The tourism industry: administrative levels and methods of forming
Автор: Dmitrieva Tamara Evgenevna, Schenyavsky Vitaly Anatolevich
Журнал: Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast @volnc-esc-en
Рубрика: Regional economy the issue theme: tourism
Статья в выпуске: 1 (5) т.2, 2009 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The article describes how to assess the potential and the formation of cultural and recreational area at the country, region, and municipality level. The position of the international approach to evaluating the competitiveness of the tourism sector and travelling are revealed and the trends of its development in Russia identified. On submission of the Komi Republic, the resources are described and the goals of regional tourism forming are set, and also the analysis and design of prerequisites for the development of municipal districts cultural and recreational complex experience is presented.
Tourism competitiveness index, tourism development management, tourist and recreational zoning, cultural and recreational complex
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147223119
IDR: 147223119 | УДК: 338.467.6:338.48(470.13)
Текст научной статьи The tourism industry: administrative levels and methods of forming
Tamara E.
DMITRIEVA
Ph. D. in Geographical Sciences,
Senior scientific associate, Institute for Socio-economic and energy problems of the Komi North SC UB RAS
Vitaly A.
SCHENYAVSKY
Ph. D. in Economics,
Senior scientific associate, Institute for Socio-economic and energy problems of the Komi North SC UB RAS
The development of the tourism sector and in the broad sense of «experiences economy » (as the type of economic activity bringing together tourism, travel, cultural and recreational area is increasingly refer to) is based on the transformation of cultural and natural resources as a source of surplus value – a sustainable global trend, increasing in postindustrial society. As the most dynamic sectors of world economy, tourism has become an attractive field of activity in Russia, its regions and municipalities.
In this regard, the analysis of the key positions of assessing the situation of the Russian Federation in the global tourism industry, as well as internal development and problems of its formation is an important scientific and methodological and management challenge. Without claiming to complete the solution, let us have a look at some features of "experiences economy" in the country, regional and municipal levels, drawing on the expertise of colleagues, and the results of their research on the Komi Republic.
Country level – global approach
Having multiplicative effect tourism industry improves citizens’ life quality and the general economic outlook. In seeking to create an environment for tourism, the Government improves the infrastructure; in addition, "experiences economy" positively affects the growth of the cultural outlook and environmental sustainability, fixing local residents’ attention on the values of the environment, encouraging businesses to environmental improvements, and tourists – to the conservation of nature.
TTCI indicator measures the factors and features of attractiveness (favor) for T&T sector development in different countries. The index is based on three broad groups of parameters that contribute to competitiveness and provide it. The groups bring together more than 70 indicators and are «phased out» in three subindexes: management base, environment business and infrastructure. The first subindex covers those items that relate to the policies and scope of government, the second involves the elements of the business environment and industrial infrastructure, the third includes the human, cultural and natural components of the resource wealth of the country (table 1) .
The full contents of the parameters and indicators are given in the text of the report [13, Ch. 1, p. 5-6, Appendix A], here is only a brief commentary on some of them.
Among the political regulators not only the extent to which foreign ownership and foreign direct investment are supported by country is important, and how property rights are protected, but also environmental sustainability, so in addition to political figures, this unit includes the carbon emission and the percentage of hazardous in the country.
Safety and security is a critical factor of tourism competitiveness; the overall level of crime, violence and terrorism, road accidents, as well as the degree of trust law enforcement agencies to ensure protection is taken into account.
Table 1. The tourism sector competitiveness index composition
|
T&T sector competitiveness index |
||
|
Regulatory framework subindex |
Environment business and infrastructure subindex |
Human, cultural and natural resources subindex |
|
Political regulations and regulators |
Air Transport Infrastructure |
Human capital |
|
Environment sustainability |
Land Transport Infrastructure |
Tourism susceptibility |
|
Safety and security |
Tourist infrastructure |
Natural resources |
|
Health and hygiene |
Information and communication technology |
Cultural resources |
|
Tourism Priority |
Price competitiveness in T&T industry |
|
Care of tourism is reflected in budgetary priorities , which the Government could provide funding for major development projects, the designation of their intentions, which may have effects in terms of attracting private investment, participation in international tourism fairs and high-quality marketing destinations (places for tourism).
The characteristics of tourism infrastructure includes not only housing (number of hotel rooms), but also large car rental companies, and financial infrastructure for tourists (ATM, etc.).
Price competitiveness means the availability of prices for goods and services, airfares, fuel, accommodation, as well as the moderate taxes, which may be imposed upon travelers.
The human resources guarantee access to resources necessary for the branch growth and development. These take into account the health and education and training, the quality of which depends not only on the educational system, but also the involvement of the private sector to improve the training of specialized personnel and services.
Susceptibility of tourism is measured by the degree of openness of the society for tourism and foreign visitors, not only people but also the business leaders who consider tourism to important business contacts. The measure of tourism openness is the costs and revenues in a proportion of GDP, which gives a sense of the tourism importance concerning the size of the country.
Natural resources that provide competitive advantages the country include the location of World Heritage Site, the number of animals’ species, characterizing fauna resources, the proportion of protected areas.
Accommodation of cultural resources in each country is the most important factor in tourism competitiveness worldwide. This block includes places of world cultural heritage (UNESCO list), sports stadiums, international exhibitions and fairs.
According to the second annual Report, in 2008, Switzerland, Austria and Germany have the most attractive environment for tourism and travel. The following top ten places are oc- cupied by Australia, Spain, United Kingdom, United States, Sweden, Canada and France.
Russia took 64th place out of 130 (in 2007 it scored 68th out of 124). Our neighbors from above are Dominican Republic and China, from below are India and Egypt.
Russia has a relatively high marks for natural (22nd place) and cultural (34th place) resources, due to the presence of the World Cultural Heritage sites, as well as a well-developed air transport infrastructure (33rd place). However, land transport and tourism infrastructure are of low opinion (83rd and 66th places respectively) particularly because of the small number of available hotel rooms. Weak security and protection positions deserve serious attention (127th place) in connection with a high level of crime and violence, lack of confidence in the law enforcement agencies to ensure protection as well as the high level of road accidents. Russia is assessed as a country having a very bad environment, both business environment (very high restrictions on foreign ownership, not very good protection of property rights and visa requirements for visitors from many countries – 110th place), and nature environment (117th place). In general, the tourism sector in the country does not look like a public priority (in this position it is in the 125th rate line).
You can treat the data critically, but no doubt that they adequately take into account the factors of formation and development of "experiences economy" as an important sector of economic activity, reflect the international approach to assessing and allow to fix problem positions and direction of managerial influence in this area.
Trends in tourism development in Russia
The economic importance of tourism in the Russian Federation s is growing in recent year, but its contribution to national income remains modest and has on various estimates from 5 to more realistic 2,5–3% of GDP [8]. According to statistics in the structure of paid services to population in 2007 cultural and recreation services accounted for just 6,1%, including 1,5 – tourism; 1,6 – health-improving; 0,7 – Sport and Physical Education, 2,3% – culture.
On the basis of experts’ opinions several trends can be divided in the modern development of local tourism.
The formation of the tourism framework is starting. Identification and design of territorial frame is a sign of spatial development. Such regions as Lake Baikal, the Urals, and Altai are beginning to position themselves at the tourist market. The priority state support in the establishment of 7 tourist and recreational areas and the construction of the Olympic Games in Sochi contributes to the growth of tourism.
Strategic design of cultural and recreational specialization of macroregional economy is outlined in the directions of their development, presented in the draft Concept of long-term socio-economic development of the Russian Federation until 2020, which indicated the following:
– the preservation and incorporation of cultural heritage in the technologies of the Central region cultural tourism;
– the development of historical and cultural cluster, ecological tourism and seaside recreation of the Northwest;
– enhancing the cultural, ecological and sports tourism, with state support of historic and cultural centers in the North;
– promotion of health-improving, ski and seaside resorts brands (including the Black Sea coast resorts, the Caucasian Mineral Waters), followed by the proliferation of state infrastructure investments in the new spa centers (Dagestan, Taman, and others);
– development of a suburban type of recreation and water tourism on the Volga River and its tributaries;
– development of marine recreation, ecological and adventure tourism based on the unique natural landscape of Kamchatka, Primorye, the Kuriles.
According to the Concept the intensification of resource use must be accompanied by the development of transport and tourism infrastructure.
Globalization of the Russian tourist market. It manifests itself in the implementation of net- work formats in the hotel and shopping services to the inclusion in the global network and the formation of local networks, which increases the standards and quality of services. There is the consolidation and integration of business through specialized services to the association of tour operators, hotel owners and others. As shown by international experience the integration of services and the emergence of "tourist factories full cycle", uniting air carriers, hotel chains tour operators and tourists service under one company is promising [4].
Inter-regional integration. Inter-regional approach to creating a tourist product is a new tool for Russia.
Its use is in line with global trends crosscountry integration for mutual growth in the competitiveness of uniting nations. Thus, within the regional organization, ASEAN general qualification requirements for staff in the tourism industry are developed, common standards for hotels, nutrition, and eco-tourism are establishing. Southeast Asia countries are planning to introduce a single tourist visa to any country in ASEAN to establish uniform tourism prices for all states, as well as to promote South-East Asia as a tourist area, offering a combined tour, such as route Thailand – Laos at international tourism exhibitions [6]. There ar similar thematic lines – wine, festival – in Europe.
Increased competition of international tourist destinations and the growth of tourist flows advanced the North-West regions to unite under the concept "Windows on Russia". It is supposed to create a common marketing center, the development of new products – "Russian Winter" and "Russian soul Riddles" is planned in addition to the tourist product «Silver Ring» [7]. An interesting cross-regional and intercountry project is "The Way of the Varangians to the Greeks". Waterway will connect the areas of the Novgorod and Leningrad regions and Scandinavia. Creation of inter-regional tourist product saves on marketing and advertising. Along with this the tourists’ money is distributed across all regions.
Regions’ cultural and recreational strengthening. Attention to the "experiences economy" as an advance and priority economy was, except the disclosed above macroeconomic advantages, due to deteriorating socio-economic situation of Russian regions during the period of market reforms.
Activating the new economy resource is almost universally accompanied by the development of regional tourism development with planning the growth of its contribution to GDP, as well as the methodical study of the assessment [4, 5, 2]. The share of tourism in GDP, taking into account the "promoted" sector varies significantly: from 13,7% in the Krasnodar region to 6,5% in Karelia, 3,6% in the Novgorod region, 0,6% in Buryatia.
Local experts mark out the following key factors among those determining the competitiveness of regions in the world and the Russian tourist market, taking into account the position of the annual Report of the World Economic Forum:
-
• the availability of the territory, taking into account the infrastructure price diversity, the possibility of booking hotels, tickets to events and travel on-line, cost and speed of communication;
-
• the territory’s uniqueness in terms of "experiences economy", which requires cultural specialization work and branding of tourism resources, rich and diverse event series forming in the region;
-
• territories, claiming to welcome foreign tourists should provide safety and comfort of rest without a guide or accompanying which means loyalty to visitors, provide information about tourism objects in foreign languages, accommodation and meals;
•ecological compatibility, protecting the natural and historic environment.
These core values, along with the formation of regional clusters (tourist-food chains), the integrated development of the territory by institutional investor, marketing strategy and integration into larger scale tourist products (networks) reflect the development of new technology development of the Russian tourism [10].
"Experiences economy" design in a given region requires methodological expertise. The Center for Strategic Research "North-West’s" experience, which fulfilled tourism projects in the preparation of strategies for the Russian Federation regions, developed the concept of tourism development in Novgorod, Astrakhan Region and the Krasnoyarsk Region, focuses on the following key steps in the development of the region’s tourism industry [11].
The first is tourist potential analysis (composition, scale, significance, quality of resources, existing and potential degree of commercialization).
The second is tourism market analysis, which will give an understanding of what place on the map the territory considered as a tourist destination takes and what niche it can occupy in the future.
The third is the choice of priority tourism destinations based on the ease of the resource position commercialization.
The fourth is the development of mechanisms for tourism development, using the principles of:
-
• integrated development of the territory for the creation of new tourism infrastructure in the region;
-
• the cluster approach to the organization through communication between all parties to the tourist business, and supporting industries to ensure maximum multiplier effect of activities;
-
• cultural policy of human development as a resource of hospitality, while preserving the cultural identity of the population, which is also a tourist resource of the territory.
Tourism in the Komi Republic: Opportunities and Challenges
Depending on the degree of tourist development Komi Republic is an ill-developed closed tourist region. Paid services in 2007 included cultural and recreational services 3,8%, including 1,5 – tourism; 0,9 – health-improving; 0,7 – Sport and Physical Education; 0,7% – the culture of [12].
Natural and cultural resources. In the republic there are 253 protected areas (PAs), including Pechoro-Ilychsky State Biosphere
Reserve and National Park "Yugyd-Va" (World Natural Heritage Site), 173 state nature reserves and 78 natural monuments. The total area of the protected areas covers more than 6 million hectares, representing approximately 14,6% of the Republic territory and higher than average.
The most promising for the development of tourism are the mountainous regions of the republic: Circumpolar, Polar and Northern Urals. Alpine forms of relief are attractive for the construction of ski trails, ecological trails, the construction of recreational and ski facilities.
In Pechoro-Ilychskiy Reserve the world's first experimental moose farm operates, the Museum of Nature is created, ecological trails are laid, and environmental camps are organized. The main value of the national park "Yugyd-Va" is primeval landscape. Hiking and water trails are popular here. Currently, the park is visited by 4-5 thousand people a year.
Historical and cultural potential is presented by various types of historical monuments, memorial sites, museums, buildings and structures associated with historical events. In the Komi Republic there are 820 cultural heritage sites in the official account including: archeology – 508, architecture – 170, history – 118, monumental art – 24. The museum network brings together 119 museums of different professional focus. Among them there are art, literature, local history, folklore, scientific, institutional and memorial museums. Promising tourism resources are archeological finds, objects of religious architecture, the Gulag era legacy.
Recreation and tourism facilities
In 2007, 57 tourist firms acted in the republic, which handled 26,6 thousand visiting tourists. The total number of tourists was 27,4 people to 1000 of the population. According to expert estimates, the number of tourists arriving amateur is increasing: for instance, only on the territory of the urban district "Inta" about 3-3,5 thousand tourists arrive every year.
In the hotel industry there are 64 hotels and similar collective means of accommodation with a capacity of about 6 thousand people. In general, hotels loss, utilization of available seats is 0,3 (effective rate is considered to be not less than 0,65). Within the rooms of hotels and similar accommodation rooms 70% of them have a category.
There are 20 resorts organizations and recreations with 1 782 seats. The number of citizens who were placed through the collective means of accommodation in 2006 amounted to 176,3 thousand people, 16,8 thousand of which had vouchers.
Tourist-recreational zoning
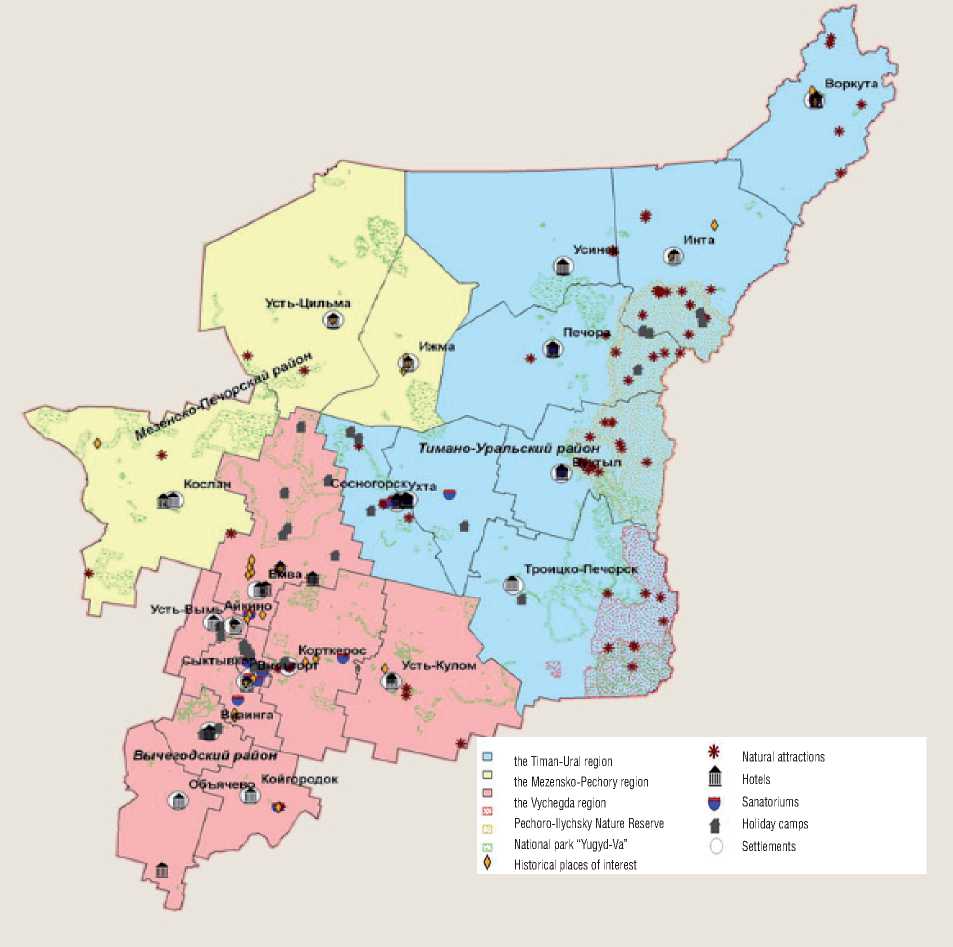
Given the historic, cultural and landscape diversity in the territory of the Komi Republic, its settlement and industrial development, preservation of identity three tourist and recreational areas are marked out (fig. 1) :
^ Timan-Urals region in primeval habitats and landscapes, and retained the capacity of northern extreme rest;
^ Mezensk-Pechora region, where the powerful natural-recreational potential makes ethnic components of tourist resources more pronounced;
^ the Vychegda region is more economically developed, with different types of settlement, environmental, historical and cultural resources diversity.
A generalized characteristic of the areas is presented in table 2 .
The development of tourist and recreational areas is causing the formation of tourist centers and specialized areas. Recreation centers can appear in urban districts "Syktyvkar", "Ukhta", "Inta", "Vorkuta", in the municipal areas "Pechora", "Vuktyl', "Troitsko-Pechory". This will be facilitated by the developed infrastructure, existing facilities tourist industry, culture, sports, historical monuments, as well as organizations involved in tourism activities.
Activities forming the tourism sector of the Republic
In 2008, "The concept of tourism development in the Komi Republic in the period up to 2020" was adopted; it identifies promising types of inbound and outbound tourism, the potential tourism centers. Important areas of project activities to develop the regional economy tourism sector are:
Figure 1. Tourist and recreational areas of the Komi Republic
-
- development and maintenance of modern information base (assessment of cultural and recreational potential, the result of which will be an electronic inventory of tourism resources and products; maintaining a roster of network objects – collective accommodation facilities with their condition and density assessment; development of the catalog and illustrated atlas describing the tourist routes to products, areas and types of tourism);
– the formation of tourist-recreational carcass from the various sites of tourist-recreation areas and centers, ethno-cultural centers, ethnic villages, multifunctional complexes, tourist bases, etc.;
– development and implementation of marketing strategy to promote regional tourism products;
– creation of infrastructure related to the field of tourism;
Table 2. Potential tourist and recreational areas of the Komi Republic
|
The main points of tourist facilities and attractiveness |
The main types of tourist and recreational activity |
|
Timan-Ural tourist and recreational area |
|
|
Vorkuta : Memorial Cemetery of Terror Victims (Jur-Shor), a memorial sign «Victims of Political Repression of 1930s – 1950s» Rocky limestone canyon (Niyayu river), Payer Mountain (1472 m) Inta : «the main gate of Polar Ural», Narodnaya Mountain Pechora, Inta: unique landscapes of the National Park «Yugyd-Wa» |
The memorial, cultural, educational, mountain, water, eco-tourism Weekend leisure, children's recreation, sanatorium treatment |
|
Ukhta : architectural ensembles Timan routes for recreational tourism in the wake of the geological and topographical parties. The unique natural and historical landscapes Sosnogorsk : Memorial to victims of political repression, local museums and the sights associated with the industrial development of the region «Cossack circle», Festival of Slavic culture, Orthodox music, rock music |
|
|
Vuktyl : Pechoro-Ilychsky State Biosphere Reserve as the object of World Cultural and Natural Heritage («Virgin Komi Forests») Troitsko-Pechorsk : «Seven dimwits» on the ridge Manpupuner, mountain range «Torreporreiz», or «Ruins of nonexistent city». Unique moose farm, museums, tours |
Environmental, cultural, educational, active water, ski, sport tourism |
|
Mezensko-Pechory tourist and recreational area |
|
|
Izhma : linguistic and cultural specificity of the Izhma Komi household, Herdsmen traditions, folk crafts (products of reindeer fur). Holidays of the Komi-Izhma people – «Lud», hunters day, herdsmen day |
Cultural-cognitive, pilgrimage, eco and sports tourism |
|
Ust-Tzilma : distinct region with traditional rites and songs. Holiday «Krasnaya Gorka», symbolizing the labor peak of a year, time for adolescents to become youth Product crafts: carving wooden utensils, Pizhma spoon, amulet and wedding belts, mittens and socks with ornament |
Cultural-cognitive, pilgrimage, eco and sports tourism |
|
Udora : the Udors is an ethnic group of Komi-zyryan having their own dialect Komi language and traditions. Distinctive folklore and folk crafts. Ethnic Village Patrakovo , old villages with churches Vazhgort , Koslan , a place of pilgrimage – Ioanikeeva cell, Ship thicket – a monument described by M. Prishvin, river Yirva |
The pilgrimage, eco-tourism, ethnotourism, cultural tourism |
|
Vychegda tourist and recreational area |
|
|
Syktyvkar : Komi Republic capital, cultural and scientific center. The monumental attractions. Europe's largest timber complex. Stephen of Perm’s Cathedral Ust-Kulomsky region : current Stefan-Ulian Trinity Monastery (Ulyanov village) The Syktyvdinsk region : Yb settlement – a perspective tourist ethnographic complex The Koygorod region : memorable places associated with the displaced The Sysolsk region : in Kuratovo settlement – a traditional folk ritual feast «Gazha-valay» and the feast devoted to the Komi poet Ivan Kuratovu. In Pyeldino settlement – Ethnic Center «Spring», the school museum The Priluzsk region : Church of the Blessed Virgin Mary Assumption built in 1882 – 1884 that is a monument of religious architecture. The annual festival of folk bands «Luza dorsa gazh» (Obyachevo settlement) |
Business, cultural, educational, pilgrimage, eco, sports tourism |
|
Ust-Vym: stone churches of Stephen of Perm (1755 – 1767) Archangel Michael (1795 – 1806), a complex of Zemstvo Hospital buildings (1903 – 1911), historical-ethnographic museum, housing of the end of XIX – beg. XX century. Seregovo : salt fish and resort |
Weekend Leisure, children's recreation, sanatorium treatment |
– creating a favorable business environment development of tourist and recreational activities;
– investment projects support in tourism.
Cultural and recreational complex of municipal entities: the prerequisites of forming and direction of development
Integrated approach to the problems and prospects of development of tourist-recrea- tional sphere is realized in the evaluation of the capacity development of municipalities of the Komi Republic [3]. The study of the municipal district (MD) cultural and recreational complex (CRC) includes an analysis of the prerequisites, the rationale for and mechanisms of its formation. Such a scheme, approved in many regions, seems to be the most produc- tive and can be used in the organization of the local authorities for development strategy of the activity [2].
Geological location has a direct impact on market size of cultural and recreational services provided. In ensuring the availability and quality of services an important role is played by the density of road networks, availability of bus service.
Landscape diversity, specialties of the relief and rivers with picturesque places, the assessment of mushrooms and berries stocks are the key positions of the attractiveness of natural and recreational resources.
Cultural and recreational wealth of the area is historical heritage , represented by both tangible and intangible elements. Traditionally, it includes places of worship, not only churches and chapels, but also special, holy place for the people. Historical range of traditional crafts is another forward-looking element, activation of which is connected to the reconstruction of crafts, restoring them to new forms – training and gift shops, artisan houses of ethnic villages, etc. The wealth of the territory consists of famous fellow countryman. Their way and cultural contributions can and should be subject to display and disseminate conducted in various forms.
Hospitality infrastructure in a broad sense includes not only the existing facilities network , providing the intensity and diversity of cultural and recreational activities within the museum, children's cultural institutions, art groups, businesses that provide recreation, but also things that can be used for recreation. It is important to take into account both the services representatives and beneficiaries. Among them there are children's and adult social institutions (orphanages, shelters, rehabilitation centers, health resorts, summer camps, etc.) which could become active objects with their features and characteristics determining their place in the cultural and recreational network.
In the infrastructure framework of the Republic’s cultural recreation areas one can mark out organizational structures different in their type and kind of supported activities, but similar in initiatives and committed people.
Of particular importance in the formation of municipal CRC are holiday calendar activities . Patronal feast, "prescribed" in certain locations, the activities associated with the celebration of the famous countrymen, folk and contemporary music festivals play a big role in streamlining and organization of culture and recreation, support the old traditions and build new ones.
The real advance in the CRC organization depends on the success of the project activities. Ambitions and initiative of administrations, institutions of education and culture, creative teams, representatives of the people to develop their own proposals and participation in national and international projects are important here.
The CRC contour is basically modeled by such directions as organizing cultural and recreational areas and centers of different types and learning traditional art and craft activities.
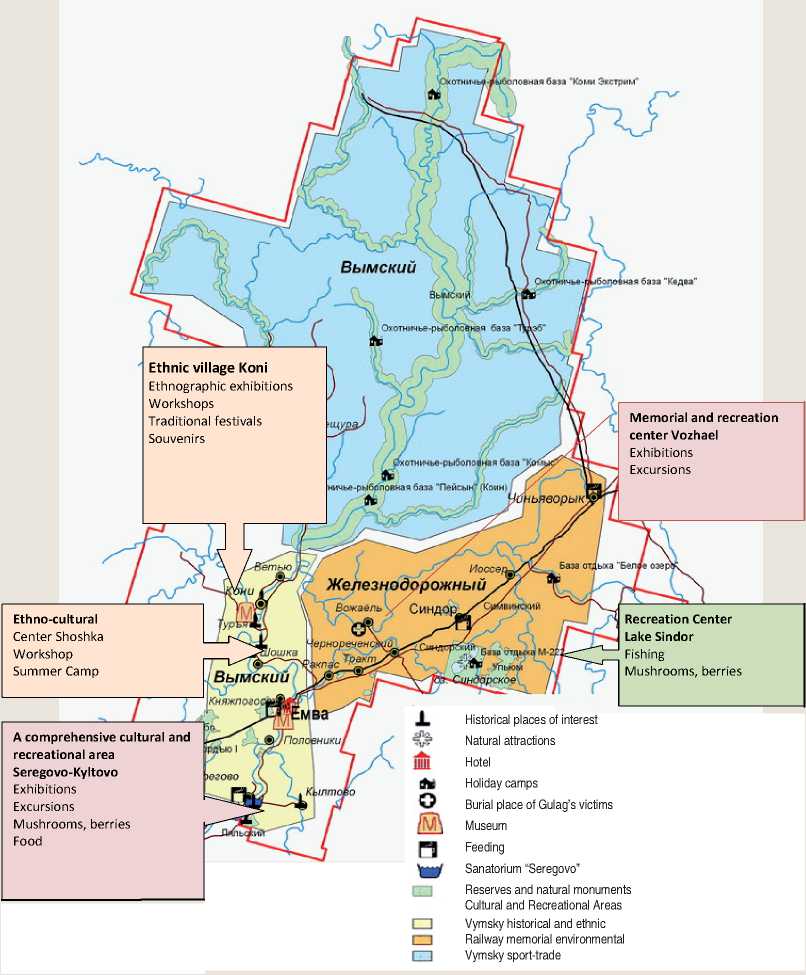
A variety of local features creates a sufficient diversity of cultural and recreational areas in health-improving, historical, cultural, ethnocultural background and their combinations, supplemented by business components. These examples are presented in the schematic map (fig. 2) .
Recreation and health-improving specialization is spread more widely. These are winter recreation, such as "Zelenetskie Alps" (near Syktyvkar), year-round hunting and fishing holiday camps in the MD "Knyazhpogostsky" etc. Such a country vacation with a duration of two days of tours and more, with the opportunities for fishing, hunting, gathering mushrooms and berries can be arranged in other places, as recommended in the research and analytical reports prepared for certain areas.
Recreation and health-improving centers also include Seregovo resort, which lies north of the city of Syktyvkar, its balneological base is represented by mineral waters used for bathing and other external procedures.
Figure 2. Cultural and recreational complex of "Knyazhpogostsky" municipal district
Вымский ювнаябаза"Dei
(Койн)
гворь/^
Синдор
ГСК1
|Кмяжлого<
^Лоловмикш
К^лт< у Иоссе} южный /
(отничье-рыбопо^ная база ернореченсА жпас ^Р9^
зтничье-мболовная база “Коми Экстрим"
Recreation Center
Lake Sindor
Fishing
Mushrooms, berries о йш
л
О
№
I ^ I
Historical places of interest Natural attractions
Hotel
Holiday camps
Burial place of Gulag’s victims
Museum
Feeding
Sanatorium “Seregovo”
Reserves and natural monuments
Cultural and Recreational Areas
Vymsky historical and ethnic Railway memorial environmental
Vymsky sport-trade
A comprehensive cultural and recreational area Seregovo-Kyltovo
Exhibitions
Excursions
Mushrooms, berries Food еная база "Кедва"
Ethno-cultural
Center Shoshka Workshop Summer Camp
Memorial and recreation center Vozhael Exhibitions
Excursions
Ethnic village Koni Ethnographic exhibitions Workshops
Traditional festivals
Souvenirs
A potential center in Ust-Vym settlement can serve as a striking example of history and cultural specialization. Its background is a powerful historical potential, associated with the largest figure of medieval Russia Stephen of Perm, churches, Michael-The Archangel Monastery, National History Museum, architectural monuments. Important prerequisites for the development of the center are a multiyear practice of tours and festivals (festival "Ust-Vymskie Dawns"), the preservation of folk traditions and local work with children.
Features of a number of regions connected with special migrants’ settlements, the Gulag’s activities determine the memorial specificity of historical and cultural specialization. Such specificity is characteristic for many districts and towns of the Komi Republic, and must be necessarily reflected in the tourist and recreational activities.
Ethno-cultura l specialization is attractive because of revival of ancient villages, a successful experience of which can be found in Finland and Karelia. The basis for establishing such facilities in the Komi Republic is a historic area of crafts preservation, shopping places (fairs). Here one can get acquainted with the house of Komi, Komi national cuisine, national features of hunting and fishing, with farmhouses, Komi customs, traditions and legends. Historical prototypes of ethnic villages were met in all the surveyed areas.
Integrated cultural and recreational direction supposes a combination of historical and ethnic components with suburban leisure of varying lengths.
This may be a zone "The Finno-Ugric village" in the Yb settlement (municipal district "Syktyvdinsky"), where it is supposed to erect a complex of buildings and structures for yearround recreation.
In the project Glotovo – Yirva (municipal district "Udorsky") it is possible to combine historical and cultural components of the Glotovo settlement which has Hristorozhdestvenskaya church with roots in the XVI century, legends of the village grounds, ancient perevolok Yirva – Vorykva, famous countrymen, opportunity to use the holiday calendar, and the development of the exposition, restoration activities in the context of the historical village, as well as the natural capacity of river Yirva.
In some settlements there are favorable conditions for combination of cultural, recreational and agricultural components. This is a traditional animal husbandry and gardening, which provide visitors with food and, in turn, receive steady sales. In the former settlements of iron factories Nyuvchim (MD "Syktyvdinsky"), Kazhim and Nyuchpas (MDS "Koygorodsky") one can find the survived attractions which may become the nucleus of cultural exposure after carrying out rehabilitation work, and ponds are already being used for fish farming.
Studying traditional artistic and trade activities is a constructive form of employment growth of northern peoples in the Nordic countries. For example, among the training courses of the Education Center in Sami region in Lapland (Finland) there is the traditional reindeer husbandry, tourism (guide-conductor, tourism services manager), Sami handicraft, wood, precious stones and metals treatment.
In the Komi Republic a center of crafts is created (Vylgort settlement near the city of Syktyvkar). The Center will be both educational and methodical organization of training and retraining for teachers of handicraft, the fine arts, masters of crafts and arts and crafts amateurs. In the future, ethnic villages can become a platform for learning artistic skills.
Organization of cultural and recreational complex
Mechanisms for CRC formation refer to the areas of strategic planning, finance, information and personnel security.
Designation of CRC strategic contour can be arranged in a special document or embedded in the overall area development program, preferably with fixation of certain projects. Many areas already study these directions, primarily in tourism, and in the specially designed units.
Diversification of funding sources is an important moment of the implementation of district plans and projects. One of the real funding sources is the inclusion of regional projects in Republican efforts to develop tourism and culture. Financial support can be obtained from the Ministry of National Policy, which conducts an annual grant competition "Ethnic Initiate" among the dozens of projects in five categories. The maximum size of the grant is100 thousand rubles.
One of the sources of financial support for cultural and recreational projects could be an inland regional competition’s fund, similar to the Republican "Ethnic Initiate". An example is the charitable fund of JSC "Lukoil" and LLC "Lukoil-Komi", which organizes contests of social and cultural projects in the Usinsk city.
Foreign aid in the implementation of the ethno-cultural projects remains virtually an untapped source. Karelia has a successful experience in this respect. Thus, over the past eight years Finnish organizations sent about 50 thousand euros for the revival of the historic villages of Karelia Kinerma.
Informational maintenance and advertising is an indispensable element in the formation of the CRC. It is supposed to develop and maintain recreational and cultural unit at the regional site, the publication of leaflets, special informational publications designed for the investor, including information about the object to the state directory of investment projects.
Education in cultural and recreational aspect includes such forms of work as classes with diverse «agenda» (master classes, exhibition of decorative arts and crafts, and history excursions to a particular area, etc.). Ethnographic shift in the camps, not only for children, but families are becoming increasingly popular in the Finno-Ugric regions, including the Komi Republic. During these shifts children get better acquainted with the life, customs and traditions of their forefathers, study national types of arts and crafts in stationary or mobile workshops with the help of mobile means (road shows and computer programs).
Training is an urgent task to develop new areas of municipal and regional economy, which would require professional eco- and ethno-instructors (guides), managers of tourism. Taking into account the interests in the tourism promotion their training can be organized not only in Syktyvkar State University, but other educational institutions of the Republic.
Municipalities have a variety of cultural and recreational potential and varying size of the market. However, there is no doubt that an ethnographic focus and national flavor culture, combined with opportunities for various forms of recreation, while ensuring targeted and the actual mechanisms at district and national levels will help establish a new promising sector of municipal economy with its necessary contribution to the financial income and local employment.
Список литературы The tourism industry: administrative levels and methods of forming
- Andreev, V.V. Assessment of tourism and its impact on the economy of the Krasnodar Territory/V.V. Andreev, SH.D. Sovmen, E.N. Khilko//Issues of Statistics. -2008. -№ 4. -P. 33-41.
- Dmitrieva, T.E. Cultural and recreational potential of the municipal development/T.E. Dmitrieva, V.A. Schenyavsky//Region. -2008. -№ 8. -P. 43-47.
- The municipal entities potential development: the content, assessment, management (based on the materials of the Komi Republic)/authors. -Syktyvkar: Komi Scientific Center of UB RAS, 2008. -344 p.
- Smirnova, I. Tourism as a resource/I. Smirnova//Russian expert review. New resources of Russia. -2008. -№ 1 (24). -P. 39-43.
- Stepanova, S.V. Tourism influence on the socio-economic development of the region (on the example of the Karelia Republic)/S.V. Stepanova: abstract of Ph. D. thesis. -Petrozavodsk, 2008.
- Golovin, S. Tourism unites/S. Golovin//Expert. -2006. -№ 5. -Feb., 6. . -Access mode: http://www. href='contents.asp?titleid=9287' title='Эксперт'>Expert.ru/
- Zubova, E. Tourism brings regions together/E. Zubova//Expert North-West. -2007. -№ 40. -Oct.,
- -Access mode: http://www.expert.ru/printissues/northwest/2007/40/
- What proportion of tourism in the country's GDP? RATA news: the daily electronic newspaper for the professional tourism business. -2007. -08-01 . -Access mode: http://www.ratanews.ru
- Kolotnecha, O. Calculating tourism/O. Kolotnecha//Expert North-West. -2008. -№ 4. -28 Jan. . -Access mode: http://www.expert.ru/printissues/northwest/2008/04/
- Movily, V.V. New technology for tourism development/V.V. Movily: transcript of speech//roundtable «Prospects of inbound tourism development in the North-West» materials. -St.-Petersburg, 2007 . -Access mode: http://www.csr_nw.ru
- Smirnova, I. Tourism development managing in the region/I. Smirnova: Presentation of report//TSSR «Severo_Zapad» materials. -St.-Petersburg, 2007 . -Access mode: http://www.csr_nw.ru
- Tourism and tourist resources of the Komi Republic: Collection/Territorial body of Federal State Statistics Service of the Komi Republic. -Syktyvkar, 2006. -100 p.
- The Travel & Tourism Competitiveness Report 2008. Balancing Economic Development and Environmental Sustainability . -Access mode: http://www.weforum.org/en/media/publications/CompetitivenessReports/index.htm/


