Therapeutic effects of hydroethanolic extract of Erythrina senegalensis in diclofenac sodium-induced hepatotoxicity male Wistar rat: biochemical, redox potential and histopathological outcomes
Автор: Ezihe Ch.I., Agu S.T., Rabo N.D., Ochigbo V.N.
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 3 т.19, 2023 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Background: Hepatotoxicity is one of the main side effects associated with Diclofenac sodium (DFS) administration. The present study aimed to examine the therapeutic effects of hydroethanolic leaf extract of Erythrina senegalensis (HELEES) on DFS-induced hepatotoxicity. Thirty male Wistar rats, 5 per group, were used in this study. They were randomly divided into 6 experimental groups (A-F) and treated for 21 days. Rats in Group A served as the control group and received distilled water orally; group B was given DFS at 10 mg/kg body weight intraperitoneally (IP). HELEES were given to groups C and D at doses of 200 and 400 mg/kg body weight, respectively. Groups E and F were given DFS at 10 mg/kg + HELEES at 200 and 400 mg/kg respectively. Results: DFS administration significantly increased the bilirubin concentration and serum transaminases (ALT, AST, GGT, and ALP) and LDH; total protein and albumin were significantly inhibited. There was a significant reduction in hepatic reduced glutathione (GSH), glutathione-S-transferase (GST), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and nitric oxide (NO) activity, together with a significant increase in hepatic malondialdehyde (MAD), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and catalase (CAT). However, concurrent treatment with DFS + HELEES ameliorated the DFS-induced hepatotoxicity and oxidative stress. The results suggest that HELEES may offer some therapeutic effects against hepatic damage. In contrast to the control and HELEES-only groups, which had normal hepatic tissue morphology, rats given DFS alone developed hepatic necrosis and periportal inflammation, with the presence of numerous inflammatory cells and Kuppel cells. Examinations of liver samples from the groups given Concurrent treatment with DFS and HELEES revealed patterns that were comparable to those seen in the control group. Combining DFS with HELEES has always reduced the impact of DFS. Conclusions: Collectively, HELEES enhanced hepatic function in DFS-treated rats by suppressing nitrosative and oxidative stress.
Diclofenac, erythrina senegalensis, liver, oxidative stress, rats
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143180568
IDR: 143180568
Текст научной статьи Therapeutic effects of hydroethanolic extract of Erythrina senegalensis in diclofenac sodium-induced hepatotoxicity male Wistar rat: biochemical, redox potential and histopathological outcomes
The clinical relevance of diclofenac sodium (2-[2,6-dichloranilino] phenylacetic acid) cannot be underrated. The drug is a well-known nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic agent (Vohra et al ., 2016), which has been widely used in the management of several chronic disease conditions, such as degenerative joint disease, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, osteoarthritis (Thanagari et al ., 2012), actinic keratosis (Kavasi et al ., 2017), among others. The European Medicines Agency (EMVA/CVMP) (2014) noted that although its primary use is in humans, it is also permitted for veterinary use in several European member states. Additionally, from the 1990s to 2006, the Indian subcontinent registered it for use in treating inflammatory conditions in domesticated ungulates ( isebrough, 2006). It exerts its therapeutic effects by blocking the activity of cyclo-oxygenase-2, thereby inhibiting the formation of prostaglandins from arachidonic acid. (Aycan et al., 2018; upta et al ., 2020; Adeyemi et al ., 2019).
Despite the drug's evident therapeutic effects, diclofenac sodium (DSF) usage is known to injure the different organs in both humans and animals (Huo et al ., 2020). DF intoxication can lead to a variety of symptoms, including those that are I tract-related (such as nausea, abdominal pain, gastritis, and vomiting), skin-related (such as urticaria and itching and redness of the skin), renal- as well as liver-related (such as liver injury), in addition to other non-specific symptoms (general weakness) (Boelasterli, 2003; or and Saksena, 2011).
The efficiency of antioxidants found in herbal medicine and their potential to prevent drug-induced liver damage has drawn the attention of researchers worldwide. (Singh et al ., 2016). There has been a paradigm shift toward the treatment of liver disorders with natural remedies rather than conventional medication in recent years (Singh et al ., 2016). Natural products rich in triterpenes, flavonoids, or polyphenols, have now been established as powerful hepatoprotective agents ( upta et al ., 2002, 2004; King and Cousins, 2006; Upadhyay et al ., 2007, 2008, 2010a, b).
ES is one of the typical medicinal herbs used to treat chronic liver disorders in Western Africa. The plant's aerial portions are used as emmenagogues, to induce abortion, and to treat digestive issues like diarrhea and stomachaches (Christensen et al., 2015; Larsen et al ., 2016 The leaves are used to treat a variety of conditions including pain, fever, nausea, secondary sterility, diarrhea, jaundice, and malaria (Togola et al ., 2008). It has been demonstrated that the stem bark possesses hepatoprotective effects (Donfack et al ., 2008). Additionally, the plant's extracts are used typically to treat wounds, parasites, and bacterial infections (Kone et al ., 2012; Ilodigwe et al. , 2014).
As a result of the fact that there seems to be a paucity of scientific reports on the ameliorative effect of HELEES against drug-induced oxidative stress and hepatotoxicity in rats, coupled with the claims by traditional medicine practitioners that the plant extract is effective in the management of liver diseases in humans, there is need for scientific studies to validate this claim. Therefore, this study was initiated to evaluate the therapeutic effects of HELEES against DFS-induced oxidative stress and hepatotoxicity in rats.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Chemicals and kits
The drug DFS is an injectable liquid purchased from the North China Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd, 115 Hainan oad, Shijiazhuang, Hebei, China. . Each 3 ml ampoule contains 75 mg of DFS.
The reagent kits for biochemical assays were purchased from andox Laboratories Ltd, United Kingdom. All the reagents used are of analytical grade.
Plant Material and Plant Extraction
The ES leaves were harvested from the premises of the College of Agriculture arkawa, Plateau state. The plant was identified by a taxonomist; a voucher specimen number UAM/FH/242/21 already exists in the College of Forestry herbarium, Federal University of Agriculture, Makurdi, Benue State.
Preparation of HELEES
The leaves were washed under a running tap and air dried for one month in the laboratory at room temperature, the leaves were pulverized using an electric blender and then sieved using a locally made mesh.
Briefly, the solvent mixture was prepared by adding 800 ml of distilled water to 200 ml of absolute ethanol and mixing. Then, 100 g of the pulverized sample was macerated in 1000 ml of aqueous ethanol mixture and allowed to stand for 72 hrs. The mixture was sieved with a white piece of cloth and the liquid obtained was filtered with Whatman no. 1 filter papers. The filtrate was concentrated in a water bath at 45 °C, and the extract obtained was dried to a constant weight in a desiccator. The concentrated HELEES were weighed, and every 100g of the powdered leaves yielded 7g of extracts.
Experimental animals and management
Thirty adult male Wistar rats ( Rattus norvegicus ) weighing 200–250 g, were used for this study. They were purchased as litters at the age of 6 weeks from National Veterinary esearch Institute (NV I), Vom,
Plateau state. Then they were kept in plastic cages to grow unto maturity and acclimatized for about 4 weeks in the Department of Veterinary Physiology and Biochemistry research laboratory, Federal University of Agriculture, Makurdi, Nigeria. The rats were kept under normal environmental conditions of 12 h dark and 12 h light cycle, with an average temperature of 29°C. They were fed with standard animal feeds, produced by rand Cereal and Oil Mills Ltd, Jos, Nigeria, and clean water ad libitum . The rats were handled with care according to International guidelines for the use of laboratory animals. (NIH, 1978).
Preparation of DFS
The method of Hassan et al. (2021) was adopted for the preparation of DFS to be administered with some modification. The dose to be administered in volume to groups B, E, and F rats were calculated using the 10 mg/kg body weight dosage, and a single dose of the drug was suspended in 0.2 ml of normal saline (0.9 g/dL NaCl) solution.
Experimental Procedure
Thirty (30) male albino rats weighing (100-118g) were used. The rats were assigned to six experimental groups of five rats each.
-
• roup A received 0.2 ml normal saline intraperitoneally (ip)
-
• roup B received 10mg/kg of DFS ip.
-
• roup C received 200mg/kg of HELEES orally.
-
• roup D received 400mg/kg of HELEES orally.
-
• roup E received 10mg/kg of DFS ip and 200mg/kg of HELEES orally.
-
• roup F received 10mg/kg of DFS ip and 400mg/kg of HELEES orally.
All treatments with DS and HELEES were done concurrently for 21 days. During this treatment weekly and observed for signs of toxicity and death daily of toxicity and death on daily basis.
Collection and Preparation of Blood and Tissues
On day 22, the rats were sacrificed by cervical dislocation, and blood from the orbital sinus into plain sample bottles for serum biochemistry. The blood samples in plain bottles were centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 5 minutes to obtain serum and stored at 40ºC until used for analysis. A midventral abdominal incision was made on each male rat. The liver samples were excised, attaching connective tissues were removed, rinsed in normal saline, and weighed using Mettler Balance (C282001, China) according to Abu and Uchendu (2011).
Hepatic tissue preparation for biochemical assays
The rats were sacrificed by cervical dislocation 24 hours after the last treatment. The liver was removed and weighed and a portion of it was rinsed in 1.15% potassium chloride (KCl) and homogenized in potassium phosphate buffer (0.1 M, pH 7.4) and centrifuged at 12, 000 g for 15 minutes to obtain the post mitochondrial fraction (PMF)/cytosolic fractions. The PMF of the liver was obtained and subsequently stored at -20°C until the time of use.
Antioxidant Assays
A spectrophotometer was used to examine the biochemical parameters: the reduced glutathione ( SH) level was evaluated using the liver homogenate according to the technique of Jollow et al (1974). According to the approach described by Wright et al (1981), lipid peroxidation was measured by measuring the quantities of Malondialdehyde formed as a result of lipid peroxidation. According to Mohandas et al., the activity of the enzyme glutathione peroxidase ( Px) was determined (1985). Catalase (CAT) activity was determined according to the method of Claiborne (1985). The level of SOD activity was determined by the method of Misra and Fridovich (1972). lutathione-S-transferase ( ST) was determined by the method of Habig et al . (1974). The level of H 2 O 2 was assessed by H 2 O 2 -mediated horseradish peroxidase-dependent oxidation of phenol red by the method of Pick and Keisari (1981). Nitrite assay was done using riess reagent with some modifications of the method of reen et al. (1982).
Biochemical Assays
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) was estimated calorimetrically using the method described by Thefeld et al., (1974). Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) was estimated calorimetrically using the method described by Thefeld et al. (1974). Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) was estimated calorimetrically using the method described by Thomas (1998). The serum total protein was assayed by the Biuret reaction (Thomas, 1998). The procedure is based on the binding reaction between albumin in the serum and the bromocresol-green dye (Doumas et al., 1975). Serum lobulin was estimated using the biuret reaction method of serum globulin determination (Alberto et al., 1966).
Histopathological Analysis
Statistical analysis
All the data were expressed as the mean ± standard error of the mean. Statistical significance between more than two groups was tested using one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's test using a computer-based fitting program (Prism, raph pad 8.01). Values of P<0.05 were considered significant.
RESULTS
HELEES administration abrogated DFS-induced hepatocellular toxicity in Wistar rats
The activities of serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), and alanine aminotransferase (AST) together with total bilirubin level increased significantly (p<0.05) in DFS-only treated rats compared to the control (Table 1). The therapeutic effects of HELEES were demonstrated with a significant (p < 0.05) reduction in the serum ALT, ALP, AST, and total bilirubin of rats co-treated with DFS and HELEES plus (200 and 400 mg/kg) (Table 1). There was a significant reduction in the levels of total protein and the globulin was significantly (p<0.05) reduced in the group administered DFS alone when compared to the control group and the groups administered HELEES only, however, concurrent treatments resulted in the ameliorative effects.
Table 2. Shows that the injection of DFS led to a remarkable increase ( p < 0.05) in hepatic CAT and SOD activities in the DIC-alone treated group relative to the control animals. However, treatment with HELEES at doses of 200 and 400 mg/kg remarkably elevated liver SOD and CAT activities relative to the DIC-alone treated group. Also, there was a noticeable ( p < 0.05) decline in liver Px activity in the DSF-alone treated group compared to the control animals. However, the administration of HELEES at doses of 200 and 400 mg/kg caused a remarkable increase ( p < 0.05) in liver
Px activity in comparison with the DSF-alone injected group. Also, injection of DSF caused a noticeable decline ( p < 0.05) in liver SH and ST compared to the control group (Table 3). However, in groups given a combined treatment of HELEES at varying doses and
DFS (groups E and F), liver SH and ST were noticeably elevated ( p < 0.05) compared to the second group (DIC-alone injected group).
Histopathological findings
Table 1 Ameliorative effects of HELEES on the serum biochemical parameters in DFS-induced toxicity in male albino rats for 21 Days
|
PA AMETE S |
roup A |
roup B |
roup C |
roup D |
roup E |
roup F |
|
ALT (u/l) |
21.00±0.58 |
38.00±5.03a |
26.33±3.48 |
30.00±2.65 |
21.00±1.53b |
22.00±1.53b |
|
AST (u/l) |
26.00±3.06 |
73.00±2.08a |
30.67±1.33 |
25.33±4.41 |
38.67±1.76b |
44.00±2.00b |
|
ALP (u/l) |
31.03±0.95 |
52.10±4.36a |
42.40±6.65 |
33.50±1.99 |
38.77±0.66 |
36.84±1.53 |
|
T Prot (g/l) |
69.57±0.44 |
45.90±1.06a |
68.13±2.46 |
66.63±2.26 |
65.70±2.01b |
68.47±3.50b |
|
ALB (g/l) |
42.00±1.16 |
42.93±0.52 |
40.57±2.74 |
43.70±2.33 |
41.03±0.69 |
40.43±1.68 |
|
LO (g/l) |
27.57±1.36 |
15.30±2.19a |
21.80±0.76 |
22.93±2.07 |
24.10±2.80 |
28.50±3.97b |
|
BIL (mg/dl) |
0.4±0.19 |
5.47±0.76a |
0.87±0.27 |
0.87±0.43 |
2.03±0.37b |
0.87±0.23b |
Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 5).. a Significant difference at (p< 0.05) when groups B, C, D, E and F are compared with group A. b Significant difference at (p< 0.05) when groups E and F are compared with group B. Alanine aminotransferase: ALT; Aspartate aminotransferase: AST; Alkaline phosphatase: ALP; Total protein: T Prot; Albumin: ALB; lobulin: LO; Bilirubin: BIL.
Table 2 Effects of HELEES and DFS on the liver tissue antioxidant capacity, nitrite content, and MDA of experimental rats
|
PA AMETE S |
roup A |
roup B |
roup C |
roup D |
roup E |
roup F |
|
SH (mg/mg tissue) |
48.53±1,17 |
27.60±0.58a |
50.77±0.45 |
52.45±1.46 |
33.16±0.37b |
36.62±0.62 b |
|
ST (mg/mg tissue) |
0.08±0.00 |
0.03±0.00 a |
0.09±0.00 |
0.08±0.00 |
0.05± 0.02 b |
0.47±0.01 b |
|
Px (mg/mg tissue) |
110.00±0.67 |
67.1±1.13 a |
112±0.44 |
116.1±1.01 |
72.4±0.59 b |
78.6±0.48 b |
|
SOD (m/mg tissue) |
2.00±0.20 |
2.50±0.25 a |
2.00±0.21 |
2.01±0.27b |
2.10±0.33 b |
2.10±0.42 b |
|
CAT (mM/mg tissue) |
2.89± 1.43 b |
4.87±0.02 |
2.65±2.00 b |
2.62±2.13 |
3.23 ±0.033 b |
3.42±0.03 b |
|
MDA (nM/mg tissue) |
6.93±2.04 |
19.01±5.20 a |
7.03±3.10 |
7.00±3.00 |
14.87±0.18 b |
14.45±0.39 b |
|
NO (U/mg protein) |
0.24±0.00 |
0.05±0.01 a |
0.35±0.00 |
0.34±0.00 |
0.23±0.00 b |
0.28±0.01 b |
Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 5).
a Significant difference at (p< 0.05) when groups B, C, D, E, and F are compared with group A.
b Significant difference at (p< 0.05) when groups E and F are compared with group B.
ST: glutathione-s-transferase, Px: glutathione peroxidase, SH: reduced glutathione, SOD: superoxide dismutase CAT: catalase, MDA: malondialdehyde, NO: nitric oxide
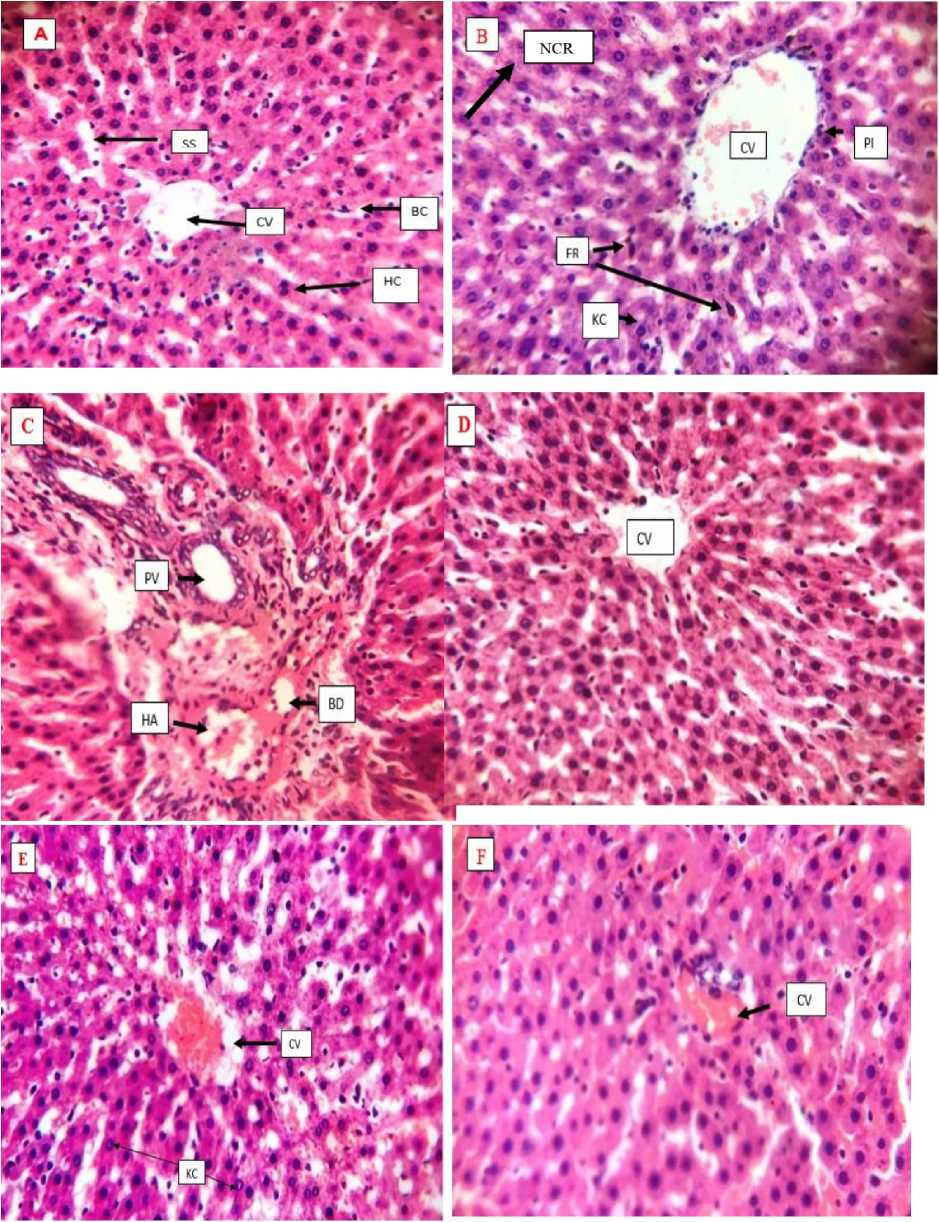
Figure 1 epresentative photomicrographs of liver tissues sections (×400) in male Wistar rats treated with DFS and HELEES (A): control rats show normal liver architecture with the central vein (CV), bile canaliculi (BC), hepatocytes (HC), and sinusoids (SS). DFS alone-treated rats (B)showed areas of necrosis (NC ), periportal inflammation (PI) area with numerous inflammatory cells, presence of ferritin (F ) and numerous kupffer cells (KC), HELEES alone treated rats at the dose of 200 and 400mg/kg ( roup C & D) showed normal hepatic morphology similar to that of the group (A) with the liver of those of (C) showing the portal vein (PV), bile duct (BD), and hepatic artery (HA), rats treated with DFS + HELEES at 200 and 400mg/kg (group E & F) are the recovery groups and showed normal hepatic architecture.
DISCUSSION
T he therapeutic dosages of DFS are usually safe, however high doses of the drug can be hazardous to both human and animal tissues. The toxicity effects are caused by the reactive metabolites of DCF: 4Õ hydroxy 3 diclofenac, 5Õ hydroxy 4 diclofenac, and 5Õ hydroxy 6 diclofenac (Boerma et al., 2012; den Braver et al ., 2016; Lazarska et al ., 2018). The conjugation of DFS with reduced SH and inactivated by ST (Dragovic et al ., 2013; Vredenburg et al ., 2014) enhances the excretion of DCF-metabolite from the body system (Daly, 2017) with subsequent reduction, developing disposition enzyme and enhancing cellular antioxidant status will therefore reduce DFS-associated toxicities. Our research on the combined administration of HELEES and DFS reinforces the hypothesis that plants can mitigate the toxicity caused by pharmaceuticals.
Hepatic transaminases (ALT, AST, T, ALP) and LDH are widely used as biomarkers for hepatic injury, and in this present study, the serum levels of transaminases were elevated (p < 0.05) in rats treated with DCF, and as previously reported (Alabi et al ., 2017; Aycan et al ., 2018; Peter et al ., 2017), leading to release of enzymes into the bloodstream. Markers of liver damage and hepatocyte death are due to membrane breakdown of the liver cell and ultimate leakage of several contents from the intracellular to extracellular milieu (Wang et al., 2015; Kobylinska et al ., 2015; Nagai et al ., 2016). According to our results, treatment of DFS in tandem with HELEES at varying doses abrogated the DFS-induced hepatotoxicity with the consequent reduction in the activities of the hepatic transaminases and LDP in a dose-dependent fashion. . The toxicity associated with DFS might be due to the toxic metabolite following the metabolism of DFS after its administration (Boerma et al ., 2012). Furthermore, medicinal foods that contain antioxidants might be of potential benefit to patients with liver damage.
esearch has established that DFS treatment could result in OS generation which leads to increased oxidative stress as a result of the decline in the antioxidant system activities ( alati et al., 2002). In this very research, the administration of DFS caused a significant (p<0.05) reduction in hepatic NO and reduced glutathione content together with a significant increase in hepatic MDA content. Therefore, we propose from this study that DFS administration enhanced both hepatic oxidative and nitrosative stress. The observed reduction in the NO content following DFS might be related to the superoxide radical anion that can combine with NO, thereby facilitating its reduction. The combination of NO and superoxide radical anion forms peroxynitrite (Wen et al., 2015), which is a cytotoxic molecule that can damage important macromolecules like proteins, DNA, and ribonucleic acid ( NA). Peroxynitrite has also been reported to participate in nitrosative stress (Lee et al., 2016). Conversely, it was observed that concurrent treatment enhanced an enhancement in the levels of NO in the rats which shows the abrogative effects of HELEES against nitrosative stress.
On the other hand, the activities of the antioxidant defense system were altered differently. The hepatic glutathione-S-transferase ( ST) and glutathione peroxidase ( Px) were significantly inhibited following DFS administration, by contrast, co-treatment of the rats with DFS and HELEES restored the activities of the antioxidant defense. The hepatic superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) activities in the DFS-treated group increased significantly (p<0.05) relative to the control group and the groups administered HELEES only. The SOD partakes in the first line of defense during oxidative stress by converting superoxide anion radical (O2-) to H2O2 while Px and CAT quench H2O2 to water and oxygen (O2), respectively. Furthermore, ST detoxifies toxic electrophiles including DFS metabolites with the help of SH as a cofactor to more soluble and less toxic metabolites that can easily be excreted by the kidney (Chen et al., 2015; Beyerle et al., 2015). Also, the improvement in hepatic SH, ST, and Px by the varying doses of HELEES when co-administered with DFS suggests that HELEES is not pro-oxidant in nature. Hence, it could be taken in the use of phytochemicals as antioxidants for chemoprevention. The observed reduction in the activities of ST and Px might suggest the production/generation of OS/free radicals by DFS, thus aggravating the buildup of toxic metabolites of DFS, which further exacerbates the hepatotoxicity effect of DFS. On the contrary, the increase in the activity of SOD and CAT could be said to be an adaptive response of hepatic tissue to DFS toxicity. The mechanism through which DFS induces antioxidant enzyme activity might be via up-regulating SOD and CAT messenger ribonucleic acid (m NA) and activation of the Nrf2-A E pathway. Hence, the therapeutic effect and the antioxidant activities of HELEES were demonstrated by reducing the hepatic transaminases, and hepatic markers of oxidative stress, and improving the antioxidant defense system in a dose-dependent manner. In addition, excessive production of NO was observed in a similar work, which was indicative of nitrosative stress (Wanyong et al., 2015). HELEES administration with DFS may be potentially beneficial to liver damage patients by modulating, ameliorating, or reversing hepatotoxicity. The ameliorative effect of HELEES in the present study could be ascribed to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. The results suggest that HELEES may confer protection against hepatic drug-induced damage. However, the major limitation of this study was the lack of funding.
CONCLUSIONS
Oral administration of HELEES to rats reduced the harmful effects of DFS on the liver by rebalancing redox potential, preventing cell death, and offering cytoprotection. These results are extremely important because they open doors for the application of HELEES in addressing DFS-related problems and break new ground for examining its applicability in addressing additional harmful DFS side effects.
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
We thank Mr. Vincent Upev the Chief Technology of the Laboratory of Veterinary Physiology and Biochemistry at the Federal University of Agriculture in Makurdi, Benue State, for technical assistance.
Список литературы Therapeutic effects of hydroethanolic extract of Erythrina senegalensis in diclofenac sodium-induced hepatotoxicity male Wistar rat: biochemical, redox potential and histopathological outcomes
- Abu, A. H., & Uchendu, C.N. (2010). Antispermatogenic effects of aqueous ethanolic extract of Hymenocardia acida stem bark in Wister rats. Journal of medicinal plants Research, 4(23): 24942502.
- Adeyemi, W.J., Omoniyi, J.A., Olayiwola, A., Ibrahim, M, Ogunyemi, O., & Olayaki, L.A. (2019). Elevated reproductive toxicity effects of diclofenac after withdrawal: investigation of the therapeutic role of melatonin, Toxicol. Rep. 1:571-577, https://doi.org/10.1016Zj.toxrep.2019.06.009.
- Alabi, Q. K., Akomolafe, O. R., Olukiran, S. O., Adeyemi, W. J., Nafiu, A. O., Adefisayo, M. A., Omole, J. G., Kajewole, D. I., & Odujoko, O. O. (2017). The Garcinia kola biflavonoid kolaviron attenuates experimental hepatotoxicity induced by diclofenac. Pathophysiology, 24: 281-290.
- Alabi, Q.K., & Akomolafe, R. O. (2020). Kolaviron diminishes diclofenac-induced liver and kidney toxicity in Wistar rats by suppressing inflammatory events, upregulating antioxidant defenses, and improving hematological indices. Dose-Response, 18(1), 1559325819899256. https://doi.org/10.1177/1559325819899256.
- Alberto, F., Charles, S,. & Hary, G. (1966). An improved method for determination of serum albumin and globulin. Clinical chemistry, Oxford academia, 12 (4), 194-205.
- Aycan, I .O., Elpek, O., Akkaya, B., Kirac, E., Tuzcu, H., Kaya, S., Coskunfirat, N., & Aslan, M. (2018). Diclofenac-induced gastrointestinal and renal toxicity is alleviated by thymoquinone treatment, Food Chemicals and Toxicology. 118: 795-804, https://doi. org/10.1016/j.fct.2018.06.038.
- Basavraj, S.T., Fefar, D.T., Prajapati, K.S., Jivani, B.M., Thakor, K.B., Patel, J.H., Ghodasara, D.J., Joshi, B.P., & Undhad, V.V. (2012). Haematobiochemical alterations induced by diclofenac-sodium toxicity in Swiss albino mice. Veterinary World, 5(7):417-419
- Beyerle, J., Frei, E., Stiborova, M., Habermann, N., Ulrich., & C. M. Biotransformation of xenobiotics in the human colon and rectum and its association with colorectal cancer. Drug Metab Rev. 2015;47(2);199-221.
- Boelasterli, U.A (2003). Diclofenac-induced liver injury: a paradigm of idiosyncratic drug toxicity, Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 192 (2003) 307-322, https://doi.org/10.1016/ s0041-008x(03)00368-5.
- Boelsterli, U.A. (2002a). Mechanisms underlying the hepatotoxicity of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, in: Kaplowitz, N., DeLeve, L. (Eds.), Drug-Induced Liver Disease, Marcel Dekker, New York, pp.345-375.
- Boelsterli, U.A. (2002b). Xenobiotic acyl glucuronides and acyl CoA thioesters as protein-reactive metabolites with the potential to cause idiosyncratic drug reactions. Current Drug Metabolism. 3, 439450.
- Boelsterli, U.A. (2002c). Mechanisms of NSAID-induced hepatotoxicity: focus on nimesulide. Drug Safety, 28, 109-121.
- Boerma, J.S., Dragovic, S., Vermeulen, N.P., & Commandeur, J.N.M. (2012). Mass spectrometry characterization of protein adducts of multiple P450- dependent reactive intermediates of diclofenac to human glutathione-S-transferase P1-1. Chemical Research and Toxicology, 25: 25322541.
- den Braver MW, Zhang Y, Venkataraman H, Venkataraman, H., Vermeulen, N.P.E., & Commandeur, J.N.M. (2016). Simulation of interindividual differences in inactivation of reactive parabenzoquinone imine metabolites of diclofenac by glutathione S-transferases in human liver cytosol. Toxicological Letter, 255: 52-62.
- Cantoni, L., Valaperta, R., Ponsoda, X., Castell, J., Barella, V., Rizzardini, D., Mangolini, M., Lhauri, A., &Villa, P. (2003). Induction of hepatic hem oxygenase-1 by diclofenac in Diclofenac toxicity to hepatocytes: a role for drug metabolism in cell toxicity. J Ethnopharmacol, 89:217-219.
- Chen, R., Wang, J., Zhang, Y., Tang, S., & Zhan, S. (2015). Key factors of susceptibility to antituberculosis drug-induced hepatotoxicity. Archives of Toxicology, 89(6):883-897
- Christensen, C.B,, Soelberg, J., Stensvold, C.R., & Jager, A. K. (2015) Activity of medicinal plants from Ghana against the parasitic gut protist Blastocystis. J Ethnopharmacol 174: 569- 575.
- Claiborne A. (1985) Catalase activity. In: Greenwald RA (ed) CRC handbook of methods in oxygen radical research. CRC Press, Boca Raton , pp.283-284.
- Daly, A. K. (2017). Are polymorphisms in genes relevant to drug disposition predictors of susceptibility to drug-induced liver injury? Pharmaceutical Research. 34: 1564-1569
- Donfack, J. H., Njayou, F. N., Rodrigue, T. K., Chuisseu, D. D. P., Tchana, N. A.,Vita, Finzi, P., Tchouanguep, M. F., Ngadjui, T. B., & Moundipa, F. P. (2008). Study of A Hepatoprotective and Antioxidant Fraction from Erythrina Senegalensis Stem Bark Extract: In Vitro And In Vivo. Pharmacologyonline 1: 120-130.
- Doumas, B.T. (1975). Standard for Total Serum protein assay. Clinical chemistry, Oxford academia. 21(8):1159-1166, https://doi.org/10.1093/clinchem/ 21.8.1159
- Dragovic, S., Boerma, J.S., Vermeulen, N.P, & Commandeur, J.N.M. (2013). Effect of human glutathione S-transferases on glutathione-dependent inactivation of cytochrome P450-dependent reactive intermediates of diclofenac. Chemical Research and Toxicology. 26(11):1632-41. doi: 10.1021/tx400204d. Epub 2013
- Esmaeilzadeh, M., Heidarian, E., Shaghaghi, M., Roshanmehr, H., Najafi, M., Moradi, A., Nouri, A. (2020). Gallic acid mitigates diclofenac-induced liver toxicity by modulating oxidative stress and suppressing IL-1b gene expression in male rats. Pharmaceutical Biology. 58(1): 590e596. https://doi.org/10.1080/ 13880209.2020.1777169
- European Medicines Agency (EMVA/CVMP) (2014). CVMP assessment report under Article 30(3) of Regulation (EC) No 726/2004.
- https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/report/ cvmp-assessmentreport-under-article-303-regulation-ec-no-726/ .
- Galati, G., Tafazoli, S., Sabzevari, O., Chan, T. S., & O'Brien, P. J. (2002). Idiosyncratic NSAID drug drug-inducedative stress. Chem Biol Interact. 142(1-2):25-41.
- Gor, A. P., & Saksena, M. (2011). Adverse drug reactions of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in orthopedic patients, Journal of Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapy. 2 (1):26-29, https://doi.org/10.4103/0976-500X.77104.
- Green, L. C., Wagner, D. A., Glogowski, J., Skipper, P. L., Wishnok, J. S., & Tannenbaum, S. R. (1982) Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N] nitrate in biological fluids. Anal of Biochemistry, 126:131138.
- Gupta, Y. K., Sharma, M., & Chaudhary, G. (2002). Pyrogallol-induced hepatotoxicity in rats: a model to evaluate antioxidant hepatoprotective agents. Methods Find. Experimental and Clinical Pharmacology. 24, 497-500. doi: 10.1358/mf.2002.24.8.705070
- Gupta, A., Kumar, R., Ganguly, R., Singh, A. K., Rana, H. K, & Pandey, A. k (2020). Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and hepatoprotective activities of Terminalia bellirica and its bioactive component ellagic acid against diclofenac induced oxidative stress and hepatotoxicity, Toxicological Report. 24: 44-52.
- Habig, W. H., Pabst, M. J., & Jakoby, W. B. (1974) Glutathione-S-transferases: the first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 249:7130-7139.
- Hassan, R. A., Hozayen, W. G., Abo, S. H. T., Al-Muzafar, H. M., Amin, K. A., Ahmed, O. M. (2021). Naringin and Hesperidin Counteract Diclofenac-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Male Wistar Rats via Their Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Antiapoptotic Activities. Oxidative and Medical Cell Longevity, 11; 2021:9990091. doi: 10.1155/2021/9990091.
- Huo, X., Meng, Q., Wang, C., Wu, J., Wang, C., Zhu, Y., Ma, X., Sun, H., & Liu, K. (2020). Protective efect of cilastatin against diclofenac-induced nephrotoxicity through interaction with diclofenac acyl glucuronide via organic anion transporters. British Journal of Pharmacology, 177(9), 1933-1948. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.14957
- Ilodigwe, E., Okonkwo, B., Agbata, C., Ajaghaku, D., & Eze, P. (2014). Wound healing activity of ethanol leaf extract of Erythrina senegalensis. British Journal of Pharmacological Research 4(4): 531.
- Jollow, D. J., Mitchell, J. R., Zampaglione, N., & Gillette, J. R. (1974). Bromobenzene induced liver necrosis: protective role of glutathione and evidence for 3, 4-bromobenzene oxide as the hepatotoxic metabolite. Pharmacology; 11:151-169
- Kavasi, R., Berdiaki, A., Spyridaki, I., Corsini, E., Tsatsakis, A., Tzanakakis, G., & Nikitovic, D. (2017). HA metabolism in skin homeostasis and inflammatory disease, Food Chemical and Toxicol. 101:128-138.
- King, J. C., & Cousins, R. J. (2006). "Zinc," in Modern Nutrition in Health and Disease, 10th Edn, eds M. E. Shils, M. Shike, A. C. Ross, B. Caballero, and R. J. Cousins (Philadelphia, PA: Lipponcott Williams and Wilkins), 271-285
- Kobylinska, L., Havrylyuk, D. Y., Ryabtseva, A. O., Mitina, N. E., Zaichenko, O. S., Lesyk, R. B, et al. (2015a). Biochemical indicators of hepatotoxicity in blood serum of rats under the effect of novel 4-thiazolidinone derivatives and doxorubicin and their complexes with a polyethyleneglycol-containing nanoscale polymeric carrier. Ukraine Biochemical Journal. 87(2):122-132
- Kone, W. M., Vargas, M., & Keiser, J. (2012). Anthelmintic activity of medicinal plants used in Cte d'lvoire for treating parasitic diseases. Parasitological Research, 110(6): 2351-2362.
- Larsen, B. H. V., Soelberg, J., Kristiansen, U., & Jager, A. K. (2016). Uterine contraction induced by Ghanaian plants used to induce abortion. South African Journal Botany, 106: 137-139.
- Lazarska, K. E., Dekker, S. J., Vermeulen, N. P. E, & Commandeur, J. N. M (2018). Effect of UGT2B7*2 and CYP2C8*4 polymorphisms on diclofenac metabolism. Toxicological Letter. 284: 70-78. https://rioi.org/10.1016/jtoxlet.2017.11.038
- Lee, C. T, Yu, L. E., & Wang, J. Y. (2016). Nitroxide antioxidant as a potential strategy to attenuate the oxidative/nitrosative stress induced by hydrogen peroxide plus nitric oxide in cultured neurons. Nitric Oxide. 54:38-50.
- Lillie, R. D., & Fullmer, H. M. (1976). Histopathologic technic and practical histochemistry, 4th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York.
- Lim, M.S., Lim, P. L. K., Gupta, R., & Boelsterli, U. A. (2006). Critical role of free cytosolic calcium, but not uncoupling, in mitochondrial permeability transition and cell death induced by diclofenac oxidative metabolites in immortalized. Toxicology and applied pharmacology, 217 (3), 322-331, 2006
- Masubuchi, Y., Nakayama, S., & Horie, T. (2002). Role of mitochondrial permeability transition in diclofenac-induced hepatocyte injury in rats. Hepatology. 35:(3),544-551, 2002.
- Misra, H. P., & Fridovich, I. (1972). The role of superoxide anion in the auto-oxidation of nephrine and a simple assay for superoxide dismutase. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 247:3170-3175.
- Mohandas, M., Marshall, J. J., Duggin, G. G., Horvath, J. S., & Tiller, D. (1984) Differential distribution of glutathione and glutathione related enzymes in rabbit kidney. Cancer Research, 44:5086-509.
- Nagai, K., Fukuno, S., Oda, A., & Konishi, H. (2016). Protective effects of taurine on doxorubicin-induced acute hepatotoxicity through suppression of oxidative stress and apoptotic responses. Anticancer Drugs, 27(1):17-23.
- National Institute of Health (N.I.H). (1985). Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. DHEW publication; Office of Science and Health Reports; Bethsaida; U.S.A.
- Rogoveanu, O.C., Calina, D., Cucu, M.G., Burada, F., Docea, A.O., Sosoi, S., Stefan, E., Ioana, M., & Burada, E. (2018). Association of cytokine gene polymorphisms with osteoarthritis susceptibility, Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine. 16:26592664.
- Peter, S. J, Basha, S. K., Giridharan, R., Lavinya, U., & Sabina, E.P. (2017). Suppressive effect of Spirulina fusiformis on diclofenac-induced hepato-renal injury and gastrointestinal ulcer in Wistar albino rats: a biochemical and histological approach. Biomedical Pharmacotherapy, 88: 11-18. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.01.032
- Pick, A., & Keisari, Y. (1981). Superoxide anion and H2O2 production by chemically elicited peritoneal macrophages-induction by multiple nonphagocytic stimulus. Cell Immunology. 59:301-308.
- Risebrough, R. W. (2006). Diclofenac: A new environmental poison in south Asia. Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society, 103:239-250.
- Singh, D,. Cho, W.C., & Upadhyay, G. (2016). Drug-Induced Liver Toxicity and Prevention by Herbal Antioxidants: An Overview. Frontier of Physiology. 6:363. doi:10.3389/fphys.2015.00363
- Siu, W. P., Pamela B. L. P., Calivarathan L., Urs A. B. (2008). Bax-mediated mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP), distinct from the mitochondrial permeability transition, is a key mechanism in diclofenac-induced hepatocyte injury: Multiple protective roles of cyclosporin A. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, (227):,451-461,ISSN 0041-008X,https://doi.org/10.1016
- Teoh, N.C., & Farel, G. C. (2003). Hepatotoxicity associated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Clinics in Liver Disease, 7(2):401 - 413
- Thanagari, B.S., Fefar, D.T., Prajapati, K. S., Jivani, B.M., Thakor, K.B., Patel, J.H., Ghodasara, D.J., Joshi, B.P., & Undhad, V.V. (2012). Haemato-biochemical alterations induced by diclofenac sodium toxicity in Swiss albino mice, Veterinary World, 5:417-419.
- Thefeld, W., Hoffmeister, H., Busch, E.W., Koller, P.U., & Vollmar, J. (1994). Reference values for the determination of GOT, GPT and ALP amongst other parameters in serum with optimal standard methods. Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift, 99:343-344.
- Thomas, L. (1998). Clinical Laboratory Diagnostics: Use and Assessment of Clinical Laboratory Results. Ist Ed. TH-Books, Frankfurt, Germany,
- Togola, A., Austarheim, I., T., Diallo, A. D., & Paulsen, B.S. (2008). Ethnopharmacological uses of Erythrina senegalensis: a comparison of three areas in Mali, and link between traditional knowledge and modern biological science. Journal of Ethnobiology and Ethnomedicine, 4:6. doi:10.1186/1746-4269-4-6.
- Uetrecht, J.P. (1999). New concepts in immunology relevant to idiosyncratic drug reactions: the "Danger Hypothesis" and innate immune system. Chemical Research and Toxicology, 12:387-395.
- Upadhyay, G., Kumar, A., & Singh, M. P. (2007). Effect of silymarin on pyrogallol- and rifampicin-induced hepatotoxicity in mouse. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 565, 190-201. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.03.004
- Upadhyay, G., Singh, A. K., Kumar, A., Prakash, O., & Singh, M. P. (2008). Resveratrol modulates pyrogallol-induced changes in hepatic toxicity markers, xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes and oxidative stress. European Journal of Pharmacology. 596, 146-152. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.08.019
- Upadhyay, G., Tiwari, M. N., Prakash, O., Jyoti, A., Shanker, R., & Singh, M. P. (2010b). Involvement of multiple molecular events in pyrogallolinduced hepatotoxicity and silymarin-mediated protection: evidence from gene expression profiles. Food and Chemical Toxicology. 48, 1660-1670. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2010.03.04
- Vohra, F., & Raut, A. (2016). Comparative efficacy, safety, and tolerability of diclofenac and aceclofenac in musculoskeletal pain management: a systematic review, Indian Journal of Pain 30:3-6.
- Vredenburg, G., Elias, N. S., Venkataraman H., Hendriks, D. F., Vermeulen, N.P., Commandeur, J. N., & Vos, J. C. (2014). Human NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1)-mediated inactivation of reactive quinone imine metabolites of diclofenac and mefenamic acid. Chemical Research in Toxicology, 27: 576-586. doi: 10.1021/tx400431k.
- Wang, Y., Mei, X., Yuan, J., Lu, W., Li, B., & Xu, D. (2015). Taurine zinc solid dispersions attenuate doxorubicin-induced hepatotoxicity and cardiotoxicity in rats. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 289(1):1-11.
- Wanyong, Y., Zefeng, T., Xiufeng, X., Dawei, D., Xiaoyan, L., Ying, Z., & Yaogao, F. (2015). Tempol alleviates intracerebral hemorrhage-induced brain injury possibly by attenuating nitrative stress. Neuroreport. 26(14):842-9. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000000434
- Wen, J., Li, H., Zhang, Y., Li, X., & Liu, F. (2015). Modification of HSP proteins and Ca2+ are responsible for the NO-derived peroxynitrite-mediated neurological damage in PC12 cell. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Pathology, 8(5):4492-4502.
- Wright, J. R., Colby, H. D,. & Miles, P. R. (1981). Cytosolic factors which affect microsomal lipid peroxidation in lung and liver. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 206: 296- 304. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90095-3.


