The reality, efforts, and obstacles of local development in Algeria: the case of Annaba province
Автор: Khoualed A., Lebza A., Tayeb A.B.
Журнал: Вестник Витебского государственного технологического университета @vestnik-vstu
Рубрика: Экономика
Статья в выпуске: 3 (49), 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Local development is a fundamental process upon which the developmental policy of the state is based, as it is considered a basic starting point for achieving comprehensive national development. Local development relies on a participatory approach that ensures the involvement of all actors in bringing about development in a specific area. Since what may be suitable in one area may not be applicable in another, this study aims to examine the reality of local development in Annaba Province (the fourth largest city in Algeria) and to analyze the various efforts and obstacles to achieving local development in the province. To achieve the aforementioned objectives, the descriptive method was used, and a field internship was conducted at the Directorate of Programming and Budget Follow - up in Annaba Province, where all statistics and information relevant to the topic were collected and analyzed. The study concluded with a key finding that despite all the efforts made to develop Annaba Province through municipal development plans (PCD), decentralized sectoral programs (PSD), various programs for recovering unused industrial land, supporting private investors, and encouraging entrepreneurial projects for youth, there are still many problems that need urgent solutions. The foremost of these problems include the high percentage of incomplete projects, bureaucracy, weak human resources, poor performance standards and criteria, and the lack of incentive systems.
Local development, socio-economic factors, investment projects, industry, annaba province
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142243619
IDR: 142243619 | УДК: 330.3(65) | DOI: 10.24412/2079-7958-2024-3-148-162
Текст научной статьи The reality, efforts, and obstacles of local development in Algeria: the case of Annaba province
DOI:
Development, in its broadest sense, has been the foremost concern for developing countries since the end of World War II. Studies in various branches of social sciences have increasingly focused on the developmental perspective, especially as the majority of developing countries were newly independent and striving to establish their own developmental models. Local development in these countries faced numerous obstacles, particularly within the context of the new global order which imposed challenges on their ability to benefit from the global market advantages. Furthermore, the phenomenon of transcontinental terrorism exacerbated the already difficult situations in these countries by reducing foreign investments due to the security challenges they faced. In addition, various social, economic, political, and cultural barriers further impeded the progress of local communities.
Algeria, as one of the developing countries, experiences almost the same challenges, among which the internal challenges are the most prominent. After gaining independence from France in 1962, the Algerian government initiated the building of state institutions and the establishment of a model entirely independent of the Western economy, adopting a socialist economic system for an extended period until the late 1980s. With the onset of the 1990s and due to the numerous issues accompanying the implementation of the socialist system, Algeria shifted towards a free-market system. However, with the government’s retention of strategic sectors, this resulted in a mixed economy of socialism and capitalism that Algeria experiences today. Additional internal challenges include the "Black Decade" and the terrorism tragedy of the 1990s, overreliance on hydrocarbon rents, and a population explosion not matched by sufficient development levels. External factors such as ideological and cultural legacies of colonialism, economic and scientific dependency, technological challenges, and the issue of external debt also play significant roles.
Thus, it is evident that the topic of local development provides a better explanation for the main issues Algeria faces and their causes, considering that local development is a fundamental element in the economic growth of nations. Economists discuss several elements of economic development, including capital, raw materials, the level of technological advancement, and skilled labor. However, the most critical elements for progress, prosperity, and the optimal utilization of available resources—be they human or natural—remain local development, which is of immense importance in supporting the local economy.
Given that individuals are products of their environment, this study aims to examine the state of local development in the Province of Annaba, the fourth-largest city in Algeria by economic activity. Annaba houses the largest iron and steel plant in Africa and boasts numerous tourism and commercial assets, alongside a significant network of infrastructure and transportation (port, airport, railways, roads). This study will also attempt to uncover the various difficulties in achieving local development in the province, in addition to the various efforts made by the government to overcome these obstacles.
Previous Studies
Another study conducted by (Bahouri, 2023) attempted to clarify the reality of social policy in Algeria and uncover its role in improving local development. To achieve this objective, the researcher conducted a descriptive study focusing on the main areas of social policy's contribution to local development, including health, education, housing, living standards, employment, and others. The study concluded that Algeria faces several challenges in achieving comprehensive local development and must work on several fronts, including political will, effective civil society participation, social justice, and investment in human capital.
Another study by (Ferdj, 2020) aimed to analyze the factors of local development and regional dynamics in Blida Province (central Algeria), highlighting its economic and social characteristics as critical elements for achieving regional development. The researcher conducted a field survey on a sample of 110 companies specializing in agrifood production in the province. The study found that the main supportive factors for local development in the province include its historical background in agri-food production, entrepreneurial culture, availability of road and transport networks, raw materials, suppliers, and skilled labor. The study also noted the absence of effective links between companies and local organizations.
(Lamrani, 2021) study aimed to examine the problem of socio-economic development in the Soummam Valley in the Kabylie region (northern Algeria). To achieve this objective, the researcher conducted a comprehensive study of the various social and economic dynamics in the agri-food sector in the Soummam Valley. The study concluded that projects in this sector have positively impacted local populations by creating new job opportunities, income distribution, product availability, and more. However, the researcher also noted several challenges, including weak regional governance and the need for better environmental protection in the region's projects.
(Boubir, 2018) study aimed to propose an effective participatory approach to local development in Tébessa Province (eastern Algeria), which faces several challenges, including being a border province with weak investments and government funding, deteriorating agriculture and industry, and difficult natural conditions as the province is part of arid regions. Based on the participatory approach and SWOT analysis, the researcher proposed several prudent strategies, focusing on four key sectors: hydraulics, mining industry, agriculture, and tourism, alongside greater attention to infrastructure.
A recent study by (Abboudi, 2014) aimed to reveal the reality and prospects of local development in Guelma Province (eastern Algeria). To achieve this objective, the researcher used two approaches:
– A theoretical one to demonstrate the concepts related to the study.
– A regional approach combining several subapproaches to identify local opportunities offered by Guelma Province and highlight the potential wealth of its lands.
The study concluded that, despite not being a coastal province, Guelma possesses many encouraging factors for achieving sustainable local development, especially if greater attention is paid to the agriculture and tourism sectors.
Theoretical Framework
Local development is a collective process that reflects the cultural, social, and economic coexistence, identity of communities, and family life (Nina et al, 2019, p. 151). According to (Sekuła, 2022, p. 60), several fundamental approaches can be distinguished in defining local development based on the criteria of the local community and its needs, as well as the criterion of changes occurring within the local arrangement. The following figure illustrates this (figure 1).
The following are some elements associated with inputs, outputs, and outcomes (Jouen, et al., 2010, p. 11):
– Inputs: Region, sense of belonging, community, bottom-up approach, partnership, self-potential, proximity.
– Outputs: Quality, efficiency, transition, diversity, new methods, increased local value, access to services, self-help, increased income and revenues, and local
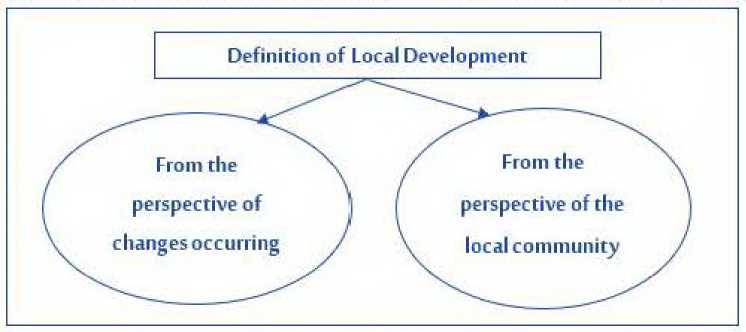
Figure 1 – Criteria for Distinguishing Definitions of Local Development
Source: (Sekuła, 2022, p. 60).
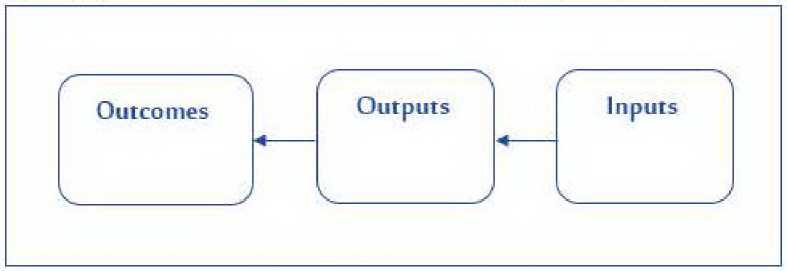
Figure 2 – Local Development as a Process (Inputs, Outputs, Outcomes)
Source: (Jouen, et al., 2010).
beneficiaries.
– Outcomes: Development, strategy, renewal, effectiveness, future, social innovation, empowerment, legitimacy, well-being, facilities, and collective intelligence are all aspects of collective and public goods.
Therefore, there are several contemporary fields contributing to achieving local development, including: tourism and educational tourism (Tomasi, Paviotti, & Cavicchi, 2020), education, mining, geotourism (Xu & Wu, 2022), climate change, sustainable local development, social innovation (Nyseth & Hamdouch, 2019), social diversity, creativity, and traditional communities. Thus, it is possible to discern a close correlation between local development and other factors that are not exclusively associated with the economic and social spheres, but also with the environmental. The term "local development" is no longer perceived as an isolated occurrence;
Methodology
This study primarily aims to examine the current state of local development in Algeria. Given the difficulty in measuring the level of local development across the entire Algerian territory, the study focuses on Annaba Province, the fourth largest city in Algeria. The analysis covers the local development status in this province, the efforts undertaken, and the obstacles hindering the developmental process. Additionally, this study seeks to provide a preliminary examination that contributes to the enrichment of the subject of local development in Algeria, drawing the attention of researchers and specialists to its importance and paving the way for further future research and studies.
Analysis of Efforts and Obstacles to Local Development in Annaba Province
Overview of Annaba Province
Annaba Province is located in the northeast of Algeria, 600 km east of the capital Algiers, 150 km from Constantine, and approximately 80 km west of the northeastern Tunisian border. According to the latest general housing and population census in 2020, its population is 802,768 inhabitants.
According to the administrative division of 2019, which included the creation of a new administrative district, the administrative division of Annaba Province now comprises 06 districts and 12 municipalities as follows (table 1).
Thanks to its strategic geographic location, natural resources, diverse infrastructure, and history, Annaba stands out as an industrial and tourist hub, particularly due to the following attributes:
– It has an 80 km-long coastline along the Mediterranean Sea.
– It boasts a diverse infrastructure network, including multi-service land, sea, and air facilities (a port with a container terminal, an international airport, a railway station, and two bus stations (national and regional)).
– Significant maritime capabilities, with an annual fishing capacity of approximately 30,000 tons.
– Exceptional tourism potential from its numerous small coastal beaches, including Sidi Akacha in Chetaibi, Jenan El Bey in Seraïdi, Ain Achir in Annaba, and one of the world's most beautiful bays in Chetaibi.
– A rich industrial base with large national and international industrial complexes (ARCELOR MITTAL, FERTIAL, FERROVIAL).
– Two university poles meeting international standards with a total capacity of 53,000 students.
– A technology park (Techno Park) whose mission is to create the best conditions to foster innovation by bringing together strategic partners.
To assess the state of local development in Annaba Province, the following will be analyzed: Municipal Development Plans (PCD), decentralized sectoral programs (PSD), and the status of investment projects in the province.
Figure 3 – Map of Annaba Province
Source: Prepared by the researchers based on data provided by the Directorate of Programming and Budget Monitoring of the Province of Annaba.
Table 1 – Administrative Division of Annaba Province
|
Districts |
Municipalities |
|
Province Delegation of Mostafa Ben Aouda |
Oued El Aneb |
|
Annaba |
Annaba, Seraïdi |
|
El Bouni |
El Bouni |
|
Berrahal |
Berrahal, El Tarf |
|
El Hadjar |
El Hadjar, Sidi Amar |
|
Ain Berda |
Ain Berda, El Alama, El Sherka |
|
Chetaibi |
Chetaibi |
Source: Prepared by the researchers based on data from the (Ministry of Interior, 2024).
Municipal Development Plans (PCD)
This program was initiated under Decree 81/380 as part of implementing the decentralization policy in managing public expenditure and granting a degree of autonomy to local authorities in realizing economic and social development projects within their municipalities. This is because local authorities are more aware of their municipalities' realities and local development needs. These programs oversee the implementation of several local development projects, including those related to agriculture, irrigation, economic, social, and administrative facilities, environment, health and sanitation, education and youth, urban planning activities, sanitation, water networks, and road and forest track infrastructure.
According to data obtained from the Directorate of Programming and Budget Follow-up, Annaba Province benefited from a financial allocation of 1,700,000,000 DZD under the 2022 Municipal Development Plan (figure 4).
The distribution of financial amounts allocated to municipal development programs is subject to several considerations, particularly population size and local development levels. Thus, it is natural to observe an imbalance between municipalities, especially between major poles characterized by their population weight, urban expansion, and economic significance, which necessitate large amounts of funds to provide services and infrastructure, and smaller municipalities with modest populations and limited urban expansion. However, this should not justify the neglect or exclusion of isolated municipalities from local development across various economic and social sectors.
The distribution of municipal program funds has not been equal or balanced. This might be considered natural if we base it on the principles of population size and urban expansion in certain cities, particularly major poles such as the municipalities of Annaba and El Bouni, which are district centers with significant population sizes and urban expansion, requiring substantial financial allocations to develop infrastructure and provide various essential services for the citizens. In contrast, some medium and small municipalities, such as Berrahal, Sidi Amar, and Seraidi, have been allocated less financial amounts due to their modest populations. The following figure illustrates the distribution of the population in the Province of Annaba by municipality (figure 5).
It is observed that the majority of the population of Annaba is concentrated in both the municipality of Annaba and the municipality of El Bouni, with more than half of the total population of the Province of Annaba, which is 609,499 inhabitants according to the latest statistics, residing in these two municipalities. This explains their urban expansion and economic significance, which necessitate substantial amounts of funds to provide services and infrastructure.
Regarding the registered projects, they can be illustrated in the following figure 6.
It is observed that the registered projects within the municipal development plan, totaling 200 projects, primarily targeted activities related to road construction, sanitation, urban development, and drinking water supply. It is worth noting that the financial allocations and projects designated for each municipality were distributed based on specific criteria, including population density and the projects proposed by the municipalities. This methodology allowed for creating a balance between municipalities and diversifying the proposed projects for registration,
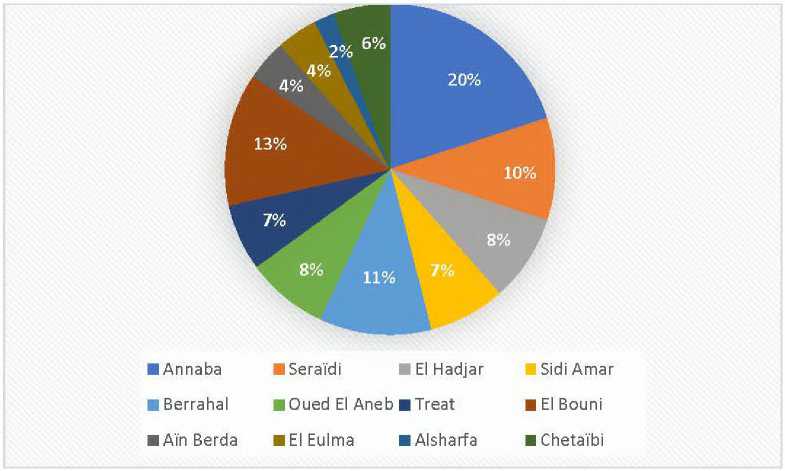
Figure 4 – Geographical Distribution of Financial Amounts of the Municipal Development Plan across the Province
Source: Prepared by the researchers based on data provided by the Directorate of Programming and Budget Monitoring of the Province of Annaba.
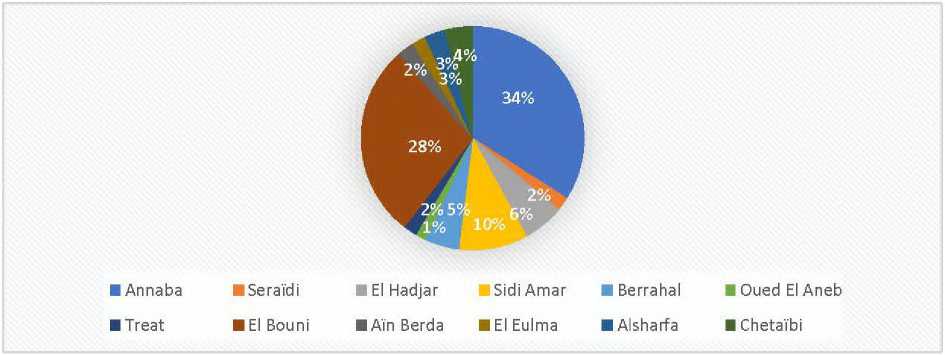
Figure 5 – Distribution of the Population of the Province of Annaba by Municipality
Source: Prepared by the researchers based on data provided by the Directorate of Programming and Budget Monitoring of the Province of Annaba.
-
■ Roads and Pathways ■ Urban Development ■ Drinking Water Supply Environment
-
■ Sanitation ■ Sports ■ Cleanliness and Health ■ Local Markets
-
■ Educational Facilities ■ Administrative Facilities
Figure 6 – Registered Projects within the Municipal Development Plans for the Year 2022
Source: Prepared by the researchers based on data provided by the Directorate of Programming and Budget Monitoring of the Province of Annaba.
thereby addressing the concerns and needs of citizens.
Decentralized Sectoral Programs (PSD)
The sectoral programs are one of the main elements of public investment directed towards development at the national level, implemented by the regional authorities. These programs encompass various major activity sectors such as infrastructure, services, and economic and social activities, covering a wide geographical area at the regional level and sometimes including other regions, particularly concerning roads and water resources. Under this program, the province benefited in 2022 from a state equipment budget amounting to 5,539,300,000 DZD, of which 2,408,600,000 DZD was allocated to decentralized sectoral programs, registering 19 projects as detailed in the following table 2 and figure 7.
The municipalities of Annaba and El Bouni received 5 and 4 projects, respectively. Meanwhile, the municipality of Sidi Amar received 3 projects within the decentralized sectoral program. The remaining registered projects were distributed among other municipalities such as El Chouhada, Chetaibi, and El Eulma. It is worth noting that the financial allocations and projects designated for each municipality were distributed based on specific criteria, including population density and the projects proposed by the municipalities. This methodology allowed for creating a balance between municipalities and diversifying the
Table 2 – Registered Projects within the Decentralized Sectoral Program for the Year 2022
|
Sector |
Number of Projects |
Financial Allocation (DZD) |
|
Road Infrastructure |
04 |
1,387,737,000 |
|
Youth and Sports |
10 |
929,600,000 |
|
Training and Workforce |
01 |
9.000.000 |
|
Health |
04 |
82.263.000 |
|
Total |
19 |
2.408.600.000 |
Source: Prepared by the researchers based on data provided by the Directorate of Programming and Budget Monitoring of the Province of Annaba.
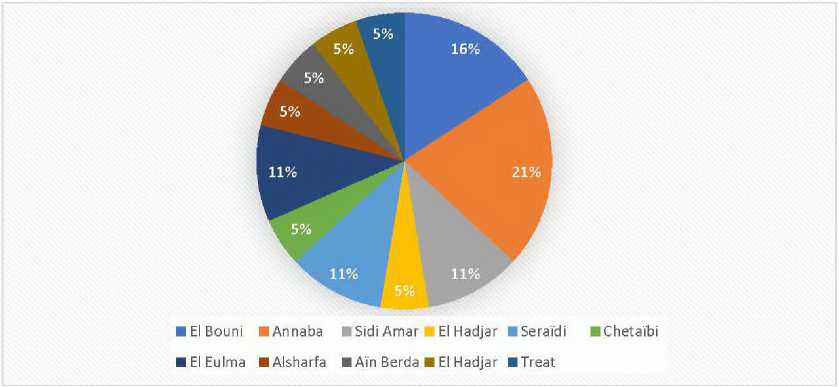
Figure 7 – Distribution of Registered Projects within the Decentralized Sectoral Program for the Year 2022 by Municipality
Source: Prepared by the researchers based on data provided by the Directorate of Programming and Budget Monitoring of the Province of Annaba.
proposed projects for registration, thereby addressing the concerns and needs of citizens.
-
3.4 Status of Investment Projects in the Province of Annaba
-
3.5 Obstacles and Efforts for Local Development in the Annaba Province
Industrial real estate in the Province of Annaba is concentrated in 5 industrial zones: Berrahal, El Bouni, Sidi Amar, El Hadjar, and Ain Berda, as illustrated in the following figure 8 and table 3.
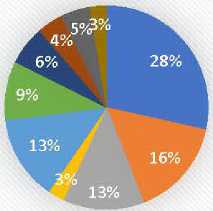
The total number of registered projects in the province reached 314, some of which were operational and others under construction. These projects occupied an area estimated at 749.95 square hectares with full capacity in some industrial areas such as El-Hadjar, Sidi Amar, and El-Bouni, as well as the old industrial area of Berrahal. Subsequently, a new industrial area in Berrahal, estimated at 367 square hectares, is under development. As for the distribution of projects by sector, it is illustrated in the following figure 9.
The previous figure illustrates the distribution of projects by sector of activity, where the largest percentage is for the food industries with 82 projects, followed by the pharmaceutical and home appliance industries, respectively. Then come the chemical industries and services, and finally, the traditional industries, which had the lowest percentage among the aforementioned sectors.
Through the field internship conducted in the Annaba Province, specifically at the Directorate of Programming and Budget Monitoring of the Annaba Province, in addition to the tangible reality data, it is found that there are many obstacles hindering comprehensive local development in the Annaba Province. The most notable obstacles can be summarized as follows:
– Despite the efforts made, bureaucracy remains one of the main problems hindering local development in the Annaba Province, through complex administrative procedures, pervasive routine, and extreme slowness in issuing orders and decisions.
– The provincial administration suffers from a significant shortage in the staffing and professional competence of employees and users.
– Regarding projects, the Annaba Province suffers from the lack of land provision for investors and businessmen, which results in missed opportunities for financial or practical benefits and reduces the scale of unemployment.
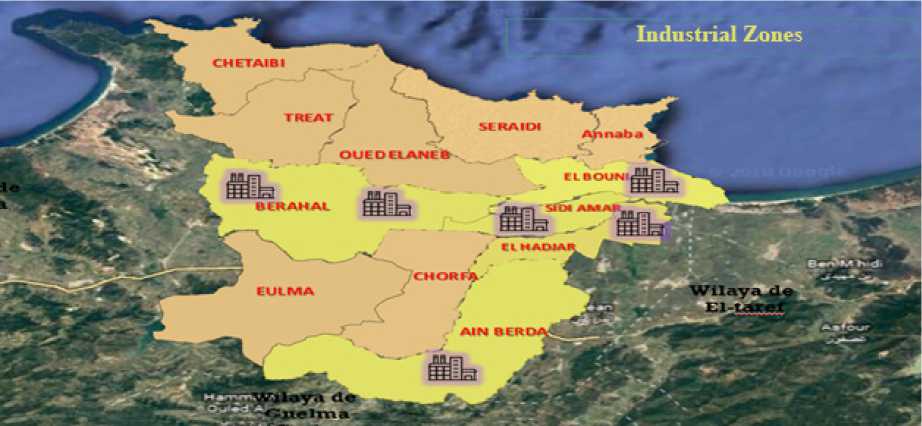
Figure 8 – Distribution of Industrial Zones in the Province of Annaba
Source: Directorate of Programming and Budget Monitoring of the Province of Annaba.
Table 3 – General Data on Industrial Zones in the Province of Annaba
|
Designation |
Area (ha) |
N. Plots |
Area of Plots (ha) |
N. Allocated Plots |
Allocated Area (ha) |
N. Vacant Plots |
Vacant Area (ha) |
Development Status |
N. Projects |
|
Al Hadjar |
117.4 |
68 |
101.6 |
68 |
101.6 |
0 |
0 |
Prepared |
61 |
|
Sidi Amar |
62.59 |
57 |
55.8 |
57 |
55.8 |
0 |
0 |
Prepared |
50 |
|
Berrahal |
121.8 |
86 |
116.8 |
84 |
115.42 |
2 |
1.38 |
Prepared |
63 |
|
El Bouni |
50.68 |
62 |
40.05 |
62 |
40.05 |
0 |
0 |
Prepared |
50 |
|
Ain Berda |
101 |
140 |
79.1 |
107 |
62.5 |
33 |
16.6 |
In Progress |
82 |
|
Berrahal |
367 |
32 |
356.6 |
13 |
22.32 |
10 |
334.3 |
Unprepared |
8 |
|
Total |
820.5 |
436 |
749.95 |
391 |
397.69 |
45 |
352.28 |
/ |
314 |
Source: Prepared by the researchers based on data provided by the Directorate of Programming and Budget Monitoring of the Province of Annaba.
– Weak performance foundations and standards and the lack of incentive systems.
– Natural factors, where climate changes, especially drought waves resulting from unprecedented high temperatures in the province, have had severe effects, with agricultural production in the province declining dangerously, unlike previous periods when the province was considered an important food basket for Algeria.
– Many development projects are in a state of freeze, which has contributed to slowing the development pace of the province, especially those half-completed projects. Here we record 96 stalled projects at a rate of 31%, representing a third of the registered projects in the Annaba Province, which is a very high percentage.
To address the various aforementioned obstacles, a provincial committee was established pursuant to
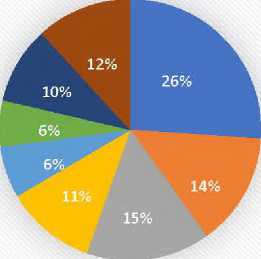
-
■ Food Industry ■ Pharmaceutical Industry
-
■ Electrical and Home Appliances Industry Chemical Industry
-
■ Storage and Packaging ■ Craft industry
-
■ Shipbuilding and Repair ■ Services
Figure 9 – Distribution of registered projects by sector of activity
Source: Prepared by the researchers based on the data provided by the Directorate of Programming and Budget Monitoring of the Province of Annaba.
Provincial Decision No. 21/3450 dated October 24, 2021, and expanded to include the district heads to inspect facilities and grant operating licenses. A sub-provincial committee was also established pursuant to Decision No. 22/380 dated January 6, 2022, to inspect investment projects and assess their readiness for review by the committee. Consequently, the following measures were taken to overcome those obstacles:
– A unit was established to study building permits, where 36 building permits were issued to investors, thus providing 1,000 jobs in workshops to implement these projects, and upon entering the operational phase, they will provide 1,500 direct jobs.
– Requests for activity change were studied by the CALPIREF committee, which was reactivated to consider requests from investors with stalled projects due to requests to change their activity to meet market demands. Approval was granted, enabling 11 investors to change their activity and granting them updated new privilege decisions with the new and required activity.
– Additionally, it is necessary to take into account government instructions regarding the promotion of the national economy in the field of investment promotion, particularly:
-
• Reviewing the legal texts related to economic real estate.
-
• Recovering unused industrial land, as there are lands granted to investors for 10 years but have not been utilized until now.
-
• Industrial land should be granted based on the terms of reference, with the first clause being that if the land is not utilized after 6 months, it is withdrawn from the investor; the land is for those who work it.
-
• Involving private investors in developing these areas through cooperatives to reduce the burden on the state.
-
• Reviving the spirit of entrepreneurship among the youth.
-
• Working to put the one-stop-shop into service from now until the end of the year, enabling national and foreign investors to benefit from its services.
Conclusion
The topic of local development has gained increasing attention in many countries, particularly in developing nations, either at the level of their economic policy or in academic and scientific research. Local development aims to address the developmental imbalance these countries generally suffer from, especially given the changing nature of the state's role and the fact that local development is primarily linked to internal factors that can be largely controlled rather than external factors that are difficult to manage.
Algeria is currently striving to achieve comprehensive and sustainable local development to permanently overcome the problems and crises it faces, like other developing countries. The results of the study on the reality of local development in the Annaba Province, serving as a model for Algerian provinces, revealed significant efforts by the government to support local development in the province through: funding various infrastructure plans (PCD) and decentralized sectoral programs (PSD), contributing to the establishment and development of industrial areas in the province, involving private investors, and promoting entrepreneurship among the youth, among other measures. However, there remain numerous obstacles preventing the enhancement and sustainability of local development in the Annaba Province, including bureaucracy, weak human resource training, lack of land availability for investors, weak performance standards, lack of incentive systems, natural factors, etc., which have resulted in a third of the province's projects being stalled and incomplete.
Based on this, the following suggestions can be offered to support local development in the Annaba Province:
– Ensure integrated local development, as local development must adopt a comprehensive concept from social development to political, economic, ethical, psychological development, and the development of education, scientific research, and technology.
– Activate the role of the General Inspectorate of the province in terms of oversight and coordination with the regional audit chambers of the Regional Court of Accounts to assist the governor in eliminating manipulation in the ways projects are granted and executed.
– Encourage local investment in the province by incentivizing it through tax reductions and various other facilitations.
– Adopt a wide-ranging agricultural reform program in the province that includes organizing land ownership and redistribution, alongside focusing on traditional and family farming in municipalities and districts.
– Continue supporting the creation of small and medium-sized enterprises, facilitating their access to funding and other measures that help incubate and develop them. Given that the topic of start-ups is currently gaining significant momentum in Algeria, support for youth, especially university graduates, in realizing their start-up projects should be continued.
– Within the Ministry of the Interior's efforts to modernize the sector, it is necessary to increase the training level of administrative and technical employees of the province to raise efficiency levels, in addition to continuing the digitization approach in the province and generalizing it.
Список литературы The reality, efforts, and obstacles of local development in Algeria: the case of Annaba province
- Abboudi, N. (2014). Sustainable Local Development in the Province of Guelma: Realities and Perspectives. Thesis to obtain the grade of Doctor in Urban Planning. Constantine, Algeria: University of Constantine 3.
- Bahouri, N. (2023). Social Policy and Its Role in Achieving Local Development in Algeria. Journal of Echoes Legal and Political Studies, 6(1), pp. 154-173.
- Bendiabdellah, A., Benabou, D. and Tabeti, H. (2014). Governance and Local Development in Algeria: Illustration of the Perception Of Local Actors through the Use Of Cognitive Mapping. Journal of Economics and Management, 13(1), pp. 48-55.
- Benmahdi, H. and Benberrah, S. (2024). The Impact of the Contribution of Transport Means in Achieving Sustainable Local Development Programmes: The Case Of Algeria. Internationa! Journal of Professional Business Review, 9(7), pp. 1-20.
- Boubir, H. (2018). A Participatory Strategy for Local Development: The Case of the Territory of Tebessa in Nqena.Romanian Journal of Geography, 62(1), pp. 99-113. doi:10.30892/gtg.40122-818.
- Boulhila, S., Alouat, M., Rezzaz, M. and Schmitz, S. (2022). Towards Development Models of Local Cultural Tourism through the Involvement of Local Actors (Province of Constantine, Algeria). GeoJournal of Tourism and Geosites, 40(1), pp. 9-19. doi:10.30892/gtg.40101-797.
- □ouII, S. and Slimani, I. (2016). Tourism Impact on the Social Development in Algeria. Journal of Economics and Sustainable Development, 7(4), pp. 55-59.
- Elliott, R. and Timulak, L. [20Z\). Essentials of Descriptive-Interpretive Qualitative Research: A Generic Approach. Washington: American Psychological Association.
- Ferdj, Y. (2020). The Process of Local Development in Algeria: Exploratory Study of the Case of the Province of Blida. J ournal of Economy and Human Development, 11(3), pp. 373-387.
- Ferdj, Y., Hamadi, A. and Datoussaid, A. (2023). Local and Territorial Economic Development in Algeria: State of Play. Journal of Business and Trade Economics, 8(1), pp. 510-530.
- Fertas, L., Alouat, M. and Benmahamed, H. (2022). Thermal Tourism as a Driver of Local Development: An Illustration of Opportunities and Constraints. Case Study of Hammam-Guergour in the Province of Setif, Algeria. GeoJournal of Tourism and Geosites, 40(1), pp. 136-143. doi:10.30892/gtg.40116-812.
- Herizi, R. and Belkacem, D. (2016). Local Industrial Development in Algeria. Journal of Business and Retail Management Research, 10(3), pp. 24-33.
- Jouen, M., Kolosy, K., PellegrinJ., Ramsden, P., Szegvani, P. and Chambón, N. (2010). Cohesion Support for Local Development: Best Practice and Future Policy Options. Final Report. European Commission.
- Kelfaoui, A., Rezzaz, M. and Kherrour, L. (2021). Revitalization of Mountain Rural Tourism as a Tool for Sustainable Local Development in Kabylie (Algeria): The Case Of Yakouren Municipality. GeoJournal of Tourism and Geosites, 34(1), pp. 112-125. doi:10.30892/gtg.34115-626.
- Kisman, Z. and Tasar, I. (2014). The Key Elements Of Local Development. Journal ofProcedia Economics and Finance, 15, pp. 1689-1696. doi:10.1016/S2212-5671(14)00642-X.
- Lamrani, L. (2021). Actors, Territorial Dynamics, and Local Development: The Case of the Soummam Valley in Algeria. Thesis to Obtain the Grade of Doctor in Economic Sciences. Grenoble, France: University of Grenoble Alpes.
- Milán-García, J., Uribe-Toril, J., Ruiz-Real, J. and De Pablo Valenciano, J. (2019). Sustainable Local Development: An Overview of the State of Knowledge. Resources, 8(1), pp. 1-18. doi:10.3390/resources8010031.
- Nina, DA, Fernandez, G.Q. and Cuesta, P.S. (2019). Describing Local Development in Indigenous Peoples. Journal of Sustainable Development, 12(1), pp. 148-155. doi:10.5539/jsd.v12n1p148.
- Nyseth, T. and Hamdouch, A. (2019). The Transformative Power of Social Innovation in Urban Planning and Local Development. Journal of Urban Planning, 4(1), pp. 1-6. doi:10.17645/up.v4i1.1950.
- Ruiz-Real, J., Uribe-Toril, J., De Pablo Valenciano, J. and Pires Manso, J. (2019). Ibero-American Research on Local Development: An Analysis of Its Evolution and New Trends. Resources, 8(3), pp. 1-16. doi:10.3390/resources8030124.
- Sekuta, A. (2022). Local Development-The Definition Aspect in the 21st Century. Company at the Turn of the 21st Century. Rzeszów: University of Technology.
- Tomasi, S., Paviotti, G. and Cavicchi, A. (2020). Educational Tourism and Local Development: The Role of Universities. Sustainabilitv, 12(14), pp. 1-15. doi:10.3390/su12176766.
- Xu, K. and Wu, W. (2022). Geoparks and Geotourism in China: A Sustainable Approach to Geoheritage Conservation and Local Development - A Review. Land, 11(9), pp. 1-20. doi:10.3390/land11091493.


