Восстановление растений табака после обработки ионами меди
Автор: Тугбаева А.С., Ермошин А.А., Плотников Д.С., Киселева И.С.
Журнал: Вестник Пермского университета. Серия: Биология @vestnik-psu-bio
Рубрика: Экология
Статья в выпуске: 4, 2020 года.
Бесплатный доступ
Последействие ионов меди (100 и 300 мкМ) на размеры органов, содержание маркеров стресса (перекись водорода, перекисное окисление липидов - ПОЛ) и компонентов антиоксидантного статуса (супероксиддисмутаза - СОД и гваяколовая пероксидаза - ГПО) были изучены в корнях, стебле и листьях Nicotiana tabacum L. Показано, что растения табака чувствительны к длительному воздействию 100 и 300 мкМ Cu2+. Обе концентрации ингибировали рост корней, тогда как длина, толщина побегов и площадь листьев уменьшались только в случае предварительной обработки 300 мкМ Cu2+; то есть рост надземных органов был подавлен значительно меньше, чем корней. Уровень ПОЛ и содержание перекиси водорода в корнях в этих условиях также были выше, что указывает на более сильную нагрузку на корни, чем на стебли и листья. Активность антиоксидантных ферментов СОД и ГПО в корнях и надземных органах специфически изменялась в зависимости от концентрации ионов меди и типа органа. В корнях наблюдалось снижение активности СОД и повышение активности ГПО при предварительной обработке 300 мкМ Cu2+ по сравнению с контролем и 100 мкМ Cu2+, тогда как в стебле и листьях активность ферментов снижалась. Полученные данные свидетельствуют о неполном восстановлении растений в условиях последействия ионов меди.
Ионы меди, пероксид водорода, перекисное окисление липидов, гваяколовая пероксидаза, супероксиддисмутаза, табак
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147229670
IDR: 147229670 | УДК: 581.14, | DOI: 10.17072/1994-9952-2020-4-344-351
Текст научной статьи Восстановление растений табака после обработки ионами меди
Загрязнение земель ионами тяжелых металлов (ТМ) представляет серьезную экологическую проблему для отраслей сельского хозяйства, приводя к потере урожаев и ухудшению качества продукции [Mohammed et al., 2011].
Некоторые из ТМ являются эссенциальными и в низких концентрациях необходимы для живых организмов. Так, ионы меди обеспечивают поддержание структуры белков, входят в состав каталитических центров ферментов, необходимы для работы электронтранспортных цепей митохондрий и хлоропластов, биосинтеза хлорофилла и т. д. [Yruela, 2005]. Диапазон толерантности живых организмов к ионам меди достаточно узок.
Ионы меди в клетках катализируют образование активных форм кислорода (АФК) в реакциях Фентона и Хабера – Вейса, что ведет к усилению окислительных процессов [Yruela, 2005; Abdelgawad et al., 2020]. У растений избыток Cu2+ в тканях листа вызывает хлорозы, негативно влияет на процессы фотосинтеза и фотодыхания, замедляет скорость роста и прирост биомассы [Yruela, 2005]. Однако после снятия стресса, вызванного действием ионов тяжелых металлов, растения способны восстанавливаться [Drost et al., 2007; Holubek et al., 2020]. Сведений об изменениях маркеров стресса в период последействия неблагоприятных факторов и восстановления роста не так много, в сравнении с данными о прямом действии стрессоров.
Типичным проявлением стресса является рост активных форм кислорода. Количество АФК регулируется ферментативными и неферментативными антиоксидантными системами. Показано, что активность антиоксидантных ферментов (каталазы, пероксидазы I и III класса, СОД) и накопление низкомолекулярных антиоксидантов зависят от силы и продолжительности действия стрессового фактора [Ku et al., 2012; Chen et al, 2015].
Несмотря на то, что эффекты ионов меди изучены на примере многих растений, далеко не все аспекты роста и физиологии растений после снятия действия стрессора охарактеризованы детально. Цель настоящей работы – изучение последействия разных концентраций ионов меди в среде на размеры органов и антиоксидантный статус растений N. tabacum в длительном модельном эксперименте.
Материал и методы исследования
В качестве объекта использовали растения табака ( Nicotiana tabacum L.), который является модельным и широко используется в лабораторных экспериментах. Растения табака сорта Petite Havana линии SR1 культивировали на предварительно проавтоклавированном субстрате – смесь перлит : вермикулит в соотношении 1 : 1 на среде Кноппа без добавления ионов меди (контроль) и при добавлении CuSO 4 в концентрации 100 (вариант 1) или 300 (вариант 2) мкМ/л в течение первых 20 дней после появления всходов. С 20 по 40 день растения выращивали на среде Кнопа без добавления ионов меди. Фотопериод составил 16/8 (день/ночь), температура 23°С. Все измерения проводили на 40-дневных растениях.
В предварительном опыте по оценке влияния ионов меди на всхожесть семян табака было выявлено, что добавление 100 мкМ Cu2+ стимулировало прорастание семян (28.6% от контроля), не влияло на длину корешка в 5-ти дневных проростках (4.8 мм против 5.0 мм в контроле); при 300 мкМ Cu2+ всхожесть семян не изменилась (-2.8% от всхоже- сти семян в контроле), но уменьшилась длина корешка (1.7 мм против 5.0 мм в контроле), следовательно, обработка этой концентрацией ионов меди ингибировала рост проростков табака. Это обусловило выбор концентраций CuSO4 в данной работе.
Для оценки последействия ионов меди на растения табака измеряли длину корня, стебля, длину и ширину третьего листа (без учета длины черешка). Выборка составила 30 растений для каждой группы. Толщину корня (зона проведения) и стебля (первое междоузлие выше семядолей) измеряли на поперечных срезах с использованием ПО SIMAGIS MesoPlant. Площадь листа рассчитывали как произведение длины на ширину, умноженное на коэффициент k =0.653 [Moustakas and Ntzanis, 1998].
Активность ферментов антиоксидантной защиты определяли в грубом экстракте тканей растений спектрофотометрически. Для получения грубого экстракта навески корней, стеблей и листьев (третий лист) гомогенизировали на холоде в 0.05 М Tris-HCl буфере (pH 7.0), центрифугировали при температуре 4°С.
Активность СОД оценивали по способности фермента ингибировать фотоокисление нитросине-го тетразолия и выражали в усл. ед. / мг бел-ка*мин [Beauchamp, Fridovich, 1971]. Активность ГПО измеряли по скорости окисления гваякола и выражали в мМ гваякола / мг белка*мин [Chance, Maehly, 1955]. Содержание белка в пробах определяли по Бредфорд [Bradford, 1976], используя в качестве стандарта бычий сывороточный альбумин [Zaia et al, 2005].
Грубый экстракт ферментов использовали также для определения содержания Н 2 О 2 с помощью метода, основанного на окислении пероксидом хелатов ксиленолового оранжевого с ионами железа (III) [Bellincampi et al., 2000] и выражали в мкМ пероксида / г сухой массы.
Интенсивность ПОЛ оценивали спектрофотометрически по количеству малонового диальдегида, взаимодействующего с тиобарбитуровой кислотой (ТБК), и выражали в мкМ ТБК-реагирующих продуктов (ТБК-РП) / г сухой массы [Uchiyama, Mihara, 1978].
Оптическую плотность растворов при определении активности СОД, ПОЛ, содержания белка и пероксида водорода измеряли в 96-луночном планшете на спектрофотометре Tecan Infinity M 200 Pro («Tecan», Austria), а при определении активности ГПО – на приборе Shimadzu UV-1800 («Shimadzu», Japan).
Измерения проводили в трех биологических и трех аналитических повторностях. Результаты представлены в виде значения среднего арифметического и ошибки. Статистическую обработку данных проводили в программе STATISTICA 10 для
Windows 10 с применением t -критерия Стьюдента, U -критерия Манна-Уитни, непараметрического коэффициента корреляции Спирмена при уровне значимости p < 0.05.
Результаты и их обсуждение
На этапе восстановления после снятия действия ионов меди наблюдали изменение размеров растений N. tabacum (рис. 1, табл. 1).
В варианте 1 (предобработка 100 мкМ Cu2+) длина главного корня была достоверно меньше относительно контроля, однако его толщина в зоне проведения увеличилась. Высота и толщина стебля, площадь листовой пластинки не изменились в этом случае, в сравнении с контролем, тогда как предобработка 300 мкМ Cu2+ привела к статистически значимому уменьшению длины и толщины корня на 14%, высоты и толщины стебля на 14% и 15%, площади листа 39% относительно контроля, соответственно.
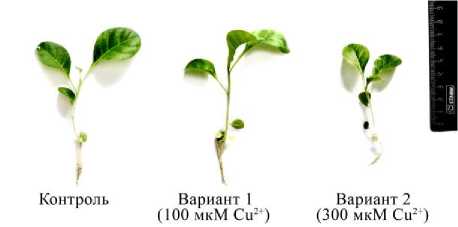
Рис. 1 . Морфология растений N. tabacum в период восстановления после снятия действия Cu2+
Уменьшение длины главного корня, высоты растений и площади листа является неспецифической реакцией растений на действие тяжелых металлов. У проростков Trifolium repens L. в присутствии 200 мкМ Cu2+ показано 50%-ное уменьшение длины корня [Ермошин и др., 2013]; у Withania somnifera L. длина корня и высота побега также уменьшались [Khatun et al., 2008]. Утолще- ние корня при действии умеренных концентраций Cu2+ рассматривают как адаптивную реакцию, которая способствует увеличению внутренней поверхности корня, связыванию ионов меди в апо-пласте клеток ризодермы и коры [Bouazizi et al., 2010]. Уменьшение диаметра корня при действии высоких концентраций Cu2+ может быть причиной подавления роста клеток растяжением вследствие усиления их лигнификации и снижения эластичности клеточных стенок при связывании их с ионами тяжелых металлов, нарушения транспорта ауксинов и кислого роста, снижения активности экспан-синов [Hamim et al., 2018]. В исследованиях C.M. Cook и соавторов [1997] описано снижение площади листьев у Phaseolus vulgaris L. при действии 160 мкМ ионов меди. При изучении последействия ионов кадмия описано восстановление роста побега и первых листьев растений Glycine max L. У растений, предобработанных более высокими концентрациями Cd2+, отмечали сокращение длины корня как одного из признаков фитотоксичности этого металла [Holubek et al., 2020]. Уменьшение размеров органов растений при избытке ионов тяжелых металлов в среде связывают с накоплением АФК, усилением процессов ПОЛ [Khatun et al., 2008].
В период восстановления после действия ионов меди содержание пероксида водорода было выше в листьях во всех вариантах опыта по сравнению с тканями корня и стебля (табл. 2). В этих органах фотосинтез и дыхание являются источником Н 2 О 2. Несмотря на 20-дневный период восстановления содержание пероксида во всех органах было достоверно выше в сравнении с контрольным вариантом: в варианте 1 (100 мкМ Cu2+) в тканях корня выше в 2.1 раза, стебля и листа – в 1.4 раза по сравнению с контролем. В варианте 2 (300 мкМ Cu2+) эффекты были выражены сильнее: содержание Н 2 О 2 относительно контроля в корне было выше в 4.5 раза, в стебле – в 1.6 раза и в листе – в 2.3 раза, при уровне значимости различий p = 0.03.
Таблица 1
Влияние последействия ионов меди на размеры органов растений N. tabacum
|
Вариант (предобработка) |
Длина, см |
Диаметр, мкм |
Площадь листа, мм2 |
||
|
Корень |
Стебель |
Корень |
Стебель |
||
|
Контроль (H 2 O) |
3.79±0.02 |
4.93±0.02 |
739±16 |
1146 ± 58 |
443 ± 19 |
|
Вариант 1 (100 мкМ Cu2+) |
3.25±0.02* |
4.77±0.03 |
820±13* |
1100 ± 32 |
436 ± 19 |
|
Вариант 2 (300 мкМ Cu2+) |
3.24±0.01* |
4.23±0.03*a |
634 ± 25*a |
971 ± 48*a |
268 ± 13*a |
Примечание. * – Статистически значимое отличие относительно контроля (p < 0.05); a – статистически значимое отличие относительно условий 100 мкМ ионов меди (p < 0.05).
Наиболее высокий уровень ПОЛ показан в корнях во всех вариантах относительно стебля и листьев. В варианте 1 у предобработанных 100 мкМ Cu2+ растений количество ТБК-РП относительно контроля в тканях корня и стебля было больше в
1.4 и 1.6 раза соответственно, в тканях листа – в 1.1 раза. В варианте 2 этот эффект был выражен сильнее: в тканях корня интенсивность ПОЛ достоверно возросла относительно контроля в 2.1 раза (при p = 0.02). В стебле и листьях этот показа- тель превышал уровень в контроле в 3.7 и 2.9 раза, соответственно (отличие достоверно при p = 0.005).
Мы предполагаем, также как Printz et al, [2016], что в период восстановления растений по- сле действия стрессора, ионы Cu2+, непрочно адсорбированные в клеточных стенках, могли вымываться из них в апопласт и проникать в цитоплазму, вызывая образование АФК.
Таблица 2
Содержание пероксида водорода и ТБК-РП в органах N. tabacum , предобработанных разными концентрациями ионов меди (в расчете на г сухой массы)
|
Вариант (предобработка) |
Корень |
Стебель |
Лист |
|||
|
Н 2 О 2 , мкМ |
ТБК-РП, мкМ |
Н 2 О 2 , мкМ |
ТБК-РП, мкМ |
Н 2 О 2 , мкМ |
ТБК-РП, мкМ |
|
|
Контроль (H 2 O) |
0.71 ± 0.04 |
7.04 ± 0.25 |
3.50 ± 0.07 |
1.57 ± 0.04 |
8.43 ± 0.08 |
3.46 ±0.19 |
|
Вариант 1 (100 мкМ Cu2+) |
1.53 ± 0.13* |
9.85 ± 0.42* |
4.90 ± 0.19* |
2.46 ± 0.19* |
11.83 ± 0.36* |
3.91 ±0.10* |
|
Вариант 2 (300 мкМ Cu2+) |
3.22 ± 0.02*а |
15.02 ± 0.28a |
5.56 ± 0.17*а |
5.03 ± 0.09*a |
19.85 ±0.23*a |
9.97 ± 0.11*a |
Примечание. * – Статистически значимое отличие относительно контроля (p<0.05); a – статистически значимое отличие относительно условий 100 мкМ ионов меди (p<0.05).
Увеличение содержания пероксида водорода и интенсивности ПОЛ в органах табака и, как следствие, развитие стресса, вероятно, и привело к угнетению роста у предобработанных ионами меди растений в сравнении с контролем, что проявилось в уменьшении размеров осевых органов и площади листа. Полученные данные о накоплении АФК и продуктов ПОЛ в условиях последействия Cu2+ свидетельствуют о том, что полного восстановления физиологического состояния растений за 20 дней после действия стрессора не происходит.
Известно, что в поддержание окислительновосстановительного баланса в клетках вовлечены ферментные системы и низкомолекулярные антиоксиданты. Результаты наших исследований показали, что активность СОД статистически значимо снижалась в клетках корня и побега у предобрабо-танных ионами меди растений (рис. 2). Падение активности СОД в ответ на избыток Cu2+ в среде описано в растениях Zea mays L., Phyllostachys edulis J. Houz. и, возможно, является следствием инактивации работы фермента продуктом реакции – пероксидом водорода, или нарушения его конформации в результате окислительных процессов [Chen et al, 2015; Abdelgawad et al, 2020]. Возможно, и в условиях последействия ионов меди рост содержания пероксида водорода вызывал продукт-ное ингибирование СОД.
Другой фермент антиоксидантной защиты – ГПО ответственна за утилизацию перекисей. Этот фермент может освобождать клетки от Н2О2, образованного как ферментом СОД, так и другими ферментами, например, гликолатоксидазой. В стеблях и листьях N. tabacum во всех вариантах опыта активность ГПО была ниже, чем в корнях. Увеличение количества Н2О2 в корнях в условиях последействия 100 и 300 мкМ Cu2+ сопровождалось ростом активности ГПО на 90 и 106%, соответственно. При этом в стебле наблюдали снижение активности ГПО на 36% относительно кон- троля только в варианте 2, а в листьях – на 59 и 73%, соответственно, в 1-м и 2-м вариантах опыта (отличие статистически значимо, p = 0.03).
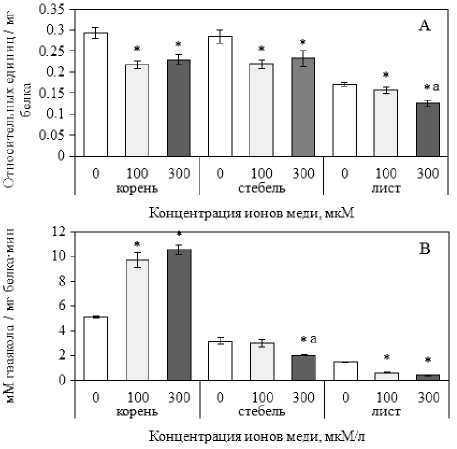
Рис. 2. Активность антиоксидантных ферментов в тканях растений N. tabacum , пред-обработанных разными концентрациями ионов меди:
А – супероксиддисмутаза; В – гваяколовая пероксидаза; * – статистически значимое отличие относительно контроля (p < 0.05); a – статистически значимое отличие относительно условий 100 мкМ ионов меди (p < 0.05)
Возможно, разница в трендах изменения активности ГПО в корнях и надземных органах связана с тем, что корень выполняет барьерную функцию и не позволяет ионам меди в больших количествах транспортироваться в стебель и листья [Cuypers et al., 2016; Abdelgawad et al., 2020]. Следовательно, в этих органах окислительный стресс не так сильно выражен, как в корнях, о чем свидетельствуют более низкие значения содержания ТБК-РП в них в сравнении с корнем. При этом важно отметить, что содержание пероксида водорода в стеблях и листьях больше, чем в корнях и в контроле, и в опытных вариантах. Вероятно, это связано со значительно более высокой активностью ГПО в корнях, быстро расщепляющей Н2О2, чем в стеблях и листьях. Кроме того, зеленые части растений, осуществляющие фотосинтез, имеют дополнительные источники пероксида водорода в фотосинтетической цепи переноса электронов [Abdelgawad et al., 2020] и в гликолатном пути фотосинтеза.
Кроме того, разные изоформы ГПО в корнях и побеге могут отличаться по чувствительности к АФК и продуктам ПОЛ [Maksimovic et al, 2008]. В клетках растений существуют также другие пероксидазы, избавляющие их от Н 2 О 2 .
Роль пероксидаз в реакциях на стресс, вызванный ионами меди, была отмечена у многих растений: Arabidopsis thaliana L. , Oryza sativa L. и др. [Mostofa and Fujita, 2013; Thounaojam et al., 2014].
Показано, что активность ГПО в тканях разных органов зависит от стадии жизненного цикла растений: на стадии вегетации максимальная активность в корнях и низкая в листьях, на стадии бутонизации она возрастает в листьях и снижается в корнях [Maksimovic et al, 2008].
Таким образом, у табака, предварительно обработанного ионами меди, в сравнении с контрольными растениями, в пост-стрессовый период наблюдали увеличение содержания пероксида водорода и ТБК-РП, являющихся маркерами стресса, что указывает на неполную реабилитацию растений. При этом рост надземных органов был подавлен значительно меньше, чем корня.
Заключение
Были определены реакции разных органов растений N. tabacum в период последействия 100 и 300 мкМ Cu2+. Установлено, что растения N. taba-cum чувствительны к этим концентрациям Cu2+, и в период после снятия действия стрессора растут хуже, чем растения, не подвергавшиеся стрессу. Уровень ПОЛ и содержание пероксида водорода были выше в предварительно стрессированных растениях. Одной из реакций растений на последействие избытка ионов меди в среде явилось увеличение активности ГПО в корне. Однако активность СОД во всех органах растения уменьшалась. При этом снижения количества стрессовых маркеров (пероксид водорода и ТБК-РП) не происходило. Органом, испытывающим наиболее сильное последействие Cu2+, являлся корень. Его вероятная барьерная роль ограничивала транспорт ионов меди в побег и обеспечивала менее существенное торможение роста этих органов. Таким образом, в 20-дневный период последействия ионов меди рас- тения табака восстанавливали рост, однако не достигали показателей контрольных растений.
Работа выполнена при поддержке Министерства науки и высшего образования Российской Федерации (соглашение № 02.A03.21.0006).
Список литературы Восстановление растений табака после обработки ионами меди
- Ермошин А.А., Цибизова М.Н., Киселёва И.С. Влияние ионов меди и алюминия на развитие проростков Trifolium repens L. // Вестник Томского государственного университета. Сер. Биология. 2013. Т. 3, № 23. С. 120-126.
- Abdelgawad H. et al. Maize roots and shoots show distinct profiles of oxidative stress and antioxidant defense under heavy metal toxicity // Environmental Pollution. 2020. Vol. 258. P. 113705.
- Beauchamp C., Fridovich L. Superoxide dismutase: Improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels // Analytical Biochemistry. 1971. Vol. 44, № 1. P. 276-287.
- Bellincampi D. et al. Extracellular H2O2 induced by oligogalacturonics is not involved in the inhibition of the auxin-regulated rolB gene expression in tobacco leaf explants // Plant Physiology. 2000. Vol. 122. P. 1379-1385.
- Bouazizi H. et al. Cell wall accumulation of Cu ions and modulation of lignifying enzymes in primary leaves of bean seedlings exposed to excess copper // Biological Trace Element Research. 2011. Vol. 139. P. 97-107.
- Bradford M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding // Analytical Biochemistry. 1976. Vol. 72. P. 248254.
- Chance B., Maehly A.C. Assay catalase and peroxi-dase // Methods in Enzymology. 1955. Vol. 2. P. 764-775.
- Chen J. et al. Copper induced oxidative stresses, anti-oxidant responses and phytoremediation potential of Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens) // Scientific Reports. 2015. Vol. 5, № 13554.
- Cook C.M. et al. Effects of copper on the growth, photosynthesis and nutrient concentration of Phaseolus plants // Photosynthetica. 1997. Vol. 34. P. 179-193.
- Cuypers A. et al. Hydrogen peroxide, signaling in disguise during metal phytotoxicity // Frontiers in Plant Science. 2016. Vol. 7. P. 470.
- Drost W. et al. Heavy metal toxicity to Lemna minor: studies on the time dependence of growth inhibition and the recovery after exposure // Chemo-sphere. 2007. Vol. 67, № 1. P. 36-43.
- Elleuch A. et al. Morphological and biochemical behavior of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) under copper stress // Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety. 2013. Vol. 98. P. 46-53.
- Hamim H., Miftahudin M., Setyaningsih L. Cellular and ultrastructure alteration of plant roots in response to metal stress. In Plant growth and regulation-alterations to sustain unfavorable conditions. London: IntechOpen, 2018. pp 21-41.
- Holubek R. et al. The recovery of soybean pants under short-term cadmium stress // Plants. 2020. Vol. 9. P. 782.
- Khatun S. et al. Copper toxicity in Withania somnifera: Growth and antioxidant enzymes responses of in vitro grown plants // Environmental and Experimental Botany. 2008. Vol. 64. P. 279-285.
- Ku H.-M. et al. The effect of water deficit and excess copper on proline metabolism in Nicotiana ben-thamiana // Biologia Plantarum. 2012. Vol. 56, № 2. P. 337-343.
- Maksimovic J.D. et al. Peroxidase activity and phenolic compounds content in maize root and leaf apoplast and their association with growth // Plant Science. 2008. Vol. 175, № 5. P. 656-662.
- Mohammed A.S., Kapri A., Goel R. Heavy metal pollution: source, impact, and remedies // Biomanagement of Metal-Contaminated Soils. 2011. P. 1-28.
- MostofaM.G., FujitaM. Salicylic acid alleviates copper toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings by up-regulating antioxidative and glyoxalase systems // Ecotoxicology. 2013. Vol. 22. P. 959-973.
- Moustakas N.K., Ntzanis H. Estimating flue-cured tobacco leaf area from linear measurements, under mediterranean conditions // Agr. Med. 1998. Vol. 128. P. 226-231.
- Printz B. et al. Copper trafficking in plants and its implication in cell wall dynamics // Front. Plant Sci. 2016. Vol. 7. P. 601.
- Thounaojam T.C. et al. Zinc ameliorates copper-induced oxidative stress in developing rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings // Protoplasma. 2014. Vol. 251, № 1. P. 61-69.
- Uchiyama M., Mihara M. Determination of malo-naldehyde precursor in tissues by thiobarbituric acid test // Analytical Biochemistry. 1978. Vol. 86, № 1. P. 287-297
- Vijayarengan P., Jose M.D. Changes in growth, pigments and phytoremediating capability of four plant species under copper stress // Journal of Environmental Biology. 2014. Vol. 21, № 5. P. 119-126.
- Yruela I. Copper in plants // Brazilian Journal of Plant Physiology. 2005. Vol. 17. P. 145-156.
- Zaia D.M. et al. Spectrophotometric determination of total proteins in blood plasma: a comparative study among dye-binding methods // Brazilian archives of biology and technology. 2005. Vol. 48, № 3. P. 385-388.


