The Influence of thickness on residual flexural strength of composite with low-velocity impact damages: Experimental study
Автор: Kudryavtsev O.A., Ignatova A.V., Olivenko N.A.
Статья в выпуске: 3, 2021 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Assessment of the residual strength of composite structural elements that can be subjected to low-velocity impact during operation is still a vital engineering problem. Its solution requires not only the understanding of the basic mechanisms of energy dissipation in composites but, the study of factors affecting the impact resistance of the material. The thickness is one of the main parameters that affects the mechanical behaviour of the composite at low-velocity impacts and, as a consequence, its residual strength. This paper presents the experimental study of the material thickness and impact energy influence on the residual flexural strength of woven glass fibre-reinforced plastic specimens. At the first stage of the study, low-velocity impact tests with different impact energies on GFRP plate specimens with the thickness of 2 mm, 4 mm, and 6 mm were carried out. At the second stage, the beam specimens were cut out from the plate specimens with impact damages, and three-point bending tests were carried out. The dependencies of the residual flexural strength were obtained at various impact energies for all specimen thicknesses. The sensitivity of the Flexure-After-Impact test protocol to the delamination and fibre damages in the composite specimens were assessed.
Polymer-matrix composites, glass fibre-reinforced plastic, low-velocity impact, impact damages, flexure-after-impact, residual strength
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/146282369
IDR: 146282369 | УДК: 620.171.34, | DOI: 10.15593/perm.mech/2021.3.01
Текст научной статьи The Influence of thickness on residual flexural strength of composite with low-velocity impact damages: Experimental study
ВЕСТНИК ПНИПУ. МЕХАНИКА № 3, 2021PNRPU MECHANICS BULLETIN
Low interlaminar strength and brittle nature of fracture are the main disadvantages of traditional polymer matrix composites (PMCs) that lead to the low impact resistance of structures made of these materials. Low-velocity impact (LVI) with velocities of up to 10-20 m/s is the common phenomenon in the operation of composite structures. LVI can cause not only easily detectable defects in the material but, also, barely visible impact damages (BVID), for example, delamination that significantly reduces the residual strength and service life of the entire structure [1–3]. Experimental and computational research of the mechanisms of deformation and fracture of PMCs under low-velocity impact has been conducted for more than 50 years. The scientists considered various factors that affect their impact resistance, and ways to increase the residual strength of the composite after impact as well. Hundreds of articles with the results of such studies have been published to date. Several recent articles containing fairly detailed and structured reviews on this topic should be noted [4–7].
One of the main parameters influencing the behaviour of the composite during low-velocity impact is the material thickness. In [8], the authors studied the LVI-behaviour of CFRP specimens of three thicknesses (4, 8 and 16 reinforcement layers). It was shown that the maximum impact force linearly depends on the thickness of the material, while the dependency of the absorbed energy on the thickness had a power-law character. Quaresimin et al. [9] carried out LVI tests of CFRP specimens with thicknesses of 1.25 mm and 2.40 mm. The experiments showed that the maximum contact force and load corresponding to the onset of the fracture were mainly determined by the thickness of the laminate. Similar results were obtained in [10–13] on other composites.
There are also a few studies of thickness influence on the residual composite strength at various impact energies. Shim and Yang [14] experimentally examined the effect of impact and laminate parameters on the residual mechanical properties of 1.62 mm and 3.24 mm thick CFRPs. It was found out that the residual compressive strength for both thicknesses of the composite decreased almost linearly regardless of the impactor geometry and the lay-up arrangement in the considered range of impact energies (5-14 J). In [15], the authors used the results of LVI tests of CFRP specimens with thicknesses of 2 mm, 4 mm, and 6 mm to verify numerical models that predicted LVI damages to the composite and its residual compressive strength. In contrast to the results obtained in [14], the residual compressive strength decreased nonlinearly with the increase of the impact energy. After reaching a certain threshold impact energy, the residual strength stopped changing and was equal to ~ 50% of the initial one.
In both studies, the authors used the Compression-After-Impact (CAI) protocol [16–19] to assess the residual strength of the composites. CAI protocol is the most com- mon method of assessing the residual strength of material after impact. Despite its widespread use, CAI tests have several significant disadvantages including sensitivity to clamping conditions, limitations on specimen thickness, and strength assessment under compression only [20]. Currently, alternative methods for assessing residual strength such as Flexure-After-Impact (FAI) protocol [21–26] or Tension-After-Impact (TAI) protocol [27–30] are being considered. The reason is that structures with impact damages can operate under conditions of tension and bending, and the use of only the CAI protocol will be incorrect in these cases. FAI tests are easier to implement than TAI as smaller specimens can be used, and there is no need to glue tabs. Therefore, FAI protocol is the most suitable alternative to compression testing in assessing the residual strength of a composite.
The purpose of this work was to study the influence of material thickness and impact energy on the residual flexural strength of woven GFRP experimentally. The article structure is as follows: Section 1 contains the description of the material, specimens, and test methods; results and discussion of the LVI and FAI tests are presented in Section 2.
1. Materials and Methods 1.1. Materials and specimens
In the study, an industrially produced GFRP (STEF®, PJSC «Electroizolit») was used. The composite is based on hot curing epoxy-phenol matrix and glass fabric. Three nominal thicknesses 2 mm (2.1 ± 0.05 mm), 4 mm (4.1 ± 0.1 mm) and 6 mm (6.1 ± 0.05 mm) were considered. 10, 20 and 30 layers of E-glass plain weave fabric (Fig. 1) were used as reinforcement (the composite ply thickness of 0.20-0.21 mm). The density of the composite was 1.77–1.79 g/cm3. The average volume fibres fraction was 42 % for all three thicknesses (burning method). Thus, the areal density of the glass fabric was about 180 g/m2. The elastic and strength characteristics of the material were determined during quasi-static tests on specimens with the thickness of 4 mm. A universal testing machine INSTRON 5900R with appropriate tests fixtures was used for this purpose. The obtained data are
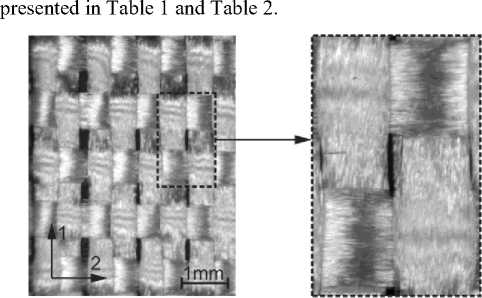
Fig. 1. Plain weave structure of the glass fabric
Table 1
Elastic properties of the GFRP
|
Young's moduli (GPa) |
Shear moduli (GPa) |
Poisson’s ratios |
||||||
|
E 1 |
E 2 |
E 3 |
G 12 |
G 13 |
G 23 |
μ 12 |
μ 13 |
μ 23 |
|
23.7±0.6 |
21.9±0.6 |
9.5±0.1 |
4.9±0.3 |
4.2±0.2 |
3.7±0.2 |
0.16 |
0.19 |
0.18 |
Table 2
Strength properties of the GFRP
|
Ultimate tensile strength (MPa) |
Ultimate compressive strength (MPa) |
|
|
F 1t |
F 2t |
F 3c |
|
403±14 |
304±10 |
480±15 |
The results of static tests showed that the tensile strength in the warp direction was higher by 30% compared to the strength in the weft direction. The discrepancy in the test results is explained by different curvature of warp and weft threads (Fig. 1).
Low-velocity impact tests were carried out on specimens with in-plane dimensions of 100×100 mm. The specimens were cut from a GFRP sheet. After drop-weight impact, the beam specimens with the dimensions of 40×100 mm were cut from the plate specimens with the warp direction aligned to the longitudinal axis of the beam (Fig. 2).
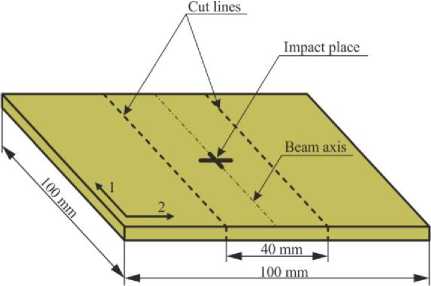
Fig. 2. Specimen cutting scheme
-
1.2. Low-velocity impact tests and Flexure-After-Impact tests
Low-velocity impact tests were performed on INSTRON CEAST 9350 drop-weight tower machine with the pneumatically operated anti-rebound system. The steel ring with the outer/inner diameters of 100/72 mm was used as a support fixture. The plate specimens were placed on the ring support without additional clamping (Fig. 3).
A cone impactor INSTRON 7529.841 with hemispherical tip (12.7 mm radius) was used in all impact tests. The impactor mass was 5.095 kg in all cases. To obtain desirable impact energy, striker velocity was varied. Three specimens per each impact energy level were tested. Table 3 contains information on the energy levels and impactor velocities in LVI tests for all specimen types. The ranges of impact energies for different thicknesses were selected during preliminary tests so that the crack length in the weft direction did not exceed half the specimen width.
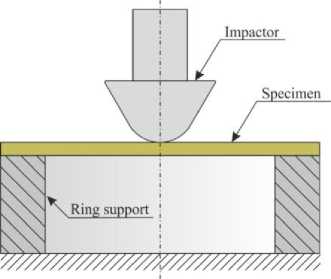
Fig. 3. Scheme of the LVI tests
Table 3
Impact energies and impactor velocities for specimens with different thickness
|
Energy level |
Impact energy (J) / impactor velocity (m/s) |
||
|
2 mm |
4 mm |
6 mm |
|
|
1 |
1 / 0.63 |
2.5 / 0.99 |
5 / 1.40 |
|
2 |
2 / 0.89 |
5 / 1.40 |
10 / 1.98 |
|
3 |
3 / 1.09 |
7.5 / 1.72 |
15 / 2.43 |
|
4 |
4 / 1.25 |
10 / 1.98 |
20 / 2.80 |
|
5 |
5 / 1.40 |
12.5 / 2.22 |
25 / 3.13 |
|
6 |
6 / 1.53 |
15 / 2.43 |
30 / 3.43 |
|
7 |
7 / 1.66 |
17.5 / 2.62 |
35 / 3.71 |
|
8 |
8 / 1.77 |
20 / 2.80 |
40 / 3.96 |
|
9 |
9 / 1.88 |
22.5 / 2.97 |
45 / 4.20 |
|
10 |
10 / 1.98 |
25 / 3.13 |
50 / 4.43 |
FAI tests of the beam specimens were carried out on the universal testing machine INSTRON 5900R using a three-point bending fixture. The span length was 40 mm, and the diameter of loading and support pins was 10 mm. Loading velocity was 5 mm/min. During the bending tests, the specimens with impact damages were positioned so that the loading pin was in the middle of the defect on the impact side.
To determine the relative residual flexural strength, bending tests of undamaged specimens were carried out with the same span length for all three thicknesses. The width of specimens was 40 mm. 10 specimens per thickness were tested. The flexural strength of specimens without defects aF0 was 529 ± 16 MPa, 551 ± 15 MPa and 573 ± 15 MPa for the specimens with thicknesses of 2 mm, 4 mm and 6 mm, respectively. The relative residual strength of the specimens after im pact was determined as to RS = ——, where aF is flexural a F 0
strength of the specimen after the impact.
2. Results and Discussion
Low-velocity impact tests showed delamination and fibre breakage to be the dominant failure mechanisms for specimens of all three thicknesses. At the same time, the ratio between the sizes of delamination and fibre breakage areas was different due to its dependency on thickness and impact energy. Fig. 4 shows the fracture patterns (backlight observation) of the specimens of three thicknesses subjected to the impact with the energy of 10 J. It can be seen that in the 2 mm thick specimen the main damage mode was fibre breakage, whereas the delamination was the result of cracks propagation. The delamination area was much higher than that of fibre breakage in the 4 mm thick specimen, whereas in the 6 mm thick specimen only delamination was observed. The central part of the 6 mm thick specimens, located directly under the impactor, was less damaged at impact energies up to 25 J. This phenomenon was not observed for the specimens of two other thicknesses.
The dependencies of the total damaged area on the impact energy for all three thicknesses are shown in Fig. 5. For all three thicknesses, there is a range where the increase of the impact energy leads to a slight change in the damaged area. The presence of this range is connected with the onset of fibre breakage in the specimens which is confirmed by the dependency of the crack length in the weft direction (breakage of warp yarns) on the impact energy (Fig. 6). The energies 3 J, 10 J, and 35 J correlated with the beginning of fibre breakage and the appearance of the cracks for specimens with thicknesses of 2 mm, 4 mm, and 6 mm, respectively.
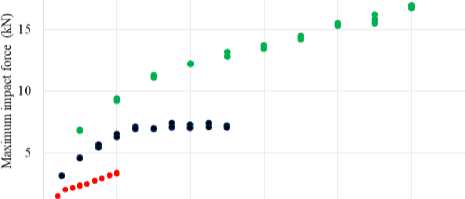
Fig. 5 shows that the appearance of the dependencies of the total damaged area vs. impact energy changed at these impact energies. The dependencies of the maximum force on the impact energy (Fig. 7) also changed their appearance at energies above 3 J and 10 J for specimens with thicknesses of 2 and 4 mm, respectively. At the same time, the dependency for 6 mm specimens did not have a noticeable change. A possible reason is the insignificant effect of short cracks on the overall stiffness of the thick specimens with intra-/interlaminar damages. The contribution of the fibre breakage zone to the total damaged area decreased with the increase of the composite thickness that was in good agreement with the data obtained in [31].
2 mm 4 mm 6 mm
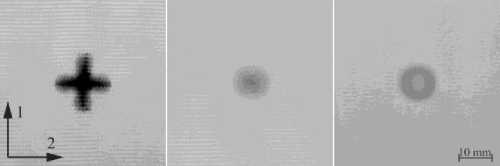
Fig. 4. Damage patterns for specimens impacted at the energy of 10 J
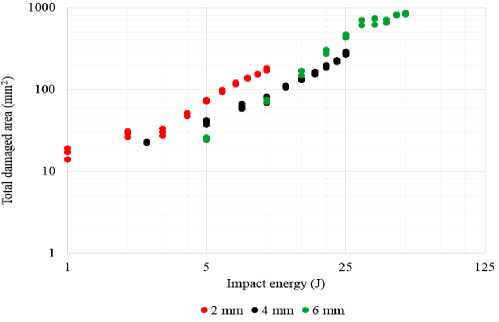
Fig. 5. Total damaged area vs. impact energy
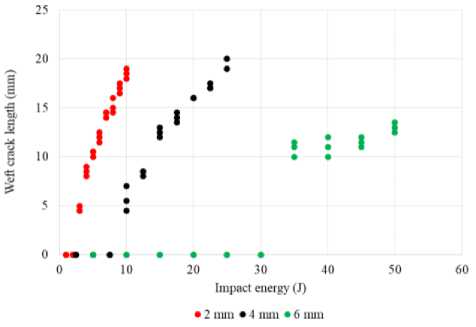
Fig. 6. Crack length in the weft direction vs. impact energy
0 10 20 30 40 50 60
Impact energy (J)
• 2mm • 4mm • 6mm
Fig. 7. Maximum impact force vs. impact energy
The dependencies of the residual flexural strength on impact energy had a similar appearance for specimens of all thicknesses (Fig. 8). A polynomial of the second degree was used to approximate the experimental points. The residual strength of the material changed within the range of the undamaged material strength (± 5–7 %) up to a certain threshold. A noticeable decrease in residual strength occurred after exceeding the threshold impact energy. Despite the similarity of the dependencies of the residual strength on the impact energy, the fracture patterns of specimens that had similar residual strength were noticeably different. Fig. 9 shows photos of the specimens with different thicknesses and with close residual strengths after low-velocity impact tests.
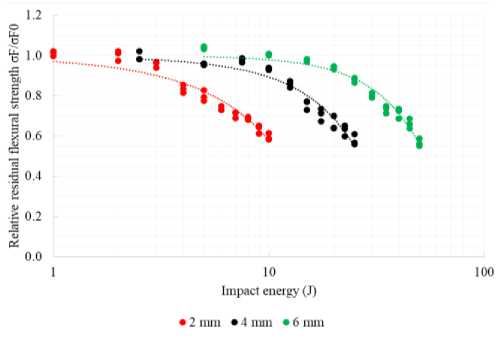
Fig. 8. Relative residual flexural strength vs. impact energy
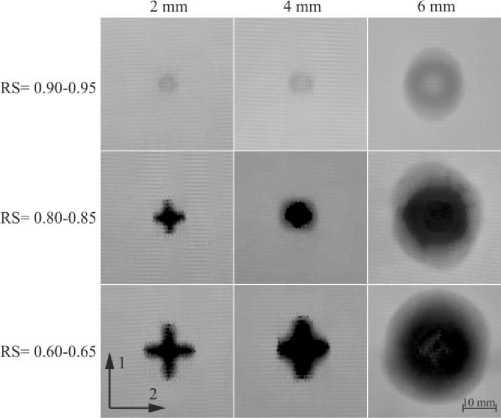
Fig. 9. Impact damages of specimens with different thicknesses
Under impacts leading to the decrease in the residual strength by 5–10 %, the dominant damage mode in the specimens with thicknesses of 2 mm and 4 mm was intralaminar matrix fracture. Delamination was the only fracture mode in 6 mm thick specimens with the same residual strength. The damaged area in 6 mm thick specimens was, on average, 7–10 times higher than in the specimens with thicknesses of 2 mm and 4 mm. Since the residual strength was the same in all cases, it can be concluded that intralaminar damages have a more significant effect on the residual flexural strength than delamination. In all cases, the decrease in the residual strength by 15– 20 % was accompanied by the fibre breakage and the formation of the weft crack with the length of 8–12 mm. Total damaged areas were significantly different in this case. Further residual strength decreasing up to 40% for the specimens with the thicknesses of 2 mm and 4 mm was associated with the formation of 18–20 mm weft cracks (a half the beam specimen width) and cruciform damaged zone. On 6 mm thick specimens, the weft crack length did not exceed 13 mm, and the size of the delamination zone was an order of magnitude larger than the size of the fibre breakage zone.
Comparison of the residual flexural strength data and the fracture patterns allows to conclude that the sensitivity of the composite residual flexural strength to the presence of delamination decreases with the increase in the thickness of the composite. For example, delamination did not lead to a significant reduce in the residual strength of 6 mm thick composite until its size did not exceed half the width of the beam specimen. It should be noted that the data obtained are valid only for the selected width of the beam specimen and span length during bending tests. It is of interest to evaluate the influence of these parameters on the FAI test results.
Conclusion
The article presents the experimental study of the material thickness and impact energy influence on the residual flexural strength of woven glass fibre-reinforced composite STEF. LVI tests of plate specimens and following FAI tests of beam specimens with impact damages were performed. For specimens with thicknesses of 2 mm, 4 mm, and 6 mm a drop in residual flexural strength of up to 60 % was recorded at impact energies of 10 J, 25 J and 50 J, respectively. Under impact energies leading to the decrease in residual strength by 5–10 %, the damaged area in 6 mm specimens was on average 7–10 times higher than in specimens with thicknesses of 2 mm and 4 mm. It was found that the contribution of various LVI fracture mechanisms to the decrease of the residual flexural strength of the specimens changes disproportionately to the thickness. Thus, significantly different fracture patterns for specimens of different thickness with close relative residual flexural strengths were observed.
It should be noted that both test methods for residual strength assessment and the requirements for the specimens should be determined on the basis of the operating conditions of a particular composite structure. FAI protocol demonstrated a high sensitivity to the presence of fibre breakage, interlaminar and intralaminar damages in the composite. At the same time, further studies are necessary to determine the permissible dimensions of the specimens (thickness and width) and test parameters (tree-point of four-point bending tests, distance between support pins) as well. This will help ensure the stability of the tests results and compare them correctly.
Acknowledgments
The reported study was funded by RFBR, project number 19-29-13007.
Список литературы The Influence of thickness on residual flexural strength of composite with low-velocity impact damages: Experimental study
- Cantwell W.J., Morton J. The impact resistance of composite materials - a review. Composites, 1991, vol. 22(5), pp. 347-362.
- Richardson M.O.W., Wisheart M.J. Review of low-velocity impact properties of composite materials. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 1996, vol. 27, pp. 1123-1131.
- Abrate S. Impact on Laminated Composite Materials. ASME. Appl. Mech. Rev., 1991, vol. 44(4), pp. 155-190.
- Hathyri F., ElkiheL B., Delaunois F. Review of damages prediction in a composite material at low velocity impact. Global Journal of Engineering and Technology Advances, 2019, vol. 1(1), pp. 027-042.
- Shah S.Z.H., Karuppanan S., Megat-Yusoff P.S.M., Sajid Z. Impact resistance and damage tolerance of fiber reinforced composites: A review. Composite Structures, 2019, vol. 217, pp. 100-121.
- Andrew J.J., Srinivasan S.M., Arockiarajan A., Dhakal H.N. Parameters influencing the impact response of fiber-reinforced polymer matrix composite materials: A critical review. Composite Structures, 2019, vol. 224, article 111007.
- González E.V., Maimí P., Sainz de Aja J.R., Cruz P., Camanho P.P. Effects of interply hybridization on the damage resistance and tolerance of composite laminates. Composite Structures, 2014, vol. 108, pp. 319-331.
- Belingardi G., Vadori R. Influence of the laminate thickness in low velocity impact behavior of composite material plate. Composite Structures, 2003, vol. 61, pp. 27-38.
- Quaresimin M., Ricotta M., Martello L., Mian S. Energy absorption in composite laminates under impact loading. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2013, vol. 44, pp. 133-140.
- Evci C. Thickness-dependent energy dissipation characteristics of laminated composites subjected to low velocity impact. Composite Structures, 2015, vol. 133, pp. 508-521.
- Mahesh V., Joladarashi S., Kulkarni S.M. Influence of laminate thickness and impactor shape on low velocity impact response of jute-epoxy composite: FE study. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2019, vol. 28, pp. 545-550.
- Wagih A., Maimí P., Blanco N., González E.V. Scaling effects of composite laminates under out-of-plane loading. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2019, vol. 116, pp. 1-12.
- Panettieri E., Fanteria D., Montemurro M., Froustey C. Low-velocity impact tests on carbon/epoxy composite laminates: A benchmark study. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2016, vol. 107, pp. 9-21.
- Shim V.P.W., Yang L.M. Characterization of the residual mechanical properties of woven fabric reinforced composites after low-velocity impact. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2005, vol. 47(4-5), pp. 647-665.
- Sachse R., Pickett A.K., Middendorf P. Simulation of impact and residual strength of thick laminate composites. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2020, vol. 195, article 108070.
- GOST 33496-2015. Polymer composites. Method for testing the resistance to damage during a falling weight impact.
- GOST 33495-2015. Polymer composites. Test method for compression after impact.
- ASTM D 7136 / 7136M - 15. Standard Test Method for Measuring the Damage Resistance of a Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Matrix Composite to a Drop-Weight Impact Event.
- ASTM D 7137 / D7137M - 17. Standard Test Method for Compressive Residual Strength Properties of Damaged Polymer Matrix Composite Plates.
- Hart K.R., Chia P.X.L., Sheridan L.E., Wetzel E.D., Sottos N.R., White S.R. Comparison of Compression-After-Impact and Flexure-After-Impact protocols for 2D and 3D woven fiber-reinforced composites. Composites: Part A, 2017, vol. 101, pp. 471-479.
- Sarasini F., Tirillò J., Valente M., Ferrante L., Cioffi S., Ianacce S., Sorrentino L. Hybrid composites based on aramid and basalt woven fabrics: Impact damage modes and residual flexural properties. Materials and Design, 2013, vol. 49, pp. 290-302.
- Liu Q., Guo O., Ju Y., Lin Y., Li Q. Impact responses and residual flexural properties of narrow CFRP laminates. Composite Structures, 2014, vol. 111, pp. 332-339.
- Zhang Z.Y., Richardson M.O.W. Low velocity impact induced damage evaluation and its effect on the residual flexural properties of pultruded GRP composites. Composite Structures, 2007, vol. 81, pp. 195-201.
- Wagih A., Sebaey T.A., Yudhanto A., Lubineau G. Post-impact flexural behavior of carbon-aramid/epoxy hybrid composites. Composite Structures, 2020, vol. 239, article 112022.
- Santiuste C., Sanchez-Saez S., Barbero E. Residual flexural strength after low-velocity impact in glass/polyester composite beams. Composite Structures, 2010, vol. 92. pp. 25-30.
- Yuan B., Ye M., Hu Y., Cheng F., Hu X. Flexure and flexure-after-impact properties of carbon fibre composites interleaved with ultra-thin non-woven aramid fibre veils. Composites Part A, 2020, vol. 131, article 105813.
- Wildemann V.E, Staroverov O.A., Tretyakov M.P. Deformation and failure of polymer composite materials under preliminary cyclic and low-velocity impacts. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2020, vol. 747, article 012034.
- Malhotra A., Guild F.J. Impact damage to composite laminates: Effect of impact location. Applied Composite Materials, 2014, vol. 21(1), pp. 165-177.
- Bogenfeld R., Schmiedel P., Kuruvadi N., Wille T., Kreikemeier J. An experimental study of the damage growth in composite laminates under tension-fatigue after impact. Composites Science and Technology, 2020, vol. 191, article 108082.
- Rogani A., Navarro P., Marguet S., Ferrero J.F., Lanouette C. Tensile post-impact behaviour of thin carbon/epoxy and glass/epoxy hybrid woven laminates - Part I: Experimental study. Composite Structures, 2019, vol. 230, 111508.
- Sreekantha Reddy T., Mogulanna K., Gopinadha Reddy K., Rama Subba Reddy P., Madhu V. Effect of thickness on behaviour of E-glass/epoxy composite laminates under low velocity impact. Procedia Structural Integrity, 2019, vol. 14, pp. 265-272.


