The role of endocrinological changes and obesity in the pathogenesis and origin of psoriasis
Автор: Umarova Muhabbat, Abdunabieva Hakima, Abdurahimov Abdukhalim, Nugmanov Ozodbek, Toshpulatov Bekmirza
Журнал: Re-health journal @re-health
Рубрика: Дерматовенерология
Статья в выпуске: 2,3 (6), 2020 года.
Бесплатный доступ
In spite of the fact that many developments are recorded in the treatment and pathogenesis of psoriasis, its etiology still remains obscure. Psoriasis is a chronic, common skin disease, which affects the patient’s quality of life to the highest degree. Several exogenous factors and endogenous hormonal changes may act as triggers for psoriasis. The skin possesses a true endocrine system, which is very important in multiple systemic diseases. A number of conditions are associated with psoriasis, and its severity can also be influenced by hormones and obesity. Hormones which can influence the psoriasis clinical manifestations: glucocorticoids, epinephrine, thyroid hormones, prolactin, sex hormones and insulin.
Psoriaz, jinsiy gormonlar, prolaktin, glyukokortikoidlar, epinefrin, qalqonsimon gormonlar, psoriasis, sex hormones, prolactin, glucocorticoids, epinephrine, thyroid hormones
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14125581
IDR: 14125581 | DOI: 10.24411/2181-0443/2020-10080
Текст научной статьи The role of endocrinological changes and obesity in the pathogenesis and origin of psoriasis
Introduction: Psoriasis vulgaris, an immunologically mediated skin disease, is a common disorder, having as main pathogenetic mechanisms the chronic inflammation and keratinocytes hyperproliferation [1]. The keratinocytes differentiation is altered and the expression of genes in the psoriasis plaque may also be affected [2]. The antimicrobial peptides and proteins production during the innate and adaptive immune response reflect the genetic susceptibility to psoriasis [3]. Psoriasis vulgaris is not a life threatening disease, but it affects severly the quality of life; there is still no causative treatment [4]. Due to the psoriasis chronicity and the absence of a curative definitely treatment [5], the disease prevalence remains a question [6]. In addition the role of endocrinological factors in the origin of psoriasis has long been known. It can be especially difficult in the first stage of pregnancy [7]. The onset of psoriasis vulgaris may be at any age, but two peaks were observed, around 20–30 and over 50 years of age [9]; pediatric psoriasis can reach about 30% of all cases [10]. The early onset of chronic plaque psoriasis in white population was associated with 36 genetic loci [11], a finding which supports the assumption that the age of onset is, at least partially, genetically determined [12].
Interdependence of psoriasis and insulin. A possible pathogenetic link between psoriasis and atherosclerosis has been identified by S. Boehncke and other scientists. They took 39 consecutive “moderate” grade “severe plaque” type psoriasis patients for the study. The intima-media thickness of the carotid artery was measured using ultrasound and an oral glucose tolerance test was performed to assess the homeostasis model of insulin resistance (HOMA). Thus, a correlation between BMI and HOMA (P <0 • 02) as well as BMI and vascular wall thickness (P <0 • 05) was successfully identified. As for psoriasis, they also found that there was a significant correlation between psoriasis area and weight index (PASI) and insulin secretion. They also found that several measurements of insulin resistance were significantly associated with PASI [14].
Interdependence of psoriasis and stress hormones. Endocrine and immune reactions are both highly influenced by stress. At the same time, the evolution is marked by the important stressful moments in life. The hypothalamic-pituitary-suprarenal axis controls the stress hormones, cortisol and epinephrine, which are antagonists and have important effects on immune system. Immune cells (macrophages, lymphocytes T and B) express beta-adrenergic receptor and epinephrine induces multiple but dual immune responses: promotes macrophages responses through increasing secretion of cytokines TNF-α, IL-1, IL-10, and regulates the level of T and B lymphocyte function. Also, it has bee observed that an acute activation of the sympathetic nervous system attenuates the innate immune response. The immunomodulation in stress takes place through intersections in signaling cascade at different levels: for example, stress signals in immune response are regulated through the key Nuclear Factor-kappaB (NF-κB) and the epinephrine stimulation of β2-adrenergic receptors, expressed on immune cells, intersect with the NF-κB signaling cascade. Glucocorticoids prevent the inflammatory changes by inhibiting the migration of leukocytes and suppressing T cells. The stimulation of epinephrine and adrenergic receptors may also exert some corticosteroid effects. The cortisol response to stress is diminished in psoriasis. The psoriatic patients present higher levels of epinephrine and adrenocorticotropic hormone and lower levels of cortisol and corticotrophin releasing factor. Epinephrine can modulate the remission phase and cortisol the eruption phase. The stress link in psoriasis is sustained also by the fact that a regular physical activity may have favorable effect on psoriasis evolution. Through metabolic and psycho-neuro-immune effects, a regular exercise influences positively the metabolic comorbidities, lowers the risk and the onset of psoriasis [15,32].
Interdependence of psoriasis and thyroid hormones. Propylthiouracil, an antithyroid preparation, was successfully used both in local and systemic treatment of psoriasis. Although the mechanism of action was unclear, it was suggested that this drug might have a regulatory effect on the T cells in the psoriasis plaque. Propylthiouracil increased the number of total and suppressor/cytotoxic T cells and reduced activated lymphocytes in psoriatic plaques. Other anti-thyroid agents, such as methimazole and thiamazole, have also been used successfully in the treatment of psoriasis. This means that thyroid hormones may have unknown effects on the disease. It is postulated that T3 receptors may play a role in the synthesis of keratin. The existence of T3 receptors on the skin was also proved. Propylthiouracil, which is known to be an anti-thyroid drug, may affect the keratin synthesis process by binding to nuclear T3 receptors. It is also known that T3 has a major role in the regulation of cell growth and differentiation. Moreover, it has been stated that T3 and T4 have hyperproliferative effect on the skin by EGF. In this study the serum TT4 and FT3 levels were significantly higher in psoriatics than in the control group. The average PASI scores were significantly higher in these patients and this may be due to the direct or indirect effects of thyroid hormones on the course of psoriasis. Thus excessive production of thyroid hormones may aggravate psoriasis. The skin may be a target organ for thyroid hormones and these hormones increase EGF and therefore accelerate epidermal proliferation. The role of these hormones on the etiopathogenesis of psoriasis will become clearer when the effect of thyroid hormones on keratinocytes and the anti-proliferative effect of anti-thyroid drugs on psoriasis are better demonstrated with experimental studies. Meanwhile, it may be useful to check the thyroid function in patients with uncontrolled and relapsing psoriasis [16].
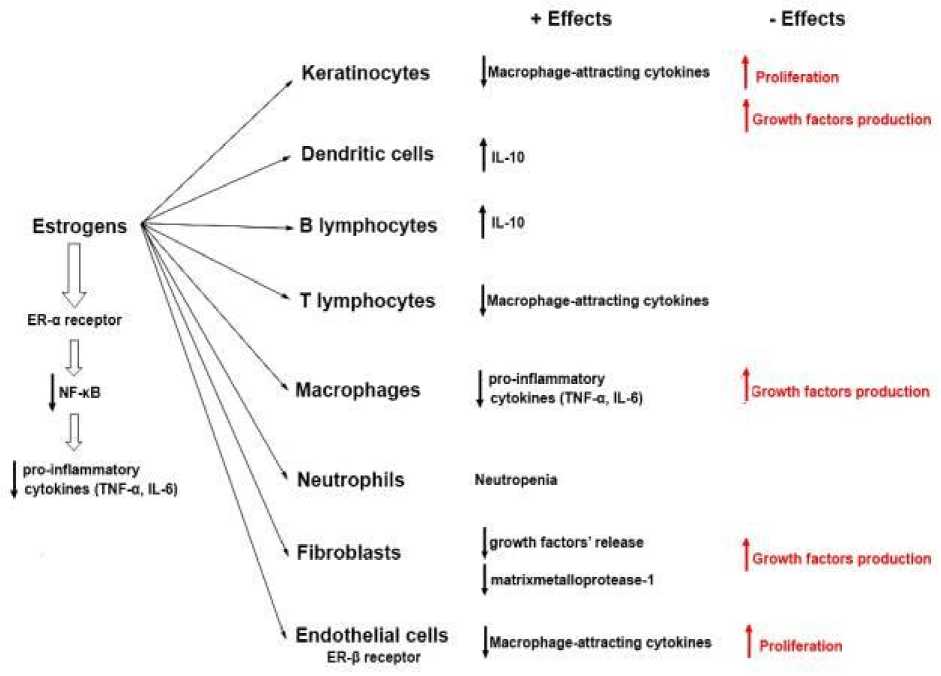
Interdependence of psoriasis and sex hormones. Extremely high levels of hormonal and immunological changes occur during pregnancy, as maternal adaptations to the developing fetus. The evolution of psoriasis is variable during pregnancy [17]. At mid pregnancy (around 30th week of gestation), the patients’ psoriatic symptoms can diminish (in >50%) or worsening (in >20%) [18]. A possible explanation could be that at this moment, there is an immunity shift from Th2 to Th1, mainly due to the increased levels of estrogen, progesterone and cortisol (Figure 1) [19]. Other chronic immune diseases Th1-driven were shown to improve during pregnancy, such as multiple sclerosis [20] and rheumatoid arthritis [21]. Therefore, it was supposed that the increased hormone levels improve the psoriatic symptoms [22]. Due to the decrease in hormonal levels after parturition and during menopause, the psoriasis severity seems to accentuate. In these conditions, it was assumed that the flares occurring in the postpartum period represent rather a return to the initial level than a true worsening [18]. A moderate or severe form of psoriasis can increase the risk for a poor outcome in pregnancy [23], abortions, eclampsia, premature rupture of membranes, or macrosomia [24], but this can be due to the multiple comorbidities associated with psoriasis, which can represent risk factors in pregnancy. Definitely, psoriasis does not represent a contraindication for a pregnancy [22]. If a systemic treatment is necessary, mothers are told not to nurse because the drugs may be excreted in milk [25]. During menopause, the estrogen level decline and a low-grade inflammation may appear [26], meaning that menopause may aggravate the psoriasis evolution [27]. This fact is in concordance with the observation that after menopause the incidence of chronic inflammatory diseases in women became closer or higher than the incidence in males [28]. The epidermis, dermis and hair follicle and the associated sebaceous glands express androgen receptors, and the skin is an important androgen target [29]. Androgen hormones influence the homeostasis of the epidermal barrier, the growth and differentiation of the hair and the sebaceous gland [30]. They also antagonize the macrophage’s production of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which can prolong the inflammation and the wound healing. The adrenal androgens decrease in chronic inflammatory diseases and the therapies based on androgen can aggravate/exacerbate psoriasis [31]. Prolactin (PRL) is the pituitary hormone of lactation and reproduction. The epidermal keratinocytes express receptors for prolactin and the hormone has proliferative effects on keratinocytes , epithelial cells, and lymphocytes. There is a true “PRL–skin connection”. PRL exerts a variety of immunostimulative effects which may promote the development of psoriasis: it enhances keratinocytes chemokine production (IL-17) and favors infiltration with Th lymphocytes, stimulates IFN-γ production and promotes angiogenesis, regulates the maturation of T cells. According to those multiple immune roles, hyperprolactinemia was observed in several autoimmune diseases (lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, Sjogren’s syndrome, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, multiple sclerosis). PRL is involved in the psoriasis etiopathogenesis and this role of prolactin is sustained by the observations that psoriasis can be aggravated during the development of prolactinoma. A significant decrease in prolactin level in patients with psoriasis was noticed after systemic treatment. Several studies have shown a positive relation between serum prolactin levels and psoriasis severity. Bromocriptine, used in prolactinoma, may be useful in the psoriasis treatment [32].
* Effects • Effects
Proliferation
Growth factors production
| IL-10
ER-o receptor
T lymphocytes
Macrophage-attracting cytokine*
Growth factors production
Fibroblasts growth factors' release matrixmetalloprotease-1
Growth factors production
Endothelial cells
ER-p receptor
Macrophage-attracting cytokines
Proliferation
Keratlnocytes
Dendritic cells
Macrophage-attracting cytokines
| IL-10
Estrogens
В lymphocytes
|nf-*b
( pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-a, IL-6)
Macrophages
Neutrophils
I pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-o, IL-6)
Neutropenia
Figure 1: Positive and negative effects of estrogens, differently mediated by ER-α and ER-β [ 19]
Interdependence of psoriasis and obesity. Also, there is a relationship between leptin, obesity and psoriasis. But there are contradictive reports regarding the leptin levels in psoriasis, significantly decreased or higher. But, an argument for the leptin molecular link between psoriasis and metabolic comorbidities is represented by the higher serum levels of leptin in overweight or obese psoriatic patients. Strongly associated with insulin resistance are both psoriasis and obesity. In both, there are also common pro-inflammatory pathways involved (TNF-α, IL-6). Reducing the obesity chronic low-level inflammation may improve insulin sensitivity and leptin levels [32]. Association between Psoriasis and Obesity One of the first reports about the relationship between psoriasis and obesity came from Sweden in a study including 159,200 individuals who were followed up over a 10-year period [33] . In the study, the authors found an association between women with psoriasis and obesity. In 1995, Henseler and Christophers [34] conducted a registry-based
Obesity Biological effects
|
Adiponectin ↓ |
Appetite ↑ Insulin sensitivity ↑ Glucose uptake by white adipose tissue and skeletal muscle ↑ Oxidation of free fatty acid in liver and skeletal muscle ↑ |
|
Leptin ↑ |
Resting energy expenditure ↑ Lipolysis ↑ Hepatic lipogenesis ↓ |
|
Resistin ↑ |
Insulin resistance ↑ Free fatty acid release by white adipose tissue ↑ |
|
Visfatin ↑ |
Probably insulin-like effects |
Table 1. Biological effects and regulation of major adipokines in the obese state
Conclusion: Even though the sex hormones and prolactin are the most implicated in psoriasis pathogenesis and clinical manifestations, there are a lot of other hormonal mechanisms with significant influence on the evolution of psoriasis, therefore new therapeutic ways need to be explored. At the same time, a hormonal assessment should be performed in patients with psoriasis, in order to correctly diagnose and treat pathologies that may be related with psoriasis exacerbations. Due to the pathogenic complexity, there a curative treatment for psoriasis is still missing and hormonal therapeutic interventions may relieve the clinical phenomena in psoriasis. Evidence is strongly suggestive that obesity, through pro-inflammatory pathways, predisposes to the development of psoriasis and that obesity aggravates existing psoriasis. While larger, randomized trials are needed to fully elucidate the potential effect of weight reduction on the severity of psoriasis, current knowledge supports the necessity of nutritional care as part of the management of psoriasis, in particular as weight loss has a substantial and positive effect on the cardiovascular risk profile in these patients. Also, treating overweight patients with psoriasis imposes certain problems such as increased risk of adverse events, reduced efficacy of biologicals, and higher treatment costs, which further underscore that weight reduction in these patients should be one of the aims of their management.
Список литературы The role of endocrinological changes and obesity in the pathogenesis and origin of psoriasis
- Gudjonsson JE, Elder JT. Psoriasis: epidemiology. Clin Dermatol. 2007;25(6):535-546.
- Liu Y, Krueger JG, Bowcock AM. Psoriasis: genetic associations and immune system changes. Genes Immun. 2007;8(1):1-12.
- Batycka-Baran A, Maj J, Wolf R, Szepietowski JC. The new insight into the role of antimicrobial proteins-alarmins in the immunopathogenesis of psoriasis. J Immunol Res. 2014.
- Schafer T. Epidemiology of psoriasis. Review and the German perspective. Dermatology. 2006;212(4):327-337.
- Naldi L. Epidemiology of psoriasis. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 2004;3(2):121- 128.


