The microstructure organization and functional peculiarities of Euphorbia paralias L. and Polygonum maritimum L. - halophytic plants from dunes of Pomorie lake (Bulgaria)
Автор: Kosakivska I.V., Babenko L.M., Shcherbatiuk M.M., Vedenicheva N.P., Sheyko O.A., Ivanova A.P., Angelova L.E., Maslenkova L.T.
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 2 т.13, 2017 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The aim of this research was to investigate the leaf surface microstructure, pigments spectrum, hormones status and lipids composition of halophytes Polygonum maritimum L. and Euphorbia paralias L. that grow under natural conditions on the dunes of Pomorie Lake, (Bulgaria). It was shown that the existence in saline and dry soils provided among others adaptive mechanisms by specific microstructure of leaf. The adaxial and abaxial surfaces of P. maritimum leaves are covered with a dense layer of cuticle wax, stomata are located on the leaf both sides below the cuticle level. In E. paralias the cuticle is also well developed on the adaxial surface of leaf laminas. The epidermis of the leaf lower side is covered with a less dense cuticle layer formed by large wax crystals. This plant has stoma pores only on the abaxial side of small leaves below the cuticle level and they are surrounded with hump-shaped cuticle constructions. A high amount of carotenoids (as compared with that of chlorophylls) in P. maritimum leaves indicates that these pigments have a light-collecting function and could transfer an additional energy to chlorophylls. The high performance liquid chromatography method has been used to provide a qualitative and quantitative analysis of hormones. It was shown that in leaves of E. paralias and P. maritimum free abscisic (ABA) and conjugated indole-3-acetic (IAA) acids prevailed. A high level of active ABA is correlated with the salt tolerance and ability to survive and grow in stress conditions. A high level of conjugated form of IAA demonstrated that activity of this hormone is limited. The cytokinins qualitative and quantitative analyses demonstrated that in E. paralias leaves zeatin forms dominated, and the level of inactive cytokinins ( cis -zeatin and zeatin-O-glucoside) was much higher than that of active ones ( trans -zeatin and zeatin riboside). P. maritinum leaves contained a significant quantity of isopentenyl forms - isopentenyladenine and isopentenyladenosine, and among zeatin forms, zeatin-O-glucoside prevailed. Studies on the fatty acids content showed that in halophytes the salt resistance mechanism is based on the regulation of plasmatic membrane transport function that involves non-saturated fatty acids. The presence of a large amount of saturated fatty acids provides a decrease of membrane permeability and better resistance against soil salinity.
Euphorbia paralias l, polygonum maritimum l, microstructure, phytohormones, pigments, lipids
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14323949
IDR: 14323949
Текст научной статьи The microstructure organization and functional peculiarities of Euphorbia paralias L. and Polygonum maritimum L. - halophytic plants from dunes of Pomorie lake (Bulgaria)
Soil salinity is one of the major ecological factors that limit plant growth and productivity (Vinocur, Altman 2005). High concentrations of salt ions are known to cause disturbances in cell division, disintegrate the cytoplasm membrane structure, inhibit enzyme activity, have a negative effect on carbon assimilation, absorption of mineral nutrients, etc. (Kusnetsov et al. 2003; Hassine et al., 2009). Adaptation to salinity occurs at the different hierarchy levels from the molecular to population one (Glenn, Brown, 1999; Munns, Tester, 2008). Halophytes are a heterogeneous group of plants that unites representatives of various taxa, living forms and ecological types. Adapted to vegetation under salinity conditions, halophytes account for 1% of the world`s flora (Kumari et al., 2015). High salt concentrations in soil, even being wet enough, were shown to make a required moisture supply to plants impossible, and in some cases, halophytes are regarded as plants occurring in physically wet but physiologically dry habitats (Lokhande, Suprasan, 2012). Adaptation to the existence in saline soils results from the implementation of various metabolic and physiological strategies. Thus, euhalophytes accumulate salts in the middle of the plant, krinohalophytes, on the contrary, remove salts out while glycophytes are salt-impermeable (Henkel, 1982). Existence in saline soils affected the halophyte phenotypic characteristics. Succulence is typical of euhalophytes whereas glycohalophyte leaves have a xeromorphic structure. Krinohalophytes excrete salts through special salt glands. Euhalophytes are characterized by a great size of photosynthesizing cells while in krino- and glycohalophytes chlorenchyma cells are much smaller (Jennings, 1968). A successful adaptation to the environment depends substantially on optimal functioning of the assimilation machinery and indicators of its state are the photosynthetic pigments content and chloroplast ultrastructure. Chlorophylls and carotenoids are associated with protein complexes within photosynthetic membranes and localized mostly on gran thylacoid membranes and in minor quantities, on internal and external membranes of chloroplasts (Andrianova Tarchevsky, 2000; Smolikova, Medvedev, 2015; Stumskaya, Wurtzela, 2013). Chlorophyll a is the main pigment involved in photosynthesis whereas chlorophyll b executes a complementary function aimed to increase light-collecting abilities of the pigment complex in the red light short-wave region (Kochubey et al., 2014). The carotenoid major functions are light-collecting, antioxidating, photoprotecting and structural ones (Smolikova, Medvedev, 2015; Cuttriss, Pogson, 2004; Stumskaya, Wurtzela, 2013). The photosynthetic apparatus efficiency depends on the compliance of its structural and functional characteristics with climatic and ecological conditions. The photosynthetic pigments content and ratio are criteria to assess the efficiency of the photosynthetic apparatus functioning (Lichtenthaller, Buschmann, 2001).
An important role in adaptation to salinity is played by phytohormones. ABA was shown to be involved under drought conditions in the formation of responses as a trigger that activated signal cascades (Osakabe et al. , 2014). The accumulation of an active ABA provoked stomata closure (Nejad, Meeteren, 2007). Exogenous ABA increased salt tolerance in plants of glycophytes bean (Khadri et al. , 2006) and rice (Li et al. , 2010). Added of exogenous ABA under salinity conditions promoted the viability of halophyte Mesembryanthemum crystallinum L., contributed to biomass accumulation and preservation of photosynthetic pigments content, decreased intensity of oxidative stress (Shevyakova et al. , 2013). ABA treatment resulted in 10% reduction of transpiration in M. сrystallinum , and thereby decreased moisture loss and diminished negative effects of the salt stress osmotic component (Kuznetsov et al. , 2003). In contrast to glycophytes and facultative halophytes, euhalophytes were discovered to have a high constitutive ABA content (Ivanova et al. , 2015). However, a facultative halophyte M. crystallinum had much lower constitutive level of endogenous ABA than it was observed in glycophyte Phaseolus vulgaris L. (Vedenicheva et al. , 2010; Schevyakova et al. , 2010). Involvement of auxins in the plant salt tolerance formation has been studied insufficiently. Glycophytes were revealed to show both some reduction of IAA content and accumulation of this hormone under salt stress conditions (Vedenicheva et al. , 2011). In M. crystallinum halophyte leaves the IAA level was found to be higher (Vedenicheva et al. , 2010)
than that of glycophyte of Ph. vulgaris (Schevyakova et al. , 2010). In our previous investigation we have shown that the level of endogenous ABA was higher than that of IAA and the free form of ABA and conjugated form of IAA prevailed in the leaves of euhalophyte plant Eryngium maritimum L. (Ivanova et al , 2015). Plant salt tolerance is controlled by endogenous cytokinins. However, the level of these hormones in salt-affected glycophytes usually diminishes (Munns, Tester, 2008; Javid et al. , 2011; Ghanem et al. , 2011), it was established that the salt-tolerant variety of alfalfa had a higher constitutive level of cytokinins (by 1.5–2 times) than the weakly resistant one (Ben Salah et al. , 2013). Increased synthesis of cytokinins in the roots of tomatoes improved significantly the salt tolerance of plants, slowed the aging of leaves, and maintained vegetative growth and productivity under salinity (Albаcete et al. , 2010). A positive effect of ABA treatment on salt tolerance of M. crystallinum is associated with maintaining a certain content of cytokinins (Stetsenko et al. , 2015), which are known to possess an attracting ability. That is exactly the hormonal regulation of assimilation flows during the osmotic (independent of the action of specific ions) phase of salinity that affects, apparently, the ability of plants to sustain growth and survive in salt stress conditions (Perez-Alfocea et al. , 2010; Albаcete et al. , 2014). The ratio of ABA and cytokinins active forms in leaves of M. crystallinum under salinity conditions significantly changes (Stetsenko et al. , 2015).
A widespread cation of the salt stress is Na+ that is toxic to plants. Permeability of the plasmatic membrane – the first barrier on the way of Na+ – depends on the lipid bilayer state that is conditioned by the ratio between sterols and phospholipids and saturation of fatty acid residuals (Ivanova et al. , 2000; 2003; Wada, Murata, 2009).
The majority of researches focus on the study of the salt tolerance of glycophytes (Fricke et al., 2004; Munns, Tester, 2008; Munns et al., 2006; Shevyakova et al., 2010) and facultative halophytes (Vedenicheva et al. 2011, Shevyakova et al., 2013, Stetsenko et al., 2015), whereas the peculiarities of plants that have different mechanisms of adaptation to salt effects are almost unstudied. The aim of our study was to examine the microstructure of the leaf surface, hormones status, pigment spectrum and lipids composition of euhalophyte Euphorbia paralias L. and glycohalophyte Polygonum maritimum L. that grow under natural conditions. We suggested that in halophytes the adaptation strategy formation involves the complex of structural and functional reconstructions that cover specific features in the phytohormone system, pigment complex, lipid composition, microstructure of leaf surface and determine a successful plant existence in salinity conditions.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We studied halophyte plants Polygonum maritimum L., and Euphorbia paralias L. that grew on the dunes under natural conditions of Pomorie Lake (Bulgaria) whose high salinity (60-80%) contributed to the formation of a unique ecological environment. The glycohalophyte Polygonum maritimum L. (sea knotgrass) is a perennial herb characterized by an increased salt content and high cell pressure that enable to absorb moisture from rather concentrated soil solutions. It occurs in the Mediterranean region and is also found in Northern England and on Channel Islands. Its 50 cm long trailing stalk is weak and xeromorphic, grew in saline soils. The euhalophyte Euphorbia paraliast L. (sea spurge) is a 25-70 cm long (sometimes its length reaches 100 cm) perennial herb, hemicryptophyte is adapted to saline soils and tolerant to salty water splashes effects. It has a long branchy root, 3 – 5 mm long stalk, relatively numerous, strong, upright leaves. Leaves and shoots color is bluish-green, stalk lower parts often redden. E. paralias leaves are assidenous, naked, no dissected 30 mm long, 15 mm wide. Leaf shape in the lower stalk part is prolate-ellipsoidal with a blunt tip and above that part there is lanceolate with a sharp tip. The species is widespread in Western Europe and the Mediterranean. The samples of plants were collected in August 2015 from the sand dunes near Pomorie Lake (soil salinity was 330-350 mg of salts per 100 g of soil). The average temperature of air was 25-28°C. The plants were collected during the flowering phase. Plant material for the scanning electron microscopy was fixed in 70° ethanol. Fixed samples were dehydrated in ethanol solution at increasing concentrations. Following the treatment with absolute alcohol, samples were placed on objective tables and adhered there using adhesive tape, kept there for some time to reach an air-dry condition and covered with a layer of gold in the ion coating chamber to provide conductivity. The surface of P. maritimum and E. paralias leaves was studied by means of the scanning electron microscope JEOL JSM-6060 LA. Structure dimensions on microphotographs were measured using the program ImageJ 1.49v, involving a scale bar set up by the instrument on picture. Photosynthetic pigments were extracted with 80% aqueous acetone (Wellburn, 1994). Spectra were recorded using a spectrophotometer Spekord M-40. For lipid analysis small pieces from the aerial parts were extracted consecutively with chloroform-methanol (2:1) to obtain the total lipophylic extracts. The isolation of total fatty acids and the analysis of their fatty acid composition were performed using thin-layer and gas chromatographic techniques (Christie, 1989). Extraction of hormones and determination of free and conjugated forms of ABA, indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) and cytokinins were performed according to the method (Musatenko et al., 2003; Kosakivska et al., 2014). Qualitative and quantitative analysis of phytohormones performed using high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) on a chromatograph Agilent 1200 LC system with diode array detector G 1315 B (USA), column Eclipse XDB-C 18, with the parameters 4.6 x 150 mm, size of particles – 5 microns. Chromatograms were calculated using the software ChemStation (version 3.1 V.) in offline mode. Experiments were carried out in three biological and five analytical replicates. Digital materials were processed statistically using the programs MS Excel 2003 and Origin 6.0. Significant differences were assessed by Student's criterion, using a 5% level of significance (P < 0,05).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Studies of the leaf surface microstructure. P. maritimum leaves are narrow, long with a leathery texture and folded edges, have silver-colored stipules. The adaxial surface is green-colored, smooth by touch. The epidermis is covered by a dense cuticle layer. Adaxial surface microphotographs obtained using the scanning electron microscopy show that a thick cuticle layer forms a network of large folds (Fig. 1a). Stomata pores are located below the cuticle surface (Fig. 1b). Stomata number per 1 mm2 – 156,6±8,4, length of stomata pores in dry substance – 11,2±2,1 µm. The microstructure of leaf lamina abaxial surface is similar to that of adaxial one. The lower surface also has clear-cut stomata (Fig. 1c). Stomata pores are under the epidermis level. The number of stomata per 1 mm2 reaches 158,3±4,5. An average length of stomata pore opening is close to that of the adaxial side.
Thus, the adaxial and abaxial surfaces of the leaf lamina in glycophyte P. maritimum are characterized by a practically similar number of stomata and similar values of stomata pores sizes. In many flowering plants stomata are known to be located on the leaf both sides (Evert 2007; Evert et al. , 2013). However, in xeromorphs and species that are characterized by xeromorphy, location of stomata pores below the basic cuticle level might be regarded as adaptation to droughty conditions.
Euhalophyte E. paralias is a perennial herbaceous plant having a creeping stem. Its leaves are sessile, 30 mm long and 15 mm wide. Scanning electron microphotographs of the leaf adaxial surface show that the epidermis is covered with a layer of very dense cuticular wax that results in a glossy surface effect. The cuticle produces an extensive network of small folds. The wax layer is homogenous and smooth. No stomata are seen on the adaxial side (Fig. 2a). The leaf abaxial surface of E. paralias contains stomata. The epidermis is covered with a substantial cuticle layer that along with hump-shaped protrusions, cause some roughness of the leaf lower side (Fig. 2b). Stomata pores are below the epidermis level, surrounded by several hump-shaped constructions (Fig. 2c). The number of stomata per 1 mm2 reaches 124,1±2,3. An average length of the stomata pore does not exceed 10 µm.
Lack of stomata on the adaxial surface and their insignificant number on the abaxial surface of the leaf lamina, a well-developed cuticle, a large leaf thickness belong to the structural components that enable E. paralias to adapt to specific conditions of growing. Our previous studies have indicated that the adaxial and abaxial leaf surfaces of euhalophytes Eryngium maritimum L. have well-developed cuticle and stomata pores placed below the surface of the epidermis (Ivanova et al., 2015).
Photosynthetic pigments . It was shown that in leaves of glycohalophyte P. maritimum the content of chlorophylls а and b, and carotenoids was higher than that of euhalophyte E. paralias . The level of carotenoids in both species exceeded the chlorophyll b content (Fig. 3) The level of chlorophylls was lower as compared with that in mesophyte plant Triticum aestivum L., the content of carotenoids was also two times lower than in winter wheat leaves (Babenko et al. , 2014).
Carotenoids are known to protect the reaction sites from chlorophyll photoinhibition and photooxidation (Lichtenthaller, 1987, Lichtenthaller, Buschmann, 2001) and improve light-collecting characteristics of the photosynthetic mechanism (Bailey et al. , 2004). The ratio of chlorophylls a/b in the studied species was within the range of 2,7-2,8 (Fig. 4). In general, the ratio between pigments was similar to that in winter wheat (Babenko et al. , 2014). Thus, the key role in a photosynthetic activity in glycohalophyte P. maritimum and euhalophyte E. paralias is played by chlorophyll a . However, a high amount of carotenoids (as compared with an amount of chlorophylls) indicates that these pigments have a light-collecting function and could transfer an additional energy to chlorophylls. P. maritimum leaves, which are much smaller in their size than those of E. paralias , were characterized by a higher carotenoid content that contributes to an effective application of solar light (Rozentsvet et al. 2013).
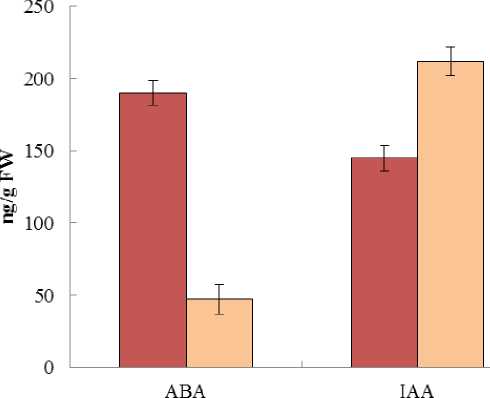
Phytohormones. We have shown that in leaves of E. paralias and P. maritimum the content of a free form of ABA exceeded that of conjugated form 3,5–4 times. The level of a free form of ABA was higher in leaves of glycophyte P. maritimum (Fig. 5, 6).
It was previously shown that as compared to Arabidopsis thaliana L. the expression of genes responsible for ABA biosynthesis and metabolism was more intensive in a salt-tolerant plant Thellungiella halophylla L.(Xiong, 2007). ABA-deficient mutants are more sensitive to salt stresses than wild species (Xiong, 2007). It suggests that high levels of free active ABA in E. paralias and P. maritimum may be a regulatory basis of the wild plant salt tolerance. It is confirmed by information that ABA treatment that is known to rise the endogenous ABA content (Stetsenko et al., 2015) reduced osmotic stress negative effects in Arabidopsis on moisture content, osmotic potential, stomata closure, proline and chlorophyll content whereas in unstressed conditions ABA had no significant effects on these characteristics (Ozfidan et al., 2013). It should be noted that in contrast to E. paralias a higher content of ABA in P. maritimum coincides with a pigment higher content in leavers. Under stress conditions ABA is known to be synthesized from carotenoids through xantoxin (Kličová et al., 2002). It appears that there is a close relationship between the pigment and hormone systems in the studied plants. So, a physiological significance of higher ABA levels that we have discovered in halophytes, having different mechanisms of salt tolerance, consists probably in a defense effect of this hormone and maintaining the normal functions of plants growing saline soils.
In both studied species the conjugated form of IAA prevailed. As compared to euhalophyte E. paralias glycohalophyte P. maritimum contained large amounts of conjugated and free forms of IAA. However , the auxin involvement in salinity reactions is proved by the fact that exogenous auxins alleviated a growth inhibiting effect of salt stress in many plants (Javid et al. , 2011). The results of bacterial application on T. aestivum indicate that the growth reduction caused by NaCl decreased through application of IAA produced by bacterial strains (Orhan, 2016). This effect of auxins is an indirect evidence of their involvement in salt tolerance formation. It is known that in a bound state IAA loses activity and could be used as a transport form or be a depot of phytohormone (Veselov et al. , 2007; Bejguz, Piotrowska, 2009). The predominance of conjugated IAA demonstrated that activity of the hormone in P. maritimum and E. paralias is limited and therefore a regulatory function of IAA in these plants salt tolerance is questionable.
P. maritinum and E. paralias plants differ considerably in their content of endogenous cytokinins. P. maritinum leaves contained significant amounts of isopentenyl forms – isopentenyladenosine and isopentenyladenine, and among zeatin forms zeatin-O- glucoside prevailed (Fig. 7). In leaves of E. paralias the zeatin forms were predominant (Fig. 8), but the level of inactive cytokinins (cis-zeatin and zeatin-O-glucoside ) was considerably higher than that of active ones (transzeatin and zeatin riboside).
Cytokinins are known to be an important regulatory factor of plant stress tolerance. Many plants pretreated with cytokinin demonstrated an improved salt tolerance (Zwack, Rashotte, 2015). Some experimental results suggested that the homeostasis of cytokinins in plant cells broken through over-expression of the cytokinin biosynthesis gene could modulate salt stress responses in Arabidopsis (Wang et al., 2015). Mutant plants lacking some specific cytokinin signalling components enhanced tolerance to drought and salt stresses (Zwack, Rashotte, 2015), indicating the complex interactions between cytokinin and salt stress signalling. As our experiments show halophytes, having different salt tolerance patterns, differ considerably in cytokinins metabolism. Glycohalophyte P. maritinum, impermeable for salts, accumulates cytokinins of the isopentenyl type that is not typical of higher plants under normal conditions. Some increase in the content of isopentenyladenosine and isopentenyladenine occurred in glycophyte Ph. vulgaris and facultative halophyte M. crystallinum affected by NaCl (Vedenicheva et al., 2011). In euhalophyte E. paralias that can congest salts, inactive cytokinins forms were dominant as in plants whose growth intensity is low (Vedenicheva, 2016). Furthermore, in contrast to E. paralias, an increased content of pigments in P. maritinum leaves coincides with a higher total concentration of cytokinins and their active forms. Cytokinins are known to play some role in preserving the structure and function of the photosynthetic machinery under stress conditions (Cherniad'ev, 2009). Cytokinin treatment retains higher transcript levels of photosystem II-related genes, maintains the chlorophyll a/b ratio resulting in the stability of photosynthetic pigment complexes and functional stay-greenness in rice (Talla et al., 2016). Thus, the species specificity of the studied halophytes cytokinin status may be associated with the type of their strategy concerning survival in saline soils.
Lipids composition. It was shown that the main fatty acids in E. paralias leaves were palmitic, linoleic and linolenic. The content of 16:1 acid is low. In P. maritimum the amount of saturated fatty acids was higher than that of E. paralias . There are same significant differences in the proportion of linoleic and linolenic acids in these halophyte plants. In E. paralias the amount of linolenic acid is higher than that of P. maritimum . In general, the amount of saturated fatty acid in both plants is high in comparison with other terrestrial plants. The similar phenomenon was observed in other halophyte plants and seems to be typical for salt-stressed plants (Ivanova et al. , 2000; 2003). A high content of saturated fatty acid leads to some decrease in the membrane permeability and better resistance of halophytic plants to soil salinity. The plant membrane fluidity depends also on the content of unsaturated linoleic (18:2) and linolenic (18:3) acids. An increase in salinity involves some growth of the amount of 18:2 (Table). Studies conducted by other researchers on wheat seedlings demonstrated that environmental salinity enhanced fatty acids saturation (Mansour et al. , 2002). It was also shown that in contrast to a saltsensitive tomato variety the fatty acids saturation in cell plasmatic membranes of a salt-tolerant tomato variety was higher (Rodriguez-Rosales et al. , 1999). On that ground, authors suggested that fatty acid saturation is involved in plant adaptation to salinity through a decrease in membrane fluidity and as a result, in the membrane permeability for ions, particularly for Na+. However, a high content of unsaturated fatty acids as well as fatty acids with a long carbon chain affects the functioning of membrane-bound enzymes, particularly those that are components of the ion active transport (Allakhverdiev et al. , 1999, Azachi et al. , 2002). These findings give reason to suggest that the regulation of plasmatic membrane transport function that involves unsaturated fatty acids is a component of the salt defense mechanism in euhalophyte and glycophytes.
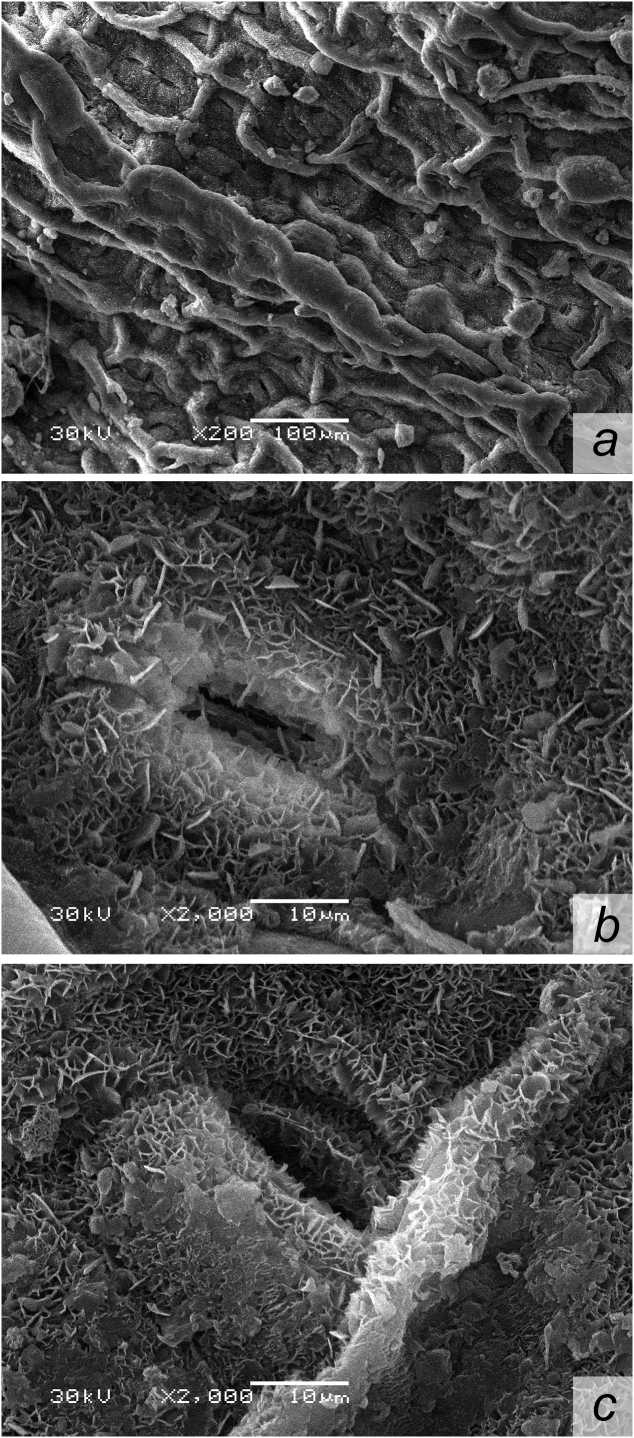
Figure 1. Microstructure of leaf lamina adaxial surface in Polygonum maritinum L. (a) Stoma on the leaf lamina adaxial
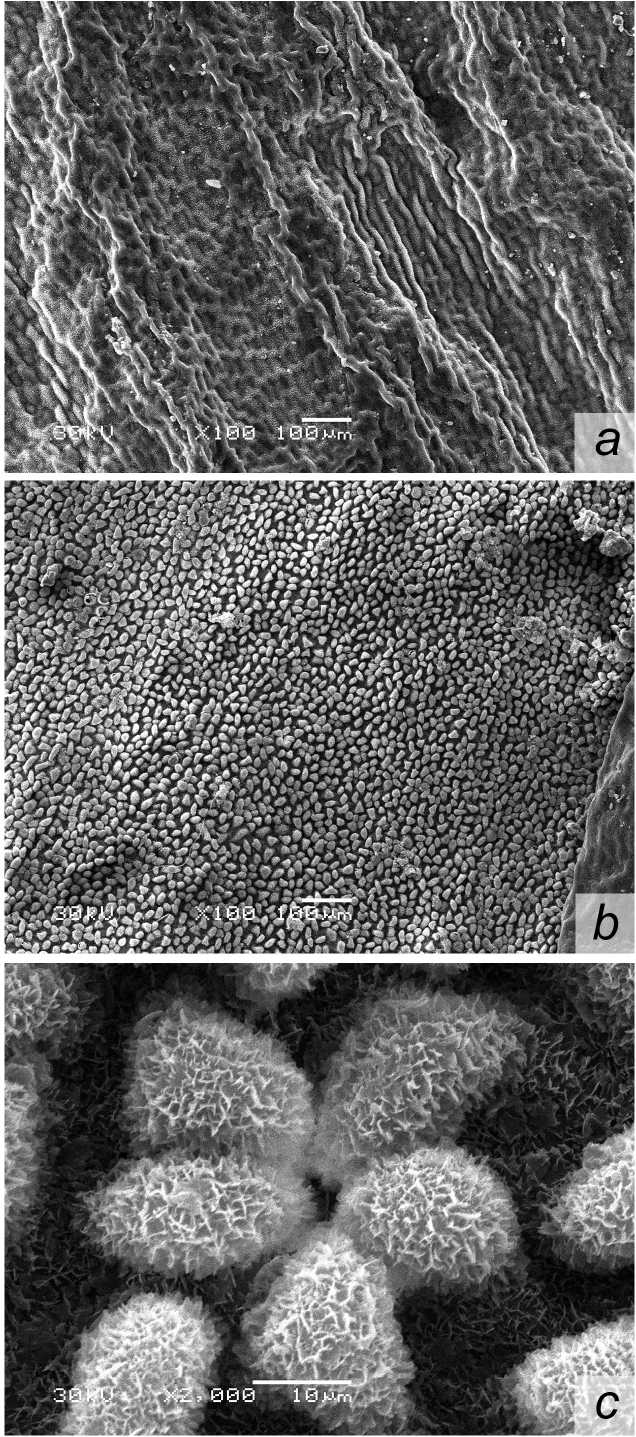
Figure 2. Microstructure of leaf lamina adaxial surface in Euphorbia paralias L. (a); Microstructure of leaf lamina abaxial
surface (b); Stoma on the leaf lamina abaxial surface (c).
surface (b); Stoma surrounded by humpshaped cuticle constructions on the leaf lamina abaxial surface (c).
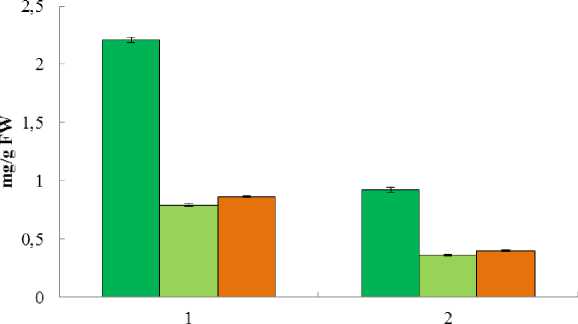
Figure 3. Pigments content in leaves of Polygonum maritimum L. (1) and Euphorbia paralias L. (2) (mg/g FW).
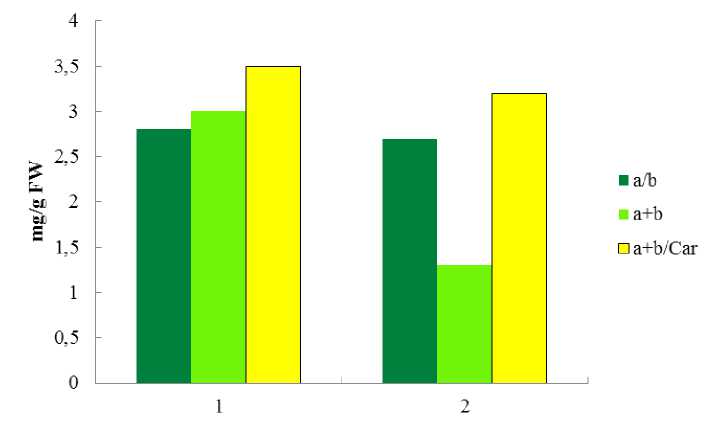
Figure 4. The ratio of pigments classes in leaves of Polygonum maritimum L. (1) and Euphorbia paralias L. (2) (mg/g FW).
■ free
□ conjugated
Figure 5. The free and conjugated ABA and IAA content in leaves of P. maritimum (ng/g FW).
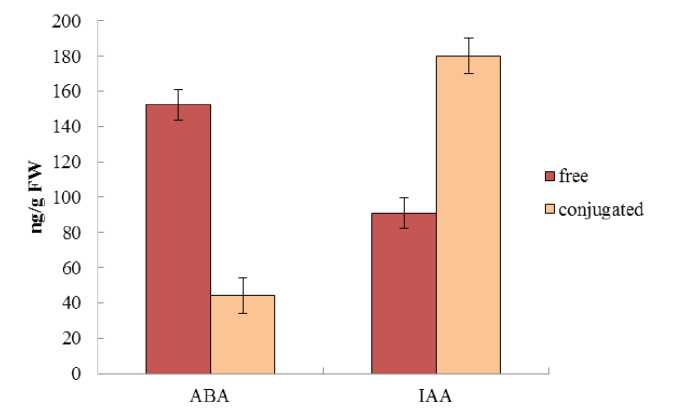
Figure 6. The free and conjugated ABA and IAA content in leaves of E. paralias (ng/g FW).
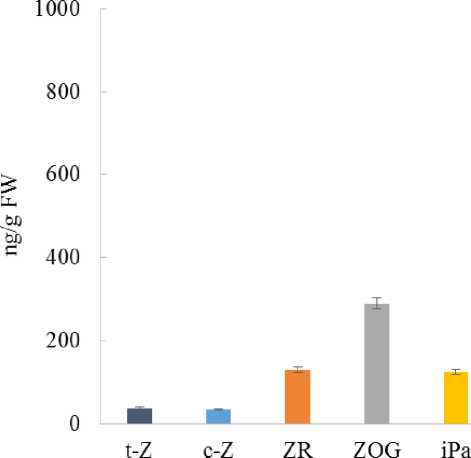
Figure 7. The content of cytokinins (ng/g FW) in the leaves of Polygonum maritimum L. *Note: t-Z – trans-zeatin, c-Z – ciszeatin, ZR – zeatin riboside, ZOG – zeatin-O-glucoside, iPa – isopentenyladenosine and iP – isopentenyladenine, ∑ – cytokinins total.
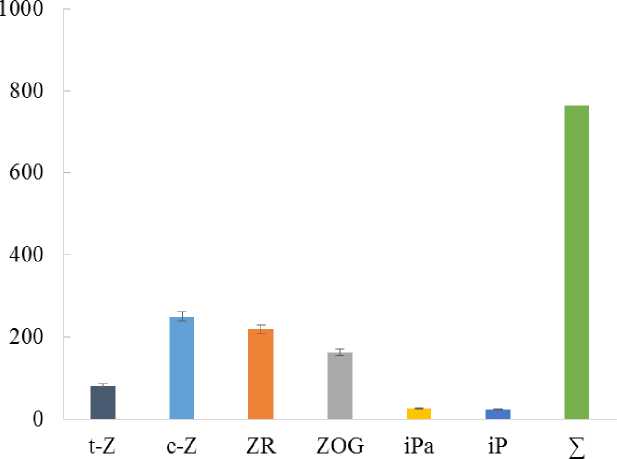
Figure 8. The content of cytokinins (ng/g FW) in the leaves of Euphorbia paralias L.
Table 1. Fatty acids in Euphorbia paralias L. and Polygonum maritimum L. leaves.
|
Plant |
Fatty acids (wt % of total) |
||||||||
|
Lipid class |
12:0 |
14:0 |
16:0 |
16:1 |
18:0 |
18:1 |
18:2 |
18:3 |
20:0 |
|
Polygonum maritimum |
3.15 |
2.93 |
21.87 |
1.49 |
3.24 |
8.32 |
16.04 |
39.14 |
3.82 |
|
Euphorbia paralias |
0.67 |
3.43 |
21.20 |
1.12 |
3.34 |
2.10 |
12.21 |
51.71 |
4.22 |
CONCLUSION
Thus, the existence in saline and dry soils of glycohalophyte Polygonum maritimum and euhalophyte Euphorbia paralias provided among others adaptive mechanisms by a specific microstructure of the leaf, adaxial and abaxial surfaces of which have well-developed cuticle and pores of stomata placed below the surface of the cuticle. A specific feature of euhalophyte E. paralias is the presence of stomata pores only on the leaf lamina abaxial surface. Each stoma is surrounded by hump-shaped cuticle constructions. In contrast to euhalophyte E. paralias glycohalophyte P. maritimum is characterized by a higher content of photosynthetic pigments in leaves Chlorophyll a plays a key role in photosynthetic activity. However, a high amount of carotenoids (as compared with amount of chlorophylls) indicates that these pigments have a light-collecting function and could transfer an additional energy to chlorophylls. The analysis of the phytohormone system indicated that the salt tolerance formation involves ABA, a free form of which in leaves of both halophytes prevailed Moreover, P. maritimum leaves had higher concentrations of endogenous phytohormones (ABA IAA and cytokinins). A high level of conjugated form of IAA demonstrated that activity of the hormone is limited. The content of cytokinins of the іР-line in glycohalophyte P. maritimum was considerably higher than that of euhalophyte E. paralias. The presence of a large amount of saturated fatty acids causes a decrease in membrane permeability and better resistance to soil salinity.
The results of our study demonstrate that in halophytes the formation of adaptation strategy involves the complex of structural and functional reconstructions that covers specific features in the phytohormone system, pigment complex, lipid composition, surface microstructure of leaves and determines a successful existence in saline conditions.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was completed in the frames of bilateral project between Ukrainian Academy of Sciences and Bulgarian Academy of Sciences (2014-2018).
Список литературы The microstructure organization and functional peculiarities of Euphorbia paralias L. and Polygonum maritimum L. - halophytic plants from dunes of Pomorie lake (Bulgaria)
- Akhiyarova G.R., Sabirzhanova I.B., Veselov D.S., Frike V. (2005) The Participation of hormones in the resumption of the growth of wheat shoots at short-term salinity NaCl. Fiziologiya rasteniy, 52, 891-896. (In Russian)
- Albacete A., Cantero-Navarro E., Balibrea M.E., Grosskinsky D.K., Gonzalez M.C., Martinez-Andujar C., Smigocki A.C., Roitsch T., Perez-Alfocea F. (2014) Hormonal and metabolic regulation of tomato fruit sink activity and yield under salinity. J. Exp. Bot., 65, 6081-6095
- Albacete A., Ghanem M.E., Dodd I.C., Pérez-Alfocea F. (2010) Principal component analysis of hormone profiling data suggests an important role for cytokinins in regulating senescence of salinised tomato. Plant Signaling and Behavior, 5, 44-46
- Allakhverdiev S.I., Hishiyama Y., Suzuki I. (1999) Genetic engineering of the unsaturation of fatty acid in membrane lipids alters the tolerance of Synechocystis to salt stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 96, 5862-5867
- Andrianova Y.E., Tarchevsky I.A.(2000) Chlorophyll and plant productivity. Moscow: Science, 135.
- Atanasova L., Pissurska M., Stoyanov I. (1996) Cytokinins and growth responses of maize and pea plants to salt stress. Bulg. J. Plant Physiol., 22, 2231
- Azachi M., Sadka A., Fisher M. (2002) Salt induction of fatty acid elongase and membrane lipid modifications in the extreme halotolerant alga Dunaliella salina. Plant Physiol., 129, 1320-1329
- Babenko L.M., Kosakivska I.V., Akimov Yu.A., Klymchuk D.O., Skaternya T.D. (2014) Effect of temperature stresses on pigment сontent, lipoxygenase activity and cell ultrastructure of winter wheat seedlings. Genetics and Plant Physiology, 4 (1-2), 117-125
- Bailey S., Horton P., Walters R.G. (2004) Acclimation of Arabidopsis thaliana to the light environment: the relationship between photosynthetic function and chloroplast composition. Planta, 218, 793-802
- Bajguz A., Piotrowska A. (2009) Conjugates of auxin and cytokinin. Phytochemistry, 70, 957-969
- Ben Salah I., Albacete A., Messedi D., Gandour M., Martínez Andújar C., Zribi K., Martínez V., Abdelly C., Pérez-Alfocea F. (2013) Hormonal responses of nodulated Medicago ciliaris lines differing in salt tolerance. Environ. Exp. Bot., 86, P. 35-43
- Blankenship R.E. (2002) Molecular mechanisms of photosynthesis. Oxford: Blackwell Science Ltd, UK. 321 p
- Cherniad'ev I.I. (2009) The protective action of cytokinins on the photosynthetic machinery and productivity of plants under stress. Applied Biochemical Microbiology, 45, 351-362
- Christie W.W. (1989) Gas Chromatography and Lipids: a Practical Guide. The Oily Press, Ayr, Scotland. 184 p
- Cuttriss A.J., Pogson B.J. (2004) Carotenoids. Plant pigments and their manipulation. Ed. Davies K.M. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 57-91
- Del Pozo J.C., Lopez Mataz M.A., Ramirez-Parra E., Gutierrez C. (2005) Hormonal control of the plant cell cycle. Physiol. Plant., 123, 173-183
- Evert R.F. (2007) Esau's plant anatomy. Third edition. -Hoboken, New Jersey.: Wiley Interscience,. -607 p
- Raven P.H., Evert R.F., Eichhorn S.E. (2013) Raven Biology of Plants. Eighth edition. New York.: W.H. Freeman and Co. Publishers,. -880 p
- Fricke W., Akhiyarova G., Veselov D., Kudoyarova G. (2004) Rapid and tissue-specific changes in ABA and in growth rate response to salinity in barley leaves. J. Exp. Bot., 55, 1115-1123
- Ghanem M.E., Albacete A., Smigocki A.C. (2011) Root-synthesized cytokinins improve shoot growth and fruit yield in salinized tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) plants. J. Exp. Bot., 62, 125-140
- Glenn E.P., Brown J.J. (1999) Salt tolerance and crop potential of halophytes. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci., 18, 227-255
- Hassine A.B., Ghanem M.E., Bouzid S., Lutts S. (2009) Abscisic acid has contrasting effects on salt excretion and polyamine concentrations of an inland and a coastal population of the Mediterranean xero-halophyte species Atriplex halimus. Ann. Bot., 104, 925-936
- Henkel P.A. (1982) Physiology of heat-and drought resistance. M.: Nauka, 280 p.
- Ivanova A., Khozin-Goldberg I., Kamenarska Z., Nechev J., Cohen Z., Popov S., Stefanov K. (2003) Lipophylic Compounds from Euphorbia peplis L. -a halophytic plant from the Bulgarian Black Sea Coast. Z. Naturforsch., 58, 783-788
- Ivanova A., Nechev J., Stefanov K. (2000) Lipid composition of some halophyte plants from the Black Sea coast of Bulgaria. Compt. rend. Acad. Bulg. Sci., 53, 83-86
- Ivanova A.P., Tsonev T.D., Peeva V.N., Najdenski H.M., Tsvetkova I.V., Babenko L.M., Shcherbatiuk M.M., Sheiko O.A. Kosakivska I.V. (2015) Euhalophyte Eryngium maritimum L.: the Microstructure and Functional Characteristics. J. Stress Physiol. Biochem., 11(3), 52-61
- Javid M.G., Soroosshzadeh A., Moradi F., Sanavy S.A.M.M., Allahdadi I. (2011) The role of phytohormones in alleviating salt stress in crop plants. Australian J. Crop Plants, 5, 726-734
- Jennings H. (1968) Halophytes, succulence and sodium in plants -a unified theory. New Phytol., 67, 899-911
- Khadri M., Tejera N.A., Lluch C. (2006) Alleviation of salt stress in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) by exogenous abscisic acid supply. J. Plant Growth Regul., 25, 110119
- Kličová Š., Šebánek J., Hudeová M., Vitková H., Vlašinová H. (2002) The effect of fluridone and flurochloridone on the incidence of albinism in pea (Pisum sativum) and on the abscission of leaves of privet (Ligustrum vulgare). Rostlinna Vyroba, 48, 255-260
- Kochubey S.M., Bondarenko O.Yu., Shevchenko V.V. (2014) Photosynthesis. V 1. Structural organization and functional features of the light phase of photosynthesis. -K.: Logos, 384 p. (In Russian)
- Kosakivska I.V., Voytenko L.V., Likhnyovskiy R.V., Ustinova A.Y. (2014) Effect of temperature on accumulation of abscisic acid and indole-3-acetic acid in Triticum aestivum L. seedlings. Genetics and Plant Physiology, 4 (3-4), 201-208
- Kumari A., Das P., Pradeep K. (2015) Proteomics, metabolomics, and ionomics perspectives of salinity tolerance in halophytes, Front. Plant Sci., 6, 1-20
- Kusnetsov Vl.V., Kruglova A.G., Molodyuk O.I., Karyagin V.V., Meshcheryakov A.B., Ragulin V.V., Rakitin V.Yu., Kholodova V.P. (2003) Hormonal regulation of Crassulacean Acid Metabolism (CAM) and inter-organ stress signal transduction. Phytohormones in Plant Biotechnology and Agriculture. Eds. Macháčková I., Romanov G.A. Dordrecht: Kluwer, 195-203
- Li X.-J., Yang M.-F., Chen H., Qu L.-Q., Chen F., Shen S.-H. (2010) Abscisic acid pretreatment enhances salt tolerance of rice seedlings: proteomic evidence. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1804, 929-940
- Lichtenthaler H.K., Buschmann C. (2001) Chlorophylls and Carotenoids: Measurement and Characterization by UVVIS Spectroscopy. Current Protocols in Food Analytical Chemistry, F4.3.1-F4.3.8
- Lichtenthaller H.K. (1987) Chlorophylls and Carotenoids: Pigments of Photosynthetic Biomembranes. Methods in enzymology, 148, 350-382
- Lokhande V.H., Suprasan M.P. (2012) Prospects of Halophytes in Understanding and Managing Abiotic Stress Tolerance. Environmental adaptations and Stress Tolerance of Plants in the Era of Climate Change/eds. P. Ahmad, M.N.V. Prasad. Springer science. Business Media, 29-56
- Mansour M.M.F., Salama K.H.A., Al-Mutawa M.M. (2002) Effects of NaCl and polyamines on plasma membrane lipids of wheat roots. Biol. Plant, 45, 235-239
- Munns R., James R.A., Luchli A. (2006) Approaches to increasing the salt tolerance of wheat and other cereals. J. Exp. Bot., 57, 1025-1043
- Musatenko L., Vedenicheva N., Vasyuk V., Generalova V., Martyn G., Sytnik K. (2003) Phytohormones in seedlings of maize hybrids differing in their tolerance to high temperatures. Russian J. Plant Physiology, 50, 499-504
- Nejad A.R., van Meeteren U. (2007) The role of abscisic acid in disturbed stomatal response characteristics of Tradescantia virginiana during growth at high relative air humidity. J. Exp. Bot., 58 (3), 627-636
- Orhan F. (2016) Alleviation of salt stress by halotolerant and halophilic growth-promoting bacteria in wheat (Triticum aestivum). Brazilian J. Microbiol., 47, 621-627
- Osakabe Y., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K., Shinozaki K., Tran L.S. (2014) ABA control of plant macroelement membrane transport systems in response to water deficit and high salinity. New Phytologist., 202, 35-49
- Ozfidan C., Turkan I., Sekmen A.H., Seckin B. (2013) Time course analysis of ABA and non-ionic osmotic stress-induced changes in water status, chlorophyll fluorescence and osmotic adjustment in Arabidopsis thaliana wild-type (Columbia) and ABA-deficient mutant (aba2). Environ. Exp. Bot., 86, 44-51
- Perez-Alfocea F., Albacete A., Ghanem M., Dodd I.C. (2010) Hormonal regulation of source-sink relations to maintain crop productivity under salinity: a case study of root-to-shoot signalling in tomato. Functional Plant Biol., 37, 592-603
- Piotrowska A., Bajguz A. (2011) Conjugates of abscisic acid, brassinosteroids, ethylene, gibberellins and jasmonates. Phytochenistry, 72, 2097-2112
- Rodriguez-Rosales M.P., Kerbek L., Bueno P. (1999) Changes induced by NaCl in lipid content and composition, lipoxygenase, plasma membrane H+-ATPase and antioxidant enzyme activities of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum. Mill) calli. Plant Sci, 143, 143-150
- Rozentsvet О.А., Nesterov V.N, Bogdanova Е.S. (2013) The structurally functional characteristic of the photosynthetic device of halophytes, differing by salts accumulation. Izvestiya Samarskogo nauchnogo tsentra РАН, 15, 2189-2195
- Shevyakova N.I., Musatenko L.I., Stetsenko L.A., Rakitin V.Yu., Vedenicheva N.P., Voytenko L.V., Kuznetsov Vl.V. (2010) The effect of salinity on growth performance Phaseolus vulgaris L. plants, phytohormones content and polyamines. Fiziologiya i biokhimiya kulturnykh. rasteniy, 42, 483-490
- Shevyakova N.I., Musatenko L.I., Stetsenko L.A., Vedenicheva N.P., Rakitin V.Yu., Kuznetsov Vl.V. (2013) Effect of ABA on the contents of proline, polyamines, and cytokinins in the common ice plants under salt stress. Russ. J. Plant Physiol, 60, 741-748
- Smolikova G.N., Medvedev S.S. (2015). SEED CAROTENOIDS: SYNTHESIS, DIVERSITY, AND FUNCTIONS. RUSSIAN JOURNAL OF PLANT PHYSIOLOGY, 62, 1-13. (In Russian)
- Stetsenko L.A., Vedenicheva N.P., Likhnevsky R. V., Kuznetsov Vl.V. (2015) Influence of abscisic acid and fluridone on the content of phytohormones and polyamines and the level of oxidative stress in plants of Mesembryanthemum crystallinum L. under salinity. Biology Bulletin, 42, 98-107
- Stumskaya M., Wurtzela E. (2013) The carotenoid biosynthetic pathway: thinking in all dimensions. Plant Sci., 208, 182-193
- Talla S.K., Panigrahy M., Kappara S., Nirosha P., Neelamraju S. (2016) Cytokinin delays dark-induced senescence in rice by maintaining the chlorophyll cycle and photosynthetic complexes. J. Exp. Bot., 67, 1839-1851
- Vedenecheva N.P., Voytenko L.V., Musatenko L.I., Stetsenko L.A., Shevyakova N.I. (2010) Solification effects on the phytohormone content in leaves Mesembryanthenum crystallinum L. The Bull. Kharkiv Natl. Agr. Univ., 3 (21), 30-36.
- Vedenicheva N.P. (2016) Cytokinins as a regulators of plant organs growth under different conditions. The Bulletin of Kharkiv National Agrarian University. Ser. Biology. 1 (37), 6-26. (In Ukrainian)
- Vedenicheva N.P., Voytenko L.V., Musatenko L.I., Stetsenko L.A., Shevyakova N.I. (2010) Effect of salinity on plant hormones content in the leaves of Mesembryanthemum crystallinum L. The Bulletin of Kharkiv National Agrarian University, 3, 30-36
- Vedenicheva N.P., Voytenko L.V., Musatenko L.I., Stetsenko L.A., Shevyakova N.I. (2011) Changes of phytohormones content in halo-and glycophytes under salinity. Studia Biologica, 5, 37-44
- Veselov D.S., Veselov S.Yu., Vysotskaya L.B, Kudoyarova G.R., Farkhutdinov R.G. (2007) Plant hormones: regulation of the concentration, the relationship with growth and water exchange. Science, Moscow. 356 p
- Vinocur B., Altman A. (2005) Recent advances in engineering plant tolerance to abiotic stress: achievements and limitation. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 16, 123-132
- Wada H., Murata N. (2009) Lipids in Thylakoid membranes and Photosynthetic Cells. In: Wada H., Murata N. (eds.), Lipids in Photosynthesis: Essential and Regulatory Function. N. Dordrecht: Springer,. P. 1-9
- Wang Y., Shen W., Chan Z., Wu Y. (2015) Endogenous cytokinin overproduction modulates ROS homeostasis and decrease salt stress resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Front Plant Sci., 6, 1004-1023
- Wellburn A. (1994) The spectral determination of chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b, as well as total carotenoids, using various solvents with spectrophotometers of different resolution. J. Plant Physiol., 144, 307-313
- Xiong L. Abscisic acid in plant response and adaptation to drought and salt stress//Advances in molecular breeding toward drought and salt tolerant crops. Eds. M.A. Jenks, P.M. Hasegawa, S.M. Jain. -Berlin: Springer, 2007. -P. 193-221
- Yongyin W., Mopper S., Hasenstein K.H. (2001) Effects of salinity on endogenous ABA, IAA, JA and SA in Iris hexagona. J. Chem. Ecol., 27, 327-342
- Zwack P.J., Rashotte A.M. (2015) Interaction between cytokinin signalling and abiotic stress responses. J. Exp. Bot., 66, 4863-4871


