Web Search Customization Approach Using Redundant Web Usage Data Association and Clustering
Автор: N. Krishnaiah, G. Narsimha
Журнал: International Journal of Information Engineering and Electronic Business(IJIEEB) @ijieeb
Статья в выпуске: 4 vol.8, 2016 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The massive growth of web consists of huge number of redundant information in related to some context. Due to which the need of information through a search provide high number of duplicate results which makes user to navigate number of sites to find the needed information. Users often miss their search pages when they browse the large and complex navigation of the web. Web customization is based on the use of the web logs can take advantage of the knowledge necessary to study the content and the structure of the internet to support. Searching information can be improvised in support of the implicit information generated by the web server in form logs for various web documents visited by users. This paper proposes a web search customization approach (WSCA) using redundant web usage data association and hierarchal clustering. Association generates a multilevel association for redundant data in the web navigation sites and clustering generates a cluster of frequent access patterns. The approach will improvise the real-time customization and also cost requirement for generating customized resources. The experiment evaluation shows an improvisation in precision rate in relevant to different queries against existing clustering approach.
Clustering, Association, Web Search, Web Usage logs, Customization, Redundant data
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/15013430
IDR: 15013430
Текст научной статьи Web Search Customization Approach Using Redundant Web Usage Data Association and Clustering
Published Online July 2016 in MECS
The growth of the Internet search engine's dependence increases the wide range of challenges and at the same time to provide more relevant results to the user. Search engines mostly presents the same results for different types of user when same type of question are requested without any knowledge about their different information needs and preferences [1],[8],[9],[10].
To provide information based on the user query often fail to land the required page because of the very short context text of the query [21]. Results of individual topics or key questions will mingle in the event list, which means that users will need to go through a lot of irrelevant results to find those which are interested, but in mostly the search engines fails to identifies the results which can be relevant to user query and can meet the intention [12],[17]. A typical search engine gives the same results regardless of the intent of the user. Therefore, the search can be customized, which can provide the relevant results to the user.
The most difficult problem that must be met during the customization process is a violation of user privacy. Many users either directly or indirectly avoiding the use of cookies or disclose personal data in the registration forms, and are not willing to visit websites that are prone to disclose personal information. In both cases, the user name will not be used without their permission and in many cases they have lost all records of their activities.
A user with cookie technology, in addition to the disclosure of such information is at the user site without permission, it is exchanged between sites and agreed to provide their personal information [11], [18]. Main information on the data collected from the Web site to communicate to the user, and the problem for something different ways, therefore, the process of reading the privacy policy of the user will be trimmed to an automatic data flag.
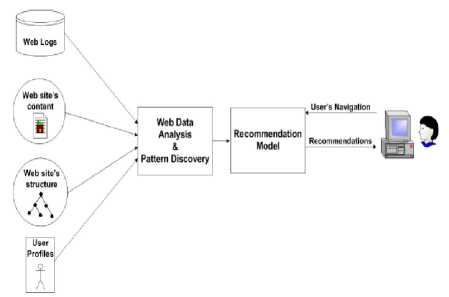
Fig.1. Conventional Web Customization Approaches
Many conventional methods [22], [23], [27],[28] are proposed for web search has been developed using hybrid content-based collaborative filtering techniques, location preferences, and collaborative filtering with technical web content filtering based on support proposed options which are valued based on the recommendations on the website as shown in Fig.1.
However, most users surf websites proxy name these methods suffer from a major disadvantage [5], and it is difficult to get their identities [3]. Based on user feedback, or to register their interest are some of the positive development in the customization system. These systems are users require time and will therefore not use this method. Web server logs, and the latest technology derived from data stored to find interesting patterns Web application is based on the usage logs [6],[8].
A novel web search customization approach (WSCA) to search the user's query related web information has been proposed using association and clustering mining techniques to overcome this problem. Following paper is organized as, section-2 discusses the related works, section-3 discusses the proposed customization approach, section-4 discusses the experiment evaluation and results and finally section-5 discuss the conclusion.
-
II. Related Works
The customized user information needs to be having information of interest to each user search [2]. As a rapidly growing competition in the search market, some search engines were introduced customized search, such as Google Customized Search where can define the cluster of websites they are interested in different category. Some systems respond to user information processing needs of Web search use or to provide a better service for the accuracy, users that have already registered to their communities as demographic data [26],[29]. This method requires users to search beyond the hand to take additional steps to set by their preferences. So, the approaches should be developed which are definitely able to identify information needs of users. Because of the increasing need for customized search, researchers should be made to provide the relevant information by user's conditions.
The clustering technique [15], [19], [20], [30] groups together similar items based on a set of similar characteristics. Clustering is one of the most common techniques used for web usage mining and analysis [4]. It tries to group similar browsing patterns in this mining and analysis direction. Such as the standard k-means clustering algorithm is used to partition the space domain users based on the number of clusters, or the similarity distance among users [24],[25].
Jespersen et al. [8] proposed an analytical hybrid approach using click-stream sequences for visitor analysis. Sequences that can be used for mining activities of mining on the Web are hypertext, which is used in probabilistic language mix in the fact table. Mobasher et al. [9] discuss a unique process of knowledge discovery on the Web data and automatic online web page and uses web personalization system of mining-related activities.
Chi et al. [10] present "LumberJack" for building user profile based on clustering of user session and statistical analysis in traditional of traffic utilizing k-mean algorithm.
T.T. Sang Nguyen et al. [6] discuss an effectively means of a website's domain and web application by integrating knowledge-enhancement proposed a novel method to deliver improved Web page recommendation. The two new models represent domain knowledge to discuss it. Knowledge is the first model to represent the domain ontology. The second model is defined critical network are automatically generated to represent each of the domain, web pages, and they use relationships. Another new model, the conceptual prediction, domain knowledge and integrated use of web reviews definition of knowledge and web knowledge, a semantic network is proposed to automatically generate. Many questions have been developed to effectively investigate knowledge bases. Based on these questions, suggestions candidate proposed to create a series of strategies on the web page.
Bin Jiang et al. [4] progressively and systematically modeled uncertain objects respectively, both continuous and discrete random variable are modeled as continuous and discrete domains as uncertainty model objects. It uses Kullback-Leibler divergence similarity measure for distinguish uncertain objects in both continuous and discrete cases. It also integrates into partitioning and density-based clustering methods to cluster uncertain data. In particular, the ongoing fragmentation computing using KL is expensive or infeasible. To speed up the process of changing the calculation kernel estimation using Gauss faster rate KL by the ongoing fragmentation of the case to deal with the problem.
-
F. Akhlaghian et.al [11] presents a customized searching mechanism based on ontology and fuzzy clustering. The proposed personalize engines using an automatic network fuzzy concept for constructing customization search result. The main purpose of the use of ontology is to improve the design concepts based on common Fuzzy cluster network built according to the user.
K. J Kim and S. B. Cho [18] also proposed a customization approach using fuzzy approach for clustering documents, retrieving and analyzing the linked web documents.
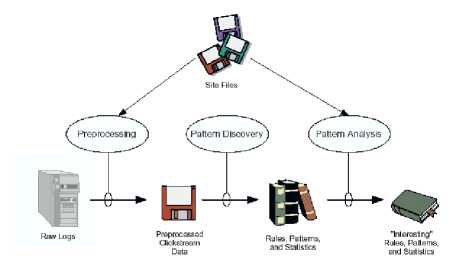
Fig.2. Web usage mining Process
Web usage mining (WUM) analyzing the web log data in the different data mining application as shown in Fig.2.
Mainly, used to extract web server log data of different websites. The standard model found in related to this have a central problem which is identified very interesting. It is necessary to exploit the huge source of World Wide Web to identifies the required knowledge for the advantage of organization needs in different domain and also in the need of user interest prediction and recommendation.
Web usage mining analyzes the behaviour of users according to the data recorded in search engine and Web site access logs. A large amount of search logs accumulated by web search engines in form of user clickthrough data. These logs typically contain user-submitted search queries, followed by the URL of Web pages, which are clicked by users in the corresponding search result page. Although these clicks do not reflect the exact relevance, they provide valuable indications to the users’ intention by associating a set of query terms with a set of web pages. If a user clicks on a web page link, it is likely that the web page link is appropriate to the query, or at least related to some extent. Several applications have been proposed along this direction, such as term suggestion [9], query expansion [7], and clustering of query [5][6].
Current search engine extracts a big list of results extracted for a query keywords matching. Most of the users are only interested on the top few results retrieved. However, the demand of presenting query relevant results to satisfy the user need is a top priority in information extraction and customization.
It seems highly complex in terms of finding relevance information without user support, because learning a user requirement completely depends on user individuality. The ambiguity in learning the preferences of two different user for the same query " Rock Star " might be different. It might be matching to a movie video, a game, a music album or picture. In all this ambiguity scenario a search engine always a face the challenge to learn what exactly the user intend to search.
-
III. Web Search Customization Approach
The integration of web customization and search engines need to be installed to improvise the speed and accuracy in the information retrieval for different web search. The use of a person's profile or on the basis of the output in a gesture of good results and expectations of interest for a variety of queries, so search engines can be customized to match all interests [7].
We proposed a custom web search customization Approach (WSCA) for search improvisation through effective association and clustering the redundant web usage data. It implements a user web log usage processing for customizing search results as presented in Fig.3.
User sends a search request to online web server where the server made the search operation and sends the result for the customization and at the same time web server save all the activity performs in web log file. User log file consists of the record timestamp, user system IP, type of request made, selected link URL and request link status code. To construct a Hierarchical clustered model [15] of the relevant usage data cluster it implements a frequent pattern mining in relate association to a query. Processing utility that updates the occasional cluster of log data is a background process. This approach reduces the cost of real-time processing.
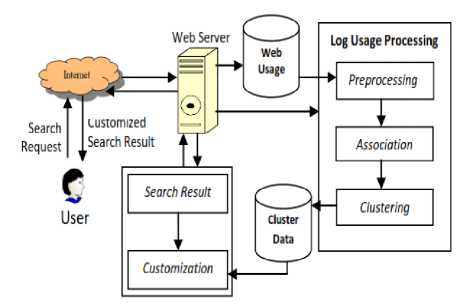
Fig.3. Framework for Web search Customization
-
A. Pre-processing of Web Usage Data
The purpose of Pre-processing is an act of processing of the log files record information on the use of web. Apply statistical and data mining techniques with regard to the use of this web site for more information about the interest and potential of the relations between the inner pages and users clustering web page can be identified by the preprocessing.
A web server for access to the server log file store for each Web page. Web log files, users, sessions, page views, etc. can be achieved by a user to log into the server in a normal text file. Each line in the log file represents a Web request. When a visitor requests a web page that contains two images, which are available on the Web page to post pictures of the lines are also appended to the log file. IP of Web site URL of the current page to the requested file or folder and demand of each line of type, location, date and time stamped with the name and address of the position of the user's computer code and the user ID of the requested file claim and size is specified.
By removing noise and conflict in the data files and log preprocessing to improve help improve the quality of information for data normalization. It cleanses the web page data corresponding written addresses, for example, an error, the graphics, the script file is the process of analyzing log files, and easily converts the data to normalize for the association and clustering.
-
B. Association of Web Usage Data
Using Association we recognize patterns using data mining techniques [16]. It helps to obtain information related to data based on some rules. To build an association pattern on a pre-processed data a multilevel association (MLA) rule mining is applied. A MLA rules helps in data log mining efficiently with the use of an hierarchal model support, which is based on a top-down strategy employed where it calculates the association of item sets of each level for working down in the hierarchy level in a more detail conceptual until no more related items sets found as shown in Fig.4.
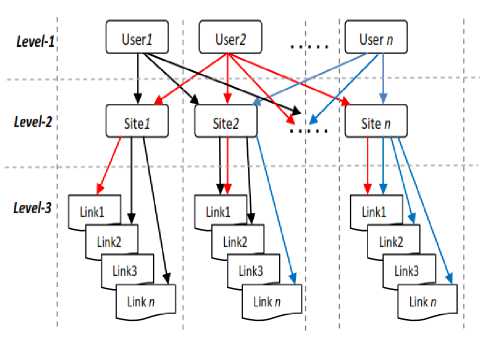
Fig.4. Multilevel Association of users log data Links
Let's assume a set consists of a collection of log records as, V= {v1, v2, . . . , vn } and another set of users as U = {u1,u2, . . . , un}. Then, using a normal association of V against each user in U we builds a top-down hierarchal association if the frequent occurrence of each v n >= 2.
-
C. Clustering of Web Usage Data Using Hierarchical Clustering
Hierarchical clustering solutions, are greatly interested for number of real-time application and different domains, which are generally in a form of tree structure known as dendograms. The level of tree provides a view of abstraction of the data at different level. It allows flat partitions of data to analyze in a granularity at different level to evaluate the consistency of clustering. The consistency of partition makes it ideal for visualization and discover the required clustering solutions. Even it was observed that a cluster of data may have many subclusters, this support to make its more flexible and natural solution for the application or domain having such subclusters in the underlying layers.
Hierarchical clustering solutions mainly use agglomerative algorithms [4], [19], [20] primarily to construct the clusters, where objects are tagged to its own cluster and pairing of clusters are repeatedly form until the complete tree structure are formed.
Based on the above associated data we can form an individual user cluster based on their link concept similarity. A cluster of information can be considered a type of data compression or equipment may be grouped into different categories, and so, but it is necessary for the collection of a large set of samples, the sample in each group and the label. A top-down method which is a divisive hierarchical clustering method [14] which is being used to group data to form a structure tree as shown in Fig.5.
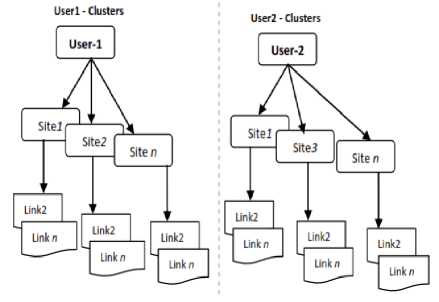
Fig.5. Hierarchical clustering of log data based Link Association
-
D. Web Search Customization Mechanism
To perform the web search customizations we integrate both association and clustering mechanism a runs a reranking algorithm in relate to the retrieve results. To customize the result we compute three measures using cluster pattern and results retrieved against the query as, website visiting frequency terms as, V f req , accessed link frequency term as , L f req , and average frequency term as U avg .
Let's assume a query Q is requested by a user U and we assume that a set of cluster pattern as C u being generated, and for this query we collected 10 top results retrieved in a vector as R and each results is mapped to a link. To compute the V f req , we find the frequency of site link occurring in the Cu against the total distinct web sites links in level-1 as k received for a query, it can be represented as equation-1,
V freq
I П -о« k^ C u ) ^ U ) distinct ( ( ( k ^ C ) ^ k ) ^ U )
and, to compute a L f req we find the frequency of link t occurring in the Cu against the total distinct web links in level-2 as m received for a query, it can be represented as equation-2,
L = I " = 0(( ti ,mi e C u ) ^ U ) (2)
freq distinct ( ( ( t , m ^ C ) * t , m ; ) ^ U )
Based on the computation of V freq and L freq we compute user average access as U avg using the equation-3,
U avg ^f V fe L+ L freq ) X100 (3)
the obtained Uavg measure will be computed for each results and it utilized for customization. The higher the Uavg the higher the relevancy to the query is considered and the entire results are ordered from higher to lower for the reply. This approach improvises a user web search and also meets the user interest based on their log history. We evaluate this approach in the following section using Google search results.
-
IV. Experiemnt Evaluations
-
A. Web Usage Log Datasets
A web log is a transcript of transactions made between a set of users and a set of servers. Fig.6 shows several lines of a typical log. For historical reasons, many web logs use the same format. The fields are separated by white space, typically a single space, although some fields are additionally quoted.
To evaluate the proposed approach we implemented the framework using Java and Apache web server. Apache web server implements real time methods to handle the request and response from users and also generates the respective web log files. To generate a log base we repetitively performs 3 different queries in related to songs downloading, online purchasing and online booking. Based on the generated data we construct the cluster through a multilevel association. Each search increases the user navigation and its relevant cluster patterns. The improvisation of user cluster pattern improves the user customization as well as user interest relevancy.
the customized results with varying the number of search result using the equation-4,
CP r =
-
• Precision: Precision is defined as the proportion of the number of relevant suggestions to the number of all customizations. In other words, precision measures the accuracy of the customizations.
1 5 | n | ^ | precision =
| S |
-
• Coverage: Coverage measures the ability of the customizations system to produce all the relevant results that are likely to be visited by the user. In other words, it shows how well the customizations covers all the pages that the user is likely to visit .It is calculated to measure the effectiveness of the customization system to produce correct suggested results, given by,
Coverage =------ | W |
Fig.6. Web Usage Log Data
-
• Fl-Measure: Ideally, a customization look for high precision and high coverage. A single measure that present this is the F1 measure which can defined as,
2 x Pr ecison x Coverage
F 1 - Measure = (7)
Pr ecision + Coverage
-
• R-Measure: In this evaluation the metrics precision- and coverage will be used to determine success rate of the customization. R-Measure is calculated by the ratio of coverage and the size of the customization result set,
Coverage
R1 - Measure = -------- (8)
| W |
The obtained results cluster pattern further evaluated to understands the effectiveness in terms of coverage, precision, F1-Measure and R-Measure in relevant to the query.
To evaluate this a test data T is divided into two sets. Set one consisting of n records, where n ϵ T, is considered as customized records of users. The second set, consists of W records need to be evaluated for the suggestion. The sets of results generated for suggestion denoted as S .
-
B. Evaluation Measures
-
• Customized Precision : It measure the efficiency of the approach we calculate the customized precision as CPR for the retrieve the results against
-
C. Result Analysis
In relate to the performance evaluation, we compare the proposed approach with an existing fuzzy approach [18] for document retrieval. The fuzzy approach performs the customization based on the user profile information. To do this performance analysis we consider 10 clusters for our approach and for fuzzy approach [18] we considered 3 users profiles.
The evaluation of the proposal has made using three users with different support threshold to compute the effect of the measures. The observed results shows an improvisation in precision and coverage rate as shown in Table-1.
Table 1. Result Evaluation Measures of different Users at different Support Threshold
|
Log Users |
Sup. Th. |
Precision |
Coverage |
Fl-Measure |
Ri-Measure |
|
User! |
2 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
0.011363637 |
|
4 |
0.5176471 |
0.48235294 |
0.4993772 |
0.010962567 |
|
|
6 |
0.5641026 |
0.43589744 |
0.49178174 |
0.00990676 |
|
|
8 |
0.5714286 |
0.42857143 |
0.48979595 |
0.0097402595 |
|
|
10 |
0.60273975 |
0.39726028 |
0.47888914 |
0.009028642 |
|
|
User2 |
2 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
0.02631579 |
|
4 |
0.5135135 |
0.4864865 |
0.49963477 |
0.025604552 |
|
|
6 |
0.5135135 |
0.4861865 |
0.49963477 |
0.025604552 |
|
|
8 |
0.5135135 |
0.4861865 |
0.49963477 |
0.025604552 |
|
|
10 |
0.5277778 |
0.4722222 |
0.49845678 |
0.024853801 |
|
|
User3 |
2 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
0.011904762 |
|
4 |
0.54545456 |
0.45454547 |
0.4958678 |
0.010822511 |
|
|
6 |
0.64615387 |
0.35384616 |
0.45727813 |
0.008424909 |
|
|
8 |
0.67741936 |
0.32258061 |
0.43704474 |
0.0076804915 |
|
|
10 |
0.7 |
0.3 |
0.42000002 |
0.0071428576 |
(1). Customized Precision
Fig.7 presents the customization precision of the proposed approach for 3 different users against the increment of cluster patterns. It shows that precision of result increasing with support of cluster patterns. It proves that support web usage log cluster data can be a useful input for web search customization. The experiment analysis also observed that in case high irrelevant log record in web usage low down the precision also.
approach [18]. The analysis of precision in varying the number of search results against different query shows an improvisation and shown low recall rate. The Fuzzy approach [18] customization depends on defined user profile. It is not possible for user to define all its interest in one instance which can meet the huge web information. It requires an automatic customization support which can be provided by WSC approach through effectively building the usage cluster patterns.
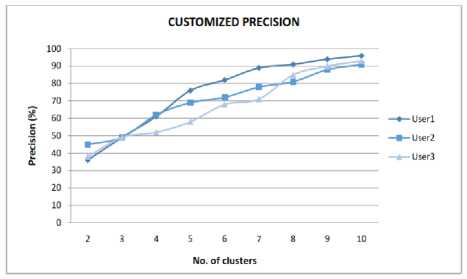
Fig.7. Customized Precision percentage
(2). Precision and Recall Performance
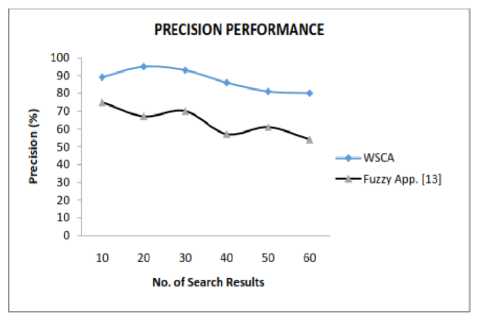
Fig.8. Precision Comparison between Proposed and Fuzzy Approach
Fig.8 and Fig.9, presents the precision and recall comparison of our WSC approach and existing Fuzzy
V. Conclusion
Web information search using web search engines facing a user's dissatisfaction want due to high ambiguous user queries. It also faces privacy concern to share data of different users for building customization knowledge. It required an implicit data which should not void the privacy and also support the customization. Web usage log generated by web server is a kind of data which can be used for search customization.
This paper, presents an efficient approach to improvise the web search using this web usage log through an integrated multilevel association and hierarchal clustering to construct a customized knowledge. Using this clustered pattern knowledge we efficiently able to provide precise result against the query result. The experiment result shows an improvisation in the customization precision and also in compare to the existing approach which is based on user profile shows an improvisation. The impact of both user profile and web usage log to form integrated clusters for user web search customization and user interest can be evaluated in the future works.
Список литературы Web Search Customization Approach Using Redundant Web Usage Data Association and Clustering
- Fatima, C. Luca and M. Hobbs, "Free-text user queries for semantic search", IEEE 13th International Conference on Industrial Informatics (INDIN), Page : 838 - 843, July 2015.
- S. S. Bhaskar and B. Tidke, "A New Approach and Compressive Survey on Restructuring User Search Results by Using Feedback Session",Int. Conf. in Computing Communication Control and Automation (ICCUBEA), Page: 479 - 484, Feb. 2015.
- R. M. Kaingade and H. A. Tirmare, "Personalization of Web Search based on privacy protected and auto-constructed user profile", Int. Conference in Adv. in Computing, Comm. and Informatics (ICACCI), Page.818 - 823, Aug. 2015.
- Bin Jiang, Jian Pei, Yufei Tao, Member, and Xuemin Lin, "Clustering Uncertain Data Based on Probability Distribution Similarity", IEEE Transactions On Knowledge And Data Engineering, Vol. 25, No. 4, April 2013.
- Wael K. Hanna, Aziza S. Aseem, M. B. Senousy,"Issues and Challenges of User Intent Discovery (UID) during Web Search", IJITCS, vol.7, no.7, pp.66-76, DOI: 10.5815/ijitcs.2015.07.08, 2015.
- Thi Thanh Sang Nguyen, Hai Yan Lu, and Jie Lu, "Web-Page Recommendation Based on Web Usage and Domain", Knowledge IEEE Transactions On Knowledge and Data Engineering, Vol. 26, No. 10, October 2014.
- Yiyao Lu, Hai He, Hongkun Zhao, Weiyi Meng, and Clement Yu, "Annotating Search Results from Web Databases", IEEE Transactions On Knowledge And Data Engineering, Vol. 25, No. 3, March 2013
- Jespersean S.E., Throhauge J., and Bach T., "A hybrid approach to Web Usage Mining, Data Warehousing and Knowledge Discovery", Springer Verlag Germany, pp73-82, 2002.
- Mobasher, B., Dai, H., Luo, T., & Nakagawa, M., "Effective Personalization Based on Association Rule Discovery from Web Usage Data", Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on Web Information and Data Management, 2001.
- Chi E.H., Rosien A. and Heer J.," LumberJack:Intelligent Discovey and Analysis of Web User Traffic Composition", In Proceedings of ACMSIGKDD Workshop on Web Mining for Usage Patterns and User Profiles, Canada, ACM press, 2002.
- F. Akhlaghian, B. Arzanian and P. Moradi, "A Personalized Search Engine Using Ontology-Based Fuzzy Concept Networks", International Conference on Data Storage and Data Engineering (DSDE), Pages. 137 - 141, 2010.
- R. C. de Amorim, B. Mirkin, and J. Q. Gan, "Anomalous pattern based clustering of mental tasks with subject independent learning some preliminary results", Artificial Intelligence Research, 1(1):46{54, 2012.
- Omar Y. Alshamesti,Ismail M. Romi,"Optimal Clustering Algorithms for Data Mining", IJIEEB, vol.5, no.2, pp.22-27, DOI: 10.5815/ijieeb.2013.02.04, 2013.
- I.S. Dhillon, S. Mallela, and R. Kumar, "A Divisive Information Theoretic Feature Clustering Algorithm for Text Classification", J. Machine Learning Research, vol. 3, pp. 1265-1287, 2003.
- H.P. Kriegel and M. Pfeifle, "Hierarchical Density-Based Clustering of Uncertain Data", Proc. IEEE Int'l Conf. Data Mining (ICDM), 2005.
- Jugendra Dongre, Gend Lal Prajapati and S.V. Tokekar, " The Role of Apriori Algorithm for Finding the Association Rules in Data Mining", IEEE International Conference on Issues and Challenges in Intelligent Computing Techniques, 2014.
- L. Cao, Y. Zhao, and C. Zhang, "Mining impact-targeted activity patterns in imbalanced data", IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng., vol. 20, no. 8, pp. 1053-1066, Aug. 2008.
- Kyung-Joong Kim and Sung-Bae Cho, "A personalized Web search engine using fuzzy concept network with link structure", Joint 9th IFSA World Congress and 20th NAFIPS International Conference, Vol. 1, Pages. 81 - 86, 2005.
- Baker L.D. and McCallum A.K., "Distributional clustering of words for text classification", In Proceedings of the 21st Annual international ACM SIGIR Conf. on Research and Development in info. Retrieval, pp 96103, 1998.
- Hongwei Yang, "A Document Clustering Algorithm for Web Search Engine Retrieval System", IEEE International Conference on e-Education, e-Business, e-Management and e-Learning, 978-0-7695-3948-5/10, 2010.
- R. Cheng, D.V. Kalashnikov, and S. Prabhakar, "Evaluating Probabilistic Queries over Imprecise Data", Proc. ACM SIGMOD Int'l Conf. Management of Data (SIGMOD), 2003.
- H. Cheng, X. Yan, J. Han, and C.-W. Hsu, "Discriminative frequent pattern analysis for effective classification", in Proc. ICDE, pp. 716-725, 2007.
- A. Jorge, "Hierarchical clustering for thematic browsing and summarization of large sets of association rules", in Proc. SDM, pp. 178-187, 2004.
- Liu, W. Hsu, and Y. Ma, "Integrating classification and association rule mining", in Proc. 4th Int. Conf. Knowl. Discov. Data Mining (KDD), pp. 80-86, 1998.
- M. Plasse, N. Niang, G. Saporta, A. Villeminot, and L. Leblond, "Combined use of association rules mining and clustering methods to find relevant links between binary rare attributes in a large data set", Comput. Statist. Data Anal., vol. 52, no. 1, pp. 596-613, Sep. 2007.
- Douglass R. Cutting, David R. Karger, Jan O. Pedersen, and John W. Tukey, "Scatter or Gather: A Cluster-based Approach to Browsing Large Document Collections", SIGIR '92, Pages 318 - 329, 1992.
- Daphe Koller and Mehran Sahami, "Hierarchically classifying documents using very few words", Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Machine Learning (ML), Nashville, Tennessee, Pages 170-178, 1997.
- L. Zhuang, and H. Dai. "A Maximal Frequent Itemset Approach for Document Clustering", Computer and Information Technology, CIT. The Fourth International Conference, pp. 970 - 977, 2004.
- Y. LI, and S.M. Chung., "Text Document Clustering Based on Frequent Word Sequences", In Proceedings of the. CIKM, 2005. Bremen, Germany, Nov.-5, 2005
- Lent, A. N. Swami, and J. Widom, "Clustering association rules", in Proc. ICDE, pp. 220-231, 1977.


