Влияние температуры на активность липоксигеназы в разновидностях Triticum aestivum L., отличающихся устойчивостью к абиотическим стрессорам
Автор: Бабенко Л.М.
Журнал: Журнал стресс-физиологии и биохимии @jspb
Статья в выпуске: 4 т.13, 2017 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Проанализированы эффекты высоких (+ 400 ° С, 2 ч) и низких положительных (+ 40 ° С, 2 ч) температур на активность липоксигеназы в разновидностях Triticum aestivum L., отличающихся своей стойкостью к абиотическим стрессорам. Впервые 9-липоксигеназная активность была идентифицирована в надземной части и корнях 14-дневных растений трех новых сортов озимой пшеницы, отобранных в Украине. Увеличение активности липоксигеназы как в надземной, так и в корневой частях растения оказалось неспецифическим ответом на гипертермию и гипотермию. Интенсивность реакции на тепловой стресс была значительно выше, чем у холодных эффектов. В надземной части жаростойкого сорта Yatran 60 кратковременная гипертермия вызывала четырехкратное увеличение активности липоксигеназы с рНопр5,5 и шестикратное увеличение активности липоксигеназы с рНопт 6.3. Активность липоксигеназы с рНопр в корнях возрастала в полтора раза. Активность липоксигеназы с рНопт 7,0 в надземной части морозостойкого сорта Володарка, подвергнутого гипертермии, увеличилась в полтора раза, а активность липоксигеназы с рНопт 6,0 - 1,3 раза, а в корнях активность липоксигеназы с рНопт 6,5 увеличилась на три время. В надземной части экологически гибкого сорта Подолянка, подвергнутого кратковременной гипертермии, активность липоксигеназы с рНопт 7.5 увеличивалась в полтора раза, липоксигеназа с рНопт в 5,5 - 1,7 раза, а в корнях активность липоксигеназы с рНопт 6,5 - почти в два раза. Наиболее выраженный ответ на гипертермию произошел в жаростойкой разновидности Ятран 60. Обсуждаются перспективы использования липоксигеназы в качестве маркера устойчивости растений, а также возможное вовлечение липоксигеназной активности в формирование механизмов адаптации клеток.
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14324024
IDR: 14324024
Текст научной статьи Влияние температуры на активность липоксигеназы в разновидностях Triticum aestivum L., отличающихся устойчивостью к абиотическим стрессорам
Одной из центральных проблем современной теоретической и практической биологии является изучение молекулярных и клеточных механизмов адаптации растений к абиотическим стрессам. Глобальные изменения климата, усиление антропогенной нагрузки на биосферу, которое сопровождается снижением агроэкологической надежности растениеводства, придает особое значение таким исследованиям. Экстремальные температуры являются одним из самых распространенных природных стрессоров, которые провоцируют нарушение водного режима, замедляют рост, влияют на урожайность аграрных культур (Hurkman, Wood, 2011; Barlow et al., 2015; Hatfield, Prueger, 2015). Среди компонентов, задействованных в формировании адаптивных реакций, важное место занимают сигнальные соединения, к которым относится ферменты липоксигеназы (ЛОГ) (Porta, Rocha–Sosa, 2002; Feussner, Wasternack, 2002). Липоксигеназный каскад является источником физиологически активных соединений – оксилипинов (Stumpe, Feussner, 2006; Mosblech et al. 2009; Savchenko et al., 2014; Babenko et al., 2017). Ключевой фермент каскада – ЛОГ (линолеат: оксидоредуктаза кислорода, EC 1.13.11.12) – металопротеин, катализирующий гидропере-окисление полиненасыщенных жирных кислот (ПНЖК) в липидах, содержащих цис, цис-1,4-пентадиеновые фрагменты. Образование гидропероксидов конъюгированных диенов – основная реакция в каскаде, приводящая к образованию семи энзиматических ветвей (Feussner, Waster, 2002; Andreou, Feussner, 2009; Ivanov et al., 2010; Joo, Oh, 2012; Babenko et al., 2017), конечными продуктами которых являются биологически активные метаболиты (Feussner, Waster, 2002; Meng et al., 2017), вовлекаемые в регуляцию процессов роста, развития а также в формирование соответствующих реакций на сигналы внешней среды и обеспечивающие определенную связь между царствами живых организмов (Van der Ent et al., 2009; Christensen, Kolomiets 2011; Savchenko et al., 2014; Borrego, Kolomiets, 2012, 2016; Babenko et al., 2014, 2017; Wasternack, 2007). Семейство ЛОГ можно разделить на две группы: 9-ЛОГ и 13-ЛОГ. 9-ЛОГ катализирует реакцию образования 9-гидропероксидов, а 13-ЛОГ – 13-гидропероксидов ПНЖК (Ivanov et al., 2010; Borrego, Kolomiets, 2016). Существование множественных изоформ липоксигеназы и различная субклеточная локализация предполагают полифункциональность этого фермента и вовлечение его в различные процессы в клетке (Kulkarni et al., 2002; Braido et al., 2004; Pokotylo et.al, 2015; Babenko et.al, 2017). Липоксигеназа найдена более чем у 60 видов живых организмов (Ivanov et al., 2010; Borrego, Kolomiets, 2016). Фермент задействован в образовании вторичных метаболитов, в том числе летучих альдегидов и жасмонатов, выполняющих ключевую роль в формировании защитных реакций растений (Savchenko et al., 2014; Roy et al 2011; Babenko et al., 2015; Tiwari et al., 2016; Babenko et al., 2017; Meng et al., 2017 Wasternack, Song, 2017). Роль других оксилипинов в качестве продуктов каскада ЛОГ, так же изучена достаточно подробно. Как электрофильные соединения оксилипины образуют конъюгаты с клеточными нуклеофилами, среди которых тиолы, аминогруппы нуклеиновых кислот и протеинов (Davoine et al., 2008, Chan et al., 2012). Принимая во внимание, что липоксигеназа как сигнальная молекула участвует в формировании реакций-ответов на стрессорные воздействия, целью настоящей работы было изучение эффектов кратковременной гипо- и гипертермии на активность энзима сортов Triticum arstivum L. с различной устойчивостью к абиотическим стрессам.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Исследования проводили с 14-дневными растениями озимой пшеницы Triticum aestivum L. новых высокопродуктивных сортов украинской селекции Ятрань 60, Володарка и Подолянка Morgun et. al., 2008). Сорт Володарка короткостебельный, высокоинтенсивного типа отличается морозо- и засухоустойчивостью, выращивается в Лесостепи и Полесье. Сорт Ятрань 60 – короткостебельный, интенсивного типа, характеризуется высокой жаро- и засухоустойчивостью, выращивается в Лесостепи,
Полесье и Степной зоне Украины. Экологически пластичный сорт Подолянка – среднерослый, интенсивного типа, универсального использования, характеризуется множественной устойчивостью к абиотическим стрессорам. Откалиброванные семена, промытые в дистиллированной воде, помещали в чашки Петри на увлажненную раствором Кнопа фильтровальную бумагу и переносили в термостат, где они находились в темноте при температуре +24°С в течение суток. Затем чашки Петри с проросшими семенами помещали на 14 суток в камеру искусственного климата при температуре +24°С, освещении 180 мкмоль/м2×сек. Фотопериод составлял 16/8 ч (день/ночь). Для создания условий теплового и холодового стрессов 14-дневные растения подвергали кратковременному (в течение 2 ч) воздействию температур +40°С и +4°С при указанном ранее режиме освещения. Для выделения препарата ЛОГ навески растительного материала гомогенизировали в охлажденном до + 4°С 0,1 М фосфатном буфере (pH 6,3), содержащем 2 мМ фенилметилсульфоилфторид (ФМСФ), 0,04% метабисульфит натрия (вес/объем). Гомогенат центрифугировали в течение 30 мин при 4000 х g при температуре + 4°С. Полученный супернатант использовали для определения активности ЛОГ. Для построения кривых pH-зависимости стационарных скоростей реакции липоксигеназного окисления линолевой кислоты использовали 0,1 М натрийацетатный (pH 4,0-5,5), 0,1 М натрий-фосфатный (pH 6-8) i 0,1 М боратный (pH 8,0-9,5) буферные растворы. Концентрации линолевой кислоты в реакционной смеси общим объемом 2,5 мл составила 100 мкМ в присутствии 0,02% луброл РХ (вес/объем). Определение активности ЛОГ проводили на спектрофотометре Specord M-40 (Gibian, Vandenberg; 1987). Реакцию инициировала путем добавления 50-100 мкл фермента (концентрация белка составляла 0,5-1,5 мг/мл) и проводили в условиях постоянной температуры 25 ± 0,1◦С. За ходом реакции наблюдали, учитывая увеличение оптической плотности реакционной смесь при λ = 235 нм, соответствующей максимальному поглощению сопряженного диенового хромофора в молекуле гидропероксида линоленовой кислоты, молярный коэффициент екстинкции которого составляет 23000 M-1 см-1 (Gibian, Vandenberg, 1987). Содержание белка определяли по методу (Bradford, 1976). Опыты проводили в двух биологических и трех аналитических повторносиях. В каждую биологическую повторность отбирали по 40 растений. При построении кинетических зависимостей использовали средние значения Vst, которые определяли в трех измерениях (разница между величинами составляла не более 5%). Статистическую обработку результатов проводили t-тестом Стьюдента, статистически достоверной считали разницу при р≤ 0,05. На графиках и диаграммах представлены средние арифметические и их стандартные ошибки.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Синтез сигнальных соединений, задействованных в адаптации растений к стрессам, рассматривается как одна из главных физиологических функций липоксигеназ (Savchenko et al. , 2014; Babenko et.al, 2017). Изменение липоксигеназной активности, происходящее в процессе онтогенеза, указывает на существование тонких механизмов ее регуляции (Lоhelaid et.al, 2008, Ghanem et.al, 2012). Показано, что управление ЛОГ активностью осуществляется на трансляционном и посттрансляционном уровнях (Pokotylo et.al, 2015). Изоформы липоксигеназы являются растворимыми протеинами, которые находятся в строме хлоропластов, вакуолях, цитозоле, митохондриях или липидных телах (Braidot et.al, 2004; Pokotylo et.al, 2015; Babenko et.al, 2017). В противовес этому, субстраты ЛОГ плохо растворимы в водной среде при физиологическом значении рН. Предполагается, что возможным механизмом активации растворимых ЛОГ является их факультативная Ca2+-зависимая ассоциация с клеточными мембранами (Youn et.al, 2006) Известно, что активность ЛОГ регулируется при помощи фосфорилирования (Thivierge et.al, 2010), а также высвобождением больших количеств субстрата ЛОГ – ПНЖК.
В результате проведенных исследований было показано, что в надземной части 14-дневных растений жароустойчивого сорта Ятрань 60 содержится две изоформы 9-липоксигеназы: ЛОГ-1 со значением рHопт 6,3 и ЛОГ-2 со значением рНопт 5,5, тогда как в корнях локализована одна изоформа со значением рHопт 6,5 (рис. 1).
Активность изоформ ЛОГ-1 и ЛОГ-2 в надземной части растений существенно увеличивалась после кратковременной гипертермии (рис. 2).
Реакция на кратковременное действие низкой температуры была менее выраженной (рис. 2). Рост активности ЛОГ после теплового стресса косвенно указывает на возможность вовлечения продуктов липоксигеназного каскада в процессы формирования адаптационных и стабилизационных защитных механизмов у жароустойчивого сорта Ятрань 60.
В надземной части 14-дневных растений морозоустойчивого сорта Володарка также были выявлены две изоформы 9-ЛОГ: ЛОГ-1 (рН опт 7,0) и ЛОГ-2 (рН опт 6,0), в корнях — одна 9-ЛОГ (рН опт 6,5) (рис. 3).
Активность ЛОГ в надземной части и корнях 14дневных растений морозоустойчивого сорта Володарка значительно увеличивалась после кратковременной гипертермии. Эффект кратковременного действия низкой температуры был менее выраженным (рис. 4). Рост активности ЛОГ после теплового стресса наблюдался на фоне определённых ультраструктурных изменений, среди которых формированием многочисленных липидных капель в цитоплазме клеток мезофилла листьев (Babenko et al., 2014). Липидные капли, которые до последнего времени рассматривались как депо запасных липидов, согласно новым сведениям позиционируются в качестве участников цитоплазматического сигналинга, осуществляемого благодаря наличию в них целого ряда протеинов, среди которых ЛОГ (Van der Schoot et al., 2011; Pokotylo et al., 2015). У морозоустойчивого сорта Володарка прослеживается определенная связь между увеличением количества липидных капель и ростом ЛОГ активности после гипертермии.
В надземной части 14-дневных растений экологически пластичного сорта Подолянка также были выявлены две изоформы 9-ЛОГ: ЛОГ-1 (рН опт 7,5) и ЛОГ-2 (рН опт 5,5), в корнях — одна 9-ЛОГ (рН опт 6,5) (рис. 5).
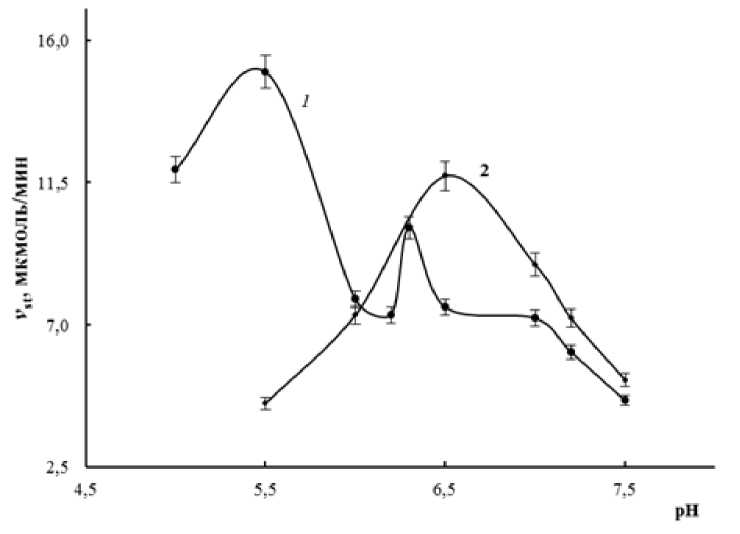
Figure 1. Зависимость стационарной скорости реакции (Vst) окисления линолевой кислоты от рН инкубационный среды в надземной части (1) и корнях (2) 14-дневных растений Triticum aestivum сорта Ятрань 60.
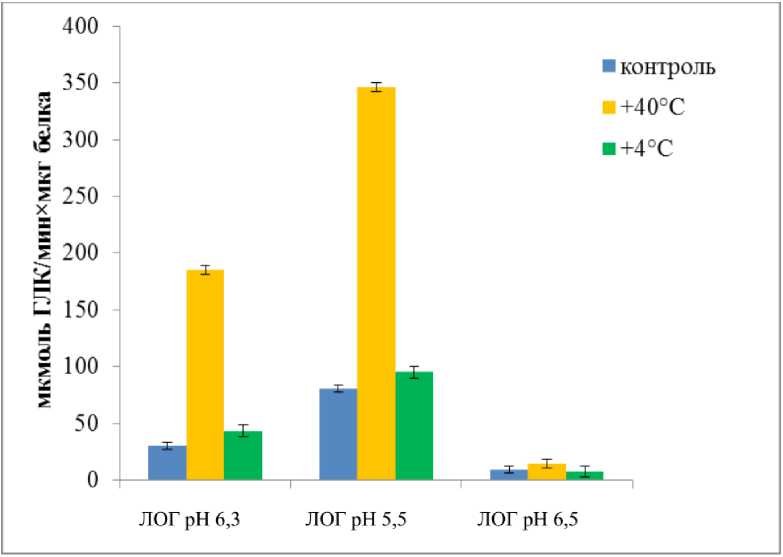
Figure 2. Активность изоформ 9-ЛОГ в надземной части и корнях 14-дневных проростков Triticum
aestivum сорта Ятрань 60 в контроле и после кратковременного действия высокой и низкой
положительной температуры
٭ Примечание – тут и в последующих упоминаниях ГЛК – гидропероксид линолевой кислоты
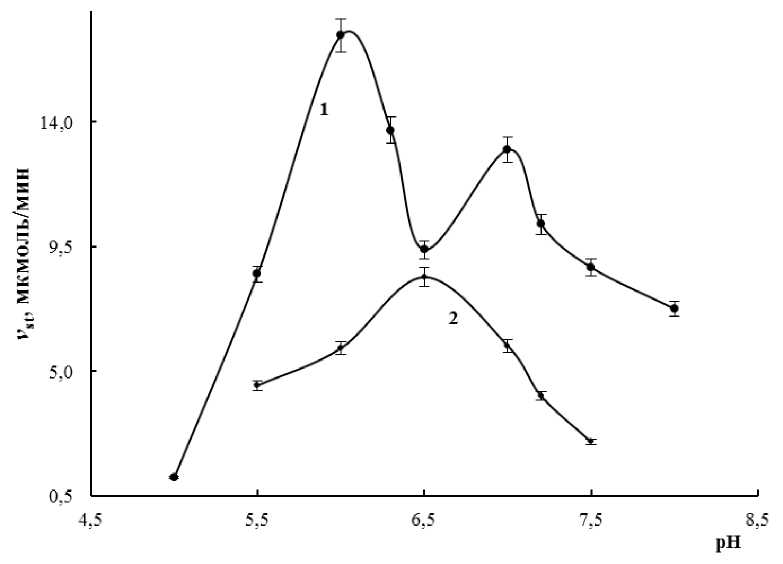
Figure 3. Зависимость стационарной скорости реакции (Vst) окисления линолевой кислоты от рН инкубационного среды в надземной части (1) и корнях (2) 14-дневных растений T riticum aestivum сорта Володарка.
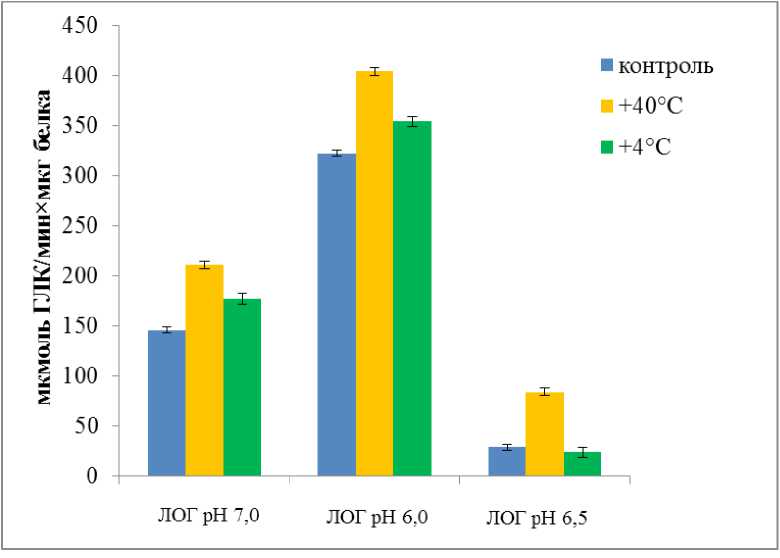
Figure 4. Активность изоформ 9-ЛОГ в надземной части и корнях 14-дневных растений Triticum aestivum сорта Володарка в контроле и после кратковременного действия высокой и низкой положительной температуры.
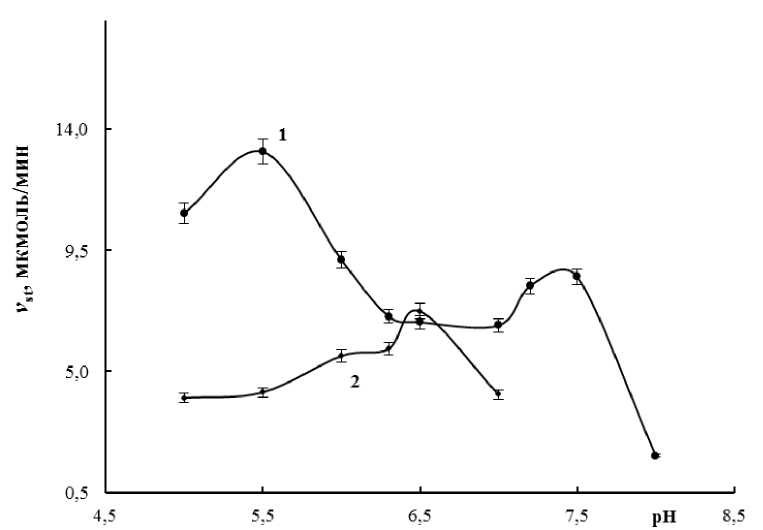
Figure 5. Зависимость стационарной скорости реакции (Vst) окисления линолевой кислоты от рН инкубационного среды в надземной части (1) и корнях (2) проростков Triticum aestivum сорта Подолянка.
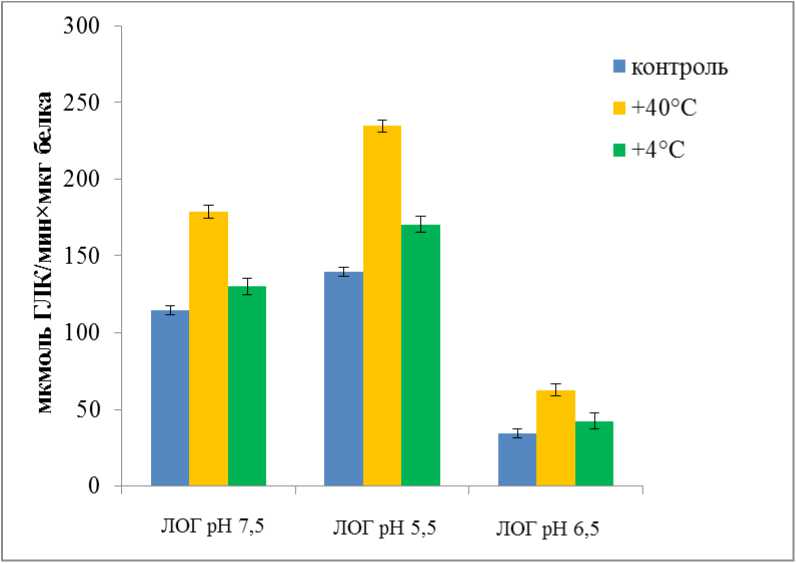
Figure 6. Активность изоформ 9-ЛОГ в надземной части и корнях 14-дневных растений Triticum aestivum сорта Подоляна в контроле и после кратковременного действия высокой и низкой положительной температуры.
Так же как и у растений сорта Володарка и сорта Ятрань 60 активность ЛОГ в надземной части и корнях растений универсального сорта Подолянка значительно возрастала после кратковременной гипертермии (рис. 6). Такие изменения в метаболизме наблюдались на фоне изменений ультраструктуры. В строме хлоропластов клеток мезофила листьев при кратковременной гипертермии происходило значительное накопление пластоглобул (данные не опубликованы). Протеомные и ультраструктурные исследования пластоглобул свидетельствуют об их участии в стабилизации тилакоидных мембран при окислительных повреждениях в результате различных стрессов, они являются местом хранения липидообразных веществ (таких как каротиноиды, токоферол, пластохинон) и специфичных для пластоглобул протеинов с энзимными и структурными функциями (Austin et al. , 2006; Vidi et al. , 2006).
Функционирование 9-ЛОГ ассоциируется преимущественно с цитоплазматической мембраной
(Porta, Rocha-Sosa, 2002). В тоже время 9-ЛОГ активность локализована на мембранах хлоропластов, тонопласте, мембранах липидных капель и митохондрий (Braidot et al. , 2004; Pokotylo et al. , 2015; Babenko et al. , 2017). Активность ЛОГ рассматривают как биологический маркер физиологического состояния растения (Braidot et al. , 2004; Babenko et al. , 2014). Выявленные в настоящем исследовании изменения в активности ЛОГ позволяют сделать следующие выводы. Неспецифической реакцией на гипертермию и гипотермию оказалось увеличение липоксигеназной активности, как в надземной, так и корневой части растений. Интенсивность реакции на тепловой стресс значительно превышала такую на холодовое воздействие. Наиболее выраженной была реакция на гипертермию у жароустойчивого сорта Ятрань 60. Выявленная нами ранее связь между активностью липоксигеназы и теплоустойчивостью сортов Brassica napus var. Oleifera Kosakivska et al. , 2012), а также представленные в настоящей публикации результаты позволяют рассматривать ЛОГ в качестве возможного маркера теплоустойчивости растений.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Работа выполнена в рамках проекта «Фитогормональная система новых генотипов Triticum aestivum L. и её диких предков при действии экстремальных климатических факторов», финансированного Национальной академией наук Украины.
Список литературы Влияние температуры на активность липоксигеназы в разновидностях Triticum aestivum L., отличающихся устойчивостью к абиотическим стрессорам
- Andreou A, Feussner I. (2009) Lipoxygenases -Structure and reaction mechanism. Phytochemistry, 70(13-14), 1504-1510
- Austin J.R., Frost E., Vidi P.A, Kessler F., Staehelin L.A. (2006) Plastoglobules are lipoprotein subcompartments of the chloroplast that are permanently coupled to thylakoid membranes and contain biosynthetic enzymes. PlantCell, 18, 1693-1703
- Babenko L.М., Kosakivska I.V., Skaterna T.D. (2015) Jasmonic acid: a role in the regulation of biotechnology and biochemical processes in plants. Biotechnologia acta, 8(2), 36-51
- Babenko L.М., Kosakivska I.V., Akimov Yu.A., Klymchuk D.O., Skaternya T.D.(2014) Еffect of temperature stresses on pigment content, lipoxygenase activity and cell ultrastructure of winter wheat seedlings. Genetics and plant physiology, 4 (1-2), 117-125
- Babenko L.М., Shcherbatiuk M.M., Skaterna T.D, Kosakivska I.V. (2017) Lipoxygenases and their metabolites in formation of plant stress tolerance. Ukr. Biochem. J., 89(1), 5-21
- Barlow K.M., Christy B.P., O’Leary G.J., Riffkin P.A., Nuttall J.G. (2015) Simulating the impact of extreme heat and frost events on wheat crop production: a review. Field Crops Res., 17, 109-119
- Borrego Е.J., Kolomiets M.V. 2016 Synthesis and Functions of Jasmonates in Maize. Plants., 5(4), 41-69
- Borrego E.J., Kolomiets M.V. (2012) Lipid-mediated signaling between fungi and plants. In Biocommunication of Fungi; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 249-260
- Bradford M. M. (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem., 72(2), 248 -254
- Braidot E., Petrussa E., Micolini S. (2004) Biochemical and immunochemical evidences for the presence of lipoxygenase in plant mitochondria. J. Exp. Bot., 55(403), 1655-1662
- Chan T., Shimizu Y., Pospíšil P., Nijo N., Fujiwara A., Taninaka Y. (2012) Control of photosystem II: Lipid peroxidation accelerates photoinhibition under excessive illumination. PLoS ONE., 7(12), 52100
- Christensen S.A., Kolomiets M.V. (2011) The lipid language of plant-fungal interactions. Fungal Genet. Biol., 48, 4-14
- Davoine C., Falletti O., Douki T., Iacazio G., Ennar N., Montillet J.-L., Triantaphylidès C. (2006) Adducts of oxylipin electrophiles to glutathione reflect a 13 specificity of the downstream lipoxygenase pathway in the tobacco hypersensitive response. Plant Physiol., 140(4), 1484-1493
- Feussner I., Wasternack C. (2002) The lipoxygenase pathway. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 53, 275-297
- Ghanem M. E., Ghars M. A., Frettinger P., PérezAlfocea F., Lutts S., Wathelet J.-P., du Jardin P., Fauconnier M.-L. (2012) Organ-dependent oxylipin signature in leaves and roots of salinized tomato plants (Solanum lycopersicum). J. Plant Physiol., 169(11), 1090-1101
- Gibian M.J., Vandenberg P. (1987) Product yield in oxygenation of linoleate by soybean lipoxygenase: The value of the molar extinction coefficient in the spectrophotometric assay. Anal. Biochem., 163(2), 343-349
- Hatfield J., Prueger J. (2015) Temperature extremes: Effect on plant growth and development. Weather and Climate Extremes., 10, 4-10
- Hurkman W.J., Wood D.F. (2011) High temperature during grain fill alters the morphology of protein and starch deposits in the starchy endosperm cells of developing wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grain. J. Agric. Food Chem. 59(9), 4938-4946
- Ivanov I, Heydeck D, Hofheinz K, Roffeis J, O'Donnell VB, Kuhn H, Walther M. (2010) Molecular enzymology of lipoxygenases. Arch Biochem Biophys. 503(2), 161-174
- Joo Y-C., Oh D-K. (2012) Lipoxygenases: Potential starting biocatalysts for the synthesis of signaling compounds. Biotechnol. Advances. 30, 1524-1532
- Kosakivska I.V., Babenko L.M., Ystinova A.U., Skaterna T.D., Demievska K. (2012) The influence of temperature conditions on lipoxygenase activity in seedling of rape Brassica napus var. Oleifera. Dopovidi Nats. Acad. Nauk Ukrainy., 6, 134-137 (In Ukrainian)
- Kulkarni S., Das S., Funk C. (2002) Molecular basis of the specific subcellular localization of the C2-like domain of 5-lipoxygenase. J. Biol. Chem., 277(15), 13167-13174
- Lоhelaid H., Järving R., Valmsen K., Varvas K., Kreen M., Järving I., Samel N. (2008) Identification of a functional allene oxide synthase-lipoxygenase fusion protein in the soft coral Gersemia fruticosa suggests the generality of this pathway in octocorals. Biochim. Biophys. Acta., 1780(2), 315-321. (In Ukrainian)
- Meng K., Hou Y., Han Y, Ban Q., He Y., Suo J., Rao J. (2017) Exploring the Functions of 9-Lipoxygenase (DkLOX3) in Ultrastructural Changes and Hormonal Stress Response during Persimmon Fruit Storage Int. J. Mol. Sci., 18(3), 589-592
- Morgun V.V., Sanin E.V., Shvartau V.V. (2009) The club has 100 centners. Varieties and technologies of cultivation of high harvests of winter wheat. Kyiv: Logos.: 87p. (In Ukrainian)
- Mosblech A., Feussner I., Heilmann I. (2009) Oxylipins: structurally diverse metabolites from fatty acid oxidation. Plant Physiol. Biochem., 47, 511-517
- Pokotylo IV, Kolesnikov YS, Derevyanchuk MV, Kharitonenko AI, Kravets V.S. (2015) Lipoxygenases and plant cell metabolism regulation. Ukr Biochem J. 87(2), 41-55.
- Porta H., Rocha-Sosa M. (2002) Plant lipoxygenases. Physiological and molecular features. Plant Physiol., 130(1), 15-21
- Roy S., Maheshwari N, Chauhan R., Kumar Sen N. (2011) Structure prediction and functional characterization of secondary metabolite proteins of Ocimum. Bioinformation. 6(8), 315-319
- Savchenko T.V., Zastrijnaja O.M., Klimov V.V. (2014) Oxylipins and Plant Abiotic Stress Resistance. Biochemistry (Mosc.), 79(4), 362-375
- Stumpe M, Feussner I. (2006) Formation of oxylipins by CYP74 enzymes. Phytochemical Reviews, 5, 347-357
- Thivierge K., Prado A., Driscoll B. T., Bonneil É., Thibault P., Bede J. C. (2010) Caterpillarand salivary-specific modification of plant proteins. J. Proteome Res., 9(11), 5887-5895
- Tiwari A., Avashthi H, Jha R., Srivastava A., Garg V., Pramod Ramteke W., Kumar A. (2016) Insights using the molecular model of Lipoxygenase from Finger millet (Eleusine coracana (L.)) Bioinformation, 12(3), 156-164
- Van der Ent S., Van Wees S. C., Pieterse С. M. (2009) Jasmonate signaling in plant interactions with resistance-inducing beneficial microbe. Phytochemistry, 70, 1581-1588
- Van der Schoot C., Paul L., Paul S., Rinne P. (2011) Plant lipid bodies and cell-cell signaling. A new role for an old organelle? Plant Signal Behav., 6(11), 1732-1738
- Vidi P.A, Kanwischer M., Baginsky S., Austin J.R., Csucs G., Dormann P., Kessler F, Brehein C. (2006) Tocopherol cyclase (VTE1) localization and vitamin E accumulation in chloroplast plastoglobule lipoprotein particles. J Biol Chem., 281(16), 11225-11234
- Wasternack C. (2007) Jasmonates: an update on biosynthesis, metabolism, and signaling by proteins activating and repressing transcription. Ann Bot., 100(4), 681-697
- Youn B., Sellhorn G. E., Mirchel R. J., Gaffney B. J., Grimes H. D., Kang C. (2006) Crystal structures of vegetative soybean lipoxygenase VLX-B and VLX-D, and comparisons with seed isoforms LOX-1 and LOX-3. Proteins: Structure, Function, and Bioinformatics., 65(4), 1008-1020


