The Usability of Agent-Based Simulation in Decision Support System of E-Commerce Architecture
Автор: ŠPERKA Roman, SLANINOVÁ Kateřina
Журнал: International Journal of Information Engineering and Electronic Business(IJIEEB) @ijieeb
Статья в выпуске: 1 vol.4, 2012 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Electronic commerce (e-commerce) has the potential to improve the competitiveness of the enterprises. A decision support system, used in e-commerce, is a term used to describe any software engine that enhances the user’s ability to make decisions. The paper presents a new approach for decision support system modeling. This approach is applied by a modification and extension of existing decision support system architecture by multi-agent technology and agent-based simulation models. Multi-agent technology is one of the fastest growing fields of information and communication technology – new agent-based services, products, and applications are being developed almost every day. Agent-based simulation model is applied to coordinate, control, and simulate the architecture of decision support system, used in e-commerce. The proposed architecture improves the existing decision support systems and gains competitive advantage.
E-commerce, DSS, software agent, multi-agent, MAS, architecture, simulation
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/15013099
IDR: 15013099
Текст научной статьи The Usability of Agent-Based Simulation in Decision Support System of E-Commerce Architecture
Published Online February 2012 in MECS
Electronic commerce (e-commerce) is a term for any
This work was supported by grant of Silesian University no. SGS/24/2010: The Usage of BI and BPM Systems to Efficiency Management Support.
type of business, or commercial transaction that involves the transfer of information across the Internet. It covers a range of different types of business - from consumer based retail sites, through auction or music sites, to business exchanges trading goods and services between corporations. It is currently one of the most important aspects of the Internet to emerge. E-commerce can provide many potential benefits over non-electronic commerce. Corporation is able to reduce the costs by reducing labor. The results of using e-commerce are reduced errors in keying data, reduced paper work, and reduced post costs. Another benefit is the economy of time. That means shorter lead times for payment, return on investment in advertising and faster delivery of product. The rapid dissemination of information, the digitization of record keeping and the networking capability of the Internet has improved flexibility and responsiveness and encouraged new and more efficient intermediaries. It has increased the use of outsourcing, expanded market access, reduced time to market by linking orders to production and improved internal coordination.
A decision support system (DSS), used in e-commerce, is a term used to describe any computer application that enhances the user’s ability to make decisions. DSS possibilities improve the use of e-commerce in terms of customer satisfaction. We are trying to bring the new approach into this issue called multi-agent approach. Multi-agent techniques in information and communication technology (ICT) are one of the most vibrant and fastest growing areas of information technology – new agent-based products, applications, and services are being announced on almost daily basis. The reason for this intensive interest is that the metaphor of autonomous problem solving entities cooperating and coordinating in order to achieve their desired objectives is an intuitive and natural way of the problem solving. Moreover, the conceptual apparatus of this technology provides the powerful and useful set of computational structures and processes for designing and building the complex software applications. The multi-agent techniques combined with DSS tools can help decision makers to cope with the problems of the information overload. Through the delegation of time-consuming decision-related tasks to software assistants, human decision makers can better concentrate on higher-level cognitive and analytical aspects of the decision making. The agent-based DSS, implemented in the e-commerce systems should help customers and e-commerce providers to avoid the problems described above. On the other hand we propose to extend the architecture with the simple agent-based simulation model. That allows the possibility of purchasing prediction behavior of consumers. This will ensure the providers many opportunities for penetrating the market and should be precisely a competitive advantage for them.
This conceptual paper is structured as follows. The second section explains the concepts of e-commerce, DSS’ information overload and simulations in details. The multi-agent approach and advantages of agent-based modeling and simulation are discussed in the third section. The last section presents proposed DSS architecture using multi-agent approach and simple agent-based simulation model.
2. E-commerce and decision support system
Basic e-commerce steps can be seen in Figure 1. There are three main entities: customer, merchant and payment system. Customer selects products on his personal computer through the web browser application. After confirming the order, the customer has to pay for the order through the payment server. After paying for the order, the request is sent from the client’s web browser to merchant’s web server. Merchant is verifying the payment and can dispatch the goods (not in Figure 1).
The customer decision-making process in the e-commerce environment is generally information intensive. The age of web-enabled technologies and e-commerce brings about the abundance of information accessible to decision makers. If not properly filtered and pre-processed, this amplitude of information can easily "overload" the decision maker [3]. As stated in [4], "Web has made the need for decision support even more pronounced." Currently, there is a pressing need for tools that facilitate search, pre-processing, filtering of information, automation of routine tasks, and providing decision makers with valuable options and insights [5].
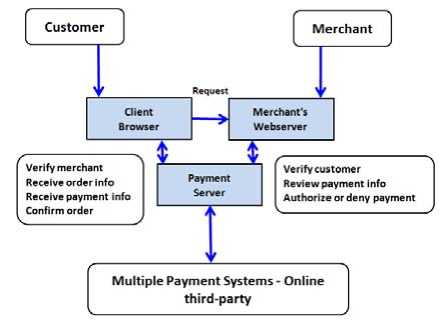
Figure 1. E-commerce steps
Providers of e-commerce services must take these specifics of decision making process into account. On the other hand they are influenced by fluctuations in the markets of all types. Nowadays the business environment is unpredictable and turbulent. Their aim is to provide the customers with quality information in their systems. The success of their business depends on it. This is why it is appropriate to use simulation and to verify important decisions before we actually do them. Simulation is the imitation of the operation of real-world system or process over time [6].
A simulation model is a representation of a real-world system that incorporates time and the changes that occur over time [7]. We use the simple agent-based simulation model in our DSS architecture of the e-commerce system. In the next section we explain the multi-agent technology principles and the advantages of agent-based simulation models [8], [9] in DSS architecture. We will also outline the differences between traditional and multi-agent simulations.
3. Multi-agent approach
Multi-agent systems are collections of single agents that are used to communicate and interact with one another to solve the problems that have been delegated by the users. The agent technology differs from the standard software due to the autonomy of intelligent agents. It undertakes the properties of the agents to achieve its user’s goals. This is done through active learning based on the situation that arises in the environment. The agent technology can be used across many fields; such as process control, operations management, information management, and education.
The term agent is very widespread. It may indicate [10] the community, body or physical system (e.g. robot), which exists in the real world. In the context of multi-agent systems, however, the term generally refers to any relatively autonomous software application or only to a small part of it. There are many sources, indicating the various definitions of an intelligent agent. The agent is an entity designed to fulfill its objectives in an adequate environment. The functions of the agent are based on perception through sensors and on actions through actuators. The agent influences the conditions in the environment in order to achieve its objectives. Some sources (e.g. [11]) depict the agent as a real or virtual object, placed in an environment, where it can perceive the environment and act. The agent is able to communicate with other agents. It has an autonomous behavior, which is based on its observations, knowledge and interactions with other agents.
The agents are internally structured. Proposed general outline of our software agent structure is presented in Figure 2. The actions of an agent are started by some message from the agents’ environment. The message is captured and analyzed by the social behavior layer of the agent and passed to the cooperation layer, which has the task of cooperation with other agents in the system. Cooperation layer interacts with the planning layer. The main task of this layer is to send the plans, assignments and conditions to the reactive layer. The reactive layer itself prepares the output action and performs it. All levels use the data regarding the agents’ knowledge of the environments, targets, goals and aims of the system, and the agents themselves, terms and conditions of the possible actions etc. stored in a special agents’ database. This database can be shared by other agents.
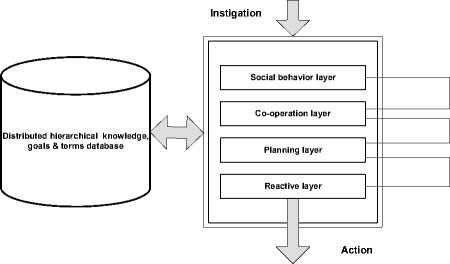
Figure 2. Layered software agent structure (adapted from [12] )
The interaction between agents is controlled by rules set in an interaction protocol. The most widely used protocol is now FIPA contract-net protocol (Figure 3). The agents must be able to negotiate the compromise, resolve conflicts, and allocate resources by agreement [13]. According to [14] a situation called negotiation is generally characterized by three elements; first a negotiation set is provided, which can be used as a collection of possible offers that an agent can make. Second the specific protocol that is used controls the agent’s interaction. Finally the strategies that have been defined for the agent to use are declared. These strategies are private and may take into account other agent’s strategies. The negotiation protocol consists of admission rules, interaction rules, validity rules, outcome determination, withdrawal rules, termination, and commitment rules.
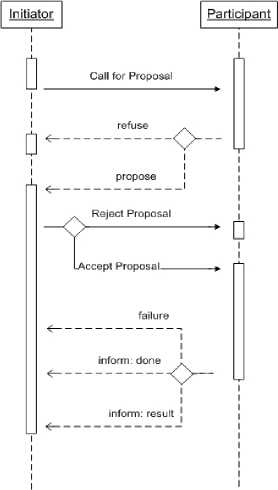
Figure 3. Contract-net protocol (adapted from [15])
There are more reasons why is the multi-agent approach suitable for the e-commerce modeling and simulations. As mentioned earlier we live in an increasingly complex world. According to [9] the systems that we need to analyze and model are becoming more complex in terms of their interdependencies. Traditional modeling tools are no longer as applicable as they once were. Some systems have always been too complex for us to adequately model and simulate. Modeling markets and customers’ behavior has traditionally relied on the notions of perfect markets, homogeneous agents, and long-run equilibrium, because these assumptions made the problems analytically and computationally tractable. Data are becoming organized into databases at finer level of granularity and computational power is advancing rapidly. We are now able to take a more realistic view through the agent-based modeling and simulation.
The main advantage of the agent-based model is the reaction of the system to changes in the environment, their flexibility, easy reconfiguration, scalability and openness to the integration of new parts. Agents may be added to the system or removed from the system. There is no problem to replace one agent with completely different implementation of the same external behavior. The existing software or hardware may be agentificated ([16] and [17]). We can provide them with the interface, which functions on the one hand as a controller of the original system and on the other hand like an agent. However, if the dynamics of the environment is predictable and not really complex, then models using classic methodologies are to be preferred.
Because of the aforementioned characteristics of agents, we tried to use them to propose an agent-based architecture of DSS in e-commerce system. This proposal deals with the simulation capabilities of the buyers’ and sellers’ behavior. The simulation functionality should be responsible for the results representation of the e-commerce provider’s business decisions. These results could be useful for the decision making process of the e-commerce provider and subsequently for the impact on the economic performance of his company. The benefit of such functionality is the possibility to predict the behavior of the buyers. Such a prediction is based on the purchase history.
4. Architecture of a multi-agent based decision support system with simulation layer
In this section, we propose DSS architecture of the e-commerce system using agent-based simulation model. We were inspired by [18] and [19]. The authors of these papers describe their existing architecture of DSS and its individual components. In our research, we modified and extended (both) models. We implemented the characteristics of simulation agents in detail. Simulation agents are integrated into simulation layer and bring to the proposed architecture special functionality. This functionality provides the interface and the mechanism to simulate merchant’s decisions before their implementation in practice.
The proposed architecture is based on four layers: interface layer, process layer, knowledge layer, and simulation layer. The whole architecture is depicted in Figure 4. The interface layer is visible from outside and it is at disposal to other agents and users. It provides the mechanisms for interacting with the facilitator and the simulation control agent. It supports inter-agent communication, collaboration, and coordination. The access to the process layer and to the knowledge layer is restricted. Other agents and users cannot directly manipulate with the content of these layers without the access privileges. The process layer contains the methods and heuristics implementing a variety of functions and processes, using by means of which an agent can respond to the requests from other agents or users. Thus, the process layer basically provides the services and computations that may be necessary for solving a particular problem. The knowledge layer contains domain-specific and domain-independent knowledge relevant to the problem solving. The simulation layer was discussed above.
-
4.1 Interface agents
-
4.2 Facilitator agent
The facilitator agent is responsible for the coordination of various tasks that need to be performed. After receiving the user input from the interface agent, the facilitator agent identifies the relevant criteria. It has to
-
4.3 Database agent
-
4.4 Simulation agents
Interface agents are divided into groups for two types of users: a buyer, and a merchant. Each of the different users has their own interface agent. Each of the interface agents provides a web interface for the users to interact with DSS in order to help to deal with several online forms, and to do data analysis activities. The user can provide a general description of the problem at hand in terms of high-level goals and objectives, or provide the specific details about the data analysis or the data mining task to be performed.
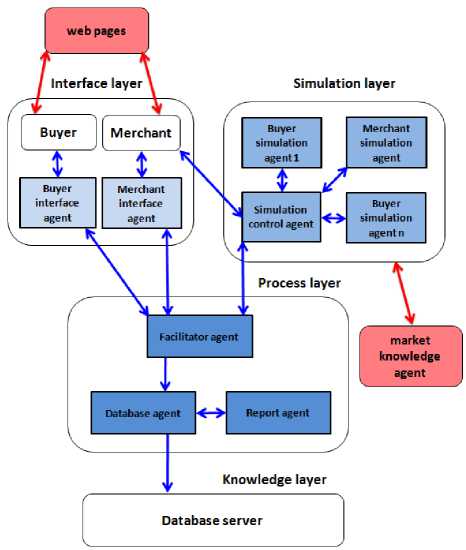
Figure 4. Decision support system based on multi-agent approach with simulation layer
The interface agents are responsible for receiving the user specifications and delivering the results. They also keep track of user preferences. They contain the methods for the inter-agent communication as well as for getting input from the user. They contact the process layer with scripts and methods for capturing the user input and communicate it to the DSS facilitator agent. The functions of the interface agents provide the web interface for the user interaction, web page for the user input and the problem description. They also ensure a feedback delivering the states of various processes and the web page containing the final results. They are responsible for the dynamic creation of HTML documents with special formatting needs, the communication of the user input with the DSS facilitator agent, for capturing the user activities and the preferences, and for the creation of the user profiles.
determine the alternatives needed to be evaluated and to generate a plan of actions, such as the ranking of alternatives. These alternatives may include the identifying of relevant data sources, requesting services from other agents, and the generating of reports. The interface module of the facilitator agent is responsible for the inter-agent communication. The facilitator agent communicates also with the simulation control agent to provide the necessary data to start the simulation according to the merchant’s requirements. The process module of the facilitator agent contains the methods for the control and coordination of various tasks. It has to generate the tasks sequence. The tasks sequence is created by the utilizing of specific formula stored in the knowledge module. The knowledge module also contains the meta-knowledge about the capabilities of other agents in the group, available data sources and databases. The facilitator agent may seek the services of a group of agents and synthesizes the final result. The functions of the facilitator agent are to identify high-level objectives and tasks, to generate tasks sequence and to delegate actions to corresponding agents, to provide intermediate feedback to the user, and to synthesize and generate the final result.
The database agent is responsible for keeping the track of the data stored in the database. It provides predefined and ad hoc retrieval capabilities. It is also responsible for the retrieving of necessary data requested by the data mining agent, getting ready for the specific data mining operation. The database agent takes also the heterogeneity of the databases into account (it may exist within the organization). It provides all the data necessary to start the simulation. The interface module of the database agent provides not only the public interface for the inter-agent communication, but also to the existing databases. This improves the inter-operability and enables the users to gain the access to a variety of data sources which otherwise might be inaccessible. The process module provides the facilities for ad hoc and predefined data retrievals. Based on the user request, the appropriate queries are generated and executed against the data warehouse. The results of these queries are communicated back to the user or other agents. The knowledge module contains the meta-data information, including local schemas and a global schema. These schemas are used in generating the necessary queries for the data retrieval. The functions of the database agent are inter-agent message communication, interface to databases, application program interface (API) to commercial database products, ad hoc and predefined data retrieval, maintenance of local and global schema and query outputs formatting based on user needs.
The simulation layer proposed herein above makes it possible to simulate the future trends of the business results. This functionality could enable the simulation agents to develop their behavior and strategies based on a combination of the history available through requesting for simulation control agent services, public information. It is available through the requesting for market knowledge agent services; and private information, available only to the specific agent at their individual knowledge module. It is expected that each simulation agent develops the individual knowledge module with the historical information, since they have the different behavior, and consequently, the different results. Based on the results from the database, the agents can build profiles of the users with expected proposed prices, limit prices, needs and capabilities. On the other hand, requests for market knowledge agent services also provide a great support for the agents that have more sophisticate behavior. This could help the merchant to predict some future actions according to the market strategies, advertisement, prices etc., and to gain more profit. The simulation control agent is responsible for the coordinating of various tasks that need to be performed in the simulation problem solving. After receiving the user input from the merchant, the simulation control agent generates a plan of actions. It identifies the data sources and requesting services from other simulation agents. The simulation control agent communicates also with the facilitator agent to receive the data from databases. It provides these data to other simulation agents according to their tasks plan. Each of the simulation agents has its own tasks plan according to its internal state. The simulation control agent uses the services of the group of the simulation agents and synthesizes the final result of the simulation.
5. Conclusions
In this paper we presented DSS architecture of the e-commerce system using the multi-agent approach and the agent-based simulation model. The multi-agent technology allows closer conduction of the e-commerce DSS to the human behavior. The multi-agent based DSS provides more valuable options and insights. The specification of the simulation layer described above allows the merchant to simulate the behavior of the buyers and thus predicts the success of the e-commerce system.
The e-commerce as a significant competitive advantage and enhanced by the possibility of DSS simulation, improves the profitability potential of a corporation. The outline of the architecture can be seen as a basis for the further research in order to develop such implementation for the real existing companies.


