The way to evaluate the impact of reputation in the internet on the organization’s activities
Автор: Safiullin M., Kurbangalieva D.
Журнал: Электронный экономический вестник Татарстана @eenrt
Рубрика: Экономика отраслей и предприятий
Статья в выпуске: 3, 2023 года.
Бесплатный доступ
In the early 1990s, the digital revolution marked a shift to a new era of competition, one that was characterized by rising new forces, such as ecosystem, information, reputation and other. These changes were driven by Internet. Therefore, this article attempts to propose an approach for assessing the role of the reputation in the internet on an organization's activities in age of digital. This can be significant for both science and practice.
Reputation, platforms, internet, market capitalization
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143182281
IDR: 143182281
Текст научной статьи The way to evaluate the impact of reputation in the internet on the organization’s activities
The biggest impact of the Internet on business is that much commerce is now transacted on the Internet. Business firms purchase from each other over the Internet, and consumers buy products directly in a similar manner. An important consequence of Internet is that it sometimes enables customers to purchase more efficiently than they could purchasing through catalogs or over the telephone. The changing flow of information created by the Internet has tipped the balance of power from sellers to buyers.
An unanticipated consequence of the Internet is that companies must adjust to a different kind of visibility than in the past. People who like or dislike the organization can disseminate this information over the Internet. Fan sites and anti-fan sites appear more frequently on the Internet. At one point, for example, over 200 Web sites could be found that expressed disapproval of Bill Gates and Microsoft. Often these negative comments can be dismissed as the work of jealous people or kooks, but the exposure can badly hurt the corporate image. Another problem is that disgruntled employees might disseminate over the Internet nasty comments about the organization [1].
The managerial action required in relation to increased visibility is to work extra hard to create fans, and deal openly with the issues that make people dislike you, what are also known as a reputation in Internet. However, reputation-building activities are typically measured using metrics that have no predictive or retrospective connection to financial returns. In our researching, we try to find the multifactorial way to evaluate both the impact of reputation in the Internet and other external environments on the organization’s activities.
The review of scientific research on the key request “reputation assessment,” “Internet reputation” and “Internet reputation assessment” allows highlighting quantitative and qualitative methods of a company’s reputation assessment in Internet [5] :
-
• Qualitative assessment methods based on determining the tone of feedback. This group of methods is the most common in the research field, as it allows to derive a single composite indicator through sociological methods of ranking, normalization, and rating. Examples of such works are the research of Yu. Grace, K. Lee, et al. [4] , P. Dorchak, et al. on the Facebook platform [2] , P. Resnick [6] , and J. Schneider on the example of the eBay and Amazon platforms [8] . Among the drawbacks of these methods, as Tadelis S [9] rightly points out, is that reviews may be biased, reducing the effectiveness of a feedback-based reputation system;
-
• Quantitative methods. Questions related to the quantification of intangible resources are always difficult. However, A. Gandini, an author of research into the study of intellectual labor in the digital economy, suggested that due to technology
and the spread of social networking, a freelancer’s reputation can be measured by the number of reputation metrics, such as “likes” which are an indicator of the popularity of publications, and “reposts” – the duplication of brand information on the personal page of the consumer or external agent [3] .
Thus, a review of research similar to the current topic shows that this issue is relevant, however, either financial organizations (commercial banks) or the reputation of an individual are used as the research object [7] . In this article we try to fill the existing gap, as there is virtually no work on measuring the impact of reputation on the activities of a business organization in both foreign and Russian literature.
As a basis for scientific papers, the methods of reputation assessment listed above, based on the analysis of quantitative metrics, are the closest to the goals of this study. At the same time, as a scientific novelty in this article, we suggest considering traditional factors, such as macroeconomic, industry, and internal, when assessing the impact of reputation on the value of companies.
The market value of a company is not a stable indicator; it can change for various external reasons (for example, depending on the phases of the economic cycle) or because of remote (beyond the year) decisions of the managers themselves. Let us picture the company’s market value formation system as a metric system that characterizes macro, industry, and internal environments trends in Fig. 1.
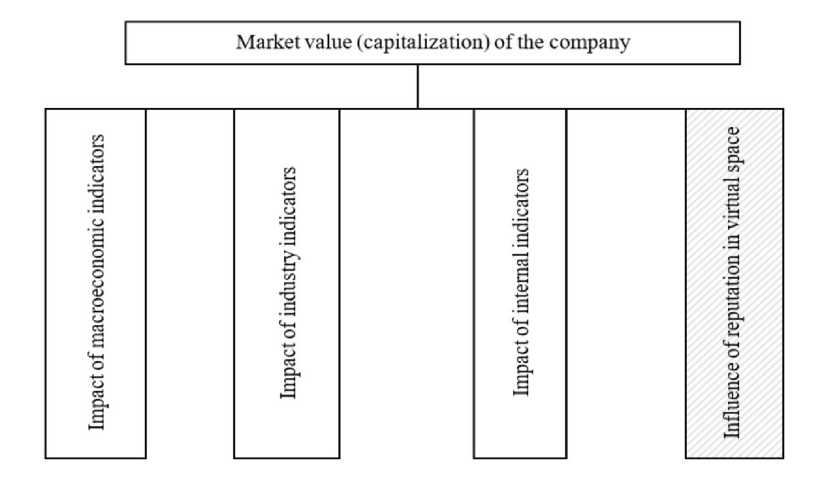
Fig. 1. The way to evaluate the impact of reputation in the internet and external factors on the organization’s activities Source: Compiled by the author.
In Fig. 1, the shaded element indicates our addition to the existing multifactorial model of assessing the market value of the company.
The first component of the impact on the market value of the company stated in this study is the impact of macroeconomic indicators. It is proposed to assess macroeconomic indicators by classifying them into two blocks that characterize socioeconomic indicators and the development of ICT in the world. This division into blocks is because theoretically, a higher level of ICT capital per capita allows the economy to achieve higher growth rates for a given level of labor costs and capital investments [10]. Therefore, as macroeconomic indicators, we use data on the level of global gross domestic product (hereinafter referred to as GDP), GDP per purchasing power parity (hereinafter referred to as PPP), the world population, the number of able-bodied and living in the city among their number. To reflect the spread of ICT, we use indicators characterizing the number of Internet users in the world, the number of sites in the world, the number of social network users, the number of active users of social platforms like Youtube.
The second indicator is the industry trend. For the current study, let us focus on the automotive sector, as it allows one to evaluate the different approaches of the company to achieve the goal of improving the market capitalization indicator. For example, the Toyota brand, which has been the world’s leading distributor for many years, relies on fundamental characteristics, while Tesla creates a certain “hype” around itself to attract investment capital.
The third component that shapes the market value of a company is internal factors. We assume that on the one hand, the number of sales, as one of the indicators of the company’s activity, forms the market capitalization. On the other hand, the market value of a company to a greater extent depends on the impact of balance sheet indicators, for example, the book value of assets or net assets.
It should be stressed that the company usually creates its virtual communities depending on the region, taking into account the language preferences of consumers and the popularity of social platforms. Taking all of the above into account, we decided to assess the Internet reputation of one official brand community according to the following criteria:
-
• Availability of a single digital information backup of the company, that is the official website of the company. As a rule, the official page contains information about the company’s mission, goals, model series, and innovations in the automotive industry, and publishes financial statements, based on which, decisions about the company’s investment attractiveness are made. In other words, this information (intangible) resource declares the brand’s image, quality, and brand in digital format;
-
• Platforms in the information space on which the official communities of the company are created should be accessible for monitoring and easily identified. The company, through its official website, strives to form communities around it with the
highest degree of its adherents’ interaction. To achieve this goal, the brand creates hyperlinks for maximum convenience for those wishing to join their community. Based on the above, we assume that these social platforms and communities shape the reputation of the organization; communities must be active, the interaction between community members is a reflection of their vitality.
We hope, that using this way to evaluate the impact of reputation in the internet and external factors on the organization’s value will help companies solve one of the biggest problems that CEOs face today. Companies that fail to stay ahead of consumers’ evolving needs are unlikely to thrive.
Список литературы The way to evaluate the impact of reputation in the internet on the organization’s activities
- Andrew J. DuBrin Essentials of Management, 8th Edition. 2009, 2006 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning - p. 481- 508.
- Dorcak P, Markovic P, Pollak F Multifactor analysis of online reputation of selected car brands. Procedia Engineering 192 - (2017) - p. 719-724.
- Gandini A. The Reputation Economy: Understanding Knowledge Work in Digital Society. Cham, Springer (2016).
- Ji YG, Li C, North M et al. Staking reputation on stakeholders: How does stakeholders' Facebook engagement help or ruin a company's reputation? Public Relations Review 43(1) - (2017) - p. 201-210.
- Kurbangalieva D. L. Review of methods for assessing and managing brand reputation on the internet: Shortcomings and prospects of scientific research. In: IX international youth symposium on management, economics and finance, Kazan State University, Kazan, 20-23 October 2020.
- Resnick P, Zeckhauser R. Trust among strangers in internet transactions: Empirical analysis of Ebays reputation system. Econ.Internet ECommerce 11(2002) - p. 33-44.
- Safiullin M.R., Elshin L.A., Kurbangalieva D.L. How does reputation economy engagement work to develop financial and economic activity? // Opción, Oficina de Publicaciones Científicas de la Facultad Experimental de Ciencias, Universidad del Zulia. Maracaibo - Venezuela / No.23 (35) (2019) - p. 376-392. EDN: REOUKJ
- Schneider J, Kortuem G, Jager J et al. Disseminating trust information in wearable communities. Personal and Ubiquitous Computing 4 (2000) - p. 245-248.
- Tadelis S Reputation and feedback systems in online platform markets. Annual Review of Economics 8 (2016) - p. 321-340.


