To the question about the research of the socio-cultural potential of the population of the Arkhangelsk region, like Arctic territory
Автор: Bobyleva N.I., Rybak E.V., Tshyhonchik N.V.
Журнал: Arctic and North @arctic-and-north
Рубрика: Sociological sciences
Статья в выпуске: 7, 2012 года.
Бесплатный доступ
In article the sociocultural potential as an element of the human capital is considered. The concept of ‘social and cultural potential’ includes social and cultural side. The authors propose their own method of studying the social and cultural development. They find it is very important to the cultural development of the Arkhangelsk region as the Arctic territory.
Socio-cultural potential, population of the Arkhangelsk region, Arctic
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/148320428
IDR: 148320428 | УДК: 304.444+57.024+303.621.34(045)
Текст научной статьи To the question about the research of the socio-cultural potential of the population of the Arkhangelsk region, like Arctic territory
Initiating and conducting research in the field of history, culture, economic and social de--‐ velopment of the region is a priority for the state policy in the Arctic up to 2020 and focused on the future development of the country in the field of science and technology [5, 2012].
Need to improve the social education of young people in the framework of special "social work" and "organization working with young people," prompted us to search for the value founda--‐ tions of modern education in the modernization of the training programs. Education, culture, and spiritual interests, values --‐ in the scientific transcription. This is implemented through the category of "social and cultural development", "social and cultural potential." Broadcast cultural values through the prism of social objects (individual, social group, region, society) are social and cultural approach in the social sciences.
On the one hand, the question of the social and cultural potential as a component of hu--‐ man capital is seen mainly in the economic, political and social sciences (U.A.Korchagin,E.V. Shulgina, V.T. Smirnov, A.N. Dobrynin, etc.). On the other hand, the category of social and cultural building is considered and the human sciences, such as the focus of education (G.I. Gerasimov, 2005).
Social work, existing in Russia as a professional body of knowledge is only 20 years old, suf--‐ fers from a lack of their own categories and borrows them from the related sciences. Such, for ex--‐ ample, is the subject of our study --‐ a socio--‐cultural potential. We consider the potential socio--‐ cultural (hereinafter --‐ UPC) as the presence of social and cultural resources in the zone of proximal development of the individual, organization, region, and this potency, the stock of the subject to learn new skills, acquire social skills to be a full--‐fledged member of society. Under the social com--‐ ponent UPC we understand the horizontal connection of man in society: the relationship between the people at the moment and in the community, under the cultural component of the CSP we mean historical, temporal relationships between the generations in the form of preserving the language, traditions and values. By the potential--‐we mean the ability of the subject to move to--‐ ward building a constructive and civilized development of the specific micro socium.
The importance of studying the UPC is currently updated the paradoxical situation in which the obvious fact is that, with very strong foundation of spiritual culture of Russian society the state of society close to degradation. Tried and tested values are lost, new ones are not formed or are present in a distorted form, often borrowed or socially destructive.
In this state, the value re--‐orientation goals and values of a specific person, people in the region are stable and consistent as far as they are arranged on the societal, up individual level. If at this time at the state level "national idea" of the socio--‐cultural development has not been formed, need to identify the person through the local society, that is the region. Researchers agree that "... in the face of serious social and economic transformation of the Russian society is quite legitimate to raise the issue of the need to identify the laws and trends of the natural development of the social and cultural integrity, which are the regions of Russia" [3, 2012]. We share this vision and emphasizing the need for a comprehensive study of social and cultural development and the ca--‐ pacity of the people of a specific region.
In this context, the interesting aspect of the analysis of current regional (urban, rural), so--‐ cio--‐cultural environment. In the classical description of a local society storyline invariably passes from stable physical characteristics (geographic location, climate, nature) through the production, making the operation of the region as a member of trade relations, to the description of cultural objects and values. A unique and distinctive cultural "face" of the region include the exact number of museums, libraries, theaters, schools, colleges, universities and other non--‐manufacturing, non--‐ profit cultural facilities and is of strategic importance. In this case, the trajectory of beingness indi--‐ vidual social objects (entities), such as a person (citizen), organization, community or region can be formed both in the modes of survival and existence, and in the mode of development.
In survival rejime of a particular society are affected, especially the most economically frag--‐ ile elements --‐ its cultural universals (language, art, traditions). Unfortunately, idioms "Rural Li--‐ brary", "provincial theater", "small schools" consistently associated with images of poverty, forgot--‐ ten, dilapidation, social disadvantage. It is in survival mode today are such important sources of social and cultural development of human potential as museums, libraries, theaters, home culture, art studios, clubs.
Ivan Ilyin, in his monumental work, "Why do we believe in Russia", said: "To live in the world --‐ is to choose and to seek, who chooses and seeks, he serves as a value ..." [2, 2012]. But is there a choice of one who exists in survival mode? What is the capacity of the people, who for years are struggling with the opportunity to enter a different mode?
In the mode of existence of social and cultural activities are conducted differently. Thea--‐ ters, libraries and museums are working for users, not just survive: possible new productions of plays, open exhibitions, theaters, coming young actors, and new experts --‐ the library. Mode of ex--‐ istence assumes the status quo, that is, at the level of achievement. But the accumulation of val--‐ ues and ideas is possible only if there sifting superficial, accidental. It is with the passage of time it turns out the real value of things, books, events, phenomena of social life, that is, when it is possi--‐ ble to compare the classic with the contemporary, the wisdom --‐ from everyday life. This is only possible if the city (region) exists in the mode of development that is transformed.
But development can be natural, such as it is now. Individual bright personalities, leaders, workers are creating new projects, programs, ideas are born, but the spontaneity in management region, the lack of a coherent strategy for its development and loose with a development agency--‐ specific create uncertainty in the development of human potential and socio--‐cultural and regional environment.
Thus, within the region (country) need to focus not only on the preservation of culture as a statement of the data or to cultural instruments (programs of socio--‐cultural activities), but pri--‐ marily on the study, forecasting and management of social and cultural potential. In the priority should be the decision of the primary tasks: what should invest the funds for social and cultural development, what priorities are maintained as a separate individual independent of mundane things --‐ traffic, the presence of a computer, telephone stability, physical access to books, plays, collections as little as possible dependent on the social (age, gender, professional) stereotypes and cultural constraints (belonging to the language of the nation, the country) and at the same time has been limited by high universal moral norms.
Social and cultural development of each individual man, and especially of the young, is a consequence of the social and cultural environment in which he is socialized. Potential of the re--‐ gion --‐ a collection of individual, social and cultural potential of the people and socio--‐economic rat--‐ ing of the region as a whole.
In the research of the social and cultural potential of the category, we are faced with a lack of elaboration problems in theoretical terms. Overall worked historiography, cultural, sociological potentials, but an approach that meets our vision problems yet to specify. Great difficulties arise when the need to empirically examine this phenomenon, since there are no methodological tools (questionnaires, interview texts) for its study.
In the method, we developed "Assessment of the socio--‐cultural potential of the population of the Arkhangelsk region" formed 12 blocks, describing the social spheres of human activity. As an assessment tool used their own social and cultural self--‐esteem building, and does not bind to the specific knowledge of the individual. Assessing thus sociocultural population potential, we do not focus on formal indexes and the whole region, and on the subjective well--‐being indicators of the subject. Questions as exempt from value stereotypes of "good or bad", regardless of age, oc--‐ cupation. Statements can be translated into a foreign language, so they do not contain complex structures and are not tied to a regional mentality.
The method includes such sections like the "man", "Family", "Society (Motherland)", "Economy adn Finance", "Informatinal Culture", "Pets in the society", "Education", "Culture", "Work, Occupation "," Hobby "," Health "and" Potential, "each of which contains about ten state--‐ ments.
Based on the working definition of the social and cultural potential, as operationalized signs blocks are areas of social science, which are value relevant. In the category of "socio--‐ cultural" part of the "social" refers to the subject of activity, and the "culture" --‐ the quality and scope of its activity. As subjects of cultural activity can be considered a person, a social group or community, region, society, humanity as a whole.
Accordingly, the sections "Man "," Family "," Society (Motherland) "," Economy and Fi--‐ nance "represent the social component of CSP, as blocks" Information Culture "," Pets in the socie--‐ ty "," Education "," Culture "" Work, Profession "," Health "," hobby "--‐ the cultural, block" potential "means the individual assessment of its development in the near future.
Each section includes three aspects: knowledge of the area, attitudinal attitude, actual be--‐ havior. This provides a measure of the importance of this sphere of life for man, and the gap be--‐ tween the declared values in the field and action in it. Here is an example (Table 1).
Table 1
Estimated figures of the Unit «Family
Knowledge
I know the history and the development of the family unit
I know the basic functions of the family, I have an idea about the role and importance of the family in the formation of human
I know the laws, regulations of the Family
Relations
I think that the upbringing and education of man begins in the family
I think that the family is an important universal value
I think that the modern family has a future
Behaviour
Follow the basic traditions of their family and adhere to standard rules of family life Resorted to the services of social services, working with the family
Emerging family misunderstandings and conflicts are resolved peacefully and on time
PCI card unit is estimated by the "Potential", which also includes nine questions (Table 2).
In the future, such issues will be addressed in each block technique as a fourth component.
Table 2
Estimated figures of the Unit «Your Potential»
Knowledge
I have a definite plan of your life for five or ten years
I know the program of development of the region, which is home
I know the state development strategy for the coming years
Relations
I believe in the implementation of their life plans
I believe in the possibility of development of the region perceive a positive development strategy
Respondents rated the statements on a four--‐point scale: 4 --‐ "I agree with the statement," 3
--‐ "in full", 2 --‐ "sufficiently", 1 --‐ "not good enough," 0 --‐ "not at all."
Evaluations to all sections of techniques get about the following picture (Figure 1).
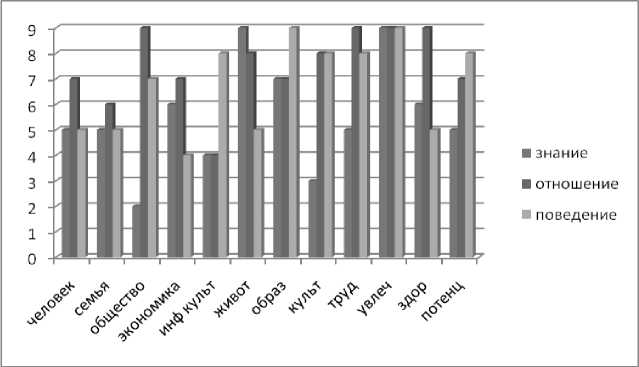
Figure 1. The results of the survey respondents used the method "Assessment of socio--‐cultural potential of the popu--‐ lation of the Arkhangelsk region"
May interpret data from the perspective of: 1) the expression of social and cultural compo--‐ nents of the UPC, 2) ratio of knowledge--‐, assessment, and behavioral aspects of a block, and 3) highlight the leading areas of interest or value, and 4) the representation of the block "potential" than other blocks.
The high scores of some units may indicate that the respondent has a wide UPC and strives to operate in a mode of development; low scores indicate more of a survival strategy or existence. Especially for blocks "Economics and Finance", "Education", "potential", etc.
The second part of the methodology is the respondent's answer to the question "Who am I" (according to the method of M. Kuhn). Qualitative analysis of responses shows to what area (block) the identity of more identify themselves, which gives an indication of the potential of the individual within the social roles and statuses.
Thus, in the present period, we have developed the estimated part of the methodology, quantitatively and in points are the parameters evaluation form developed and tested methods (electronic version), performed aerobatic stage of testing. Next, we plan to adjust the method in light of the data, to the most complete cut (transverse and longitudinal) marks UPC population of Arkhangelsk region. As a result, we expect on the basis of statistically significant, widespread, re--‐ gionally bound material to develop a list of socially important areas of social and cultural (and then specific actions), which would allow the potential of the city and the region, and enhance the po--‐ tential for the implementation of human resources. We understand that, due to the complexity of the system being studied, you may have many questions that we have yet to answer. The authors are open to dialogue and willing to listen to the views and suggestions of all the researchers in--‐ volved.
Список литературы To the question about the research of the socio-cultural potential of the population of the Arkhangelsk region, like Arctic territory
- Gerasimov G.I. Transformation of the Education – is a social and cultural potential of the development of Russian society: Dis.Doctor. Philosophy. Sciences: 09.00.11. Rostov n / a, 2005. 428 p.
- Ilyin IA Why we believe in Russia: essays / IA Ilyin. New York: Penguin Books, 2006. p. 130.
- Kôgai EA potential socio-‐cultural development of the region. [Electronic resource] / / Kursk regional NGO Society "Knowledge" of Russia. URL: http://www.mebik.ru/union/ in-‐ tell/kogay180506.htm (date of access: 21.01.2012).
- Pavel A. Russian human capital factor in the development or degradation? Monograph. Voronezh: TSIRE, 2005. 252p.
- Fundamentals of the State Policy of the Russian Federation in the Arctic for the period up to 2020 and beyond. September 18, 2008. [Electronic resource] / / URL: http://www.scrf.gov.ru/documents/98.html (date of access: 21.01.2012).


