Влияние индуцированной транспозиционной активности Р элементов на возраст-зависимые изменения репродуктивной системы и эмбриональную выживаемость Drosophila melanogaster
Автор: Юшкова Е.А.
Журнал: Известия Коми научного центра УрО РАН @izvestia-komisc
Рубрика: Научные статьи
Статья в выпуске: 4 (56), 2022 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Изучено возраст-зависимое изменение активности Р элементов в Р-М генетической системе по показателям репродуктивной системы (плодовитости и атрофии гонад) и эмбриональной выживаемости Drosophila melanogaster. Контроль за транспозиционной активностью Р элементов был осуществлен с применением тестов на стерильность и мутабильность локуса sn[w], результаты которого показали высокую мобилизацию функциональных Р последовательностей у всех возрастных групп. Увеличение с возрастом активности транспозонов было отмечено у дисгенных особей F1, полученных от стареющих родителей в индуцирующих скрещиваниях, а также у 60-суточных дисгенных потомков (по мутабильности локуса sn[w]). Показано, что Р-транспозиции влияют лишь на эмбриональную жизнеспособность, уровень которой снижался по мере старения их дисгенных родителей F1. Напротив, средняя плодовитость дисгенных самок не изменялась с возрастом и была на низком уровне по сравнению с недисгенными самками. Анализ полученных данных позволяет предположить, что в основе наблюдаемых эффектов лежат различные механизмы биологического действия старения и индуцированной Р-активности.
Р транспозоны, дисгенез, репродуктивная система, эмбриональная выживаемость, возраст-зависимые изменения
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/149141402
IDR: 149141402 | УДК: 575.11:595.773.4. | DOI: 10.19110/1994-5655-2022-4-82-91
Текст научной статьи Влияние индуцированной транспозиционной активности Р элементов на возраст-зависимые изменения репродуктивной системы и эмбриональную выживаемость Drosophila melanogaster
Мобильные генетические элементы (далее – МГЭ) представляют собой генетические факторы, способные перемещаться внутри генома эукариот и оказывать влияние на частоту спонтанного мутирования. Содержание их ДНК в геномах эукариот варьирует от 30 до 80 %. Их функции в клеточном геноме неоднозначны – они могут одновременно вести себя и как внутриклеточные стрессоры, приводящие к необратимым изменениям генетического материала (двойным разрывам ДНК, мутациям) [1], и как источники адаптивной генетической изменчивости [2]. Адаптивные свойства МГЭ связывают с их способностью влиять на экспрессию генов, отвечающих за стрессоустой-чивость организма [3, 4].
На сегодняшний день все больший интерес исследователей привлекает транспозоновая теория старения, которая предполагает, что эпигенетически подавленные МГЭ становятся вредными, поскольку клеточные механизмы защиты и контроля ухудшаются с возрастом [5]. Кро- ме того, доминирует мнение, что на генетическом уровне предрасположенность к заболеваниям зависит от изменений линейной структуры ДНК в результате мутаций, в основе которых лежат не только делеции, тандемные дупликации, амплификация генов, но и транспозиции МГЭ. Установлена причинно-следственная связь между различными заболеваниями (гемофилия, нейрофиброматоз, рак, психические расстройства) и активностью ряда МГЭ, в частности транспозонов [6-9]. У человека ДНК транспозонного происхождения составляет 54 % [10]. При одновременном воздействии внешнесредовых факторов и их индукции происходит увеличение темпа мутирования, числа геномных перестроек и, вследствие этого, возникновение определенных возраст-зависимых заболеваний [10, 11]. У Drosophila melanogaster процесс старения сопровождается нарушением репрессивной структуры гетерохроматина и повышением уровня экспрессии репортерных генов. Считают, что поддержание репрессивной структуры гетерохроматина и сохранение неактивного состояния МГЭ может оказаться ключевым для предотвращения МГЭ-обусловленных повреждений и улучшения тем самым качества жизни [12].
Имеется ряд противоречащих друг другу литературных данных, свидетельствующих, с одной стороны, об увеличении транспозиционной активности МГЭ с возрастом, и, с другой – об их снижении или неизменной активности в процессе старения. В многочисленных работах с применением разных организмов (дрожжи, нематода, дрозофила, мыши) и культур клеток человека установлено повышение активации МГЭ при старении [13–19]. На D. melanogaster показано, что с возрастом может происходить снижение транспозиций и количества копий некоторых МГЭ, что благоприятно сказывается на эмбриональной выживаемости и фертильности [2, 20]. В экспериментах по изучению молекулярных основ спонтанной эпигенетической защиты от массовых перемещений I ретроэлементов показано, что их высокая транспозиционная активность репрессируется при старении или обработке повышенной температурой реактивных I-самок [20]. Данный факт открыт и для Р транспозонов, индуцирующих дисгенные нарушения по типу Р-М [2]. Однако уровень их активности был исследован лишь у 2–4 и 21-суточных дисгенных самок. Отметим, что с возрастом также преобладают процессы деметилирования, которые приводят к хромосомным перестройкам за счет активации МГЭ [21].
Р элементы перемещаются с участием кодируемых ими ферментов транспозаз. Перемещения Р элементов происходят по механизму “разрезания и вставки”. Важную роль в ранней стадии Р-транспозиции играет кофактор GTP (гуанозинтрифосфат), который требуется для спаривания двух концов Р элемента перед ДНК эксцизией [22]. Дестабилизируя таким образом геном, транспозиции Р элементов приводят к нарушениям в функционировании клеток, что, в свою очередь, может вызывать различные патологические процессы репродуктивной системы и преждевременное старение. Более того, повышенный интерес к данным транспозонам вызван тем, что они широко рас- пространены в популяциях дрозофилы и имеют гомологов у позвоночных животных (Pgga, Pdre) и человека (Phsa) [23]. Известна высокая функциональная гомология домена THAP (Thanatos-ассоциированный белок, названный также TNP (N-терминальный сайт-специфический ДНК-свя-зывающий домен транспозазы Р элемента)) дрозофилы с доменом человека THAP9 [22]. В геноме человека 12 генов содержат THAP-домен. Только THAP9 проявляет исключительные гомологию к TNP дрозофилы и транспозазную активность в отношении Р элементов. Он может мобилизовать Р элементы как в клетках дрозофилы, так и в клетках человека. На сегодняшний день неизвестны функции THAP9 в качестве домена, связывающего транспозазу человеческого транспозона.
D. melanogaster является удобным объектом исследования возраст-зависимых изменений дисгенной активности МГЭ, поскольку имеет определенные генотипы/ци-тотипы (с наличием/отсутствием функциональных копий транспозонов), при комбинации которых можно произвести массовую индукцию транспозиций МГЭ. В связи с этим цель настоящей работы - изучение влияния индуцированной активности Р транспозонов на старение-ассоцииро-ванные показатели репродуктивной системы и эмбриональную выживаемость D. melanogaster .
Материалы и методы
В экспериментах использованы линии, полученные из коллекции Университета штата Индиана (Блумингтон, США): Harwich (Har) - строгая P-линия дикого типа, имеющая в генотипе функциональные копии Р элемента и отличающаяся свойствами индукторной линии в Р-М системе гибридного дисгенеза (ГД) [24]; Canton-S (CS) – М-линия дикого типа, не содержащая в генотипе Р элементы [25] и характеризующаяся как реактивная линия в Р-М типе ГД [24].
С целью получения особей с высоким уровнем активности Р элементов в гонадах ( Har [CS] ), самцы Har были скрещены с самками CS . Уровень индукции транспозиций Р элементов и обусловленной ими атрофии гонад является температурно-зависимым показателем. Максимальная активность транспозонов наблюдается при температуре +29 ºС, самая низкая – при +24 ºС [24]. Чтобы исключить полную стерильность дисгенных особей (с функциональными Р элементами) в работе применяли оптимальный температурный режим +25 ºС, при котором транспозиционная активность Р элементов приводит к 25–40 %-ному уровню атрофии гонад [26]. Особи, полученные в результате реципрокного скрещивания (CS[Har] ), были использованы в качестве контроля и обозначены как недисгенные особи без Р элементов.
Для контроля за уровнем возраст-зависимой индукции Р элементов проведены тесты на атрофию гонад (далее – АГ)/стерильность и мутабильность локуса singed-weak (sn[w]). Тест на АГ основан на визуализации морфологии гонад (односторонней (А1) и двусторонней (А0)) гибридных самок. Стерильность рассчитана по формуле: АГ (%) = А0 (%) + ½ А1 (%) [27]. В первой серии эксперимента проведен анализ АГ у 30–50 стареющих дисгенных/недисгенных самок F1 в трех повторностях опыта. Во второй серии эксперимента использованы 30–50 пар родительских особей каждой возрастной группы на экспериментальный вариант. Родители каждой возрастной группы отобраны для процедуры индивидуального индуцирующего и реципрокного скрещиваний, длительность которых составила двое суток. В результате индивидуальных скрещиваний (в трех повторностях опыта) получено женское потомство F1. Все самки F1 (30–100 особей), полученные от этих скрещиваний, подвергались оценке морфологии гонад в зависимости от возраста их родителей. У старых особей (в возрасте 40-60 суток) яйцепро-дукция находилась на низком уровне, поэтому количество вылетевших из куколок гибридных самок F1 колебалось в пределах 30-40 особей на повторность. Перед проведением теста на АГ все дисгенные/недисгенные самки поддерживались на питательной среде в течение трех суток для полного созревания их гонад. В данной работе атрофия гонад самцов не исследована.
Мутабильность локуса sn[w] анализировали по методу [28], позволяющему оценить транспозиционную активность полноразмерных Р элементов. Для этого одновозрастных гибридных самцов F1, взятых из исследуемых вариантов, массово скрещивали с самками тестерной линии sn[w] (генотип: y[1]sn[w]/Yy+;bw[1];st[1]) при температуре +29 °С. Линия sn[w] несет два дефектных Р элемента в локусе singed briste и имеет М-цитотип. Далее проведено индивидуальное скрещивание с самцами F1 и виргинными самками ywf/ mei-41 (генотип: mei-41/y&C(1)DX;y[1]w[1]f[1]/y) при температуре +25 °С. Линия ywf/mei-41 имеет сцепленные X-хромосомы и морфологические признаки y ( yellow – желтое тело), f (forked - недоразвитые щетинки) и w (white - белые глаза). Потомство F2 проанализировано на наличие особей, несущих мутации sn[w] (опаленные щетинки), sn[e] ( extreme singed – сильно выраженный признак, короткие изогнутые щетинки) и sn[+] (pseudowild-type - псевдодикий тип, нормальные щетинки). Общий уровень мутабильности локуса sn[w] (Msn[w]) определен по отношению особей с признаками sn[e] и sn[+] среди всех подсчитанных мух [29]. Мута-бильность локуса sn[w] изучена в пяти возрастных группах (5, 15, 35, 45 и 60 суток).
Анализ плодовитости проведен путем индивидуального скрещивания виргинных дисгенных особей F1 обоего пола. На каждый флакон с питательной средой, подкрашенной активированным углем, отбирали по пять особей каждого пола и соответствующего возраста. Особей из каждой экспериментальной группы помещали на новую среду ежедневно в течение 10 суток. Подсчет эмбрионов вели через сутки под бинокуляром “МБС-10” (Россия). Во всех полученных кладках учитывали количество эмбрионов, отложенных самками за сутки. Плодовитость оценивали как среднее число эмбрионов на одну родительскую самку. Всего проанализировано 50–100 самок на вариант на повторность. В результате трех повторностей опыта изучено 150-300 особей на вариант.
Эмбриональную выживаемость изучали одновременно с анализом показателя ‘’плодовитость’’. После подсчета количества яиц через 48 ч устанавливали количество развившихся эмбрионов. Выживаемость на эмбриональной стадии рассчитывали, как отношение числа развившихся эмбрионов к общему числу отложенных яиц.
Данные основаны на результатах трех повторностей эксперимента и представлены в виде среднего значения и соответствующей стандартной ошибки среднего на вариант. Значимость влияния возраста на исследуемые показатели определяли однофакторным дисперсионным анализом (ANOVA). Для анализа различий в анализируемых показателях в зависимости от возраста и дисгенных условий применяли двусторонний ANOVA. При значительной разнице (p<0,05) апостериорные попарные сравнения выполнены с использованием критерия Тьюки. Коэффициенты взаимодействия возраста и дисгенных условий и их достоверность найдены по формуле (Kw = ∆A(X; Y)/∆A(0; Y) + A(X; 0), где AA(X; Y) = A(X; Y) - A(0; 0) - превышение совместного действия факторов X (возраст) и Y (дисгенез) по сравнению с контролем; ∆A(0; Y) + A(X; 0) – сумма превышения эффектов при раздельном действии исследуемых факторов), приведенной в работе [30]. Статистическая обработка данных была проведена в программе Statistica (версия 7.0.61.0, StatSoft, Inc., США).
Результаты и их обсуждение
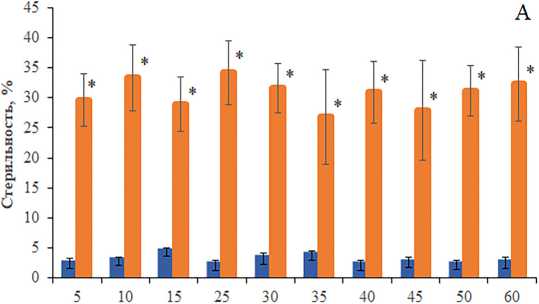
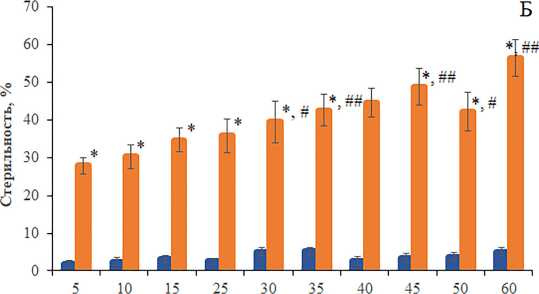
Атрофия гонад и мутабильность локуса sn[w] считают-ся одними из важных признаков, указывающих на наличие и активность Р элементов в геноме дрозофилы. Проведены три повторности эксперимента (данные объединены), согласно которым, показано, что транспозиционная активность Р элементов находится на одном и том же высоком уровне независимо от возраста стареющих самок F1 (рис. 1А). В контроле показатель “атрофия гонад” варьировал от 2.1 до 4.3 %, что укладывается в нормы, наблюдаемые при спонтанной стерильности. Однако активность Р элементов зависела от возраста родителей, участвующих в дисгенных скрещиваниях. Наибольшая стерильность (3.4–56.3 %) была зафиксирована у дисгенных самок (p<0.05-0.001), полученных от родителей в возрасте 30–60 сут (рис. 1Б). Известно, что стерильность особей в условиях Р-М дисгенной системы является следствием гибели клеток зародышевой линии на ранних стадиях онтогенеза. Это приводит к отсутствию половых клеток в гонадах самцов и самок, что является причиной общего недоразвития их у потомков F 1 [22]. Наблюдаемая атрофия гонад у потомков, зависящая от старения родителей, очевидно, вызвана так называемым «эффектом возраста родителей». Этот эффект выражается в накоплении повреждений генетического материала в родительских половых клетках, приводящий к появлению у потомства врожденных аномалий. Такие повреждения ДНК, индуцированные в процессе старения и/или различными ДНК-повреждающими агентами (облучением, токсическими веществами), могут служить дополнительным триггером активности МГЭ [31]. Таким об-
Возраст, сутки
■ Особи без Р элементов 8 Особи с Р элементами
Возраст, сутки
■ Особи без Р элементов ■ Особи с Р элементами
Рисунок 1. Стерильность самок F1 в зависимости от возраста (А) и возраста их родительских форм (Б). Различия достоверны при *p<0.0000 по сравнению с особями без Р элементов и #p<0.05, ##p<0.001 по сравнению с 5-суточными особями с Р элементами. Столбики погрешностей обозначают стандартные ошибки.
Figure 1. Sterility of F1 females depending on the age (A) and the age of their parental forms (Б). Differences are significant at *p<0.0000 compared to individuals without Р elements and #p<0.05, ##p<0.001 compared to 5-day-old individuals with Р elements. Error bars denote standard errors.
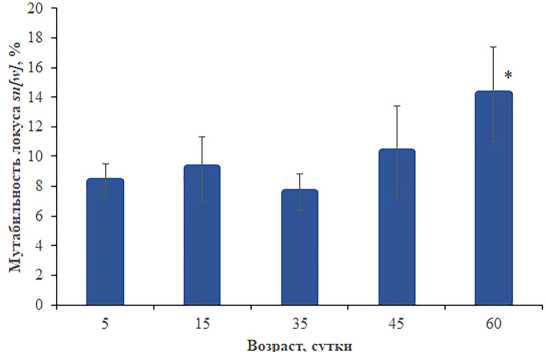
Рисунок 2. Мутабильность локуса sn[w] у особей F1 разного возраста. Различия достоверны при *p<0.05 по сравнению с 5–35-суточными дисгенными особями. Столбики погрешностей обозначают стандартные ошибки.
Figure 2. Mutability of the sn[w] locus in F1 individuals of different ages. Differences are significant at *p<0.05 compared to 5–35-day-old dysgenic individuals. Error bars denote standard errors.
в дисгенных зародышевых клетках, что приводит к повышению атрофии гонад у их потомства.
Результаты анализа мутабильности локуса sn[w] свидетельствуют о наличии активных копий Р элемента во всех возрастных дисгенных группах (рис. 2). Активность Р элементов практически неизменна у особей в возрасте 5–45 сут и возрастает лишь у 60-суточных особей (p<0.05).
Средняя плодовитость дисгенных самок была статистически значимо ниже (p<0.05–0.01, односторонний ANOVA) таковой у недисгенных особей и не зависела от возраста (рис. 3В). Однако результаты ее посуточной динамики показали, что у 45- и 60-суточных дисгенных особей уровень плодовитости на протяжении 10 сут находится на низком уровне (p<0.05, односторонний ANOVA) по сравнению с 5-суточными особями этого же генотипа (рис. 3Б). В отличие от самок с Р элементами, плодовитость самок без Р транспозонов изменялась с возрастом (рис. 3А). Начиная с 30-суточного возраста репродуктивные функции самок либо имели тенденцию к снижению, либо статистически значимо были снижены (p<0.05, односторонний ANOVA). Двусторонний тест ANOVA выявил статистически значимые различия в продукции эмбрионов между дисгенными и недисгенными генотипами (p<0.0000) и в зависимости от возраста испытуемых (p<0.0000). Взаимодействие “Дисгенные условия и возраст” также было статистически значимым (p<0.0000). Процедура попарного сравнения между недисгенными и дис-генными вариантами с использованием апостериорного критерия Тьюки позволила обнаружить значительное снижение плодовитости дисгенных самок всех возрастных групп, кроме особей в возрасте 30, 50–60 сут.
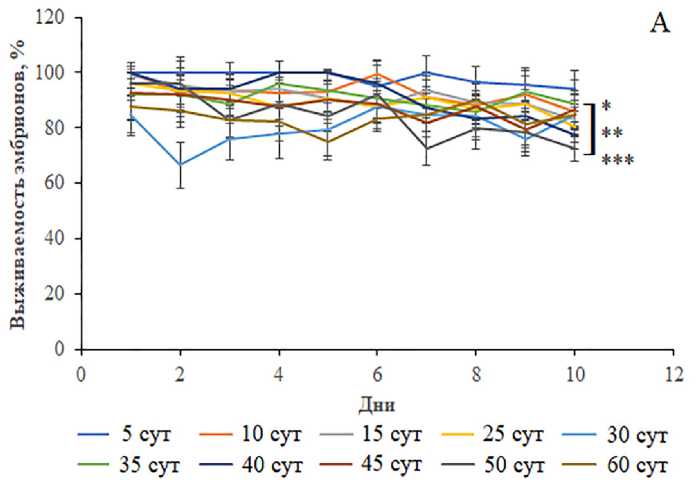
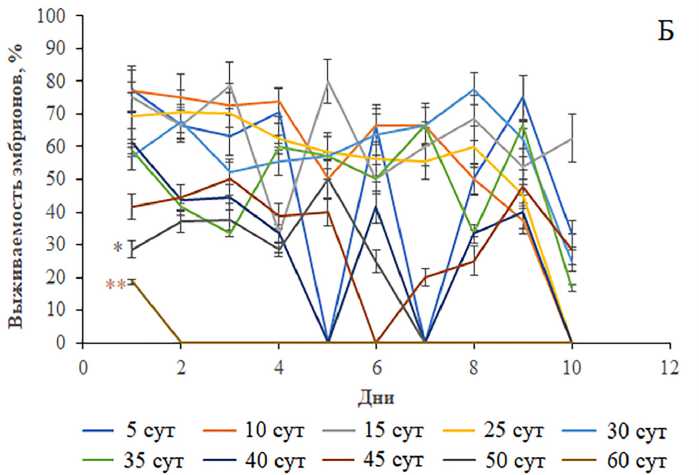
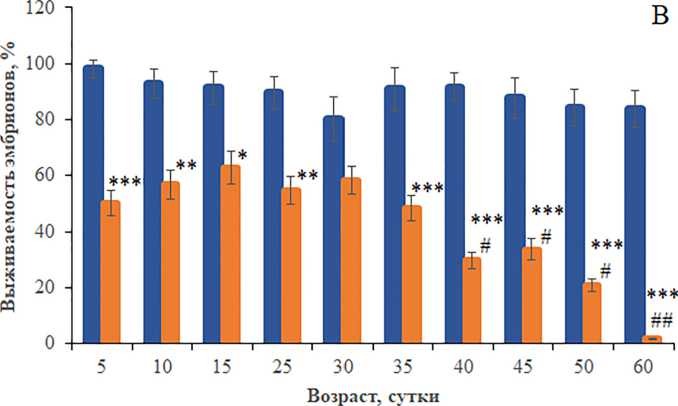
Результаты анализа средней эмбриональной выживаемости демонстрируют низкую (p<0.05–0.0000, односторонний ANOVA) жизнеспособность дис-генных эмбрионов по сравнению с недисгенны-ми потомками (рис. 4В). Эмбрионы, полученные от 40–60-суточных родителей F1, имели статистически значимую низкую (p<0.05–0.001, односторонний ANOVA) среднюю выживаемость относительно потомков, отложенных молодыми родителями. Данные кривых посуточной динамики эмбриональной выживаемости показывают, что количество выживших эмбрионов, полученных от старых мух (50–60 сут), статистически значимо (p<0.05–0.0000, односторонний ANOVA) снижено или имеет нулевые значения (рис. 4Б). Двусторонний тест ANOVA выявил статистически значимые различия в эмбриональной жизнеспособности между дисгенными и недисгенными генотипами (p<0.0000) и в зависимости от возраста родителей (p<0.0000), а также во взаимодействии факторов “Дисгенные условия и возраст” (p<0.0000).
разом, возраст-ассоциированная активация Р элементов у Апостериорный критерий Тьюки для попарного сравнения родителей способна активировать пути клеточной гибели между недисгенными и дисгенными вариантами обнару-
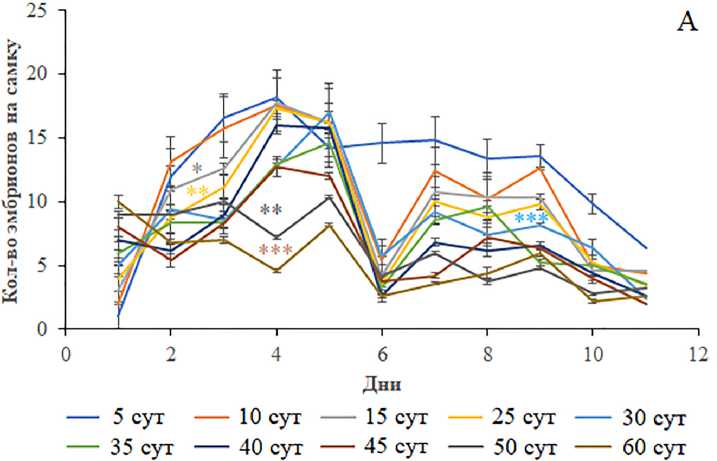
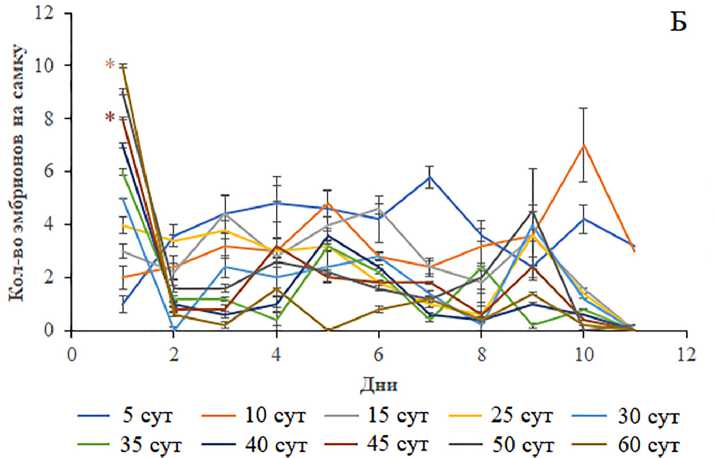
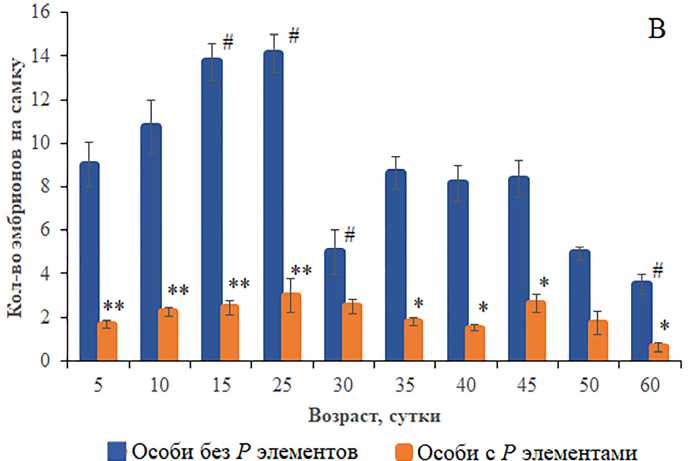
Рисунок 3. Средняя плодовитость (В) и ее посуточная динамика у особей без Р элементов (А) и особей с Р элементами (Б) разных возрастных групп. Различия достоверны при *p<0.05, **p<0.01 по сравнению с особями без Р элементов и #p<0.05 между 5-суточными особями без Р элементов (для средней плодовитости), *p<0.05, **p<0.001, ***p<0.0000 по сравнению с 5-суточными особями (для посуточной динамики плодовитости). Столбики погрешностей обозначают стандартные ошибки. Figure 3. Average fecundity (В) and its daily dynamics in individuals without P elements (A) and individuals with P elements (Б) of different age groups. Differences are significant at *p<0.05, **p<0.01 compared with individuals without P elements and #p<0.05 between 5-day-old individuals without P elements (for average fecundity), *p<0.05, **p<0.001, ***p<0.0000 compared to 5-day-old individuals (for daily dynamics of fertility). Error bars denote standard errors.
Ранее показано [2], что высокая транспозиционная активация Р элементов характерна для молодых дисгенных самок (в возрасте двух-четырех суток), фертильность которых находилась на низком уровне. По мере старения репродуктивные функции дисгенных особей в возрасте 21 сут восстанавливались. Данные настоящего исследования не подтверждают результаты Ж.С. Хурана и его соавторов и демонстрируют низкую (невосстанав-ливающуюся) фертильность всех возрастных групп F1, претерпевающих активность Р элементов. Возможно, такая невоспроизводимость результатов связана с использованием в индуцирующих скрещиваниях различных реактивных линий ( Canton-S и w1 ), отличающихся чувствительностью к инвазиям Р элементов. Считают [2], что репродуктивные функции дисгенных самок сохраняются, а в некоторых случаях восстанавливаются, за счет транспонирования резидентных элементов в кластеры пиРНК, являясь тем самым основой для создания новых пиРНК Р элементов. В результате полногеномного молекулярного исследования в яичниках дисгенных самок обнаружена сверхэкспрессия не только Р элементов, но высокие уровни экспрессии резидентных МГЭ из разных семейств. Резидентные элементы представляют собой транспозоны, которые постоянно присутствуют в геноме и являются общими для родительских форм. Резидентные элементы активируются в яичниках дисгенных самок, но не в семенниках дисгенных самцов [32]. Частота перемещения Р элементов в гонадах женского потомства в 15 раз выше, чем уровень транспозиций в гонадах самцов. Повышенная частота перемещений Р элементов у самок и связанная с ней индукция повреждений ДНК приводят к активации резидентных элементов. Подобный триггерный механизм был выявлен у D. virillis , у которой ретротранспозон Penelope в условиях дисгенеза приводит к активации четырех дополнительных семейств резидентных транспозонов [33]. Такие транспозоны вызывают разрывы ДНК, передающие сигналы для экспрессии резидентных элементов [34].
Повреждения ДНК, вызванные активностью Р жил значительное снижение выживаемости дисгенных
элементов, могут запускать Chk2-зависимое фос-фолирирование и убиквитин-зависимое разрушение Vasa, что, в свою очередь, нарушает организацию nuage – специфичная для зародышевой линии структура, участвующая в биогенезе пиРНК и молчании транспозонов [35]. В процессе старения дис-генных гибридов подавление транспозиционной активности может быть следствием возобновления сборки nuage и экспрессии белка Vasa. Возможен некий сценарий такой адаптации яичников к старению, заключающийся в том, что Р-элемент-инду-цированные повреждения ДНК через определенную цепь эмбрионов, полученных от всех возрастных родительских событий приводят к сборке nuage, накоплению Vasa, прогрупп, кроме особей в возрасте 30 сут. дукции пиРНК и молчанию транспозонов. Очевидно, этот
■ Особи без Р элементов Особи с Р элементами
Рисунок 4. Средняя эмбриональная выживаемость (В) и ее посуточная динамика у особей без Р элементов (А) и особей с Р элементами (Б) разных возрастных групп. Различия достоверны при *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.0000 по сравнению с особями без Р элементов и #p<0.05, ##p<0.001 по сравнению с 5-суточными особями с Р элементами (для средней эмбриональной выживаемости), *p<0.05, **p<0.001, ***p<0.0000 по сравнению с 5-суточными особями (для посуточной динамики эмбриональной выживаемости). Столбики погрешностей обозначают стандартные ошибки.
Figure 4. Average embryonic survival (В) and its daily dynamics in individuals without P elements (A) and individuals with P elements (Б) of different age groups. Differences are significant at *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.0000 compared with individuals without P elements and #p<0.05, ##p<0.001 compared with 5-day-old individuals with P elements (for the mean embryonic survival), *p<0.05, **p<0.001, ***p<0.0000 compared with 5-day-old individuals (for the daily dynamics of embryonic survival). Error bars denote standard errors.
сценарий не работает в случае, когда дисгенные особи получены от стареющих родителей, вступающих в размножение с комплексом нарушенных механизмов, необходимых для репарации разрывов ДНК. Возникшие в результате этого повреждения ДНК блокируют пролиферацию стволовых клеток и оогенез, а также дают время для транспозиции резидентных элементов. Причиной невосстановления фертильных функций и высокой эмбриональной смертности дисгенных особей может быть также способность функциональных Р элементов подавлять экспрессию гена Myc , поддерживающего геномную целостность в зародышевой линии за счет элиминации клеток с накопленными генетическими повреждениями [36].
С целью выяснения, какой из факторов (возраст и/или активность Р элементов) или их совместное действие в бóльшей мере влияет на исследуемые показатели, был применен расчет значений коэффициентов взаимодействия (таблица). Для всех изученных вариантов по всем исследуемым показателям прослеживается антагонистический эффект совместного действия факторов. Результаты дисперсионного анализа совместного действия возраста и индуцированной активности Р элементов на D. melanogaster показали статистически значимое влияние обоих изученных факторов как по отдельности, так и в их сочетании. Напротив, оценка коэффициентов взаимодействия выделила преимущественное действие индуцированной активности Р элементов на биологические эффекты. Неодинаковый вклад в наблюдаемые эффекты свидетельствует о различии механизмов биологического действия возраста и активации Р элементов.
Заключение
Таким образом, в исследовании выявлено негативное воздействие активности Р элементов в условиях дисгенеза на возраст-зависимые изменения репродуктивной системы и эмбриональную выживаемость D. melanogaster . Отчетливая возрастная динамика Р элементов (по показателю “стерильность”) была обнаружена у потомков F1, полученных в дисгенных скрещиваниях от родителей разного возраста. Однако по мере старения дисгенных потомков F1 стерильность и фертильность не меняются с возрастом. Полученные результаты свидетельствуют, что с возрастом индуцированная транспозиционная активность Р элементов у D. melanogaster не меняется (по показателю “атрофия гонад”), но может влиять на возраст-ассоциированные показатели репродуктивной системы и выживаемость на ранних стадиях онтогенеза.
Значения коэффициентов взаимодействия (K w ) при совместном действии возраста и дисгенных условий Values of interaction coefficients (K w ) under the combined action of age and dysgenic conditions
|
Возраст, сут. |
Показатель |
|||
|
Плодовитость |
Эмбриональная выживаемость |
Стерильность |
Мутабильность локуса sn[w] |
|
|
10 |
-0.74* |
-0.97** |
-1.15** |
- |
|
15 |
-0.54* |
-0.86* |
-1.05* |
-1.10* |
|
25 |
-0.48* |
-1.10** |
-1.15* |
- |
|
30 |
-1.96** |
-1.32** |
-1.11* |
- |
|
35 |
-1.03* |
-1.22** |
-0.94** |
-0.91* |
|
40 |
-1.16** |
-1.66** |
-1.04* |
- |
|
45 |
-0.95* |
-1.72* |
-0.94** |
-1.24** |
|
50 |
-2.23** |
-2.28** |
-1.05** |
- |
|
60 |
-4.55** |
-2.88** |
-1.10** |
-1.70** |
Примечание. Значения Kw рассчитаны относительно особей в возрасте пяти суток. Kw достоверны при *р<0.05 и **р<0.01; “-“ – нет значений. Kw< 1 результат взаимодействия оценивается как антагонистический, K w = 1 - как аддитивный, K w > 1 - как синергический.
Note. Kw values were calculated relative to individuals aged five days. Kw are significant at *p<0.05 and **p<0.01; “-“– no values. Kw< 1 the result of the interaction is assessed as antagonistic, K w = 1 - as additive, K w > 1 - as synergistic.
Список литературы Влияние индуцированной транспозиционной активности Р элементов на возраст-зависимые изменения репродуктивной системы и эмбриональную выживаемость Drosophila melanogaster
- Sleeping Beauty transposon mutagenesis in rat spermatogonial stem cells / Z. Ivics, Z. Izsvak, G. Medrano [et al.] // Nature Protocols. – 2011. – Vol. 6, N 10. – P. 1521–1535.
- Adaptation to P element transposon invasion in Drosophila melanogaster / J. S. Khurana, J. Wang, J. Xu [et al.] // Cell. – 2011. – Vol. 147, N 7. – P. 1551–1563.
- Mateo, L. A transposable element insertion confers xenobiotic resistance in Drosophila / L. Mateo, A. Ullastres, J. Gonzalez // PLOS Genetics. – 2014. – Vol. 10, N 8. – P. e1004560.
- Zhang, Y. A universal mariner transposon system for forward genetic studies in the genus clostridium / Y. Zhang, A. Grosse-Honebrink, N. P. Minton // PLOS One. – 2015. – Vol. 10, N 4. – P. e0122411.
- Piwi is required to limit exhaustion of aging somatic stem cells / P. Sousa-Victor, A. Ayyaz [et al.] // Cell Reports. – 2017. – Vol. 20, N 11. – P. 2527–2537.
- Hancks, D. C. Active human retrotransposons: variation and disease / D. C. Hancks, H. H. Kazazian // Current in Genetics & Development. – 2012. – Vol. 22, N 3. – P. 191–203.
- Majumdar, S. The human THAP9 gene encodes an active P-element DNA transposase / S. Majumdar, A. Singh, D. C. Rio // Science. – 2013. – Vol. 339, N 6118. – P. 446–448.
- Cancer gene discovery: Exploiting insertional mutagenesis / M. Ranzani, S. Annunziato, D. J. Adams [et al.] // Mol. Cancer Res. – 2013. – Vol. 11, N 10. – P. 1141–1158.
- Transposable elements and psychiatric disorders / G. Guffanti, S. Gaudi, J.H. Fallon [et al.] // Amer. J. Med. Genet. Part B-Neuropsych. Genet. – 2014. – Vol. 165, N 3. – P. 201–216.
- The complete sequence of a human genome / S. Nurk, S. Koren, A. Rhie [et al.] // Science. – 2022. – Vol. 376, N 6588. – P. 44–53.
- Kazazian, Р. Р. Mobile elements and disease / Р. Р. Kazazian // Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. – 1998. – Vol. 8, N 3. – P. 343–350.
- Chromatin-modifying genetic interventions suppress age-associated transposable element activation and extend life span in Drosophila / J. G. Wood, B. C. Jones, N. Jiang [et al.] // Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. – 2016. – Vol. 113, N 40. – P. 11277–11282.
- Slotkin, R. K. Transposable elements and the epigenetic regulation of the genome / R. K. Slotkin, R. Martienssen // Nat. Rev. Genet. – 2007. – Vol. 8, N 4. – P. 272–285.
- Maxwell, P. H. Retrotransposition is associated with genome instability during chronological aging / P. H. Max well, W. C. Burhans, M. J. Curcio // Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. – 2011. – Vol. 108, N 51. – P. 20376–20381.
- Ambati, J. Mechanisms of age-related macular degeneration / J. Ambati, B. J. Fowler // Neuron. – 2012. – Vol. 75, N 1. – P. 26–39.
- C. elegans germ cells show temperature and age-dependent expression of Cer1, a Gypsy/Ty3-related retrotransposon / S. Dennis, U. Sheth, J. L. Feldman [et al.] // PLoS Pathog. – 2012. – Vol. 8, N 3. – P. e1002591.
- Transposable elements become active and mobile in the genomes of aging mammalian somatic tissues / M. De Cecco, S. W. Criscione, A. L. Peterson [et al.] // Aging (Albany, NY). – 2013. – Vol. 5, N 12. – P. 867–883.
- Activation of transposable elements during aging and neuronal decline in Drosophila / W. Li, L. Prazak, N. Chatterjee [et al.] // Nat. Neurosci. – 2013. – Vol. 16, N 5. – P. 529–531.
- SIRT6 represses LINE1 retrotransposons by ribosylating KAP1 but this repression fails with stress and age / M. Van Meter, M. Kashyap, S. Rezazadeh [et al.] // Nat. Commun. – 2014. – Vol. 5, N 5011. – P. 1–21.
- Dramard, X. Natural epigenetic protection against the I-factor, a Drosophila LINE retrotransposon, by remnants of ancestral invasions / X. Dramard, T. Heidmann, S. Jensen // PloS One. – 2007. – Vol. 2, N 3. – P. e304.
- Epigenetic regulation of an IAP retrotransposon in the aging mouse: progressive demethylation and de-silencing of the element by its repetitive induction / W. Barbot, A. Dupressoir, V. Lazar [et al.] // Nucleic Acids Res. – 2002. – Vol. 30, N 11. – P. 2365–2373.
- Structure of a P element transposase-DNA complex reveals unusual DNA structures and GTP-DNA contacts / G. E. Ghanim, E. H. Kellogg, E. Nogales [et al.] // Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. – 2019. – Vol. 26, N 11. – P. 1013–1022.
- International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium: Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome // Nature. – 2001. – Vol. 409, N 6822. – Р. 860–921.
- Kidwell, M. G. Hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila melanogaster: sterility resulting from gonadal dysgenesis in the P–M system / M. G. Kidwell, J. B. Novy // Genetics. – 1979. – Vol. 92, N 4. – P. 1127–1140.
- Bingham, P. M. The molecular basis of P-M hybrid dysgenesis: The role of the P element, a P strain-specific transposon family / P. M. Bingham, M. G. Kidwell, G. M. Rubin // Cell. – 1982. – Vol. 29, N 8. – P. 995–1004.
- Yushkova, E. A. Vliyanie hronicheskogo oblucheniya v malyh dozah na morfologicheskie pokazateli reproduktivnoj sistemy disgennyh samok Drosophila melanogaster [Influentia irradiationis chronicae in low dosibus in parametris morphologicis systematis generationis dysgenicae Drosophila melanogaster feminae] / E. A. Yushkova // Radiacionnaya biologiya. Radioekologiya. – 2017. – Vol. 57, N 1. – P. 60–65.
- P-element repression in Drosophila melanogaster by a naturally occurring defective telomeric P copy / L. Marin, M. Lehmann, D. Nouaud [et al.] // Genetics. – 2000. – Vol. 155, N 4. – Р. 1841‒1854.
- Engels, W. R. A trans-acting product needed for P factor transposition in Drosophila / W. R. Engels // Science. – 1984. – Vol. 226, N 4679. – P. 1194–1197.
- Impairment of cytotype regulation of P-element activity in Drosophila melanogaster by mutations in the Su(var)205gene / K. J. Haley, J. R. Stuart, J. D. Raymond [et al.] // Genetics. – 2005. – Vol. 171, N 2. – P. 583–595.
- Vliyanie kombinirovannogo dejstviya ioniziruyushchego izlucheniya i solej tyazhelyh metallov na chastotu hromosomnyh aberracij v listovoj meristeme yarovogo yachmenya [Influentia compositionis actionis ionizing radiorum et metallorum salium gravium in frequentia aberrationum chromosomatum in folium meristem veris hordei] / S. A. Geras’kin, V. G. Dikarev, A. A. Udalova [et al.] // Genetika. – 1996. – Vol. 32, N 2. – P. 279–288.
- Beauregard, A. The take and give between retrotransposable elements and their hosts /A. Beauregard, M.J. Curcio, M. Belfort // Annu. Rev. Genet. – 2008. – Vol. 42.–P. 587-617.
- Eggleston, W. B. P-M hybrid dysgenesis does not mobilize other transposable element families in D. melanogaster / W. B. Eggleston, D. M. Johnson-Schlitz, W. R. Engels // Nature. – 1988. – Vol. 331, N 6154. – P. 368–370.
- Diverse transposable elements are mobilized in hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila virilis / D. A. Petrov, J. L. Schutzman, D. L. Hartl [et al.] // Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. – 1995. – Vol. 92, N 17. – P. 8050–8054.
- Human LINE-1 retrotransposon induces DNA damage and apoptosis in cancer cells / S. M. Belgnaoui, R. G. Gosden, O. J. Semmes [et al.] // Cancer Cell Int. – 2006. – Vol. 6. – 13 p.
- Specialized piRNA pathways act in germline and somatic tissues of the Drosophila ovary / C. D. Malone, J. Brennecke, M. Dus [et al.] // Cell. – 2009. – Vol. 137, N 3. – P. 522–535.
- Ota, R. Myc plays an important role in Drosophila P-M hybrid dysgenesis to eliminate germline cells with genetic damage / R. Ota, S. Kobayashi // Commun. Biol. – 2020. – Vol. 3, N 1. – P. 185.


