Treatment of patella fractures by compressive external fixation (CEF)
Автор: Bari Mofakhkharul, Shahidul Islam, Shetu Nazmul Huda, Mahfuzer Rahman
Журнал: Гений ортопедии @geniy-ortopedii
Рубрика: Оригинальные статьи
Статья в выпуске: 2, 2016 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Recently, the traditional treatment of patellar fractures is often complicated by infection and insecure fixation. Occurring complications can be treated promptly, which is cost-effective, but limits the function of the joint. The CEF apparatus proposed by us can effectively treat patella fractures with fewer complications. Transverse fractures of the patella with displacement were treated according to the method of compression external fixation, based on the principles of the Ilizarov apparatus with stretched spokes. All patients after the operation were allowed to move in the joints and load. In total, twenty-five fractures were treated with our CEF apparatus. Treatment in 12 patients was by percutaneous procedure. In the treatment of all fractures, a lasting fusion was achieved. The CEF apparatus was removed after 6-8 weeks. In 12 patients the total volume of movements was restored, the average assessment of knee joint function by Insall was 96 points, the average observation period was four years. Mild complications in the form of inflammation in the area of the spokes were observed in five patients, they were treated with local remedies and antibiotics. The CEF technique is a safe and effective method of treating patella fractures, it has advantages over conventional methods in the case of soft tissue deficiency. CEF provides rapid recovery without any additional surgical interventions.
Cef, patella fracture
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/142134613
IDR: 142134613 | УДК: 616.718.49-001.5-089.227.84 | DOI: 10.18019/1028-4427-2016-2-30-32
Текст научной статьи Treatment of patella fractures by compressive external fixation (CEF)
Transverse fracture of patella is the most common pattern, which contributes 70 % of the total [6]. When the fragments are displaced, then surgery is absolutely indicated to maintain the function of the extensor mechanism. However the nature of patella and high tensile forces challenge the standard surgical techniques used for fracture. The traditional method for patella fracture is tension band wiring (TBW) which provides sound union in most cases [4, 5, 6, 7, 9].
Complications like infection up to 12 %, fixation failure of 22 % and symptomatic hardware in 20 % to 6
% have been reported. We are reporting here, the Afgan compressive external fixator which was introduced by my friend Mr. M. Ismail Wardak.
The technique is based on tensioned biocompatible thin wire external fixation as developed by Academician Prof. Ilizarov for long bones, allows limitless motion [1, 2].
Our aim and purpose of this technique is to review the functional outcomes of patients treated with this novel method. Loss of reduction, and loss of motion, infection and need for second surgery were defined as negative outcomes.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
From January 2010 to January 2015, 25 patients were treated with displaced fractures of the patella. Displaced fractures means gap of more than 3 mm and articular steps more than 2 mm. All the 25 patients were treated by CEF. 12 patients were typical two part transverse fractures of the patella. The following atypical patterns were also treated:
Upper pole fracture – 2;
Lower pole fracture – 4;
Stellate fracture – 2;
Three part fracture – 4.
Pole fracture too small to permit passage of a wire less than 1 cm in size, are not indicated for this novel procedure.
Causes of injures were motor vehicle collision and others. The age ranges were 17 to 65 years (average 35.5 years). Out of 25 patients 20 were men and 5 were women. Time to operation ranged from 8 hours to 10 days. CEF technique is a minimally invasive, percutaneous procedure on 12 closed transverse fractures of patella presenting less than 3 days from the time of injury. The remaining 13 cases were performed through an open procedure. Open reduction was done in all open fractures, upper and lower pole fractures or when accurate reduction was not achieved percutaneously. All the surgeries were performed under spinal anesthesia. Patient follow up was continued at an average of 4 years postoperatively (range 1-4 years).
Ш Bari M.M., Islam Shahidul, Shetu N.H., Mahfuzer R.M. Treatment of patella fractures by compressive external fixation (CEF) // Гений ортопедии. 2016. № 1. С. 30-32.
Журнал клинической и экспериментальной ортопедии им. Г.А. Илизарова № 2, 2016 г.
Surgical procedure
Knee is kept in extension, the fracture fragments are reduced with the help of patellar clamp and it was confirmed by c-arm. Mild traction is applied to the skin medially and laterally to prevent the wires from kinking the skin. Two 1.5 mm wires are passed horizontally through the proximal fragment. Two additional 1.5 mm wires are placed in the distal fragment. It is to be noted that the wire pairs be as far from fracture line as possible. This allows for bowing of the wires and compression of the fracture during tensions of the device.
The wires are passed through the related holes in the clamp assembly. The clamp assemblies are connected to one another (Fig. 1).
The wires are secured by the nuts on the clamp assembly. Tensioning of the wires and compression of the fractures are done by distracting the clamps from one another by turning the distraction nut until the tension wires are tight. The joint is ranged through flexion and extension while checking the stability of fixation by c-arm.
Open reduction technique
An incision is made vertically over the patella, blood clots are cleaned. The fragments are reduced by clamp. We must palpate the articular surface from side to side to confirm the accurate reduction. The retinaculum is repaired. The wound is closed aseptically. No drains are used.
After 1st operative day it is necessary to clean the wire sites with rectified spirit or any kind of antiseptic solution. All the patients were advised to do physical therapy to increase the range of motion. Full range of motion is allowed along with full weight bearing as tolerated by the patient. Sound union was achieved and that was confirmed by X-ray. After 6 to 8 weeks the device was removed.

Fig. 1. Compressive External Fixator
RESULTS
Sound union was achieved in all the fragments at an average of 6 to 8 weeks. That was proved clinically and radiologically. Knee flexion was 90° within 2 to 3 weeks and it was up to 120° by 4 weeks. The Insall knee score for patient function obtained on 12 patients was 96 points and 2 cases who did not carry our instructions, ultimately resulted in less than 90° arc of motion. Complications included 3 wire site inflammation which managed by local care.
We found articular surface incongruity (≥2m) because of incomplete primary reduction in 2 cases (Table 1).
These three patients with articular incongruity developed patellofemoral osteoarthrosis after 3 years follow up postoperatively.
Table 1
Characteristics of fracture patella
|
Patients |
Type of fractures |
Insall knee score |
|
12 |
Transverse |
96 |
|
2 |
Upper pole |
90 |
|
4 |
Comminuted |
92 |
|
4 |
Lower pole |
95 |
|
3 |
Stellate |
92 |
|
Total = 25 |
||
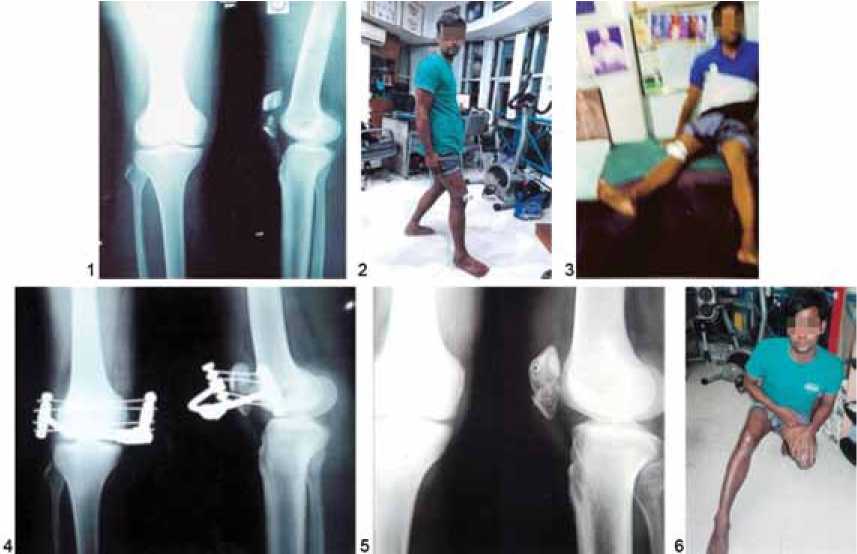
Fig. 2.: 1 – Radiograph of transverse fracture of right patella with displacement. 2 – CEF in the right patella (2nd post op). 3 – CEF in the right patella follow up after 3 weeks. 4 – Radiograph of left patella with CEF in situ (after 3 weeks). 5 – Radiographic final result of the patella after removal of CEF. 6 – Clinical appearance of the patient after treatment
DISCUSSION
Our Novel CEF method and device offers advantages compared with traditional method of treatment. All patients healed well without any major complications, despite allowing unrestricted motion.
Our cases compare favorably with the recent large series reported by Smith et al. [4], who analyzed the results of 51 patella fractures treated by TBW. The CEF technique is an external fixation which allows for adherence to the tenets of articular fracture treatment, accurate reduction with stable fixation for immediate motion, leading to the results we have reported. Early functional activity is an added benefit in our patients which is less cost effective. We did not use any brace. The potential effectiveness of CEF has advantages over the existing other technique.
The most significant advantage of CEF is the lack of retained hardware eliminating symptomatic prominence.
Infection is not a problem. So in our series we think that we should be considered for all displaced transverse, pole and selected comminuted patella fractures. Open and previously infected fractures are the best candidate for this technique. Yahmis et al. [8] described the use of ring external fixation to stabilize the comminuted patella fractures. Big advantage is percutaneously application and in the long term no retained hardware. The technique is a simple, it gives absolute stability, provides a significant decrease in hospital stay, gives rapid bone healing and rehabilitation and we think that this method should be considered in the treatment of displaced patella fractures, either open or closed.
Acknowledgement
We are grateful to Dr. Mohammad Ismail Wardak for teaching us this novel technique for treating the patella fractures by CEF.
Disclosures
The authors report no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise concerning the material or methods used in this study or the findings specified in this paper.
Список литературы Treatment of patella fractures by compressive external fixation (CEF)
- Bari M.M. A color atlas of limb lengthening, surgical reconstruction and deformity correction by Ilizarov technique. 2013. 101 pp.
- Ilizarov G.A. Transosseous osteosysthesis. Theoretical and Clinical Aspects of the Regeneration and Growth of Tissue. Springer, 1992.
- Wardak M.I., Siawash A.R., Hayda R. Fixation of patella fractures with a minimally invasive tensioned wire method: compressive external fixation//J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012. Vol. 72, N 5. P. 1393-1398.
- Early complications in the operative treatment of patella fractures/S.T. Smith, K.E. Cramer, D.E. Karges, J.T. Watson, B.R. Moed//J. Orthop. Trauma. 1997. Vol. 11, N 3. P. 183-187.
- Functional outcome of patella fractures following open reduction and internal fixation/E.H. Schemitsch, J. Weinberg, M.D. McKee, D. J.G. Stephen, H.J. Kreder, J.P. Waddell//J. Orthop. Trauma. 1999. Vol. 13, N 4. P. 279 (Abstracts).
- Whittle P.A., Wood G.W. Fractures of lower extremity. In: Campbell’s Operative Orthopaedics/Ed. T. Canale. Philadelphia: Mosby, 2003. 10th Ed. Vol. 3. P. 2725-2872.
- Efficacy of various forms of fixation of transverse fractures of the patella/M.J. Weber, C.J. Janecki, P. McLeod, C.L. Nelson, J.A. Thompson//J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 1980. Vol. 62, N 2. P. 215-220.
- Application of circular external fixator under arthroscopic control in comminuted patella fractures: technique and early results/I. Yanmis, E. Oğuz, A.S. Atesalp, H. Ozkan, M. Kürklü, B. Demiralp, M. Basbozkurt//J. Trauma. 2006. Vol. 60, N 3. P. 659-663.
- Treatment of patella fractures by compressive external fixation (CEF)/M.M. Bari, Islam Sh., N.H. Shetu, M. Rahman, M.H. Munshi, Mostofa Md. G., M.R. Islam Khan//MOJ Orthop. Rheumatol. 2015. Vol. 2, N 6. P. 00070.


