Выбор и обоснование ткани для разработки набора специальной одежды для прядильщиков
Автор: Н. Т. Гафурова, М. Э. Хужаева
Журнал: Современные инновации, системы и технологии.
Рубрика: Прикладные вопросы и задачи применения систем и технологий
Статья в выпуске: 5 (1), 2025 года.
Бесплатный доступ
В статье на основе представленных научных работ в данной области приведены результаты по систематизации и анализу данных при разработке специальной одежды для прядильщиков. На основе результатов анализа литературных данных были определены виды специальной одежды в соответствии с их назначением. Разработана классификация специальной одежды по общим характеристикам, по признакам защиты и угроз. Сделаны выводы по систематизации и анализу данных при разработке специальной одежды для прядильщиков. Также в статье представлены основные аспекты решения проблем, связанных с разработкой специальной одежды для работников прядильных цехов, таких как фактор повышения производительности труда и защиты от повышенной влажности, пыли и температуры воздуха. В работе определено количество хлопкопрядильных кластеров и прядильных предприятий в республике, а также количество работников, задействованных в процессе прядения, что является важной информацией для разработки специальной одежды, позволяющей создавать оптимальные по комфортности условия труда.
Исследование, формирование, спецодежда, анализ, прядение, предприятие
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/14133015
IDR: 14133015 | УДК: 677.074:687.157 | DOI: 10.47813/2782-2818-2025-5-1-2061-2065
Текст статьи Выбор и обоснование ткани для разработки набора специальной одежды для прядильщиков
DOI:
When selecting materials for specialized clothing for spinners, it is necessary to consider their working conditions, ergonomics of movements and safety requirements.
In recent years, the assortment of cloth with new properties for the production of special clothing has expanded significantly. There is no secret that special clothing made of cloth with high protective and physical-mechanical properties are necessary to maintain the ability to work and the health of workers. In addition to that, today a large number of special cloths with protective, hygienic, operational and aesthetic properties are being developed. These include: cloths that are resistant to friction, tearing and chemical exposure, less permeable to water, ensuring the stability of properties during operation, protecting from dust and certain environmental conditions, moisture-permeable and air-permeable, ensuring a comfortable state in the undergarment layer.
The current State Standards [1-2] impose a number of requirements for the selection of materials used to produce special clothing for protection against production factors, based on their quality indicators. The selected cloths must have high physical and mechanical properties, be resistant to abrasion and tearing, and meet hygienic requirements. Almost all natural fibers (cotton, flax, wool) and widespread chemical fibers (artificial - viscose, chemical -polyamide (PA)) [3-4] are used in the production of cloths for special clothing.
Cotton fiber cloths meet the basic hygienic requirements for special clothing, are hygroscopic, breathable and vapor-permeable, hypoallergenic, and create conditions for gas and heat exchange between humans and the environment. However, cloths made from natural fibers have high water permeability and are less durable.
In order to improve the protective properties of cloths made from natural fibers, various artificial and synthetic fibers are added to them: viscose, nylon, lavsan, nitron, etc. Most cloths made from synthetic fibers are resistant to tearing and abrasion, resistant to environmental conditions, and less permeable to water.
RESEARCH AND METHODS
In order to ensure the free movement of workers in special clothing, the choice of cloths with elastane fibers is of great importance, since they provide comfort due to their stretchability when performing active physical activities [5].
Research of protective properties from unfavorable environmental factors, which is the main indicator of the quality of special clothing, is a complex and multifaceted task, the solution of which has not lost its relevance.
In order to protect spinners from hazardous and harmful production factors, it is necessary to use materials with a smooth surface and high density, the necessary moisture and air permeability. The analysis showed that at present there are materials that meet these requirements and have high hygienic and protective properties, which creates conditions for improving the range of special clothing.
According to State Standard 11209-2014, the following requirements are imposed on special clothing:
-
• ensuring regular operation for 12 months under the conditions of production of special clothing;
-
• special clothing should be lightweight: a set should not exceed 1-2 kg;
-
• special clothing should be economical and inexpensive to produce, made of cheap materials, while ensuring high quality;
-
• special clothing should correspond to its functions, be clear and have a sufficiently presentable appearance.
The requirements specified in the state standard for special clothing include various aspects [6-7].
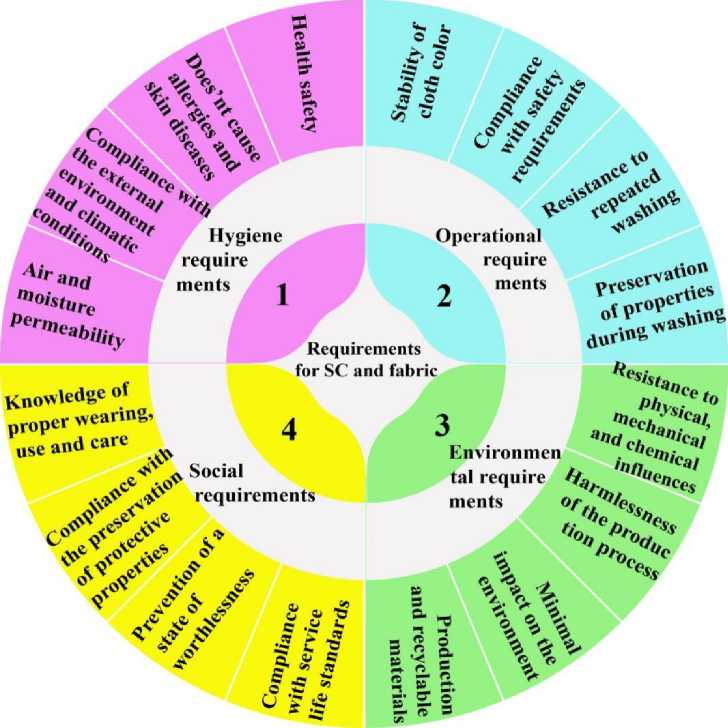
In addition, modern requirements for textile materials selected for special clothing can be expressed as follows (Fig. 1):
-
1. Hygienic requirements:
-
• special clothing (SC) should be made of materials that are safe for health, do not cause allergies and skin diseases, suitable for environmental and climatic conditions;
-
• clothing should be well breathable, have the necessary ventilation elements to prevent overheating and moisture accumulation.
-
2. Operational requirements:
-
• special clothing should not lose its properties even after repeated washing;
-
• all paints and clothing parts used for cloth must comply with safety standards.
-
3. Environmental requirements
-
• materials must be resistant to physical, mechanical and chemical influences;
-
• special clothing must have minimal impact on the environment (humidity, air temperature, dust) or be made of recyclable materials;
-
• in the process of manufacturing special clothing, it is necessary to comply with the standards for the emission of harmful substances into the atmosphere.
-
4. Social requirements
-
• it is necessary to conduct training and instructions on how to wear and properly use special clothing,
how to care for it (washing, sewing on torn buttons, repairing when seams are torn).
-
• it is necessary to protect special clothing from losing its protective properties, prevent it from becoming unusable, determine the standards for service life and regular replacement.
The choice of materials for special clothing for spinners should include a description of cloths that ensure the safety of workers and comfortable conditions for them in working conditions at the production site [7-8].
tai require merits
Hygiene
Operational require ments
Requirements for SC and fabric require ments
Social requirements
W n,oi»ltl.e Pe^bitity s ^ я
5 S ”
^«а^ч
^-»4
-s'*'
e>eX% ^
Knowledge of proper weanng, use and care ^
Fig. 1. Classification of modern requirements for cloths selected for special clothing.
LLC “Bukhara Cotton Textile” (BCT) produces a wide range of denim cloths made from cotton fiber.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Denim is a cloth used in sewing clothes. The word denim comes from the French de Nimes (from the city of Nimes). Cotton denim originated in England in the XVIII century and reached the United States by the 1830-s. At present, denim is a strong, elastic, not too thick cloth.
Denim is a cloth made by interweaving dyed warp threads and undyed weft threads. As a result of the diagonal cut, the twill weave of the cloth has a density and high elasticity. The warp threads used in the production of these cloths are usually dyed indigo [6].
Clothes made from this cloth were very comfortable, and they began to be used for work overalls and trousers.
Jeans are denim trousers that sometimes contain elastane. At present, denim is often referred to as denim cloth or jeans, although there is some confusion here.
Types of denim cloth:
-
1. Indigo (blue) denim, obtained by dyeing it with a dye obtained from a plant called indigo. It is blue on the outside and white on the inside.
-
2. Stretch denim has artificial or other elastic combined fibers added to it to make it soft and flexible.
-
3. Crush denim has been treated to create folds on the surface.
-
4. Acid-washed denim – the stain appearance is achieved by treating it with chemicals and pumice.
-
5. Raw denim – cannot be washed after dyeing. It is woven from coarser threads.
-
6. Shrink-free denim – specially treated to prevent shrinkage when washed. This applies to almost all types of jeans, except raw ones.
The assortment of cloths produced by BCT LLC is shown in Table 1, which meet the above requirements for the selection of cloths for special clothing for spinners and their structural parameters. These indicators are based on the results of experimental tests of the cloth quality control laboratory of BCT LLC.
Table 1. Composition of fibers and dimensional parameters of cloths produced by BCT LLC.
|
Name and composition of the fiber |
Name of the fabric |
Composition of cloth fibers, % |
Indicator name, unit of measurement |
||||
|
Surface density, g/m2 |
Tearing force, N (1N=kg m/s2) |
Change in dimensions after moistening or chemical treatment, % |
|||||
|
Warp |
Weft |
Warp |
Weft |
||||
|
With cotton fiber |
Vihara Marine Blue |
100% cotton |
200 |
670 |
789 |
-2.8 |
-10.8 |
|
With cotton fiber |
Atlas marina blue |
98% cotton, 2% spandex |
245 |
489 |
538 |
-1.3 |
-9.8 |
|
Atlas imperial blue |
98% cotton, 2% spandex |
247 |
474 |
648 |
-1.3 |
-9.8 |
|
|
Cappadocia marine blue |
98% cotton, 2% spandex |
251 |
648 |
655 |
-3.3 |
-8.3 |
|
|
With mixed fiber |
Samurai marine blue |
55% cotton, 2% spandex, 43% polyester |
300 |
567 |
603 |
-3.7 |
-17.3 |
|
With mixed fiber |
Atlas Oxford blue |
94% cotton, 2% spandex, 4% polyester |
301 |
557 |
583 |
-14.5 |
-33.8 |
|
Atlas Spacex OD black |
94% cotton, 1% spandex, 5% polyester |
303 |
583 |
605 |
-16.5 |
-35.8 |
|
|
Simurg imperial blue |
94% cotton, 2% spandex, 4% polyester |
305 |
569 |
521 |
-5.7 |
-13.7 |
|
|
Samurai SpaceX |
94% cotton, 2% spandex, 4% polyester |
298 |
485 |
553 |
-4.3 |
18.9 |
|
|
Khiva imperial blue |
94% cotton, 2% spandex, 4% polyester |
302 |
354 |
388 |
-2.6 |
-11.1 |
|
CONCLUSION
Compliance with regulatory requirements for special clothing is important to ensure the safety and health of workers, as well as to protect the environment. Regular inspections and standard updates help maintain high quality and safety requirements. The viability of a special garment is determined by the mechanical effects of the fabrics to be selected and the resistance to multiple washes.
In order to effectively manage physical and chemical risks in the production of spinning threads, it is necessary to carry out regular assessments of working conditions, the use of personal protective equipment (PPE), the organization of training and instructions for workers, as well as measures to improve working conditions. These activities will help reduce professional risks and ensure the safety of workers.
Assessment of working conditions requires an integrated approach in spinning factories, which includes physical, chemical, psychological and organizational aspects. It helps not only to improve the safety and health of workers, but also to increase the overall production efficiency and performance of the enterprise.
On the basis of social research carried out at spinning enterprises and the demand and suggestions of respondents, experts, information was collected that would be needed to create a new special set of clothing samples for spinners.


