Working of the development strategies of municipalities on the basis of simulation modeling
Автор: Oreshnikov Vladimir Vladimirovich, Nizamutdinov Marsel Malikhovich
Журнал: Economic and Social Changes: Facts, Trends, Forecast @volnc-esc-en
Рубрика: Мodeling and informatics
Статья в выпуске: 5 (17) т.4, 2011 года.
Бесплатный доступ
The article deals with the urgent problems and approaches to modeling the development of territorial socio-economic systems. The authors suggest an approach to working out the integrated tools for modeling the development of territory and represent some results of its practical testing within the framework of development «Comprehensive Program of Socio-Economic Development of the city district of Ufa in 2011 - 2015».
Economic policy, simulation, strategy of development, scenario analysis
Короткий адрес: https://sciup.org/147223287
IDR: 147223287 | УДК: 338.27(470.57-25)
Текст научной статьи Working of the development strategies of municipalities on the basis of simulation modeling
Economic and socio-political transformations in the Russian Federation, started in 1990s, promoted the authority decentralization and acquiring by the regions independence in the solution of the questions of socio-economic development.
At the same time the process of transformation of the socio-economic relations was accompanied by a sharp reduction of the state’s role in regulation of economic processes, by opposition between the federal center and the subjects of the Federation, by easing of in-Russian economic relations. It led to the increase of asymmetry of the territorial socio-economic development.
The dynamics of distinctions bet ween the subjects of the Russian Federation has not reduced [6].
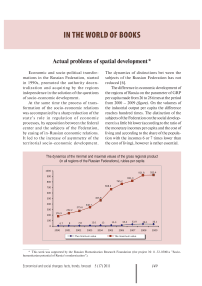
The difference in economic development of the regions of Russia on the parameter of GRP per capita made from 26 to 28 times at the period from 2000 – 2009 (figure) . On the volumes of the industrial output per capita the difference reaches hundred times. The distinction of the subjects of the Federation on the social development is a little bit lower (according to the ratio of the monetary incomes per capita and the cost of living and according to the share of the population with the incomes 6 or 7 times lower than the cost of living), however is rather essential.
The dynamics of the minimal and maximal values of the gross regional product (in all regions of the Russian Federations), rubles per capita
The minimum value The maximum value
The extremely high level and constant strengthening of the territorial differentiation of the subjects of the Russian Federation threatens with infringement of the national economic space’s integrity of and as the consequence, makes serious threat to the country safety. In this connection the problem of the spatial differentiation of the territories and search of the ways for its solution becomes the subject of the increasing number of the researches made by the leading Russian economists. The results of the researches carried out on the mentioned problematic are published in scientific journals on the regular basis.
Studying of the spatial development is one of the directions of the research activity of the Institute of economic researches of the Russian Academy of Science, headed by the academician P.A. Minakir. The basic achievements in this direction are represented in the materials of the journal “Spatial economy”. But we would like to address to P.A. Minakir’s article “Myths and the reality of the spatial economic disproportions” which was published in the first number of the journal “Federalism” in 2011. The author doesn’t only prove the reasons of differentiation of the Russian regions, but also opens the methodology of management of the regional economic development based on the strategic approach.
It is necessary to agree with P.A. Minakir’s statement that “in 1990s the spatial disproportions were considered as natural and even desirable result of the transition to the market mechanisms of distribution of economic resources…” to which the chosen liberal economic policy led. The consequence of this direction became the basic disproportions which cause anxiety and are the subject of the experts’ discussions:
-
1. Amplification of inter-regional differentiation on the parameters of the standard of living of the population, and especially on the level of its incomes.
-
2. Growing inter-regional differentiation on the level of the economic development.
-
3. Progressing depopulation in a number of the Russian regions at amplifying concentration of the population in the capital, in the regions of the Central and Southern Federal Districts.
-
4. Amplifying disproportion between the economic growth and the development of infrastructure in the most effective centers of concentration of economic power.
At the same time it would be desirable to draw the readers’ attention to such type of the territories’ differentiation, as intraregional differentiation. The researches carried out at the Institute of the socio-economic development of the territories of the Russian Academy of Science allow drawing the conclusion that the spatial development of the territory of the Vologda Oblast follows the way of polarization.
Studying of the tendencies of the spatial development showed, that in the area the city agglomeration is formed; its structure includes two cities of the regional submission (Vologda, the regional center and Cherepovets, the largest industrial center) and 13 municipal areas [7]. The development of the agglomeration zones is also promoted by the creation of the industrial park “Sheksna”.
Speaking as a whole about the spatial development of the region, it is necessary to note the increase of the quantity of the small settlements (with the number of inhabitants to 5 person) and at the same time of the large settlements (over 5 thousand person) in the structure of settlements.
Degradation of the structure of the settlements’ networks, its degeneration cause secession of the grounds from agricultural turnover and loss of the socio-economic control over many historically explored territories. This process has steady character and is connected basically to the extinction of the aged population, outflow of youth and attenuation of the industrial, social and cultural activity in villages.
Cities absorb agricultural population of the extensive territories, simultaneously creating around them powerful fields of influence on rural areas, promoting concentration in the suburbs of the agricultural production directed on city needs’ satisfaction. Therefore, where the density and the sizes of cities are greater, the wider are the areas with the developed agriculture, and the greater is the population. In the distance from cities there are the zones of the agrarian (and, hence, the general) depressions.
Thereof the polarization of separate areas accrues: a part from them (first of all the central and southern areas) concentrates the population, becoming the centers of the country-recreational activity, industry, logistical networks, etc.; the others, on the contrary, are “unpromising”, differ by the reduction of the agrarian space, disintegration of the large-scale enterprises, reduction of the population.
This tendency is most brightly characterized with the data on the significant differentiation of municipalities according to the level of the development of industry and agriculture. In 2009 the break between the leader in the volumes of the industrial production (Cherepovets) and the outsider (Nyuksenitsa District) reached hundred times. If to compare the regional municipalities (without cities of
Vologda and Cherepovets) the distinctions between them decrease a little, however all of them are rather significant. Besides the share of the areas in the Oblast’s industrial production is reduced: in 2000 it made 14.2%, and in 2009 only 9.2% [6].
The situation in agricultural production is similar. The break between the rural areas in agricultural production increases. The difference in the volumes of agricultural production per capita between the Vologda Oblast, most advanced in this plan and the area-outsider makes more than 20 times. However the changes of the developed situation are not seen. The data on the level of intensification and efficiency of agricultural production allow making such a conclusion (table) .
So, counting for 100 hectares of farmland in the suburbs (I type) in comparison with the peripheral rural areas (IV type) fixed capital is almost 4 times higher, labor sources are 2.5 times higher, productivity of the capital is 2.5 times higher, labor (work) 3.8 times higher, land is 10 times higher.
Having 35% of the agrarian lands, the facilities of the suburbs in Vologda, Cherepovets, Sheksna and Gryazovets districts make 75% of the regional volume of agricultural products. And the facilities adjoining to this zones, and peripheral, having two thirds of farmland produce only 25% [2].
Level of the intensity and efficiency of agricultural production depending on the district types of the Vologda Oblast [1]
|
Fixed capital for agriculture, thousand rubles for 100 hectares of farmland |
Manpower provisioning, people for 100 hectares of farmland |
Realized production |
||
|
thous. rub. for 100 hectares of farmland |
rub. for 100 rub. of fixed capital |
thous. rub. for 1 agricultural worker |
||
|
I type. Suburbs (5) |
||||
|
134 |
6.0 |
1476 |
109 |
246.2 |
|
II type. Areas situated nearby suburbs (6) |
||||
|
44 |
3.2 |
340 |
77 |
101.4 |
|
III type. Peripheral areas with town-like settlements (8) |
||||
|
42 |
2.7 |
203 |
48 |
74.5 |
|
IV type. Peripheral areas without town-like settlements (7) |
||||
|
36 |
2.4 |
154 |
43 |
65 |
One more aspect of the problem of the spatial development is mono-cities.
During the development of the market economy socio-economic development of the majority of mono-profile cities was characterized by negative tendencies. However the global financial and economic crisis which occurred in the second half of the year 2008 aggravated economic and social problems of mono-cities.
The authorities of all levels undertake the efforts on stabilization of the situation in monocities. There is the search of forms and methods on their support. The solution of the problems of the mono-profile cities is considered as one of the basic priorities of the state policy.
The Russian scientific community also tries to solve these problems. Scientists investigate foreign experience of management in monocities. Models and programs of the foreign mono-cities’ development are studied, the opportunity of their application to the Russian conditions is estimated. The ways of monocities’ trajectory of the steady development are offered.
As well as in other regions, in the Vologda Oblast the socio-economic development of some city settlements is determined by the work of the city-forming enterprises, first of all, in the cities of Cherepovets and Sokol. The regional and municipal authorities develop comprehensive plans of these cities’ modernization; the work on their realization is started.
However the realization of the mentioned programs is constrained with the shortage of the financial resources though the regional authorities try to find the reserves of financing. At the same time at the federal level this question is solved extremely slowly.
In P. Minakir’s article it is marked, that now the growing differentiation of the territories becomes already a political problem. At the same time the realized spatial policy does not take into account the specificity of the country.
The methodical set of influences on economic development offered by the federal governmental bodies does not promote the solution of this problem. The concept “growth points”, “zones of outstripping development”, in P. Minakir opinion, will solve the problem of economic disproportions. And it is necessary to agree with it.
In the Russian conditions, as the scientists consider, the transition to the system of engineering strategy of the development in the subjects of the Federation and federal districts which is necessary to base and coordinate with the strategy of the development of the national economy.
Now the work on the creation of the strategy of the socio-economic development of the regions is carried out under the control of the federal bodies of the government. P. Mina-kir results the circuit of management of the regional economic development.
At the same time the transition to the strategic forms of management is required by the socio-economic development of the territories at the regional level.
These questions are also solved by the ISEDT of the RAS in which works [2 – 6] the methodology of the strategic planning and mechanisms of realization of the strategy of socio-economic development in the territories are submitted. The methodical set is approved by the development of the strategy of the socioeconomic development in some municipal areas of the Vologda Oblast.
However not all the municipal formations in the area the have documents of the strategic character even at the regional level. It is impossible to speak about the presence of the strategy of the socio-economic development of settlements, especially rural ones. Besides the available strategies frequently have formal character. It also forces to doubt of the efficiency of the regional socio-economic policy directed on the alignment of the levels of economic development in the territories.
The urgency and acuteness of the problem allow concluding, that the researches of the question of the spatial differentiation of regions by the Russian scientists will be continued, and first of all regarding the development of the theoretical and methodological bases and methods of the reduction of economic disproportions. Application of the scientific experience into practice directly depends on the political will of power structures both in the center, and at the periphery.
Referevces
-
1. Kostyaev, A.I. Territorial differentiation of the conditions of managing / A.I. Kostyaev // Economist. – 2006. – № 9. – P. 27.
-
2. Problems of the regional development: 2009 – 2012 / team of authors led by Dr. of Economic Sciences, Professor V.A. Ilyin. – Vologda: VSCC CEMI RAS, 2009. – 216 p.
-
3. Spatial aspects of the regional development / ed. by V.A. Ilyin. – Vologda: VSCC CEMI RAS, 2008. – 298 p.
-
4. Regional strategy of economic growth – 2015 / [executive editor V.A. Ilyin]; VSCC CEMI RAS. – M.: Nauka, 2007. – 244 p.
-
5. Strategy of the regional development / VSCC CEMI RAS; ed. by V.A. Ilyin. – M.: Academia, 2006. – 192 p.
-
6. Uskova, T.V. Management by the steady development of the region / T.V. Uskova. – Vologda: ISEDT RAS, 2009. – 355 p.
-
7. Formation of the city agglomeration / V.A. Ilyin, S.A. Selyakova, R.Ju. Malyshev, L.G. Iogman, L.V. Dubinicheva, T.V. Uskova. – Vologda: VSCC CEMI RAS, 2006. – 126 p.
T.V. Uskova,
Deputy Director, Head of the Department of ISEDT RAS
Список литературы Working of the development strategies of municipalities on the basis of simulation modeling
- Makarov, V.L. The use of computable models in state administration/V.L. Makarov, A.R. Bakhtizin, S.S. Sulakshin. -M.: Nauchny Expert, 2007. -304 p.
- Nizamutdinov, M.M. Simulation modeling as a tool to study medium-term strategies for regional development/M.M. Nizamutdinov//Economics and Management. -2009. -№ 5. -Pp. 104-111.
- Management of socio-economic development of the region: problems, approaches and technologies/ed. D.A. Gaynanov. -M., CJSC Publishing Economics, 2008. -264 p.
- Ivanov, P. Current problems and prospects of information-analytical support of the regional government /P. Ivanov, S. Malyshev//Management Consulting. Available at: http://www.dialogvn.ru/uk/2002/n03/s02-3-06.htm
- To overcome the lack of coordination between the federal center and regions (decision of the Board of Legislators) . Available at: http://www.council.gov.ru/inf_ps/parlisurvey/2006/03/36/item963.html