Work in the age of social uncertainty:10 theses and counter-strategies
Автор: Sieg A.
Журнал: Уровень жизни населения регионов России @vcugjournal
Рубрика: Парадигмы рынка труда
Статья в выпуске: 3 (197), 2015 года.
Бесплатный доступ
In my report I want to present 10 Theses on the Future Work in the 21st century. For each hypothesis, a proposal of how to react to this development will be offered. My examples are related mainly to societies in Western Europe, who are the ones most involved in the rapid development of global capitalism. However, we suppose that the presented evolutions and issues in the foreseeable future will occur worldwide. My overarching assumption is that over the next few years the tendencies of social uncertainty and social inequality - caused by the globalized and digitized capitalism - will increase radically. My contribution is committed to the method of Horkheimer / Adorno of classical critical theory, what means to analyze actual states and to propagate - even utopian - target states.
Precarity, social uncertainty, work, technological progress, knowledge, social pathologies, exclusion
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/143182098
IDR: 143182098
Текст научной статьи Work in the age of social uncertainty:10 theses and counter-strategies
Precarity: from periphery to centerof society
The current developments in the world of work in Western European societies are an indicator of all leading and rising industrialized countries (especially Russia).
Precarious working and living conditions — mainly characterized by uncertainty concerning planning and future — were first classified as a phenomenon of lower social milieus. Recently, precarious situations have gradually attained the center of societies. Fixed-term work contracts, temporary work, on-call employment, and other forms of precarious employment contracts are not only a feature of unskilled workers, but to find at all levels of employment.
Particularly in the UK, France and Germany, more and more people are affected by precarious working conditions and, to that effect of precarious living conditions. As French sociologist Robert Castel (2011)
describes, this precariousness is associated with the abolition of social gains –for that workers have fought in countless industrial disputes — and the dismantling of the welfare state.
Counter-strategies/Intervention
A strategy to fight such a permanent uncertainty on a financial level would be the implementation of the unconditional basic income for every resident in a market area. This model is easily realizable, such as, inter alia, Daniel Häni and Enno Schmidt (2008) prove, but still fails to present ideological reservations. In addition, compliance with the minimum wage with efficient state sanctions should be enforced.
-
2 Radical technological progress
Even today, a new generation of intelligent robots is on the rise in our brave new world of work. And they rule faster and faster. For instance, German company Kuka developed the lightweight robot LBR iiwa and called it a giant technological leap. This new generation of robots is characterized by their speed, their small size and their high artificial intelligence. Currently, Google and Apple buy robotics companies in order to become the global leaders in this booming area. According to a foresight by IFR World Robotics, in the next few years theseself-directed machines that will radically change our work environment, will not only become cheaper but will increase a lot in number (IFR Statistical Department 2014).
A key area holds the so-called cloud robotics. This cloud-based robotics will develop more intelligent and complex working robots. The robot has access to information from a data cloud and therefore to a huge database so it can record information and create calculations on its own .With these new robots, more delicate work operations, which could not be done by robots like fruit harvesting or complicated surgery are possible (cf. Jung, Alexander / Schulz, Thomas 2015).
Counter-Strategies/Intervention
Even Stephen Hawking and Bill Gates do warn about the new machine intelligence. These robots are increasingly replacing jobs because they work faster, more accurately and cheaper. And even if the head of Innovation Management of BMW Stefan Bartscher declared: «Man and machine work hand in hand»1 and the robots are considered as team workers as human team workers.
However, the adoption of robots permits to spend (labour) time for other activities such as community activities or self-realization. Here again, the unconditional basic income permits social participation on the need. We will see this later in point 9.
Current Conditions and Tendencies:Structural devaluation of knowledge and people
Through the forced changing work environment through technical innovation specific knowledge has been outdated faster and faster.
On the one hand this leads to high unemployment, especially in technical-oriented professions. On the other hand, this results in an ongoing shortage of skilled workers.
Currently, for example, in Germany there is a lack of some 30 000 engineers in various technical fields while around 50 000 engineers are unemployed, whose knowledge is outdated. For many of these unemployed people it is very difficult to keep the standards. Why? Because they have been trained many years ago and they are not quite familiar with the structure and culture of the new knowledge formations. Furthermore, the current education system is not geared to the variation of the «postmodern» learning and appropriate knowledge cultures, because it is oriented in its structure and in its function sequences implicitly on the reproduction of social structures.
These mechanisms produce systematically people who do not receive the necessary core competencies for the labor market and for independent living and they are most affected by precariousness and the associated uncertainties.
Counter-Strategies/Intervention
In Western Europe, particularly in Germany, the education system is primarily a tool for the reproduction of social structure as well as the recent OECD PISA
Annual supply of industrial robots 2012-2013 and forecast for 2014-2017
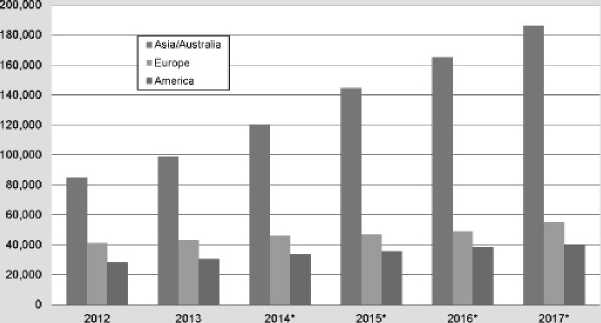
Source World Robotics 2014
Forecast
Graphic 1:
Annual supply of industrial robots 2012-2013 and forecast for 2014-2017
Source: World Robotics 2014
Bartscher, Stefan (BMW) in SPIEGEL 10/2015.
2014 could show. Thus, learning cultures and learning content in secondary schools are generally adapted to cultures of the privileged social backgrounds and alternative learning techniques and knowledge formations are sanctioned as illegitimate negative.
In different social milieus of a society, different learning cultures are internalized. In schools, universities and training institutions, however, learning cultures are favored, which correspond to the dominant milieu. This means for many people during their lifetime that they cannot participate successfully in this educational system.
Jean-Francois Lyotard, erected in his pioneering work in the year 1979 «The Postmodern Condition: A report of Knowledge» certain criteria for the knowledge of the future.
With his writing he created a template for various discussions in the modern «knowledge society». Following these discussions, various diversity approaches and the continued inclusion debate arose.
The key to our discussion of the embodiments of Lyotard diagnosis is that of the «radical pluralism» which for him includes the plurality of lifestyles, the plurality of norms, the plurality of truths and the plurality of theories (paradigmatic structures).
What does the analysis of Lyotard for the restructuring of education systems?
-
1. The still widespread reproduction of representative educational content will need to be increasingly shifted to the acquisition of core competencies.
-
2. The traditionally strong normative orientation of education is now forced to adapt to the element «discourse competence».
-
3. Theory-based instructions will be abandoned in favour of experimental designs of the educational process.
-
4. Social: From traditional ways of life, a plurality of life forms that also attracts different learning cultures and learning strategies by themselves which must be recognized as an equivalent.
Overall, the right to paid training based on different learning cultures should be required and especially the restructuring of the education system in terms of radical plurality.
Ambivalence of autonomy, flexibilityand project work
Boltanski and Chiapello (2003) show by means of their analysis of management discourse in their work «The New Spirit of Capitalism» that the categories autonomy, flexibility, project work once seen from an emancipated perspective have been turned into their opposite under the neo-liberal policies.
This leads to the emergence of a population with an unsafe working status, and / or long-term unemployment. Here demanded autonomy for forced and calls the whole personality in the form of a «roll call (s) to the subjectivity». Autonomy here does not mean more freedom of choice, but is under a dictation of action and competition.
Counter-strategie/Intervention
On temporary project work many employees in the last year of the project seem to have no more loyalty to their employer. In some companies it is to strengthen the loyalty to the employer to conclude on longer-term or permanent contracts. This is particularly reported in the daily press of Japan. Unfortunately this topic is still a desideratum of research. To limit the flexibility in terms of a dissolution of their availability in the work, particularly the policy and investigative journalism are needed which should establish a ban on these practices. In addition, clear international binding standards should be developed.
The labor entrepreneur — the ideal type of unsafe employee
A feature of the concatenation of neoliberal economics, administration and conservative social science is the installation of «invention» of social figures (see also Thesis 10).
A paradigmatic example of such a sociological concept creation which is readily taken up by the administrative side, and has become a fixed point of reference of sociological and economic expert discussion, the term of the labor entrepreneur, who discussed under the metaphor of entrepreneurial self.
Within the German debate on precarious employment the report «III. Part of the Commission’s questions about the future of Bavaria and Saxony Final Report «of 1997 is often cited. This report is in the history of the career of the «labor entrepreneur» the very basis of his career. From the administrative side, the concept of «labor entrepreneur» or the model of the «entrepreneurial self» since the publication of this manifest of the «neo-liberalization» of society takes an almost inexorable rise. The report states in part: «The vision of the future is the individual as an entrepreneur of his labor and general interest» is.
The type of the «labor entrepreneur» is characterized by «increasing self-control», «self-commodification» and «self-exploitation of their own work potential.» In parallel to find a «boost of self-management» and «self-rationalization» in everyday life instead.
Another feature of the labor entrepreneur is an ambivalent concept of autonomy, which is not there a autonomy of the worker, but an extension of responsibilities and scope that are in the interests of the contracting company. The forms of enhanced autonomy associated with «clear boundaries of autonomy based work and with an increased» pressure to perform «. The workers can make their work under these conditions, more and more «self-organized», but they are also forced.
With the construction of the «labor entrepreneur» a work of sociological type was developed, which acts as an ideal type of precarious work and life forms. There is a risk that this labor entrepreneur is on paper to a fully comprehensive model of post-modern worker.
Counter-strategy / intervention:
Scientific education and discourse analysis (detail see thesis 10).
The new philosophy of work: Dissolution of boundaries: surveillance, control and total availability
The new philosophy of work under a neoliberal perspective means the dissolution of work. This means, first, that more and more a fusion of work and leisure is taking place. Ideally, the constant availability and total control and surveillance of the workers are sought as by e-mail, phone and video surveillance.
In his book «Discipline and Punish», French philosopher Michel Foucault takes the «Panopticon»
of Jeremy Bentham as a model for the modern world of work. The «Panopticon» of Jeremy Bentham works on the principle that the monitored person cannot see if it is actually monitored. But he must assume that she is monitored and controlled. This puts her under constant pressure and changes her behavior.
Counter-Strategies/Intervention
See Counter-strategies / Intervention theses 4.
Requirements in the labor market result in social pathologies
Precarious working and living conditions that have emerged gradually due to the change in the labor market and social structures in Germany and in other Western European countries since the 1990s, do change simultaneously, as is evident from various studies, the psychological disposition and constitution of precarious employees, the unemployed but also the people who are in a traditional «normal employment».
The described effects of mental dispositions are comparable to states which traditionally occur in patients with a psychiatric diagnosis, so most strikingly, the French sociologist Alain Ehrenberg, in his work
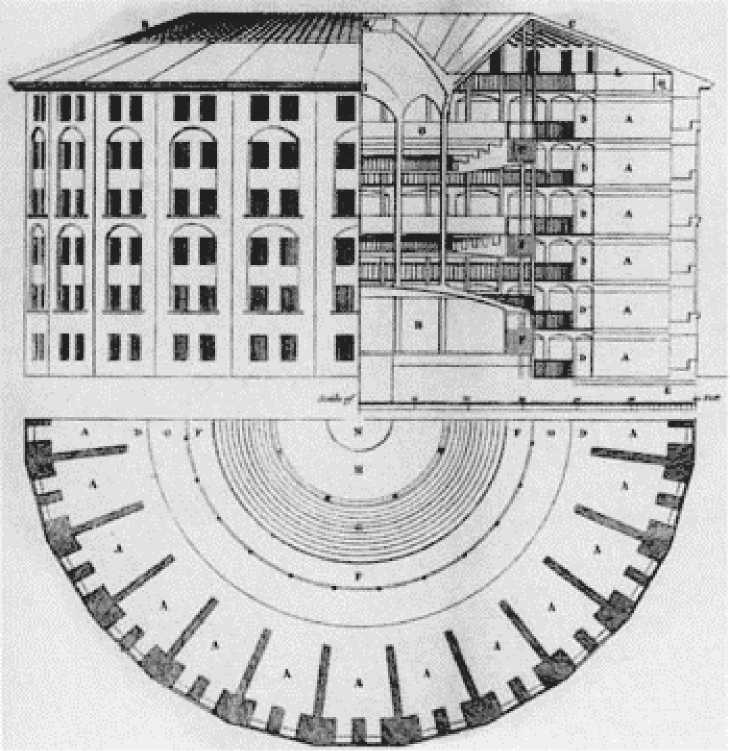
Graphic 2:
The «Panopticon» of Jeremy Bentham
Source:
«The uneasiness in the society» (Ehrenberg 2011). These are superficial: loss of social relationships, withdrawal, listlessness (inactivity), vulnerability, insecurity. The psychopathological terms for the consequences of these characteristics are: depression, vulnerability, fear.
However, the reasons for the seemingly individual psychopathologies are not medical, but they are — so the theory — primarily on the transformation of work and life in recent years due to an enhanced «mandatory autonomy» demand of the people, which in itself is a paradox.
Counter-Strategies/Intervention
Respect and appreciation for all members of society: the development of a culture of recognition. The discussion of recognition was performed without exception social philosophy in recent times. She is still a desideratum sociological, anthropological and social psychological theories.
Objectives of the intervention: life satisfaction, opportunities for a lifetime, future, anthropologically: emancipation, autonomy develop (trust in autonomy), self-realization, skills, social recognition.
Sociological theming of suffering as by qualitative interviews and qualitative studies (examples Bourdieu et al., 1997, Schultheis / Schulz 2005 Schultheis / Gemperle 2010). No taboo of suffering, no individualization of suffering, no pathologizing of suffering.
Conviction of employers using the example of studies of job satisfaction that a higher job satisfaction with a higher motivation, greater identification and thus a higher commitment, a performance and with less loss of work goes hand in hand.
Social divide is increasing: old and new inequalities reinforce
Various data show a tendency in Europe to a strong division between high-paid, insecure services and very poorly paid services. Both, however, are characterized by uncertainty. New social inequalities reinforce old social inequalities that occur to become once again (see Castel 2011).
Particularly through the development of a so-called «knowledge society» takes the differentiation of the social structure and thus the social inequality increases.
Counter-Strategie/Intervention
See Theses 10.
The superfluous — exclusion
In various publications people are described as «prohibited» or even «superfluous», who do not comply to neoliberal labor market requirements or people who do refuse these standards. Seen from a sociological- economical perspective, it is a social group that just is not excluded, but occupies the important function of a «reserve army» within the labor market system.
In the ideology of the suspended precariat the development of a new dangerous class (Guy Standing) should be avoided.
Counter-Strategies/Intervention: Thereare no superfluous people
In» The Two Faces of work «Pierre Bourdieu shows his results of socio-ethnographic research in a precapitalist society (in Kabylia in Algeria). These studies show that solidarity, community and sharing of labor income goes back to prehistoric and the utilitarian philosophy of economics, which has the «homo economicus» implemented, is inhuman.
Social science clarification
In the essay «Brave New World phrase», Bourdieu and Wacquant pointed out that during the neoliberal restructuring of the economy and society and the associated changes in the labor market, an arsenal of new concepts emerged. These are, among other concepts such as «control», «employality» or «zero tolerance». In parallel, traditional terms such as identity and flexibility are converted and associated with a new horizon of meaning. On the other hand, disappear from the media and academic discussions terms such as «exploitation», «domination» and «inequality», which are regarded as insignia of a bygone world (cf .: Bourdieu / Wacquant 2000: 1 f.).
Uncover the euphemisms this «brave new world of concepts» and to formulate a precise criticism of this epistemological based criteria, is the ethical duty of every social scientist.
„The task of sociology, according to Pierre Bourdieu, is «to uncover the most profoundly buried structures of the various social worlds which constitute the social universe, as well as the «mechanisms» which tend to ensure their reproduction or their transformation.» (Wacquant/Bourdieu 1992: 7).
Conclusion
We could show that particularly by digitization and globalization of business entities, processes in motion, the mean of life and work of many people under radical changes.
In particular, the factor of increasing uncertainty in all living and working areas will put people in the advanced industrial countries with major challenges. In addition, the social structure is further differentiated by social inequalities and it destabilizes the highly industrialized societies. Political forces, trade unions and especially scientists are encouraged to develop new responses and enforce them.
Список литературы Work in the age of social uncertainty:10 theses and counter-strategies
- Boltanski. Luc/Chiapello, Éve: Der neue Geist des Kapitalismus (2003). Konstanz: UVK.
- Bourdieu, Pierre /Wacquant, Loic (2000): Schöne neue Begriffswelt. Le Monde diplomatique, 12.05.2000.
- Bourdieu, Pierre (2004): Der Staatsadel. Konstanz: UVK.
- Bourdieu, Pierre et. al. (1997): Das Elend der Welt. Zeugnisse und Diagnosen alltäglichen Leidens an der Gesellschaft. Konstanz: UVK.
- Castel, Robert (2011): Die Krise der Arbeit. Neue Unsicherheiten und die Zukunft des Individuums. Hamburg: Hamburger Edition.


