A. Malitskaya
Журнал: Arctic and North @arctic-and-north
Рубрика: Single-industry cities of the Russian Arctic
Статья в выпуске: 26, 2017 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The article considers the current system of management of the development of single-industry settlements in the Arctic zone of the Russian Federation, the tools of strategic and program-target management of the development of single-industry cities are analyzed which are used at the state and municipal levels, the suggestions for improving the system of management of the Arctic cities are made. This system should consider both the specific character of development of each city, and to be linked with the ongoing government policy, the interests of local authorities, business and local communities. The methodology is based on the use of search and economic-statistical methods, method of comparative analysis. The main recommendations are the formation of a strategic vision for the development of promising sectors (types of economic activities) in monotowns, introduction of program-target management in the strategic planning of complex investment plans of monotowns, and elaboration of the concept of the informational platform of investment projects in single-industry cities.
Single-industry city, the Arctic zone of the Russian Federation, the system of management of the single-industry city development, the tools of state support, strategic management
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148318604
IDR: 148318604 | УДК: 332.1 | DOI: 10.17238/issn2221-2698.2017.85
Текст научной статьи The features of state and municipal management of the development of single-industry settlements in the Arctic zone of the Russian Federation
The priorities for the development of mono-profile municipal entities and the implementation of state policy for the development of the Arctic zone today are on the agenda for all key participants of management in Russia.
Modern features and trends in the development of the Arctic mono-cities have similar features and problems inherent in most mono-profile entities in Russia, which include, among others:
At the same time, the specificity of the "northern" mono-cities of the Russian Arctic, connected with their location in regions with extreme climatic and natural conditions, leaves an imprint on the nature and area of their development, the functioning of key life support systems. For such cities, there is a need to work out special effective development models based on new investment and town-planning approaches to creating a new quality of the urban environment, finding mechanisms for keeping the resident and attracting new people, and creating a favorable investment and business environment (Figure 1).
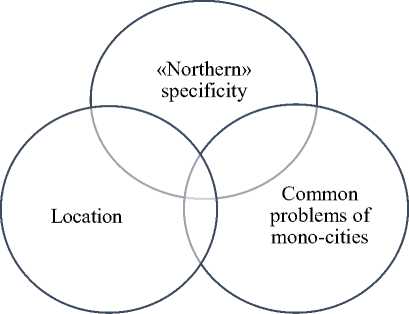
Figure 1. The paradigm of the development of the Arctic mono-cities.
There are 14 mono-cities1 in the Russian Arctic, half of which are located in the Murmansk region, 3 in the Arkhangelsk region, 2 in the Chukotka autonomous district, one in the Krasnoyarsk Territory and one in the Komi Republic [1].
Analysis of the peculiarities of the development of the Russian mono-cities of the Russian Arctic and the study of the works of the Russian scientists [2, Gerashchenko D.A.] made it possible to determine a range of actual issues, including the assessment of problems and limitations of the social and economic development of the mono-cities of the Arctic zone of the Russian Federation, which includes the following:
Limitations:
-
• unfavorable climatic conditions;
-
• limited transport accessibility;
-
• the homogeneity of the professional composition of the population and the low diversification of employment;
-
• low capitalization of territories;
-
1 E.g. Kirovsk, Onega, Revda, Kovdor, Zapoliarnyi, Monchegorsk, Novodvinsk, Olenegorsk, Beringovskii, Nikel, Severodvinsk, Norilsk, Pevek, Vorkuta (Source: Analiticheskii doklad «Monogoroda Arkticheskoi zony RF: problemy i vozmozhnosti razvitiia», IPPI, 2016)
-
• low possibility of diversification of production in the majority of mono-cities due to resource constraints;
-
• high social burden on business due to the need to implement social payments stipulated by the status of the northern territories;
-
• the need to develop specific management models for each particular mono-city.
Problems:
-
• low level of development of transport and logistics;
-
• migration outflow and low birth rate;
-
• deficiency of municipal budgets, high level of subsidy;
-
• the problem of finding investors and coordinating the financial and economic interests of investors, regions, the state and the population;
-
• poor development of the infrastructure complex, including high wear of funds, housing and communal services and social services;
-
• weak involvement of small and medium-sized business in solving key problems, inefficiency of interaction in the chain "power — business — residents — science";
-
• limited types of economic activity;
-
• lack of competence among municipal employees to accompany the implementation of complex projects and development programs;
-
• lack of unified and comprehensive methodology for monitoring social and economic development and the risks of determining competitive advantages for the subsequent adoption of effective management decisions.
It should be noted that at the level of regional governments, a whole range of activities aimed at supporting the development of single-industry cities is being implemented. One of the priority tasks that are on the agenda are modernization and increasing the profitability of the cityforming industries, improving the infrastructure of cities, creating programs for retaining the population, improving the quality of the living environment.
The problem of ineffectiveness of strategic planning documents for mono-cities
Most of the Russian Arctic mono-cities do not have worked out development strategies that define both the priorities and goals for long-term development, and link and form continuity with state policy at the regional and federal levels. In the Onega district of the Arkhangelsk region, the work is underway to develop the Strategy for the development of the Onega district until 2030 2. In the mono-cities of the Russian Arctic, there such strategic and policy documents as, for example:
-
1) Strategy of social and economic development of the municipality of the urban district "Vorkuta" for the period until 20203. Priority areas:
-
• economic development;
-
• social development;
-
• development of the municipal management system;
-
• ensuring the safety of the population.
-
2) The program of social and economic development of the municipal formation city of Norilsk until 2020. Priority areas:
-
• activation of the demographic policy;
-
• creating conditions for improving the environmental situation in the city;
-
• formation of comfortable urban environment, improvement of objects and areas of the city;
-
• modernization of urban and social infrastructure, implementation of energy saving;
-
• attraction of investments and introduction of innovations.
-
3) The program of complex development of municipal infrastructure systems of the urban settlement Revda of Levosersky district4.
The amount of financing of the Program is 1,193,078 thousand rubles, more than 50% of this sum are non-budget sources5. The schemes for heat supply, water supply and sanitation also approved in Revda.
The composition of municipal programs implemented in mono-cities (or municipal districts) also has many similar areas. For example, in the city Pevek and in the Chaun municipal district, including Pevek, municipal programs are largely socially oriented and aimed at infrastructure development (Figure 2).
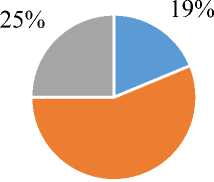
56%
-
■ Economy
-
■ Infrastructure
-
Figure 2. Structure of the approved municipal programs of the city Pevek and Chaun municipal District in the main areas of social and economic development, %
At the same time, the composition of the municipal program of the city Kirovsk covers a wider range of branches of social and economic development of the city (Figure 3).
15%
15%
■ Economy
20%
■ Infrastructure
35%
-
Figure 3. Structure of approved municipal programs of the city of Kirovsk in the main areas of social and economic
development, %
The currently implemented programs for the development of mono Orange are cities in the regions rely more on federal support measures, which account for 80% of the total project implementation costs. Nowadays most of the projects concern the solution of independent industry problems.
According to the report of the IITP, 3 of 14 arctic mono-cities had the surplus budget in 2015, and they also had a potential opportunity to invest additional funds in the development. For the most part of mono-cities, the predominance of gratuitous receipts into the budget structure is typical (Figure 4).
100%
80%
60%
40%
20%
0%
-
■ БЕЗВОЗМЕЗДНЫЕ ПОСТУПЛЕНИЯ
-
■ НАЛОГОВЫЕ И НЕНАЛОГОВЫЕ ДОХОДЫ
Figure 4. Structure of incomes of municipal entities of the Russian Arctic, according to data on the execution of budgets for 2015, %.
Orange means gratuitious receipts, and blue means taxes and other types of income.
Programs of economic orientation include both support for the development of SMEs, and the development of tourism, the implementation of the project "Salla Gate — Partnership in Business and Tourism". The city has approved programs aimed at increasing the budget efficiency, supporting of socially-oriented NGOs, and protecting the environment. There are also 10 departmental target programs, to a greater extent, in the social sphere and the development of the city's infrastructure complex.
Similar diversification of municipal programs is inherent in the city of Onega, the administrative center of the Onega municipal district of the Arkhangelsk region.
Certain problems that are typical for the Arctic monocities, are related to the quality of the development of engineering communications schemes, which not all municipalities have. Among monocities of the Russian Arctic, the following ones have approved town-planning documents, engineering communications schemes:
-
• Kirovsk (Documents of the territorial planning of the municipal entity6);
-
• Zapolyarny (Master Plan and Rules for Land Use and Development of municipal entity7);
-
• Kovdor (Heat supply scheme of the municipal entity8);
-
• Monchegorsk (Master Plan and Rules for Land Use and Development of the municipal entity9);
-
• Novodvinsk (Master Plan and Rules for Land Use and Development of the municipal entity
10 );
-
• Olenegorsk (Master Plan11);
-
• Nickel (Master Plan and Rules for Land Use and Development of the municipal entity12, supply scheme13);
-
• Severodvinsk (Master Plan and Rules for Land Use and Development of the municipal entity14);
-
• Norilsk (Master Plan and Rules for Land Use and Development of the municipal entity15);
-
• Vorkuta (Master Plan and Rules for Land Use and Development of municipal entity16).
Improving the effectiveness of municipal management
Administrations of many mono-cities, nevertheless, introduce modern practices contributing to improve the efficiency of municipal management, to involve local communities in the management process. This includes the monitoring of the quality of financial management, assessing the effectiveness of the quality of municipal management, assessing the regulatory impact, the introduction of a tool for organizing TSG, the formation of reserves of management personnel.
Interesting approach to improving the effectiveness and control of the development and implementation of municipal programs can be noted in the city of Olenegorsk. For example, the Decree of the Olenegorsk City Administration has approved the Regulations on the ProgramTarget Council of the municipal entity Olenegorsk with its subordinate territory17. The ProgramTarget Council of the municipal entity of the city of Olenegorsk with its subordinate territory, is a standing collegial advisory body formed to improve the process of forming long-term and departmental target programs of the municipal entity (hereinafter referred to as target programs), to increase the effectiveness of their implementation.
One of the priority tasks for the formation of the state policy in the development of the Arctic monocities should be the determination of the place and role of the cities in the system of resettlement and allocation of productive forces [3, Kuznetsov S.V.]. The high level of "urbanization" and low population density (high dispersion in the territory) determine the role of monocities as the main economic centers of the Arctic macroregion. One of the priority areas of the development is the formation of them as personnel, technology and service centers for the development of the Arctic territories [4, Pilyasov A.N.].
The development of the Arctic monocities as supporting economic centers of the Russian Arctic stipulates the formation of production clusters in them and the formation of an integrated approach to the development of the territory. The promising development of monocities will allow:
-
• to provide personnel potential for the development of territories for long distances by road building and creation of helicopter platforms, to provide service and repair of various technics within a zone of transport accessibility;
-
• to guarantee highly professional emergency medical care, both to the city people and residents of sparsely populated and shift camps;
-
• to create educational, scientific and production centers necessary for studying and developing the Arctic zone;
-
• to create the conditions for leisure, creative expression and various forms of social activity necessary for the full development of human potential;
-
• to create conditions for a full and comfortable residence of families with children, which significantly reduces staff turnover and improves the staff quality.
The second important task is the formation of a comfortable living environment. The leading factor in the development of the cities in this case will be the active introduction of advanced technologies in the fields of energy, transport, buildings and facilities, health and education, the development of environmentally friendly elements of the urban environment. The northern conditions necessitate the use of innovative approaches to the development of communications and urban infrastructure, increasing their wear resistance, reducing the costs of municipal funds for repairs and preventing the consequences of accidents.
The third actual task is the need to optimize and systematize existing measures of state support for monocities, including the Russian Arctic, which do not have a single methodological and substantiating basis and a clear differentiated approach to their arranging, instruments for monitoring and control of their implementation. The identified problems faced by federal executive bodies in providing state support to monocities are as follows:
-
• absence of "anchor projects", which can be realized in the given territory, i.e. for the development of which the municipal entity has corresponding competitive advantages. In some CIPs, the choice was made in favor of creating a new branch of the economy for the given territory, which is associated with the enormous costs of budgetary and extrabudgetary funds. At the same time, the municipal entity could not have a clear competitive advantage allowing to assume the unconditional success of these large projects [5, Nikiforova L.Yu.];
-
• low qualification of employees of local self-government bodies engaged in the development and implementation of instrumentation;
-
• absence of active position of local self-government bodies in the development of small business, which is the most important one in small single-industry towns;
-
• in some cases, it is impossible to establish working contacts with the town-forming enterprise;
-
• absence of scientifically grounded approaches to the allocation and classification of monoprofile municipalities for the purpose of further developing an effective state policy for their development and the formation of a system for managing the development of single-industry towns.
In these conditions, it is necessary to form a unified management system for the development of monocities, which should be clearly built and supported at the state level. The application of existing state support measures, including the possibility of establishing Priority
Social and Economic Development Area (PSEDA) in the Arctic monocities, it is necessary to structure, to select, based on the specifics of the development of the Arctic monocities, and to form a comprehensive plan (program) for their application.
The development of northern monocities will depend on the implemented investment projects and a well-thought-out system of state support measures. First, it is necessary to revise the system of selection and financing of investment projects in order to simplify them. Secondly, for monocity administrations it is necessary to develop methodological recommendations on a single list of financial and non-financial measures of state support in the line of federal executive authority and development institutions.
Managing the development of the Arctic monocities should be a coordinated and well-planned system of interactions of all levels of government, development institutions, commercial banks, business, local people.
At the level of the Government of the RF, the Federal Design Office was launched in accordance with the Resolution of the Government of the RF "On the organization of project activities in the Government of the Russian Federation" dated October 15, 2016, No. 1050, project groups were organized on priority areas of strategic development, including monocities, methodological recommendations approved for the introduction of project management in the executive branches and after the completion of the priority project (program).
In this regard, there is a need for competent use of tools and methods of project management in the implementation of major government programs in the strategic management system. The implementation of the program and project management will allow to evaluate the effectiveness of creating of the special economic zones, industrial parks, territories for priority social and economic development, and also to monitor the implementation of the passport of the priority program the Integrated development of monocities (approved by the Presidium of the Presidential Council for the Strategic Development and the Priority projects on November 30, 2011 No. 11).
Nowadays the Monocity Development Fund has been functioning since 2015, its main goal is to assist in the development of the infrastructure and diversification of monocities with the aim of stabilizing their social, demographic and economic status and attracting investments in monocities with the most difficult social and economic situation. The fund operates in singleindustry cities with the most difficult social and situation (99 monocities, according to the Government's order No. 1398-p dated July 29, 2014, including the monocities of the Russian North).
The organizational structure of the project management system for the Monocity
Development Fund is presented in Figure 5.

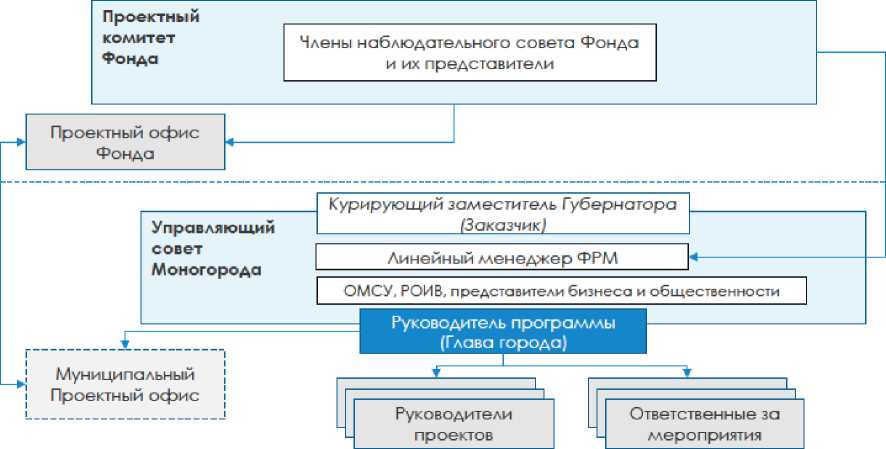
Figure 5. Organization of the project activity of the Monocity Development Fund
The specifics of the development of Arctic monocities necessitate the development of coordinated strategies and plans for their implementation, with the introduction of a program-targeted management.
In our opinion, monocity development strategy prepared by the city administration should consider the interests and prospects of the city-forming enterprise in this monocity and, thus, determine the plan for implementing the strategy based on the project management approach. According to the world practice, the cities with the highest joint interest from both the state and the city-forming enterprise turned out to be the most successful in solving the problems of the monocity. At the same time, the effectiveness of the current management policy for the development of monocities will include a set of measures aimed at supporting the creation and development of industrial parks, technoparks, innovative infrastructure and creating living conditions for monocities.
The projects for the integrated development should be worked out and implemented on the territories of monocities.
Conclusion
At the intermunicipal level, it is advisable to create a single coordinating management company (the corporation of the development of the Arctic monocities), but 100% of shares will belong to the Government of the Russian Federation, which manages the development of monocities, including:
-
• participation in the development and implementation of territorial and sectoral development strategies;
-
• development of concepts, business plans, programs for implementing of sectoral and infrastructure projects of IDT, development of investment attraction plans;
-
• initiation and structuring, the organization of economic and legal advice in the preparation of the PIDT;
-
• creation of design offices for the implementation of PIDT;
-
• monitoring of progress in the implementation of activities and projects included in the List of Activities and PIDT;
-
• forecasting and monitoring of complex social and economic development of monocities;
-
• interaction with federal executive bodies and state authorities of the Arctic subjects of the Russian Federation, key business structures on issues related to the functioning and development of monocities;
-
• providing information support to state authorities and local self-government regarding the development of monocities;
There is no one-size-fits-all approach to managing the development of monocities, as it is necessary to consider the specificity of the development of a monocity: its location, economic structure, social status and the readiness of monocity administrations to pursue a policy aimed at maintaining and implementing investment projects.
Special attention should be paid to the organization of the system of control and expenditure of budgetary funds. Due to the lack of the responsibilities of the sectoral federal executive authorities to provide information to the SASM, it is quite difficult to assess the effectiveness of financial support measures. Moreover, key indicators of the effectiveness of the implementation of state programs should be reviewed, as well as subsidies for supporting the construction of innovative infrastructure and ongoing investment projects.
The development of investment projects in monocities depends on the effectively built system of interaction between regional, municipal executive bodies, development and business institutions. And this, in turn, will in the future determine the increase in mobility of labor resources of monocities, stimulation of voluntary relocation to settlements with high potential for social and economic development and centers for economic growth.
Список литературы The features of state and municipal management of the development of single-industry settlements in the Arctic zone of the Russian Federation
- Analiticheskij doklad «Monogoroda Arkticheskoj zony RF: problemy i vozmozhnosti razvitija» [Analytical report "Monocities in the Arctic zone of the Russian Federation: problems and opportunities for development"], IPPI, 2016.
- Gerashhenko D.A. Rossijskie goroda v Arktike: novye problemy i puti ih reshenija [Russian cities in the Arctic: new challenges and solutions], Vestnik MGTU, tom 14, No. 1, 2011 g. pp. 199–205.
- Kuznecov S.V. Rol' monoprofil'nyh ekonomik v formirovanii geojekonomicheskogo prostranstva rossijskoj Arkticheskoj zony [The role of monoprofile economies in the formation of the geo-economic space of the Russian Arctic zone], Ekonomika Severo-Zapada: problemy i perspektivy razvitija, 2015, No. 3 (48), pp. 30–39.
- Piljasov A.N. Razvitie gorodov-centrov — forpostnyh baz severnogo frontira [Development of central cities — outpost bases of the northern frontier], Vestnik Severo-Vostochnogo nauchnogo centra DVO RAN, 2016, No. 1, pp. 107–118.
- Nikiforova L.Yu. Razrabotka kompleksnyh investicionnyh planov modernizacii monoprofil'nyh gorodov Arkticheskoj zony Rossijskoj Federacii [Development of integrated investment plans for the modernization of single-industry cities in the Arctic zone of the Russian Federation], Ekonomicheskoe vozrozhdenie Rossii, 2014, No. 1 (39), pp. 37–42.


