Влияние наночастиц Fe3O4 на урожайность картофеля и развитие почвенной микрофлоры
Автор: Любимова Н.А., Рабинович Г.Ю.
Журнал: Бюллетень Почвенного института им. В.В. Докучаева @byulleten-esoil
Рубрика: Спецвыпуск по результатам молодежной конференции
Статья в выпуске: S1, 2024 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Цель данной работы заключалась в исследовании как раздельного, так и совместного влияния ЖФБ (жидкофазный биопрепарат) и наночастиц Fe3O4 на урожайность картофеля сорта Скарб, а также на почвенную микрофлору. Биосинтез наночастиц Fe3O4 осуществлялся с применением экстракта зеленого чая и раствора FeSO4∙7H2O концентрацией 0.1 моль/л. Эффективность полученного ЖФБ-Fe изучали в полевых условиях на фоне внесения NPK. Результаты трехлетнего эксперимента (2020-2022 гг.) показали, что при опрыскивании вегетирующих растений 1%-ным ЖФБ-Fe урожайность картофеля увеличилась на 16.9%, а при обработке клубней перед посадкой - на 14.8% по сравнению с контролем. В то же время при использовании ЖФБ без добавления наночастиц Fe3O4 урожайность картофеля увеличилась на 9.8% при обработке по листу и на 6.8% при обработке клубней по сравнению с контролем. По результатам микробиологического анализа был рассчитан коэффициент минерализации почвы и рассмотрена зависимость урожайности картофеля от его величины. При варьировании концентрации ЖФБ-Fe обнаружена сильная, но разнонаправленная зависимость урожайности картофеля от коэффициента минерализации почвы как при обработке клубней (уравнение регрессии у = 0.2639х - 39.9329 с коэффициентом корреляции r = 0.72), так и при опрыскивании растений картофеля (уравнение регрессии у = -0.2536х + 55.882 с коэффициентом корреляции r = -0.77). Кроме того, при некорневой обработке растений картофеля 1%-ным раствором наночастиц Fe3O4 была очень сильная обратная взаимосвязь между урожайностью и количеством азоттрансформирующих микроорганизмов (коэффициент корреляции r = -0.90, при уравнении регрессии у = -0.0841х + 37.9421).
Биосинтез наночастиц, азоттрансформирующие микроорганизмы, фосфатмобилизующие микроорганизмы, коэффициент минерализации почвы
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143183580
IDR: 143183580 | УДК: 631.4 | DOI: 10.19047/0136-1694-2024-SPYC-164-192
Текст статьи Влияние наночастиц Fe3O4 на урожайность картофеля и развитие почвенной микрофлоры
ФИЦ “Почвенный институт им. В.В. Докучаева”, Россия, 119017, Москва, Пыжевский пер, 7, стр. 2, *, e-mail: , **, e-mail:
7 Bld. 2 Pyzhevskiy per., Moscow 119017, Russian Federation, *, e-mail: , **, e-mail:
Глобальный спрос на продукты питания приводит к увеличению использования химических удобрений, которые, с одной стороны, стимулируют рост и повышают урожайность растений, а с другой, негативно влияют на почву, окружающую среду и даже здоровье человека (Nongbet et al., 2022). Современной альтернативой традиционным удобрениям являются различные наноудобрения, которые повышают продуктивность растений за счет целевой доставки или медленного высвобождения питательных веществ, что позволяет в разы сократить количество вносимых химикатов (Duhan et al., 2017; Ndaba et al., 2022). Как правило, наноудобрения состоят из наночастиц, содержащих в своем составе макро- и микроэлементы, такие как азот, фосфор, калий, железо и марганец, которые доставляются в различные растительные органы и ткани (Nongbet et al., 2022).
Среди всех микроэлементов, содержащихся в почве, особое место занимает железо, так как без этого металла невозможны такие жизненно важные процессы, как синтез ДНК, дыхание и фотосинтез. За счет своих окислительно-восстановительных свойств и способности образовывать комплексы с различными лигандами железо входит в состав многих переносчиков электронов и ферментов, в том числе каталазы, пероксидазы, цитохромоксидазы, а также различных цитохромов. При этом избыток железа в ризосфере может привести к развитию окислительного стресса, проявляющегося образованием активных форм кислорода и, как следствие, перекисным окислением липидов (Иванищев, 2019а). Однако в большинстве случаев растения, наоборот, страдают от дефицита железа, проявляющегося в снижении уровня фотосинтетических реакций, провоцируя хлороз. Это связано с тем, что биологическая активность железа в почве достаточно низка, потому что в ней оно образует соединения, плохо растворимые в воде при нейтральном уровне рН и, следовательно, практически недоступные для растений, что является серьезной проблемой в сельском хозяйстве (Иванищев, 2019б). Одним из способов восполнения дефицита железа в растениях является применение Fe-содержащих удобрений, которые делятся на три основные группы: неорганические соединения железа, синтетические комплексы – железо-хелаты и природные соединения железа (Briat et al., 2015).
Наночастицы оксида железа (Fe2O3 и Fe3O4) также могут успешно использоваться в качестве железосодержащих удобре- ний. Например, при замене традиционной железосодержащей добавки на наночастицы Fe2O3 при выращивании лоропеталума китайского (Loropetalum chinense) в условиях in vitro увеличилась длина стебля и корня, а также количество корней, листьев и междоузлий на один эксплант (Babali et al., 2022). Наночастицы Fe2O3 также были успешно использованы в качестве удобрения при выращивании арахиса (Arachis hypogaea), весьма чувствительного к дефициту железа. Было показано, что наночастицы Fe2O3 при добавлении в почву способствовали росту арахиса, который проявился в увеличении длины корней, высоты растений и биомассы, а также содержания хлорофилла в листьях за счет регулирования содержания фитогормонов и активности антиоксидантных ферментов (Rui et al., 2016). Другой группой ученых было показано, что при смоделированных обильных осадках внекорневая обработка растений наножелезосодержащими удобрениями, такими как наночастицы железа, Fe3O4, α-Fe2O3 и γ-Fe2O3, позволила снизить дефицит железа и задержку роста сеянцев арахиса, выращиваемых в питательном растворе, не содержащем железа (Chen et al., 2023). В лабораторном эксперименте на растениях сои (Glycine max L.), подвергшихся воздействию некорневых и корневых добавок наночастиц Fe2O3, наночастиц Fe2O3, покрытых фульвокисло-той, и Fe-ЭДТА, было обнаружено, что наночастицы оказывали более заметное влияние на биомассу растений по сравнению с традиционным удобрением и контролем (без каких-либо добавок). Так, некорневая подкормка растений наночастицами Fe2O3, покрытыми фульвокислотой, и наночастицами Fe2O3 привела к увеличению корней на 61 и 52% и побегов на 50 и 54% по сравнению с контролем соответственно. Тогда как при обработке Fe-ЭДТА значения этих показателей были равны контролю (Yang et al., 2020).
Помимо положительного влияния на растения, наночастицы железа могут существенно влиять на свойства почвы. Так, например, достоверно известно, что наночастицы Fe3O4, которые использовались для полива растений фасоли, повлияли на химические свойства почвенной ризосферы, что проявилось в увеличении содержания общего и экстрагируемого фосфора, экстрагируемого калия и кальция, общего калия, марганца и железа и катионообменной емкости, а также в снижении содержания хлора в почве (De Souza et al., 2019).
Одними из особенно важных факторов, влияющих на качество почвы, считаются биологические показатели, поскольку почвенные организмы напрямую влияют на процессы разложения органического вещества и круговорот питательных веществ. Кроме того, разнообразие почвенных микроорганизмов и высокие уровни микробной биомассы способны увеличивать способность почвы подавлять болезни. Поэтому сохранение разнообразия и микробной биомассы является одной из задач современного земледелия (Dinesh et al., 2012). Этот факт следует учитывать при использовании наночастиц металлов, в том числе и железа, в качестве удобрений, так как очень часто наночастицы металлов могут проявлять сильные противомикробные свойства (Vitta et al., 2020).
Результаты оценки влияния наночастиц железа на образование микробных консорциумов в почве в присутствии гербицида трифлуралина показали, что наночастицы Fe(0) позволили увеличить видовое разнообразие микроорганизмов в почве и тем самым оказали благоприятное воздействие на формирование микробного консорциума, который был устойчив к трифлуралину и состоял из четырех штаммов бактерий и одного штамма грибов (Postolachi et al., 2019). S. He et al. в своей работе обнаружил, что магнитные наночастицы γFe 2 O 3 при попадании в почву могут изменять структуру сообщества почвенных бактерий, способствуя росту некоторых бактерий в почве. Кроме того, оказалось, что структура бактериального сообщества в данном случае зависит от концентрации наночастиц (He et al., 2011). В другой работе было отмечено, что влияние наночастиц Fe(0) на микробные сообщества зависит от содержания органических веществ и типа минеральных веществ почвы. Например, совместное добавление в почву 5% органического вещества (соломы) и наночастиц Fe(0) привело к снижению микробной биомассы почвы на 29% (Pawlett et al., 2013).
Еще одним способом повышения продуктивности сельскохозяйственных культур является использование различных биопрепаратов, в основе которых лежат аэробные бактерии родов
Bacillus, Azotobacter, Pseudomonas, Micrococcus, Pseudobacterium, Rhizobium, участвующие в процессах гумификации и минерализации органического вещества (Аипова и др., 2019). В результате применения биопрепаратов увеличивается корнеобразование, повышается всхожесть семян и клубней, возрастает иммунитет растений к грибковым заболеваниям, а также улучшаются потребительские свойства. Как следствие положительного влияния биопрепаратов ускоряется рост и развитие растений и повышается урожайность (Нугманова, 2017). Растения, инокулированные биопрепаратами, содержащими ризобактерии, становятся более устойчивыми к абиотическим стрессам благодаря морфологическим и биохимическим модификациям за счет различных механизмов: выработки 1-аминоциклопропан-1-карбоксилата деамина-зы, снижения производства стрессового этилена, изменения содержания фитогормонов, улучшения поглощения основных минеральных элементов, выработки внеклеточных полимерных веществ, снижения абсорбции тяжелых металлов и индукции синтеза растительных антиоксидантных ферментов и генов абиотической стрессоустойчивости (Etesami, Maheshwari, 2018).
Ранее было установлено, что при воздействии на почву и растения Fe-содержащими биопрепаратами изменяется активность ферментов, отвечающих за превращения основных биогенных элементов (углерод и азот) и окислительно-восстановительные процессы, происходящие в почве (Любимова, Рабинович, 2023).
Цель данной работы заключается в исследовании влияния как раздельного, так и совместного использования ЖФБ и наночастиц Fe 3 O 4 на урожайность картофеля сорта Скарб в условиях нечерноземной зоны, а также на микрофлору дерново-подзолистой почвы в данном агроценозе.
ОБЪЕКТЫ И МЕТОДЫ
Объекты исследований – картофель сорта Скарб, обработанный ЖФБ-Fe, содержащим в своем составе наночастицы Fe 3 O 4 , ЖФБ и наночастицами Fe 3 O 4 , а также почва под картофелем.
Согласно данным Госреестра по Северо-Западному и Центральному регионам, картофель сорта Скарб относится к средне- спелым сортам столового назначения. Растение средней высоты, промежуточного типа, полупрямостоячее с темно-зелеными открытыми листьями среднего размера. Венчик цветка средний, белый. Товарная урожайность находится в диапазоне 253–411 ц/га, на уровне стандарта для сорта Петербургский. Максимальная урожайность может достигать 508 ц/га (на 133 ц/га выше стандарта Петербургский (Вологодская обл.)). Клубень имеет овальную форму с гладкой кожурой и очень мелкие глазки. Цвет кожуры и мякоти желтый. Масса товарного клубня варьируется от 94 до138 г с содержанием крахмала 10.8–17.7% (на 0.9–1.5% ниже стандартов для сортов Петербургский, Голубизна). Клубни с хорошим вкусом. Товарность 84–99%, на уровне стандартов для сортов Голубизна, Бронницкий. Лежкость 88–99%. Устойчив к возбудителю рака картофеля и золотистой картофельной цистообразующей нематоде. По данным ВНИИ фитопатологии, восприимчив к возбудителю фитофтороза по ботве и клубням. По данным оригина-тора, устойчив к морщинистой, полосчатой мозаике. Ценность сорта заключается в устойчивости к нематодам, высокой урожайности, выровненности и высоком выходе товарных клубней, а также в их лежкости.1
Биосинтез наночастиц Fe3O4 был выполнен с применением экстракта зеленого чая (Shahwan et al., 2011) (марка “Принцесса Ява, Традиционный”, производства ООО “НЕП”) и раствора FeSO4∙7H2O концентрацией 0.1 моль/л. Для получения наночастиц экстракт зеленого чая (5 г чая на 100 мл воды нагрели на водяной бане при 80 °С в течение 20 минут) смешали с раствором сульфата железа в объемном соотношении 1 : 1 (экстракт : раствор соли) и оставили на 24 часа при температуре 55 °С для завершения реакции. При этом было отмечено выпадение хлопьевидного осадка и изменение цвета раствора со светло-зеленого на черный. После инкубации раствор был выпарен при 105 °С в течение 6 часов для получения 2.5 г порошка, содержащего наночастицы. Полученный порошок, содержащий наночастицы Fe3O4, был исследован методами просвечивающей электронной микроскопии (ПЭМ) и энер- годисперсионной рентгеновской спектроскопии (EDX), выполненными в лаборатории компании “Системы для Микроскопии и Анализа” (г. Москва).
Жидкофазный биопрепарат (ЖФБ), разработанный во Всероссийском научно-исследовательском институте мелиорированных земель, – это жидкость темно-коричневого цвета, полученная ферментацией смеси низинного торфа и навоза крупного рогатого скота с последующей экстракцией солевым раствором и имеющая слабощелочной уровень рН (7.5–8.5). В составе ЖФБ содержатся макро- и микроэлементы и биологически активные вещества, а также агрономически полезные аммонифицирующие, амилолитические, фосфатмобилизующие микроорганизмы и микроскопические грибы, количество которых может достигать 1012 КОЕ/мл (Fomicheva et al., 2023). Для получения усовершенствованного ЖФБ-Fe наночастицы были введены в готовый жидкофазный биопрепарат (ЖФБ) для усиления его полифункциональных свойств в дозе 100 мг порошка на 1 л ЖФБ. В модернизированном ЖФБ-Fe, а также в исходном ЖФБ общепринятым микробиологическим методом предельных разведений на твердых питательных средах в трехкратной аналитической повторности определяли численность мезофильных (инкубация при 28 °С) микроорганизмов: использующих минеральные формы азота – на крахмало-аммиачном агаре (КАА), использующих органические формы азота – на мясопептонном агаре (МПА).
Полевые опыты по выращиванию картофеля сорта Скарб проводили на агрополигоне Губино Всероссийского научноисследовательского института мелиорированных земель (Тверская обл.) в 2020–2022 гг. На данном участке дерново-подзолистая легкосуглинистая почва со средней степенью кислотности (рН KCI 4.8– 5.0). Количество органического углерода варьируется в диапазоне 1.2–1.5% (по Тюрину), P 2 O 5 176–190 мг/кг (по Кирсанову), K 2 O 234–247 мг/кг (по Кирсанову), N лг 35–38 мг/кг (по Тюрину и Кононовой). Картофель возделывали по технологии, принятой для культуры. Опыты проводили по фону минерального удобрения – нитроаммофоски (N 65 Р 65 К 65 ).
Продукты ЖФБ-Fe, ЖФБ, а также раствор наночастиц оксида железа (Fe НЧ) (концентрация 100 мг/л) применяли следующими способами: в 2020 г. – обработка клубней картофеля ЖФБ и ЖФБ-Fe, трехкратное опрыскивание растений картофеля ЖФБ и ЖФБ-Fe, а также совмещение указанных приемов. Концентрация биопрепаратов была одинаковой и рекомендованной для ЖФБ – 1%. В 2021 г., кроме технологических приемов (обработка клубней перед посадкой и опрыскивание растений), варьировалась концентрация ЖФБ-Fe от 0.5 до 2.0%. В 2022 г. – обработка клубней картофеля ЖФБ и ЖФБ-Fe, а также раствором наночастиц оксида железа (Fe НЧ) и трехкратное опрыскивание растений картофеля биопрепаратами ЖФБ и ЖФБ-Fe, а также раствором наночастиц оксида железа (Fe НЧ). Во всех случаях обработку клубней осуществляли за 2 ч до посадки из ручного опрыскивателя (расход – 50 л/т клубней), а некорневую обработку растений – на этапах всходов, бутонизации и цветения (расход на каждом этапе составил 1 л/га). Контроль – фон NPK. Повторность опытов четырехкратная, расположение делянок систематизированное. Общая площадь делянки составила 7 м2.
Почвенные пробы были асептически отобраны для определения численности микроорганизмов, использующих минеральные формы азота – на крахмало-аммиачном агаре (КАА), использующих органические формы азота – на мясо-пептонном агаре (МПА), и фосфатмобилизующих микроорганизмов (среда Менки-ной)2, трижды за сезон вегетации из прикорневого слоя. Так как количество микроорганизмов в течение сезона вегетации было практически одинаковым, для дальнейших расчетов были использованы средние показатели. Кроме того, для получения более полного представления о процессах, происходящих в почве под влиянием используемых биопрепаратов, в почвенных образцах оценивалось содержание легкогидролизуемого азота (по Корнфилду), NO 3 (ГОСТ 26951) и NH 4 (ГОСТ 26489).
По окончании вегетации культуры определяли биологическую урожайность картофеля и его структуру сплошным методом, взвешивая урожай с каждой учетной делянки (Доспехов, 1984).
Погодные условия и водно-воздушный режим пахотного слоя почвы вегетационного периода (май–август) в годы исследований несколько различались, что характерно для Нечерноземной зоны России. Вследствие частых дождей 2020 г. характеризовался избыточной влажностью (ГТК = 2.32), температура воздуха была ниже климатической нормы; 2021 г. можно охарактеризовать как засушливый (ГТК = 0.96), а температура воздуха несколько выше климатической нормы. Вегетационный период 2022 г. был слабозасушливым (ГТК = 1.28) с кратковременными дождями в конце мая, температура воздуха за весь вегетационный период была выше климатической нормы (Любимова, Рабинович, 2023).
Для обработки результатов исследований использовали методы дисперсионного и корреляционного анализов, заложенные в программу Microsoft Office Excel 2007. Данные в таблицах представили в виде среднеарифметического значения (объем выборки n = 4). Статистическую значимость отличий анализировали с использованием t -критерия Стьюдента (р < 0.05). Достоверность различий урожайности и элементов структуры урожая картофеля оценивали путем проведения двухфакторного дисперсионного анализа с вычислением НСР при 5%-ном уровне значимости, n = 12.
РЕЗУЛЬТАТЫ И ОБСУЖДЕНИЕ
Изменение цвета чая при получении наночастиц Fe 3 O 4 с желто-зеленого на черный, а также выпадение хлопьевидного осадка в процессе суточной инкубации раствора свидетельствовали о формировании наночастиц оксида железа. Кроме того, в процессе синтеза наночастиц было зафиксировано изменение рН растворов с 5.1 до 2.4, что также свидетельствовало о формировании наночастиц железа. Подобные изменения наблюдались и в других работах. Например, в работе М.А. Asghar et al. говорится об очень быстром изменении цвета раствора с желтого на черный при смешивании экстракта зеленого чая и раствора хлорида железа (III).
По мнению авторов, это изменение произошло из-за возникновения поверхностного плазмонного резонанса и восстановления ионов железа экстрактом чайных листьев. Кроме того, в этой работе также отмечалось снижение рН смеси с 5.2 до 2.9 (Asghar et al., 2018). V.C. Karade et al. в своей работе отметили зеленоваточерный цвет раствора при смешивании 0.1 М раствора нитрата железа и экстракта зеленого чая, что свидетельствовало о формировании наночастиц железа Fe(0). T. Shahwan et al. в своей работе отмечали появление интенсивного черного осадка при добавлении 1.0 М раствора NaOH в смесь чая и 0.1 М раствора FeCl 2 ·4H 2 O, что также свидетельствовало о формировании наночастиц железа (Shahwan et al., 2011).
Результаты ПЭМ и EDX представлены на рисунках 1 и 2. На полученной ПЭМ микрофотографии (рис. 1) видно, что в процессе биосинтеза сформировались наночастицы различной формы и размера. Так в образце присутствует фракция небольших частиц размером около 10 нм, а также наночастицы сферической формы диаметром 30–35 нм. Кроме того, встречаются наночастицы размером более 50 нм различной формы. По данным EDX спектра сильный сигнал с самым высоким процентом для железа наблюдался в области 6.3 кэВ, что указывает на чистоту и стабильность синтезированных наночастиц. При этом наличие железа и кислорода подтверждает образование наночастиц Fe 3 O 4 . Кроме того, на спектре обнаружили типичный пик оптического поглощения при 0.5 кэВ, обусловленный поверхностным плазмонным резонансом. Присутствие Cu, вероятно, связано с медной сеткой с углеродным покрытием, используемой для подготовки образцов. Тогда как пик серы в области 2.4 кэВ связан, скорее всего, с сульфат ионами, образовавшимися в процессе восстановления FeSO 4 . Таким образом, полученные результаты подтверждают восстановление сульфата железа до стабильных наночастиц Fe 3 O 4 посредством экстракта зеленого чая.
Согласно результатам микробиологического анализа добавление синтезированных наночастиц Fe 3 O 4 в ЖФБ не оказало негативного воздействия на его микрофлору, так как количество азоттрансформирующих микроорганизмов снизилось всего в 1 .2 раза
(с 25∙1011 КОЕ/мл до 20∙1011 КОЕ/мл). При этом рН обоих препаратов остается на уровне 8.5–8.6.

Рис. 1. ПЭМ-микрофотография порошка, содержащего наночастицы железа.
Fig. 1. TEM microphotography of a powder containing iron nanoparticles.
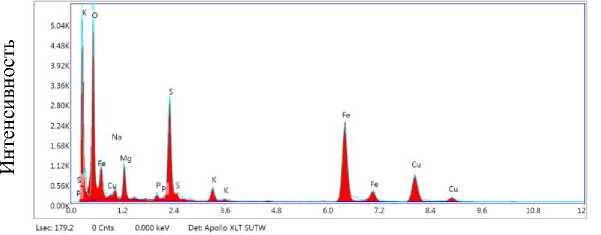
Энергия, кэВ
Рис. 2. EDX спектр порошка, содержащего наночастицы железа.
Fig. 2. EDX spectrum of powder containing iron nanoparticles.
В первый год исследований (2020) варьировались технологические приемы применения ЖФБ и ЖФБ-Fe: обработка клубней перед посадкой, некорневая обработка по листу и совмещение этих двух приемов. При этом концентрация препаратов была одинаковой (1%), как и доза, рекомендованная для ЖФБ. При обработке клубней ЖФБ и ЖФБ-Fe урожайность (табл. 1) увеличилась на 8.4 и 17.5% по сравнению с контролем (фон NPK), тогда как при опрыскивании вегетирующих растений ЖФБ и ЖФБ-Fe прибавка к контролю составила 5.5 и 10.5% соответственно. Такая прибавка к урожайности в основном была связана со средним количеством товарных клубней на один куст, число которых в контроле было равно 5, при обработке клубней ЖФБ и ЖФБ-Fe – 6 и 8, а при опрыскивании растений – 6 и 7. Отметим, что при этом средняя масса товарных клубней была практически одинаковой во всех вариантах. Однако при совмещении технологических приемов применения ЖФБ-Fe урожайность картофеля снизилась на 12.9%, по сравнению с контролем, и составила 154.7 ц/га, что, по-видимому, было связано с ингибированием развития культуры, вызванным избытком железа. В то же время в аналогичном варианте с применением исходного ЖФБ, прибавка урожайности в котором составила 6.3% (188.7 ц/га), ингибирования роста растений не отмечали. В дальнейшем исследовании вариант совмещения двух технологических приемов был исключен из схемы опыта.
В 2021 г., помимо способа применения биопрепаратов, было исследовано влияние различных концентраций (0.5%, 1% и 2%) ЖФБ-Fe на урожайность картофеля. Так, при обработке клубней 0.5%-ным ЖФБ-Fe урожайность относительно контроля увеличилась на 20.1 ц/га, а при опрыскивании растений – на 21.5 ц/га, тогда как увеличение концентрации биопрепарата до 2% способствовало увеличению урожайности всего лишь на 8.4 ц/га при обработке клубней и на 2.9 ц/га при опрыскивании растений. Вероятно, что, как и в случае совмещения двух технологических приемов, в данном случае развитие картофеля замедляется избытком железа.
Максимальная прибавка к урожайности (25.3%) во второй год исследований была получена при некорневой обработке рас- тений 1%-ным ЖФБ-Fe, а обработка клубней этим же препаратом привела к увеличению урожайности на 14.8%. При этом обработка и клубней, и растений картофеля 1%-ным ЖФБ позволила увеличить урожайность всего лишь на 5.8% и 13.7% по сравнению с контролем. Важно отметить, что применение ЖФБ-Fe любым из способов не повлияло на среднюю массу клубней картофеля (средняя масса крупных клубней составила 130–140 г, средних – 60–70 г), а существенный прирост его урожайности в варианте с использованием 1%-ного ЖФБ-Fe формировался за счет увеличения среднего количества товарных клубней с одного куста (6 клубней в контрольном варианте, 7–8 – в вариантах опыта).
В третий год исследований (2022) для выявления у разработанного ЖФБ-Fe синергетического действия его компонентов (собственно препарата и наночастиц железа) в схему опыта добав-ли применение 1%-ного раствора синтезированных наночастиц оксида железа (Fe НЧ). При использовании только наночастиц железа урожайность увеличилась на 5.3% при некорневой обработке растений и на 2.6% при обработке клубней. В то же время при обработке клубней и растений 1%-ным ЖФБ урожайность увеличилась на 6 и 10.6% соответственно, а при применении ЖФБ-Fe – на 11.7% при обработке клубней и на 15.4% при опрыскивании растений. Таким образом, при использовании ЖФБ-Fe наблюдался явный синергетический эффект от действия компонентов препарата на растения картофеля, выраженный в более существенной прибавке урожайности относительно контрольного варианта (Любимова, Рабинович, 2023).
Таким образом, наибольшая урожайность за три года исследования была получена от применения 1%-ного ЖФБ-Fe. Так, при обработке клубней средний прирост урожайности относительно контрольного варианта составил 14.8%, а при некорневой обработке растений – 16.9%, тогда как обработка клубней 1%-ным ЖФБ привела к увеличению урожайности на 6.8%, а опрыскивание растений картофеля – на 9.8% в среднем за три года. Увеличение урожайности в вариантах с применением ЖФБ-Fe по листу, вероятно, связано с тем, что железо в наноформе, полученное в результате биосинтеза, способно быстрее проникать в раститель- ный организм и участвовать во многих фундаментальных физиологических процессах растений, таких как биосинтез хлорофилла, дыхание и окислительно-восстановительные реакции. Тогда как при обработке клубней наночастицы железа, попадая в почву, частично переходят в форму, менее доступную для растения, следовательно, некорневая обработка вегетирующих растений является предпочтительным приемом использования ЖФБ-Fe (Любимова, Рабинович, 2023). Однако при применении ЖФБ-Fe также следует учитывать и погодные условия, и водно-воздушный режим пахотного слоя почвы в вегетационный период. В более влажный год (2020) наибольшая урожайность была получена при обработке клубней картофеля 1%-ным ЖФБ-Fe (табл. 1). Тогда как в засушливые и умеренно засушливые периоды (2021 и 2022 гг.) некорневая обработка растений является дополнительным источником влаги, что также влияет на повышение урожайности.
Положительное влияние наночастиц железа на продуктивность растений было замечено и в других работах. Например, S. Sharma et al. в своей работе отмечали, что после двукратной обработки растений сои наночастицами железа тестовая масса семян (масса 100 семян) увеличилась на 44% по сравнению с контролем. T. Raiesi ‑ Ardali et al. показали, что присутствующие в почве наночастицы Fe 3 O 4 , покрытые гуминовыми кислотами, существенно влияют на рост и физиологические параметры растений томата. Так, в присутствии наночастиц Fe 3 O 4 , покрытых гуминовыми кислотами, c концентрацией 50 мг/кг почвы высота растений увеличилась на 31%, по сравнению с контролем, а биомасса свежих и сухих побегов – на 68% и 97% соответственно (Raiesi ‑ Ardali et al., 2022).
Как уже упоминалось выше, микробиологические показатели относятся к наиболее важным тестовым характеристикам почвы, поскольку обитающая в почвенной толще микрофлора, обеспечивая эффективное разложение высокомолекулярных питательных веществ до доступных форм, способствует, наряду с прочими положительными проявлениями своей деятельности, повышению урожайности культурных растений.
Таблица 1. Урожайность картофеля сорта Скарб
Table 1. Yield of potato variety Skarb
|
Вариант опыта |
Урожайность картофеля, ц/га |
Средняя урожайность, ц/га |
||
|
2020 |
2021 |
2022 |
||
|
NPK (фон) – контроль |
177.5 |
163.6 |
149.4 |
163.5 |
|
Обработка клубней картофеля |
||||
|
1% ЖФБ |
192.4 (+8.4*) |
173.0 (+5.7%) |
158.4 (+6.0) |
174.6 (+6.8) |
|
0.5% ЖФБ-Fe |
- |
183.7 (+12.4) |
- |
183.7 (+12.4) |
|
1% ЖФБ-Fe |
208.6 (+17.5) |
187.8 (+14.8) |
166.9 (+11.7) |
187.8 (+14.8) |
|
2% ЖФБ-Fe |
- |
172.0 (+5.2) |
- |
172.0 (+5.2) |
|
1% Fe НЧ |
- |
- |
153.4 (-6.2) |
153.4 (-6.2) |
|
Некорневая обработка растений |
||||
|
1% ЖФБ |
187.3 (+5.5) |
186.0 (+13.7) |
165.3 (+10.6) |
179.5 (+9.8) |
|
0.5% ЖФБ-Fe |
- |
185.1 (+13.2) |
- |
185.1 (+13.2) |
|
1% ЖФБ-Fe |
196.1 (+10.5) |
204.9 (+25.2) |
172.5 (+15.5) |
191.2 (+16.9) |
|
2% ЖФБ-Fe |
- |
166.5 (+1.8) |
- |
166.5 (+1.8) |
|
1% Fe НЧ |
- |
157.3 (-3.8) |
157.3 (-3.8) |
|
|
Обработка клубней картофеля + некорневая обработка растений |
||||
|
1% ЖФБ |
188.7 (+6.3) |
- |
- |
188.7 (+6.3) |
|
1% ЖФБ-Fe |
154.7 (-12.9) |
- |
- |
154.7 (-12.9) |
|
НСР 05 по фактору А |
4.6 |
3.7 |
4.0 |
|
|
НСР 05 по фактору В |
4.6 |
4.2 |
5.6 |
|
|
НСР 05 |
8.0 |
10.6 |
7.9 |
|
Примечание. *в скобках указана прибавка к контролю в %.
Note. *The additional yield compared to the control (in %) is given in brackets.
В связи с этим было исследовано влияние нового биопрепарата ЖФБ-Fe на микрофлору почвы, а именно на содержание в почве доминантных физиологических групп микрофлоры – фосфатмо-билизующих (мобилизующих органофосфаты) и микроорганизмов, использующих минеральные и органические формы азота (азоттрансформирующие микроорганизмы). Кроме того, был рассчитан условный коэффициент минерализации почвы (Км) как отношение численности микроорганизмов, потребляющих минеральные формы азота (амилолитических), к количеству микроорганизмов, использующих преимущественно его органические формы (аммонификаторов) (табл. 2). Также с помощью регрессионного анализа была определена зависимость урожайности, сформированной в вариантах опыта, от почвенной микрофлоры. Поскольку ранее было показано (Фомичева и др., 2018), что некорневые обработки растений ЖФБ оказывают существенное влияние на микрофлору почвы, были рассмотрены оба способа применения ЖФБ-Fe по отдельности (табл. 2).
В первый год исследований при обработке клубней картофеля 1%-ным ЖФБ количество азоттрансформирующих и фос-фатмобилизующих микроорганизмов, а также коэффициент минерализации увеличились практически в 2 раза, по сравнению с контролем, тогда как обработка клубней 1%-ным ЖФБ-Fe привела к уменьшению фосфатмобилизующих микроорганизмов в 2 раза, а коэффициента минерализации в 1 .3 раза по сравнению с контролем. При этом количество азоттрансформирующих бактерий в этом варианте и в контроле было одинаковым. Данные регрессионного анализа показали, что между Км и урожайностью картофеля, а также между количеством азоттрансформирующих микроорганизмов и урожайностью существует взаимосвязь, которую можно описать уравнениями: y = -0.3892х + 86.4924 и y = -1.4060x + 313.4986. При некорневой обработке растений картофеля обоими биопрепаратами количество азоттрансформирующих микроорганизмов было одинаковым и практически равно контролю, тогда как Км снизился в 1 .3 раза по сравнению с контролем при использовании ЖФБ-Fe. В то же время количество фосфатмобилизующих микроорганизмов в этом варианте, наоборот, увеличилось в 1.4 раза по сравнению с контролем. Кроме того, были получены уравнения зависимости урожайности от коэф- фициента минерализации и количества азоттрансформирующих микроорганизмов: y = -0.1248х + 29.6902 и y = 0.0217х + 16.2325 соответственно. При совмещении двух технологических приемов применения ЖФБ и ЖФБ-Fe количество азоттрансформирующих микроорганизмов увеличилось в 1 .8 и 1.4 раза, а количество фос-фатмобилизующих микроорганизмов – в 1.4 раза в обоих вариантах по сравнению с контролем. При этом Км увеличился в 1 .4 раза по сравнению с контролем только при использовании ЖФБ. В данном случае уравнения зависимости урожайности от Км и количества азоттрансформирующих микроорганизмов имеют следующий вид: y = 0.1098x – 10.945 и y = 0.199х – 0.6325.
При варьировании концентрации ЖФБ-Fe (второй год исследований) при обработке клубней картофеля количество азоттрансформирующих микроорганизмов увеличилось в 1 .2–1.5 раза по сравнению с контролем, тогда как количество фосфатмобили-зующих бактерий возросло в 1.6–1.7 раз по сравнению с контролем (табл. 2). При этом при использовании для обработки клубней 1%-ного ЖФБ количество исследуемых микроорганизмов было таким же, как и в вариантах ЖФБ-Fe (табл. 2).
Более того, при использовании ЖФБ-Fe была обнаружена заметная обратная корреляция между концентрацией биопрепарата и количеством азоттрансформирующих микроорганизмов как при обработке клубней, так и при опрыскивании растений: коэффициенты корреляции (r) равны -0.68 и -0.65 соответственно. Помимо этого, при обработке клубней картофеля была обнаружена отрицательная умеренная связь между количеством азоттрансформирующей микрофлоры и суммой аммиачного и нитратного азота (r = -0.30), тогда как при некорневой обработке растений также наблюдалась обратная взаимосвязь между содержанием легкогидролизуемого азота (N лг , табл. 2) и микрофлорой – коэффициент корреляции r = -0.41.
Таблица 2. Результаты микробиологического и агрохимического анализов почвы под картофелем
Table 2. Results of microbiological and agrochemical analyzes of soil under potatoes
|
Год |
Вариант опыта |
Микроорганизмы |
Км |
NO 3 + NH 4 , мг/кг |
N лг , мг/кг |
|
|
Азоттранс-формирующие, млн КОЕ/г почвы |
Фосфат-мобилизующие, млн КОЕ/г почвы |
|||||
|
2020 |
Фон NPK – контроль |
21.0 ± 1.7 |
15.7 ± 2.5 |
6.78 |
44.8 ± 3.9 |
30.8 ± 2.7 |
|
2021 |
25.7 ± 0.8 |
17.6 ± 2.6 |
6.44 |
55.6 ± 3.1 |
47.8 ± 6.0 |
|
|
2022 |
21.3 ± 1.2 |
22.1 ± 4.1 |
6.36 |
78.0 ± 2.5 |
53.1 ± 2.1 |
|
|
Обработка клубней картофеля |
||||||
|
2020 |
1% ЖФБ |
43.0 ± 2.8 |
30.0 ± 3.4 |
11.62 |
25.5 ± 3.1 |
29.8 ± 1.8 |
|
1% ЖФБ-Fe |
20.2 ± 1.6 |
7.8 ± 0.3 |
5.30 |
20.4 ± 2.1 |
30.1 ± 4.5 |
|
|
2021 |
1% ЖФБ |
30.9 ± 0.4 |
29.1 ± 0.7 |
7.05 |
42.9 ± 5.4 |
34.8 ± 2.6 |
|
0.5% ЖФБ-Fe |
38.2 ± 0.3 |
27.8 ± 2.5 |
5.98 |
40.1 ± 1.3 |
32.9 ± 1.5 |
|
|
1% ЖФБ-Fe |
29.7 ± 1.7 |
29.3 ± 1.3 |
11.45 |
38.8 ± 1.6 |
32.0 ± 3.6 |
|
|
2% ЖФБ-Fe |
30.7 ± 0.8 |
27.7 ± 3.8 |
4.87 |
50.9 ± 5.0 |
36.6 ± 3.5 |
|
|
2022 |
1% ЖФБ |
31.9 ± 0.5 |
24.6 ± 3.8 |
7.74 |
66.5 ± 1.8 |
49.5 ± 1.7 |
|
1% ЖФБ-Fe |
16.5 ± 2.0 |
15.6 ± 1.9 |
3.95 |
57.4 ± 1.2 |
48.8 ± 1.7 |
|
|
1% Fe НЧ |
17.5 ± 1.9 |
15.1 ± 0.5 |
4.18 |
65.1 ± 2.0 |
53.7 ± 2.3 |
|
Продолжение таблицы 2
Table 2 continued
|
Год |
Вариант опыта |
Микроорганизмы |
Км |
NO 3 + NH 4 , мг/кг |
Nлг, мг/кг |
|
|
Азоттранс-формирующие, млн КОЕ/г почвы |
Фосфат-мобилизующие, млн КОЕ/г почвы |
|||||
|
Некорневая обработка растений |
||||||
|
2020 |
1% ЖФБ |
20.3 ± 2.3 |
13.6 ± 0.3 |
6.31 |
33.3 ± 2.7 |
29.8 ± 3.0 |
|
1% ЖФБ-Fe |
20.5 ± 1.1 |
22.2 ± 2.2 |
5.21 |
24.5 ± 1.5 |
28.0 ± 1.7 |
|
|
2021 |
1% ЖФБ |
32.9 ± 5.1 |
32.3 ± 3.4 |
13.56 |
42.8 ± 2.5 |
38.0 ± 3.8 |
|
0.5% ЖФБ-Fe |
45.1 ± 3.4 |
39.9 ± 5.4 |
7.71 |
43.2 ± 0.8 |
37.1 ± 5.1 |
|
|
1% ЖФБ-Fe |
35.7 ± 3.1 |
24.3 ± 2.3 |
2.02 |
50.5 ± 4.8 |
41.1 ± 4.0 |
|
|
2% ЖФБ-Fe |
37.1 ± 1.2 |
31.5 ± 1.2 |
11.90 |
54.1 ± 1.0 |
42.0 ± 5.9 |
|
|
2022 |
1% ЖФБ |
23.7 ± 0.1 |
21.7 ± 1.8 |
7.60 |
61.9 ± 1.3 |
52.3 ± 6.2 |
|
1% ЖФБ-Fe |
23.6 ± 5.8 |
16.1 ± 3.9 |
3.34 |
71.3 ± 2.1 |
55.8 ± 6.8 |
|
|
1% Fe НЧ |
24.9 ± 1.4 |
25.1 ± 1.9 |
3.66 |
75.1 ± 5.2 |
60.4 ± 5.1 |
|
|
Обработка клубней картофеля + некорневая обработка растений |
||||||
|
2020 |
1% ЖФБ |
36.9 ± 0.3 |
18.5 ± 1.3 |
9.78 |
31.7 ± 2.3 |
29.4 ± 1.9 |
|
1% ЖФБ-Fe |
30.1 ± 1.8 |
18.5 ± 2.8 |
6.04 |
39.7 ± 4.5 |
39.6 ± 2.3 |
|
Согласно регрессионному анализу, взаимосвязь между урожайностью картофеля и коэффициентом минерализации почвы довольно сильная и статистически значимая. Так, зависимость урожайности картофеля от Км почвы при обработке клубней описывалась уравнением регрессии у = 0.2639х – 39.9329 с коэффициентом корреляции r = 0.72, а при некорневой обработке растений картофеля зависимость оказалась обратной и описывалась уравнением регрессии у = -0.2536х + 55.882 с коэффициентом корреляции r = -0.77. Высокие значения коэффициентов корреляции доказывают, что почвенные микробиологические процессы, сформированные под влиянием исследуемых биопрепаратов, значительно влияют на урожайность картофеля. Важно отметить, что при этом урожайность картофеля практически не зависела от количества азоттрансформирующих микроорганизмов при использовании обоих технологических приемов.
При использовании для обработки клубней 1%-ного раствора наночастиц Fe3O4 (Fe НЧ) количество азоттрансформирующих и фосфатмобилизующих микроорганизмов снизилось в 1 .2 и 1.5 раза соответственно по сравнению с контролем (табл. 2). Однако при некорневой обработке картофеля численность почвенной микрофлоры практически не изменилась под влиянием Fe НЧ. Как и в предыдущий год, на данном этапе можно отметить заметную корреляцию между количеством азоттрансформирующих микроорганизмов и суммой аммиачного и нитратного азота в обоих технологических приемах – коэффициенты корреляции: r = 0.66 и r = 0.69 при обработке клубней и опрыскивании растений соответственно. Вместе с тем при некорневой обработке растений наблюдалась сильная прямая взаимосвязь между микрофлорой и содержанием легкогидролизуемого азота – коэффициент корреляции r = 0.88. Регрессионный анализ показал, что при реализации обоих технологических приемов применения исследуемых препаратов не обнаруживалась зависимость урожайности картофеля от коэффициента минерализации почвы. Отметим, что при обработке клубней картофеля прослеживалась слабая взаимосвязь между урожайностью и количеством азоттрансформирующих микроорганизмов, однако, при некорневой обработке растений данная взаи- мосвязь, наоборот, была очень сильной: коэффициент корреляции достиг r = -0.90 при уравнении регрессии у = -0.0841х + 37.9421.
ВЫВОДЫ
Результаты трехлетнего эксперимента (2020–2022 гг.) показали, что при опрыскивании вегетирующих растений 1%-ным ЖФБ-Fe урожайность картофеля увеличилась на 16.9%, а при обработке клубней перед посадкой – на 14.8% по сравнению с контролем (фон NPK). В то же время при использовании ЖФБ урожайность картофеля увеличилась на 9.8% при обработке по листу и на 6.8% при обработке клубней по сравнению с контролем. Тогда как при совмещении двух технологических приемов применения ЖФБ-Fe урожайность картофеля снизилась на 12.9%.
При исследовании почвенной микробиоты было отмечено, что введение в ЖФБ наночастиц Fe3O4 влияет на количество азоттрансформирующих и фосфатмобилизующих почвенных микроорганизмов при любом технологическом приеме применения ЖФБ-Fe. Также под влиянием наночастиц Fe3O4, введенных в ЖФБ, может изменяться коэффициент минерализации почвы, что в свою очередь может привести к изменению урожайности картофеля. При варьировании концентраций ЖФБ-Fe зависимость урожайности картофеля от Км почвы была сильной как при обработке клубней (уравнение регрессии у = 0.2639х – 39.9329 с коэффициентом корреляции r = 0.72), так и при опрыскивании растений картофеля (уравнение регрессии у = -0.2536х + 55.882 с коэффициентом корреляции r = -0.77). Кроме этого, на урожайность картофеля в некоторых случаях может оказать воздействие и количество азоттрансформирующих микроорганизмов. Например, при введении в схему опыта 1%-ного раствора наночастиц Fe3O4 при некорневой обработке растений обратная взаимосвязь между урожайностью и количеством азоттрансформирующих микроорганизмов была очень сильной: коэффициент корреляции r = -0.90, при уравнении регрессии у = -0.0841х + 37.9421, тогда как при обработке клубней подобной зависимости не наблюдалось. Таким образом, различные способы применения ЖФБ-Fe могут по-разному влиять на микрофлору почвы, что в свою очередь приводит к перестройке микробного консорциума дерново-подзолистой почвы и влечет за собой изменение в уровне почвенного плодородия, способствуя в итоге либо снижению, либо повышению урожайности картофеля. Более того, повышение урожайности при применении ЖФБ-Fe по листу, вероятно, связано с тем, что наночастицы быстрее проникают в растительный организм, стимулируя биосинтез хлорофилла, дыхание и окислительно-восстановительные реакции. Тогда как при обработке клубней наночастицы железа, попадая в почву, частично переходят в форму, менее доступную для растений, следовательно, некорневая обработка вегетирующих растений является предпочтительным приемом использования ЖФБ-Fe. Однако при применении ЖФБ и ЖФБ-Fe также следует учитывать и погодные условия и водно-воздушный режим пахотного слоя почвы в вегетационный период.
Список литературы Влияние наночастиц Fe3O4 на урожайность картофеля и развитие почвенной микрофлоры
- Аипова Р., Абдыкадырова А. Б., Курманбаев A. A. Биологические препараты в органическом земледелии // Биотехнология и селекция растений.2019. Вып. 2(4). С. 36-41. https://doi.org/10.30901/2658-6266-2019-4-o4.
- Доспехов Б.А. Методика полевого опыта (с основами статистической обработки результатов исследований). М.: Агропромиздат, 1984. 351 с.
- Иванищев В.В. Роль железа в биохимии растений // Известия ТулГУ. Естественные науки. 2019а. Вып. 3. С. 149-159.
- Иванищев В.В. Доступность железа в почве и его влияние на рост и развитие растений // Известия ТулГУ. Естественные науки. 2019б. Вып. 3. С. 127-138.
- Любимова Н.А., Рабинович Г.Ю. Влияние биопрепарата с наночастицами железа на активность почвенных ферментов и урожайность картофеля // Аграрная наука Евро-Северо-Востока. 2023. Т. 24. № 3. С. 417-429. https://doi.org/10.30766/2072-9081.2023.24.3.417-429.
- Нугманова Т.А. Использование биопрепаратов для растениеводства // Сборник научных трудов Государственного Никитского ботанического сада. 2017. Т. 144-1. С. 211-214.
- Фомичева Н.В., Рабинович Г.Ю., Смирнова Ю.Д. Влияние некорневых обработок вегетирующих растений на микрофлору почвы // Вестник Российской сельскохозяйственной науки. 2018. № 6. С. 19-23. https://doi.org/10.30850/vrsn/2018/6/19-23.
- Asghar М.А. et al. Iron, copper and silver nanoparticles: Green synthesis using green and black tea leaves extracts and evaluation of antibacterial, antifungal and aflatoxin B1 adsorption activity // LWT Food Science and Technology. 2018. Vol. 90. P. 98-107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2017.12.009.
- Babali N. et al. Synthesis of nano iron oxide and investigation of its use as a fertilizer ingredient // International Journal of Innovative Research and Reviews. 2022. Vol. 6(1). P. 6-10. URL: https://dergipark.org.tr/en/download/article-file/2553830.
- Briat J.-F., Dubos C., Gaymard F. Iron nutrition, biomass production, and plant product quality // Trends in plant science. 2015. Vol. 20. No. 1. P. 33- 40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2014.07.005.
- Chen L. et al. Comparative study of the effectiveness of nano-sized ironcontaining particles as a foliar top-dressing of peanut in rainy conditions // Agricultural Water Management. 2023. Vol. 286. P. 108392-108399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2023.108392.
- De Souza A. et al. Impact of Fe3O4 nanoparticle on nutrient accumulation in common bean plants grown in soil // SN Applied Sciences. 2019. Vol. 1. P. 308-315. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-0321-y.
- Dinesh R. et al. Engineered nanoparticles in the soil and their potential implications to microbial activity // Geoderma. 2012. Vol. 173-174. P. 19-27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2011.12.018.
- Duhan J.S. et al. Nanotechnology: The new perspective in precision agriculture // Biotechnology Reports. 2017. Vol. 15. P. 11-23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2017.03.002.
- Etesami H., Maheshwari D.K. Use of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPRs) with multiple plant growth promoting traits in stress agriculture: Action mechanisms and future prospects // Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety. 2018. Vol. 156. P. 225-246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.03.013.
- Fomicheva N., Rabinovich G., Kashkova A. The effect of the biopreparation of LPB on the yield of vegetable crops // E3S Web of Conferences. 2023. Vol. 390. P. 01016-01021.
- He S. et al. The impact of iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles on the soil bacterial community // J Soils Sediments. 2011. Vol. 11. P. 1408-1417. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-011-0415-7.
- Karade V.C. et al. Effect of reaction time on structural and magnetic properties of green-synthesized magnetic nanoparticles // Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids. 2018. Vol. 120. P. 161-166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2018.04.040.
- Ndaba B. et al. Biosynthesized metallic nanoparticles as fertilizers: An emerging precision agriculture strategy // Journal of Integrative Agriculture. 2022. Vol. 21(5). P. 1225-1242. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(21)63751-6.
- Nongbet A. et al. Nanofertilizers: a smart and sustainable attribute to modern agriculture // Plants. 2022. Vol. 11. P. 2587-2606. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11192587.
- Pawlett M. et al. The impact of Zero-valent iron nanoparticles upon soil microbial communities is context dependent // Environmental Science Pollution Research. 2013. Vol. 20. P. 1041-1049. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-0121196-2.
- Postolachi O. et al. Effect of iron nanoparticles and herbicide trifluralin on the formation of microbial consortia // Analele Universităţii din Oradea, Fascicula Biologie. 2019. Vol. 26. Is. 2. P. 117-123. URL: https://bioresearch.ro/2019-2/117-123-AUOFB.26.2.2019-POSTOLACHI.O.Effect.of.iron.nanoparticles.pdf.
- Raiesi Ardali T. et al. Improved iron use efficiency in tomato using organically coated iron oxide nanoparticles as efficient bioavailable Fe sources // Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2022. Vol. 9. P. 59-64. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40538022-00318-y.
- Rui M. at al. Iron oxide nanoparticles as a potential iron fertilizer for peanut (Arachis hypogaea) // Front. Plant Sci. 2016. Vol. 7. P. 815. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00815.
- Shahwan T. et al. Green synthesis of iron nanoparticles and their application as a Fenton-like catalyst for the degradation of aqueous cationic and anionic dyes // Chemical Engineering Journal. 2011. Vol. 172. P. 258- 266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.05.103.
- Sharma S., et al. Foliar application of organic and inorganic iron formulation induces differential detoxification response to improve growth and biofortification in soybean // Plant Physiol. Rep. 2019. Vol. 24. P.119- 128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40502-018-0412-6.
- Vitta Y. et al. Synthesis of iron nanoparticles from aqueous extract of Eucalyptus robusta Sm and evaluation of antioxidant and antimicrobial activity // Materials Science for Energy Technologies. 2020. Vol. 3. P. 97- 103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mset.2019.10.014.
- Yang X., Alidoust D., Wang C. Efects of iron oxide nanoparticles on the mineral composition and growth of soybean (Glycine maxL.) plants // Acta Physiologiae Plantarum. 2020. Vol. 42. P. 128-135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738020-03104-1.


