The role of social entrepreneurship and sustainable development in business strategies: approaches of companies in Azerbaijan and the USA to corporate social responsibility
Автор: V.M. Aleksandrova
Журнал: Экономика и бизнес: теория и практика @economyandbusiness
Статья в выпуске: 8 (126), 2025 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The article analyzes the role of social entrepreneurship (SE) and corporate social responsibility (CSR) in shaping business strategies based on the principles of sustainable development (SD). The significance of integrating CSR to address social, environmental, and economic challenges is highlighted. The approaches of companies in the USA and Azerbaijan to implementing sustainable practices, including legislative and corporate initiatives, are examined. A comparative analysis is presented, revealing cultural, economic, and political differences in CSR approaches. The prospects for integrating global SD standards into corporate strategies are noted. The article concludes that the successful development of CSR is possible through collaboration between businesses, governments, and society.
Social entrepreneurship (SE), sustainable development (SD), corporate social responsibility (CSR), business strategies, USA, Azerbaijan
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/170210670
IDR: 170210670 | DOI: 10.24412/2411-0450-2025-8-11-16
Текст научной статьи The role of social entrepreneurship and sustainable development in business strategies: approaches of companies in Azerbaijan and the USA to corporate social responsibility
The contemporary business society must develop a strategy embracing the practices of sustainable development (SD) in view of increasing stakeholder expectations and international norms. To this end, social entrepreneurship (SE) and corporate social responsibility (CSR) have been identified as most important tools to handle critical social, environmental, and economic issues. These strategies not only encourage the companies to improve their reputation and reinforce the trust of stakeholders but also enable them to attain long-term sustainability in their businesses. Of particular interest is the study of ways of implementing CSR in countries such as the USA, where such a practice has deeply rooted traditions, and Azerbaijan, where business social responsibility is just starting to actively form itself against the background of building up the domestic economy and integrating it into the world economic space.
The purpose of this article is to analyze the role of SE and CSR in the strategies of companies in two countries: the USA and Azerbaijan. The research aims to identify differences and similarities in CSR approaches and examine their impact on SD. The relevance of the topic is predetermined by the need to implement sustainable business conduct in correspondence with United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDG), which become vitally important for the preservation of ecosystems, increasing social inclusion, and providing economic stability. Such a comparison will reveal how cultural, economic, and political factors affect corporate behavior related to social responsibility in the USA and Azerbaijan.
Conceptual basis of SE and CSR, and their link to SD
Key areas of modern business practices aimed at addressing social and environmental challenges include SE and CSR. SE is characterized as a form of entrepreneurial activity that emphasizes not only profit generation but also the attainment of social objectives like enhancing the quality of life, including marginalized groups, promoting education, or safeguarding the environment [1]
Conversely, CSR involves companies voluntarily undertaking commitments to enhance social and environmental conditions, incorporating ethical principles into their operations, and taking into account the interests of all stakeholders, which include employees, customers, suppliers, and local communities. The shared aspect of these ideas is their emphasis on long-term sustainability, which enhances the reputation of businesses and their societal impact.
The interrelationship between SD and business strategies is that each of them acts upon the other. SD, resting on three pillars such as economic, environmental, and social, has transformed into an essential part of modern companies' business strategy. It provides an option for business to take account of long-term conse- quences and reduce adverse effects on environmental and social contexts, realizing innovations that are in conformity with contemporary requirements [2]. For instance, the implementation of greener technologies and decrease in carbon footprint reduce the consumption of natural resources and minimize operation costs at the same time. In its turn, social activities-investments into the professional development of workers or aid to local communities-increase business competitiveness on the market.
The basis for putting the principles of SD into practice can be seen in the introduction of international standards such as ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) and SDG. The set of ESG criteria refers to indicators that assess the actual economic impact based on a company's environmental performance, social accountability, and corporate governance. These new paradigms have turned them into key factors in investment processes, creating significant incentives that steer companies toward sustainability. Thus, the United Nations founded the SDGs in 2015 as a common agenda of 17 targets aimed at ending poverty while reaching a decent quality of life without undermining the ecosystems. The integration of SDGs into business strategies allows firms to create long-term perspectives in line with global challenges [3]. Therefore, international standards do not only guide businesses but also set the basis on which economic, social, and environmental dimensions are integrated harmoniously to attain the goal of SD.
Social entrepreneurship and sustainable development in the USA
The USA is a leading country in the sphere of SE and CSR implementation in business practices. CSR is viewed as a major component of successful businesses in the long term within the American business climate, with every branch of the government promoting it. Some of the most prominent features of CSR within US firms are the addition of environmental requirements, extensive workplace inclusion, support for local communities, and sustainable technologies. These elements not only help American companies establish their brand but also generate sustainable investments, which is of particular importance considering the increasing expectations from consumers and investors [4].
Legislative climate and government policy are of the utmost importance in determining SE and CSR in the USA for a sustainable business climate. The Clean Air Act and the Energy Independence and Security Act of federal legislation impose stringent regulatory mechanisms on the emissions of carbon and encourage green technologies. These include government programs, such as the Small Business Innovation Research and startup grants, to encourage innovations in SD and sustainability. Besides, tax incentives and subsidies-for example, the ones provided by the Inflation Reduction Act-prompt companies to invest in renewable energy, energy efficiency, and decarbonization of production processes. It grants businesses added inducements at the regional level, such as subsidy programs in California for environmentally oriented firms, the building of electric transport infrastructure, and others. Such measures create a friendly regulatory environment for the firms that would like to convert into social and environmentally sustainable activities but also provide favorable conditions under which innovative solutions for societal and environmental benefits can be set in place.
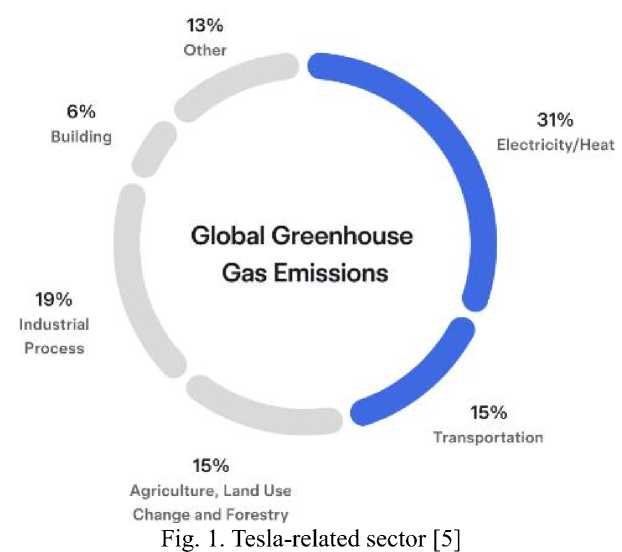
A transportation company that has adopted socially focused strategies is Tesla Inc., which prioritizes reducing carbon emissions by manufacturing electric vehicles and expanding charging infrastructure. Tesla champions sustainable transportation options and worldwide objectives aimed at reducing carbon emissions, thereby establishing itself as a leader in environmentally friendly transit. The company's reports show that, in 2023 alone, customers avoided the release of more than 20 million metric tons of CO₂ into the atmosphere (fig. 1).
Tesla aims to decarbonize production as well as the full life cycle of electric cars and wants all its factories to be carbon neutral. Each new factory it builds is greener than the previous one, showing how committed the company is to reducing the footprint of the company on the planet. Furthermore, Tesla has been pushing forward in building its Supercharger network intensively, and it is making sure that by the year 2023, it is running completely on renewable energy sources, which allows for higher use of transport modes with lower environmental impact.
Other instances are Union Pacific Railroad, the largest rail operator in the USA, that has introduced measures to enhance energy efficiency and minimize carbon emissions. In 2021, the company published its first corporate-wide climate action plan with plans to achieve net-zero emissions of greenhouse gases by 2050. Major efforts include renewing its locomotive fleet: since 2010, Union Pacific has invested approximately $3,4 billion in buying more than 1,300 new locomotives and retiring about 2,500 older, less efficient engines [6]. Besides this, it came out with an Energy Management System installed in locomotives to highlight fuel-saving opportu-nities-just like cruise control on trucks and auto-mobiles-and is installing the system in two-thirds of its active fleet. Such measures amply result in reduced emission footprints and greater environmental friendliness in company operations.
A company called Zipcar made SE widely recognized in the USA by specializing in car sharing while explicitly integrating a focus on the social and ecological sustainability of its business into its approach. Founded in 2000, Zipcar serves residents and university campuses around cities by making vehicles available on short-term rentals to replace car ownership for those individuals who can't afford cars.
The social mission of the company is to reduce transportation costs and increase mobility for a wide range of people, from students to residents of densely populated cities. Its ecological effect is significant as it decreases the quantity of personal vehicles on the streets: estimates suggest that a single shared car substitutes for 9 to 13 private cars. Zipcar also incorporates hybrid and electric cars in its fleet, thus further minimizing its carbon footprint.
Therefore, SE and SD in the USA are integral to corporate culture and government regulation, addressing global social and environmental challenges. U.S. firms demonstrate strong efficiency in applying CSR principles: lowering carbon emissions, fostering workplace inclusivity, and aiding local communities. Cases like Tesla, Union Pacific Railroad, and Zipcar showcase the variety of methods for social responsibility, encompassing cutting-edge transportation technologies, eco-friendly logistics strategies, and enhanced access to mobility. Supported by government programs and compliance with rigorous environmental regulations, U.S
Social entrepreneurship and sustainable development: legislative and corporate initiatives in Azerbaijan
Key directions of state policy and corporate strategies in Azerbaijan include SE and SD. Government programs, such as the «State Program for the Socio-Economic Development of the Regions of the Republic of Azerbaijan for 2023– 2027», actively stimulate regional business development, improve social infrastructure, and attract investments in sustainable projects [7]. The legislative framework supports these initiatives, including legal acts aimed at creating favorable conditions for small and medium-sized enterprises, such as the law on promoting entrepreneurship and tax reforms that provide benefits for environmentally and socially oriented projects.
The Small and Medium Business Development Agency (KOBIA) plays a particularly important role in integrating the principles of SE and SD. KOBIA supports the launch of startups focused on solving social problems and acts as a mediator between businesses and the government to create effective financing mechanisms.
At the legislative level, efforts toward SD are supported through the Law on Environmental Protection and related regulations governing pollutant emissions and resource use. The introduction of tax incentives for companies adopting sustainable technologies has also become an important stimulus for integrating environmentally friendly solutions. In addition, initiatives to introduce tax benefits for companies investing in sustainable technologies have been undertaken, such as a proposal to establish a legal framework for private investments in «green technologies».
Furthermore, amendments to the Tax Code included in the 2025 budget package provide tax benefits for business entities implementing projects for generating electricity from renewable sources, as well as exemptions from VAT and import duties on equipment necessary to create the relevant infrastructure.
In the transportation sector, significant corporate initiatives are also observed. For instance, AS Group Investment demonstrates a commit- ment to CSR by supporting projects for urban greening, job creation, and the improvement of urban infrastructure. The company’s CSR policy includes supporting families of war veterans and wounded individuals from the Patriotic War, providing financial aid during quarantine periods, and implementing projects to support orphanages and boarding schools. Key directions also include collaboration with the Autism Society «Together and Healthy» and sponsorship of the «ASAN Letter» project. Moreover, the company actively participates in environmental projects by creating parks and green zones and focuses on job creation in Azerbaijan and Georgia.
Despite significant progress, socially oriented projects in Azerbaijan are developing more slowly than in the USA, highlighting the need for further legislative improvements and enhanced incentives for companies adopting sustainable and socially responsible practices. Only through close cooperation between the government and businesses can the comprehensive development of SE and SD in the country be ensured.
Comparative analysis of approaches to social entrepreneurship and sustainable development: USA and Azerbaijan
A comparison of the approaches to SE and CSR in the USA and Azerbaijan reveals that, despite some similarities, the differences are shaped by cultural, economic, and political factors. While the USA has a long history of integrating CSR into business strategies, this direction in Azerbaijan is actively developing but faces certain challenges (table 1).
|
Table 1. Com |
parative analysis of approaches to SE and SD in the USA and Azerbaijan |
|
|
Criteria |
USA |
Azerbaijan |
|
Regulatory framework |
Developed legislative system encouraging the implementation of sustainable practices through tax incentives and subsidies. |
The legislative framework is at the stage of improvement but includes measures to support sustainable technologies. |
|
History of CSR |
Long history of CSR integration; SD support is already embedded in business culture. |
CSR has begun to actively develop over the past two decades. |
|
Role of Government |
The government actively implements incentives through grants, tax benefits, emission regulations, and ESG development. |
The government is just beginning to create mechanisms for supporting CSR and introducing ESG practices. |
|
Role of business |
Businesses act as drivers of CSR innovation, including investments in green technologies and social projects. |
Businesses are beginning to recognize the importance of CSR, but most initiatives are linked to large companies. |
|
Focus of CSR |
Environmental sustainability, inclusion, and the development of local communities. |
Social assistance to vulnerable groups, support for educational and cultural projects. |
|
Cultural factors |
High transparency and openness in business; public expectations stimulate CSR implementation. |
Traditions of philanthropy and social assistance; predominant influence of large companies. |
Cultural characteristics are important in shaping the approaches to CSR in both countries. In the USA, corporate transparency and public responsibility are critical elements of business culture, driven by pressure from investors, consumers, and regulatory bodies. In contrast, in Azerbaijan, the approach to CSR is often defined by traditions of philanthropy and the personal initiatives of large companies such as SOCAR or PASHA Holding. In the USA, the main challenge is to further expand ESG standards and overcome the resistance of a number of industries. At the same time, high readiness of business and society for innovation provides steady movement.
The current main problems in Azerbaijan are the lack of structured government support, lack of awareness among small and medium-sized enterprises, and insufficient resources for the implementation of CSR projects. However, the interest in sustainable practices that has been growing lately and the example of large companies create a foundation for the development of this direction.
The prospects for both countries are linked to the integration of global ESG standards and increasing business engagement in addressing social and environmental issues [8]. In Azerbaijan, the focus should be on developing a clear regula- tory framework and creating incentives for small and medium-sized businesses to participate in sustainable initiatives. The USA, on the other hand, could focus on deepening cross-industry collaboration and improving the effectiveness of existing programs.
Conclusion
Two significant factors in the development of business strategy are SE and SD, driven by the growing importance of CSR in addressing various environmental, social, and economic challenges. Comparing the approaches of the USA and Azerbaijan, one may notice that despite cultural, economic, and political drivers for diversities, both countries make great efforts to combine principles of SD into business practices. In the USA, good legislative conditions, high business transparency, and an active role on the part of government contributed much to CSR implementation. It is at the very beginning in Azerbaijan and needs further support from the government, an improvement of regulatory frameworks, and engagement on the part of small and mediumsized enterprises. The experience of the two countries underlines that SE and CSR can succeed only in a collaborative manner by business, governments, and society if global SDG are to be met.


