The role of liquid biopsy in the diagnosis of glioblastoma progression
Автор: Ryabova A.I., Novikov V.A., Choynzonov E.L., Spirina L.V., Yunusova N.V., Ponomareva A.A., Tamkovich S.N., Gribova O.V.
Журнал: Сибирский онкологический журнал @siboncoj
Рубрика: Обзоры
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.21, 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Purpose: to summarize available data on the diagnostic value of various circulating biomarkers for the detection of glioblastoma recurrence. material and methods. a literature search was conducted using pubmed exocarta and silVa databases. results. glioblastoma multiforme (gBm) is the most common glioma in adults with an unfavorable prognosis. treatment of tumor recurrence can improve the survival of patients. Neuroimaging is the standard method of diagnosing brain tumor recurrence. However, a neuroimaging method to clearly distinguish between pseudo progression and tumor progression has not been found to date. current molecular tumor profiling relies heavily on tissue resection or biopsy. tissue profiling has several disadvantages in the central nervous system’s tumors, including the challenge associated with invasive biopsy, the heterogeneous nature of many malignancies where a small biopsy can under represent the mutational profile. liquid biopsy is a promising method in diagnosing malignant tumors. Blood collection is a simple, minimally invasive procedure, but cerebrospinal fluid allows tumor markers to be detected more confidently. However, collection of cerebrospinal fluid is a complex and invasive procedure that can be accompanied by serious complications. conclusion. Biological fluid markers such as circulating tumor cells, extracellular vesicles, cell-free dNa and cell-free RNa allow for the detection of gmB, determination of molecular genetic features of cancer during response to therapy, and early detection of gBm recurrence.
Extracellular vesicles, cell-free dna, cell-free rna, circulating tumor cells, glioblastoma recurrence, tumor diagnostics
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/140295084
IDR: 140295084 | УДК: 616-006.484.04-036.17-076 | DOI: 10.21294/1814-4861-2022-21-3-104-116
Текст научной статьи The role of liquid biopsy in the diagnosis of glioblastoma progression
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is the most frequently diagnosed and aggressive glial brain tumor. It is characterized by rapid progression and poor prognosis. According to the results of the Central Brain Tumor Registry of the United States, the largest population register of tumors of the central nervous system, the overall one-year survival of patients with GBM is about 40 %, and the five-year survival is 5–7 % [1]. Even with the current standard of combined treatment in significant randomized Phase III trials, the median progression-free survival does not exceed 11 months. The overall survival is less than two years [2–4]. Currently, the definite diagnosis is established on histological examination of the biopsy samples. How well a tumor will respond to treatment, remain in remission, or recur after treatment depends on the specific tumor type and its molecular makeup [5]. The significant advances in brain imaging have resulted in more detailed anatomic and functional localization of gliomas concerning the eloquent cortex and improvements in microsurgical techniques, and enhanced adjuvant stereotactic radiation delivery. But a recurrent tumor remains a huge issue in modern oncology [6].
The adequate treatment of recurrent GBM can prolong patients’ survival and improve their quality of life [7]. Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), widely used during GBM patients’ follow-up, has no 100 % sensitivity and specificity. A contrast accumulation in the brain during MRI after radiation therapy may indicate the recurrent tumor and the phenomenon of “pseudoprogression” or radiation-induced necrosis. Pseudoprogression occurs in 10–30 % of patients with GBM, usually during the first 12 weeks after adjuvant chemoradiotherapy (CRT) [8]. The opposite phenomenon, namely “pseudo-response”, is characterized by a rapid decrease in contrast enhancement accumulation and stabilization of the blood-brain barrier under the influence of antiangiogenic therapy. It does not indicate an exact tumor response to treatment [8, 9]. Perfusion MRI and nuclear medicine techniques can distinguish between the actively growing tumor and post-radiation necrosis [10]; however, these techniques are not available in all clinics and cannot always detect a recurrent tumor in the early stages [11, 12]. Biopsy verification of GBM recurrence is not performed due to the highly invasive nature of the procedure and complications that may worsen the patient’s condition. When it is impossible to distinguish pseudo-progression from GBM progression, treatment decisions are usually delayed until imaging techniques clarify tumor behavior [13]. Delayed treatment often leads to tumor growth, an increase in the neurological deficit, and poor prognosis.
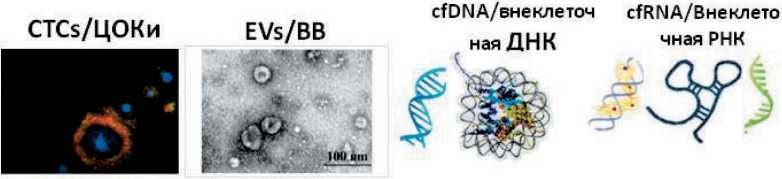
DNA-based GBM markers include IDH1 , IDH2 , MGMT , EGFR mutations and 1p/19q co-deletion [14]. Besides, GBM secrete specific tumor markers (soluble proteins, circulating nucleic acids) both independently and as part of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) and extracellular vesicles (EVs) into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Then these biomarkers can cross the intact blood-brain barrier [15, 16], and it is possible to detect them in the blood of GBM patients. By this reason the potential of the so-called “liquid biopsy” in the diagnosis and treatment of glial tumors, including GBM, is being actively investigated [17–19]. The advantage of liquid biopsy is that it reflects the entire tumor’s genetic diversity and allows repeated studies without the risk of serious complications. The main circulating biomarkers found in biological fluids in GBM patients are CTCs, EVs, circulating coding and non-coding nucleic acids. Currently, GBM does not have a reliable biomarker in serum or CSF. There is no agreed guidance on using single or multiple GBM biomarkers assessments in a clinical setting [19–21]. Accordingly, literature data were analyzed regarding the role of CTCs, EVs, and cell-free nucleic acids secreted into the CSF and blood in the diagnosis of recurrent glioblastoma.
Circulating tumor cells
The importance of detecting of CTCs in CSF and peripheral blood to assess tumor progression and response to therapy has been shown in numerous studies in malignant tumors of various localizations [22–24]. Since extracranial metastases are observed only in 0.2-0.5 % of GBM patients [25, 26], for a long time, it was believed that a unique microenvironment in the brain prevented the migration of glioma cells into the bloodstream [26]. The first attempt to detect CTCs in blood using real time quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assay for the detection of mRNA encoding glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in GBM patients was unsuccessful [27]. The following attempts were made only a decade later. In 2014, in several studies, tumor cells were found in the peripheral blood of GBM patients. Müller and colleagues (2014) isolated CTCs from blood in GBM patients using a fluorescence immunocytochemical analysis with an anti-GFAP antibody as a putative marker for CTCs of glioblastoma. Only 29 out of 141 (20.6 %) patients were found to have 1 to 22 GFAP-positive cells that contained GBM-associated genomic aberrations [25].
For CTCs detection in blood, Sullivan et al. (2014) used CTC isolation protocol with staining with a combination of antibodies to CD14, CD16, CD45, and nuclear staining with DAPI. The number of CTCs detected in 12 patients with a progressive brain tumor was higher (median 11.8 cells per ml) than in 21 patients with stable disease (median 2.1 cells per ml) (p<0.001). Single CTCs isolated from GBM patients demonstrated enrichment for mesenchymal over neural differentiation markers compared with primary GBMs [28].
MacArthur et al. (2014) developed a CTC detection method in the blood samples of GBM patients using an adenoviral-based probe to telomerase reverse transcriptase. The CTC status was confirmed by a FISH study of GFAP and nestin expressions, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) amplification, and the absence of epithelial cell adhesion marker. CTCs were detected in 8 out of 11 (72.7 %) patients with high-grade glioma before starting radiation therapy; the average value was 8.8 cells in ml of blood. The CTC’s diagnostic significance for the early differential diagnosis of progression and pseudoprogression was shown in two cases [11].
Gao et al. (2016) used the determination of chromosome 8 aneuploidy using CEP8-FISH method to detect CTCs. The study included 31 patients with primary WHO grade II-IV gliomas including 11 patients with glioblastoma. The incidence of CTCs in the peripheral blood of patients with grade II–IV glioma was 83 %, 63 %, and 82 %, respectively, with no statistically significant differences (p=0.525). All detected CTCs showed five or more copies of chromosome 8, with the number of CTCs varied from 1 to 10 per 7.5 ml of blood. In five patients with a new growing lesion on the first MRI scan after radiation therapy, the possibility of determining the quantity of CTCs in the peripheral blood for early differential diagnosis of a tumor and radiation necrosis was confirmed [12].
The detection of CTCs is a promising approach to the GMB diagnosis since reliable gliomas markers have not yet been established. The use of various techniques made it possible to isolate CTCs from the blood of GBM patients in 82 % of cases. A clear relationship
Table/Таблица miRNA expression levels as biomarkers of treatment response in GBM patients Уровни экспрессии микроРНК как биомаркеры ответа на лечение у пациентов с глиобластомой
|
miRNAs |
Sample information/ Информация об образцах |
Treatment modality/ Лечение |
Level after treatment/ Уровень маркера после лечения |
References/ Ссылки |
|
miR-10b miR-21 |
CSF, 19 GBM patients/ ЦСЖ 19 больных ГБ |
Remission vs progression/ Ремиссия vs прогрессии |
Decrease in remis-sion/ Снижение при ремиссии |
Teplyuk N.M. et al., 2012 [93] |
|
miR-21 |
Plasma, 10 GBM patients/ Плазма 10 больных ГБ |
Chemoradiation/ Химиорадиотерапия |
Decrease/ Снижение |
Wang Q. et al., 2012 [92] |
|
miR-128, miR-342-3p |
Plasma, 10 GBM patients/ Плазма 10 больных ГБ |
Surgery, Chemoradiation/ Хирургия, химиорадиотерапия |
Increase/ Повышение |
Wang Q. et al., 2012 [92] |
|
miR-15b, miR-23a, miR-133a, miR-150, miR-197, miR-497, miR-548b-5p |
Serum, 26 GBM patients/ Сыворотка 26 больных ГБ |
Surgery/ Хирургия |
Increase/ Повышение |
Yang C. et al., 2013 [109] |
|
miR-454-3p |
Plasma, 22 GBM patients/ Плазма 22 больных ГБ |
Surgery/ Хирургия |
Decrease/ Снижение |
Shao N. et al., 2015 [110] |
|
miR-128 |
Serum, 59 glioma patients (Grade I–IV)/ Сыворотка 59 больных с глиомами |
Surgery/ Хирургия |
Increase/ Повышение |
Sun J. et a.l, 2015 [111] |
|
miR-185 |
Plasma, 19 GBM patients/ Плазма 19 больных ГБ |
Chemoradiation/ Химиорадиотерапия |
Decrease/ Снижение |
Tang H. et al., 2015 [112] |
|
miR-205 |
Serum, 10 glioma patients (Grade I–IV)/ Сыворотка 10 больных с глиомами |
Surgery/ Хирургия |
Increase/ Повышение |
Yue X. et al., 2016 [108] |
|
miR-26a |
Serum, 15 GBM patients/ Сыворотка 15 больных ГБ |
Surgery/ Хирургия |
Decrease/ Снижение |
Parviz H.M. et al., 2019 [113] |
|
miR-214 |
Serum, 30 glioma patients (Grade I–IV)/ Сыворотка 30 больных с глиомами |
Surgery/ Хирургия |
Decrease/ Снижение |
Wang J. et al., 2019 [114] |
Note: CSF – cerebrospinal fluid, GB – glioblastoma.
Примечание: ЦСЖ – цереброспинальная жидкость, ГБ – глиобластома.
between the number of CTCs and tumor progression/ pseudoprogression has been shown [17, 18, 25, 28]. However, the quantity of studies is limited, the quantity of patient samples are not representative, and different CTCs isolation approaches make it difficult to compare the results. There are several limitations to the widespread use of CTCs as a biomarker for glioblastoma progression: 1) the detection of GBM CTCs in the peripheral blood requires a complex combination of technologies and relatively immediate blood sample processing; 2) the method with optimal sensitivity and specificity has not been determined yet. The frequency of CTCs released into the peripheral blood from GBM has not been established.
A major advantage of the next generation sequencing approach for detecting CTCs is the simultaneous identification of several markers relevant for GBM diagnostics, allowing molecular diagnostics on cytological specimens [29].
Extracellular vesicles
EVs are extracellular structures enclosed in a lipid bilayer, secreted or released by normal and tumor cells. EVs can be divided into exosomes, microvesicles, and apoptotic bodies based on the size, morphology, and biogenesis mechanism [30]. EVs released by GBM cells contain a wide range of molecules, including nucleic acids and proteins, which correspond to the primary tumor cells’ specific molecular features and are changed during treatment [21, 31, 32]. Simultaneously, the lipid membrane protects the EVs’ internal contents from enzymatic degradation [30, 33]. It has been shown that EVs from tumor cells cross intact blood-brain barrier and can be found in the blood of GBM patients [16]. EVs can be isolated from CSF and blood plasma by ultracentrifugation, ultrafiltration, or immunoprecipitation. Transmission electron microscopy, nanoparticle tracking analysis, flow cytometry, or western blotting are usually performed to confirm the EVs nature [34, 35].
EVs produced by GBM tumors have been shown to play an essential role in cellular communication and modulation of the tumor microenvironment. They provide tumor heterogeneity, modulate proliferation, reprogram metabolic activity, induce angiogenesis and invasion, and contribute to suppression of the immune response and acquisition of drug resistance [36, 37]. As GBM-derived EVs contain specific “molecular signatures” of their parental cells and can transmigrate across the blood-brain barrier, they are considered a valuable source of potential diagnostic biomarkers.
Several studies have noted a significant increase in the EVs in GBM patients’ blood than people with other malignant neoplasms of the central nervous system and healthy ones [38, 39], however, no correlation was found between the EVs level and the patient’s overall survival [40]. Koch et al. (2014) examined serum microvesicles’ levels in 11 patients with GBM. Samples were collected before CRT, and 1, 3, 6, 12, and 24 months after CRT. A statistically significant difference in the number of microvesicles in tumor progression cases was found compared to patients who responded to treatment (p=0.014) [41]. Andre-Gregoire et al. (2018) isolated exosomes from plasma of six patients with newly diagnosed GBM and healthy donors. Isolated EVs in both groups of patients had a comparable average diameter of 80 nm. However, the exosomes concentration in patients’ plasma with GBM was higher than in the control group [38].
Osti et al. (2019) examined patients with GBM (n=43), healthy people (n=33), and patients with other central nervous system malignancies (n=25). Plasma samples were purified by differential centrifugation with ultrafiltration through a 0.22 μm filter. The average size of EVs in GBM patients and the validation group was about 150 nm. The number of circulating EVs was significantly higher in GBM patients than in healthy controls and patients with metastatic and extra-brain tumors. It has been shown that the EVs level increased in preoperative plasma samples, reliably decreases after the resection of the primary tumor, and again increases with the tumor relapse (p=0.028) [39].
As previously shown by J.M. Fiqueroa et al (2017) CSF-derived EVs contain RNA signatures reflective of the underlying molecular genetic status of GBMs in terms of wtEGFR expression and EGFRvIII status. The high specificity (up to 98 %) of the CSF-derived EV diagnostic test gives us an accurate determination of positive EGFRvIII tumor status which can be useful for therapy strategy [21]. Shao et al. (2012) analyzed a panel of four GBM-related proteins (EGFR, EGFRvIII, podoplanin (PDPN), and isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1) in EVs obtained from the serum of 12 glioblastoma patients. It was shown that EVs demonstrate a distinct molecular signature of the tumor, and increased expression of EGFR, EGFRvIII, PDPN, and IDH1 R132H made it possible to diagnose GBM with an accuracy of 36 % to 76 % using separate markers. When the results were combined, the accuracy increased to 91 %. The drug response index calculated based on the relative changes in the amount of GBM EVs, and the expression levels of EVs biomarkers before and after CTC made it possible to reliably differentiate patients with progression from those who responded to therapy (p<0.005) [42].
Currently, vesicular miRNAs are the most attractive for differential diagnosis, diagnosis of glioblastoma recurrence and assessment of the effectiveness of its therapy. The study of miRNAs obtained from EVs showed the possibility of distinguishing of GBM from non-oncologic patients based on the increased content of miR-21 in CSF EVs with high sensitivity and specificity (87 % and 93 %, respectively) [43]. Ebarahimkhani et al. found twenty-six microRNAs, differentially expressed in GBM patient exosomes. Combination of just four miRNAs (miR-182-5p, miR-328-3p miR-485-3p, miR-486-5p) distinguished GBM patients from healthy controls with 100 % accuracy [44]. A recent meta-analysis found 24 EVs derived RNA biomarkers for GBM diagnosis, and the overall sensitivity and specificity of 16 ones in the meta-analysis were 76 % and 80 %, respectively [45]. Santangelo et al. (2018) evaluated the expression levels of blood-derived exosomal miR-21, miR-222, and miR-124-3p from 25 patients with high-grade gliomas before and after surgery. The assessment of these miRNAs expression in samples obtained after surgery showed a sharp decrease in the number of individual miRNAs: miR-21 (p<0.001), miR-222 (p<0.01), and miR-124-3p (p<0.001), as well as in the cumulative expression level of the studied miRNAs (p<0.001) [46]. Lan et al. (2018) investigated the exosomal miR-301a in the serum of 7 patients with GBM before surgery, two weeks after surgery, and during tumor progression. It was found that its level was significantly higher in patients with glioma than in healthy controls and patients with non-glial tumors (p<0.01). The blood-derived miR-301a exosomal expression was decreased considerably after surgery (p<0.01) and again increased in the GBM recurrence (p<0.01) [47]. In the next study, the exosomal miR-210 level was studied in 10 patients with GBM. Blood samples were taken before the primary tumor's surgical treatment, after surgery, and after diagnosis of disease recurrence. The miR-210 level was significantly reduced after surgery (p<0.01) and at the time of the GBM recurrence (p<0.01) [48].
The expediency of detecting various subpopulations of blood plasma exosomes for evaluating the effectiveness of immunotherapy in patients with recurrent forms of glioblastomas after standard therapy has been shown. Galbo et al. (2017) evaluated the level of blood serum exosomes expressing CD9, GFAP, and survivin on their surface in 8 patients with recurrent malignant gliomas during anti-survivin immunotherapy [49]. Survivin is a family member of apoptosis protein inhibitors associated with poor prognosis and refractoriness to treatment in various cancer types, including gliomas [50]. It was shown that the CD9+/ survivin+ exosomes proportion in patients with glioma was 9.1 % and only 0.43 % in the control group. There was a statistically significant increase in the CD9+/sur-vivin+ exosomes level (p=0.0299) and CD9+/GFAP+/ survivin+ exosomes (p=0.0225) in glioma progression. The authors suggested that the CD9, survivin, and GFAP combined detection on exosomes' surface could be used to assess tumor response in patients receiving survivin-based immunotherapy and to monitor glioma progression. Wang et al. (2019) compared the EGFR expression in serum EVs of 23 patients with glioma before and one week after surgery. Most GBM is characterized by the EGFR1 overexpression; therefore, an EGFR serum level analysis appears to be a promising biomarker [33].
The disadvantages of using EVs as diagnostic material include the duration of vesicles isolation and the presence of a large volume of CSF and blood. There is a problem of isolating the total pool and the pool of tumor EVs, since the concentration of a specific marker of gliomas GFAP on vesicles will be several hundred times lower than on cells of the original tumor due to the peculiarities of exosome biogenesis [30, 51]. There also remains the dilemma of using CSF or blood as a source of total EV or individual EV fractions for the early diagnosis of gliobastoma recurrence, as predictor and prognostic biomarkers.
Cell-free DNA
Extracellular nucleic acids (cfNAs) circulate in the blood as a part of supramolecular complexes, such as nucleosomes, complexes with proteins and lipoproteins, and can bound to the surface of blood cells [52]. Sources of cell-free DNA (cfDNA) are apoptosis, necrosis and active secretion by cells [53]. cfDNA seems to be a promising real-time tumor load biomarker, which can provide minimally invasive monitoring of the response to anti-tumor therapy [54].
Recent studies have confirmed the feasibility of using cfDNA quantification as a biomarker for GBM progression. In a prospective study, Nørøxe et al. (2019) evaluated blood samples from newly diagnosed GBM patients from the date of diagnosis or the start of treatment until disease progression. They observed the highest cfDNA values before surgical procedure and during tumor progression. Determining the cfDNA level helped to differentiate actual tumor progression from pseudoprogression in 3 cases [55].
In another single-center pilot study, Bagley et al. (2020) evaluated plasma cfDNA levels in 42 patients with newly diagnosed GBM from the date of diagnosis until disease progression. Before treatment, patients with GBM had a higher plasma cfDNA concentration than healthy patients in the control group (average 13.4 vs 6.7 ng/ml, p<0.001). A significant increase in plasma cfDNA was found during disease progression in most patients [54]. Thus, the level of cfDNA in peripheral blood can be a valid biomarker of disease progression.
Since an increase of concentration of ctDNA is not specific disease marker (cfDNA high level in the blood was also described in patients with autoimmune diseases [56], sepsis and systemic inflammatory response syndrome [57], myocardial infarction [58], ect., detection of tumor specific genetic alterations can significantly increase the method specificity.
The first attempts to determine tumor ctDNA in the blood of patients with GBM relied on the identification of prognostically significant genetic markers, such as methylation profiles of individual gene promotors, loss of heterozygosity of chromosome 10, IDH1 mutation, and EGFRvIII deletion [59–64]. Some studies have shown that tumor ctDNA can be isolated from the GBM patient’s blood in 15–88.8 % of cases [54, 62, 65–71].
The possibility of detecting tumor DNA in the CSF of a patient with glioblastoma was first reported by Rhodes et al. in 1995 when they determined tumor‐ derived p53 DNA in cisternal CSF at autopsy using allele-specific PCR [72]. Wang et al. examined CSF collected during surgery in 11 patients with GBM. In all the cases, tumor bulk was adjacent to the CSF space (the subarachnoid area or the ventricular wall) and had detectable tumor DNA in CSF [70]. The ctDNA analysis in patients with gliomas allows determining the gene’s methylation status, predicting the patients’ response to therapy. The sensitivity and specificity are about 59 and 100 %, respectively [62, 69]. The sensitivity in the detection of ctDNA in the CSF in GBM patients reaches 70 % [69], and in cases of tumor node adherence it is 100 % [70–71]. To test whether the amount of detectable mutant DNA in plasma can reflect the tumor’s state, the authors amplified the mutant DNA from these patients’ plasma. In two cases with total tumor resection, no ctDNA was detected in the blood plasma, while in one case, a residual amount of ctDNA was detected, reflecting incomplete tumor resection [64].
Further studies have focused on genome-wide tumor sequencing and the use of multi-gene panels to detect tumor ctDNA. The relationship between the ctDNA gene methylation and therapy response or tumor recurrence in the available literature is not described. There was no information about the disease stage, mutational profile of the tumor tissues, and its relationship to the blood gene status. In the study Bagley et al. (2019), at least one somatic mutation was detected in preoperative plasma samples from 11 of 20 (55 %) patients with newly diagnosed GBM using next-generation sequencing (NGS). However, none of the plasma mutations were identified in the corresponding tumor samples [54]. Such results can be partially explained by the pronounced molecular heterogeneity of GBM, which is found even within a single tumor bulk [8]. The tremendous success in detecting tumor ctDNA in the blood of patients with glioblastoma was achieved by Ahmed et al. (2019), which analyzed 27 patients with malignant gliomas using NGS and their specialized 50-gene panel. In 24 out of 27 (88.8 %) patients, ctDNA was detected. A good correlation was obtained between NGS results in plasma and PCR in tumor samples [68].
De Mattos-Arruda et al. compared the ratio of tumor ctDNA in plasma and CSF based on somatic genomic changes detected in tumors by exomic sequencing [73]. At least one tumor mutation was detected in CSF of 4 GBM patients, while in the blood plasma, the tests were negative. To assess the feasibility of using tumor ctDNA as a biomarker of disease progression, the frequency of mutant alleles in CSF and blood was determined in 2 patients using digital PCR during anti-tumor therapy. The tumor ctDNA level in CSF decreased with the response to systemic therapy and increased in disease progression. In a larger study using targeted analysis based on NGS, Miller et al. (2019) evaluated many diffuse gliomas, including 46 adult patients with GBM. Tumor DNA was detected in 59 % patients with glioblastoma. The tumor ctDNA presence in CSF was associated with tumor progression (p=0.0005), higher tumor burden (p=0.0000017), and tumor spread to the CSF space (p=0.02). Based on the results obtained, the authors suggested that tumor ctDNA in CSF may be an early indicator of glioma progression [74].
A low detection rate of tumor mutations in patients' peripheral blood makes it difficult to use tumor ctDNA as a biomarker of GBM progression. The study of CSF for tumor mutations seems more promising. However, lumbar puncture is not always possible to perform, as it is accompanied by some complications and the refusal of patients to participate in studies requiring lumbar puncture [75].
Cell-free RNAs
The cell-free RNA (ctRNA) secreted by glioblastoma cells could prove a valuable resource for biomarker discovery. Tumor-released ctRNA may be coding and non-coding. Non-coding RNA play an essential role in almost all tumor genesis, including tumor initiation, progression, therapy resistance, and can be found in the blood and CSF of patients with gliomas [18, 76–78].
To date, several studies confirming the diagnostic [79, 80], prognostic [81–85], and predictive role [86, 87] of circular RNA (circRNA) in patients with brain gliomas have been published. Despite the existing possibility of detecting circRNA in body fluids, the expression of circRNA was determined mainly in tumor tissue. The potential of circRNA in the non-invasive diagnosis of glioblastoma recurrence is currently unclear. The role of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) as a biomarker has been studied somewhat more broadly. More and more studies suggest lncRNAs to be promising diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets in many cancers, including gliomas.
Understanding the role of lncRNAs in gliomas may lead to discovering the novel molecular mechanisms behind glioma biological features [88]. In particular, it was shown, that the high TP73-AS1 and MALAT1 predict poor prognosis in primary GBM cohorts and these lncRNAs promote tumor aggressiveness and temozolamide (TMZ) resistance in GMB patients [89, 90]. LncRNA may also be ideal for gene/pro-tein delivery in future brain cancer therapies [91]. However, there is no information about the study of lncRNA levels in the blood or CSF of patients with GBM during the treatment course and follow-up in the available literature.
The plasma levels of miR-21, miR-128, and miR-342-3p were significantly altered in GBM patients compared to normal controls, that could discriminate glioma from healthy controls with high specificity and sensitivity [92]. MiR-10b and miR-21 in the CSF are significantly increased in patients with GBM. Quantification of as few as seven microRNAs in CSF enables differential recognition of glioblastoma and metastatic brain cancer using computational machine learning tools with high accuracy (91–99 %) [93, 94]. The signature of miRNAs in serum, including miR-128, miR-342-3p, miR-194, miR-628-3p, allows distinguishing of blood samples from patients with GBM and healthy control groups (the accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity is 81 %, 79 %, and 81 %, respectively) [95, 96].
The relationship between miRNAs dysregulation and prognosis in patients with GBM was shown. The miRNA expression signature of 10 microRNAs in glioblastoma samples can predict GBM patient survival [97]. MiR-182, miR-20a-5p, miR-106a-5p and miR-222-3p high level and miR-182, miR-145-5p, and miR-485-3p decreased level in the GBM patients’ blood are significantly associated with worse survival [98–100]. Many studies have evaluated surgery's effect and combined modality treatment on the miRNA levels in blood or CSF [76, 92, 101–112]. For example, miR-125b-2 and miR-223 play a role in tumor sensitivity to TMZ chemotherapy [101, 102], and miR-21, miR-128, miR-301a and miR-145-5p maintain the resistance to radiation therapy [103–106].
The diagnostic value of miRNA as a biomarker for glioblastoma recurrence has been shown only in a few studies on a small amount of clinical material [46, 48, 93]. Teplyuk et al. (2012) found the elevated miR-21 and miR-10b level in CSF in only 1 of 19 GBM patients. After chemoradiotherapy, the miR-21 level in CSF was comparable with that in the control (non-tumor) group, while the miR-10b level was significantly higher than in the control group. The sharp increase in the miR-21 level and a further increase in miR-10b level at a later date (25 weeks) indicated disease progression, confirmed by MRI, PET-CT, and repeated biopsy. In this case, no single miRNA behaved as a simple tumor burden biomarker [93]. Subsequently, significant variability in miRNA profiles in the CSF of patients with glioblastoma was shown, mainly related to the CSF collection site – ventricle or lumbar puncture [107]. Yue et al. (2016) found the correlation of the miR-205 expression with relapse of cancer in the serum of 6 patients with glioblastoma studied before surgery, two weeks after surgery in a case of deterioration. Serum miR-205 levels were significantly increased in postoperative samples compared to corresponding preoperative samples (p<0.01) and were reduced again during glioblastoma recurrence (p<0.01) [108]. Oncogenic miRNAs such as miR-10b, miR-21, miR-26a, miR-214, miR-210, miR-222, miR-124-3p, miR-301a, miR-454-3p [46-48, 92-94, 99, 111–112], and suppressive miRNAs, such as miR-15b, miR-23a, miR-128, miR-133a, miR-150, miR-185, miR-197, miR-205, miR-342-3p, miR-497 и miR-548b-5р [92, 109–115] were identified as markers of response to glioblastoma therapy. In summary, miRNAs evaluated in glioblastoma patients’ biological fluids depending on the treatment modality are listed in Table 1.
Despite the small number of patients included, the studies showed the promising role of different miRNAs as GBM recurrence biomarkers. At the same time, there are several drawbacks to the widespread use of this marker. The modulation of microRNAs is a result of involvement in various physiological and pathological conditions, such as circadian rhythm, fatigue, medication intake, chronic inflammation, and various non-tumor pathologies [19, 115]. The difference in miRNA expression in different ethnic groups can also affect miRNA’s diagnostic value [114]. There is also no generally accepted endogenous control for the quantitative determination of circulating miRNAs due to the significant variability between the samples and the relatively low body fluids expression [111–114].
Conclusion
The works of the last decade more and more convincingly prove that liquid biopsy of cerebrospinal fluid and blood (or its individual components) of patients with GBM can be used both for differential diagnosis of a tumor and for evaluating the effectiveness of antitumor therapy, since it is a safer technology for obtaining a molecular portrait of a tumor. Detection of tumor
Tumor biomarkers in CSF and blood/Опухолевые маркеры в ЦСЖ и крови
|
Advantages/Достоинства: |
Limitations/Недостатки: |
|||
|
CF |
s/цс ж |
High concentration of tumor markers/Высокая концентрация опухолевых маркеров Surrogate to tissue blopsy/Идентичная биопсии ткани Reveal tumor heterogeneity/Выявляет опухолевую гетерогенность Personalized therapy/Пригодна для персонализированнойтерапии Treatment respond/Пригодна для оценки терапевтического ответа |
com pl i cati on/Инва зи вн ая процедура., возможны серьезные осложнения
|
|
|
Bl к |
1 |
Minimal invasive procedure/Минимально инвазивная процедура Possibility of multiple sampling of biomaterial for monitoring of disease/Возможность многократного отбора проб биоматериала для мониторинга болезни Reveal tumor heterogeneity/Выявляет опухолевую гетерогенность Personalized therapy/Пригодна для персонализированной терапии Treatment respond/Пригодна для оценки терапевтического ответа |
|
Fig. 1. Current status and future perspectives of liquid biopsy in GBM.
Note: EVs, extracellular vesicles; CTCs – circulating tumor cells; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; CFS, cerebrospinal fluid; cfDNA, cell-free DNA; cfRNA, cell-free RNA
Рис. 1. Текущее состояние и перспективы жидкой биопсии при ГБМ.
Примечание: ВВ – внеклеточные везикулы; ЦОКи – циркулирующие опухолевые клетки;
МРТ – магнитно-резонансная томография; ЦСЖ – спинномозговая жидкость
markers in the CSF and/or blood of patients will make it possible to individualize the treatment of patients and timely monitor the effectiveness of antitumor therapy. Nevertheless, liquid biopsy still has a number of limitations for widespread use in practical medicine (Fig. 1). Therefore, a large number of studies are needed to test the efficacy and reliability of liquid biopsy in pa- tients with GBM, and we need to continuously develop simpler and more accurate methods for monitoring biomarkers and evaluating efficacy. We believe that CSCs, EVs, cfDNA, and cfRNA in cerebrospinal fluid and/or blood will have broad application prospects in the diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment response of patients with glioblastoma in the future.
Список литературы The role of liquid biopsy in the diagnosis of glioblastoma progression
- Ostrom Q.T., Cioffi G., Gittleman H., Patil N., Waite K., Kruchko C., Barnholtz-Sloan J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 20122016. Neuro Oncol. 2019; 21(5):1-100. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noz150.
- ChinotO.L., Wick W., Mason W., HenrikssonR., SaranF., NishikawaR., Carpentier A.F., Hoang-Xuan K., Kavan P., Cernea D., Brandes A.A., Hilton M., Abrey L., Cloughesy T. Bevacizumab plus radiotherapy-temozolomide for newly diagnosed glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2014; 370(8): 709-22. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1308345.
- GilbertM.R., Dignam J.J., Armstrong T.S., Wefel J.S., BlumenthalD. T., Vogelbaum M.A., Colman H., Chakravarti A., Pugh S., Won M., Jeraj R., Brown P.D., Jaeckle K.A., SchiffD., Stieber V.W., Brachman D.G., Werner-WasikM., Tremont-LukatsI.W., SulmanE.P., AldapeK.D., Curran W.J. Jr., Mehta M.P. A randomized trial of bevacizumab for newly diagnosed glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2014; 370(8): 699-708. doi: 10.1056/ NEJMoa1308573.
- Stupp R., Taillibert S., Kanner A., Read W., Steinberg D., Lher-mitte B., Toms S., Idbaih A., Ahluwalia M.S., Fink K., Di Meco F., Lieber-man F., Zhu J.J., Stragliotto G., Tran D., Brem S., Hottinger A., Kirson E.D., Lavy-Shahaf G., Weinberg U., Kim C.Y., PaekS.H., Nicholas G., Bruna J., HirteH., WellerM., Palti Y., HegiM.E., Ram Z. Effect of Tumor-Treating Fields Plus Maintenance Temozolomide vs Maintenance Temozolomide Alone on Survival in Patients With Glioblastoma: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2017; 318(23): 2306-16. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.18718.
- Louis D.N., Perry A., Reifenberger G., von Deimling A., Figarella-Branger D., Cavenee W.K., Ohgaki H., Wiestler O.D., Kleihues P., EllisonD.W. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: a summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016; 131(6): 803-20. doi: 10.1007/s00401-016-1545-1.
- Soffietti R., Franchino F., Magistrello M., Pellerino A., Rudà R. Perspectives of Personalized Chemotherapy of Gliomas Based on Molecular Tumor Profiling. Prog Neurol Surg. 2018; 31: 168-79. doi: 10.1159/000467378.
- Weller M., Le Rhun E., Preusser M., Tonn J.C., Roth P. How we treat glioblastoma. ESMO Open. 2019; 4(2). doi: 10.1136/esmoo-pen-2019-000520.
- Strauss S.B., Meng A., Ebani E.J., Chiang G.C. Imaging Glioblastoma Posttreatment: Progression, Pseudoprogression, Pseudoresponse, Radiation Necrosis. Radiol Clin North Am. 2019; 57(6): 1199-216. doi: 10.1016/j.rcl.2019.07.003.
- Arevalo O.D., Soto C., Rabiei P., Kamali A., Ballester L.Y., Es-quenazi Y., Zhu J.J., Riascos R.F. Assessment of Glioblastoma Response in the Era of Bevacizumab: Longstanding and Emergent Challenges in the Imaging Evaluation of Pseudoresponse. Front Neurol. 2019; 10: 460. doi: 10.3389/fneur. 2019.00460.
- Zikou A., Sioka C., Alexiou G.A., Fotopoulos A., Voulgaris S., Argyropoulou M.I. Radiation Necrosis, Pseudoprogression, Pseudor-esponse, and Tumor Recurrence: Imaging Challenges for the Evaluation of Treated Gliomas. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2018; 2018: 6828396. doi: 10.1155/2018/6828396.
- Macarthur K.M., Kao G.D., Chandrasekaran S., Alonso-Basan-ta M., Chapman C., Lustig R.A., Wileyto E.P., Hahn S.M., Dorsey J.F. Detection of brain tumor cells in the peripheral blood by a telomerase promoter-based assay. Cancer Res. 2014; 74(8): 2152-9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-0813.
- Gao F., Cui Y., Jiang H., Sui D., Wang Y., Jiang Z., Zhao J., Lin S. Circulating tumor cell is a common property of brain glioma and promotes the monitoring system. Oncotarget. 2016; 7(44): 71330-40. doi: 10.18632/ oncotarget.11114.
- Mohammadi H., Shiue K., Grass G.D., Verma V., Engellandt K., Daubner D., Schackert G., Gondim M.J., Gondim D., Vortmeyer A.O., Kamer A.P., William J., Robinson T.J., Watson G., Yu H.H.M., Lauten-schlaeger T. Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 mutant glioblastomas demonstrate a decreased rate of pseudoprogression: a multi-institutional experience. Neurooncol Pract. 2020; 7(2): 185-95. doi: 10.1093/nop/npz050.
- SottorivaA., Spiteri I., Piccirillo S.G., Touloumis A., Collins V.P., Marioni J.C., Curtis C., Watts C., Tavaré S. Intratumor heterogeneity in human glioblastoma reflects cancer evolutionary dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013; 110(10): 4009-14. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1219747110.
- DraaismaK., ChatzipliA., TaphoornM., KerkhofM., Weyerbrock A., SansonM., HoebenA., Lukacova S., Lombardi G., Leenstra S., HanseM., Fleischeuer R., Watts C., McAbee J., Angelopoulos N., Gorlia T., Golfinopoulos V., Kros J.M., VerhaakR.G.W., Bours V., van den Bent M.J., McDermott U., Robe P.A., French P.J. Molecular Evolution of IDH WildType Glioblastomas Treated With Standard of Care Affects Survival and Design of Precision Medicine Trials: A Report From the EORTC 1542 Study. J Clin Oncol. 2020; 38(1): 81-99. doi: 10.1200/jc0.19.00367.
- García-Romero N., Carrión-Navarro J., Esteban-Rubio S., Lázaro-IbáñezE., Peris-CeldaM., AlonsoM.M., Guzmán-De-Villoria J., Fernández-Carballal C., deMendivil A.O., García-Duque S., Escobedo-Lucea C., Prat-AcínR., Belda-Iniesta C., Ayuso-Sacido A. DNA sequences within glioma-derived extracellular vesicles can cross the intact blood-brain barrier and be detected in peripheral blood of patients. Oncotarget. 2017; 8(1): 1416-28. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13635.
- Shankar G.M., Balaj L., Stott S.L., NahedB., Carter B.S. Liquid biopsy for brain tumors. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2017; 17(10): 943-7. doi: 10.1080/14737159.2017.1374854.
- Müller Bark J., Kulasinghe A., Chua B., Day B. W., Punyadeera C. Circulating biomarkers in patients with glioblastoma. Br J Cancer. 2020; 122(3): 295-305. doi: 10.1038/s41416-019-0603-6.
- Silantyev A.S., Falzone L., Libra M., Gurina O.I., Kardashova K.S., Nikolouzakis T.K., Nosyrev A.E., Sutton C.W., Mitsias P.D., Tsatsakis A. Current and Future Trends on Diagnosis and Prognosis of Glioblastoma: From Molecular Biology to Proteomics. Cells. 2019; 8(8): 863. doi: 10.3390/cells8080863.
- Quddusi A., Shamim M.S. Serum biomarkers for glioblastoma multiforme. J Pak Med Assoc. 2019; 69(6): 913-4.
- Figueroa J.M., Skog J., Akers J., Li H., Komotar R., Jensen R., Ringel F., Yang I., Kalkanis S., Thompson R., LoGuidice L., Berghoff E., Parsa A., Liau L., Curry W., Cahill D., Bettegowda C., Lang F.F., ChioccaE.A., Henson J., Kim R., BreakefieldX., Chen C., MesserK., Höchberg F., Carter B.S. Detection of wild-type EGFR amplification and EGFRvIII mutation in CSF-derived extracellular vesicles of glioblastoma patients. Neuro Oncol. 2017; 19(11): 1494-1502. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nox085.
- Lee J.S., Melisko M.E., Magbanua M.J., Kablanian A.T., Scott J.H., Rugo H.S., Park J.W. Detection of cerebrospinal fluid tumor cells and its clinical relevance in leptomeningeal metastasis of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2015; 154(2): 339-49. doi: 10.1007/ s10549-015-3610-1.
- 23.MalaniR., FleisherM., Kumthekar P., LinX., OmuroA., GrovesM.D., Lin N. U., MeliskoM., Lassman A.B., Jeyapalan S., Seidman A., Skakodub A., BoireA., DeAngelisL.M., RosenblumM., Raizer J., PentsovaE. Cerebrospinal fluid circulating tumor cells as a quantifiable measurement of leptome-ningeal metastases in patients with HER2 positive cancer. J Neurooncol. 2020; 148(3): 599-606. doi: 10.1007/s11060-020-03555-z.
- Katz R.L., Zaidi T.M., Ni X. Liquid Biopsy: Recent Advances in the Detection of Circulating Tumor Cells and Their Clinical Applications. In: Bui MM, Pantanowitz L (eds). Modern Techniques in Cytopathology. Monogr Clin Cytol. Basel, Karger. 2020; 25: 43-66. doi: 10.1159/000455780.
- Müller C., Holtschmidt J., Auer M., Heitzer E., Lamszus K., Schulte A., Matschke J., Langer-Freitag S., Gasch C., Stoupiec M., Mauermann O., Peine S., Glatzel M., Speicher M.R., Geigl J.B., Westphal M., Pantel K., Riethdorf S. Hematogenous dissemination of glioblastoma multiforme. Sci Transl Med. 2014; 6(247). doi: 10.1126/ scitranslmed.3009095.
- Carvalho J.A.D.V., Barbosa C.C.L., Feher O., Maldaun M.V.C., Camargo V.P., MoraesF.Y., Marta G.N. Systemic dissemination of glioblastoma: literature review. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2019; 65(3): 460-8. doi: 10.1590/1806-9282.65.3.460.
- Böhm C., Wassmann H., Paulus W. No evidence of tumour cells in blood of patients with glioma. Mol Pathol. 2003; 56(3): 187-9. doi: 10.1136/mp.56.3.187.
- Sullivan J.P., Nahed B. V., MaddenM. W., Oliveira S.M., Springer S., Bhere D., Chi A.S., Wakimoto H., Rothenberg S.M., Sequist L.V., Kapur R., ShahK., IafrateA.J., Curry W.T., Loeffler J.S., Batchelor T.T., LouisD.N., TonerM., Maheswaran S., HaberD.A. Brain tumor cells in circulation are enriched for mesenchymal gene expression. Cancer Discov. 2014; 4(11): 1299-309. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-14-0471.
- Kolostova K., Pospisilova E., Pavlickova V., Bartos R., Sames M., Pawlak I., Bobek V. Next generation sequencing of glioblastoma circulating tumor cells: non-invasive solution for disease monitoring. Am J Transl Res. 2021; 13(5): 4489-99.
- Hallal S., Ebrahimkhani S., Shivalingam B., Graeber M.B., Kaufman K.L., Buckland M.E. The emerging clinical potential of circulating extracellular vesicles for non-invasive glioma diagnosis and disease monitoring. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2019; 36(2): 29-39. doi: 10.1007/ s10014-019-00335-0.
- Chen W.W., Balaj L., Liau L.M., Samuels M.L., Kotsopoulos S.K., Maguire C.A., Loguidice L., Soto H., Garrett M., Zhu L.D., Sivaraman S., Chen C., Wong E.T., Carter B.S., Hochberg F.H., Breakefield X.O., Skog J. BEAMing and Droplet Digital PCR Analysis of Mutant IDH1 mRNA in Glioma Patient Serum and Cerebrospinal Fluid Extracellular Vesicles. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2013; 2(7): 109. doi: 10.1038/ mtna.2013.28.
- Lane R., Simon T., Vintu M., Solkin B., Koch B., Stewart N., Benstead-Hume G., Pearl F.M.G., Critchley G., Stebbing J., Giamas G. Cell-derived extracellular vesicles can be used as a biomarker reservoir for glioblastoma tumor subtyping. Commun Biol. 2019; 2: 315. doi: 10.1038/ s42003-019-0560-x.
- Wang H., Jiang D., Li W., XiangX., Zhao J., Yu B., Wang C., He Z., Zhu L., Yang Y. Evaluation of serum extracellular vesicles as noninvasive diagnostic markers of glioma. Theranostics. 2019; 9(18): 5347-58.
- Morishita M., Takahashi Y., Nishikawa M., Takakura Y. Phar-macokinetics of Exosomes-An Important Factor for Elucidating the Biological Roles of Exosomes and for the Development of Exosome-Based Therapeutics. J Pharm Sci. 2017; 106(9): 2265-9. doi: 10.1016/j. xphs.2017.02.030.
- Tamkovich S.N., Yunusova N.V., Stakheeva M.N., Somov A.K., Frolova A.Y., Kirushina N.A., Afanasyev S.G., Grigoryeva A.E,. Laktio-novP.P., Kondakova I.V. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from blood plasma of breast cancer and colorectal cancer patients. Biomed Khim. 2017; 63(2):165-9. doi: 10.18097/PBMC20176302165.
- Ciccocioppo F., Lanuti P., Marchisio M., Miscia S. Extracellular Vesicles Involvement in the Modulation of the Glioblastoma Environment. J Oncol. 2020; 2020: 3961735. doi: 10.1155/2020/3961735.
- Yekula A., Yekula A., Muralidharan K., Kang K., Carter B.S., Balaj L. Extracellular Vesicles in Glioblastoma Tumor Microenvironment. Front Immunol. 2020; 10: 3137. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.03137.
- André-Grégoire G., Bidère N., Gavard J. Temozolomide affects Extracellular Vesicles Released by Glioblastoma Cells. Biochimie. 2018; 155: 11-5. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2018.02.007.
- Osti D., Del Bene M., Rappa G., Santos M., Matafora V., Richi-chi C., Faletti S., Beznoussenko G.V., MironovA., BachiA., FornasariL., Bongetta D., Gaetani P., DiMeco F., Lorico A., Pelicci G. Clinical Significance of Extracellular Vesicles in Plasma from Glioblastoma Patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2019; 25(1): 266-76. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-1941.
- Evans S.M., Putt M., Yang X.Y., Lustig R.A., Martinez-Lage M., Williams D., Desai A., Wolf R., Brem S., Koch C.J. Initial evidence that blood-borne microvesicles are biomarkers for recurrence and survival in newly diagnosed glioblastoma patients. J Neurooncol. 2016; 127(2): 391-400. doi: 10.1007/s11060-015-2051-3.
- Koch C.J., Lustig R.A., Yang X.Y., Jenkins W.T., WolfR.L., Martinez-Lage M., Desai A., Williams D., Evans S.M. Microvesicles as a Biomarker for Tumor Progression versus Treatment Effect in Radiation/ Temozolomide-Treated Glioblastoma Patients. Transl Oncol. 2014; 7(6): 752-8. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2014.10.004.
- Shao H., Chung J., Balaj L., Charest A., Bigner D.D., Carter B.S., HochbergF.H., BreakefieldX.O., WeisslederR., LeeH. Protein typing of circulating microvesicles allows real-time monitoring of glioblastoma therapy. Nat Med. 2012; 18(12): 1835-40. doi: 10.1038/nm.2994.
- Akers J.C., Ramakrishnan V., Kim R., Skog J., Nakano I., Pingle S., Kalinina J., Hua W., Kesari S., Mao Y., BreakefieldX.O., HochbergF.H., Van Meir E.G., Carter B.S., Chen C.C. MiR-21 in the extracellular vesicles (EVs) of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF): a platform for glioblastoma biomarker development. PLoS One. 2013; 8(10): 78115. doi: 10.1371/ journal.pone.0078115.
- Ebrahimkhani S., Vafaee F., Hallal S., Wei H., Lee M.Y.T., Young P.E., SatgunaseelanL., BeadnallH., BarnettM.H., Shivalingam B., Suter C.M., BucklandM.E., Kaufman K.L. Deep sequencing of circulating exosomal microRNA allows non-invasive glioblastoma diagnosis. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2018; 2: 28. doi: 10.1038/s41698-018-0071-0.
- Jafari D., Tiyuri A., Rezaei E., Moradi Y., Jafari R., Jokar Shoorijeh F., Barati M. Diagnostic accuracy of cerebrospinal fluid and serum-isolated extracellular vesicles for glioblastoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2020; 20(11): 1075-85. doi: 10.1080/14737159.2020.1844006.
- Santangelo A., Imbrucè P., Gardenghi B., Belli L., Agushi R., Tamanini A., Munari S., Bossi A.M., Scambi I., Benati D., Mariotti R., Di Gennaro G., Sbarbati A., Eccher A., Ricciardi G.K., Ciceri E.M., Sala F., Pinna G., Lippi G., Cabrini G., Dechecchi M.C. A microRNA signature from serum exosomes of patients with glioma as complementary diagnostic biomarker. J Neurooncol. 2018; 136(1): 51-62. doi: 10.1007/ s11060-017-2639-x.
- Lan F., Qing Q., Pan Q., Hu M., Yu H., Yue X. Serum exosomal miR-301a as a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for human glioma. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2018; 41(1): 25-33. doi: 10.1007/s13402-017-0355-3.
- Lan F., Yue X., Xia T. Exosomal microRNA-210 is a potentially non-invasive biomarker for the diagnosis and prognosis of glioma. Oncol Lett. 2020; 19(3): 1967-74. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11249.
- Galbo P.M. Jr., Ciesielski M.J., Figel S., Maguire O., Qiu J., Wiltsie L., Minderman H., Fenstermaker R.A. Circulating CD9+/GFAP+/ survivin+ exosomes in malignant glioma patients following survivin vaccination. Oncotarget. 2017; 8(70): 114722-35. doi: 10.18632/onco-target.21773.
- Lv S., Dai C., Liu Y., Shi R., Tang Z., Han M., Bian R., Sun B., Wang R. Retraction Note to: The Impact of Survivin on Prognosis and Clinicopathology of Glioma Patients: A Systematic Meta-Analysis. Mol Neurobiol. 2017; 54(3): 2376. doi: 10.1007/s12035-017-0402-0.
- Brennan K., Martin K., FitzGerald S.P., O'Sullivan J., Wu Y., Blanco A., Richardson C., Mc Gee M.M. A comparison of methods for the isolation and separation of extracellular vesicles from protein and lipid particles in human serum. Sci Rep. 2020. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/ s41598-020-57497-7.
- Tamkovich S., Bryzgunova O. Protease Activity and CellFree DNA in Blood Plasma of Healthy Donors and Breast Cancer Patients. J Immunoassay Immunochem. 2016; 37(2): 141-53. doi: 10.1080/15321819.2015.1069745.
- Bryzgunova O.E., Tamkovich S.N., CherepanovaA.V., Yarmosh-chukS.V., Permyakova V.I., Anykeeva O.Y., LaktionovP.P. Redistribution of Free- and Cell-Surface-Bound DNA in Blood of Benign and Malignant Prostate Tumor Patients. Acta Naturae. 2015; 7(2): 115-8.
- Bagley S.J., Nabavizadeh S.A., Mays J.J., Till J.E., Ware J.B., Levy S., Sarchiapone W., Hussain J., Prior T., Guiry S., Christensen T., Yee S.S., NasrallahM.P., Morrissette J.J.D., Binder Z.A., O'RourkeD.M., Cucchiara A.J., Brem S., Desai A.S., Carpenter E.L. Clinical Utility of Plasma Cell-Free DNA in Adult Patients with Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma: A Pilot Prospective Study. Clin Cancer Res. 2020; 26(2): 397-407. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-2533.
- N0r0xe D.S., 0strup O., Yde C.W., Ahlborn L.B., Nielsen F.C., Michaelsen S.R., Larsen V.A., Skj0th-Rasmussen J., Brennum J., HamerlikP., Poulsen H.S., Lassen U. Cell-free DNA in newly diagnosed patients with glioblastoma - a clinical prospective feasibility study. Oncotarget. 2019; 10(43): 4397-4406. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27030.
- Duvvuri B., Lood C. Cell-Free DNA as a Biomarker in Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases. Front Immunol. 2019; 10: 502. doi: 10.3389/ fimmu.2019.00502.
- Hou Y.Q., Liang D.Y., Lou X.L., Zhang M., Zhang Z.H., Zhang L.R. Branched DNA-based Alu quantitative assay for cell-free plasma DNA levels in patients with sepsis or systemic inflammatory response syndrome. J Crit Care. 2016; 31(1): 90-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2015.10.013.
- Jing R., Cui M., Wang H., Ju S. Cell-free DNA: characteristics, detection and its applications in myocardial infarction. Curr Pharm Des. 2013; 19(28): 5135-45. doi: 10.2174/1381612811319280012.
- Balana C., Ramirez J.L., TaronM., Roussos Y., Ariza A., BallesterR., Sarries C., Mendez P., Sanchez J.J., Rosell R. O6-methyl-guanine-DNA methyltransferase methylation in serum and tumor DNA predicts response to 1,3-bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea but not to temozolamide plus cispla-tin in glioblastoma multiforme. Clin Cancer Res. 2003; 9(4): 1461-8.
- Weaver K.D., Grossman S.A., Herman J.G. Methylated tumor-specific DNA as a plasma biomarker in patients with glioma. Cancer Invest. 2006; 24(1): 35-40. doi: 10.1080/07357900500449546.
- Majchrzak-Celinska A., Paluszczak J., Kleszcz R., Magiera M., Barciszewska A.M., Nowak S., Baer-Dubowska W. Detection of MGMT, RASSF1A, p15INK4B, and p14ARF promoter methylation in circulating tumor-derived DNA of central nervous system cancer patients. J Appl Genet. 2013; 54(3): 335-44. doi: 10.1007/s13353-013-0149-x.
- Lavon I., Refael M., Zelikovitch B., Shalom E., Siegal T. Serum DNA can define tumor-specific genetic and epigenetic markers in glio-mas of various grades. Neuro Oncol. 2010; 12(2): 173-80. doi: 10.1093/ neuonc/nop041.
- BoisselierB., GallegoPerez-Larraya J., RossettoM., LabussiereM., CiccarinoP., Marie Y., Delattre J.Y., SansonM. Detection of IDH1 mutation in the plasma of patients with glioma. Neurology. 2012; 79(16): 1693-8. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e31826e9b0a.
- SalkeniM.A., Zarzour A., Ansay T.Y., McPhersonC.M., WarnickR.E., Rixe O., Bahassi elM. Detection of EGFRvIII mutant DNA in the peripheral blood of brain tumor patients. J Neurooncol. 2013; 115(1): 27-35. doi: 10.1007/s11060-013-1209-0.
- Bettegowda C., Sausen M., Leary R.J., Kinde I., Wang Y., Agrawal N., BartlettB.R., WangH., LuberB., AlaniR.M., AntonarakisE.S., AzadN.S., Bardelli A., Brem H., Cameron J.L., Lee C.C., Fecher L.A., Gallia G.L., Gibbs P., Le D., Giuntoli R.L., Goggins M., Hogarty M.D., Holdhoff M., Hong S.M., Jiao Y., Juhl H.H., Kim J.J., Siravegna G., Laheru D.A., Lauricella C., Lim M., Lipson E.J., Marie S.K., Netto G.J., Oliner K.S., OliviA., OlssonL., Riggins G.J., Sartore-BianchiA., SchmidtK., Shih l.M., Oba-Shinjo S.M., Siena S., Theodorescu D., Tie J., Harkins T.T., Veronese S., Wang T.L., Weingart J.D., Wolfgang C.L., Wood L.D., Xing D., HrubanR.H., Wu J., AllenP.J., SchmidtC.M., ChotiM.A., Velculescu V.E., KinzlerK.W., Vogelstein B., Papadopoulos N., Diaz L.A. Jr. Detection of circulating tumor DNA in early- and late-stage human malignancies. Sci Transl Med. 2014; 6(224). doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3007094.
- Schwaederle M., Husain H., Fanta P.T., Piccioni D.E., Kesari S., Schwab R.B., Banks K.C., Lanman R.B., Talasaz A., Parker B.A., Kurzrock R. Detection rate of actionable mutations in diverse cancers using a biopsy-free (blood) circulating tumor cell DNA assay. Oncotarget. 2016; 7(9): 9707-17. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7110.
- Piccioni D.E., Achrol A.S., Kiedrowski L.A., Banks K.C., Boucher N., Barkhoudarian G., Kelly D.F., Juarez T., Lanman R.B., Raymond V.M., Nguyen M., Truong J.D., Heng A., Gill J., Saria M., Pingle S.C., Kesari S. Analysis of cell-free circulating tumor DNA in 419 patients with gliob-lastoma and other primary brain tumors. CNS Oncol. 2019; 8(2). doi: 10.2217/cns-2018-0015.
- Ahmed K.I., Govardhan H.B., Roy M., Naveen T., Siddanna P., Sridhar P., Suma M.N., Nelson N. Cell-free circulating tumor DNA in patients with high-grade glioma as diagnostic biomarker - A guide to future directive. Indian J Cancer. 2019; 56(1): 65-9. doi: 10.4103/ijc. IJC_551_17.
- Wang Z., Jiang W., Wang Y., Guo Y., Cong Z., Du F., Song B. MGMT promoter methylation in serum and cerebrospinal fluid as a tumor-specific biomarker of glioma. Biomed Rep. 3(4) (2015), 543-548.
- Wang Y., Springer S., Zhang M., McMahon K.W., Kinde I., Dob-byn L., Ptak J., Brem H., Chaichana K., Gallia G.L., Gokaslan Z.L., Groves M.L., Jallo G.I., Lim M., Olivi A., Quinones-Hinojosa A., Riga-montiD., Riggins G.J., SciubbaD.M., Weingart J.D., Wolinsky J.P., YeX., Oba-Shinjo S.M., Marie S.K., Holdhoff M., Agrawal N., Diaz L.A. Jr., Papadopoulos N., Kinzler K.W., Vogelstein B., Bettegowda C. Detection of tumor-derived DNA in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with primary tumors of the brain and spinal cord. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2015; 112(31): 9704-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1511694112.
- Osei E., Walters P., Masella O., Tennant Q., FishwickA., Dadzie E., Bhangu A., Darko J. A review of predictive, prognostic and diagnostic biomarkers for brain tumours: Towards personalised and targeted cancer therapy. J Radiother Pract. 2019; 1-16.
- Rhodes C.H., Honsinger C., Sorenson G.D. PCR-detection of tumor-derived p53 DNA in cerebrospinal fluid. Am J Clin Pathol. 1995; 103(4): 404-8. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/103.4.404.
- De Mattos-Arruda L., Mayor R., Ng C.K.Y., Weigelt B., Martínez-Ricarte F., Torrejon D., Oliveira M., Arias A., Raventos C., Tang J., Guerini-Rocco E., Martínez-Sáez E., Lois S., Marín O., de la Cruz X., Piscuoglio S., Towers R., Vivancos A., Peg V., Ramon y Cajal S., Carles J., Rodon J., González-Cao M., Tabernero J., Felip E., Sahuquillo J., Berger M.F., Cortes J., Reis-Filho J.S., Seoane J. Cerebrospinal fluid-derived circulating tumour DNA better represents the genomic alterations of brain tumours than plasma. Nat Commun. 2015; 6: 8839. doi: 10.1038/ ncomms9839.
- Miller A.M., Shah R.H., Pentsova E.I., Pourmaleki M., Briggs S., Distefano N., Zheng Y., Skakodub A., Mehta S.A., Campos C., Hsieh W.Y., Selcuklu S.D., Ling L., Meng F., Jing X., Samoila A., Bale T.A., Tsui D.W.Y., Grommes C., Viale A., Souweidane M.M., Tabar V., Brennan C.W., Reiner A.S., Rosenblum M., Panageas K.S., DeAngelis L.M., Young R.J., BergerM.F., Mellinghoff I.K. Tracking tumour evolution in glioma through liquid biopsies of cerebrospinal fluid. Nature. 2019; 565(7741): 654-8. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-0882-3.
- Day G.S., Rappai T., Sathyan S., Morris J.C. Deciphering the factors that influence participation in studies requiring serial lumbar punctures. Alzheimers Dement (Amst). 2020; 12(1). doi: 10.1002/dad2.12003.
- Zhang Y., Cruickshanks N., Pahuski M., Yuan F., Dutta A., Schiff D., Purow B., Abounader R. Noncoding RNAs in Glioblastoma. In: De Vleeschouwer S, editor. Glioblastoma [Internet]. Brisbane (AU): Codon Publications; 2017.
- Zorofchian S., IqbalF., RaoM., Aung P.P., Esquenazi Y., Ballester L.Y. Circulating tumour DNA, microRNA and metabolites in cerebrospinal fluid as biomarkers for central nervous system malignancies. J Clin Pathol. 2019; 72(4): 271-80. doi: 10.1136/jclinpath-2018-205414.
- DuanX., Liu D., Wang Y., Chen Z. Circular RNAhsa_circ_0074362 Promotes Glioma Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion by Attenuating the Inhibition of miR-1236-3p on HOXB7 Expression. DNA Cell Biol. 2018; 37(11): 917-24. doi: 10.1089/dna.2018.4311.
- Song X., Zhang N., Han P., Moon B.S., Lai R.K., Wang K., Lu W. Circular RNA profile in gliomas revealed by identification tool UROBORUS. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016; 44(9). doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw075.
- 80.BarbagalloD., CaponnettoA., CirnigliaroM., BrexD., BarbagalloC., D'Angeli F., Morrone A., Caltabiano R., Barbagallo G.M., Ragusa M., DiPietro C., Hansen T.B., PurrelloM. CircSMARCA5 Inhibits Migration of Glioblastoma Multiforme Cells by Regulating a Molecular Axis Involving Splicing Factors SRSF1/SRSF3/PTB. Int J Mol Sci. 2018; 19(2): 480. doi: 10.3390/ijms19020480.
- Wang Y., SuiX., Zhao H., Cong L., Li Y., Xin T., GuoM., Hao W. Decreased circular RNA hsa_circ_0001649 predicts unfavorable prognosis in glioma and exerts oncogenic properties in vitro and in vivo. Gene. 2018; 676: 117-22. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.07.037.
- Barbagallo D., CaponnettoA., BrexD., Mirabella F., Barbagallo C., Lauretta G., Morrone A., Certo F., Broggi G., Caltabiano R., Barbagallo G.M., Spina-Purrello V., Ragusa M., Di Pietro C., Hansen T.B., Purrello M. CircSMARCA5 Regulates VEGFA mRNA Splicing and Angiogenesis in Glioblastoma Multiforme Through the Binding of SRSF1. Cancers (Basel). 2019; 11(2): 194. doi: 10.3390/cancers11020194.
- Jin P., Huang Y., Zhu P., Zou Y., Shao T., Wang O. CircRNA cir-cHIPK3 serves as a prognostic marker to promote glioma progression by regulating miR-654/IGF2BP3 signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018; 503(3): 1570-4. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.07.081.
- Zhang M., Huang N., Yang X., Luo J., Yan S., Xiao F., Chen W., Gao X., Zhao K., Zhou H., Li Z., Ming L., Xie B., Zhang N. A novel protein encoded by the circular form of the SHPRH gene suppresses glioma tumorigenesis. Oncogene. 2018; 37(13): 1805-14. doi: 10.1038/ s41388-017-0019-9.
- Yang M., Li G., Fan L., Zhang G., Xu J., Zhang J. Circular RNA circ_0034642 elevates BATF3 expression and promotes cell proliferation and invasion through miR-1205 in glioma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019; 508(3): 980-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.12.052.
- LeiB., Huang Y., Zhou Z., Zhao Y., Thapa A.J., Li W., Cai W., Deng Y. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0076248 promotes oncogenesis of glioma by sponging miR-181a to modulate SIRT1 expression. J Cell Biochem. 2019; 120(4): 6698-6708. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27966.
- Ding C., Yi X., Wu X., Bu X., Wang^ D., Wu Z., Zhang G., Gu J., Kang D. Exosome-mediated transfer of circRNA CircNFIX enhances temozolomide resistance in glioma. Cancer Lett. 2020; 479: 1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.03.002.
- DeOcesano-Pereira C., Machado R.A.C., Chudzinski-TavassiA.M., Sogayar M.C. Emerging Roles and Potential Applications of Non-Coding RNAs in Glioblastoma. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21(7): 2611. doi: 10.3390/ ijms21072611.
- Chen W., Xu X.K., Li J.L., Kong K.K., Li H., Chen C., He J., Wang F., Li P., Ge X.S., Li F.C. MALAT1 is a prognostic factor in glioblas-toma multiforme and induces chemoresistance to temozolomide through suppressing miR-203 and promoting thymidylate synthase expression. Oncotarget. 2017; 8(14): 22783-99. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15199.
- 90.Mazor G., LevinL., Picard D., Ahmadov U., CarénH., Borkhardt A., Reifenberger G., Leprivier G., Remke M., Rotblat B. The lncRNA TP73-AS1 is linked to aggressiveness in glioblastoma and promotes temozolo-mide resistance in glioblastoma cancer stem cells. Cell Death Dis. 2019; 10(3): 246. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1477-5.
- Liu Q., Qi C., Li G., Su W. Prediction of the Outcome for Patients with Glioblastoma with lncRNA Expression Profiles. Biomed Res Int. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/5076467.
- Wang Q., Li P., Li A., Jiang W., Wang H., Wang J., Xie K. Plasma specific miRNAs as predictive biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of glioma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2012; 31(1): 97. doi: 10.1186/17569966-31-97.
- Teplyuk N.M., Mollenhauer B., Gabriely G., Giese A., Kim E., Smolsky M., KimR.Y., SariaM.G., Pastorino S., Kesari S., Krichevsky A.M. MicroRNAs in cerebrospinal fluid identify glioblastoma and metastatic brain cancers and reflect disease activity. Neuro Oncol. 2012; 14(6): 689-700. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nos074.
- Roth P., Wischhusen J., Happold C., Chandran P.A., Hofer S., Eisele G., WellerM., Keller A. A specific miRNA signature in the peripheral blood of glioblastoma patients. J Neurochem. 2011; 118(3): 449-57. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07307.x.
- ManterolaL., GuruceagaE., GállegoPérez-Larraya J., González-HuarrizM., Jauregui P., Tejada S., Diez-Valle R., Segura V., SamprónN., Barrena C., Ruiz I., Agirre A., Ayuso A., Rodríguez J., González A., Xipell E., Matheu A., López deMunain A., Tuñón T., Zazpe I., García-Foncillas J., Paris S., Delattre J.Y., Alonso M.M. A small noncoding RNA signature found in exosomes of GBM patient serum as a diagnostic tool. Neuro Oncol. 2014; 16(4): 520-7. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/not218.
- Zhang Y., Ta W.W., Sun P.F., Meng Y.F., Zhao C.Z. Diagnostic and prognostic significance of serum miR-145-5p expression in glioblastoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019; 12(7): 2536-43.
- Srinivasan S., Patric I.R., Somasundaram K. A ten-microRNA expression signature predicts survival in glioblastoma. PLoS One. 2011; 6(3). doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017438.
- Xiao Y., ZhangL., Song Z., Guo C., Zhu J., Li Z., Zhu S. Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Plasma Circulating MicroRNA-182 in Human Glioma. Med Sci Monit. 2016; 22: 855-62. doi: 10.12659/ msm.897164.
- Zhao H., Shen J., Hodges T.R., Song^ R., Fuller G.N., Heimber-ger A.B. Serum microRNA profiling in patients with glioblastoma: a survival analysis. Mol Cancer. 2017; 16(1): 59. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0628-5.
- Wang Z.Q., Zhang M.Y., Deng M.L., Weng N.Q., Wang H.Y., Wu S.X. Low serum level of miR-485-3p predicts poor survival in patients with glioblastoma. PLoS One. 2017; 12(9). doi: 10.1371/journal. pone.0184969.
- Shi L., Zhang S., Feng K., Wu F., Wan Y., Wang Z., Zhang J., Wang Y., Yan W., Fu Z., You Y. MicroRNA-125b-2 confers human gliob-lastoma stem cells resistance to temozolomide through the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis. Int J Oncol. 2012; 40(1): 119-29. doi: 10.3892/ ijo.2011.1179.
- Huang B.S., Luo Q.Z., Han Y., Huang D., Tang Q.P., Wu L.X. MiR-223/PAX6 Axis Regulates Glioblastoma Stem Cell Proliferation and the Chemo Resistance to TMZ via Regulating PI3K/Akt Pathway. J Cell Biochem. 2017; 118(10): 3452-61. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26003.
- GwakH.S., Kim T.H., Jo G.H., Kim Y.J., KwakH.J., Kim J.H., Yin J., Yoo H., Lee S.H., Park J.B. Silencing of microRNA-21 confers radio-sensitivity through inhibition of the PI3K/AKT pathway and enhancing autophagy in malignant glioma cell lines. PLoS One. 2012; 7(10). doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047449.
- Sun J., Ye L., Wang C., Li N., Wang D., Li X. MicroRNA-128 increases glioma cell radio-sensitivity by suppressing senescent evasion through oncogene Bmi-1. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018; 11(3): 1423-30.
- YueX., LanF., Xia T. Hypoxic Glioma Cell-Secreted Exosomal miR-301a Activates Wnt/ß-catenin Signaling and Promotes Radiation Resistance by Targeting TCEAL7. Mol Ther. 2019; 27(11): 1939-49. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.07.011.
- Zhang^ Y., Ta W.W., Sun P.F., Meng Y.F., Zhao C.Z. Diagnostic and prognostic significance of serum miR-145-5p expression in glioblastoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019; 12(7): 2536-43.
- Zhou Q., Liu J., Quan J., Liu W, Tan H., Li W. MicroRNAs as potential biomarkers for the diagnosis of glioma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Sci. 2018; 109(9): 2651-9. doi: 10.1111/ cas.13714.
- Yue X., Lan F., Hu M., Pan Q., Wang Q., Wang J. Downregula-tion of serum microRNA-205 as a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for human glioma. J Neurosurg. 2016; 124(1): 122-8. doi: 10.3171/2015.1.JNS141577.
- Yang C, Wang C, Chen X., Chen S, Zhang Y, Zhi F, Wang J., Li L., Zhou X., Li N., Pan H., Zhang J., Zen K., Zhang C.Y., Zhang C. Identification of seven serum microRNAs from a genome-wide serum microRNA expression profile as potential noninvasive biomarkers for malignant astrocytomas. Int J Cancer. 2013; 132(1): 116-27. doi: 10.1002/ ijc.27657.
- ShaoN., Wang L., Xue L., WangR., Lan Q. Plasma miR-454-3p as a potential prognostic indicator in human glioma. Neurol Sci. 2015; 36(2): 309-13. doi: 10.1007/s10072-014-1938-7.
- Sun J., Liao K., Wu X., Huang J., Zhang S., Lu X. Serum micro-RNA-128 as a biomarker for diagnosis of glioma. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015; 8(1): 456-63.
- TangH., Liu Q., LiuX., YeF., XieX., XieX., WuM. Plasma miR-185 as a predictive biomarker for prognosis of malignant glioma. J Cancer Res Ther. 2015; 11(3): 630-4. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.146121.
- ParvizHamidiM., Haddad G., Ostadrahimi S., Ostadrahimi N., Sadeghi S., Fayaz S., Fard-Esfahani P. Circulating miR-26a and miR-21 as biomarkers for glioblastoma multiform. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2019; 66(2): 261-5. doi: 10.1002/bab.1707.
- Wang J., Che F., Zhang J., Zhang M., Xiao S., Liu Y, Zhou L., Su Q., You C., Lu Y., Heng X. Diagnostic and Prognostic Potential of Serum Cell-Free microRNA-214 in Glioma. World Neurosurg. 2019; 125: 1217-25. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2019.02.009.
- Akers J.C., Hua W., Li H., Ramakrishnan V., Yang Z., Quan K., Zhu W., Li J., Figueroa J., Hirshman B.R., Miller B., Piccioni D., Ringel F., Komotar R., Messer K., Galasko D.R., Hochberg F., Mao Y., Carter B.S., Chen C.C. A cerebrospinal fluid microRNA signature as biomarker for glioblastoma. Oncotarget. 2017; 8(40): 68769-79. doi: 10.18632/onco-target.18332.


