The formation of digital space at the municipal level: overview of settlements' websites
Автор: Prokopev Egor A., Kurilo Anna E., Gubina Olga V.
Журнал: Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast @volnc-esc-en
Рубрика: Development of municipal formations
Статья в выпуске: 5 (65) т.12, 2019 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The formation of digital economy and transition to electronic government impose qualitatively different demands to authorities' presence on the Internet. Local authorities are not an exception here. Due to modest financial capabilities of many municipalities, their websites, objectively, cannot match the level of federal and regional web portals. The necessity to meet modern requirements implies the search for acceptable ways to be present online. The article attempts to determine the current state of spatial distribution of municipal authorities' digital involvement on the settlement level. To achieve it, we revealed the ways of being present on the Internet, checked the availability of connections between websites of municipalities, gathered information characterizing disclosure of information about dynamics of municipal institution development, identified additional Internet communication channels, and built cartograms. The research includes 313 urban and rural settlements in the Republic of Karelia, the Arkhangelsk, Vologda, Leningrad, and Murmansk oblasts. The results of the study indicate that the digital space of this territory at the municipal level is almost completely formed and has a low degree of mutual integration of its Internet resources. It is shown that the most popular way of providing information about the settlement on the Internet - website - is not the best. It is revealed that local governments rarely use social media as an auxiliary or alternative channel of Internet communication with local residents. It is noted that the majority of settlements orientate toward practices used in settlements of their municipal district, while creating and maintaining webpages without borrowing the experience of neighboring districts and regions. The results of this study might be used for qualitative improvement of municipalities' activities conducted online and formation of e-government on regional and municipal levels.
Digital economy, electronic government, municipalities, website, settlements
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147224223
IDR: 147224223 | УДК: 332.05 | DOI: 10.15838/esc.2019.5.65.5
Текст научной статьи The formation of digital space at the municipal level: overview of settlements' websites
Modern people live in the world where information and communication technologies (ICT) enter into all aspects of their everyday life and professional activities. Without “omnipresent” and mobile internet, people, especially in large cities, will not be able to use numerous “smart” devices, which allow overcoming accelerating rates of life. According to K. Schwab [1], the world is close to the beginning of the fourth industrial revolution which will fundamentally change our life, our work, and our communication. ICT is the link element which will more successfully satisfy people’s needs and demands. Of course, government authorities understand that development of a new industrial evolution technologies and creation of necessary infrastructure is mandatory for provision of Russia’s global competitiveness. That is why authorities adopted the strategy of digitalization and digital economy building.
Current ICTs allow gathering, processing, analyzing, and keeping of large data which are necessary for making optimal management decisions. Today, large data technologies are actively used by commercial enterprises [24] and banking structures [5, 6]. The spheres of educational [7, 8] and medical services are developing [9]. The sphere of state and municipal management is no exception. This is where the use of large data can significantly improve the quality and efficiency of services [10]: for example, to manage urban traffic [11], to reduce costs of housing and communal services [12], to improve the accuracy of forecasting and modeling, to plan the construction of necessary infrastructure1. This is the reason why significant attention is paid to the development of “electronic government” (e-government). This term might be defined as the configuration of the public services system that supports the solution of administrative tasks and ensures the involvement of citizens in governance with the help of ICT [10].
Since 2008, the institutional environment of the digital economy development has been changing in our country [13, 14]. The national program “The digital economy of the Russian Federation”2 will have been finished until 2024. As the result, digital technologies and platform solutions will be as close as possible to citizens and business entities. It will help to broaden the specter of municipal services provided in electronic form and to organize smooth operation of public services that ensure the security of digital interaction. Events, stated in national project, mostly contribute to provision of medical, educational and other municipal services.
It should be noted that the development of the practice of conversing public services into electronic format [15] contributes to the unnoticed and easy (for business and population) collection of large amounts of information. In 2018, there were 3.59 million contracts, worth 6.85 billion rubles3, signed in Russia through a single information system in the area of procurement. 60 million applications4 were received through official Public Services Portal. Integration of such data with indicators, acquired by Rosstat, line ministries and services, regional and local authorities, within a single information system allows seeing Russia as a single economic space. For now, data accumulated by public municipal authorities are not fully used in analytical work [16]. In this regard, there is still a lot of work to be done in the field of creating various public information systems and their “seamless” integration.
Nowadays, e-government is viewed as the way of increasing availability, transparency, openness, and quality of services provided to people by public and municipal authorities, although it was initially intended to be used as the way of reducing costs. The following examples are given in the work of Munoz-Canavate and Hipola [17] which show the advantage of electronic services: in Canada, it was calculated that the provision of one service after citizen’s personal appeal costs 44 Canadian dollars, by mail – 38 dollars, by phone – 8 dollars, by the Internet – less than 1 dollar. In the justification of “i2010 Initiative” given by the European Commission, it was stated that implementation of electronic administration across the European Union will cut costs by 50 billion euros. At the same time, it should be noted that this process also leads to the necessity of providing funding for equipment purchase, special software development and its technical support, fulfilling legislative personal data protection requirements, personnel training [18].
There are attempts to calculate similar and more complex indices for our country on the regional level [20]. However, it is impossible to organize e-government without including municipalities, because this is the level where authorities best understand people’s needs.
Taking into account problems of municipal institution’s budgets formation, it is possible to ask: are Russian municipal authorities ready for digital economy?
To answer this question, we need to assess launch context of e-government on the level of settlements’ administration. There were the following indicators in Spain: 1) computers and communication’s costs in different administrative bodies; 2) the percentage of computers with access to the Internet and intranet; 3) the list of current services that the administration provides through its sites [17]. It is impossible to apply these indicators for out study because two groups are not included in official free-access statistics databases and, unlike many countries [21–23], the most part of popular services are provided through “Public Services Portal” in Russia, not through settlements’ websites. On the other hand, the availability of the settlement’s website, its content, and update frequency is, in a way, an indicator showing the level of ICT development, local administrations’ attention to the sphere, and their financial capabilities. According to these ideas, we chose websites of urban and rural settlements as the object of our research.
Settlement’s website is its face in the global electronic world. It becomes the primary source of information for many people and companies interested in this specific settlement [23]. Settlement’s website is included in the category of public portals which function is provision of information and universal public services to local residents, foreign investors, and travelers [24]. In Russia, the websites of urban and rural settlements perform a purely informational function, which includes ensuring the availability of information about local authorities’ actions. According to national law, there is no requirement of having own website.
Nevertheless, it is important and modern way of informational transparency and authorities’ maximum publicity implementation [25– 27]. It is not advised to completely ignore the possibilities of using it.
The purpose of the research is to define a current state of spatial distribution of municipal authorities’ digital involvement on the settlement level. Despite the importance of creating a single digital space in Russia, which concerns the implementation of ICTs in local governments’ work and necessity of their presence on the Internet, very few Russian scholars studied this topic on the example if municipal institutions’ websites. They paid special attention to websites of municipal regions [26–31] or cities [32, 33]. Foreign scholars primarily study large municipalities [34–37], because they have financial resources to develop complex websites, to offer a great number of services, and keep more qualified personnel. Residents of urban territories are more likely to demand advanced Internetservices and infrastructure than people of rural areas [22], that is why foreign scholars prefer studying cities’ websites [21, 22, 38, 39], and they choose settlements with more than 20 thousand people population.
This approach excludes small settlements from the research and avoids the problem of “digital inequality”, which is mostly acute for rural areas[40]. It does not allow seeing all the territory as a single digital space, which keeps mutual integration of the Internet-resources as one of the most important “pillars” [41].
Unlike these studies, our methodology includes a continuous coverage of municipal regions, urban and rural settlements’ websites in the studied area, which is not limited to one region. It also includes adjacent municipal areas of neighboring RF subjects. It allows identifying settlements which do not have their own Internet-resources, showing connections between official websites of municipal institutions, and present the existing practice of providing information about settlement in the Internet and experience exchange between municipalities. The latter is greatly important for small settlements, because, due to the lack of financial and human resources, they need to look for acceptable ways of being present in the Internet. It predetermines practical importance of the study.
Data and methods
The research included 313 settlements from 41 municipal region and urban districts of the Republic of Karelia7, the Arkhangelsk, Vologda, Leningrad, and Murmansk oblasts. In addition to the municipal districts of the neighboring regions adjacent to the border of the Republic of Karelia, the neighboring municipal districts of the Arkhangelsk, Vologda, and Leningrad oblasts were analyzed. The algorithm of the conducted work included the following stages: 1) determination of the method of providing information about the settlement on the Internet; 2) analysis of mutual integration of Internet resources; 3) search of information about the dynamics of the settlement development on the official website; 4) identification of additional channels of Internet communication used by the settlement’s administration; 5) collection of information about the developer of the website; 6) construction of cartograms.
First of all, with the help of municipal regions’ websites and search systems, we determined each settlement’s method of presenting the information on the Internet: 1) own website; 2) website based on the website of the municipal district (second-level domain); 3) page on the website of the municipal district; 4) information is not provided.
Then we analyzed mutual integration of selected Internet-resources. It is quite easy to check connections between Internet-resources: we needed to find external links to other websites on the analyzed website and to check its correct updating in case of changes in the email address of the external website [42]. Websites of municipal region and entity should be interconnected by links. For example, you should have an opportunity to go to the website of the RF municipal region and entity from the settlement’s website, and the website of municipal region should have links to websites of all settlements and RF entity included in it. Presence or absence of such “transitions” shows the attitude of local authorities toward to issues of its Internet-resources integration. For each independent settlement’s website (method 1), we defined the presence of links to websites of its municipal district and the RF entity subject8. The website of the municipal district had links to the settlement’s website. We considered a link to be missing if we had found broken or incorrect link.
In addition to ranking settlements by the way they provide information about themselves on the Internet and determining the links between resources, it was decided to collect additional information characterizing the disclosure of data concerning the dynamics of settlement’s development and the use of additional Internet communication channels.
Public speeches and reports on the results of municipal institution head’s work, or reports on socio-economic development of municipal institution, available for free access, may represent dynamic of settlement’s development. The choice of these documents is caused by the following ideas: 1) availability of statistical information on different spheres of work; 2) they contain settlement’s most relevant problems and significant events; 3) they are interesting for settlement’s citizens foreign investors; 4) there is no requirement to publish them on the website. We cannot ignore the timeliness of uploaded data. Since the data collection from settlements’ websites was carried out in January of 2019, we took into account only reports and presentations for 20179. Earlier reports and presentations were not analyzed due to their low relevance.
Also, we reviewed social networks as additional channels of the Internet-communication [34, 38]. We checked whether settlements had official groups on social networks. We considered them “official” if settlements’ websites, or settlement’s pages on the municipal region’s website, had a link to this group [34].
It is obvious that this information, offered for collection, is not sufficient for a comprehensive assessment of municipalities’ websites [27, 30], but it can also be used to assess the pages of settlements on the sites of municipal districts. At the same time, the search for specific documents on the website of the settlement allows you to see the variety of approaches applied to the placement of information and to assess the easiness of using the resource itself.
The emphasis on interregional borders allows answering the questions: do authorities of “border” municipal institutions look at practices adopted within the region, or do they adopt the experience of neighboring regions? The very placement of information on the Internet, where borders and barriers are almost absent, allows many people to see it, including those who need to solve a similar problem. In this sense, the experience of neighboring municipalities is always available: it is possible to assess it from the outside, and to ask people, who conducted this work, about the convenience of the selected placement option, prices, implementation period, developer’s characteristics, service quality, existence of problems, etc. Therefore, we additionally collected information about the name of the developer in settlements with its own website (method 1). In addition to development companies, website constructors were taken into account. Its usage by local authorities shows their desire to create a website at minimal cost.
Cartograms were built on the basis of the collected data in the geographic information system QGIS 3.4 Madeira. We used vector maps as the cartographic basis with administrative regions’ borders from the service NextGIS.
Results
The most popular way of providing official information about a settlement is an own website: 214 out of 313 settlements have it. The second most popular way is a page on the website of a municipal district (80 settlements). 13 settlements use websites made on the basis of municipal district’s website: this way of providing information is used only in the Leningrad and Arkhangelsk oblasts. There are also 6 settlements in these regions which do not provide information according to one of the above-mentioned ways (Fig. 1) .
Figure 1. Ways of presenting official information about the settlement on the Internet
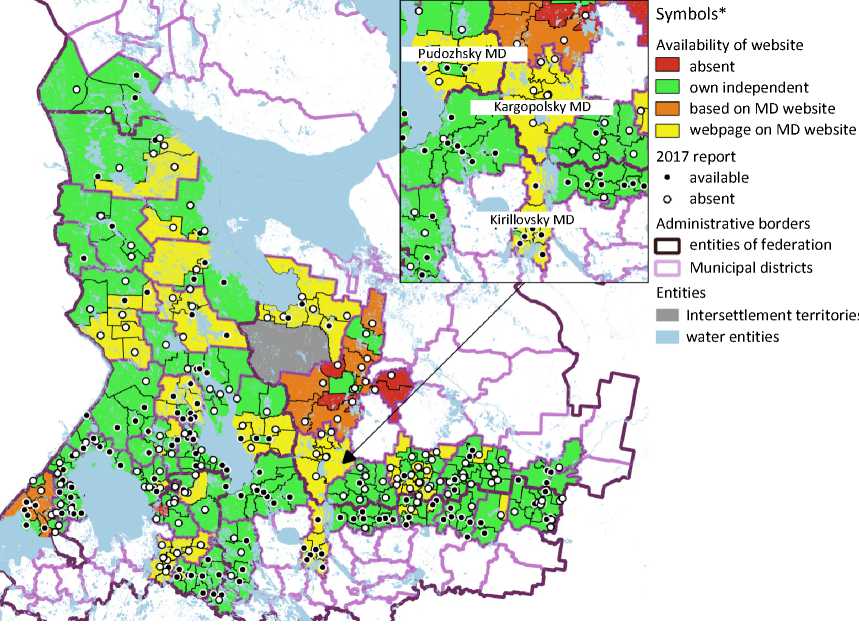
Pudozhsky MD
Kargopolsky MD
Kirillovsky MD
2017 report available о absent
Availability of website □ absent own independent based on MD website webpage on MD website
Symbols*
Administrative borders
□ entities of federation
^Q Municipal districts
Entities
■ Intersettlement territ ■ water entities
* MD – municipal district Source: own compilation.
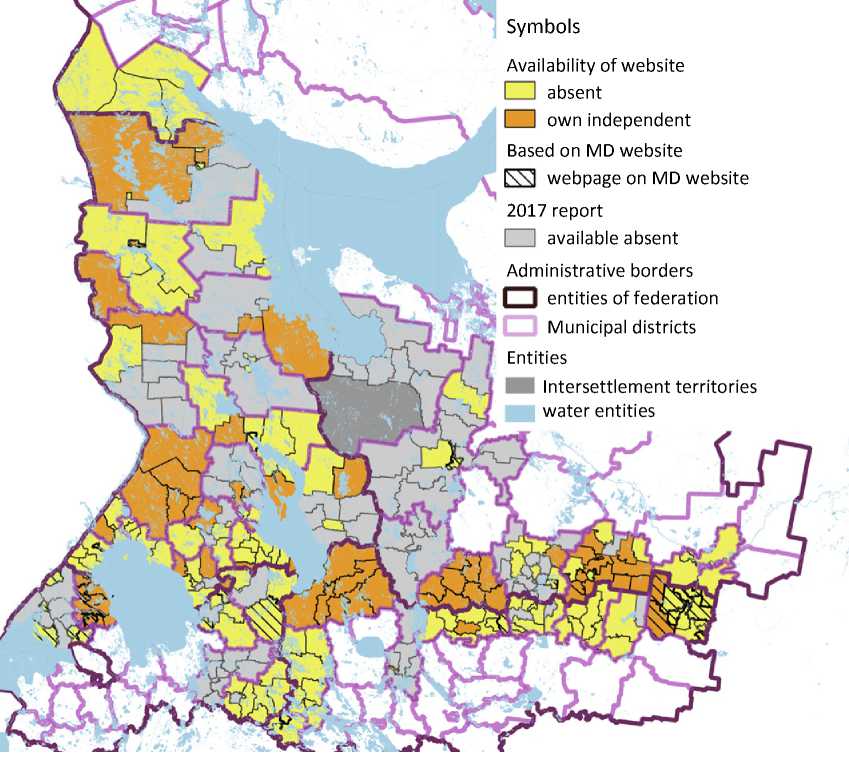
Figure 2. Interconnections between websites of settlements and municipal districts
Symbols
Availability of website absent own independent
Based on MD website webpage on MD website
2017 report available absent
Administrative borders entities of federation
Municipal districts
Entities
Intersettlement territories water entities
Source: own compilation.
Two settlements in the Leningrad Oblast completely (Vyborg) and partially (Priozersk) transferred powers of the administration to the municipal district: this is the reason of absence of information there. Four settlements of Plesetsky Municipal District, situated in the Arkhangelsk Oblast, had only contact details of administrations’ heads, which was not enough to include these municipalities in the group of settlements with a page on the municipal district’s website.
The analysis of the degree of municipalities’ websites integration shows absence of links for transition from settlement’s own website to the municipality’s website in 85% of cases. The situation is slightly better in case of links to regional government Internet-portals: 92 out of 214 settlements’ websites have this link. At the same time, it is possible to access 2/3 of settlements’ websites by clicking on the links given on municipal districts’ websites (Fig. 2). Some of the studied web-resources had broken links leading to old versions of settlements and districts’ websites. However, there is an example of broader integration between resources: website of Vinnitskoe rural settlement situated in Podporozhsky District of the Leningrad Oblast has links to Internet-resources of other settlements of this municipal district10.
Reports on the results of socio-economic development for 2017 (often these data are included in the report on the results of the work of the settlement’s head) are available on the Internet-resources of 141, out of 313, studied settlements. If we add reports for earlier years, this number will be 216. It is impossible to ignore difficulties of searching and gathering necessary documents. First of all, they can be found on different sections of the website: “Documents”; “Texts of speeches”; “Reports”; “Administration”; “Head of the Settlement”; “News”; “Decisions of the Council”, etc. Another problem – inconvenient navigation: you need to scroll through too many pages to find the right one11.
Besides, these reports can be attached as supplementary material to the decision of the settlement’s council on the report of the head: often the name of the file contains only the date and number of the decision. It should be noted that in a number of settlements, where there are no reports, only the decisions of the council are published on the website.
Local authorities barely use social services: links to groups in the social media “VKontakte”12
are given only on 15 settlements’ websites; 11 of them are included in Velsky District of the Arkhangelsk Oblast. Taking into account the fact that information about 9 out of 11 settlements is presented very concisely only on the page of Velsky District, we can point out that a group in “VKontakte” is a free alternative to an official website for informing residents about current events and announcements13.
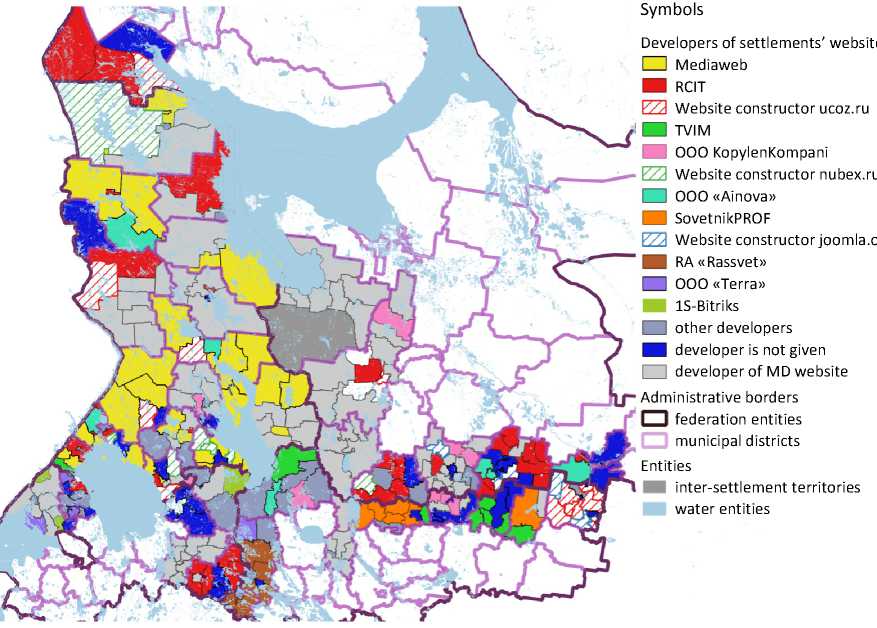
The collection of data about websites’ development companies showed that local governments used the services of 29 different companies and 6 different website constructors. 43 websites did not have information about the developer. Figure 3 presents the most common developers14.
The most popular developers are “Mediaweb” and “RCIT” (34 and 33 websites, respectively). The first company is situated in Petrozavodsk and develops wide-range area websites only in the Republic of Karelia. The second company specializes in developing website of municipal institutions, and it works across all the country. Most of the developers, marked on the map, specialize in creating websites for government institutions and are registered in other regions of the Russian Federation. The cost of their services starts at 20 thousand rubles.
Comparison of settlements’ websites showed that “border” settlements primarily take into account experiences of settlement from there area while choosing a website developer. It is interesting to look at border settlements in Pudozhsky, Kargopolsky, and Kirillovsky districts (Fig. 1): most of these settlements
Figure 3. The geography of developing companies
Symbols
Developers of settlements’ websi Mediaweb
■ RCIT
■ TVIM
□ OOO KopylenKompani
Website constructor nubex.r
OOO «Ainova»
□ SovetnikPROF
Website constructor joomla.
■ RA «Rassvet»
OOO «Terra»
■ 1S-Bitriks
□ other developers
■ developer is not given developer of MD website
Administrative borders □ federation entities □ municipal districts
Entities
■ inter-settlement territories ■ water entities
Source: own compilation.
do not have websites, but all the necessary information is given on districts’ websites15. At the same time, settlements in neighboring municipal districts have their own websites or websites based on district’s Internet-portal.
Discussion
There are practically no settlements left in the studied territory that are not represented on the Internet. Many of them have their own websites, which allows us to say that there are favorable starting conditions for e-government development (one of key elements of digital economy) at the municipal level. However, having processed the information about settlements, which is given on settlements’ own websites and on municipal districts’ websites, we see that this work is considered perfunctory by many municipalities: the information is usually poorly structured, it is not updated, and several sections of websites remain empty. Possibly, this problem is connected to lack of technical specialists due to insufficient funding and absence of administrative employees’ necessary competences. It needs to be mentioned that maintenance of websites is not one of municipal authorities’ priorities. That’s why its development is residual for them, and it is conducted only to comply with formal requirements.
It causes the problem of weak integration between municipal Internet-resources which interferes with formation of a single digital space. The situation with links from settlements’ independent websites to districts’ websites proves it. It is not mandatory according to formal requirements, but, in our opinion, these links should be present due to logic of public management. Another practical aspect of this problem’s solution is improvement of settlement’s identification by website’s users (for example, tourists, investors): quite often it does not contain district’s name; even a name of a region is sometimes absent. It is especially relevant in case of coincidences of settlements’ names: in studied regions we found 24 of such coincidences. The most common (8 times) name of a settlement is Nikolskoye: we found four such settlements in the Vologda Oblast, two – in the Arkhangelsk and Leningrad oblasts.
The question concerning the best way to provide information about settlement on the Internet (especially, rural) also remains debatable. The acquired results show that own website is not the best option. In domestic and foreign works [23, 30] availability of independent municipality’s website is called “an advantage”, because, due to having first level domain name, it is better indexed in searching systems, and, therefore, and easier to find the necessary information about the settlement. Besides, direct access to a website ensures rapid loading of the necessary information. On the other hand, settlement pays for creation of own website, hosting, maintenance service, and web-administrator’s wages.
Making a choice in favor of own website while having limited finances, settlement’s authorities will prefer sticking to cheapest options: standard website or usage of website’s constructor. The first one will, probably, have more or less clear structure [21] and basic functions not including local specifics. The second variant allows creating more unique product with ill-conceived navigation and incorrectly working elements16. At the same time, even the first option does not guarantee fulfillment of all obligations from developing company concerning above-mentioned shortcomings and resource placement17.
At the same time, we should not forget that function of a RF municipal institution’s website is strictly informational. Taking into account the fact that the average number of district’s settlements in our sample is 4 (median - 7), creation of websites to ensure information openness in a typical area might cost more than 100 thousand rubles18. In this case, in our opinion, the most rational form of providing settlement’s information on the Internet is a webpage on the website of municipal district. Experience of Italian peripheral areas, concerning introduction of e-government, shows that only joint efforts of small municipalities and concentration of their resources allow achieving the required level of service quality through economy of scale [18]. Instead of spending 100 thousand rubles on each settlement’s website, it is possible to create well-working Internetportal of a municipal district, which will make it possible to create settlements’ websites in the same design [29] and place all important settlements’ information in corresponding and structured sections. Obviously, cost of service and maintenance of one web-resource will be much lower.
-
16 A typical case when the free trial period of the addin, which provides the version of the website for the visually impaired people, has ended, and this feature becomes unavailable without paying a subscription fee.
-
17 For example, website of Vytegorsky District of the Vologda Oblast has a second level domain name (http:// vytegra.munrus.ru), and first level domain name (http:// munrus.ru) belongs to Ugut settlement of Surgutsky Municipal District situated in Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug.
-
18 4 settlement websites and 1 municipal district website.
It does not mean that settlement’s authorities must completely abandon work on informing population through the Internet by giving it to district’s authorities. They still have to collect all official documents which will be uploaded on district’s website: settlement’s budget; information on income; resolutions and orders of settlement’s administration; decisions of the settlement’s council, etc. In addition to the settlement’s page on the district’ s web-resource, a settlement group should be created in the most popular local social network, where the settlement’s authorities will distribute important information: public hearings announcements; subbotniks; litter removal; restrictions concerning ice walking; bus schedule; changes in the current legislation, etc.
Currently, municipalities rarely use social networks, although it is quite simple and understandable way of communication, especially for young people. In comparison with development and maintenance of the website, social networks are charge-free (you pay only to employees) and easy to understand.
Lack of positive experience diffusion between neighboring municipalities of the RF bordering entities is a cause for concern: social networks are not used, successful ways of information placement, as well as forms and content of reports, are not borrowed. Despite the assertion that there are no barriers on the Internet, administrative boundaries, due to lack of unified national standards in the digital information sphere, formed by municipal authorities are clearly distinguished and not blurred.
Conclusion
We may conclude that, despite all the problems, the digital space at the municipal level is almost completely formed, and it has a low degree of mutual integration of its resources. Absence of detailed national standards on presenting official information about settlements on the Internet makes current practice inefficient. At the same time, the suggested approach makes it possible to improve these efforts by finding the best practices in similar settlements outside the “home” region.
Future studies are related to a more detailed research of municipalities’ digital development and detailed analysis of municipal authorities’ websites. Better understanding of intermunicipal cooperation can assist in the formation of organization models and transformation of municipal e-government.
Despite above-mentioned restrictions, the results of this study might be used for digital policy planning and decision-making at the regional and municipal level. It might also be used for geographical analysis of digital spatial development, collection of relevant sociological information on settlements’ problems, and enhancement of ICT implementation at the level of municipal authorities.
Список литературы The formation of digital space at the municipal level: overview of settlements' websites
- Schwab K. The Fourth Industrial Revolution. Moscow: Eksmo, 2016. 138 p.
- Deursen A., Rompay T. Accepting the Internet-of-Things in our homes: The role of user skills. Telematics and Informatics, 2019, vol. 36, pp. 147-156. DOI: 10.1016/j.tele.2018.12.004
- Garin-Munoz T., Lopez R., Perez-Amaral T., Herguera I., Valarezo A. Models for individual adoption of eCommerce, eBanking and eGovernment in Spain. Telecommunications Policy, 2019, vol. 43, pp. 100-111. DOI: 10.1016/j.telpol.2018.01.002
- Tapeh A.G., Rahgozar M. A knowledge-based question answering system for B2C eCommerce. Knowledge- Based Systems, 2008, vol. 21, pp. 946-950. DOI: 10.1016/j.knosys.2008.04.005
- Rodrigues L.F., Oliveira A., Costa C. Does ease-of-use contributes to the perception of enjoyment? A case of gamification in e-banking. Computers in Human Behavior, 2016, vol. 61, pp. 114-121. DOI: 10.1016/j.chb.2016.03.015
- Soukal I., Hedvicakova M. Retail core banking services e-banking client cluster identification. Procedia Computer Science, 2011, vol. 3, pp. 1205-1210.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.procs.2010.12.195
- Rodrigues H., Almeida F., Figueiredo V., Lopes S. Tracking e-learning through published papers: A systematic review. Computers & Education, 2019, vol. 136, pp. 87-98.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.compedu.2019.03.007
- Cakmak E., Yilmaz S.M. E-learning from the Perspective of Right to Education. Procedia Social and Behavioral Sciences, 2014, vol. 116, pp. 426-430.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.01.234
- Om A. E-medicine: what it means for patients. The American Journal of Medicine, 2015, vol. 128, pp. 1268-1269.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2015.06.029
- Jun C.N., Chung C.J. Big data analysis of local government 3.0: focusing on Gyeongsangbuk-do in Korea. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 2016, vol. 110, pp. 3-12.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.techfore.2015.11.007
- Seliverstov Ya.A., Seliverstov S.A. Classification analysis of traffic flows on the graphic-analytical model of urban transport network. Zhurnal "Vestnik transporta Povolzh'ya"=Bulletin of Transport of the Volga Region, 2017, no. 6, pp. 83-97. (In Russian).
- Larionova Yu.V. The main trends of public policy in housing and communal services sphere. Nedvizhimost: economika, upravlenie=Realty: Economics, Management, 2018, no. 3, pp. 18-22. (In Russian).
- Kurilo A.E., Prokop'ev E.A. Development of digital technologies in the system of public and municipal administration. Problemy rynochnoi ekonomiki=Market Economy Problems, 2019, no. 2, pp. 35-44. 10.33051/2500-2325-2019-2-35-44. (In Russian).
- DOI: 10.33051/2500-2325-2019-2-35-44.(InRussian)
- Kurilo A.E., Prokop'ev E.A., Sachuk T.V., Ivashko E.E. Possibilities of information technologies application in the Northwestern Federal District municipal administration. Ekonomicheskii analiz: teoriya i praktika=Economic Analysis: Theory and Practice, 2018, vol. 17, no. 12 (483), pp. 1325-1339. 10.24891/ea.17.12.1325. (In Russian).
- DOI: 10.24891/ea.17.12.1325.(InRussian)
- Twizeyimana J.D., Andersson A. The public value of E-Government - a literature review. Government Information Quarterly, 2019, vol. 36, no. 2, pp. 167-178.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.giq.2019.01.001
- Gubareva T.V., Lukovnikova E.I. Features of large data new information technologies application. Problemy sotsial'no-ekonomicheskogo razvitiya Sibiri= Issues of Socio-Economic Development of Siberia, 2015, no. 2, pp. 24-31. (In Russian).
- Muñoz-Cañavate A., Hípola P. Electronic administration in Spain: From its beginnings to the present. Government Information Quarterly, 2011, vol. 28, no. 1, pp. 74-90.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.giq.2010.05.008
- Ferro E., Sorrentino M. Can intermunicipal collaboration help the diffusion of E-Government in peripheral areas? Evidence from Italy. Government Information Quarterly, 2010, vol. 27, no. 1, pp. 17-25. 10.1016/j. giq.2009.07.005
- DOI: 10.1016/j.giq.2009.07.005
- Wu J., Guo D. Measuring E-government performance of provincial government website in China with slacks- based efficiency measurement. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 2015, vol. 96, pp. 25-31.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.techfore.2015.01.007
- Stepanova V.V., Ukhanova A.V., Grigorishchin A.V., Yakhyaev D.B. Evaluating digital ecosystems in Russia's regions. Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast, 2019, vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 73-90. 10.15838/esc.2019.2.62.4. (In Russian).
- DOI: 10.15838/esc.2019.2.62.4.(InRussian)
- Feeney M.K., Brown A. Are small cities online? Content, ranking, and variation of U.S. municipal websites. Government Information Quarterly, 2017, vol. 34, no. 1, pp. 62-74.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.giq.2016.10.005
- Arduini D., Denni M., Lucchese M., Nurra A., Zanfei A. The role of technology, organization and contextual factors in the development of e-Government services: An empirical analysis on Italian Local Public Administrations. Structural Change and Economic Dynamics, 2013, vol. 27, pp. 177-189.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.strueco.2013.06.007
- Youngblood N.E., Mackiewicz J. A usability analysis of municipal government website home pages in Alabama. Government Information Quarterly, 2012, vol. 29, no. 4, pp. 582-588.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.giq.2011.12.010
- Wang F. Explaining the low utilization of government websites: using a grounded theory approach. Government Information Quarterly, 2014, vol. 31, no. 4, pp. 610-621
- DOI: 10.1016/j.giq.2014.04.004
- Vavilov N.S. Problems of e-democracy implementation on the local level. Voprosy ekonomiki i prava=Economic and Law Issues, 2015, no. 4, pp. 7-10. (In Russian).
- Gazizova L.I. Formation of municipal authorities' image in electronic mass media (on the example of the Republic of Bashkortostan). Vestnik Tomskogo gosudarstvennogo universiteta. Filosofiya. Sotsiologiya. Politologiya=Tomsk State University Journal of Philosophy, Sociology and Political Science, 2013, no. 3, pp. 37-47. (In Russian).
- Togloeva D.P. The analysis of information openness of local governments' activity in the Republic of Buryatia. Upravlenets=The Manager, 2012, no. 1-2, pp. 36-41. (In Russian).
- Sidorova A.V., Barchukova T.A. Information openness of public authorities: analysis of information and telecommunication technologies usage on the municipal level. Ekonomika. Innovatsii. Upravlenie kachestvom=Economy. Innovations. Quality management, 2017, no. 4, pp. 22-26. (In Russian).
- Kovrikova O.I., Stefanovskaya N.A. E-government as a political and communication infrastructure of municipalities. Vestnik Tambovskogo universiteta. Seriya: "Gumanitarnye nauki"=Tambov University Review. Series Humanities, 2015, no. 8. pp. 22-29. (In Russian).
- Gaisinskii I.E., Nikonenko N.D., Perova M.V. Study of some aspects of efficiency improving of municipal institutions' websites. Gosudarstvennoe i munitsipal'noe upravlenie. Uchenye zapiski SKAGS=State and Municipal Management. Scholar Notes, 2015, no. 4, pp. 75-81. (In Russian).
- Reutov E.V., Brusenskaya R.A. Mechanisms of feedback formation in regional and municipal management. Nauchnye vedomosti Belgorodskogo gosudarstvennogo universiteta. Seriya: "Istoriya. Politologiya"=Belgorod State University Scientific Bulletin. History. Politology, 2010, no. 7, pp. 222-228. (In Russian).
- Kalimullina G.D., Zhilin D.A., Tselishcheva E.F. Analysis of creating open budget on the municipal level. Goroda i mestnye soobshchestva=Cities and Local Communities, 2017, vol. 2, pp. 64-76. (In Russian).
- Pyasetskaya E.N. Information and communication processes of city management: research experience. Srednerusskii vestnik obshchestvennykh nauk=Central Russian Journal of Social Sciences, 2014, no. 6, pp. 148-154. (In Russian).
- Bonsón E., Royo S., Ratkai M. Citizens' engagement on local governments' Facebook sites. An empirical analysis: The impact of different media and content types in Western Europe. Government Information Quarterly, 2015, vol. 32, no. 1, pp. 52-62.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.giq.2014.11.001
- Galera A.N., Berjillos A., Lozano M.R., Valencia P.T. Transparency of sustainability information in local governments: English-speaking and Nordic cross-country analysis. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2014, vol. 64, pp. 495-504.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2013.07.038
- Karkin N., Janssen M. Evaluating websites from a public value perspective: A review of Turkish local government websites. International Journal of Information Management, 2014, vol. 34, no. 3, pp. 351-363. 10.1016/j. ijinfomgt.2013.11.004
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2013.11.004
- Elling S., Lentz L., de Jong M., van den Bergh H. Measuring the quality of governmental websites in a controlled versus an online setting with the "Website Evaluation Questionnaire". Government Information Quarterly, 2012, vol. 29, no. 3, pp. 383-393.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.giq.2011.11.004
- Lev-On A., Steinfeld N. Local engagement online: municipal Facebook pages as hubs of interaction. Government Information Quarterly, 2015, vol. 32, no. 3, pp. 299-307.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.giq.2015.05.007
- Cegarra-Navarro J.-G., Pachón J.R.C., Cegarra J.L.M. E-government and citizen's engagement with local affairs through e-websites: The case of Spanish municipalities. International Journal of Information Management, 2012, vol. 32, no. 5, pp. 469-478.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2012.02.008
- Sannikova T.D. Digital inequality as a negative factor for the well-being of rural population. Vestnik nauki=Bulletin of Science, 2018, no. 6, vol. 1, pp. 21-27. (In Russian).
- Fietkiewicz K.J., Mainka A., Stock W.G. eGovernment in cities of the knowledge society. An empirical investigation of Smart Cities' governmental websites. Government Information Quarterly, 2017, vol. 34, no. 1, pp. 75-83.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.giq.2016.08.003
- Papadomichelaki X., Mentzas G. e-GovQual: A multiple-item scale for assessing e-government service quality. Government Information Quarterly, 2012, vol. 29, no. 1, pp. 98-109.
- DOI: 10.1016/j.giq.2011.08.011


